南方医科大学学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (1): 141-149.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2026.01.15
崔运能1,2( ), 冯敏清3,4,5, 姚亮凤2, 严杰文2, 李闻瀚6, 黄燕平6(
), 冯敏清3,4,5, 姚亮凤2, 严杰文2, 李闻瀚6, 黄燕平6( )
)
收稿日期:2025-06-20
出版日期:2026-01-20
发布日期:2026-01-16
通讯作者:
黄燕平
E-mail:letitb@163.com;yale.huangyp@fosu.edu.cn
作者简介:崔运能,在读博士研究生,E-mail: letitb@163.com
基金资助:
Yunneng CUI1,2( ), Minqing FENG3,4,5, Liangfeng YAO2, Jiewen YAN2, Wenhan LI6, Yanping HUANG6(
), Minqing FENG3,4,5, Liangfeng YAO2, Jiewen YAN2, Wenhan LI6, Yanping HUANG6( )
)
Received:2025-06-20
Online:2026-01-20
Published:2026-01-16
Contact:
Yanping HUANG
E-mail:letitb@163.com;yale.huangyp@fosu.edu.cn
摘要:
目的 探讨不同欠采样方法在解决小样本数据类别不平衡问题中的应用,以提高机器学习模型术前预测子宫肌瘤高强度聚焦超声(HIFU)消融效果的准确性。 方法 收集在佛山市妇幼保健院就诊的140例HIFU治疗子宫肌瘤患者临床及影像学数据,其中高消融率组104例,低消融率组36例,提取患者MRI-T2WI影像组学特征,构建HIFU治疗机器学习预测模型。应用7种欠采样方法,即随机欠采样(RUS)、重复编辑最近邻(RENN)、全K最近邻(AllKNN)、近邻缺失-3(NM)、凝聚最近邻(CNN)、邻域清理规则(NCR)和实例硬度阈值(IHT),使用4种机器学习模型,即K最近邻(KNN)、随机森林(RF)、支持向量机(SVM)和多层感知机(MLP)共计构建28种预测模型处理类别不平衡数据,并通过5折交叉验证方法、以受试者工作特征曲线下面积(AUC)、准确率、召回率和特异性等评估各模型性能。 结果 欠采样方法与机器学习模型交叉组合的结果为:4种最佳组合AUC即CNN-RF为0.772(95%置信区间:0.566~0.942)、NM-SVM为0.797(95%置信区间:0.600~0.950)以及CNN-KNN和NM-MLP均为0.822(95%置信区间分别为0.635~0.964、0.632~0.960)。各机器学习模型的AUC在欠采样后均显著增高,其中以MLP模型改善最明显;各模型的召回率也显著增加,即CNN-RF召回率增加0.389、NM-SVM为0.836、CNN-KNN为0.532、NM-MLP为0.372。 结论 欠采样方法可有效解决小样本类别不平衡问题,为构建子宫肌瘤HIFU消融效果的机器学习预测模型提供新思路。
崔运能, 冯敏清, 姚亮凤, 严杰文, 李闻瀚, 黄燕平. 基于欠采样的影像组学机器学习模型术前预测子宫肌瘤高强度聚焦超声消融效果[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2026, 46(1): 141-149.
Yunneng CUI, Minqing FENG, Liangfeng YAO, Jiewen YAN, Wenhan LI, Yanping HUANG. Enhancement of radiomics-based machine learning models for predicting efficacy of high-intensity focused ultrasound ablation of uterine fibroids using undersampling methods[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2026, 46(1): 141-149.
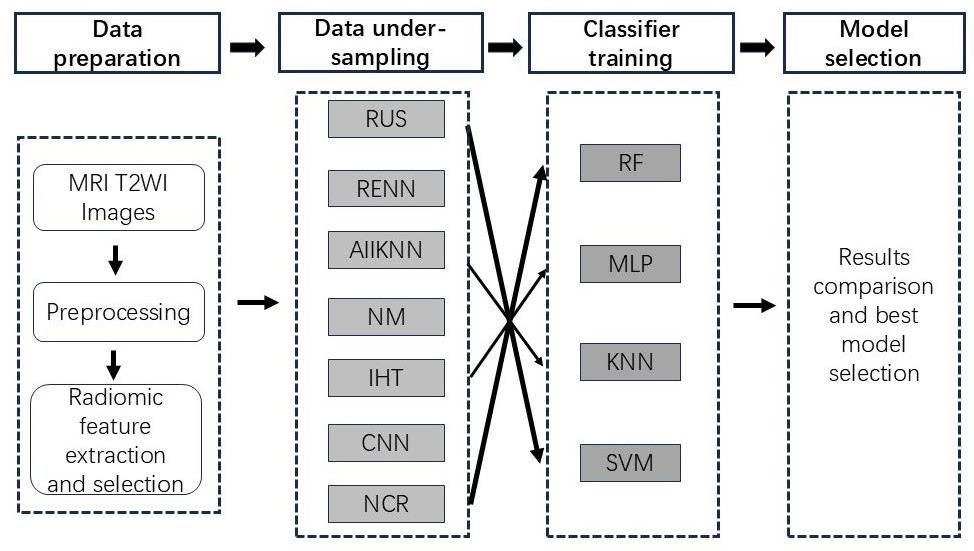
图1 主要数据处理步骤示意图。
Fig.1 Diagram of the main data processing procedures in this study. Seven undersampling methods are used in combination with 4 types of classifiers to construct predictive models for HIFU treatment of uterine fibroids.
