南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (8): 1616-1624.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.08.06
• • 上一篇
许嘉蓉1,2( ), 黄傲1,2, 丁祉恺1,2, 鲍宇1, 赵仓焕3, 蔡文智1,2(
), 黄傲1,2, 丁祉恺1,2, 鲍宇1, 赵仓焕3, 蔡文智1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2025-02-21
出版日期:2025-08-20
发布日期:2025-09-05
通讯作者:
蔡文智
E-mail:jiarong_xu@163.com;caiwzh@smu.edu.cn
作者简介:许嘉蓉,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: jiarong_xu@163.com
基金资助:
Jiarong XU1,2( ), Ao HUANG1,2, Zhikai DING1,2, Yu BAO1, Canghuan ZHAO3, Wenzhi CAI1,2(
), Ao HUANG1,2, Zhikai DING1,2, Yu BAO1, Canghuan ZHAO3, Wenzhi CAI1,2( )
)
Received:2025-02-21
Online:2025-08-20
Published:2025-09-05
Contact:
Wenzhi CAI
E-mail:jiarong_xu@163.com;caiwzh@smu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
目的 观察子午流注针法治疗失眠症的疗效及其对谷氨酸(Glu)/γ-氨基丁酸(GABA)-谷氨酰胺(Gln)代谢环路的调节作用。 方法 40只雄性SD大鼠随机分为对照组、模型组、纳甲组和纳子组, 10只/组。模型组、纳甲组和纳子组接受对氯苯丙氨酸腹腔注射后建立失眠大鼠模型并通过戊巴比妥钠睡眠协同实验进行模型评价。造模成功后,纳甲组与纳子组予以子午流注针法治疗7 d。采用苏木精-伊红染色观察下丘脑病理组织,采用高效液相色谱(HPLC)-质谱法(MS)/MS测定下丘脑中神经递质Glu和GABA的含量,采用免疫组织化学法(IHC)检测下丘脑中GABAA受体(GABAAR)的表达。采用免疫印迹法检测下丘脑谷氨酸脱羧酶(GAD65/67)和谷氨酰胺合成酶(GS)的表达水平。 结果 与模型组比较,子午流注针刺组谷氨酸含量降低(P<0.01),GABAA受体表达降低(P<0.01),GABA含量升高(P<0.05),谷氨酸/氨基丁酸比值降低。与模型组比较,子午流注针刺组下丘脑GAD65(P<0.01)、GAD67(P<0.05)蛋白表达增加,GS蛋白表达减少(P<0.01)。 结论 子午流注针刺可能通过调节Glu/GABA-Gln代谢,产生镇静催眠作用,影响Glu和GABA的合成和分解,恢复Glu和GABA之间的兴奋/抑制平衡。
许嘉蓉, 黄傲, 丁祉恺, 鲍宇, 赵仓焕, 蔡文智. 子午流注针法对失眠大鼠Glu/GABA-Gln代谢环路异常的调节作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(8): 1616-1624.
Jiarong XU, Ao HUANG, Zhikai DING, Yu BAO, Canghuan ZHAO, Wenzhi CAI. Ziwuliuzhu acupuncture modulates Glu/GABA‑Gln metabolic loop abnormalities in insomniac rats[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(8): 1616-1624.
