南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (5): 1063-1073.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.05.20
郭晓娟1( ), 杜瑞娟1,2, 陈丽平1,2, 郭克磊1,2, 周彪1,2, 卞华1,2, 韩立1,2(
), 杜瑞娟1,2, 陈丽平1,2, 郭克磊1,2, 周彪1,2, 卞华1,2, 韩立1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2024-08-13
出版日期:2025-05-20
发布日期:2025-05-23
通讯作者:
韩立
E-mail:3152044@nyist.edu.cn;hanli@nyist.edu.cn
作者简介:郭晓娟,副教授,E-mail: 3152044@nyist.edu.cn
基金资助:
Xiaojuan GUO1( ), Ruijuan DU1,2, Liping CHEN1,2, Kelei GUO1,2, Biao ZHOU1,2, Hua BIAN1,2, Li HAN1,2(
), Ruijuan DU1,2, Liping CHEN1,2, Kelei GUO1,2, Biao ZHOU1,2, Hua BIAN1,2, Li HAN1,2( )
)
Received:2024-08-13
Online:2025-05-20
Published:2025-05-23
Contact:
Li HAN
E-mail:3152044@nyist.edu.cn;hanli@nyist.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
目的 探讨WW结构域E3泛素连接酶1(WWP1)表达与卵巢癌肿瘤微环境(TME)免疫浸润调控的关系。 方法 从TCGA获取卵巢癌患者数据,以中位值为截断值分为WWP1高表达和低表达组。生物信息学方法分析WWP1表达与卵巢癌预后关系;TISCH2比较WWP1在卵巢癌转移和化疗后TME不同免疫细胞亚型的差异;TIMER分析WWP1表达对TME免疫细胞浸润和体细胞拷贝数变异的影响;TIGER分析WWP1表达与卵巢癌不同免疫细胞亚型演化的关系;深度学习模型分析TCGA病理染色图像,确定WWP1对卵巢癌患者TME的影响;WWP1高表达前后的SKOV3细胞进行转录组测序,比较差异基因并进行免疫浸润验证分析;在SKOV3和SKOV3/DDP裸鼠肿瘤组织中采用多色免疫荧光比较分析免疫标志物差异。 结果 WWP1高表达卵巢癌患者的整体生存率低于WWP1低表达患者(P=0.0012)。高表达WWP1、Stage IV 等与卵巢癌不良预后相关(P<0.05)。卵巢癌转移或化疗后,TME中恶性肿瘤细胞、肿瘤相关成纤维细胞比例明显升高,WWP1表达比例亦明显增高(P<0.05)。WWP1表达与TME中促肿瘤免疫抑制性细胞正相关(r=0.1323~0.3955,P<0.05),与抑制肿瘤的免疫浸润细胞负相关(r=-0.1949~-0.1333,P<0.05)。CD8+T细胞浸润水平与WWP1的深度缺失和染色体水平缺失有关,中性粒细胞浸润水平与WWP1高度扩增有关(P<0.05)。随着WWP1 表达升高,TME中CD8+、NK T细胞比例逐渐减少,髓样细胞和B细胞逐渐演化为不同细胞亚型。TCGA患者病理标本HE染色、高表达WWP1的SKOV3细胞转录组测序和裸鼠肿瘤组织多色免疫荧光分析确认了与生信分析相似的TME免疫细胞浸润结果。 结论 WWP1可能是卵巢癌的一个预后预测因子和潜在的TME免疫调控靶点。
郭晓娟, 杜瑞娟, 陈丽平, 郭克磊, 周彪, 卞华, 韩立. WW结构域E3泛素连接酶1调控卵巢癌肿瘤微环境中的免疫浸润[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(5): 1063-1073.
Xiaojuan GUO, Ruijuan DU, Liping CHEN, Kelei GUO, Biao ZHOU, Hua BIAN, Li HAN. WW domain-containing ubiquitin E3 ligase 1 regulates immune infiltration in tumor microenvironment of ovarian cancer[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 1063-1073.
