Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (11): 2427-2436.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.11.15
Previous Articles Next Articles
Ming YI1( ), Ye LUO2, Lu WU1, Zeheng WU3, Cuiping JIANG1, Shiyu CHEN3, Xiao KE3(
), Ye LUO2, Lu WU1, Zeheng WU3, Cuiping JIANG1, Shiyu CHEN3, Xiao KE3( )
)
Received:2025-05-09
Online:2025-11-20
Published:2025-11-28
Contact:
Xiao KE
E-mail:mingming8909@163.com;xiaokehospital@126.com
Ming YI, Ye LUO, Lu WU, Zeheng WU, Cuiping JIANG, Shiyu CHEN, Xiao KE. Astragaloside IV alleviates D-GAL-induced endothelial cell senescence by promoting mitochondrial autophagy via inhibiting the PINK1/Parkin pathway[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(11): 2427-2436.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.11.15
| Gene | Primer sequences (5'-3') |
|---|---|
| human-GAPDH | F:GGAGCGAGATCCCTCCAAAAT |
| R:GGCTGTTGTCATACTTCTCATGG | |
| human-TP53 (P53) | F:CAGCACATGACGGAGGTTGT |
| R:TCATCCAAATACTCCACACGC | |
| human-p21 | F:TGTCCGTCAGAACCCATGC |
| R:AAAGTCGAAGTTCCATCGCTC | |
| Human-PINK1 | F: GCCTCATCGAGGAAAAACAGG |
| R: GTCTCGTGTCCAACGGGTC | |
| Human-parkin | F:GTGTTTGTCAGGTTCAACTCCA |
| R:GAAAATCACACGCAACTGGTC | |
| Human-p62 | F:GCACCCCAATGTGATCTGC |
| R:CGCTACACAAGTCGTAGTCTGG | |
| Human-Baclin1 | F:CCATGCAGGTGAGCTTCGT |
| R:GAATCTGCGAGAGACACCATC |
Tab.1 Primers sequences for qRT-PCR
| Gene | Primer sequences (5'-3') |
|---|---|
| human-GAPDH | F:GGAGCGAGATCCCTCCAAAAT |
| R:GGCTGTTGTCATACTTCTCATGG | |
| human-TP53 (P53) | F:CAGCACATGACGGAGGTTGT |
| R:TCATCCAAATACTCCACACGC | |
| human-p21 | F:TGTCCGTCAGAACCCATGC |
| R:AAAGTCGAAGTTCCATCGCTC | |
| Human-PINK1 | F: GCCTCATCGAGGAAAAACAGG |
| R: GTCTCGTGTCCAACGGGTC | |
| Human-parkin | F:GTGTTTGTCAGGTTCAACTCCA |
| R:GAAAATCACACGCAACTGGTC | |
| Human-p62 | F:GCACCCCAATGTGATCTGC |
| R:CGCTACACAAGTCGTAGTCTGG | |
| Human-Baclin1 | F:CCATGCAGGTGAGCTTCGT |
| R:GAATCTGCGAGAGACACCATC |

Fig.1 Effect of AS-IV on viability of D-GAL-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). A: Effect of different concentrations of D-GAL on HUVEC viability. B: Viability of HUVECs with different treatments. ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001 vs NC group; ####P<0.0001 vs D-gal group.
