南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (4): 819-828.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.04.17
储菲1( ), 陈孝华2, 宋博文2, 杨晶晶2, 左芦根2,3(
), 陈孝华2, 宋博文2, 杨晶晶2, 左芦根2,3( )
)
收稿日期:2025-02-07
出版日期:2025-04-20
发布日期:2025-04-28
通讯作者:
左芦根
E-mail:fiona1215@aliyun.com;zuolugen@126.com
作者简介:储 菲,主管药师,E-mail: fiona1215@aliyun.com
基金资助:
Fei CHU1( ), Xiaohua CHEN2, Bowen SONG2, Jingjing YANG2, Lugen ZUO2,3(
), Xiaohua CHEN2, Bowen SONG2, Jingjing YANG2, Lugen ZUO2,3( )
)
Received:2025-02-07
Online:2025-04-20
Published:2025-04-28
Contact:
Lugen ZUO
E-mail:fiona1215@aliyun.com;zuolugen@126.com
Supported by:摘要:
目的 探讨苏荠宁黄酮(MOS)改善实验性结肠炎的作用和机制。 方法 通过C57BL/6J小鼠饮用2.5% 葡聚糖硫酸钠(DSS)诱导实验性结肠炎,并采用腹腔注射MOS(200 mg/kg)进行干预。实验小鼠共分为4组(n=6):WT、WT+MOS、DSS和DSS+MOS组,通过检测小鼠体质量、结肠长度、HE染色、肠屏障功能和TUNEL染色来评估MOS对拮抗结肠炎和肠上皮细胞凋亡的作用。体外通过脂多糖(LPS,100 μg/mL)刺激小鼠结肠类器官,并采用MOS(120 μmol/L)进行干预。体外实验共分为4组:Control、Control+MOS、LPS和LPS+MOS组,以评估MOS对LPS诱导的肠屏障损伤和炎症反应的药理作用。网络药理学分析MOS作用的功能学途径和分子机制,并联合免疫印迹检测验证细胞凋亡相关蛋白的表达及其调控机制。 结果 体内实验表明MOS治疗改善DSS小鼠的体质量减轻(P<0.05)、DAI评分(P<0.05)、结肠缩短(P<0.05)、结肠组织炎症评分(P<0.05)和促炎因子(TNF-α、IL-1β、IL-6和IFN-γ,P<0.05)的表达。肠屏障功能检测表明,MOS治疗降低血中的FITC-Dextran(P<0.05)和I-FABP的浓度,并增加了肠上皮细胞间紧密连接蛋白的表达(ZO-1和claudin-1,P<0.05)。体外实验显示MOS治疗能够改善LPS诱导的结肠类器官的炎症因子水平和肠上皮细胞屏障的损伤(P<0.05)。免疫印迹结果表明,MOS干预在体内和体外都下调C-caspase3和BAX的表达(P<0.05),并上调抗凋亡蛋白Bcl-2的表达(P<0.05)。机制分析表明,DSS小鼠结肠组织和LPS刺激的结肠类器官的PI3K和AKT蛋白的磷酸化水平都被MOS抑制(P<0.05)。 结论 MOS可能通过PI3K/AKT信号抑制肠上皮细胞凋亡,从而改善肠道屏障的完整性并缓解实验性结肠炎。
储菲, 陈孝华, 宋博文, 杨晶晶, 左芦根. 苏荠宁黄酮通过抑制PI3K/AKT信号通路拮抗肠上皮细胞凋亡改善小鼠实验性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 819-828.
