南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (12): 2639-2645.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.12.11
• • 上一篇
收稿日期:2025-06-29
出版日期:2025-12-20
发布日期:2025-12-22
通讯作者:
李飞
E-mail:wangr05@qq.com;leagcen@163.com
作者简介:王 飞,在读博士研究生,E-mail: wangr05@qq.com
基金资助:
Fei WANG1( ), Weiran LI1, Xiang SHANG1, Fei LI2(
), Weiran LI1, Xiang SHANG1, Fei LI2( )
)
Received:2025-06-29
Online:2025-12-20
Published:2025-12-22
Contact:
Fei LI
E-mail:wangr05@qq.com;leagcen@163.com
摘要:
目的 构建并验证一套适用于中国农村社区老年人群的认知障碍风险预测模型。 方法 基于2011年中国健康与养老追踪调查横断面数据,纳入年龄≥60岁的农村社区老年人共2228例,按7∶3比例随机分为训练集(1560例)和内部验证集(668例)。收集包括人口社会学特征、生活方式与行为习惯、慢性病史、身体功能与主观健康状态等38个候选变量。采用最小绝对收缩与选择算子(LASSO)回归筛选特征变量,再以多因素Logistic回归确定独立危险因素,并据此构建认知障碍预测列线图。通过受试者工作特征曲线(ROC)和校准曲线评估模型的判别力与拟合度,采用决策曲线分析(DCA)评价其临床应用价值。 结果 LASSO及多因素Logistic回归分析显示,年龄、受教育年限、饮酒情况、收缩压、握力及抑郁状态为认知障碍的独立影响因素。所构建的列线图在训练集和验证集中的ROC曲线下面积分别为0.839(95% CI: 0.814~0.864)和0.840(95% CI: 0.801~0.879),显示出良好的预测性能。校准曲线提示模型拟合良好,DCA结果进一步证实该模型具备较高的临床实用性。 结论 本研究构建的基于LASSO筛选变量的认知障碍预测列线图具有较高的预测准确性、判别能力及潜在临床应用价值,可为中国农村老年人群的认知障碍风险早期识别与干预提供参考工具。
王飞, 李蔚然, 尚祥, 李飞. 中国农村社区老年人认知障碍预测模型的构建与验证——基于中国健康与养老追踪调查数据库[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(12): 2639-2645.
Fei WANG, Weiran LI, Xiang SHANG, Fei LI. Development and validation of a risk prediction model for cognitive impairment in rural elderly Chinese populations: evidence from the CHARLS study[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(12): 2639-2645.
| Variable | No Cognitive impairment (n=1331) | Cognitive impairment (n=229) | P# | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Female | 601 (45.2) | 147 (64.2) | <0.001 |
| Male | 730 (54.8) | 82 (35.8) | ||
| Age (year) | 66 (62, 71) | 70 (64, 76) | <0.001 | |
| Marital status | Unmarried | 205 (15.4) | 66 (28.8) | <0.001 |
| Married/Other | 1126 (84.6) | 163 (71.2) | ||
| Education | Below primary | 405 (30.4) | 182 (79.5) | <0.001 |
| Primary school | 375 (28.2) | 38 (16.6) | ||
| Middle school | 304 (22.8) | 6 (2.6) | ||
| High school and above | 247 (18.6) | 3 (1.3) | ||
| Life satisfaction | Low | 119 (8.9) | 38 (16.6) | 0.002 |
| Moderate | 911 (68.4) | 141 (61.6) | ||
| High | 301 (22.6) | 50 (21.8) | ||
| Smoking | No | 971 (73.0) | 172 (75.1) | 0.496 |
| Yes | 360 (27.0) | 57 (24.9) | ||
| Alcohol drinking | No | 897 (67.4) | 187 (81.7) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 434 (32.6) | 42 (18.3) | ||
| Sleep duration | <6 h | 368 (27.6) | 89 (38.9) | <0.001 |