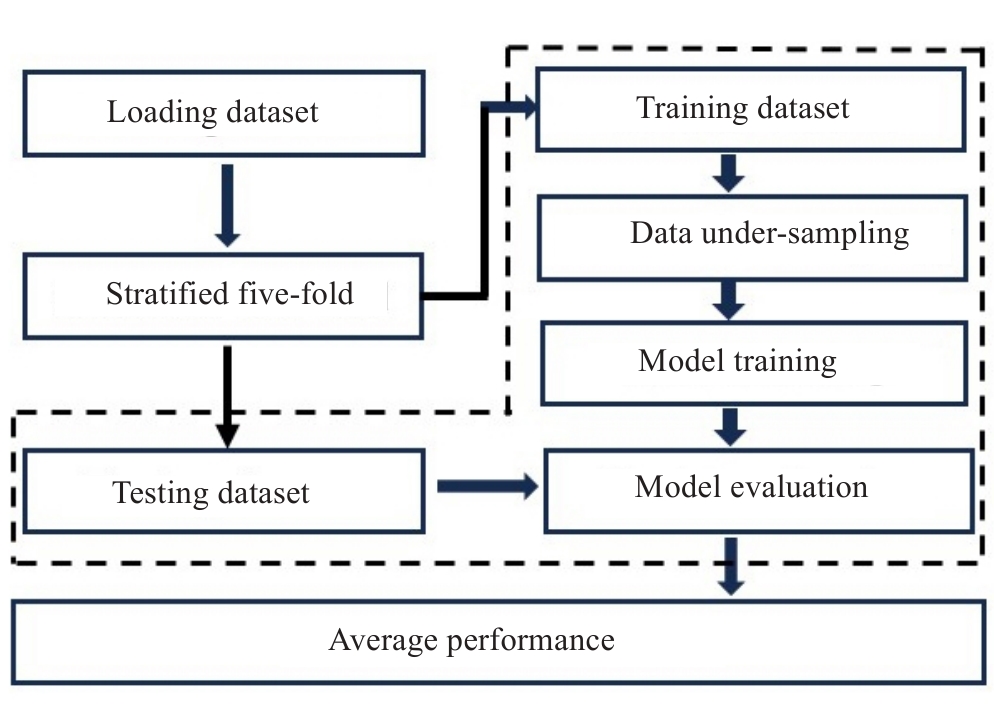
图3 模型建立和评估流程图
Fig.3 Flowchart of model establishment and evaluation in this study. The procedures boxed using dotted lines are repeated 5 times for the 5-fold cross-validation scheme.