Fei CHU, Xiaohua CHEN, Bowen SONG, Jingjing YANG, Lugen ZUO. Moslosooflavone ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice by suppressing intestinal epithelium apoptosis via inhibiting the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 819-828.
| Gene | Forward (5'-3') | Reverse (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| TNF-α | CAGGCGGTGCCTATGTCTC | CGATCACCCCGAAGTTCAGTAG |
| IL-1β | GAAATGCCACCTTTTGACAGTG | TGGATGCTCTCATCAGGACAG |
| IL-6 | TCTATACCACTTCACAAGTCGGA | GAATTGCCATTGCACAACTCTTT |
| IFN-γ | ACAGCAAGGCGAAAAAGGATG | TGGTGGACCACTCGGATGA |
| GAPDH | TGGCCTTCCGTGTTCCTAC | GAGTTGCTGTTGAAGTCGCA |
表1 目标基因引物序列
Tab.1 Primer sequences for the target gene
| Gene | Forward (5'-3') | Reverse (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| TNF-α | CAGGCGGTGCCTATGTCTC | CGATCACCCCGAAGTTCAGTAG |
| IL-1β | GAAATGCCACCTTTTGACAGTG | TGGATGCTCTCATCAGGACAG |
| IL-6 | TCTATACCACTTCACAAGTCGGA | GAATTGCCATTGCACAACTCTTT |
| IFN-γ | ACAGCAAGGCGAAAAAGGATG | TGGTGGACCACTCGGATGA |
| GAPDH | TGGCCTTCCGTGTTCCTAC | GAGTTGCTGTTGAAGTCGCA |
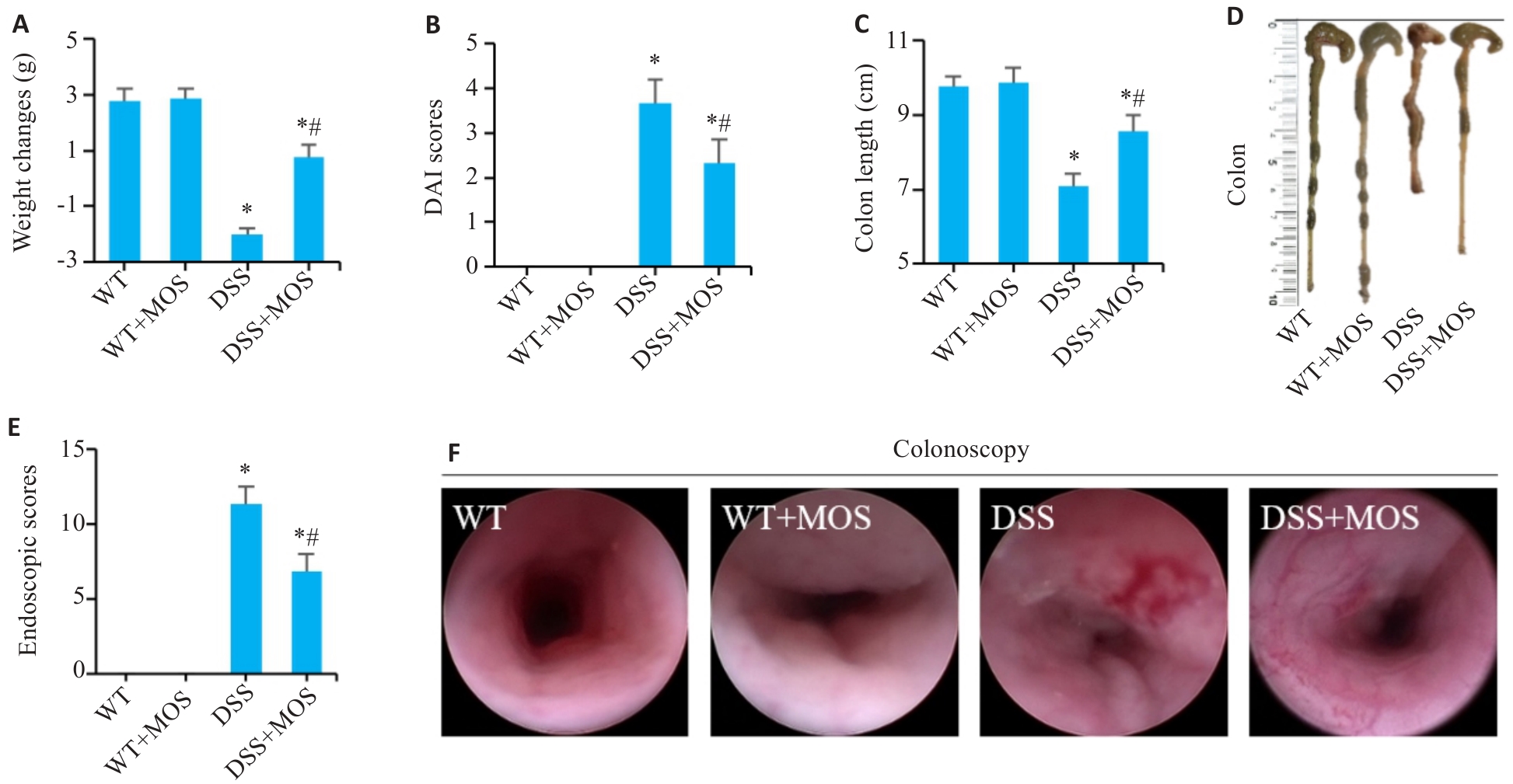
图1 MOS对DSS小鼠结肠炎症状的影响
Fig.1 Effect of MOS on symptoms in DSS mice. A: Weight changes. B: DAI scores. C, D: Colon length. E, F: Colonoscopy and endoscopic scores. n=6, *P<0.05 vs WT; #P<0.05 vs DSS.
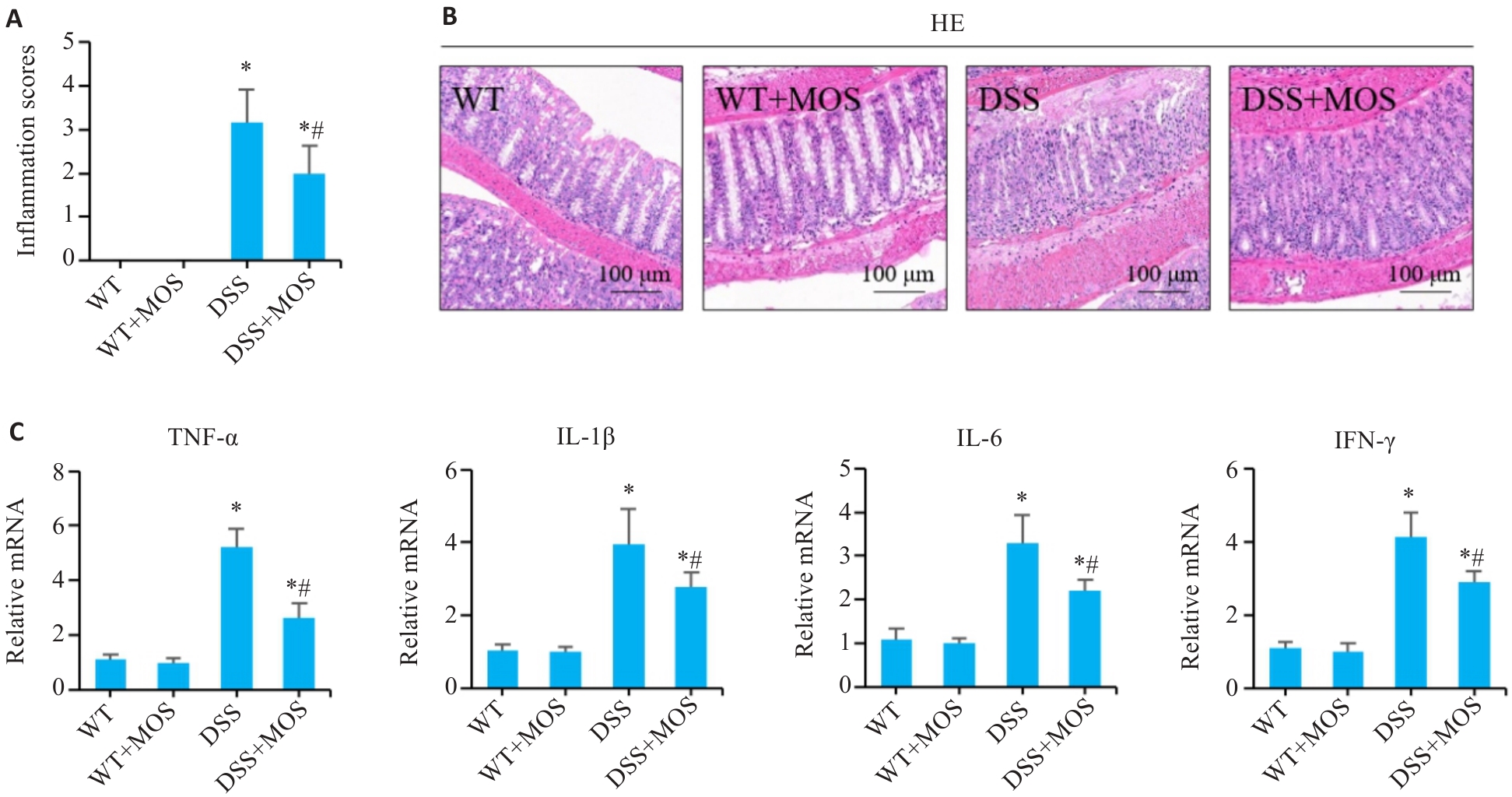
图2 MOS改善DSS小鼠的结肠黏膜损伤
Fig.2 MOS improves intestinal mucosal damage in DSS-treated mice. A, B: HE staining of mouse colon tissues and the inflammation scores. C: Relative mRNA levels of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 and IFN-γ in the colon tissues. n=6, *P<0.05 vs WT; #P<0.05 vs DSS.
