南方医科大学学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (1): 131-140.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2026.01.14
乔通1,3( ), 尹林1, 张可妮1, 牛民主3, 黄菊2, 耿志军2, 李静1,2, 胡建国1,2(
), 尹林1, 张可妮1, 牛民主3, 黄菊2, 耿志军2, 李静1,2, 胡建国1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2025-05-19
出版日期:2026-01-20
发布日期:2026-01-16
通讯作者:
胡建国
E-mail:qt1231126@163.com;jghu9200@bbmu.edu.cn
作者简介:乔 通,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: qt1231126@163.com
基金资助:
Tong QIAO1,3( ), Lin YIN1, Keni ZHANG1, Minzhu NIU3, Ju HUANG2, Zhijun Geng2, Jing LI1,2, Jianguo HU1,2(
), Lin YIN1, Keni ZHANG1, Minzhu NIU3, Ju HUANG2, Zhijun Geng2, Jing LI1,2, Jianguo HU1,2( )
)
Received:2025-05-19
Online:2026-01-20
Published:2026-01-16
Contact:
Jianguo HU
E-mail:qt1231126@163.com;jghu9200@bbmu.edu.cn
摘要:
目的 探讨茯苓新酸A(PAA)调控肠上皮细胞自噬对葡聚糖硫酸钠(DSS)诱导的小鼠结肠炎的作用和机制。 方法 18只C57BL/6小鼠随机分为对照组(WT组)、DSS模型组(DSS组)及PAA干预组(10 mg/kg),6只/组,评估小鼠体质量、结肠长度、疾病活动指数(DAI)及组织病理学评分等变化;构建DSS诱导的Caco-2细胞损伤模型,检测肠屏障蛋白(ZO-1、Claudin-1)、凋亡相关蛋白(Bcl-2/Bax/C-caspase3)及自噬标志物(LC3-II/I、P62)表达。通过分子对接和Western blotting分析PAA的作用机制。 结果 PAA显著改善DSS小鼠的体质量下降(P<0.05)、结肠缩短(P<0.05)及DAI评分升高(P<0.05),并降低结肠组织中促炎因子IL-1β和TNF-α水平(P<0.05)。此外,HE染色显示PAA缓解结肠隐窝损伤,降低炎症细胞浸润和炎症评分(P<0.05),AB-PAS染色显示PAA干预小鼠肠黏膜杯状细胞数量显著高于DSS组。PAA抑制了DSS诱导的紧密连接蛋白(ZO-1和Claudin-1)表达降低(P<0.05)和肠上皮细胞凋亡(降低Bax、C-caspase3,上调Bcl-2,P<0.05)。进一步分析发现,PAA可显著激活肠上皮细胞自噬水平(LC3-II/I比值升高,P62水平降低,P<0.05)。机制研究表明,PAA可通过靶向调控AMPK/mTOR信号,激活自噬并抑制肠上皮细胞凋亡。 结论 PAA通过AMPK/mTOR介导的自噬激活与肠上皮细胞凋亡途径,保护肠屏障功能和改善DSS诱导的小鼠结肠炎。
乔通, 尹林, 张可妮, 牛民主, 黄菊, 耿志军, 李静, 胡建国. 茯苓新酸A通过调节AMPK/mTOR介导的自噬来减轻葡聚糖硫酸钠诱导的小鼠结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2026, 46(1): 131-140.
Tong QIAO, Lin YIN, Keni ZHANG, Minzhu NIU, Ju HUANG, Zhijun Geng, Jing LI, Jianguo HU. Poricoic acid A alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice by regulating AMPK/mTOR-mediated autophagy and inhibiting intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2026, 46(1): 131-140.
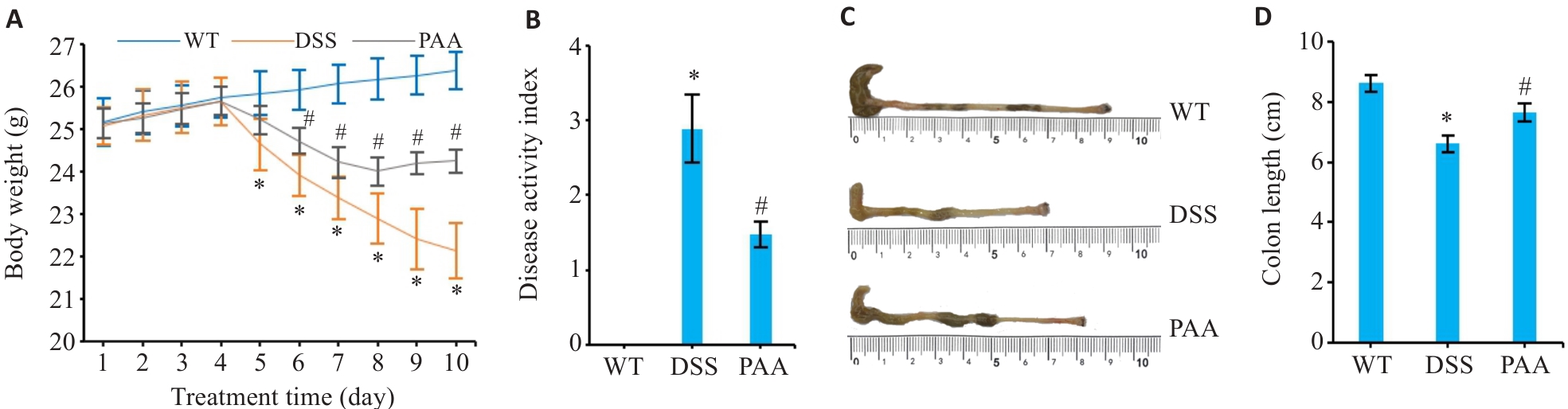
图1 PAA干预对DSS小鼠结肠炎症状的影响
Fig.1 Therapeutic effects of PAA on DSS-induced colitis in mice. A: Changes in body weight of the mice. B: Disease activity index (DAI) scoring. C: Macroscopic evaluation of colon morphology. D: Quantitative analysis of colon length. WT: Wild type group; DSS: DSS-induced model group; PAA: Treatment group DSS. n=6, *P<0.05 vs WT group. #P<0.05 vs DSS group.