| Models | AUC (95% CI) | Accuracy | Recall | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RUS-KNN | 0.792(0.586-0.958) | 0.679 | 0.728 | 0.664 |
| RENN-KNN | 0.736(0.519-0.925) | 0.643 | 0.678 | 0.637 |
| AllKNN-KNN | 0.708(0.465-0.909) | 0.679 | 0.750 | 0.655 |
| NM-KNN | 0.769(0.558-0.939) | 0.679 | 0.782 | 0.646 |
| CNN-KNN | 0.822(0.635-0.964) | 0.714 | 0.675 | 0.733 |
| NCR-KNN | 0.734(0.507-0.927) | 0.664 | 0.618 | 0.684 |
| IHT-KNN | 0.710(0.479-0.909) | 0.664 | 0.728 | 0.646 |
| KNN-baseline | 0.784(0.571-0.955) | 0.750 | 0.143 | 0.962 |
表1 与KNN相关的各种模型的性能
Tab.1 Performances of different models associated with KNN learning
| Models | AUC (95% CI) | Accuracy | Recall | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RUS-KNN | 0.792(0.586-0.958) | 0.679 | 0.728 | 0.664 |
| RENN-KNN | 0.736(0.519-0.925) | 0.643 | 0.678 | 0.637 |
| AllKNN-KNN | 0.708(0.465-0.909) | 0.679 | 0.750 | 0.655 |
| NM-KNN | 0.769(0.558-0.939) | 0.679 | 0.782 | 0.646 |
| CNN-KNN | 0.822(0.635-0.964) | 0.714 | 0.675 | 0.733 |
| NCR-KNN | 0.734(0.507-0.927) | 0.664 | 0.618 | 0.684 |
| IHT-KNN | 0.710(0.479-0.909) | 0.664 | 0.728 | 0.646 |
| KNN-baseline | 0.784(0.571-0.955) | 0.750 | 0.143 | 0.962 |
| Models | AUC (95% CI) | Accuracy | Recall | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RUS-RF | 0.768(0.556-0.932) | 0.636 | 0.696 | 0.617 |
| RENN-RF | 0.722(0.504-0.907) | 0.543 | 0.793 | 0.465 |
| AllKNN-RF | 0.692(0.476-0.883) | 0.593 | 0.675 | 0.569 |
| NM-RF | 0.701(0.475-0.892) | 0.579 | 0.586 | 0.580 |
| CNN-RF | 0.772(0.566-0.942) | 0.700 | 0.725 | 0.694 |
| NCR-RF | 0.672(0.466-0.876) | 0.614 | 0.504 | 0.656 |
| IHT-RF | 0.656(0.430-0.854) | 0.550 | 0.750 | 0.482 |
| RF-baseline | 0.731(0.518-0.909) | 0.750 | 0.336 | 0.895 |
表2 与RF相关的各种模型的性能
Tab.2 Performances of different models associated with RF learning
| Models | AUC (95% CI) | Accuracy | Recall | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RUS-RF | 0.768(0.556-0.932) | 0.636 | 0.696 | 0.617 |
| RENN-RF | 0.722(0.504-0.907) | 0.543 | 0.793 | 0.465 |
| AllKNN-RF | 0.692(0.476-0.883) | 0.593 | 0.675 | 0.569 |
| NM-RF | 0.701(0.475-0.892) | 0.579 | 0.586 | 0.580 |
| CNN-RF | 0.772(0.566-0.942) | 0.700 | 0.725 | 0.694 |
| NCR-RF | 0.672(0.466-0.876) | 0.614 | 0.504 | 0.656 |
| IHT-RF | 0.656(0.430-0.854) | 0.550 | 0.750 | 0.482 |
| RF-baseline | 0.731(0.518-0.909) | 0.750 | 0.336 | 0.895 |
| Models | AUC (95% CI) | Accuracy | Recall | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RUS-SVM | 0.791(0.595-0.955) | 0.728 | 0.807 | 0.702 |