| Characteristics | Low expression of WWP1 | High expression of WWP1 | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Case (n) | 185 | 187 | |
| Figo Clinical stage [n (%)] | 0.0012 | ||
| Stage III | 152 (40.9%) | 139 (37.4%) | |
| Stage IV | 20 (5.4%) | 37 (9.9%) | |
| Stage II | 11 (2.9%) | 12 (3.2%) | |
| Stage I | 1 (0.2%) | - | |
| Primary therapy outcome [n (%)] | <0.0001 | ||
| PD | 13 (3.5%) | 11 (3.0%) | |
| SD | 11 (3.0%) | 11 (3.0%) | |
| PR | 18 (4.8%) | 25 (6.7%) | |
| CR | 109 (29.3%) | 101 (27.2%) | |
| Race [n (%)] | 0.846 | ||
| Asian | 7 (1.6%) | 4 (1.6%) | |
| Black or african american | 14 (3.8%) | 11 (3%) | |
| White | 155 (41.7%) | 168 (45.2%) | |
| Age [median (IQR)] | 61 (51, 71) | 58 (51, 65) | 0.039 |
表1 卵巢癌患者资料和WWP1表达情况
Tab.1 Clinical characteristics of ovarian cancer patients with low and high WWP1 expression levels
| Characteristics | Low expression of WWP1 | High expression of WWP1 | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Case (n) | 185 | 187 | |
| Figo Clinical stage [n (%)] | 0.0012 | ||
| Stage III | 152 (40.9%) | 139 (37.4%) | |
| Stage IV | 20 (5.4%) | 37 (9.9%) | |
| Stage II | 11 (2.9%) | 12 (3.2%) | |
| Stage I | 1 (0.2%) | - | |
| Primary therapy outcome [n (%)] | <0.0001 | ||
| PD | 13 (3.5%) | 11 (3.0%) | |
| SD | 11 (3.0%) | 11 (3.0%) | |
| PR | 18 (4.8%) | 25 (6.7%) | |
| CR | 109 (29.3%) | 101 (27.2%) | |
| Race [n (%)] | 0.846 | ||
| Asian | 7 (1.6%) | 4 (1.6%) | |
| Black or african american | 14 (3.8%) | 11 (3%) | |
| White | 155 (41.7%) | 168 (45.2%) | |
| Age [median (IQR)] | 61 (51, 71) | 58 (51, 65) | 0.039 |
| Characteristics | Case (n) | Univariate analysis | Multivariate analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard ratio (95% CI) | P | Hazard ratio (95% CI) | P | |||
| WWP1 | 372 | |||||
| Low | 185 | Reference | Reference | |||
| High | 187 | 1.499 (1.156-1.942) | 0.002 | 0.024 | ||
| Clinical stage | 372 | |||||
| I & II | 24 | Reference | ||||
| III | 291 | 2.058 (0.911-4.649) | 0.083 | |||
| IV | 57 | 2.556 (1.085-6.025) | 0.032 | |||
| Tumor status | 337 | |||||
| Tumor free | 72 | Reference | Reference | |||
| With tumor | 265 | 9.598 (4.487-20.532) | < 0.001 | 15.691 (3.811-64.606) | <0.001 | |
| Primary therapy outcome | 299 | < 0.001 | ||||
| PD | 24 | Reference | Reference | |||