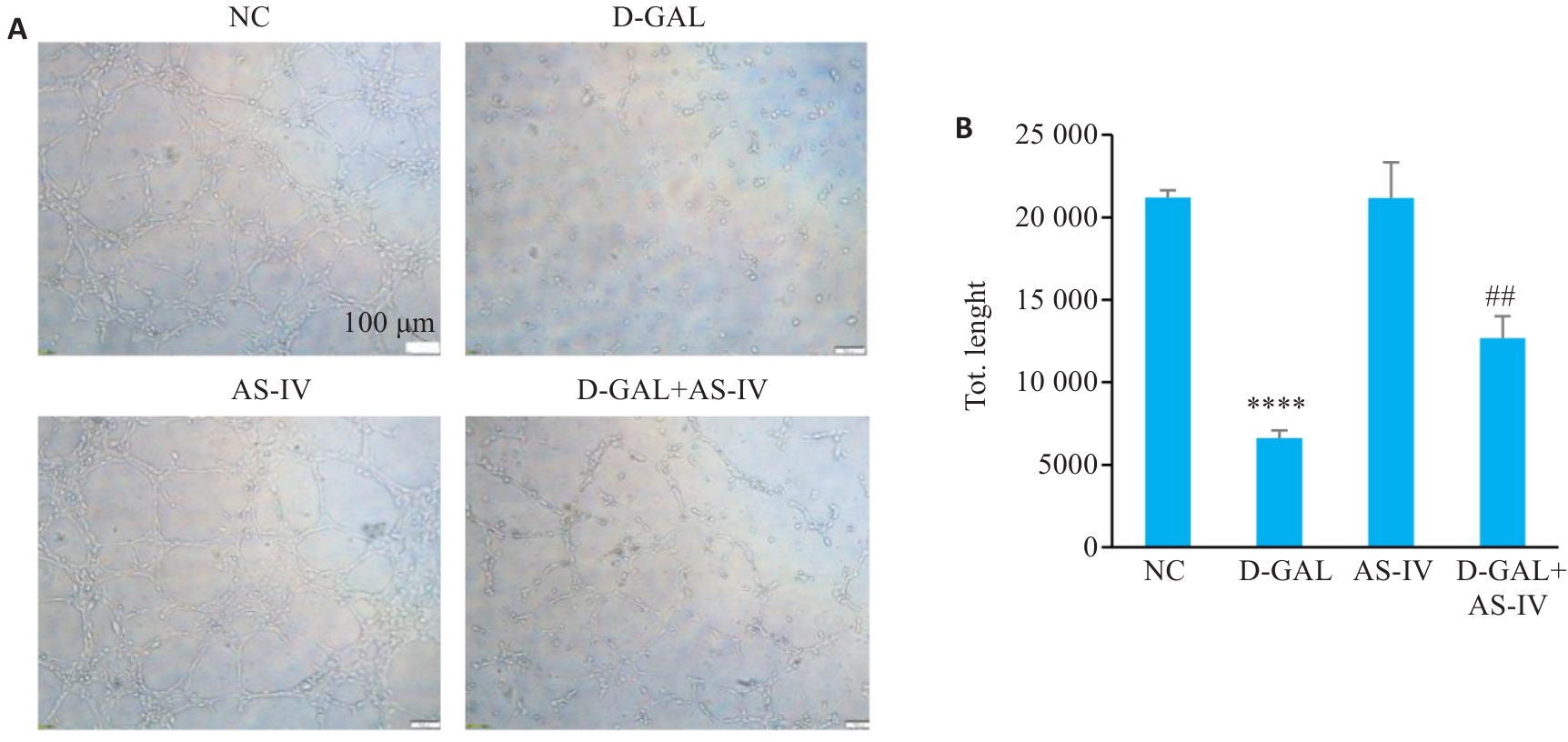
Fig.2 Effect of AS-IV on tube formation ability of HUVEC induced by D-GAL. A: Tubule formation assay images of HUVEC cells after treatment with various groups. B: Statistical graph of the tubule formation assay (Scale bar=100 μm), ****P<0.0001 vs NC group, ##P<0.01 vs D-GAL group.

Fig.3 Effect of AS-IV on migration ability of D-GAL-induced HUVECs. A: Observation of migration of HUVECs after different treatments (Scale bar=200 μm). B: Wound healing rates of HUVECs with different treatments. ****P<0.0001 vs NC group; ###P<0.001 vs D-GAL group.