| RENN-SVM | 0.702(0.363-0.828) | 0.593 | 0.843 | 0.513 |
| AllKNN-SVM | 0.708(0.490-0.895) | 0.629 | 0.778 | 0.579 |
| NM-SVM | 0.797(0.600-0.950) | 0.664 | 0.836 | 0.607 |
| CNN-SVM | 0.782(0.577-0.950) | 0.757 | 0.700 | 0.780 |
| NCR-SVM | 0.714(0.495-0.902) | 0.671 | 0.643 | 0.684 |
| IHT-SVM | 0.734(0.511-0.912) | 0.621 | 0.778 | 0.568 |
| SVM-baseline | 0.712(0.485-0.910) | 0.743 | 0 | 1 |
表3 与SVM相关各种模型的性能
Tab.3 Performances of different models associated with SVM learning
| Models | AUC (95% CI) | Accuracy | Recall | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RUS-SVM | 0.791(0.595-0.955) | 0.728 | 0.807 | 0.702 |
| RENN-SVM | 0.702(0.363-0.828) | 0.593 | 0.843 | 0.513 |
| AllKNN-SVM | 0.708(0.490-0.895) | 0.629 | 0.778 | 0.579 |
| NM-SVM | 0.797(0.600-0.950) | 0.664 | 0.836 | 0.607 |
| CNN-SVM | 0.782(0.577-0.950) | 0.757 | 0.700 | 0.780 |
| NCR-SVM | 0.714(0.495-0.902) | 0.671 | 0.643 | 0.684 |
| IHT-SVM | 0.734(0.511-0.912) | 0.621 | 0.778 | 0.568 |
| SVM-baseline | 0.712(0.485-0.910) | 0.743 | 0 | 1 |
| Models | AUC (95% CI) | Accuracy | Recall | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RUS-MLP | 0.791(0.593-0.949) | 0.657 | 0.721 | 0.634 |
| RENN-MLP | 0.723(0.504-0.910) | 0.607 | 0.818 | 0.541 |
| AllKNN-MLP | 0.729(0.520-0.911) | 0.664 | 0.807 | 0.616 |
| NM-MLP | 0.822(0.632-0.960) | 0.729 | 0.786 | 0.713 |
| CNN-MLP | 0.782(0.570-0.954) | 0.679 | 0.728 | 0.666 |
| NCR-MLP | 0.730(0.499-0.913) | 0.693 | 0.614 | 0.722 |
| IHT-MLP | 0.736(0.530-0.909) | 0.629 | 0.811 | 0.568 |
| MLP-baseline | 0.710(0.467-0.911) | 0.736 | 0.414 | 0.847 |
表4 与MLP相关的各种模型的性能
Tab.4 Performances of different models associated with MLP learning
| Models | AUC (95% CI) | Accuracy | Recall | Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RUS-MLP | 0.791(0.593-0.949) | 0.657 | 0.721 | 0.634 |
| RENN-MLP | 0.723(0.504-0.910) | 0.607 | 0.818 | 0.541 |
| AllKNN-MLP | 0.729(0.520-0.911) | 0.664 | 0.807 | 0.616 |
| NM-MLP | 0.822(0.632-0.960) | 0.729 | 0.786 | 0.713 |
| CNN-MLP | 0.782(0.570-0.954) | 0.679 | 0.728 | 0.666 |
| NCR-MLP | 0.730(0.499-0.913) | 0.693 | 0.614 | 0.722 |
| IHT-MLP | 0.736(0.530-0.909) | 0.629 | 0.811 | 0.568 |
| MLP-baseline | 0.710(0.467-0.911) | 0.736 | 0.414 | 0.847 |
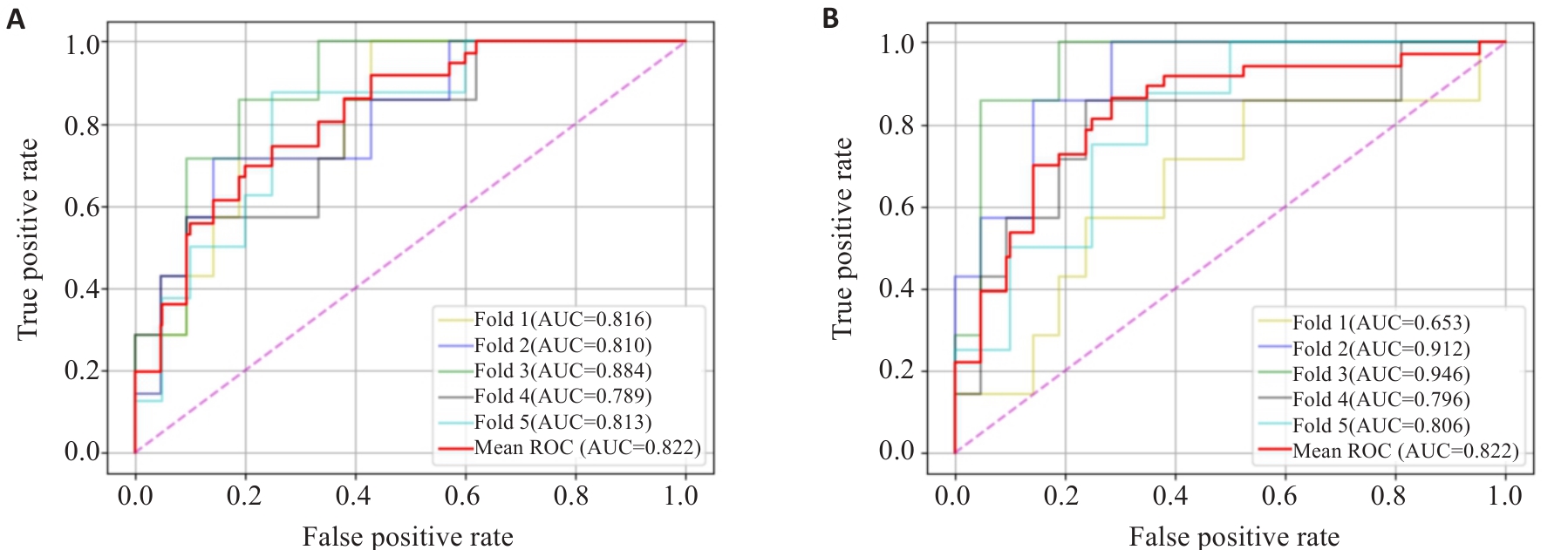
图4 五折交叉验证测试的两个最佳模型的ROC及AUC: (A)CNN-KNN和(B)NM-MLP
Fig.4 ROC and AUC for the 5-fold cross-validation tests of the two best models: CNN-KNN (A) andNM-MLP (B).