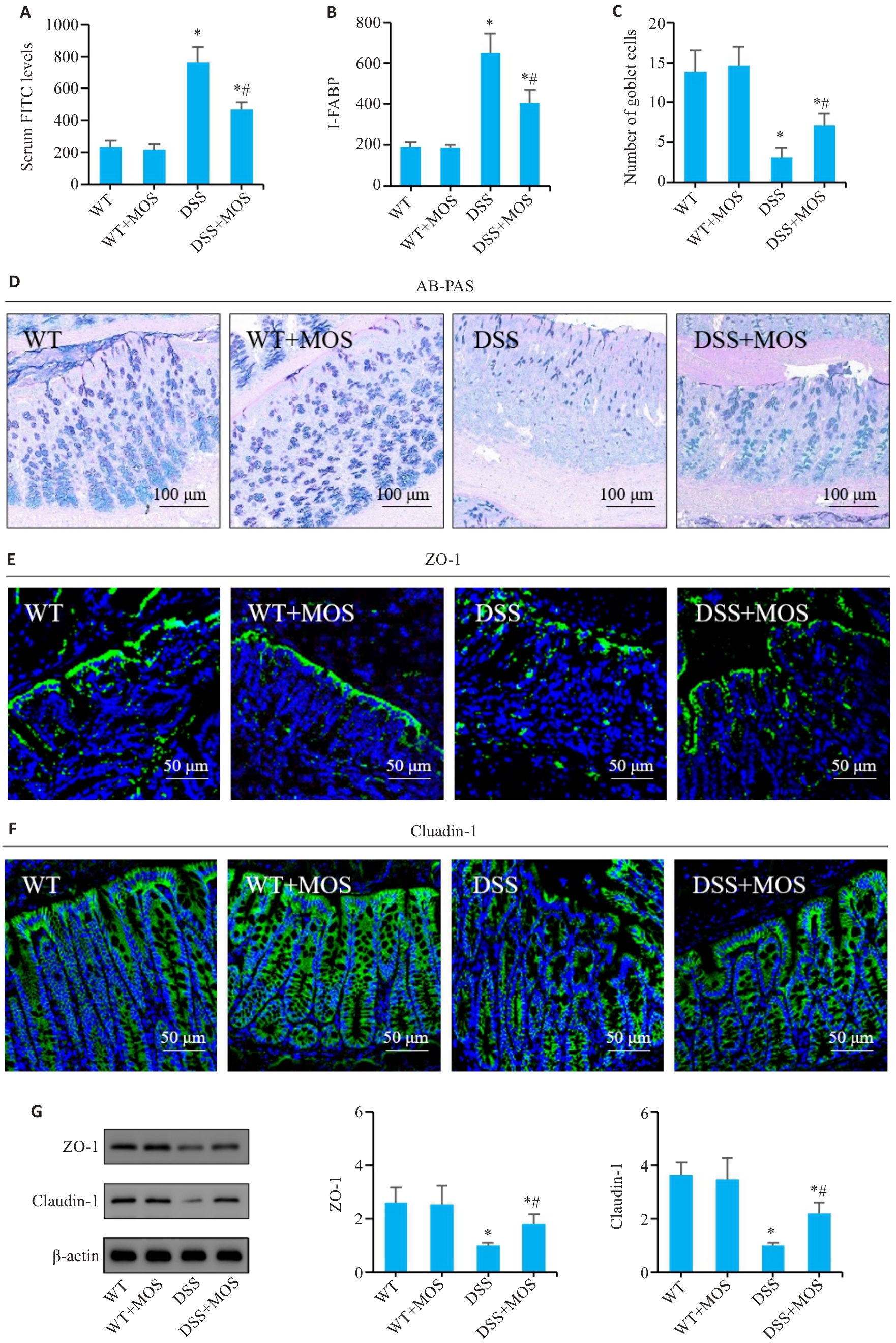
图3 MOS对DSS小鼠的肠屏障功能的影响
Fig.3 Effect of MOS on intestinal barrier function in DSS-treated mice. A, B: Comparison of serum FITC levels and I-FABP among the groups. C: Number of goblet cells. D: AB-PAS staining. E, F: Immunofluorescence assay of ZO-1 and claudin-1 expression. G: Western blotting for claudin-1 and ZO-1 expressions. n=6, *P<0.05 vs WT; #P<0.05 vs DSS.