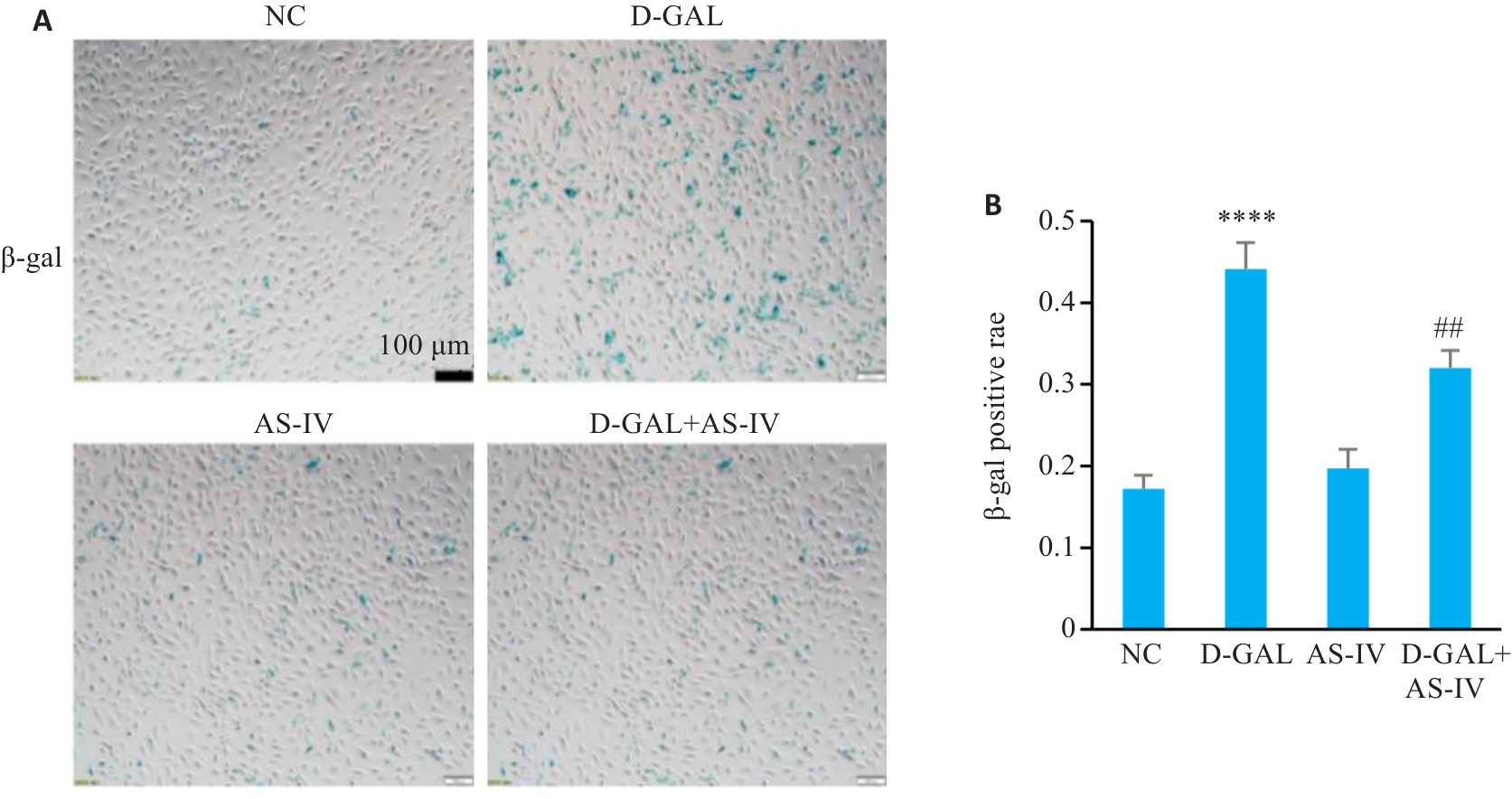
Fig.4 Effect of AS-IV on SA‑β‑Gal staining positivity rate in D-GAL-induced HUVECs. A: SA‑β-Gal staining of HUVEC cells with different treatments (Scale bar=100 μm). B: SA-β-Gal staining positiving rates of the cells. ****P<0.0001 vs NC group; ##P<0.01 vs D-GAL group.