| 6-8 h | 887 (66.6) | 117 (51.1) | ||
| >8 h | 76 (5.7) | 23 (10.0) | ||
| Social activities | No | 583 (43.8) | 135 (59.0) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 748 (56.2) | 94 (41.0) | ||
| Tap water access | No | 234 (17.6) | 69 (30.1) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 1097 (82.4) | 160 (69.9) | ||
| Hypertension | No | 559 (42.0) | 73 (31.9) | 0.004 |
| Yes | 772 (58.0) | 156 (68.1) | ||
| Diabetes | No | 1095 (82.3) | 192 (83.8) | 0.563 |
| Yes | 236 (17.7) | 37 (16.2) | ||
| Cancer | No | 1313 (98.6) | 227 (99.1) | 0.756 |
| Yes | 18 (1.4) | 2 (0.9) | ||
| Lung disease | No | 1166 (87.6) | 197 (86.0) | 0.507 |
| Yes | 165 (12.4) | 32 (14.0) | ||
| Heart disease | No | 1035 (77.8) | 183 (79.9) | 0.467 |
| Yes | 296 (22.2) | 46 (20.1) | ||
| Stroke | No | 1277 (95.9) | 220 (96.1) | 0.928 |
| Yes | 54 (4.1) | 9 (3.9) | ||
| Arthritis | No | 898 (67.5) | 146 (63.8) | 0.270 |
| Yes | 433 (32.5) | 83 (36.2) | ||
| Dyslipidemia | No | 1083 (81.4) | 203 (88.6) | 0.007 |
| Yes | 248 (18.6) | 26 (11.4) | ||
| Liver disease | No | 1271 (95.5) | 222 (96.9) | 0.317 |
| Yes | 60 (4.5) | 7 (3.1) | ||
| Kidney disease | No | 1246 (93.6) | 215 (93.9) | 0.876 |
| Yes | 85 (6.4) | 14 (6.1) | ||
| Gastrointestinal disease | No | 1066 (80.1) | 170 (74.2) | 0.044 |
| Yes | 265 (19.9) | 59 (25.8) | ||
| Asthma | No | 1260 (94.7) | 218 (95.2) | 0.740 |
| Yes | 71 (5.3) | 11 (4.8) | ||
| Hip fracture | No | 1315 (98.8) | 223 (97.4) | 0.120 |
| Yes | 16 (1.2) | 6 (2.6) | ||
| Visual impairment | No | 324 (24.3) | 35 (15.3) | 0.003 |
| Yes | 1,007 (75.7) | 194 (84.7) | ||
| Hearing impairment | No | 606 (45.5) | 83 (36.2) | 0.009 |
| Yes | 725 (54.5) | 146 (63.8) | ||
| Depression | No | 975 (73.3) | 104 (45.4) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 356 (26.7) | 125 (54.6) | ||
| Pain | No | 1033 (77.6) | 148 (64.6) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 298 (22.4) | 81 (35.4) | ||
| Self-rated health | Poor | 295 (22.2) | 74 (32.3) | 0.001 |
| Fair | 720 (54.1) | 117 (51.1) | ||
| Good | 316 (23.7) | 38 (16.6) | ||
| ADL | 0.00 (0.00, 0.00) | 0.00 (0.00, 1.00) | <0.001 | |
| IADL | 0.00 (0.00, 0.00) | 0.00 (0.00, 2.00) | <0.001 | |
| Waist circumference | 87 (83, 93) | 87 (81, 92) | 0.003 | |
| BMI | 24.6 (22.3, 25.9) | 23.4 (20.8, 24.8) | <0.001 | |
| Handgrip strength | 29 (24, 33) | 23 (19, 27) | <0.001 | |
| SBP | 135 (124, 144) | 140 (126, 153) | <0.001 | |
| DBP | 76 (70, 82) | 77 (71, 84) | 0.007 | |