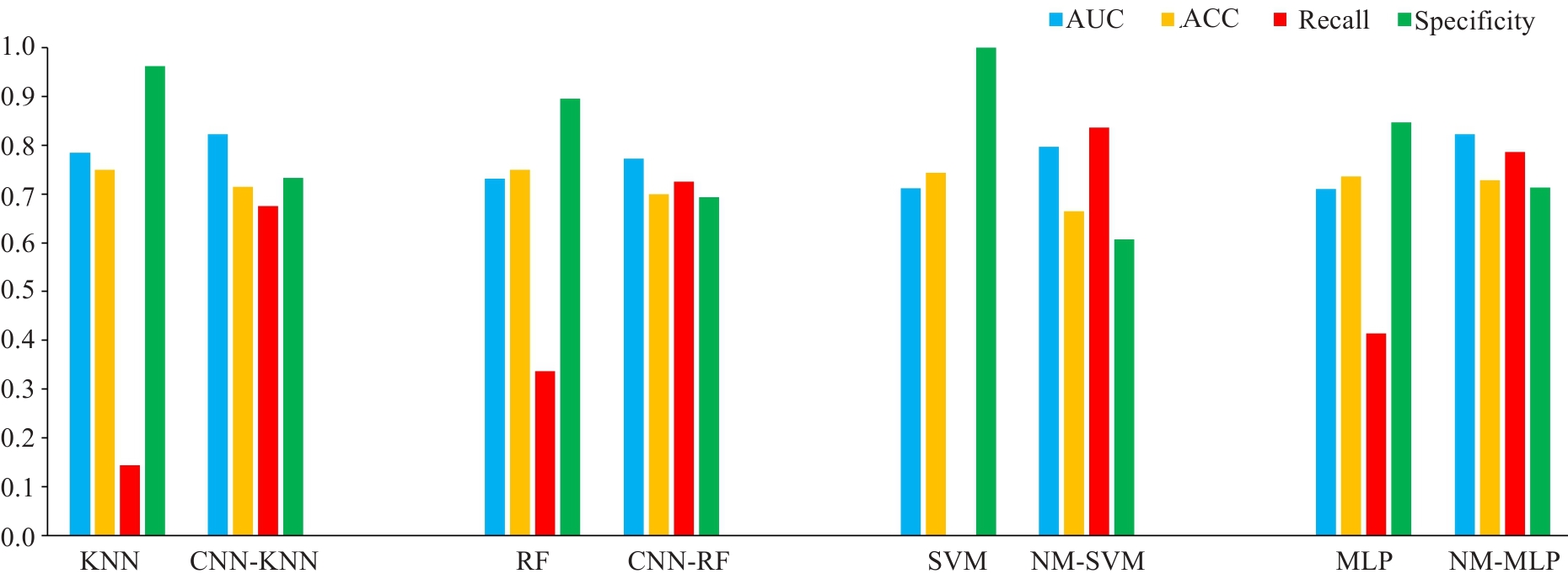
图5 使用、未使用欠采样的KNN、RF、SVM和MLP模型的预测性能比较(包含AUC、准确率、召回率和特异性)
Fig.5 Comparison of prediction performances (AUC, accuracy, recall and specificity) among KNN, RF, SVM and MLP models without and with under-sampling. ACC: Accuracy.