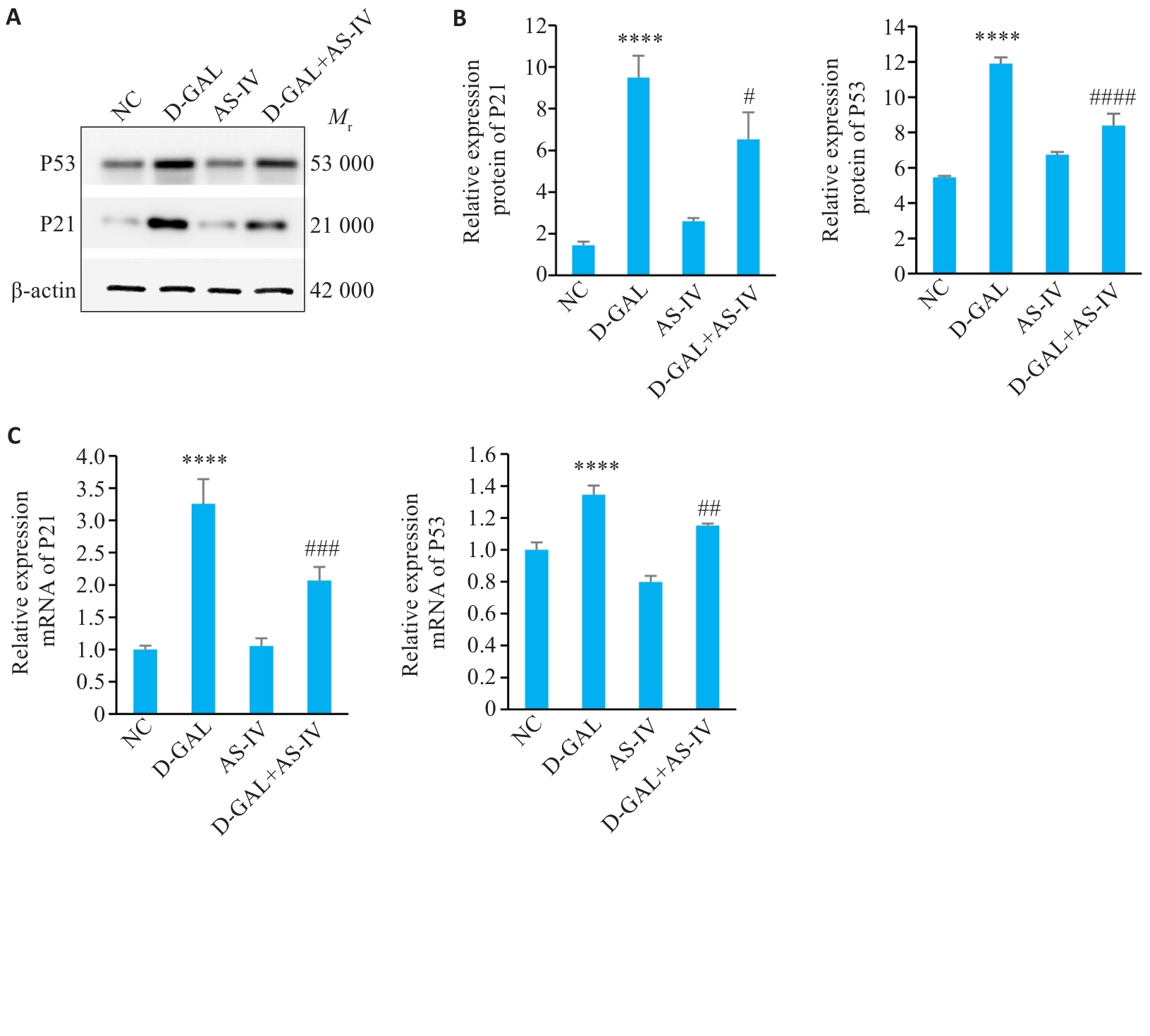
Fig.5 Effect of AS-IV on the Expression of P21 and P53 in D-GAL-Induced HUVEC Cells. A: Protein band diagram of P53 and P21 in four groups of cells. B, C: Statistical graph of P21 and P53 gene and protein expression.****P<0.0001 vs NC group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001, ####P<0.0001 vs D-GAL group.