| SD | 22 | 0.441 (0.217-0.896) | 0.024 | 0.397 (0.187-0.845) | 0.016 | |
| PR | 43 | 0.652 (0.384-1.108) | 0.114 | 0.659 (0.374-1.160) | 0.148 | |
| CR | 210 | 0.154 (0.095-0.250) | <0.001 | 0.179 (0.106-0.302) | <0.001 | |
| Tumor residual | 336 | |||||
| No | 68 | Reference | ||||
| Yes | 268 | 2.223 (1.441-3.430) | <0.001 | |||
| Age (year) | 372 | |||||
| ≤60 | 207 | Reference | ||||
| >60 | 165 | 1.352 (1.045-1.749) | 0.022 | |||
表2 WWP1表达相关风险因素的单因素和多因素分析
Tab.2 Univariate and multivariate analyses of the risk factors for poor prognosis of ovarian cancer patients
| Characteristics | Case (n) | Univariate analysis | Multivariate analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard ratio (95% CI) | P | Hazard ratio (95% CI) | P | |||
| WWP1 | 372 | |||||
| Low | 185 | Reference | Reference | |||
| High | 187 | 1.499 (1.156-1.942) | 0.002 | 0.024 | ||
| Clinical stage | 372 | |||||
| I & II | 24 | Reference | ||||
| III | 291 | 2.058 (0.911-4.649) | 0.083 | |||
| IV | 57 | 2.556 (1.085-6.025) | 0.032 | |||
| Tumor status | 337 | |||||
| Tumor free | 72 | Reference | Reference | |||
| With tumor | 265 | 9.598 (4.487-20.532) | < 0.001 | 15.691 (3.811-64.606) | <0.001 | |
| Primary therapy outcome | 299 | < 0.001 | ||||
| PD | 24 | Reference | Reference | |||
| SD | 22 | 0.441 (0.217-0.896) | 0.024 | 0.397 (0.187-0.845) | 0.016 | |
| PR | 43 | 0.652 (0.384-1.108) | 0.114 | 0.659 (0.374-1.160) | 0.148 | |
| CR | 210 | 0.154 (0.095-0.250) | <0.001 | 0.179 (0.106-0.302) | <0.001 | |
| Tumor residual | 336 | |||||
| No | 68 | Reference | ||||
| Yes | 268 | 2.223 (1.441-3.430) | <0.001 | |||
| Age (year) | 372 | |||||
| ≤60 | 207 | Reference | ||||
| >60 | 165 | 1.352 (1.045-1.749) | 0.022 | |||
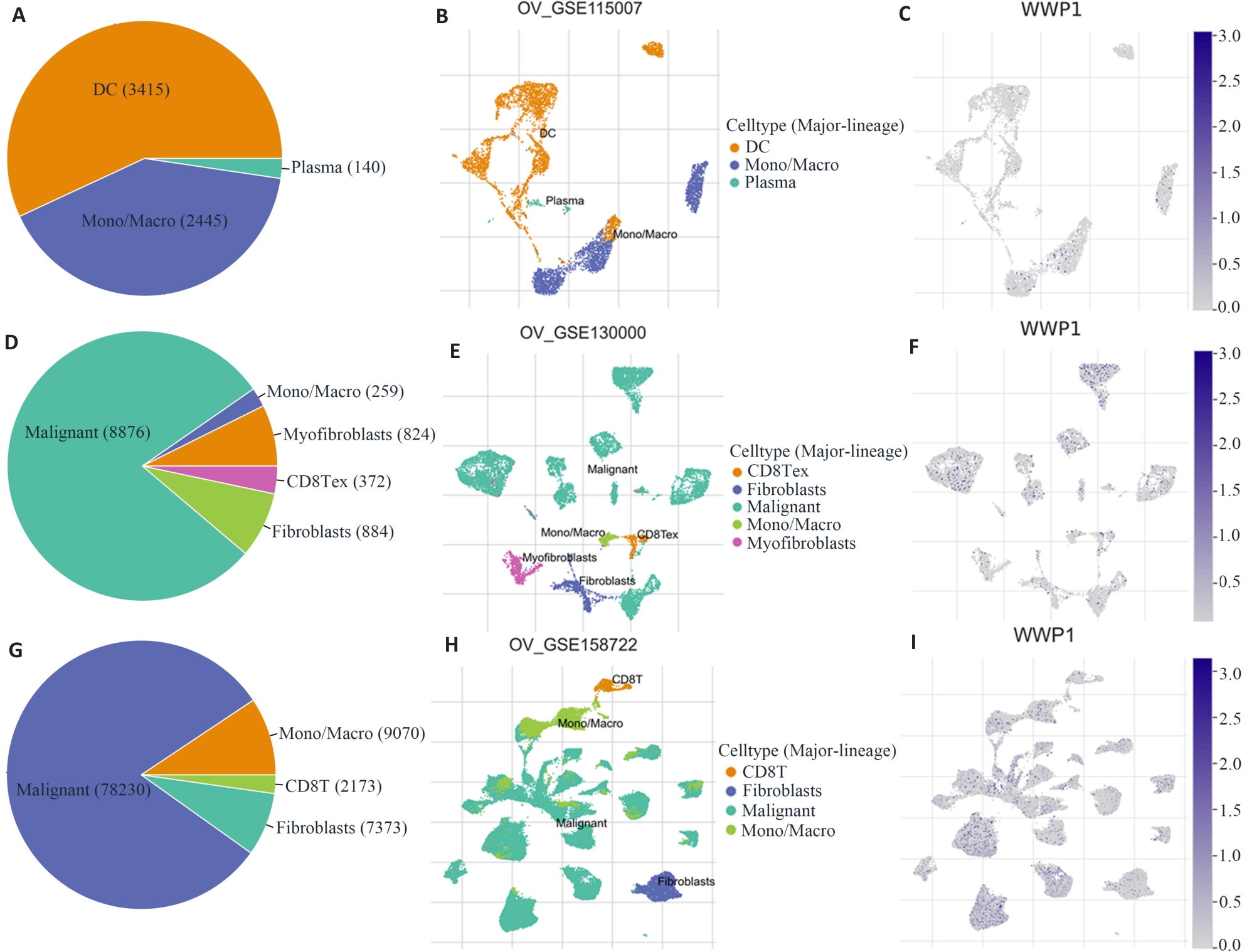
图2 卵巢癌转移或化疗后TME细胞亚群分布和WWP1表达变化
Fig.2 Analysis of WWP1-related cell type distribution in primary tumor, primary plus metastatic tumor, and primary tumor plus chemotherapy using scRNA seq database. A, B, D, E, G, H: Cell types and their distribution. C, F, I: Distribution of WWP1 in different cells in OV_GSE115007, OV_GSE130000 and OV_GSE158722 datasets.

图3 卵巢癌免疫浸润细胞与WWP1表达相关性
Fig.3 Correlation between immune infiltration and WWP1 expression in ovarian cancer. XCELL, CIBERSORT, CIBERSORT-ABS, QUANTISEQ, EPIC, MCPCOUNTER and TIMER are different immune infiltration algorithms.