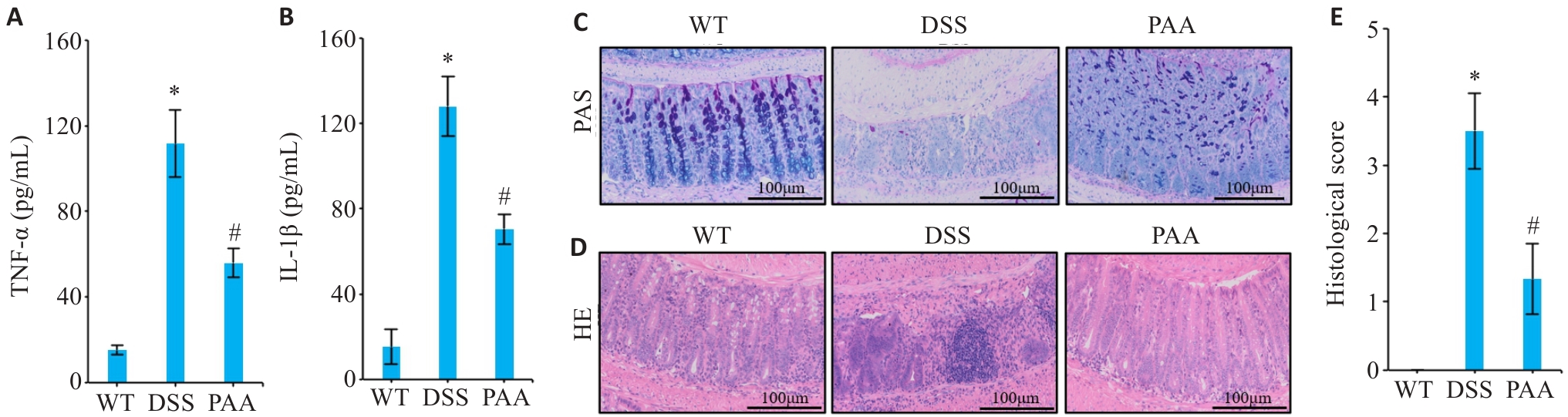
图2 PAA干预对DSS小鼠肠道炎症因子表达和组织病理损伤的影响
Fig.2 Effects of PAA intervention on intestinal histopathological damage and expression of inflammatory factors in DSS mice. A, B: ELISA results of TNF-α (A) and IL-1β (B) in mice intestinal mucosa. C: AB-PAS staining of colon tissues in different groups. D: HE staining of colon tissues in different groups. E: Histopathological scores of colon tissues. n=6, *P<0.05 vs WT group. #P<0.05 vs DSS group.
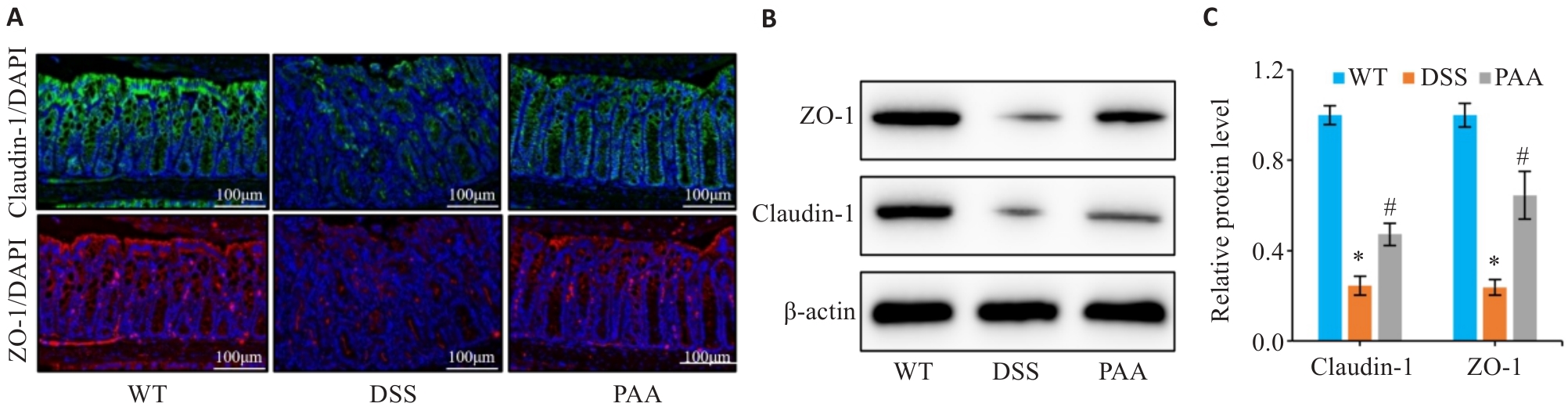
图3 PAA干预对DSS小鼠肠屏障的影响
Fig.3 Effect of PAA on intestinal barrier function in DSS-induced colitis mice. A: Immunofluorescence staining of ZO-1 and claudin-1 in the colon. B, C: Quantitative analysis of ZO-1 and claudin-1 expression levels in the intestinal mucosa by Western blotting. n=6, *P<0.05 vs WT group; #P<0.05 vs DSS group.
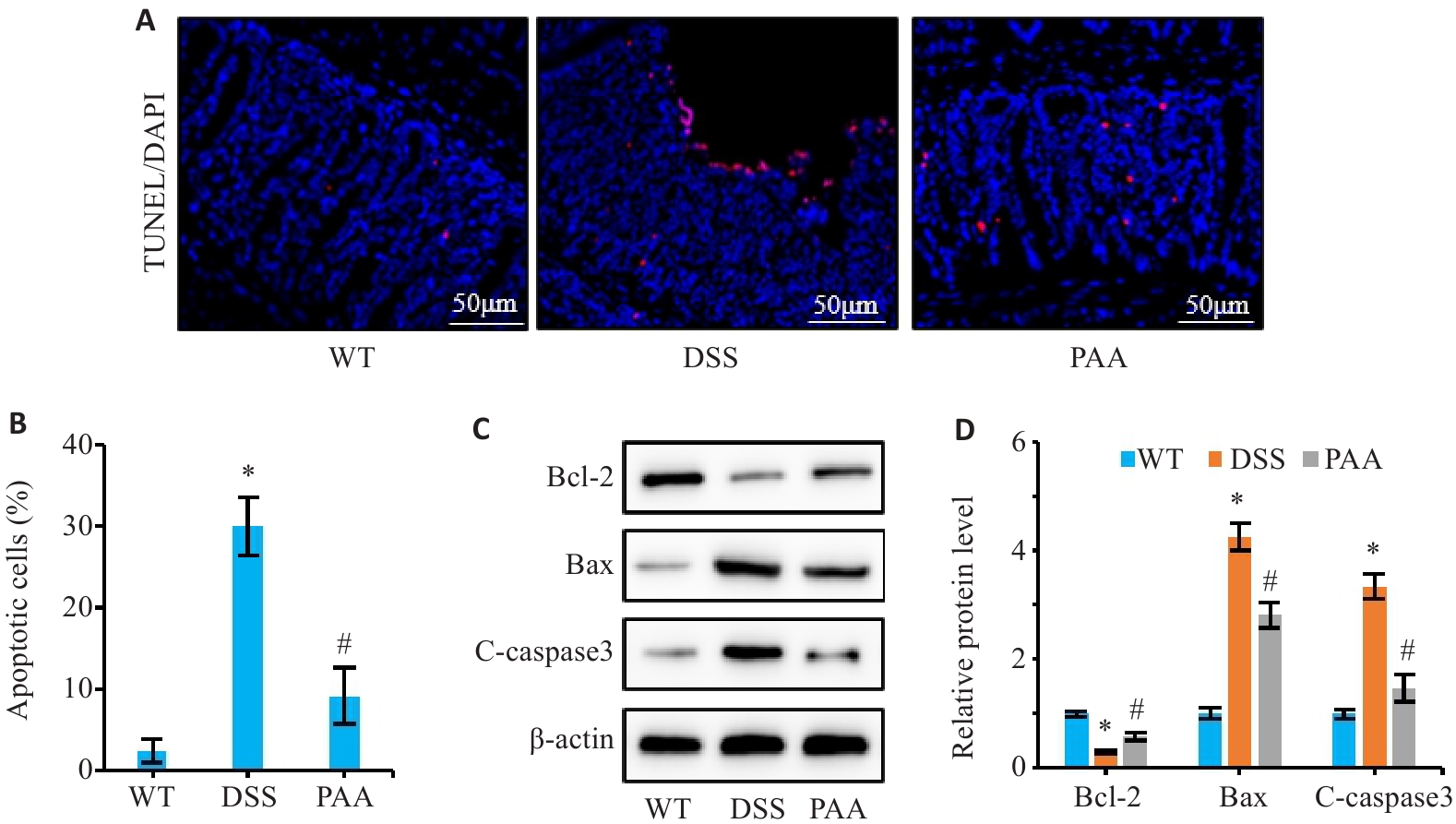
图4 PAA对DSS小鼠肠上皮细胞凋亡的影响
Fig.4 Effect of PAA on intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis in DSS-induced colitis mice. A: TUNEL staining of colon tissues. B: Quantitative analysis of intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis rate. C, D: Western blotting of Bcl-2, Bax, and cleaved caspase-3 (C-caspase3) expression levels in colonic mucosa. n=6, *P<0.05 vs WT group; #P<0.05 vs DSS group.