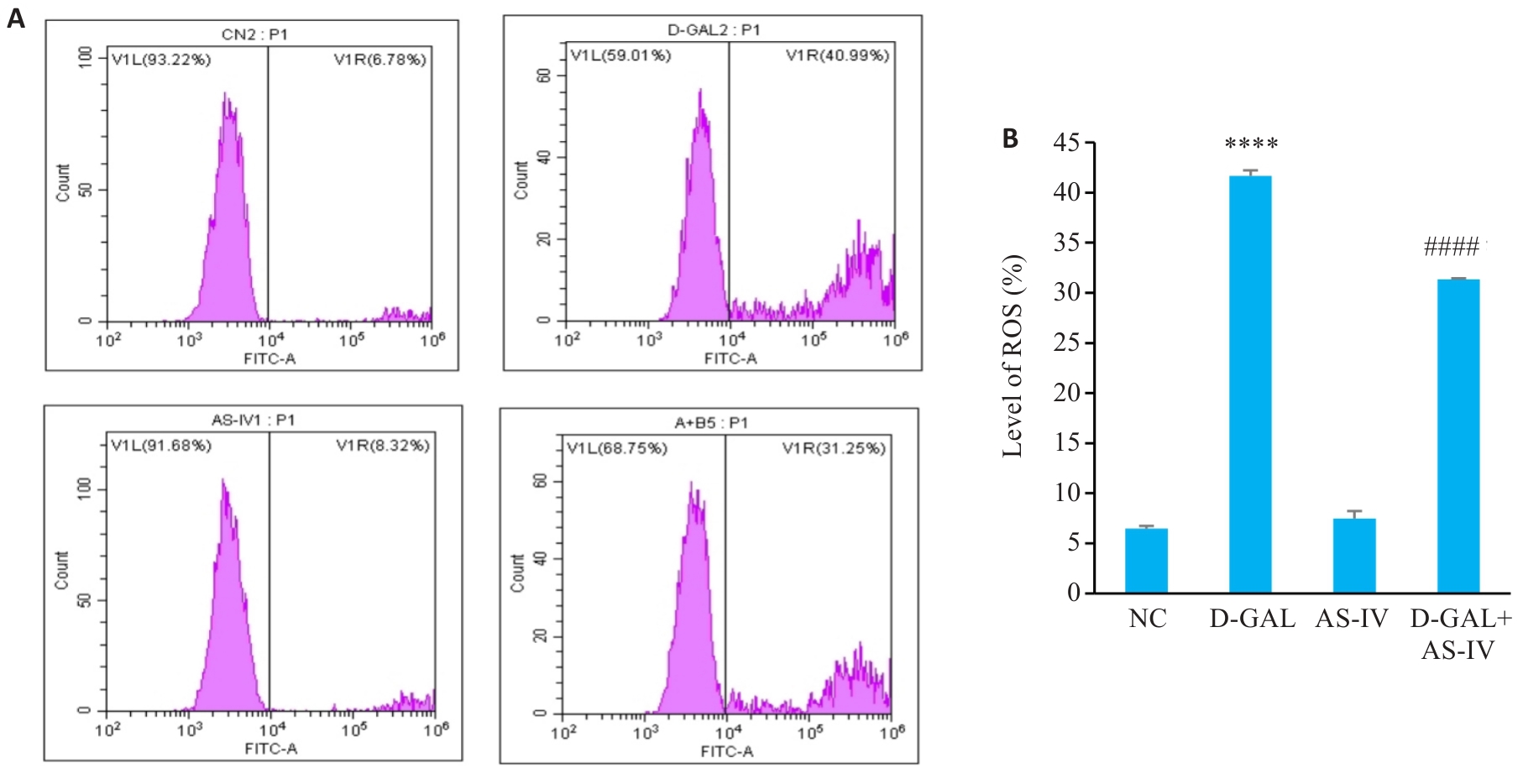
Fig.7 Effect of AS-IV on percentage of ROS-positive HUVECs induced by D-GAL. A: ROS levels in HUVEC cells with different treatments. B: Statistical graph of ROS levels. ****P<0.0001 vs NC group; ####P<0.0001 vs D-gal group.

Fig.8 Effect of AS-IV on autophagosome-lysosome fusion and autophagy flux in D-GAL-induced HUVECs. A: Autophagy flux assay of HUVECs with different treatments (Scale bar=50 μm). B: Statistical graph of puncta counts. ****P<0.0001 vs control group; ####P<0.0001 vs D-GAL group.