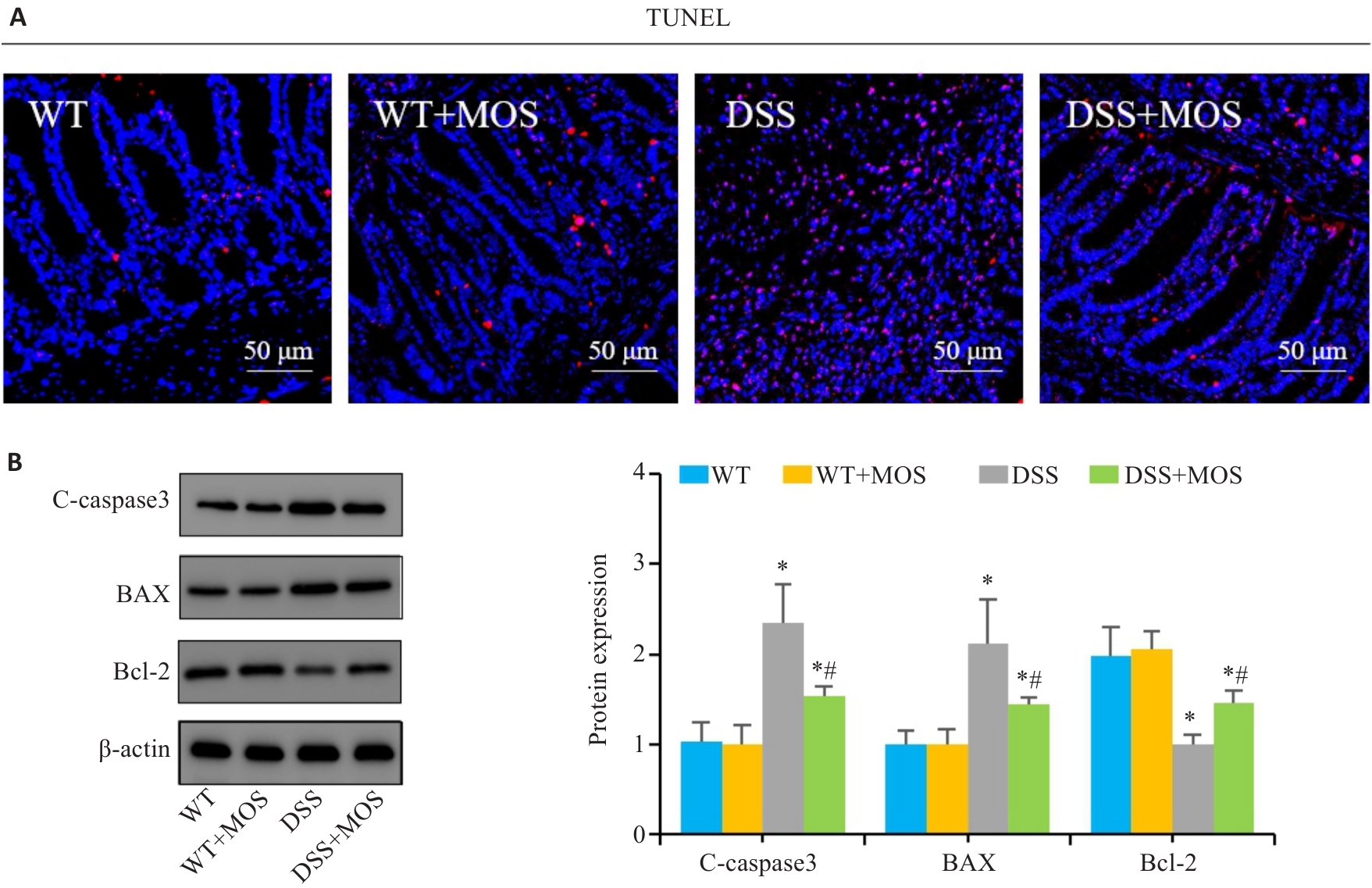
图4 MOS对DSS小鼠的肠上皮细胞凋亡的影响
Fig.4 Effect of MOS on intestinal epithelium apoptosis in DSS-treated mice. A: TUNEL staining. B: Western blotting for C-caspase-3, Bax and Bcl-2. n=6,*P<0.05 vs WT; #P<0.05 vs DSS.
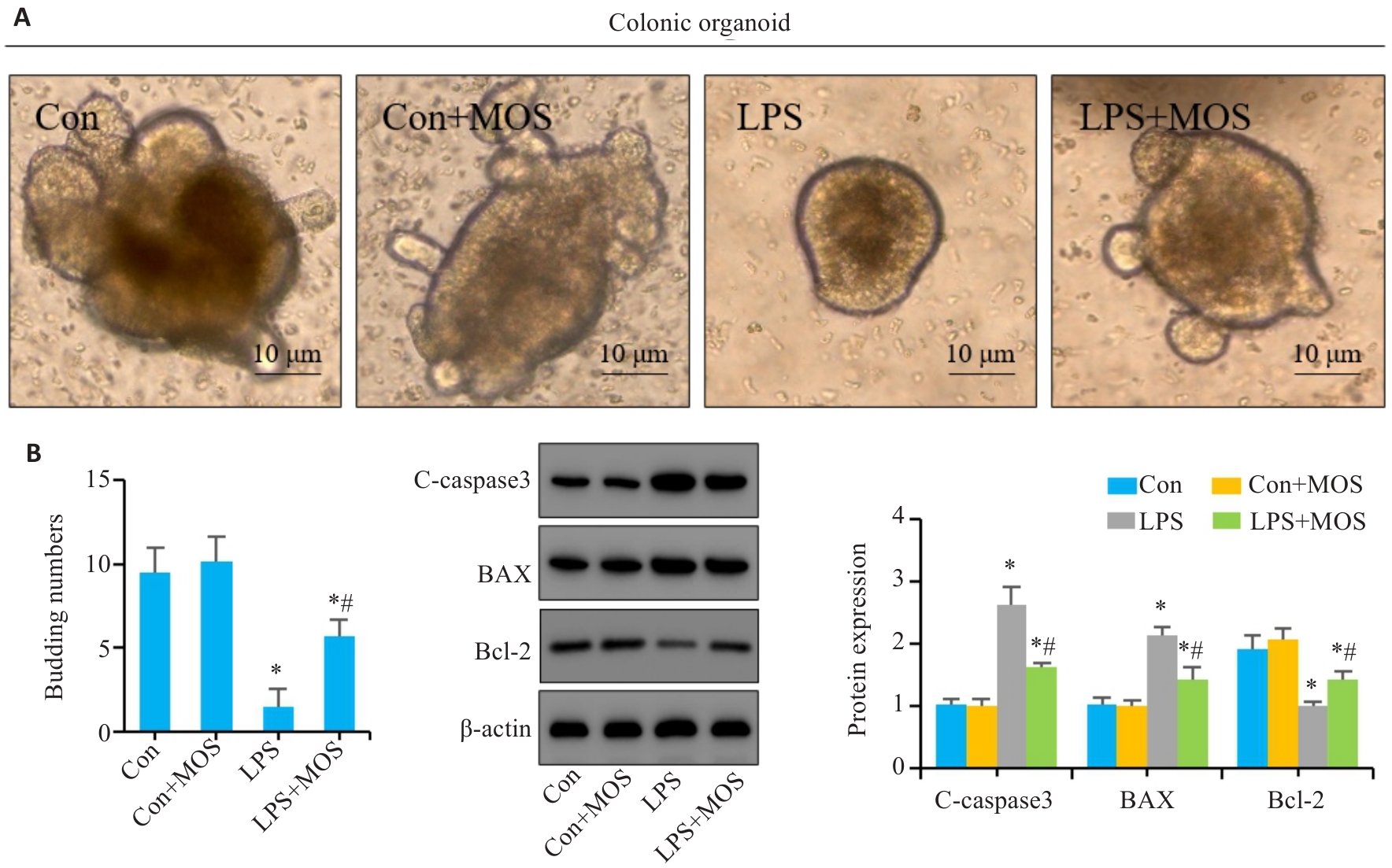
图5 MOS对LPS诱导的结肠类器官肠上皮细胞凋亡的影响
Fig.5 Effect of MOS on LPS-induced intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis in mouse colon organoids. A: Representative images of colon organoids. B: Number of organoids budding. C: Western blotting for C-caspase-3, Bax and Bcl-2. n=6,*P<0.05 vs Con; #P<0.05 vs LPS.