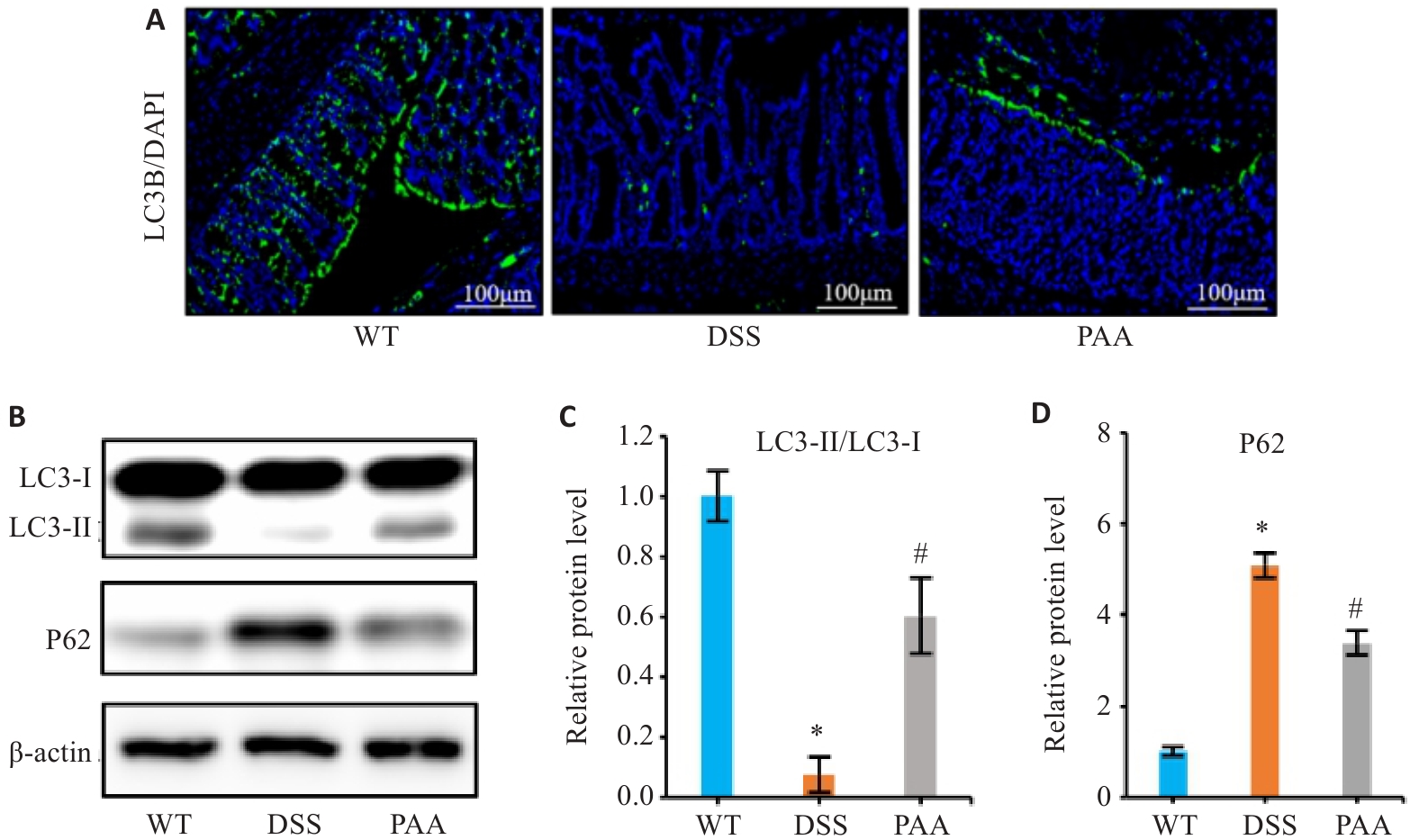
图5 PAA对DSS诱导的IBD小鼠模型中细胞自噬的影响
Fig.5 Effects of PAA on cellular autophagy in DSS-induced colitis mouse models. A: Immunofluorescence images of LC3B in the colon. B: Western blotting of LC3-I, LC3-II, and P62 expressions in the intestinal mucosa. C: Quantitative analysis of the LC3-II/LC3-I protein ratio. D: Quantitative analysis of P62 protein expression. n=6, *P<0.05 vs WT group; #P<0.05 vs DSS group.