| Disability | No | 1136 (85.3) | 160 (69.9) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 195 (14.7) | 69 (30.1) | ||
| History of falls | No | 1133 (85.1) | 182 (79.5) | 0.030 |
| Yes | 198 (14.9) | 47 (20.5) | ||
| Tooth loss | No | 1199 (90.1) | 177 (77.3) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 132 (9.9) | 52 (22.7) |
表1 训练集参与者基线特征表
Tab.1 Baseline characteristics of the participants in the training set
| Variable | No Cognitive impairment (n=1331) | Cognitive impairment (n=229) | P# | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Female | 601 (45.2) | 147 (64.2) | <0.001 |
| Male | 730 (54.8) | 82 (35.8) | ||
| Age (year) | 66 (62, 71) | 70 (64, 76) | <0.001 | |
| Marital status | Unmarried | 205 (15.4) | 66 (28.8) | <0.001 |
| Married/Other | 1126 (84.6) | 163 (71.2) | ||
| Education | Below primary | 405 (30.4) | 182 (79.5) | <0.001 |
| Primary school | 375 (28.2) | 38 (16.6) | ||
| Middle school | 304 (22.8) | 6 (2.6) | ||
| High school and above | 247 (18.6) | 3 (1.3) | ||
| Life satisfaction | Low | 119 (8.9) | 38 (16.6) | 0.002 |
| Moderate | 911 (68.4) | 141 (61.6) | ||
| High | 301 (22.6) | 50 (21.8) | ||
| Smoking | No | 971 (73.0) | 172 (75.1) | 0.496 |
| Yes | 360 (27.0) | 57 (24.9) | ||
| Alcohol drinking | No | 897 (67.4) | 187 (81.7) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 434 (32.6) | 42 (18.3) | ||
| Sleep duration | <6 h | 368 (27.6) | 89 (38.9) | <0.001 |
| 6-8 h | 887 (66.6) | 117 (51.1) | ||
| >8 h | 76 (5.7) | 23 (10.0) | ||
| Social activities | No | 583 (43.8) | 135 (59.0) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 748 (56.2) | 94 (41.0) | ||
| Tap water access | No | 234 (17.6) | 69 (30.1) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 1097 (82.4) | 160 (69.9) | ||
| Hypertension | No | 559 (42.0) | 73 (31.9) | 0.004 |
| Yes | 772 (58.0) | 156 (68.1) | ||
| Diabetes | No | 1095 (82.3) | 192 (83.8) | 0.563 |
| Yes | 236 (17.7) | 37 (16.2) | ||
| Cancer | No | 1313 (98.6) | 227 (99.1) | 0.756 |
| Yes | 18 (1.4) | 2 (0.9) | ||
| Lung disease | No | 1166 (87.6) | 197 (86.0) | 0.507 |
| Yes | 165 (12.4) | 32 (14.0) | ||
| Heart disease | No | 1035 (77.8) | 183 (79.9) | 0.467 |
| Yes | 296 (22.2) | 46 (20.1) | ||
| Stroke | No | 1277 (95.9) | 220 (96.1) | 0.928 |
| Yes | 54 (4.1) | 9 (3.9) | ||
| Arthritis | No | 898 (67.5) | 146 (63.8) | 0.270 |
| Yes | 433 (32.5) | 83 (36.2) | ||
| Dyslipidemia | No | 1083 (81.4) | 203 (88.6) | 0.007 |