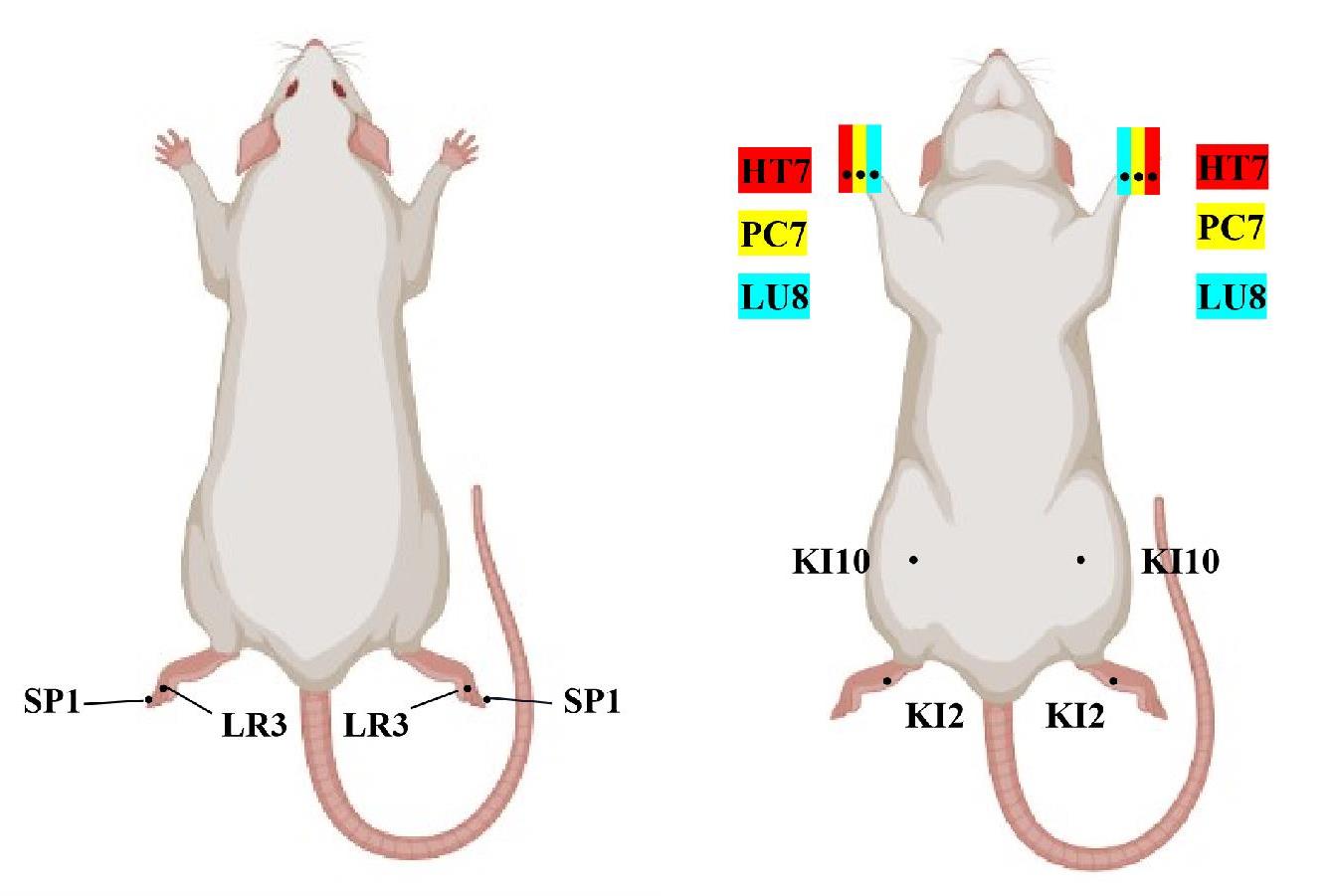
图1 大鼠的俯卧位和仰卧位取穴图
Fig.1 Illustration of the locations of the chosen acupoints in rats in the prone and supine positions. Rats were stimulated using specific acupuncture points with anatomical correspondence to human acupoints. The SP1 (Yinbai) is located at the medial aspect of the big toe, approximately 0.1 cun posterior to the corner of the nail. LR3 (Taichong) is in the depression distal to the junction of the 1st and 2nd metatarsal bones. HT7 (Shenmen) is in the transverse crease of the wrist of the forepaw, radial to the flexor carpi ulnaris tendon. PC7 (Daling) is on the midpoint of the transverse crease of the wrist between the tendons of the palmaris longus and flexor carpi radialis. LU8 (Jingqu) is in the depression between the styloid process of the radius and the radial side, 1 cun above the transverse crease of the wrist. KI2 (Rangu) is located on the medial border of the foot, inferior to the tuberosity of the navicular bone, at the junction of the pink and pale skin. KI10 (Yingu) is located on the medial side of the popliteal fossa between the tendons of the semitendinosus and semimembranosus.
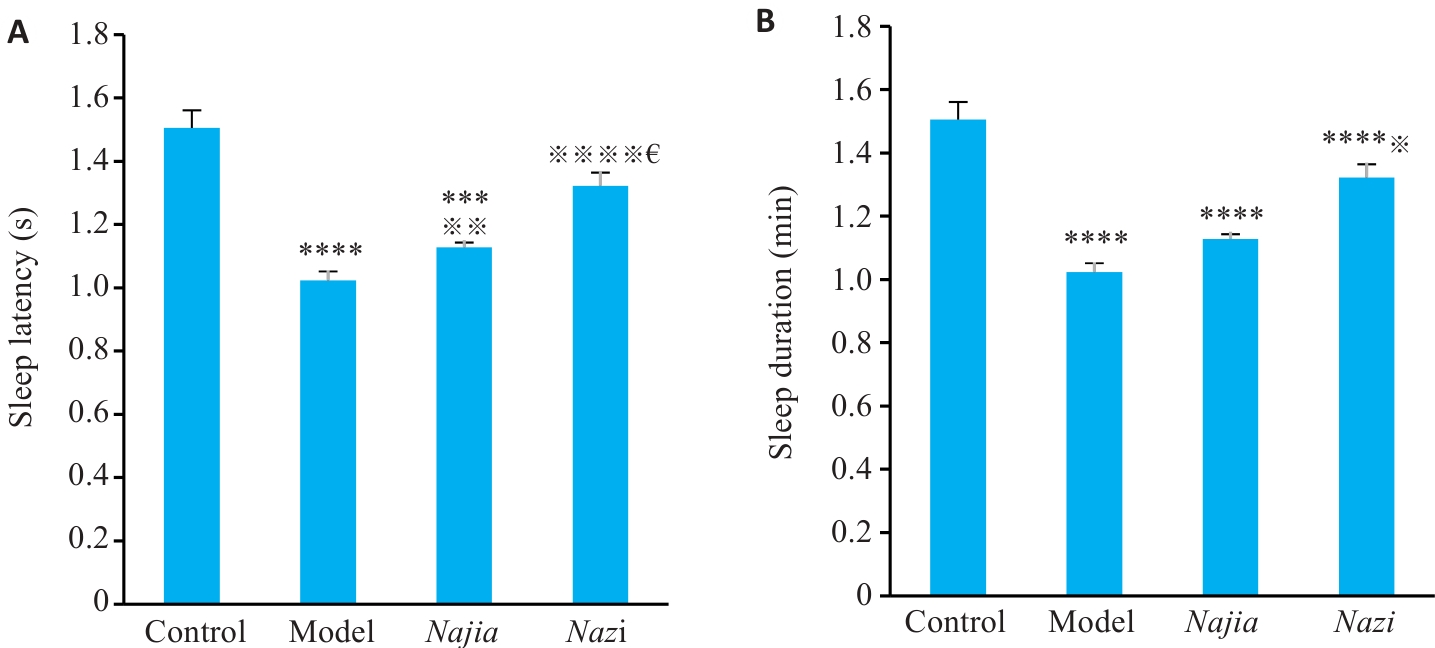
图2 造模后大鼠戊巴比妥钠睡眠协同实验比较
Fig.2 Results of pentobarbital sodium-induced sleep test (sleep latency and sleep duration) in the 4 groups (Mean±SD, n=10). A: Sleep latency. B: Sleep duration. ****P<0.0001, ***P<0.001 vs the control group; ※P<0.05, ※※P<0.01, ※※※※P<0.0001 vs model group; €P<0.05 vsNajia group.