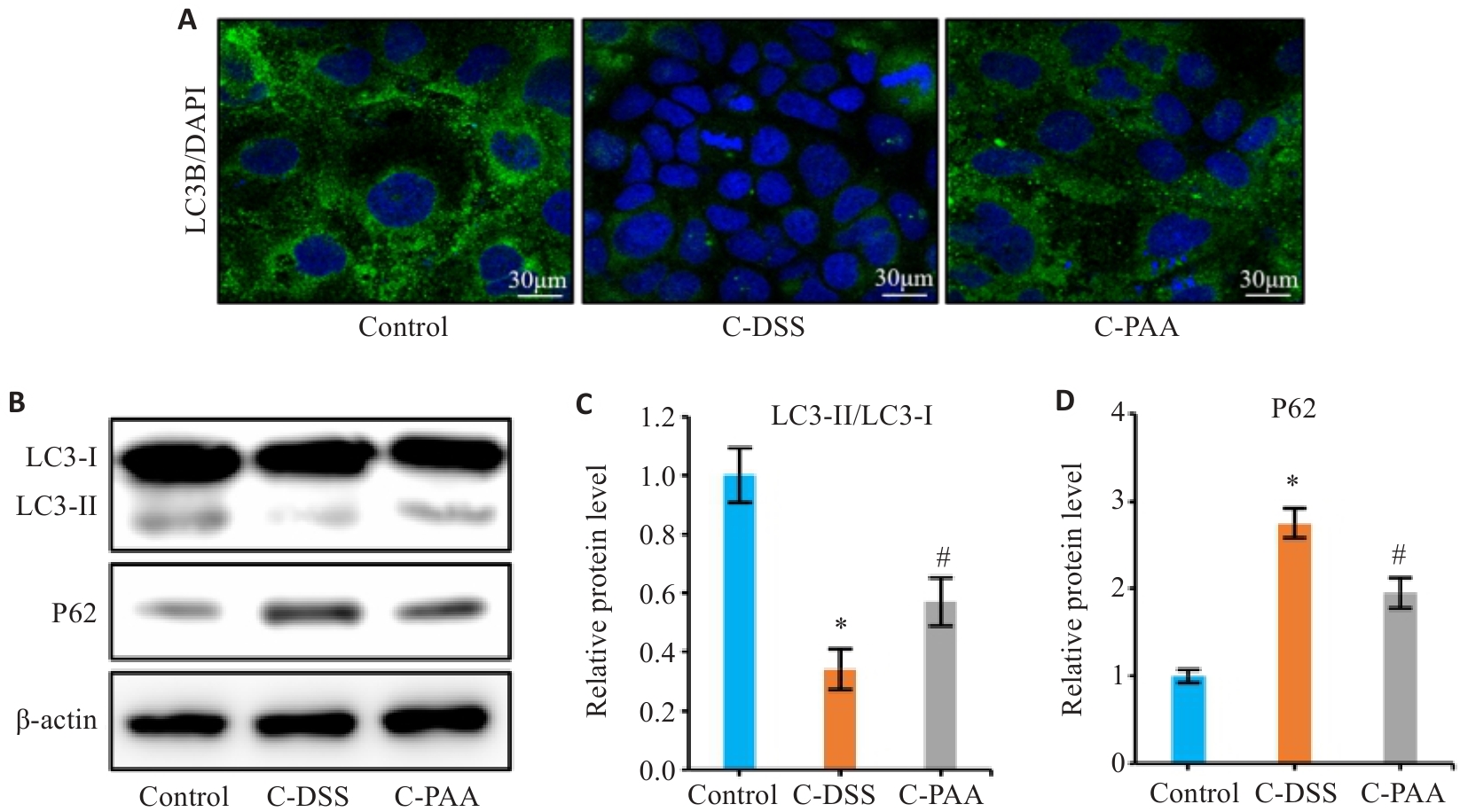
图6 PAA对DSS诱导的模型中Caco-2细胞自噬的影响
Fig.6 Effect of PAA on autophagy in DSS-induced Caco-2 cells. A: Immunofluorescence staining of LC3B in Caco-2 cells. B: Western blotting of LC3-I, LC3-II, and P62 expression. C: Quantitative analysis of the LC3-II/LC3-I ratio. D: Quantitative analysis of P62 protein level. Control: Normal control group; C-DSS: DSS-induced model group; C-PAA: PAA treatment group. n=3, *P<0.05 vs Control group; #P<0.05 vs C-DSS group.
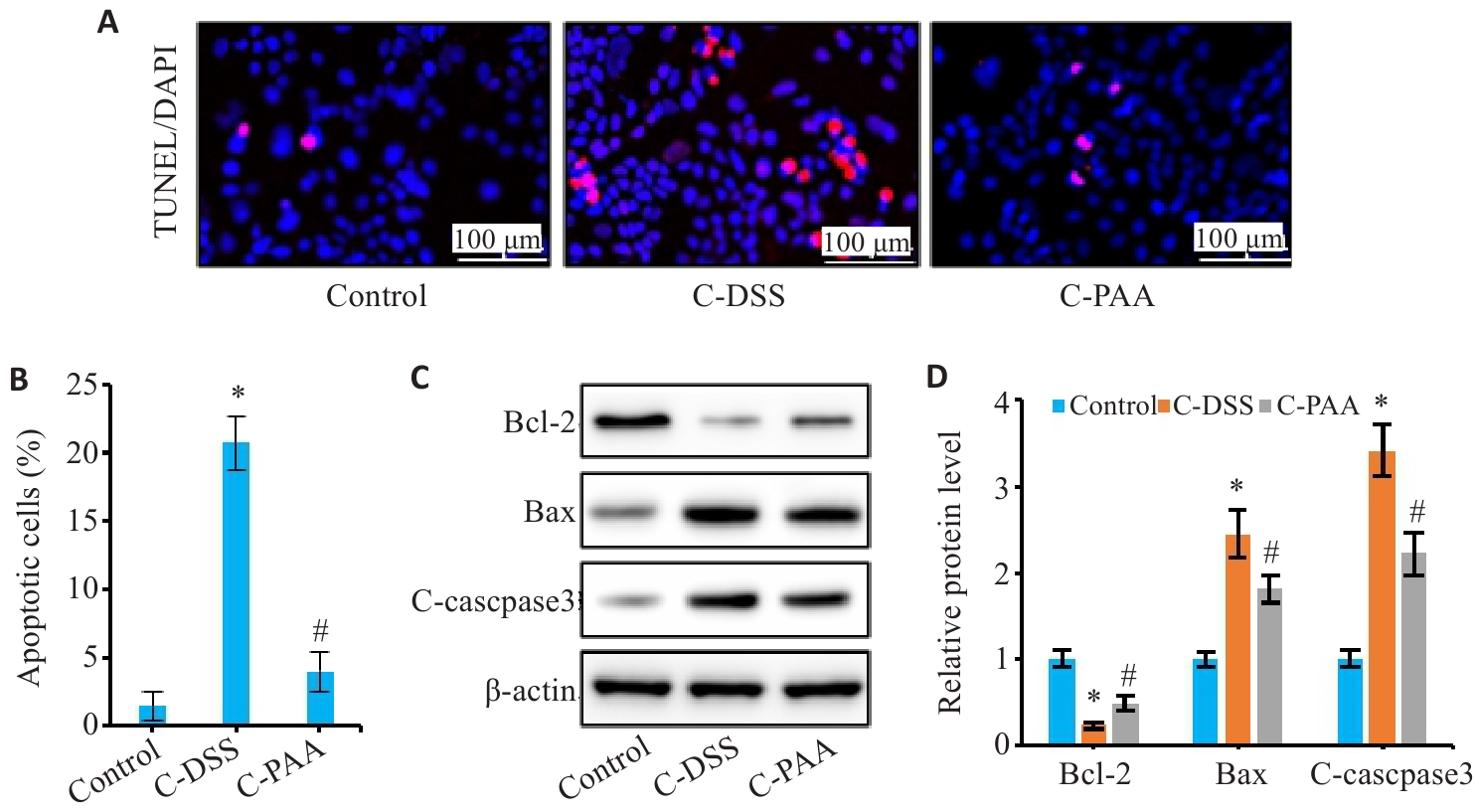
图7 PAA抑制DSS诱导的Caco-2细胞凋亡
Fig.7 Effect of PAA on DSS-induced apoptosis of Caco-2 cells. A: TUNEL staining of Caco-2 cells. B: Quantitative analysis of apoptosis rate. C: Western blotting of Bcl-2, Bax, and C-caspase3 expressions. D: Relative protein expression levels of Bcl-2, Bax, and C-caspase3. n=3, *P<0.05 vs Control group; #P<0.05 vs C-DSS group.