| Yes | 248 (18.6) | 26 (11.4) | ||
| Liver disease | No | 1271 (95.5) | 222 (96.9) | 0.317 |
| Yes | 60 (4.5) | 7 (3.1) | ||
| Kidney disease | No | 1246 (93.6) | 215 (93.9) | 0.876 |
| Yes | 85 (6.4) | 14 (6.1) | ||
| Gastrointestinal disease | No | 1066 (80.1) | 170 (74.2) | 0.044 |
| Yes | 265 (19.9) | 59 (25.8) | ||
| Asthma | No | 1260 (94.7) | 218 (95.2) | 0.740 |
| Yes | 71 (5.3) | 11 (4.8) | ||
| Hip fracture | No | 1315 (98.8) | 223 (97.4) | 0.120 |
| Yes | 16 (1.2) | 6 (2.6) | ||
| Visual impairment | No | 324 (24.3) | 35 (15.3) | 0.003 |
| Yes | 1,007 (75.7) | 194 (84.7) | ||
| Hearing impairment | No | 606 (45.5) | 83 (36.2) | 0.009 |
| Yes | 725 (54.5) | 146 (63.8) | ||
| Depression | No | 975 (73.3) | 104 (45.4) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 356 (26.7) | 125 (54.6) | ||
| Pain | No | 1033 (77.6) | 148 (64.6) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 298 (22.4) | 81 (35.4) | ||
| Self-rated health | Poor | 295 (22.2) | 74 (32.3) | 0.001 |
| Fair | 720 (54.1) | 117 (51.1) | ||
| Good | 316 (23.7) | 38 (16.6) | ||
| ADL | 0.00 (0.00, 0.00) | 0.00 (0.00, 1.00) | <0.001 | |
| IADL | 0.00 (0.00, 0.00) | 0.00 (0.00, 2.00) | <0.001 | |
| Waist circumference | 87 (83, 93) | 87 (81, 92) | 0.003 | |
| BMI | 24.6 (22.3, 25.9) | 23.4 (20.8, 24.8) | <0.001 | |
| Handgrip strength | 29 (24, 33) | 23 (19, 27) | <0.001 | |
| SBP | 135 (124, 144) | 140 (126, 153) | <0.001 | |
| DBP | 76 (70, 82) | 77 (71, 84) | 0.007 | |
| Disability | No | 1136 (85.3) | 160 (69.9) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 195 (14.7) | 69 (30.1) | ||
| History of falls | No | 1133 (85.1) | 182 (79.5) | 0.030 |
| Yes | 198 (14.9) | 47 (20.5) | ||
| Tooth loss | No | 1199 (90.1) | 177 (77.3) | <0.001 |
| Yes | 132 (9.9) | 52 (22.7) |

图1 基于LASSO回归的特征筛选过程
Fig.1 Feature selection process based on LASSO regression. A: Optimal penalty parameter λ selected based on 10-fold cross-validation. The left dashed line indicates the λ corresponding to the minimum mean cross-validated error, and the right dashed line represents λ1se, the largest λ within one standard error of the minimum. B: LASSO coefficient profile plot showing how the coefficients of each variable evolve as the λ value changes. The dashed line marks the selected optimal λ. C: Key variables selected by LASSO and their corresponding regression coefficients. Negative coefficients indicate risk factors, and positive coefficients represent protective factors.