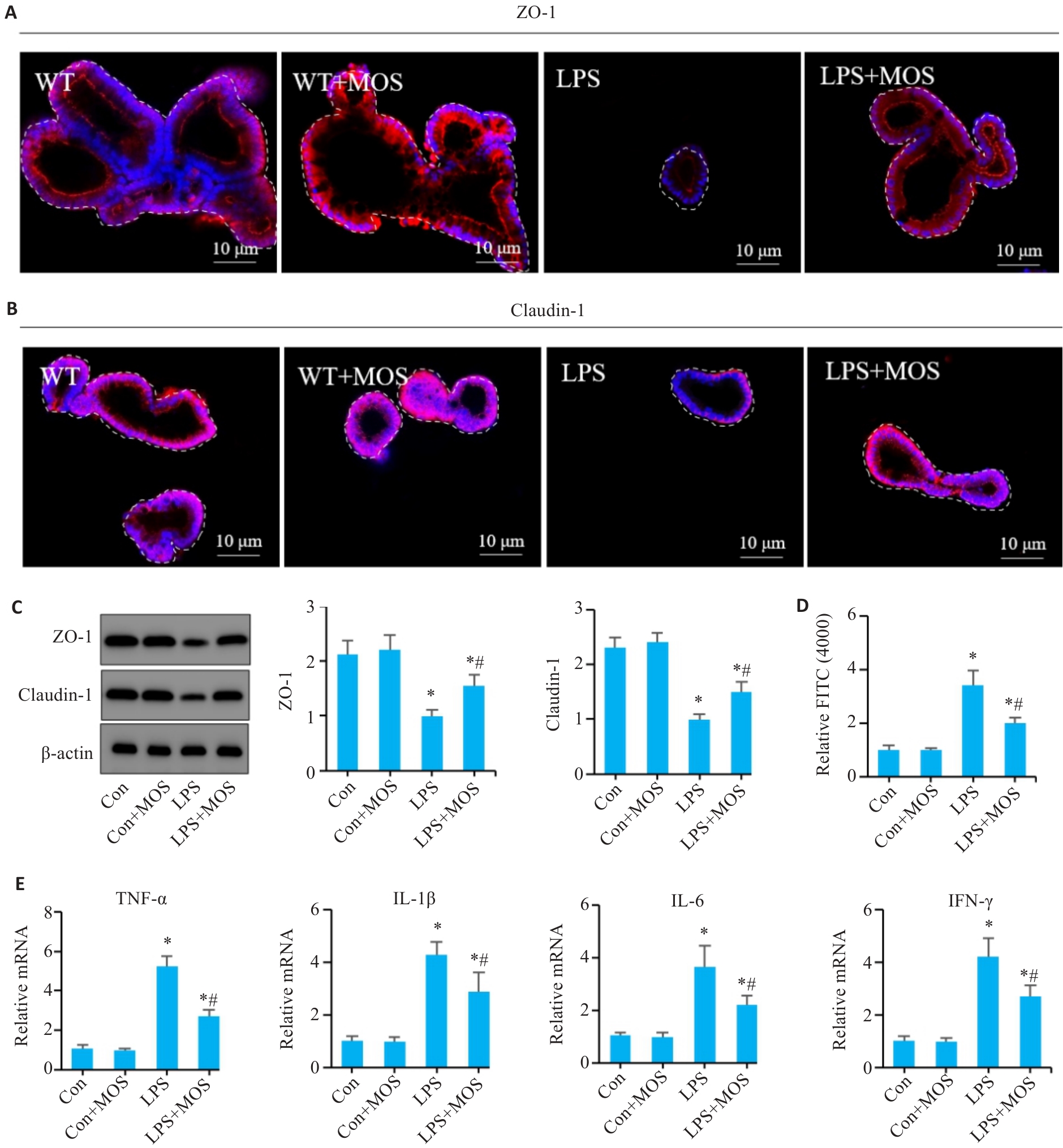
图6 MOS对LPS诱导的肠类器官屏障功能和炎症反应的影响
Fig.6 Effects of MOS on barrier function and inflammation in LPS-induced intestinal organoids. A, B: Immunofluorescence assay of ZO-1 and claudin-1. C: Western blotting of ZO-1and claudin-1. D: Permeability assay of the intestinal barrier. E: qRT-PCR for detecting mRNA levels of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and INF-γ in the colonic organoids. n=6, *P<0.05 vs Con; #P<0.05 vs LPS.