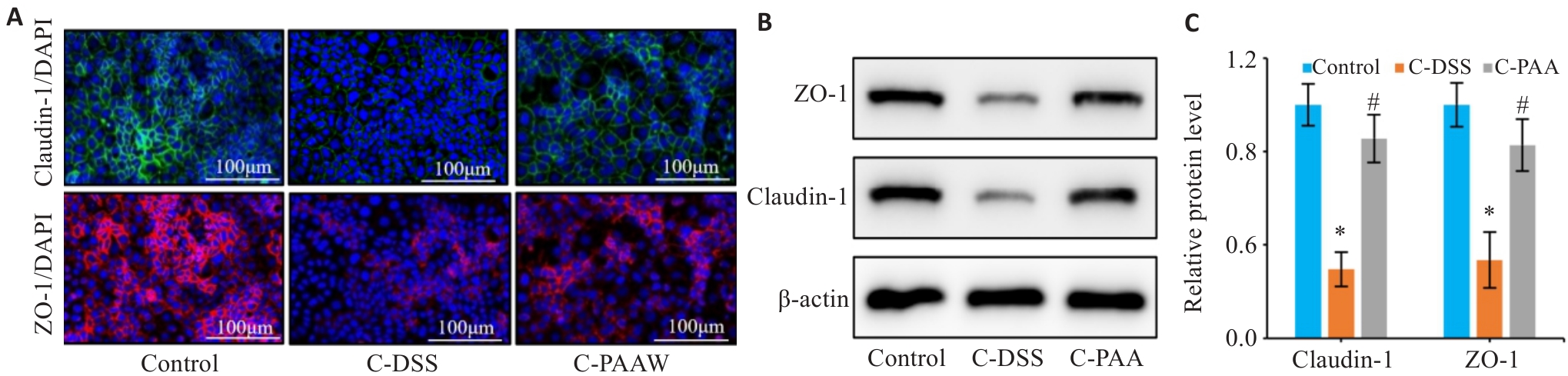
图8 PAA干预对DSS诱导的Caco-2细胞屏障损伤的影响
Fig. 8 Therapeutic effects of PAA on DSS-induced barrier damage in Caco-2 cells. A: Immunofluorescence staining of ZO-1 and claudin-1 in Caco-2 cells (Scale bar=100 μm). B, C: Western blotting for detecting protein expression levels of ZO-1 (B) and claudin-1 (C) in Caco-2 cells. n=3, *P<0.05 vs Control group. #P<0.05 vs C-DSS group.
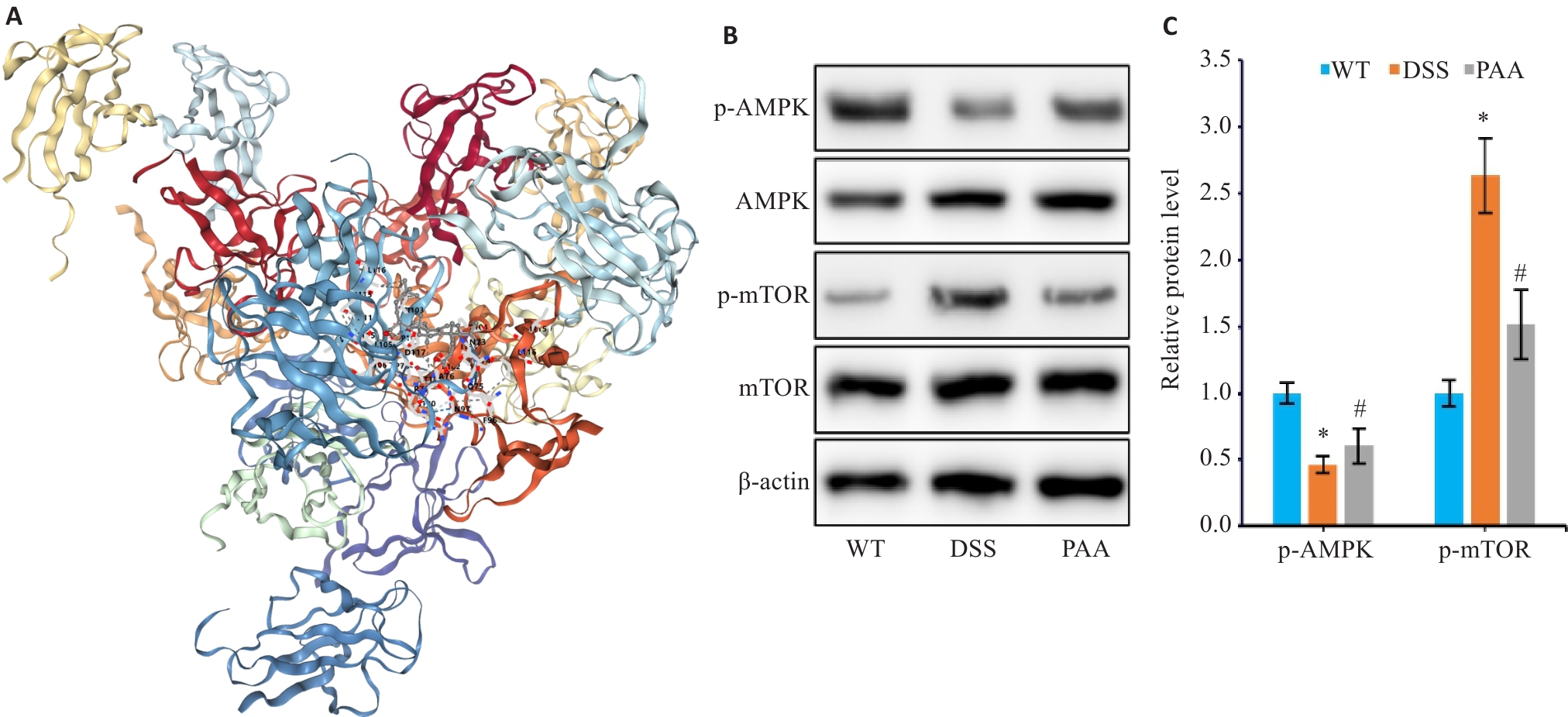
图9 PAA干预对体内AMPK通路的影响
Fig.9 Effect of PAA on the AMPK/mTOR pathway in the mouse models. A: Molecular docking analysis of PAA with AMPK. B, C: Western blotting for detecting protein expression levels of p-AMPK, AMPK, p-mTOR, and mTOR in mouse colon tissues. n=6, *P<0.05 vs WT group; #P<0.05 vs DSS group.