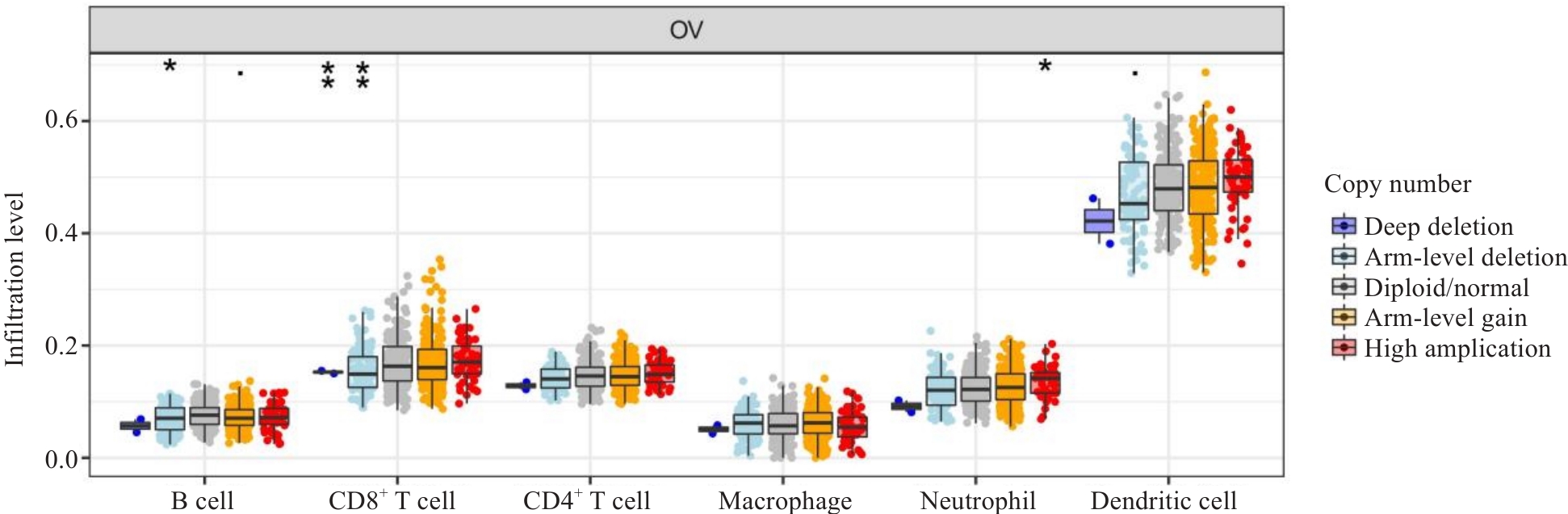
图4 WWP1对卵巢癌免疫浸润细胞拷贝数变异影响
Fig.4 Correlation between immune infiltration and WWP1 expression in ovarian cancer. XCELL,CIBERSORT, CIBERSORT-ABS, QUANTISEQ, EPIC, MCPCOUNTER and TIMER are different immune infiltration algorithms. *P <0.05, **P<0.01.
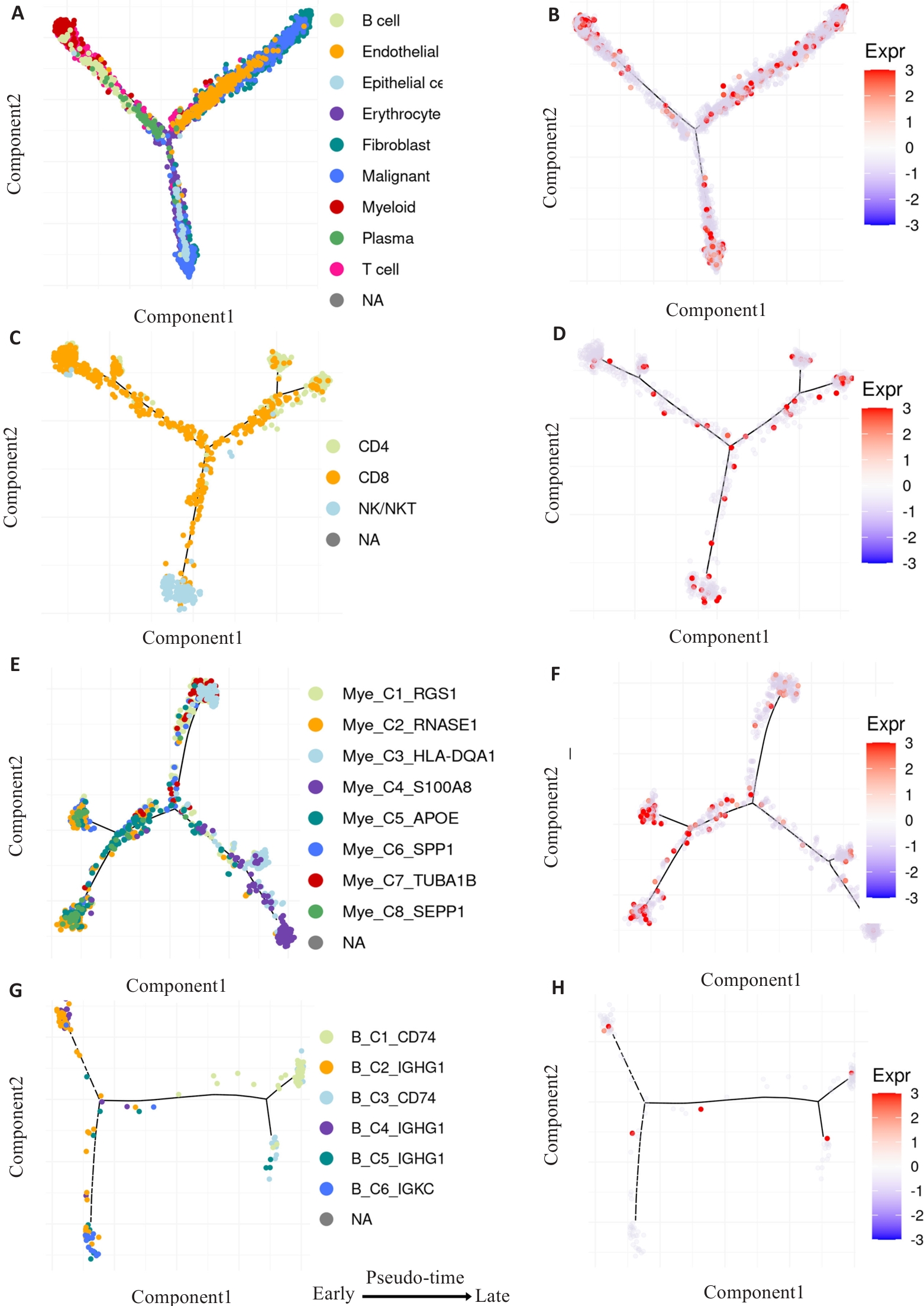
图5 拟时序分析卵巢癌WWP1表达对免疫浸润细胞动态变化的影响
Fig.5 Pseudo-time analysis of the effect of WWP1 expression on dynamic changes of infiltrating immune cells in ovarian cancer. A, C, E, G: Developmental trajectories of the pooled infiltrating immune