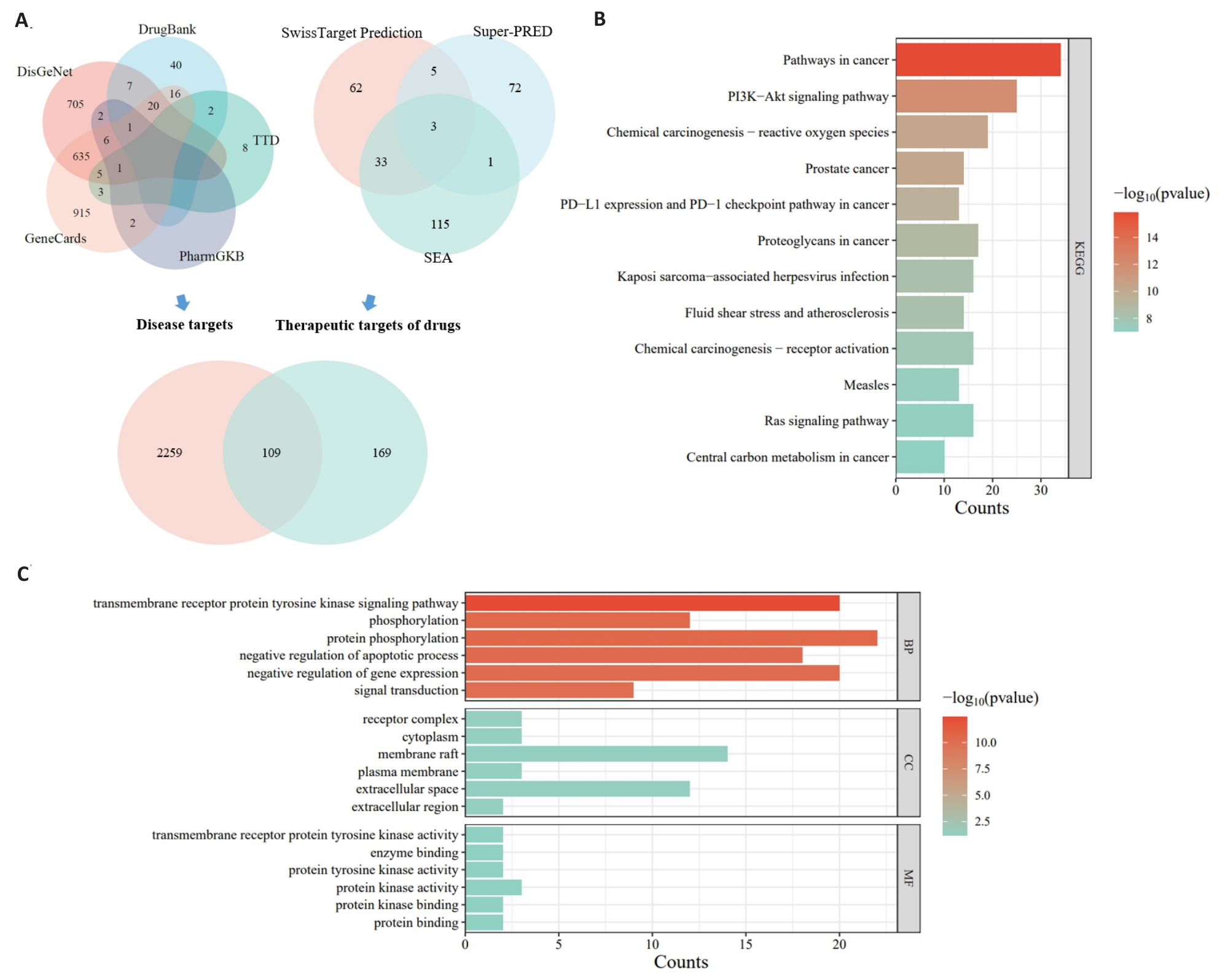
图7 网络药理学分析MOS的抗凋亡作用可能和PI3K/AKT信号有关
Fig.7 Network pharmacological analysis of the anti-apoptotic effect of MOS involving PI3K/AKT signaling. A: Venn diagram. B: GO enrichment analysis. C: KEGG enrichment analysis.
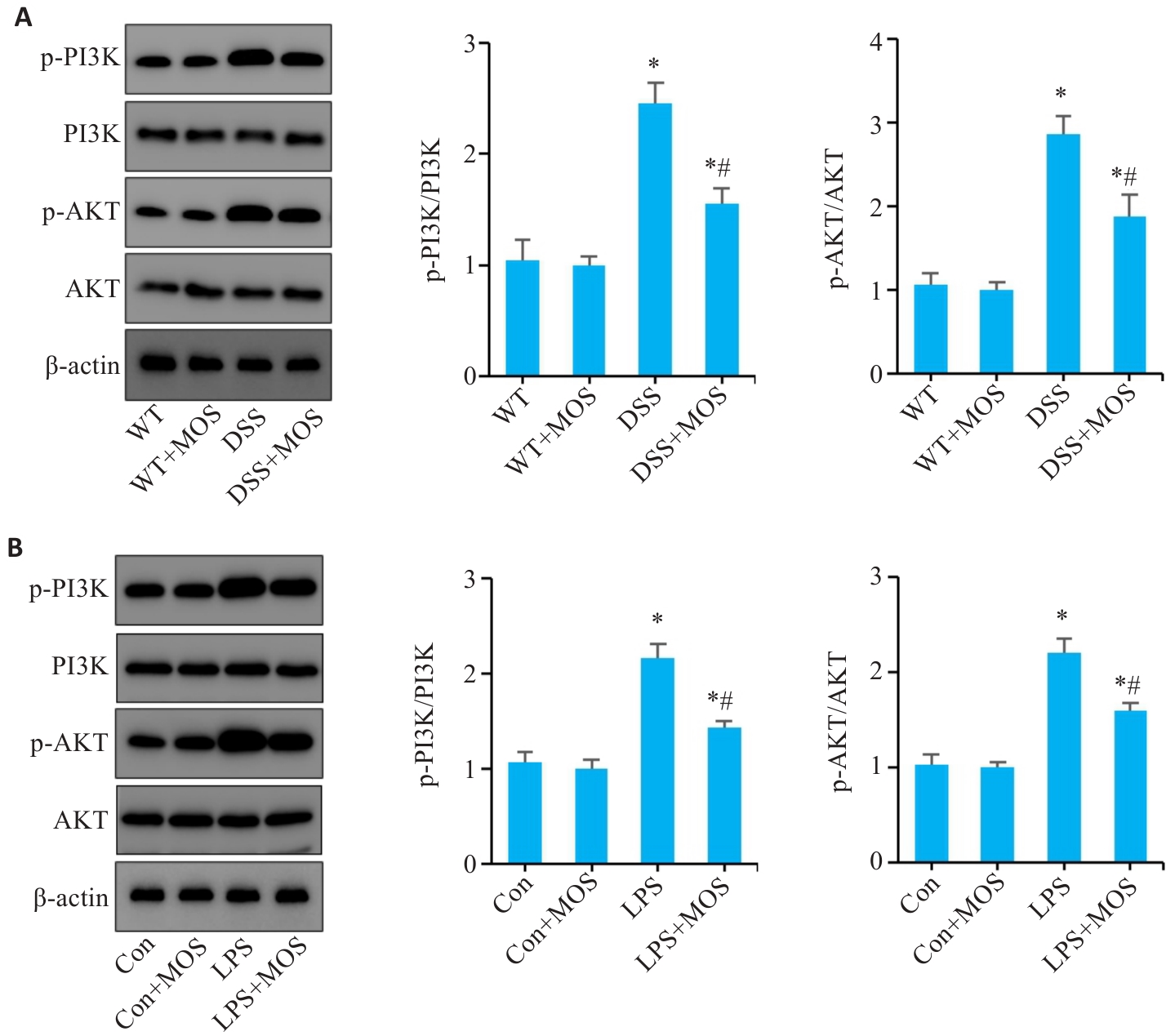
图8 MOS干预拮抗肠上皮细胞的凋亡可能和PI3K/AKT信号通路有关
Fig.8 MOS inhibits apoptosis of intestinal epithelial cells possibly through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. A: Western blotting of PI3K, p-PI3K, AKT and p-AKT expressions in the colon tissue. B: Western blotting of PI3K, p-PI3K, AKT and p-AKT expressions in the colonic organoids. n=6, *P<0.05 vs WT or Con; #P<0.05 vs DSS or LPS.