| [1] | Giuliani E, As-Sanie S, Marsh EE. Epidemiology and management of uterine fibroids[J]. Int J Gynaecol Obstet, 2020, 149(1): 3-9. doi:10.1002/ijgo.13102 |
| [2] | Management of symptomatic uterine leiomyomas: ACOG practice bulletin, number 228[J]. Obstet Gynecol, 2021, 137(6): e100-15. doi:10.1097/aog.0000000000004401 |
| [3] | Grube M, Neis F, Brucker SY, et al. Uterine fibroids - current trends and strategies[J]. Surg Technol Int, 2019, 34: 257-63. |
| [4] | Haviv E, Schwarzman P, Bernstein EH, et al. Subsequent pregnancy outcomes after abdominal vs. laparoscopic myomectomy[J]. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med, 2022, 35(25): 8219-25. doi:10.1080/14767058.2021.1967315 |
| [5] | Hajian-Tilaki K. Sample size estimation in diagnostic test studies of biomedical informatics[J]. J Biomed Inform, 2014, 48: 193-204. doi:10.1016/j.jbi.2014.02.013 |
| [6] | Liu L, Wang T, Lei B. Ultrasound-guided microwave ablation in the management of symptomatic uterine myomas: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Minim Invasive Gynecol, 2021, 28(12): 1982-92. doi:10.1016/j.jmig.2021.06.020 |
| [7] | Jenne JW, Preusser T, Günther M. High-intensity focused ultrasound: principles, therapy guidance, simulations and applications[J]. Z Für Med Phys, 2012, 22(4): 311-22. doi:10.1016/j.zemedi.2012.07.001 |
| [8] | Machtinger R, Inbar Y, Cohen-Eylon S, et al. MR-guided focus ultrasound (MRgFUS) for symptomatic uterine fibroids: predictors of treatment success[J]. Hum Reprod, 2012, 27(12): 3425-31. doi:10.1093/humrep/des333 |
| [9] | Mindjuk I, Trumm CG, Herzog P, et al. MRI predictors of clinical success in MR-guided focused ultrasound (MRgFUS) treatments of uterine fibroids: results from a single centre[J]. Eur Radiol, 2015, 25(5): 1317-28. doi:10.1007/s00330-014-3538-6 |
| [10] | Lambin P, Rios-Velazquez E, Leijenaar R, et al. Radiomics: Extracting more information from medical images using advanced feature analysis[J]. Eur J Cancer, 2012, 48(4): 441-6. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2011.11.036 |
| [11] | Avanzo M, Wei L, Stancanello J, et al. Machine and deep learning methods for radiomics[J]. Med Phys, 2020, 47(5): e185-202. doi:10.1002/mp.13678 |
| [12] | Yip SS, Aerts HJ. Applications and limitations of radiomics[J]. Phys Med Biol, 2016, 61(13): R150-66. doi:10.1088/0031-9155/61/13/r150 |
| [13] | Hocquelet A, Denis de Senneville B, Frulio N, et al. Magnetic resonance texture parameters are associated with ablation efficiency in MR-guided high-intensity focussed ultrasound treatment of uterine fibroids[J]. Int J Hyperthermia, 2017, 33(2): 142-9. doi:10.1080/02656736.2016.1241432 |
| [14] | Li ZC, Zhang J, Song Y, et al. Utilization of radiomics to predict long-term outcome of magnetic resonance-guided focused ultrasound ablation therapy in adenomyosis[J]. Eur Radiol, 2021, 31(1): 392-402. doi:10.1007/s00330-020-07076-1 |
| [15] | Zheng Y, Chen L, Liu M, et al. Prediction of clinical outcome for high-intensity focused ultrasound ablation of uterine leiomyomas using multiparametric MRI radiomics-based machine leaning model[J]. Front Oncol, 2021, 11: 618604. doi:10.3389/fonc.2021.618604 |
| [16] | Li DC, Liu CW, Hu SC. A learning method for the class imbalance problem with medical data sets[J]. Comput Biol Med, 2010, 40(5): 509-18. doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2010.03.005 |
| [17] | Galar M, Fernandez A, Barrenechea E, et al. A review on ensembles for the class imbalance problem: bagging-, boosting-, and hybrid-based approaches[J]. IEEE Trans Syst, Man, Cybern C, 42(4): 463-84. doi:10.1109/tsmcc.2011.2161285 |