| Variable | OR | 95% CI | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 1.06 | 1.03, 1.09 | <0.001 |
| Education (Reference: Below Primary School) | |||
| Primary school | 0.29 | 0.19, 0.43 | <0.001 |
| Middle school | 0.06 | 0.03, 0.15 | <0.001 |
| High school and above | 0.04 | 0.01, 0.13 | <0.001 |
| Alcohol drinking (Reference: No) | 0.64 | 0.42, 0.96 | 0.032 |
| SBP | 1.01 | 1.00, 1.02 | 0.005 |
| Handgrip strength | 0.97 | 0.95,0.99 | 0.003 |
| Depression (Reference: No) | 2.06 | 1.45, 2.94 | <0.001 |
表2 老年人群认知障碍风险因素的Logistic回归分析
Tab.2 Logistic regression analysis of risk factors for cognitive impairment in the elderly individuals
| Variable | OR | 95% CI | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 1.06 | 1.03, 1.09 | <0.001 |
| Education (Reference: Below Primary School) | |||
| Primary school | 0.29 | 0.19, 0.43 | <0.001 |
| Middle school | 0.06 | 0.03, 0.15 | <0.001 |
| High school and above | 0.04 | 0.01, 0.13 | <0.001 |
| Alcohol drinking (Reference: No) | 0.64 | 0.42, 0.96 | 0.032 |
| SBP | 1.01 | 1.00, 1.02 | 0.005 |
| Handgrip strength | 0.97 | 0.95,0.99 | 0.003 |
| Depression (Reference: No) | 2.06 | 1.45, 2.94 | <0.001 |
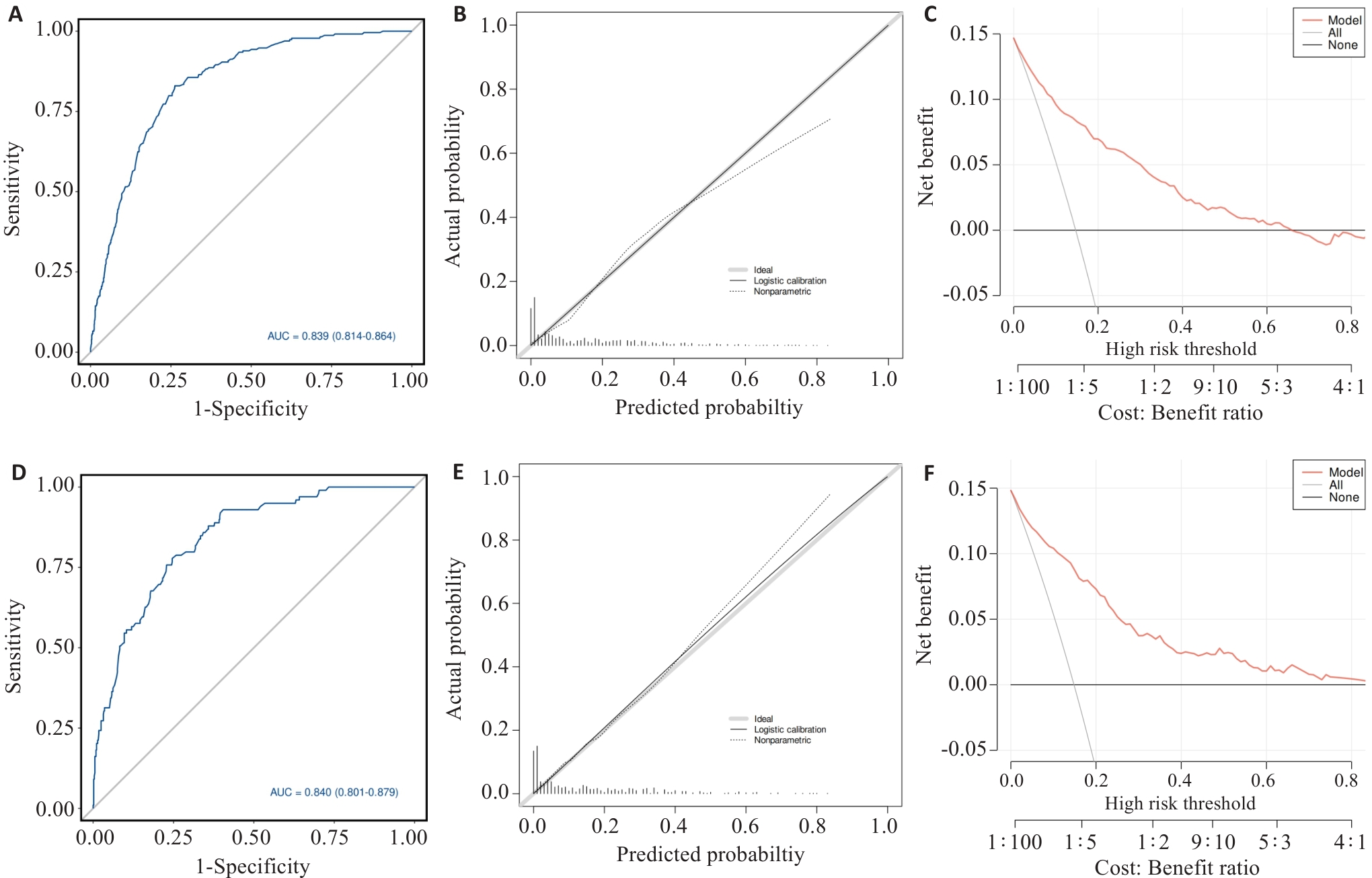
图3 模型在训练集与验证集中的预测性能评估图
Fig.3 Performance evaluation of the predictive model in the training and validation cohorts. A: Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve in the training set. B: Calibration curve in the training set. C: Decision curve analysis (DCA) in the training set. D: ROC curve in the internal validation set. E: Calibration curve in the internal validation set. F: DCA in the internal validation set.