Fig.9 Effect of AS-IV on expression of PINK1/Parkin pathway and autophagy-related proteins in D-GAL-induced HUVECs. A: Protein bands of P62, LC3II/I, Beclin, PINK1, and Parkin in the 4 groups. B: Relative mRNA expressions of P62, Beclin, PINK, and Parkin. C: Statistical graph of grayscale values of the protein bands of P62, LC3II/I, Beclin, PINK1, and Parkin. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001 vs NC group; #P<0.05, ###P<0.001, ####P<0.0001 vs D-gal group.

Fig.10 Effect of MTK458 on autophagosome-lysosome fusion and autophagy flux in D-GAL-induced HUVECs. A: Autophagy flux assay of HUVECs with different treatments (Scale bar=50 μm). B: Statistical graph of puncta counts. ****P<0.0001 vs NC group; ####P<0.0001 vs D-gal group; △△△△P<0.0001 vs D-gal+AS-IV group.
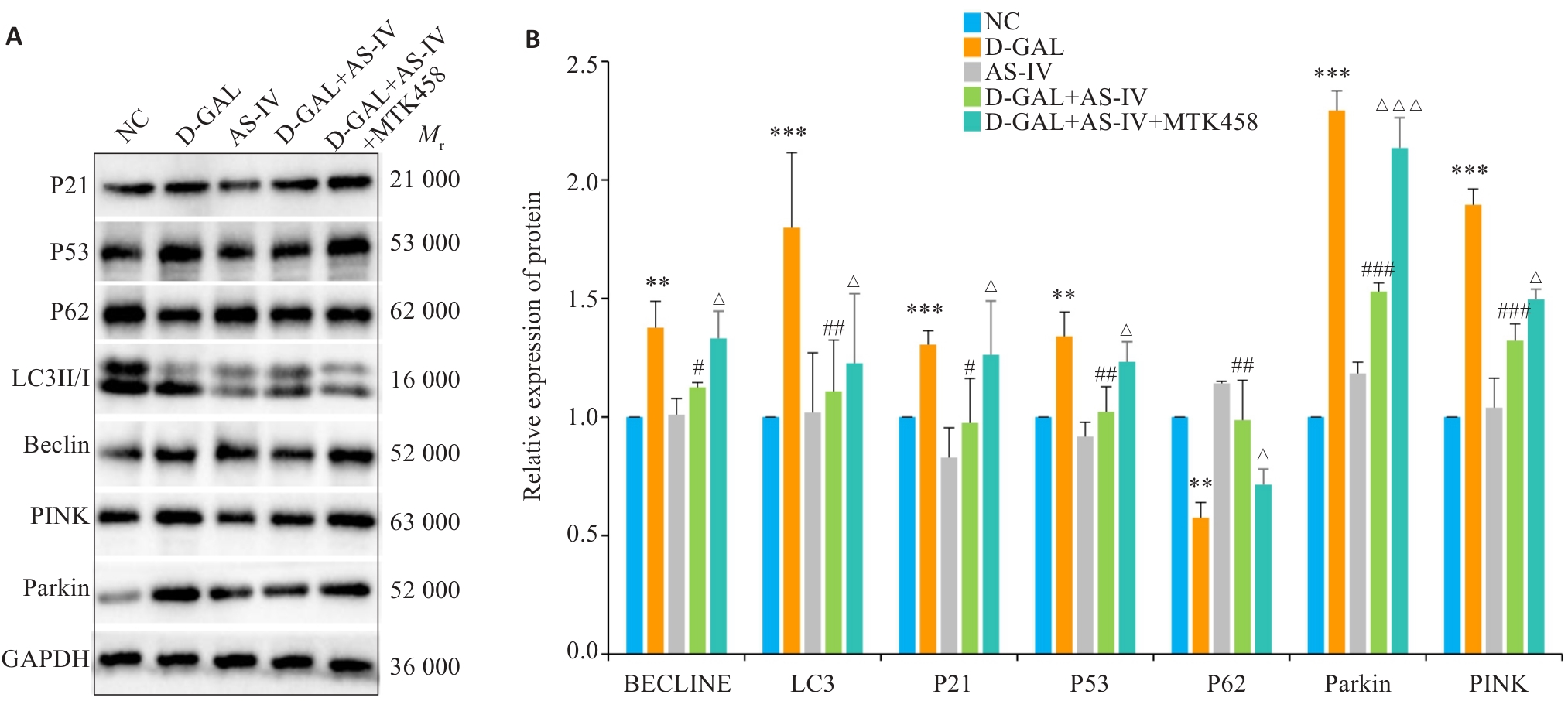
Fig.11 Effect of MTK458 on the PINK1/Parkin pathway and expressions of proteins related to cellular senescence and autophagy in D-GAL-induced HUVECs. A: Protein bands in the 5 groups of cells. B: Statistical graph of grayscale values of the protein bands. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs NC group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001 vs D-gal group; △P<0.05, △△△P<0.001 vs D-gal+AS-IV group.