| [18] | Funaki K, Fukunishi H, Funaki T, et al. Magnetic resonance-guided focused ultrasound surgery for uterine fibroids: relationship between the therapeutic effects and signal intensity of preexisting T2-weighted magnetic resonance images[J]. Am J Obstet Gynecol, 2007, 196(2): 184.e1-6. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2006.08.030 |
| [19] | Kim YS, Lim HK, Park MJ, et al. Screening magnetic resonance imaging-based prediction model for assessing immediate therapeutic response to magnetic resonance imaging-guided high-intensity focused ultrasound ablation of uterine fibroids[J]. Invest Radiol, 2016, 51(1): 15-24. doi:10.1097/rli.0000000000000199 |
| [20] | Jiang Y, Qin S, Wang Y, et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion-weighted MRI for predicting the efficacy of high-intensity focused ultrasound ablation for uterine fibroids[J]. Front Oncol, 2023, 13: 1178649. doi:10.3389/fonc.2023.1178649 |
| [21] | Carré A, Klausner G, Edjlali M, et al. Standardization of brain MR images across machines and protocols: bridging the gap for MRI-based radiomics[J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1): 12340. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-69298-z |
| [22] | Nyul LG, Udupa JK, Zhang X. New variants of a method of MRI scale standardization[J]. IEEE Trans Med Imaging, 19(2): 143-50. doi:10.1109/42.836373 |
| [23] | Zwanenburg A, Vallières M, Abdalah MA, et al. The image biomarker standardization initiative: standardized quantitative radiomics for high-throughput image-based phenotyping[J]. Radiology, 2020, 295(2): 328-38. doi:10.1148/radiol.2020191145 |
| [24] | Kira K, Rendell LA. A practical approach to feature selection[C]//Proceedings of the 9th International Workshop on Machine Learning(ML 1992), Aberdeen, Scotland, UK, July 1-3, 1992.[S.l.]: Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc, 1992: 249-26. doi:10.1016/b978-1-55860-247-2.50037-1 |
| [25] | Prusa J, Khoshgoftaar TM, Dittman DJ, et al. Using random undersampling to alleviate class imbalance on tweet sentiment data[C]//2015 IEEE International Conference on Information Reuse and Integration. August 13-15, 2015. San Francisco, CA, USA. IEEE, 2015: 197-202. doi:10.1109/iri.2015.39 |
| [26] | Tomek I. An experiment with the edited nearest-neighbor rule[J]. IEEE Trans Syst, Man, Cybern, SMC-6(6): 448-52. doi:10.1109/tsmc.1976.4309523 |
| [27] | Wilson DL. Asymptotic properties of nearest neighbor rules using edited data[J]. IEEE Trans Syst, Man, Cybern, SMC-2(3): 408-21. doi:10.1109/tsmc.1972.4309137 |
| [28] | Zhang JP, Mani I: kNN approach to unbalanced data distributions: A case study involving information extraction. In: Proceeding of International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML 2003), Workshop on Learning from Imbalanced Data Sets: 2003; Washington D.C.: ICML; 2003: 1-7. |
| [29] | Hart P. The condensed nearest neighbor rule (Corresp.)[J]. IEEE Trans Inform Theory, 14(3): 515-6. doi:10.1109/tit.1968.1054155 |
| [30] | Laurikkala J. Improving identification of difficult small classes by balancing class distribution[M]//Artificial Intelligence in Medicine. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2001: 63-6. doi:10.1007/3-540-48229-6_9 |
| [31] | Smith MR, Martinez T, Giraud-Carrier C. An instance level analysis of data complexity[J]. Mach Learn, 2014, 95(2): 225-56. doi:10.1007/s10994-013-5422-z |
| [32] | Tomaszewski MR, Gillies RJ. The biological meaning of radiomic features[J]. Radiology, 2021, 298(3): 505-16. doi:10.1148/radiol.2021202553 |
| [33] | Zhao WP, Chen JY, Chen WZ. Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI serves as a predictor of HIFU treatment outcome for uterine fibroids with hyperintensity in T2-weighted images[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2016, 11(1): 328-34. doi:10.3892/etm.2015.2879 |