| [1] | Jiang Y, Cui M, Tian W, et al. Lifestyle, multi-omics features, and preclinical dementia among Chinese: The Taizhou Imaging Study[J]. Alzheimers Dement, 2021, 17(1): 18-28. doi:10.1002/alz.12171 |
| [2] | Jia L, Du Y, Chu L, et al. Prevalence, risk factors, and management of dementia and mild cognitive impairment in adults aged 60 years or older in China: a cross-sectional study[J]. Lancet Public Health, 2020, 5(12): e661-71. doi:10.1016/s2468-2667(20)30185-7 |
| [3] | 王英全,梁景宏,贾瑞霞,等.2020-2050年中国阿尔茨海默病患病情况预测研究[J].阿尔茨海默病及相关病,2019,2(01):289-98. |
| [4] | Ren Y, Dong Y, Hou T, et al. Prevalence, incidence, and progression of cognitive impairment, No dementia among rural-dwelling Chinese older adults[J]. J Alzheimers Dis, 2022, 85(4): 1583-92. doi:10.3233/jad-215236 |
| [5] | 首都医科大学宣武医院国家神经疾病医学中心, 中国疾病预防控制中心慢性非传染性疾病预防控制中心, 国家卫生健康委能力建设和继续教育中心, 等. 中国阿尔茨海默病蓝皮书(精简版)[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2024, 104(29): 2701-27. |
| [6] | Xue C, Li J, Hao M, et al. High prevalence of subjective cognitive decline in older Chinese adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Front Public Health, 2023, 11: 1277995. doi:10.3389/fpubh.2023.1277995 |
| [7] | Pu LN, Pan DG, Wang HH, et al. A predictive model for the risk of cognitive impairment in community middle-aged and older adults[J]. Asian J Psychiatry, 2023, 79: 103380. doi:10.1016/j.ajp.2022.103380 |
| [8] | 赵晓晴, 郭桐桐, 张欣怡, 等. 社区老年人认知障碍风险预测模型的构建与验证研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2025, 28(22): 2776-90. |
| [9] | Geethadevi GM, Peel R, Bell JS, et al. Validity of three risk prediction models for dementia or cognitive impairment in Australia[J]. Age Ageing, 2022, 51(12): afac307. doi:10.1093/ageing/afac307 |
| [10] | Zhao Y, Hu Y, Smith JP, et al. Cohort profile: the China health and retirement longitudinal study (CHARLS)[J]. Int J Epidemiol, 2014, 43(1): 61-8. doi:10.1093/ije/dys203 |
| [11] | Chu L, Wu Y, Karjalainen H, et al. Lifespan exposures to rural-urban conditions and later-life cognitive function[J]. Alzheimers Dement, 2025, 21(6): e70267. doi:10.1002/alz.70267 |
| [12] | Li L, Zhuang L, Xu Z, et al. U-shaped relationship between non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and cognitive impairment in Chinese middle-aged and elderly: a cross-sectional study[J]. BMC Public Health, 2024, 24(1): 1624. doi:10.1186/s12889-024-19164-8 |
| [13] | Zhou S, Song S, Jin Y, et al. Prospective association between social engagement and cognitive impairment among middle-aged and older adults: evidence from the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study[J]. BMJ Open, 2020, 10(11): e040936. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-040936 |