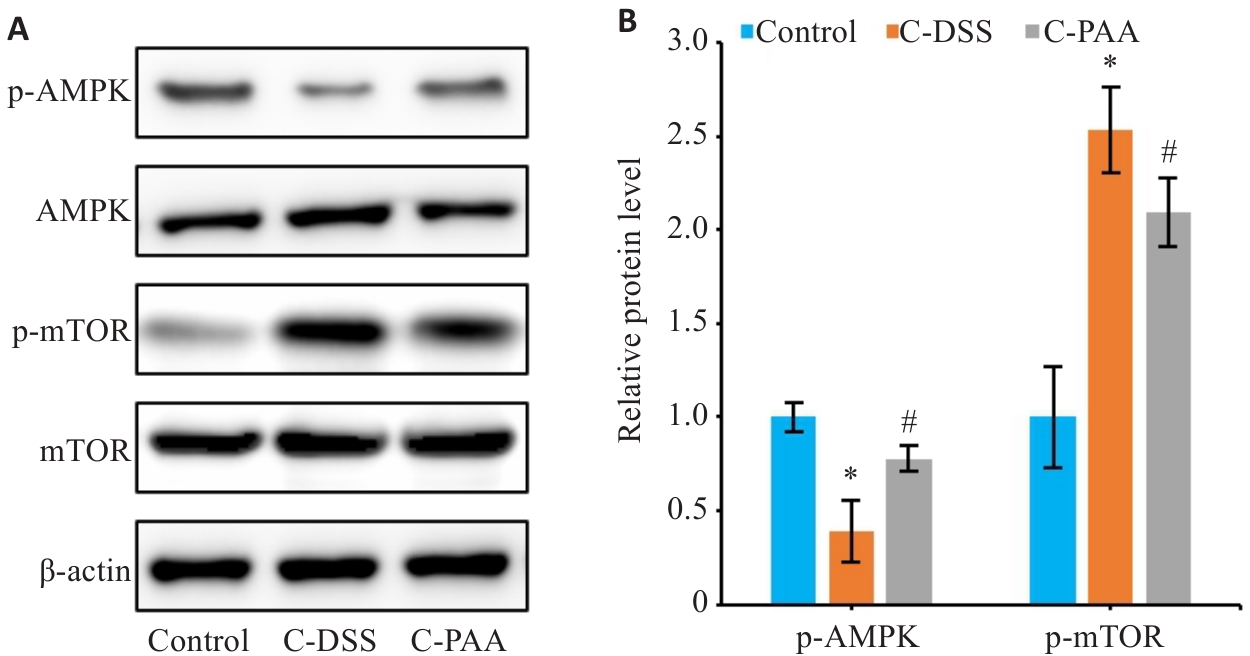
图10 PAA干预对体外AMPK/mTOR通路的影响
Fig.10 Effects of PAA treatment on AMPK/mTOR signaling in DSS-induced Caco-2 cells. A: Western blotting for p-AMPK, AMPK, p-mTOR, and mTOR expressions. B: Quantitative analysis of p-AMPK/AMPK and p-mTOR/mTOR protein expression ratios. n=3, *P<0.05 vs Control group. #P<0.05 vs C-DSS group.
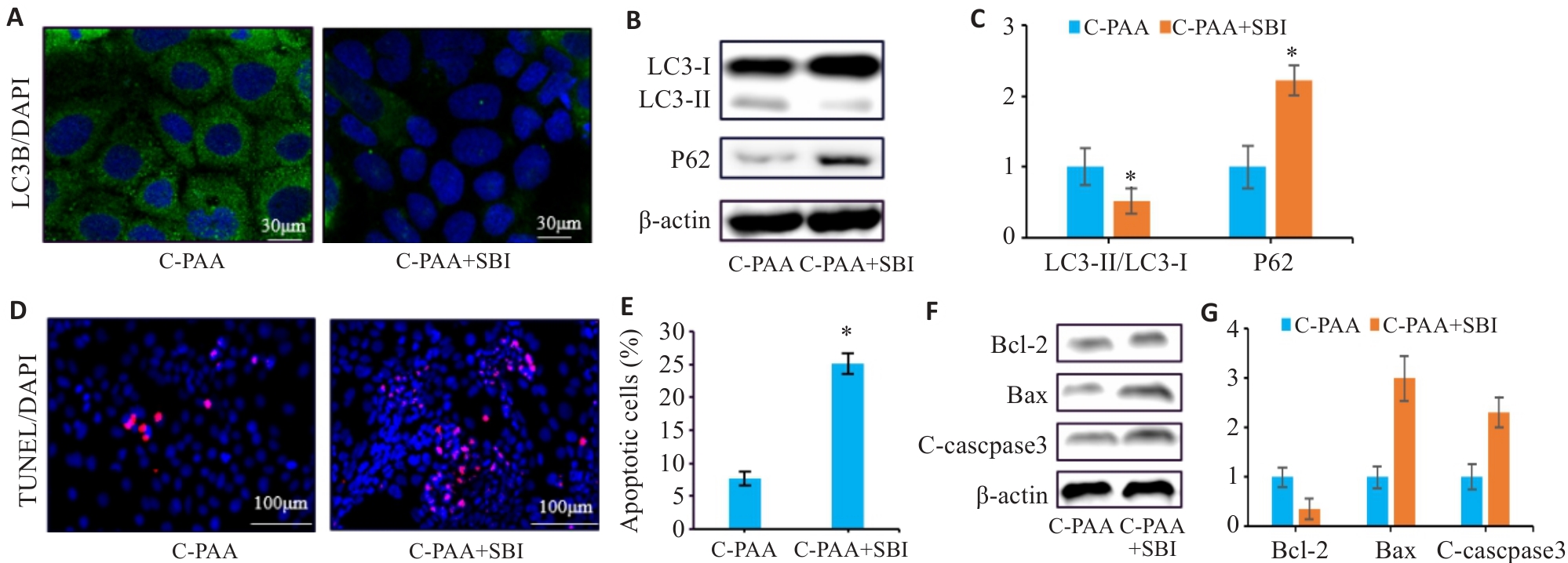
图11 SBI-0206965干预后对PAA的影响
Fig.11 PAA regulates autophagy and apoptosis in Caco-2 cells by activating the AMPK/mTOR pathway. A: Immunofluorescence staining of LC3B in Caco-2 cells. B: Western blotting for LC3-I, LC3-II, and P62 expressions. C: Quantitative analysis of the LC3-II/LC3-I ratio. D: TUNEL staining of Caco-2 cells. E: Quantitative analysis of apoptosis rate. F: Western blotting for Bcl-2, Bax, and C-caspase3 expressions. G: Relative protein expression levels of Bcl-2, Bax, and C-caspase3. C-PAA: PAA treatment group; C-PAA+SBI: PAA treatment group+SBI-0206965. n=3, *P<0.05 vs C-PAA group.