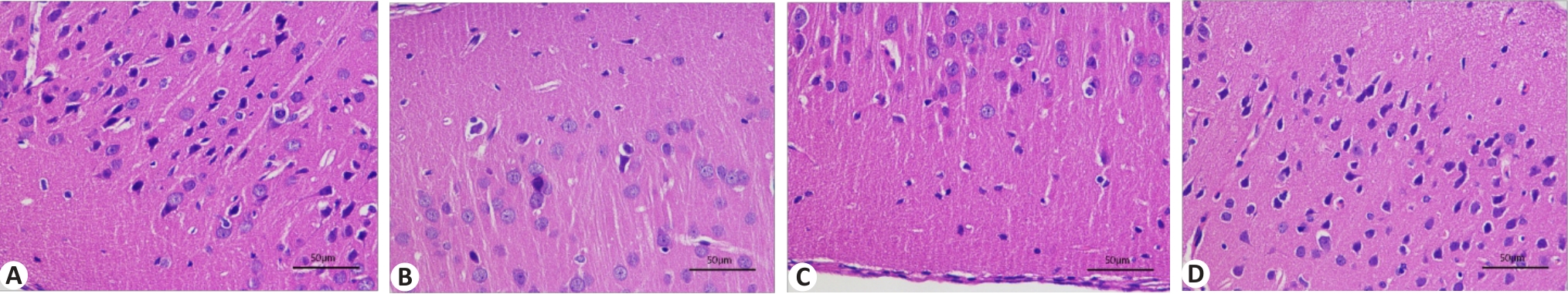
图3 各组大鼠下丘脑HE染色
Fig. 3 Pathological examination of rat hypothalamus in each group (HE staining, scale bar=50 μm). A: Control group. B: Model group. C: Najia group. D: Nazi group.
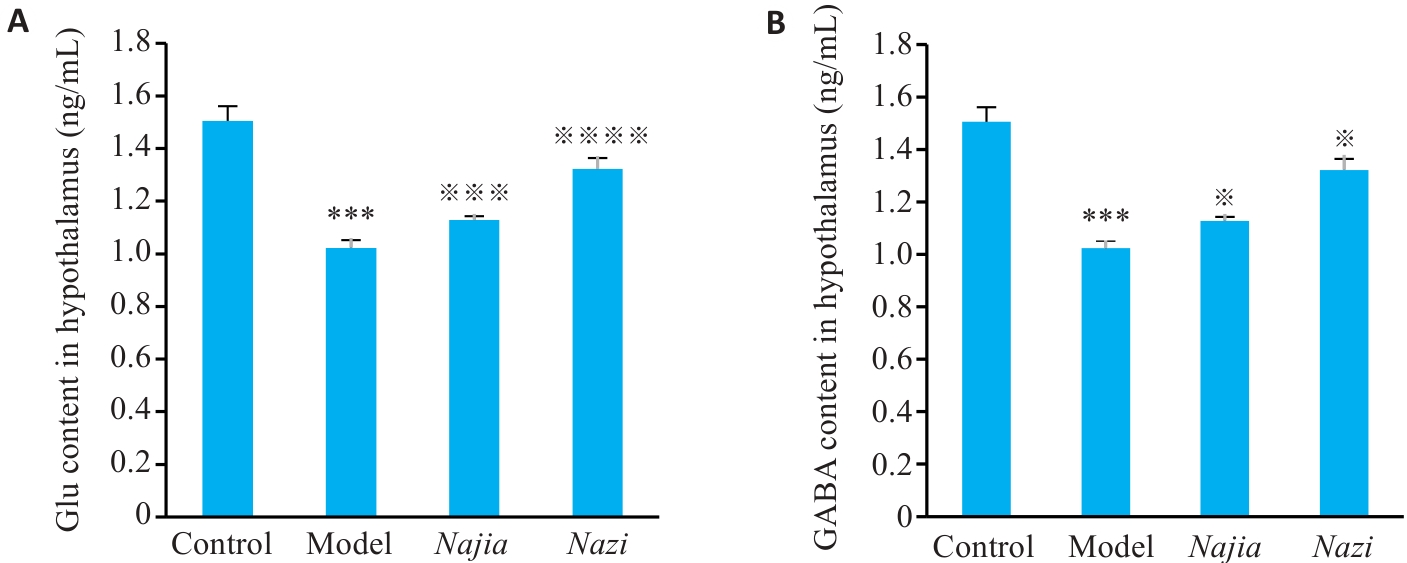
图4 各组大鼠下丘脑Glu(A)、GABA(B)表达量
Fig.4 Effect of Ziwuliuzhu acupuncture on the expression of GABA and Glu in the hypothalamus. The expression levels of Glu (A) and GABA (B) in the hypothalamus were assessed via HPLC-MS/MS. The values are the Means±SD (n=6). Post hoc LSD test: ***P<0.001 vs the control group; ※※※※P<0.0001, ※※※P<0.001, ※P<0.05 vs the model group.