| [14] | 史路平, 姚水洪, 王 薇. 中国老年人群轻度认知障碍患病率及发展趋势的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2022, 25(1): 109-14. doi:10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2021.00.315 |
| [15] | Jia LF, Quan MN, Fu Y, et al. Dementia in China: epidemiology, clinical management, and research advances[J]. Lancet Neurol, 2020, 19(1): 81-92. doi:10.1016/s1474-4422(19)30290-x |
| [16] | 公维军. 衰老相关认知功能障碍的发病机制与康复治疗[J]. 康复学报, 2024, 34(6): 529-35. |
| [17] | Arlt FA, Sperber PS, von Rennenberg R, et al. Serum anti-NMDA receptor antibodies are linked to memory impairment 12 months after stroke[J]. Mol Psychiatry, 2025, 30(4): 1359-68. doi:10.1038/s41380-024-02744-w |
| [18] | 李 月. 我国老年人认知障碍特征分析及政策研究[J]. 人口与健康, 2020, (5): 54-7. |
| [19] | Cai Y, Fang L, Li A, et al. Educational attainment, Aβ, tau, and structural brain reserve in Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Alzheimers Dement, 2025, 21(2): e14400. doi:10.1002/alz.14400 |
| [20] | Cui L, Hou NN, Wu HM, et al. Prevalence of Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease in China: an updated systematical analysis[J]. Front Aging Neurosci, 2020, 12: 603854. doi:10.3389/fnagi.2020.603854 |
| [21] | Zhang R, Shen L, Miles T, et al. Association of low to moderate alcohol drinking with cognitive functions from middle to older age among US adults[J]. JAMA Netw Open, 2020, 3(6): e207922. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.7922 |
| [22] | Huang Z, Chen R, Ho M, et al. Dynamic responses of striatal cholinergic interneurons control behavioral flexibility[J]. Sci Adv, 2024, 10(51): eadn2446. doi:10.1126/sciadv.adn2446 |
| [23] | Li CL, Zhu YD, Ma YJ, et al. Association of cumulative blood pressure with cognitive decline, dementia, and mortality[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2022, 79(14): 1321-35. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2022.01.045 |
| [24] | Zheng G, Zhou B, Fang Z, et al. Long-term visit-to-visit blood pressure variability and cognitive decline among patients with hypertension: a pooled analysis of 3 national prospective cohorts[J]. J Am Heart Assoc, 2024, 13(13): e035504. doi:10.1161/jaha.124.035504 |
| [25] | Duchowny KA, Ackley SF, Brenowitz WD, et al. Associations between handgrip strength and dementia risk, cognition, and neuroimaging outcomes in the UK biobank cohort study[J]. JAMA Netw Open, 2022, 5(6): e2218314. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.18314 |
| [26] | Kuo K, Zhang YR, Chen SD, et al. Associations of grip strength, walking pace, and the risk of incident dementia: a prospective cohort study of 340212 participants[J]. Alzheimers Dement, 2023, 19(4): 1415-27. doi:10.1002/alz.12793 |