cells, CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, NK cells, myeloid cells and B cells (The inferred direction to differentiation and maturation was from the left to the right). B, D, F, H: Dynamic expressions of WWP1 related to the differentiation and maturation along the pseudo-time axis.
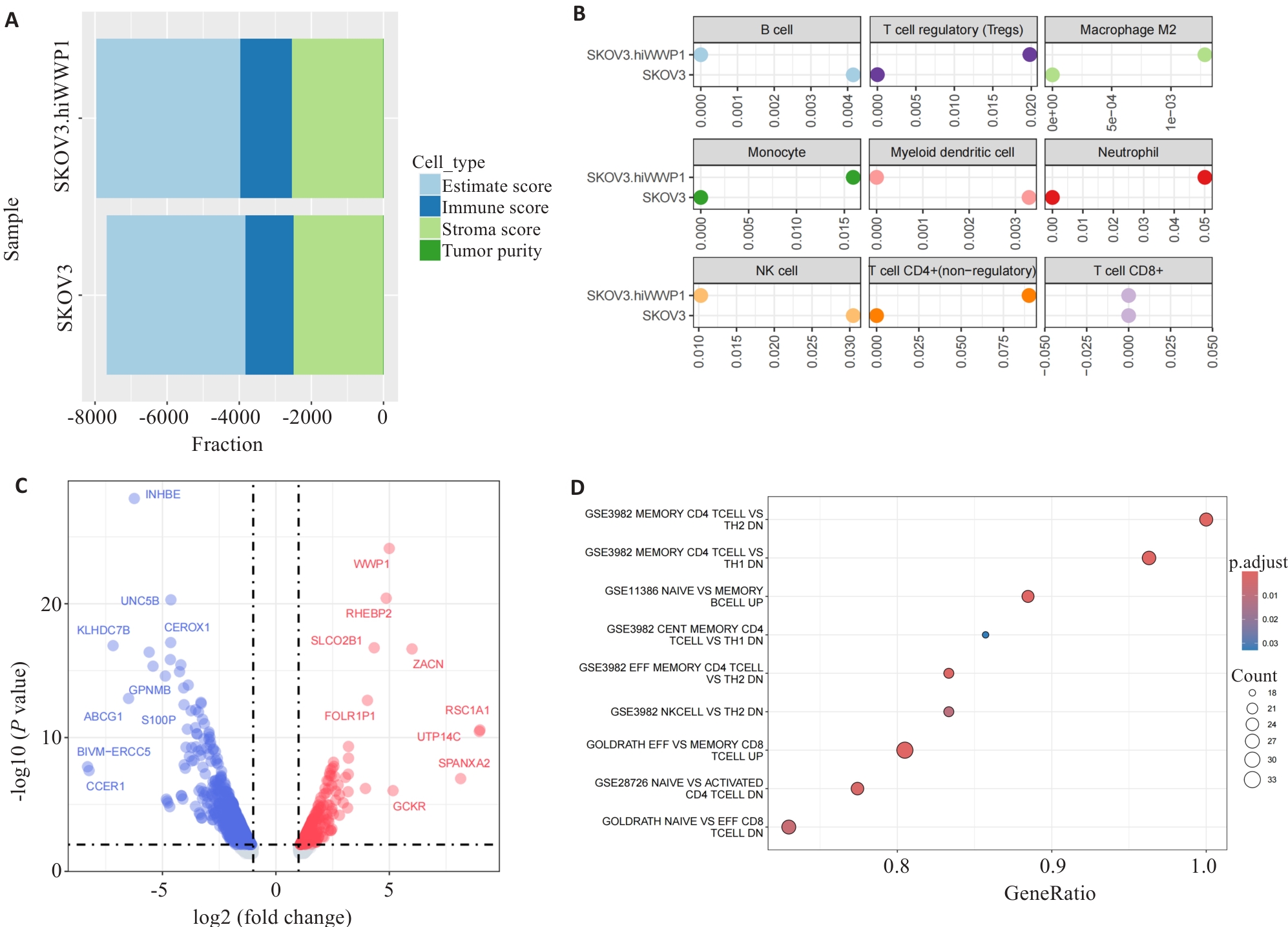
图7 SKOV3细胞高表达WWP1对免疫浸润的影响
Fig.7 Effect of WWP1 overexpression on immune infiltration in SKOV3 cells. A: Comparison of immune microenvironment. B: Comparison of immune infiltration. C: Volcano map for Top 20 difference genes. D: Comparison of immune pathways of GSEA enrichment.