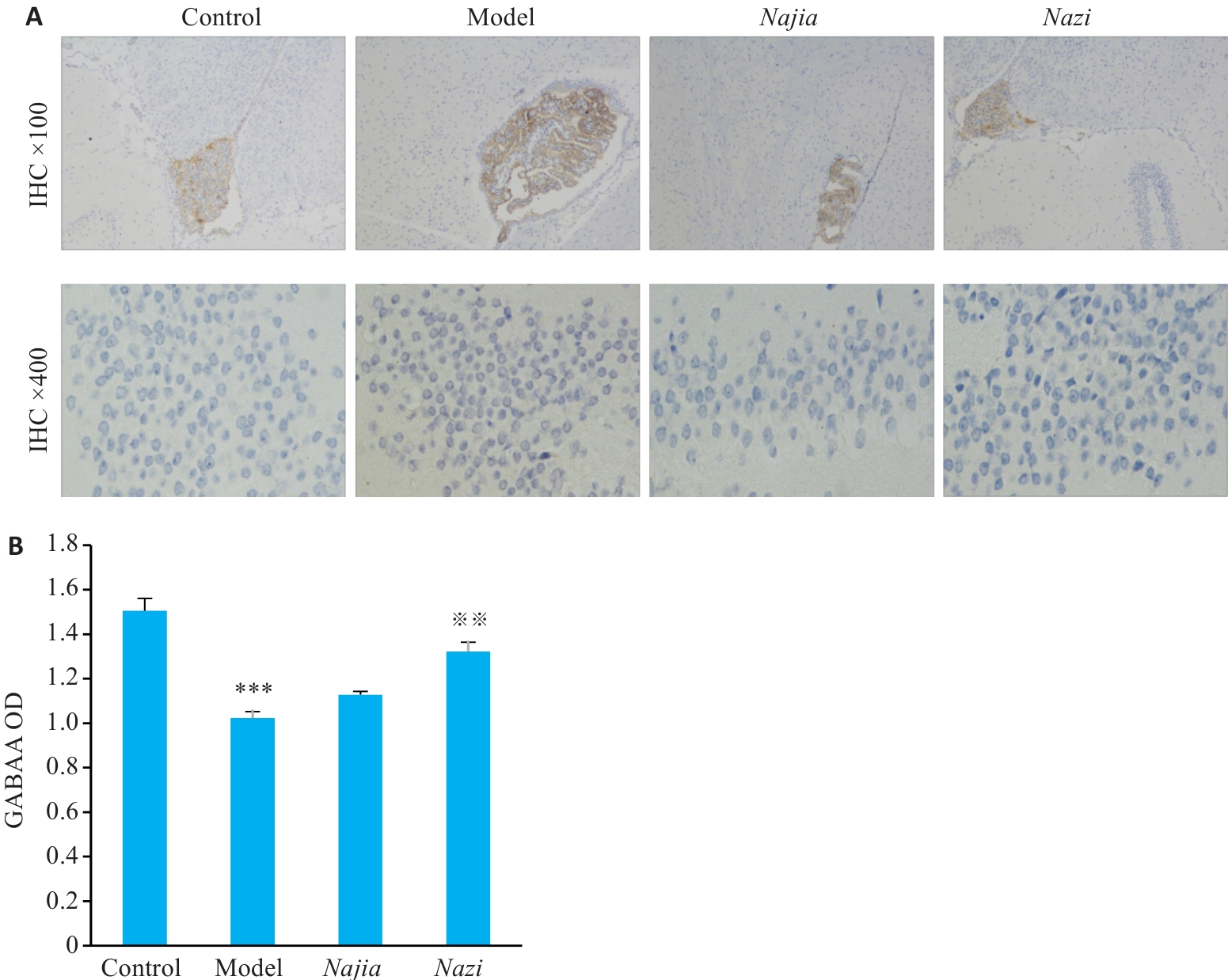
图5 四组大鼠下丘脑内GABAA受体阳性表达
Fig.5 Expressions of GABAARs in the hypo-thalamus of the rats in the 4 groups. A: Immunohistochemistry for GABAAR in the hypothalamus in each group (Original magnification: ×100 or ×400). B: Comparison of mean OD values among the groups (Mean±SD, n=6). Post hoc LSD test: **P<0.01 vs control group; ※※P<0.01 vs model group.