| 1 | Geng ZJ, Zuo LG, Li J, et al. Ginkgetin improved experimental colitis by inhibiting intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis through EGFR/PI3K/AKT signaling[J]. FASEB J, 2024, 38(14): e23817. |
| 2 | Torres J, Mehandru S, Colombel JF, et al. Crohn's disease[J]. Lancet, 2017, 389(10080): 1741-55. |
| 3 | Nóbrega VG, Silva INN, Brito BS, et al. The onset of clinical manifestations in inflammatory bowel disease patients[J]. Arq Gastroenterol, 2018, 55(3): 290-5. |
| 4 | Veauthier B, Hornecker JR. Crohn's disease: diagnosis and management[J]. Am Fam Physician, 2018, 98(11): 661-9. |
| 5 | Wu JC, Xu XQ, Duan JQ, et al. EFHD2 suppresses intestinal inflammation by blocking intestinal epithelial cell TNFR1 internalization and cell death[J]. Nat Commun, 2024, 15(1): 1282. |
| 6 | Zhu LG, Xie Z, Yang G, et al. Stanniocalcin-1 promotes PARP1-dependent cell death via JNK activation in colitis[J]. Adv Sci, 2024, 11(5): e2304123. |
| 7 | Zuo LG, Li J, Ge ST, et al. Bryostatin-1 ameliorated experimental colitis in Il-10-/- Mice by protecting the intestinal barrier and limiting immune dysfunction[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2019, 23(8): 5588-99. |
| 8 | Gupta M, Mishra V, Gulati M, et al. Natural compounds as safe therapeutic options for ulcerative colitis[J]. Inflammopharm-acology, 2022, 30(2): 397-434. |
| 9 | Xie YC, Gong SC, Wang LK, et al. Unraveling the treatment effects of Huanglian Jiedu decoction on drug-induced liver injury based on network pharmacology, molecular docking and experimental validation[J]. BMC Complement Med Ther, 2024, 24(1): 219. |
| 10 | Chao WW, Kuo YH, Lin BF. Anti-inflammatory activity of new compounds from Andrographis paniculata by NF-kappaB transactivation inhibition[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2010, 58(4): 2505-12. |
| 11 | Zhang J, Zhao T, Zhang PP, et al. Moslosooflavone protects against brain injury induced by hypobaric hypoxic via suppressing oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, energy metabolism disorder, and apoptosis[J]. J Pharm Pharmacol, 2024, 76(1): 44-56. |
| 12 | Li MX, Li MY, Lei JX, et al. Huangqin decoction ameliorates DSS-induced ulcerative colitis: Role of gut microbiota and amino acid metabolism, mTOR pathway and intestinal epithelial barrier[J]. Phytomedicine, 2022, 100: 154052. |
| 13 | Zuo LG, Geng ZJ, Song X, et al. Browning of mesenteric white adipose tissue in Crohn's disease: a new pathological change and therapeutic target[J]. J Crohns Colitis, 2023, 17(8): 1179-92. |
| 14 | Wang L, Song X, Zhou YQ, et al. Sclareol protected against intestinal barrier dysfunction ameliorating Crohn's disease-like colitis via Nrf2/NF-B/MLCK signalling[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2024, 133: 112140. |
| 15 | Zuo LG, Li J, Zhang XF, et al. Aberrant mesenteric adipose extracellular matrix remodelling is involved in adipocyte dysfunction in Crohn's disease: the role of TLR-4-mediated macrophages[J]. J Crohns Colitis, 2022, 16(11): 1762-76. |
| 16 | Tsai PJ, Huang WC, Hsieh MC, et al. Flavones isolated from scutellariae Radix suppress Propionibacterium acnes-induced cytokine production in vitro and in vivo [J]. Molecules, 2015, 21(1): E15. |
| 17 | Song Y, Song Q, Tan FY, et al. Seliciclib alleviates ulcerative colitis by inhibiting ferroptosis and improving intestinal inflammation[J]. Life Sci, 2024, 351: 122794. |
| 18 | Marincola Smith P, Choksi YA, Markham NO, et al. Colon epithelial cell TGFβ signaling modulates the expression of tight junction proteins and barrier function in mice[J]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2021, 320(6): G936-57. |
| 19 | Ma J, Zhang JQ, Wang YF, et al. Modified Gegen Qinlian decoction ameliorates DSS-induced chronic colitis in mice by restoring the intestinal mucus barrier and inhibiting the activation of γδT17 cells[J]. Phytomedicine, 2023, 111: 154660. |
| 20 | Wei YY, Fan YM, Ga Y, et al. Shaoyao decoction attenuates DSS-induced ulcerative colitis, macrophage and NLRP3 inflammasome activation through the MKP1/NF‑κB pathway[J]. Phytomedicine, 2021, 92: 153743. |
| 21 | Yang Y, Zhou XC, Jia GY, et al. Network pharmacology based research into the effect and potential mechanism of Portulaca oleracea L. polysaccharide against ulcerative colitis[J]. Comput Biol Med, 2023, 161: 106999. |
| 22 | Xu Y, Wang XC, Jiang W, et al. Porphyra haitanensis polysaccharide-functionalized selenium nanoparticles for effective alleviation of ulcerative colitis[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2023, 253(Pt 8): 127570. |
| 23 | Turpin W, Lee SH, Garay JAR, et al. Increased intestinal permeability is associated with later development of Crohn's disease[J]. Gastroenterology, 2020, 159(6): 2092-100.e5. |