| 1 | 中国抗癌协会妇科肿瘤专业委员会. 卵巢恶性肿瘤诊断与治疗指南(2021年版)[J]. 中国癌症杂志, 2021, 31(6): 490-500. DOI: 10.19538/j.fk2021060111 |
| 2 | Sosinsky A, Ambrose J, Cross W, et al. Insights for precision oncology from the integration of genomic and clinical data of 13, 880 tumors from the 100, 000 Genomes Cancer Programme[J]. Nat Med, 2024, 30(1): 279-89. |
| 3 | Liu J, Berchuck A, Backes FJ, et al. NCCN guidelines® insights: ovarian cancer/fallopian tube cancer/primary peritoneal cancer, version 3.2024[J]. J Natl Compr Canc Netw, 2024, 22(8): 512-9. |
| 4 | Zou XQ, Zhao YJ, Liang XT, et al. Double insurance for OC: miRNA-mediated platinum resistance and immune escape[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 641937. |
| 5 | Xu JF, Fang YF, Chen KL, et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals the tissue architecture in human high-grade serous ovarian cancer[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2022, 28(16): 3590-602. |
| 6 | Du YH, Shi JT, Wang JX, et al. Integration of pan-cancer single-cell and spatial transcriptomics reveals stromal cell features and therapeutic targets in tumor microenvironment[J]. Cancer Res, 2024, 84(2): 192-210. |
| 7 | El-Tanani M, Rabbani SA, Babiker R, et al. Unraveling the tumor microenvironment: Insights into cancer metastasis and therapeutic strategies[J]. Cancer Lett, 2024, 591: 216894. |
| 8 | Zhong GH, Zhao DS, Li JW, et al. WWP1 deficiency alleviates cardiac remodeling induced by simulated microgravity[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2021, 9: 739944. |
| 9 | Novelli G, Liu J, Biancolella M, et al. Inhibition of HECT E3 ligases as potential therapy for COVID-19[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2021, 12(4): 310. |
| 10 | Kishikawa T, Higuchi H, Wang LM, et al. WWP1 inactivation enhances efficacy of PI3K inhibitors while suppressing their toxicities in breast cancer models[J]. J Clin Invest, 2021, 131(24): e140436. |
| 11 | Jiang H, Li ZX, Xu W, et al. WWP1 targeting PTEN for polyubiquitination to promote bone metastasis of luminal breast cancer[J]. Sci Rep, 2024, 14(1): 29950. |
| 12 | Ye P, Chi XX, Cha JH, et al. Potential of E3 ubiquitin ligases in cancer immunity: opportunities and challenges[J]. Cells, 2021, 10(12): 3309. |
| 13 | Schrock MS, Stromberg BR, Scarberry L, et al. APC/C ubiquitin ligase: Functions and mechanisms in tumorigenesis[J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 2020, 67(Pt 2): 80-91. |
| 14 | Liao CH, Yu LP, Pang Z, et al. WWP1 targeting MUC1 for ubiquitin-mediated lysosomal degradation to suppress carcinogenesis[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2021, 6(1): 297. |
| 15 | Han Y, Wang YT, Dong X, et al. TISCH2: expanded datasets and new tools for single-cell transcriptome analyses of the tumor microenvironment[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2023, 51(D1): D1425-31. |
| 16 | Chen ZH, Luo ZW, Zhang D, et al. TIGER A web portal of tumor immunotherapy gene expression resource[J]. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics, 2023, 21(2): 337-48. |
| 17 | Qian JB, Olbrecht S, Boeckx B, et al. A pan-cancer blueprint of the heterogeneous tumor microenvironment revealed by single-cell profiling[J]. Cell Res, 2020, 30(9): 745-62. |
| 18 | Rong RC, Sheng H, Jin KW, et al. A deep learning approach for histology-based nucleus segmentation and tumor microenvironment characterization[J]. Mod Pathol, 2023, 36(8): 100196. |
| 19 | Wu TZ, Hu EQ, Xu SB, et al. clusterProfiler 4.0: a universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data[J]. Innovation, 2021, 2(3): 100141. |
| 20 | 韩 立, 郭晓娟, 杜瑞娟, 等. 芍药内酯苷对人卵巢癌多药耐药的逆转作用[J]. 中国药理学通报, 2023, 39(2): 268-74. DOI: 10.12360/CPB202102039 |