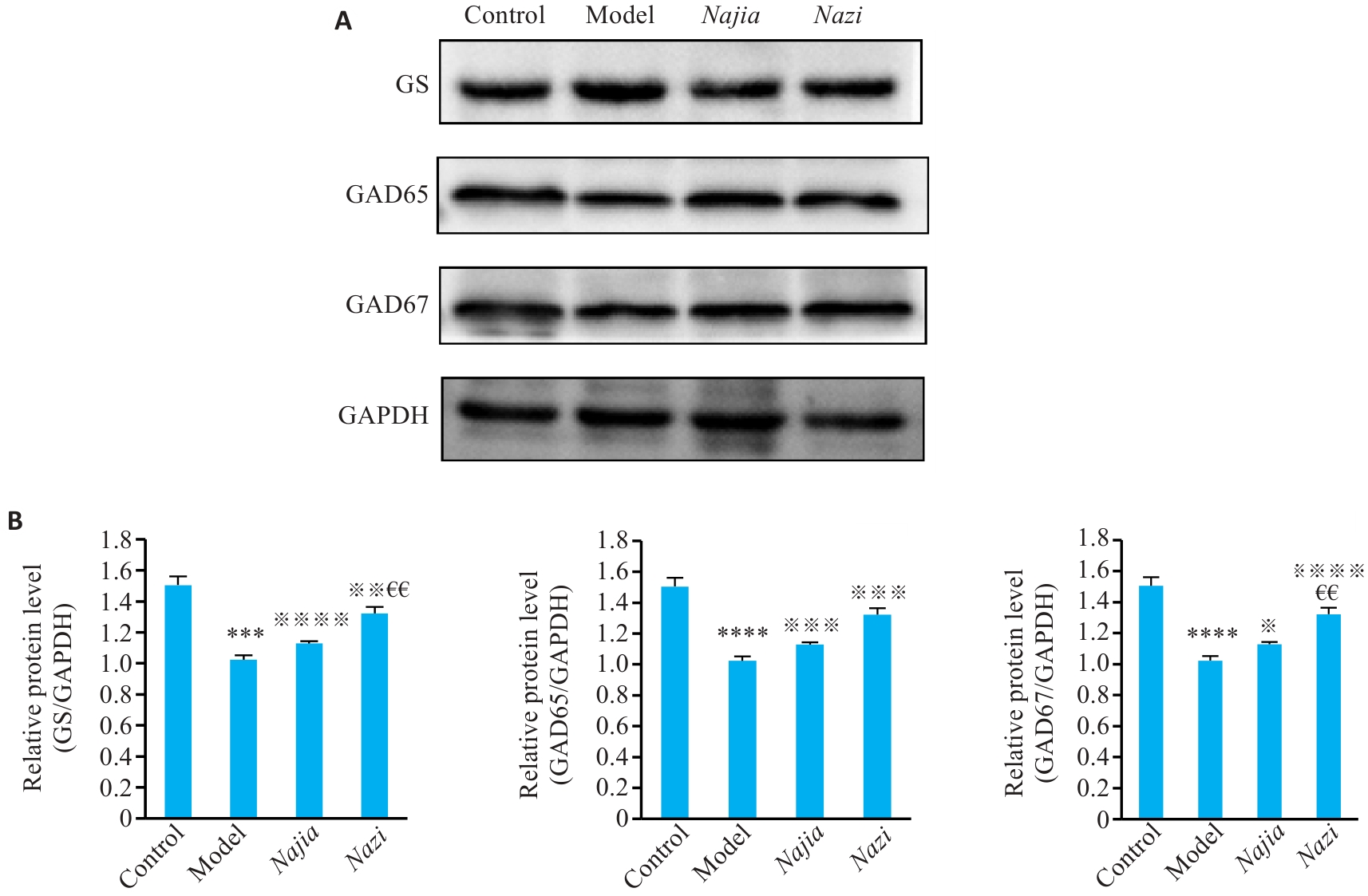
图6 各组大鼠下丘脑GAD65、GAD67和GS蛋白表达结果 (A) 及相对表达量(B)
Fig.6 Effect of Ziwuliuzhu acupuncture on expressions of protein expressions in the hypothalamus of the rats. A: Western blotting for GAD65, GAD67, and GS in the hypothalamic tissues. B: Quantitative analysis of the protein expression levels (Mean±SD). Post hoc LSD test: ****P<0.0001, ***P<0.001 vs the control group; ※※※※P<0.0001, ※※※P<0.001, ※※P<0.01, ※P<0.05 vs model group; €€P<0.01 vsNajia group.