| [34] | Fribbens C, O'Leary B, Kilburn L, et al. Plasma ESR1 mutations and the treatment of estrogen receptor-positive advanced breast cancer[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2016, 34(25): 2961-8. doi:10.1200/jco.2016.67.3061 |
| [35] | Rogers W, Thulasi Seetha S, Refaee TAG, et al. Radiomics: from qualitative to quantitative imaging[J]. Br J Radiol, 2020, 93(1108): 20190948. doi:10.1259/bjr.20190948 |
| [36] | Zheng Y, Chen L, Liu M, et al. Nonenhanced MRI-based radiomics model for preoperative prediction of nonperfused volume ratio for high-intensity focused ultrasound ablation of uterine leiomyomas[J]. Int J Hyperthermia, 2021, 38(1): 1349-58. doi:10.1080/02656736.2021.1972170 |
| [37] | Walsh R, Tardy M. A comparison of techniques for class imbalance in deep learning classification of breast cancer[J]. Diagnostics: Basel, 2022, 13(1): 67. doi:10.3390/diagnostics13010067 |
| [38] | Guo HX, Li YJ, Shang J, et al. Learning from class-imbalanced data: review of methods and applications[J]. Expert Syst Appl, 2017, 73: 220-39. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2016.12.035 |
| [39] | Kraiem MS, Sánchez-Hernández F, Moreno-García MN. Selecting the suitable resampling strategy for imbalanced data classification regarding dataset properties. an approach based on association models[J]. Appl Sci, 2021, 11(18): 8546. doi:10.3390/app11188546 |
| [40] | Li M, Wu Z, Wang W, et al. Protein-protein interaction sites prediction based on an under-sampling strategy and random forest algorithm[J]. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform, 2022, 19(6): 3646-54. doi:10.1109/tcbb.2021.3123269 |
| [1] | 张力莹, 张同贞, 赵鑫. 基于乳腺影像报告和数据系统的DWI和T2WI形态评估对乳腺病变的诊断价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1809-1817. |
| [2] | 黄启智, 谢戴鹏, 姚霖彤, 李洽轩, 吴少伟, 周海榆. 肿瘤微环境特异性CT影像组学标签预测非小细胞肺癌免疫治疗疗效[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1903-1918. |
| [3] | 姜君, 封硕, 孙银贵, 安燕. 经尿道前列腺钬激光剜除术后低体温风险预测模型:基于逻辑回归、决策树和支持向量机[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 2019-2025. |
| [4] | 董振翔, 郭义昊, 刘蔷, 张益哲, 丘倩怡, 张晓东, 冯衍秋. 基于双极读出梯度的单重复时间腰椎定量磁化率成像[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1336-1342. |
| [5] | 陈梅妹, 王洋, 雷黄伟, 张斐, 黄睿娜, 杨朝阳. 基于多种机器学习算法和语音情绪特征的阈下抑郁辨识模型构建[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 711-717. |
| [6] | 申琳, 宋翠豪, 王聪敏, 高西, 安俊红, 李承新, 梁斌, 李霞. 溃疡性结肠炎并发坏疽性脓皮病患者发生营养风险的因素及预测模型[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 514-521. |
| [7] | 王飞, 李蔚然, 尚祥, 李飞. 中国农村社区老年人认知障碍预测模型的构建与验证——基于中国健康与养老追踪调查数据库[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(12): 2639-2645. |
| [8] | 李欣洋, 许桂晓, 刘洁宏, 冯衍秋. 人工智能辅助压缩感知加速技术对鼻咽癌MRI影像组学特征提取及分期诊断模型性能的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(11): 2518-2526. |
| [9] | 李孝媛, 张逸悦, 顾雨铖, 陈霓红, 钱鑫宇, 张朋俊, 郝佳欣, 王峰. Tau蛋白沉积与脑代谢物的关联性:N-乙酰天门冬氨酸与肌酸作为进展期阿尔茨海默病的潜在生物标志物[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(11): 2350-2357. |
| [10] | 潘甚豪, 李炎坤, 伍哲维, 毛玉玲, 王春艳. 子宫内膜异位症患者新鲜胚胎移植临床妊娠率预测模型的建立与验证[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1407-1415. |
| [11] | 刘科, 马振岩, 付磊, 张丽萍, 阿鑫, 肖少波, 张震, 张洪博, 赵蕾, 钱赓. 心脏磁共振成像整体纵向应变对急性ST段抬高型心肌梗死后左心室重构的预测价值:403例前瞻性研究[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(6): 1033-1039. |
| [12] | 陈莉莉, 吴天宇, 张铭, 丁子夏, 张妍, 杨依清, 郑佳倩, 张小楠. 类风湿关节炎的潜在生物标志物及其免疫调控机制:基于GEO数据库[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(6): 1098-1108. |
| [13] | 申采玉, 王帅, 周锐盈, 汪雨贺, 高琴, 陈兴智, 杨枢. 慢性心力衰竭合并肺部感染患者院内死亡风险预测:基于可解释性机器学习方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(6): 1141-1148. |
| [14] | 左志威, 孟庆良, 崔家康, 郭克磊, 卞华. 基于硬皮病线粒体相关基因的人工神经网络模型的构建[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 920-929. |
| [15] | 戈 悦, 李建伟, 梁宏开, 侯六生, 左六二, 陈 珍, 卢剑海, 赵 新, 梁静漪, 彭 岚, 包静娜, 段佳欣, 刘 俐, 毛可晴, 曾振华, 胡鸿彬, 陈仲清. VA-ECMO患者院内死亡风险预测模型的构建及验证:一项多中心、回顾性、病例对照研究[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 491-498. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||