| 21 | Wehrli M, Guinn S, Birocchi F, et al. Mesothelin CAR T cells secreting anti-FAP/anti-CD3 molecules efficiently target pancreatic adenocarcinoma and its stroma[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2024, 30(9): 1859-77. |
| 22 | Luo YK, Xia Y, Liu D, et al. Neoadjuvant PARPi or chemotherapy in ovarian cancer informs targeting effector Treg cells for homologous-recombination-deficient tumors[J]. Cell, 2024, 187(18): 4905-25.e24. |
| 23 | de Visser KE, Joyce JA. The evolving tumor microenvironment: From cancer initiation to metastatic outgrowth[J]. Cancer Cell, 2023, 41(3): 374-403. |
| 24 | 关深元, 沈智勇, 林名岛, 等. 泛癌组织STIP1的表达与肿瘤免疫浸润及预后相关: 基于生物信息学方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(7): 1179-93. DOI: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2023.07.15 |
| 25 | Malmgren JA, Mayer M, Atwood MK, et al. Differential presentation and survival of de novo and recurrent metastatic breast cancer over time: 1990-2010[J]. Breast Cancer Res Treat, 2018, 167(2): 579-90. |
| 26 | Karagiannis GS, Pastoriza JM, Wang YR, et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy induces breast cancer metastasis through a TMEM-mediated mechanism[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2017, 9(397): eaan0026. |
| 27 | Long XH, Zhang SL, Wang YL, et al. Targeting JMJD1C to selectively disrupt tumor Treg cell fitness enhances antitumor immunity[J]. Nat Immunol, 2024, 25(3): 525-36. |
| 28 | Gu Y, Liu YF, Fu L, et al. Tumor-educated B cells selectively promote breast cancer lymph node metastasis by HSPA4-targeting IgG[J]. Nat Med, 2019, 25(2): 312-22. |
| 29 | Wang B, Xiong YQ, Li R, et al. Shorter telomere length increases the risk of lymphocyte immunodeficiency: a Mendelian randomization study[J]. Immun Inflamm Dis, 2024, 12(4): e1251. |
| 30 | Hollern D. Memory B cell fitness and anergy has significant links to cancer lethality[J]. Cell, 2024, 187(17): 4551-3. |
| 31 | Zeng Q, Mousa M, Nadukkandy AS, et al. Understanding tumour endothelial cell heterogeneity and function from single-cell omics[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2023, 23(8): 544-64. |
| 32 | Ng MSF, Kwok I, Tan L, et al. Deterministic reprogramming of neutrophils within tumors[J]. Science, 2024, 383(6679): eadf6493. |
| 33 | Wen ZW, Sun HY, Zhang ZH, et al. High baseline tumor burden-associated macrophages promote an immunosuppressive microenvironment and reduce the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors through the IGFBP2-STAT3-PD-L1 pathway[J]. Cancer Commun, 2023, 43(5): 562-81. |
| 34 | Tang PC, Chung JY, Xue VW, et al. Smad3 promotes cancer-associated fibroblasts generation via macrophage-myofibroblast transition[J]. Adv Sci, 2022, 9(1): e2101235. |
| 35 | Alspach E, Lussier DM, Miceli AP, et al. MHC-II neoantigens shape tumour immunity and response to immunotherapy[J]. Nature, 2019, 574(7780): 696-701. |
| 36 | Dean I, Lee CYC, Tuong ZK, et al. Rapid functional impairment of natural killer cells following tumor entry limits anti-tumor immunity[J]. Nat Commun, 2024, 15(1): 683. |
| 37 | Spranger S, Dai D, Horton B, et al. Tumor-residing Batf3 dendritic cells are required for effector T cell trafficking and adoptive T cell therapy[J]. Cancer Cell, 2017, 31(5): 711-23.e4. |
| 38 | Zheng ST, Ma JJ, Li JN, et al. Lower PTEN may be associated with CD8+ T cell exhaustion in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma[J]. Hum Immunol, 2023, 84(10): 551-60. |
| 39 | Exposito F, Redrado M, Houry M, et al. PTEN loss confers resistance to anti-PD-1 therapy in non-small cell lung cancer by increasing tumor infiltration of regulatory T cells[J]. Cancer Res, 2023, 83(15): 2513-26. |