| [1] | Cai CL, Kesselheim AS, Rome BN. Trends in fills, spending, and prices of doxepin for insomnia[J]. JAMA, 2025, 333(11): 999-1000. doi:10.1001/jama.2024.27526 |
| [2] | Hsu CY, Chuang YC, Chang FC, et al. Disrupted sleep homeostasis and altered expressions of clock genes in rats with chronic lead exposure[J]. Toxics, 2021, 9(9): 217. doi:10.3390/toxics9090217 |
| [3] | Patel JC, Sherpa AD, Melani R, et al. GABA co-released from striatal dopamine axons dampens phasic dopamine release through autoregulatory GABAA receptors[J]. Cell Rep, 2024, 43(3): 113834. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2024.113834 |
| [4] | Zhu X, Tang HD, Dong WY, et al. Distinct thalamocortical circuits underlie allodynia induced by tissue injury and by depression-like states[J]. Nat Neurosci, 2021, 24(4): 542-53. doi:10.1038/s41593-021-00811-x |
| [5] | Kanaan AS, Gerasch S, García-García I, et al. Pathological glutamatergic neurotransmission in Gilles de la Tourette syndrome[J]. Brain, 2017, 140(1): 218-34. doi:10.1093/brain/aww285 |
| [6] | Colic L, Li M, Demenescu LR, et al. GAD65 promoter polymorphism rs2236418 modulates harm avoidance in women via inhibition/excitation balance in the rostral ACC[J]. J Neurosci, 2018, 38(22): 5067-77. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.1985-17.2018 |
| [7] | Zhan LH, Dong YJ, Yang K, et al. Soporific effect of modified Suanzaoren decoction and its effects on the expression of CCK-8 and orexin-A[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2020, 2020: 6984087. doi:10.1155/2020/6984087 |
| [8] | Bell T, Boudes ES, Loo RS, et al. In vivo glx and glu measurements from GABA-edited MRS at 3 T[J]. NMR Biomed, 2021, 34(5): e4245. doi:10.1002/nbm.4245 |
| [9] | Bak LK, Schousboe A, Waagepetersen HS. The glutamate/GABA-glutamine cycle: aspects of transport, neurotransmitter homeostasis and ammonia transfer[J]. J Neurochem, 2006, 98(3): 641-53. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.03913.x |
| [10] | Yu X, Greenblatt HK, Greenblatt DJ. Designer benzodiazepines: an update[J]. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol, 2023, 16(2): 109-17. doi:10.1080/17512433.2023.2170349 |
| [11] | 潘胜莲, 郑士立, 周夏慧, 等. 针刺联合颈痛颗粒治疗神经根型颈椎病及对患者IL-6、TNF-α、IL-1β和血液流变学指标的影响[J]. 中国针灸, 2019, 39(12): 1274-8. doi:10.13703/j.0255-2930.2019.12.005 |
| [12] | Yu L, Yang L, Xiaoqin C, et al. Cerebral blood flow changes and their spatial correlations with GABAa and dopamine-D1 receptor explaining individual differences in chronic insomnia and the therapeutic effects of acupuncture[J]. Hum Brain Mapp, 2025, 46(4): e70183. doi:10.1002/hbm.70183 |
| [13] | Huang XR, Xu M, Xu Y, et al. Auricular acupressure for insomnia in women with breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials[J]. Medicine: Baltimore, 2025, 104(7): e41498. doi:10.1097/md.0000000000041498 |
| [14] | 管芷莹, 王 曾, 陈洪宇. 从中医时间医学论述肾系病的用药规律[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2024, 39(11): 6181-3. |
| [15] | 易夏阳, 肖姝雲, 韩华翌, 等. 从时间医学角度探讨失眠症的机理与诊疗方案 [J]. 辽宁中医杂志: 2025, 52(6): 1-8. |
| [16] | 李 艳, 郭 晖, 宋亚刚, 等. 子午流注与生物钟[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2019, 34(10): 4770-3. |
| [17] | 吴佳楠, 秦晓光, 焦陇鑫, 等. 子午流注理论在内科疾病中的临床研究进展 [J]. 实用中医内科杂志, 2024, 38(10): 35-8. doi:10.13729/j.issn.1671-7813.Z20232346 |
| [18] | 刘媛媛, 安 琪, 安军明, 等. 方氏头针结合子午流注纳子法对失眠患者血清GABA、Glu及睡眠质量的影响[J]. 针灸临床杂志, 2024, 40(6): 43-7. |
| [19] | 刘良羽, 袁秀丽, 杨小荷. 近十年针刺治疗失眠的主要临床思路概况 [J]. 内蒙古中医药, 2023, 42(2): 97-9. |
| [20] | Huang A, Xiao G, Chen Y, et al. Ziwuliuzhu acupuncture modulates clock mRNA, Bmal1 mRNA and melatonin in insomnia rats[J]. J Acupunct Meridian Stud, 2023, 16(3): 109-18. doi:10.51507/j.jams.2023.16.3.109 |
| [21] | 徐文清, 李 蔚, 殷 萱, 等. 实验小鼠常用腧穴定位研究; proceedings of the 2024中国针灸学会年会, 中国天津, F, 2024 [C]. |
| [22] | Deng J, Chen L, Liu CC, et al. Distinct thalamo-subcortical circuits underlie painful behavior and depression-like behavior following nerve injury[J]. Adv Sci: Weinh, 2024, 11(34): e2401855. doi:10.1002/advs.202401855 |