| [1] | Saha K, Subramenium Ganapathy A, Wang A, et al. Autophagy reduces the degradation and promotes membrane localization of occludin to enhance the intestinal epithelial tight junction barrier against paracellular macromolecule flux[J]. J Crohns Colitis, 2023, 17(3): 433-49. doi:10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjac148 |
| [2] | Xu J, Li S, Jin W, et al. Epithelial Gab1 calibrates RIPK3-dependent necroptosis to prevent intestinal inflammation[J]. JCI Insight, 2023, 8(6): e162701. doi:10.1172/jci.insight.162701 |
| [3] | Tran S, Juliani J, Fairlie WD, et al. The emerging roles of autophagy in intestinal epithelial cells and its links to inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Biochem Soc Trans, 2023, 51(2): 811-26. doi:10.1042/bst20221300 |
| [4] | Zhang Y, Li XZ, Li YT, et al. DNA damage-regulated autophagy modulator 1 (DRAM1) mediates autophagy and apoptosis of intestinal epithelial cells in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2021, 66(10): 3375-90. doi:10.1007/s10620-020-06697-2 |
| [5] | Chen SL, Li CM, Li W, et al. How autophagy, a potential therapeutic target, regulates intestinal inflammation[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14: 1087677. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1087677 |
| [6] | Khan S, Mentrup HL, Novak EA, et al. Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase contributes to epithelial homeostasis in intestinal inflammation via Beclin-1-mediated autophagy[J]. FASEB J, 2022, 36(5): e22282. doi:10.1096/fj.202200138r |
| [7] | Gorrepati VS, Soriano C, Johri A, et al. Abdominal pain and anxious or depressed state are independently associated with weight loss in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Crohns Colitis 360, 2020, 2(2): otaa047. doi:10.1093/crocol/otaa047 |
| [8] | Oligschlaeger Y, Yadati T, Houben T, et al. Inflammatory bowel disease: a stressed "gut/feeling"[J]. Cells, 2019, 8(7): E659. doi:10.3390/cells8070659 |
| [9] | Goll R, Moe ØK, Johnsen KM, et al. Pharmacodynamic mechanisms behind a refractory state in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. BMC Gastroenterol, 2022, 22(1): 464. doi:10.1186/s12876-022-02559-5 |
| [10] | Yibcharoenporn C, Muanprasat C, Moonwiriyakit A, et al. AMPK in intestinal health and disease: a multifaceted therapeutic target for metabolic and inflammatory disorders[J]. Drug Des Devel Ther, 2025, 19: 3029-58. doi:10.2147/dddt.s507489 |
| [11] | Olivier S, Diounou H, Pochard C, et al. Intestinal epithelial AMPK deficiency causes delayed colonic epithelial repair in DSS-induced colitis[J]. Cells, 2022, 11(4): 590. doi:10.3390/cells11040590 |
| [12] | Accordi B, Galla L, Milani G, et al. AMPK inhibition enhances apoptosis in MLL-rearranged pediatric B-acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells[J]. Leukemia, 2013, 27(5): 1019-27. doi:10.1038/leu.2012.338 |
| [13] | 曹霞, 邱 榕, 陶云平, 等. 基于Th17/Treg平衡的调节探讨参苓白术散治疗溃疡性结肠炎的疗效及作用机制[J]. 中药材, 2025, 48(1):237-41. |
| [14] | Zhang L, Yin M, Feng X, et al. Anti-inflammatory activity of four triterpenoids isolated from Poriae cutis [J]. Foods, 2021, 10(12): 3155. doi:10.3390/foods10123155 |
| [15] | Jin Q, Yin JZ, Liu ZZ. Poricoic acid A promotes angiogenesis and myocardial regeneration by inducing autophagy in myocardial infarction[J]. Tissue Cell, 2024, 88: 102401. doi:10.1016/j.tice.2024.102401 |
| [16] | Chen DQ, Wang YN, Vaziri ND, et al. Poricoic acid A activates AMPK to attenuate fibroblast activation and abnormal extracellular matrix remodelling in renal fibrosis[J]. Phytomedicine, 2020, 72: 153232. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153232 |
| [17] | Wu YW, Xu YC, Deng HH, et al. Poricoic acid a ameliorates high glucose-induced podocyte injury by regulating the AMPKα/FUNDC1 pathway[J]. Mol Biol Rep, 2024, 51(1): 1003. doi:10.1007/s11033-024-09921-8 |
| [18] | 程 扬, 宾东华, 尹园缘, 等. 参苓白术散对克罗恩病大鼠肠道炎症及PI3K/Akt信号通路的影响[J]. 中医药导报, 2024, 30(4): 30-4. |
| [19] | Roselli M, Maruszak A, Grimaldi R, et al. Galactooligosaccharide treatment alleviates DSS-induced colonic inflammation in caco-2 cell model[J]. Front Nutr, 2022, 9: 862974. doi:10.3389/fnut.2022.862974 |
| [20] | Paquette M, El-Houjeiri L, Zirden LC, et al. AMPK-dependent phosphorylation is required for transcriptional activation of TFEB and TFE3[J]. Autophagy, 2021, 17(12): 3957-75. doi:10.1080/15548627.2021.1898748 |
| [21] | Wirtz S, Popp V, Kindermann M, et al. Chemically induced mouse models of acute and chronic intestinal inflammation[J]. Nat Protoc, 2017, 12(7): 1295-309. doi:10.1038/nprot.2017.044 |
| [22] | 张 敏, 刘生宝, 张 诺, 等. 改进型“瑞士卷”法在小鼠肠道组织切片中的应用[J]. 中华病理学杂志, 2024, 53(4): 393-7. |
| [23] | Li CL, Liu MG, Deng L, et al. Oxyberberine ameliorates TNBS-induced colitis in rats through suppressing inflammation and oxidative stress via Keap1/Nrf2/NF‑κB signaling pathways[J]. Phytomedicine, 2023, 116: 154899. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154899 |
| [24] | 韩康宁, 胡俊杰, 李 娟, 等. 二妙四土汤调控JAK/STAT通路治疗湿热型湿疹大鼠的药效与作用机制[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2025, 31(9): 37-47. |
| [25] | Gareb B, Otten AT, Frijlink HW, et al. Review: local tumor necrosis factor-α inhibition in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Pharmaceutics, 2020, 12(6): E539. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics12060539 |