| [27] | Liou YJ, Tsai SJ, Bai YM, et al. Dementia risk in middle-aged patients with schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and major depressive disorder: a cohort study of 84, 824 subjects[J]. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci, 2023, 273(1): 219-27. doi:10.1007/s00406-022-01389-6 |
| [28] | Li JM, Hu T, Zhou XN, et al. The involvement of NLRP3 inflammasome in CUMS-induced AD-like pathological changes and related cognitive decline in mice[J]. J Neuroinflammation, 2023, 20(1): 112. doi:10.1186/s12974-023-02791-0 |
| [1] | 房尚萍, 刘佳梦, 岳星辰, 李欢, 利琬柠, 汤晓宇, 包鹏举. 胃印戒细胞癌的分级与预后存在种族差异:一项SEER数据库和TCGA数据库的研究[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(8): 1706-1717. |
| [2] | 于云红, 谢炜, 李慧. 柴胡疏肝汤通过上调ASIC1蛋白调节NMDAR通道改善大鼠癫痫后的认知障碍[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1506-1512. |
| [3] | 马振岩, 阿鑫, 赵蕾, 张洪博, 刘科, 赵依晴, 钱赓. 急性ST段抬高型心肌梗死经皮冠状动脉介入术后左心室不良重构的新型风险预测模型:基于心脏磁共振的多中心前瞻性研究[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 669-683. |
| [4] | 陈琦, 夏天天, 周永强, 常铭洋, 胡楠, 杨燕美, 李仲, 高月, 顾斌. 产黑普雷沃氏菌加重小鼠的牙周炎症并损伤认知功能[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 453-460. |
| [5] | 王钰岚, 方向, 陈泽铭, 阮炳坤, 韩欣礼, 唐雨婕, 朱璐瑶. 清热利胆解毒方通过调控线粒体自噬改善高铜负荷大鼠的认知功能障碍[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(11): 2437-2443. |
| [6] | 潘甚豪, 李炎坤, 伍哲维, 毛玉玲, 王春艳. 子宫内膜异位症患者新鲜胚胎移植临床妊娠率预测模型的建立与验证[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1407-1415. |
| [7] | 戈 悦, 李建伟, 梁宏开, 侯六生, 左六二, 陈 珍, 卢剑海, 赵 新, 梁静漪, 彭 岚, 包静娜, 段佳欣, 刘 俐, 毛可晴, 曾振华, 胡鸿彬, 陈仲清. VA-ECMO患者院内死亡风险预测模型的构建及验证:一项多中心、回顾性、病例对照研究[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 491-498. |
| [8] | 刘云泽, 李宬润, 郭俊唐, 刘 阳. 基于临床-影像组学列线图模型鉴别局灶性机化性肺炎与肺腺癌[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 397-404. |
| [9] | 范嘉宁, 孙莹杰, 梁 冰, 张霄燕, 肖 诚, 黄泽清. 肠道菌群在体外循环心脏手术后围手术期神经认知障碍中的作用:基于菌群人源化大鼠模型[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(6): 964-969. |
| [10] | 张奔龙, 鲁意迅, 李 力, 高云鹤, 梁文全, 郗洪庆, 王鑫鑫, 张珂诚, 陈 凛. 基于单中心490例胃神经内分泌肿瘤建立的列线图具有良好的预后预测性能[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(2): 183-190. |
| [11] | 张浩轩, 陆 进, 蒋成义, 方美芳. 基于人工智能技术的鼻咽癌风险预测模型的构建与评价[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(2): 271-279. |
| [12] | 孔德贤, 宋丽萍, 向 阳. PET/CT代谢参数与血液炎症标志物对一线化疗的非小细胞肺癌患者预后列线图的构建及临床意义[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(12): 2139-2144. |
| [13] | 王科宇, 李海侠, 邓新立, 闫双通, 裘宇容, 丛玉隆. 中国老年人群促甲状腺激素水平的多中心调查[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(1): 1-7. |
| [14] | 刘昭君, 周晓莉. 基于系统性炎症指标构建的列线图可预测心力衰竭患者的不良结局[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(8): 1149-1158. |
| [15] | 罗 钞, 王高明, 胡力文, 强 勇, 郑 超, 申 翼. 食管癌患者术后预测模型的构建和验证:基于SEER数据库[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(6): 794-804. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||