| 24 | Jarret A, Jackson R, Duizer C, et al. Enteric nervous system-derived IL-18 orchestrates mucosal barrier immunity[J]. Cell, 2020, 180(1): 50-63.e12. |
| 25 | Qiu Y, Yang H. Effects of intraepithelial lymphocyte-derived cytokines on intestinal mucosal barrier function[J]. J Interferon Cytokine Res, 2013, 33(10): 551-62. |
| 26 | Magarian Blander J. Death in the intestinal epithelium-basic biology and implications for inflammatory bowel disease[J]. FEBS J, 2016, 283(14): 2720-30. |
| 27 | Subramanian S, Geng H, Tan XD. Cell death of intestinal epithelial cells in intestinal diseases[J]. Sheng Li Xue Bao, 2020, 72(3): 308-24. |
| 28 | Liang BX, Zhong YZ, Huang YJ, et al. Underestimated health risks: polystyrene micro- and nanoplastics jointly induce intestinal barrier dysfunction by ROS-mediated epithelial cell apoptosis[J]. Part Fibre Toxicol, 2021, 18(1): 20. |
| 29 | Zhang Y, Yang X, Ge XH, et al. Puerarin attenuates neurological deficits via Bcl-2/Bax/cleaved caspase-3 and Sirt3/SOD2 apoptotic pathways in subarachnoid hemorrhage mice[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2019, 109: 726-33. |
| 30 | Zhang ZQ, Fan K, Meng JJ, et al. Deoxynivalenol hijacks the pathway of Janus kinase 2/signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 (JAK2/STAT-3) to drive caspase-3-mediated apoptosis in intestinal porcine epithelial cells[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2023, 864: 161058. |
| 31 | Eskandari E, Eaves CJ. Paradoxical roles of caspase-3 in regulating cell survival, proliferation, and tumorigenesis[J]. J Cell Biol, 2022, 221(6): e202201159. |
| 32 | Yang JL, Pi CC, Wang GH. Inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway by apigenin induces apoptosis and autophagy in hepatocellular carcinoma cells[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2018, 103: 699-707. |
| 33 | Chen SP, Peng JH, Sherchan P, et al. TREM2 activation attenuates neuroinflammation and neuronal apoptosis via PI3K/Akt pathway after intracerebral hemorrhage in mice[J]. J Neuroinflammation, 2020, 17(1): 168. |
| 34 | Yan XD, Tong XY, Jia YR, et al. Baiheqingjin formula reduces inflammation in mice with asthma by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/NF-κb signaling pathway[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2024, 321: 117565. |
| [1] | 牛民主, 殷丽霞, 乔通, 尹林, 张可妮, 胡建国, 宋传旺, 耿志军, 李静. 旱莲苷A通过调控JAK2/STAT3通路抑制M1型巨噬细胞极化改善葡聚糖硫酸钠诱导的小鼠结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1297-1306. |
| [2] | 徐皓男, 张放, 黄钰莹, 姚其盛, 管悦琴, 陈浩. 百蕊草通过调节肠道菌群和调控EGFR/PI3K/Akt信号通路改善小鼠抗生素相关性腹泻[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 285-295. |
| [3] | 裴月娇, 刘慧敏, 昕宇, 刘波. miR-124通过调控PI3K/AKT信号通路改善睡眠剥夺大鼠认知功能[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 340-346. |
| [4] | 张玉如, 万磊, 方昊翔, 李方泽, 王丽文, 李柯霏, 闫佩文, 姜辉. miR-155-5p介导PIK3R1负调控PI3K/AKT信号通路促进原发性干燥综合征人唾液腺上皮细胞增殖[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 65-71. |
| [5] | 张先恒, 刘健, 韩琦, 陈一鸣, 丁香, 陈晓露. 黄芩清热除痹胶囊通过PTEN/PI3K/AKT信号通路改善痛风性关节炎大鼠的炎症反应及尿酸、脂质代谢失衡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1450-1458. |
| [6] | 刘硕, 李静, 吴兴旺. Swertiamarin通过抑制肠上皮细胞细胞凋亡改善TNBS诱导的实验性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1545-1552. |
| [7] | 向珊, 张宗星, 江露, 刘道忠, 李玮怡, 包卓玛, 田瑞, 陈丹, 袁林. 三百棒通过调控PI3K/Akt信号通路改善胶原诱导性类风湿性关节炎大鼠的血管翳[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1582-1588. |
| [8] | 王媛媛, 陈腾, 从小凡, 李依然, 陈蕊, 张配, 孙小锦, 赵素容. 扁蒴藤素通过活性氧调控PI3K/AKT通路增强顺铂诱导鼻咽癌细胞凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 904-912. |
| [9] | 邵荣瑢, 杨 子, 张文静, 张 诺, 赵雅静, 张小凤, 左芦根, 葛思堂. 茯苓酸缓解小鼠克罗恩病:基于抑制PI3K/AKT信号通路拮抗肠上皮细胞凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(6): 935-942. |
| [10] | 肖姝喆, 成燕玲, 朱 云, 唐 芮, 古建标, 兰 林, 何志华, 刘丹琼, 耿岚岚, 程 旸, 龚四堂. WNT2b高表达的成纤维细胞破坏肠道黏膜屏障[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(2): 206-212. |
| [11] | 高晓阳, 赵晓璐, 张春艳, 颜羽昕, 金 蓉, 马月宏. 槲皮素诱导肝星状细胞凋亡:基于调控miR-146影响PI3K/Akt信号通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(10): 1725-1733. |
| [12] | 范晓丽, 王 娟, 王梨明. 甘草查尔酮A通过调控PI3K/AKT信号通路诱导肺鳞癌细胞周期阻滞[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(1): 111-116. |
| [13] | 刘见荣, 沈卫星, 程海波, 范旻旻, 肖 君, 徐长亮, 谭佳妮, 赖岳阳, 余成涛, 孙东东, 李 柳. 参白解毒方显著抑制小鼠结直肠腺瘤的形成及癌变: 基于PTEN/PI3K/AKT通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(10): 1452-1461. |
| [14] | 梁小芳, 杨 越, 徐帅帅, 刘 映, 褚晗玉, 唐 艳, 杨 飞. 微囊藻毒素-LR长期低剂量暴露诱导小鼠肾脏结构和功能损伤:基于激活PI3K/AKT信号通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(10): 1486-1494. |
| [15] | 吴胜男, 张 露, 樊红莲, 黄艳平, 宗巧凤, 高 琴, 李正红. PI3K/Akt通路在内吗啡肽-1后处理减轻大鼠心肌缺血再灌注损伤中的作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(6): 870-875. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||