| 40 | Nian ZG, Dou YC, Shen YQ, et al. Interleukin-34-orchestrated tumor-associated macrophage reprogramming is required for tumor immune escape driven by p53 inactivation[J]. Immunity, 2024, 57(10): 2344-61. e7. |
| 41 | Mathieu NA, Levin RH, Spratt DE. Exploring the roles of HERC2 and the NEDD4L HECT E3 ubiquitin ligase subfamily in p53 signaling and the DNA damage response[J]. Front Oncol, 2021, 11: 659049. |
| 42 | Borna S, Drobek A, Kralova J, et al. Transmembrane adaptor protein WBP1L regulates CXCR4 signalling and murine haematopoiesis[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2020, 24(2): 1980-92. |
| 43 | Zhu GQ, Tang Z, Huang R, et al. CD36+ cancer-associated fibroblasts provide immunosuppressive microenvironment for hepatocellular carcinoma via secretion of macrophage migration inhibitory factor[J]. Cell Discov, 2023, 9(1): 25. |
| 44 | Sakata T, Yoshio S, Yamazoe T, et al. Immunoglobulin-like transcript 2 as an impaired anti-tumor cytotoxicity marker of natural killer cells in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Front Immunol, 2024, 15: 1389411. |
| 45 | Chen Q, Shen MY, Yan M, et al. Targeting tumor-infiltrating CCR8+ regulatory T cells induces antitumor immunity through functional restoration of CD4+ Tconvs and CD8+ T cells in colorectal cancer[J]. J Transl Med, 2024, 22(1): 709. |
| 46 | da Silva SF, Murta EF, Michelin MA. ICAM2 is related to good prognosis in dendritic cell immunotherapy for cancer[J]. Immunotherapy, 2024, 16(3): 173-85. |
| [1] | 庞金龙, 赵新丽, 张振, 王豪杰, 周星琦, 杨玉梅, 李姗姗, 常小强, 李锋, 李娴. 皮肤黑色素瘤中MMRN2高表达促进肿瘤细胞的侵袭和迁移并与不良预后相关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1479-1489. |
| [2] | 高志, 吴傲, 胡仲翔, 孙培养. 类风湿性关节炎中氧化应激与免疫浸润的生物信息学分析[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 862-870. |
| [3] | 王耀彬, 陈柳燕, 罗伊凌, 申继清, 周素芳. NUF2对泛癌的预后和免疫治疗效果的预测价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 137-149. |
| [4] | 卢梓涵, 黄方俊, 蔡光瑶, 刘继红, 甄鑫. 针对缺失实验室指标多约束表征学习的卵巢癌鉴别方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 170-178. |
| [5] | 周伟, 聂军, 胡佳, 蒋艺枝, 张大发. 内质网应激相关基因在主动脉夹层疾病中的差异性表达及与免疫浸润的相关性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 859-866. |
| [6] | 王沁智, 宋冰, 郝诗睿, 肖志远, 金连辉, 郑通, 柴芳. 基于生物信息学分析CCND2在甲状腺乳头状癌中的表达及其对免疫浸润的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 981-988. |
| [7] | 邵 珊, 白薇超, 邹鹏程, 罗敏娜, 赵新汉, 雷建军. 二甲双胍阻断乳腺癌细胞-间质细胞的交互作用:基于抑制肿瘤相关成纤维细胞缺氧诱导因子-1α的表达[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 428-436. |
| [8] | 张富星, 刘国庆, 董锐, 高磊, 陆伟晨, 高连霞, 赵忠扩, 陆飞, 刘牧林. 高表达CRTAC1通过调控PI3K信号通路促进胃癌细胞增殖、迁移及免疫浸润[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(12): 2421-2433. |
| [9] | 郭晓娟, 陈丽平, 吕 芹, 杜瑞娟, 罗 琴, 张 阳, 卞 华, 韩 立. 桂枝茯苓胶囊通过调控NF-κB通路抑制卵巢癌细胞的迁移和诱导卵巢癌细胞的凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(8): 1315-1321. |
| [10] | 邓 婷, 杜伯雨, 郗雪艳. 结直肠癌细胞通过激活成纤维细胞的ERK通路诱导癌症相关成纤维细胞的形成[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(6): 943-951. |
| [11] | 张自然, 谭家乐, 于子航, 刘承栋, 王 剑, 吴德华, 白 雪. FARSB对泛肿瘤的预后和冷肿瘤微环境的分层作用:基于整合单细胞和大块组织的DNA测序[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(5): 667-679. |
| [12] | 毛建英, 杨文静, 郭 和, 董瑞丽, 任丽芳, 李树斌. 体外重建宫颈癌的三维培养模型:基于人宫颈癌组织的去细胞支架[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(2): 157-165. |
| [13] | 张伟健, 邹琸玥, 朱永娜, 王 敏, 马彩云, 武峻捷, 石 昕, 刘 茜. IL-34在舌鳞状细胞癌中的表达及意义[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(12): 2111-2117. |
| [14] | 苏莉莉, 梁晚晴, 吕振宇, 韩 啸. PLXNA1在肝癌中高表达并影响患者的生存预后及其免疫微环境[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(11): 1909-1918. |
| [15] | 赵海远, 刘 刚, 李 阳, 杨年钊, 赵 军. ANKRD6高表达是结肠癌不良预后的有效预测指标[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(10): 1715-1724. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||