| [23] | Ritter C, Buchmann A, Müller ST, et al. Evaluation of prefrontal γ-aminobutyric acid and glutamate levels in individuals with major depressive disorder using proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy[J]. JAMA Psychiatry, 2022, 79(12): 1209-16. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2022.3384 |
| [24] | Glykys J, Duquette E, Rahmati N, et al. Mannitol decreases neocortical epileptiform activity during early brain development via cotransport of chloride and water[J]. Neurobiol Dis, 2019, 125: 163-75. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2019.01.024 |
| [25] | Hao JJ, Jiang KY, Zhang X, et al. "Glu/GABA-Gln" metabolic loop abnormalities in iminodipropionitrile (IDPN)-induced dyskinetic syndrome[J]. Neurol Sci, 2021, 42(11): 4697-706. doi:10.1007/s10072-021-05570-y |
| [26] | Héja L, Simon Á, Szabó Z, et al. Feedback adaptation of synaptic excitability via glu: Na+ symport driven astrocytic GABA and gln release[J]. Neuropharmacology, 2019, 161: 107629. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2019.05.006 |
| [27] | Bracher S, Guérin K, Polyhach Y, et al. Glu-311 in external loop 4 of the sodium/proline transporter PutP is crucial for external gate closure[J]. J Biol Chem, 2016, 291(10): 4998-5008. doi:10.1074/jbc.m115.675306 |
| [28] | Nakahara T, Tsugawa S, Noda Y, et al. Glutamatergic and GABAergic metabolite levels in schizophrenia-spectrum disorders: a meta-analysis of 1H-magnetic resonance spectroscopy studies[J]. Mol Psychiatry, 2022, 27(1): 744-57. doi:10.1038/s41380-021-01297-6 |
| [29] | Shurubor YI, Krasnikov AB, Isakova EP, et al. Energy metabolites and indicative significance of α-ketoglutarate and α-ketoglutaramate in assessing the progression of chronic hepatoencephalopathy[J]. Biomolecules, 2024, 14(2): 217. doi:10.3390/biom14020217 |
| [30] | Soeiro-de-Souza MG, Henning A, Machado-Vieira R, et al. Anterior cingulate Glutamate-Glutamine cycle metabolites are altered in euthymic bipolar I disorder[J]. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol, 2015, 25(12): 2221-9. doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2015.09.020 |
| [31] | Correction to: Neurotransmitters of sleep and wakefulness in flatworms[J]. Sleep, 2022, 45(7): zsac127. doi:10.1093/sleep/zsac127 |
| [32] | Kim JH, Nam D, Park MK, et al. Randomized control trial of hand acupuncture for female stress urinary incontinence[J]. Acupunct Electrother Res, 2008, 33(3/4): 179-92. doi:10.3727/036012908803861122 |
| [33] | Matukhno AE, Sukhov AG, Sinitsyna VV. The role of GABAA and GABAB receptors in formation of evoked potentials in the barrel cortex of rats[J]. Zh Vyssh Nerv Deiat Im I P Pavlova, 2012, 62(3): 372-82. |
| [34] | Fu Y, Cui JH, Ma YY. Differential effects of aging on EEG after baclofen administration[J]. Sci China Life Sci, 2011, 54(5): 459-65. doi:10.1007/s11427-011-4170-1 |
| [35] | Winkelman JW, Buxton OM, Jensen JE, et al. Reduced brain GABA in primary insomnia: preliminary data from 4T proton magnetic reso-nance spectroscopy (1H-MRS)[J]. Sleep, 2008, 31(11): 1499-506. doi:10.1093/sleep/31.11.1499 |
| [36] | Yin X, Zhang S, Lee JH, et al. Compartmentalized ocular lymphatic system mediates eye-brain immunity[J]. Nature, 2024, 628(8006): 204-11. doi:10.1038/s41586-024-07130-8 |
| [37] | Pamidi S, Wroblewski K, Broussard J, et al. Obstructive sleep apnea in young lean men: impact on insulin sensitivity and secretion[J]. Diabetes Care, 2012, 35(11): 2384-9. doi:10.2337/dc12-0841 |
| [38] | Song Q, Wei A, Xu H, et al. An ACC-VTA-ACC positive-feedback loop mediates the persistence of neuropathic pain and emotional consequences[J]. Nat Neurosci, 2024, 27(2): 272-85. doi:10.1038/s41593-023-01519-w |