| [26] | 邵荣瑢, 杨 子, 张文静, 等. 茯苓酸缓解小鼠克罗恩病:基于抑制PPII3K/AKT信号通路拮抗肠上皮细胞凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(6): 935-42. |
| [27] | 牛民主, 殷丽霞, 段 婷, 等. 川续断皂苷Ⅵ通过抑制PI3K/AKT/NF-κB通路拮抗肠上皮细胞凋亡缓解TNBS诱导的小鼠克罗恩病样结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(12): 2335-46. |
| [28] | Robles-Vera I, Jarit-Cabanillas A, Brandi P, et al. Microbiota translocation following intestinal barrier disruption promotes Mincle-mediated training of myeloid progenitors in the bone marrow[J]. Immunity, 2025, 58(2): 381-96. e9. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2024.12.012 |
| [29] | Subramanian S, Geng H, Tan X. Cell death of intestinal epithelial cells in intestinal diseases. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2020. 72(3): 308-24. |
| [30] | Zhao H, Liu T, Yang CE, et al. Poricoic acid A attenuates renal fibrosis by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis[J]. Braz J Med Biol Res, 2024, 57: e14249. doi:10.1590/1414-431x2024e14249 |
| [31] | Liu SS, Jiang TX, Bu F, et al. Molecular mechanisms underlying the BIRC6-mediated regulation of apoptosis and autophagy[J]. Nat Commun, 2024, 15(1): 891. doi:10.1038/s41467-024-45222-1 |
| [32] | Langer R, Neppl C, Keller MD, et al. Expression analysis of autophagy related markers LC3B, p62 and HMGB1 indicate an autophagy-independent negative prognostic impact of high p62 expression in pulmonary squamous cell carcinomas[J]. Cancers: Basel, 2018, 10(9): E281. doi:10.3390/cancers10090281 |
| [33] | Cui Y, Cao X, Zhang Y, et al. Protein phosphatase 1 regulatory subunit 15 A (PPP1R15A) promoted the progression of gastric cancer by activating cell autophagy under energy stress[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2025, 44(1): 52. doi:10.1186/s13046-025-03320-y |
| [34] | Arab HH, Al-Shorbagy MY, Saad MA. Activation of autophagy and suppression of apoptosis by dapagliflozin attenuates experimental inflammatory bowel disease in rats: Targeting AMPK/mTOR, HMGB1/RAGE and Nrf2/HO-1 pathways[J]. Chem Biol Interact, 2021, 335: 109368. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2021.109368 |
| [35] | Wang Y, Liu Z, Shu S, et al. AMPK/mTOR signaling in autophagy regulation during cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury[J]. Front Physiol, 2020, 11: 619730. doi:10.3389/fphys.2020.619730 |
| [36] | Liu H, Wang Q, Shi G, et al. Emodin ameliorates renal damage and podocyte injury in a rat model of diabetic nephropathy via regulating AMPK/mTOR-mediated autophagy signaling pathway[J]. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes, 2021, 14: 1253-66. doi:10.2147/dmso.s299375 |
| [37] | Zafar H, Saier MH Jr. GutBacteroidesspecies in health and disease[J]. Gut Microbes, 2021, 13: 1848158. doi:10.1080/19490976.2020.1848158 |
| [1] | 徐嘉艺, 杨迪, 臧开来, 褚孟恩, 赵庆瑶, 李晴, 鲁森, 陈修丽, 李宁. EVA1A过表达通过调节脂质代谢和促进脂滴自噬改善非酒精性脂肪肝[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2026, 46(1): 150-158. |
| [2] | 张淑芬, 黄添容, 杨灿洪, 陈家镒, 吕田明, 张嘉发. 莱菔硫烷通过抑制Aβ42寡聚体激活的U87细胞中MAPK/NF-κB信号通路降低反应性星形胶质细胞介导的SH-SY5Y凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2026, 46(1): 191-199. |
| [3] | 林心君, 何昱霖, 施红, 刘佳绣, 胡海霞. 石斛合剂通过调控Sirt3介导的线粒体自噬通路缓解大鼠糖尿病心肌病[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2026, 46(1): 47-54. |
| [4] | 赵锦燕, 彭娇, 林明和, 朱晓勤, 黄彬, 林久茂. 清解扶正颗粒通过抑制线粒体依赖的凋亡、激活AMPK-PGC-1α通路缓解5-氟尿嘧啶引起的骨骼肌损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2026, 46(1): 94-103. |
| [5] | 王莹, 李静, 王伊迪, 华明钰, 胡玮彬, 张晓智. 原发性肝癌患者的临床结局与治疗反应预测模型:基于失巢凋亡和免疫基因[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1967-1979. |
| [6] | 陈丹丹, 任乾千, 吕梦林, 张宝文, 刘醒然, 张蒙, 王阳, 寇现娟. 天麻钩藤饮通过抑制坏死性凋亡通路改善帕金森病小鼠的运动功能障碍[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(8): 1571-1580. |
| [7] | 常笑语, 张瀚文, 曹红亭, 侯玲, 孟鑫, 陶虹, 罗彦, 李光华. 热应激对大鼠胸主动脉内皮细胞生物钟基因 Bmal1和细胞周期蛋白表达水平的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1353-1362. |
| [8] | 李玮怡, 江露, 张宗星, 陈丹, 包卓玛, 黄丽, 袁林. 强骨康疏方通过抑制HIF-1α/BNIP3自噬信号通路减少类风湿性关节炎大鼠的破骨细胞分化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1389-1396. |
| [9] | 王心恒, 邵小涵, 李童童, 张璐, 杨勤军, 叶卫东, 童佳兵, 李泽庚, 方向明. 平喘宁方通过调控HMGB1/Beclin-1轴介导的自噬改善患寒哮证大鼠的气道炎症[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1153-1162. |
| [10] | 杨毓甲, 杨丽芳, 吴雅玲, 段兆达, 于春泽, 吴春云, 于建云, 杨力. 大麻二酚经PERK-eIF2α-ATF4-CHOP通路减轻多重脑震荡大鼠的神经元内质网应激和凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1240-1250. |
| [11] | 牛民主, 殷丽霞, 乔通, 尹林, 张可妮, 胡建国, 宋传旺, 耿志军, 李静. 旱莲苷A通过调控JAK2/STAT3通路抑制M1型巨噬细胞极化改善葡聚糖硫酸钠诱导的小鼠结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1297-1306. |
| [12] | 陈悦, 肖林雨, 任侣, 宋雪, 李静, 胡建国. 水晶兰苷通过抑制PI3K/AKT信号通路减少神经元凋亡改善脊髓损伤后小鼠的运动功能[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 774-784. |
| [13] | 储菲, 陈孝华, 宋博文, 杨晶晶, 左芦根. 苏荠宁黄酮通过抑制PI3K/AKT信号通路拮抗肠上皮细胞凋亡改善小鼠实验性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 819-828. |
| [14] | 张毅, 沈昱, 万志强, 陶嵩, 柳亚魁, 王栓虎. CDKN3高表达促进胃癌细胞的迁移和侵袭:基于调控p53/NF-κB信号通路和抑制胃癌细胞凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 853-861. |
| [15] | 董妍妍, 张可敬, 储俊, 储全根. 抵当汤含药血清通过PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号通路增强高糖诱导的大鼠肾小球内皮细胞自噬[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 461-469. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||