| [39] | Rong M, Jia JJ, Lin MQ, et al. The effect of modified Qiyuan paste on mice with low immunity and sleep deprivation by regulating GABA nerve and immune system[J]. Chin Med, 2024, 19(1): 84. doi:10.1186/s13020-024-00939-5 |
| [40] | Qian J, Zheng L, Huang M, et al. Potential mechanisms of casein hexapeptide YPVEPF on stress-induced anxiety and insomnia mice and its molecular effects and key active structure[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2024, 72(12): 6189-202. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.3c05718 |
| [41] | Jiang YQ, Lee DK, Guo W, et al. Hypothalamic regulation of hippocampal CA1 interneurons by the supramammillary nucleus[J]. Cell Rep, 2024, 43(11): 114898. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114898 |
| [42] | Lust K, Maynard A, Gomes T, et al. Single-cell analyses of axolotl telencephalon organization, neurogenesis, and regeneration[J]. Science, 2022, 377(6610): eabp9262. doi:10.1126/science.abp9262 |
| [43] | Müller M, Van Liefferinge E, Tilbrook A, et al. Excess dietary Lys reduces feed intake, stimulates jejunal CCK secretion and alters essential and non-essential blood AA profile in pigs[J]. J Anim Sci Biotechnol, 2024, 15(1): 24. doi:10.1186/s40104-023-00971-9 |
| [44] | Wallis JL, Irvine MW, Jane DE, et al. An interchangeable role for kainate and metabotropic glutamate receptors in the induction of rat hippocampal mossy fiber long-term potentiation in vivo [J]. Hippocampus, 2015, 25(11): 1407-17. doi:10.1002/hipo.22460 |
| [45] | 王 磊, 黄荣高, 陈进法, 等. 多元时间针法治疗失眠症疗效对照观察[J]. 中国针灸, 2012, 32(4): 297-300. |
| [46] | 左 政, 朱勉生, 陈春信, 等. 时空针灸子午流注纳子法探析[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2023, 38(6): 2506-10. |
| [47] | 芦文科, 秦晓光, 毛宇宏, 等. 子午流注理论的临床研究进展[J]. 实用中医内科杂志, 2024, 38(8): 35-9. |
| [1] | 王堃, 左海燕, 张娇娇, 吴欣, 王文慧, 吴生兵, 周美启. 电针通过调控海马谷氨酸释放抑制HPA轴亢进从而改善急性心肌缺血大鼠的心肌损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(8): 1599-1607. |
| [2] | 何光侣, 储婉玉, 李妍, 盛鑫, 罗浩, 徐爱萍, 卞命杰, 张环环, 汪萌芽, 郑超. Orexin-A通过调节促离子型谷氨酸受体促进脊髓损伤大鼠运动功能恢复[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(5): 1023-1030. |
| [3] | 何存宝, 杨绍杰, 朱国旗. 4-(芳基乙炔基)-吡咯并[2,3-d]嘧啶通过抑制mGluR5调控ERK1/2-SGK1信号通路改善小鼠创伤后应激障碍[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 765-773. |
| [4] | 李逗逗, 肖 蓉. 大学生失眠及其与压力感知的相关关系[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(4): 795-800. |
| [5] | 李言响, 郭永馨, 曹福羊, 郭舒婷, 薛丁豪, 周志康, 郝新宇, 仝 黎, 傅 强. 抑制dmPAG区谷氨酸能神经元可减轻创伤后应激障碍小鼠的过度防御反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 420-427. |
| [6] | 刘 欢, 饶 阳, 孙传铸, 王洋涛, 齐 顺, 李 想, 田 萌, 禹 汛, 穆允凤. 宫颈癌放疗后癌因性失眠患者的大脑功能网络与个体-经颅磁刺激干预的相关性:基于图论分析[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(9): 1629-1635. |
| [7] | 张 倩, 张梅奎, 刘颖璐, 王 妍, 吕菲菲, 王毓国. 六味酸枣汤治疗围绝经期失眠的作用机制:基于网络药理学与动物实验[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(9): 1536-1547. |
| [8] | 魏茜茜, 李超红, 赵晨露, 赵宝生, 刘玉珍. 大鼠颈上神经节代谢型谷氨酸受体7,8的表达及慢性间歇性低氧对其的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(7): 1172-1178. |
| [9] | 曹福羊, 郭永馨, 郭舒婷, 周志康, 曹江北, 仝 黎, 米卫东. 激活小鼠ZI 区GABA 能神经元可促进七氟醚和丙泊酚的麻醉诱导而对麻醉维持及觉醒无影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(5): 718-726. |
| [10] | 杨鑫宇, 朱苏月, 靳 娜, 李 妍, 甄 骋, 张环环, 徐爱萍, 汪萌芽, 郑 超. Orexin-A通过激活OX1R、OX2R和非Ca2+依赖的PKC抑制新生大鼠脊髓腹角神经元的γ-氨基丁酸电流[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(5): 694-701. |
| [11] | 黄伟康, 李志铭, 吴水天, 洪静静, 文 戈. 静息态功能磁共振成像分析原发性失眠患者大脑的小世界网络[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(3): 424-429. |
| [12] | 陈 永, 刘永谱, 班素芬, 汤 瑶, 邱富娟, 肖长虹. 血液穴位注射后小鼠的注射部位发生了什么变化?[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2020, 40(09): 1225-1229. |
| [13] | 李 洋,李秀娟,谢明丹,程 莉,陈恒胜,孙 红,蒋 莉. 邻苯二甲酸二丁酯对原代培养海马神经元的毒性及机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2020, 40(02): 225-232. |
| [14] | 倪 虹,丁海虎,陶 静,王元元,陶明飞,黄 丽. 嗅觉剥夺对小鼠大脑桶状皮层谷氨酸能神经元动作电位及Ankyrin-G表达的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2020, 40(02): 262-267. |
| [15] | 余 佳,刘可智,刘 帅. 大学生应对方式与失眠的关系:反刍思维的中介效应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2020, 40(01): 137-141. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||