| [1] | Campisi J, Andersen JK, Kapahi P, et al. Cellular senescence: a link between cancer and age-related degenerative disease[J]? Semin Cancer Biol, 2011, 21(6): 354-9. |
| [2] | Minamino T, Miyauchi H, Yoshida T, et al. Endothelial cell senescence in human atherosclerosis: role of telomere in endothelial dysfunction[J]. Circulation, 2002, 105(13): 1541-4. doi:10.1161/01.cir.0000013836.85741.17 |
| [3] | Bu LL, Yuan HH, Xie LL, et al. New dawn for atherosclerosis: vascular endothelial cell senescence and death[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(20): 15160. doi:10.3390/ijms242015160 |
| [4] | Bloom SI, Islam MT, Lesniewski LA, et al. Mechanisms and consequences of endothelial cell senescence[J]. Nat Rev Cardiol, 2023, 20(1): 38-51. doi:10.1038/s41569-022-00739-0 |
| [5] | Li AQ, Gao M, Liu BL, et al. Mitochondrial autophagy: molecular mechanisms and implications for cardiovascular disease[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2022, 13(5): 444. doi:10.1038/s41419-022-04906-6 |
| [6] | Narendra DP, Youle RJ. The role of PINK1-Parkin in mitochondrial quality control[J]. Nat Cell Biol, 2024, 26(10): 1639-51. doi:10.1038/s41556-024-01513-9 |
| [7] | 齐苗苗. 黄芪甲苷通过PINK1/Parkin介导线粒体自噬改善心肌细胞氧化应激损伤的研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2021. |
| [8] | Yi SL, Zheng B, Zhu Y, et al. Melatonin ameliorates excessive PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy by enhancing SIRT1 expression in granulosa cells of PCOS[J]. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, 2020, 319(1): E91-E101. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00006.2020 |
| [9] | Sun KY, Yang PY, Zhao R, et al. Matrine attenuates D-galactose-induced aging-related behavior in mice via inhibition of cellular senescence and oxidative stress[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2018, 2018: 7108604. doi:10.1155/2018/7108604 |
| [10] | Zeng M, He YL, Yang YL, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles relieve endothelial cell senescence via recovering CTRP9 upon repressing miR-674-5p in atherosclerosis[J]. Regen Ther, 2024, 27: 354-64. doi:10.1016/j.reth.2024.03.027 |
| [11] | Chu QQ, Li YJ, Wu JC, et al. Oxysterol sensing through GPR183 triggers endothelial senescence in hypertension[J]. Circ Res, 2024, 135(7): 708-21. doi:10.1161/circresaha.124.324722 |
| [12] | Liu MM, Wang DN, Qi CY, et al. Brain ischemia causes systemic Notch1 activity in endothelial cells to drive atherosclerosis[J]. Immunity, 2024, 57(9): 2157-72. e7. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2024.07.002 |
| [13] | Wang SS, Zhang X, Ke ZZ, et al. D-galactose-induced cardiac ageing: a review of model establishment and potential interventions[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2022, 26(21): 5335-59. doi:10.1111/jcmm.17580 |
| [14] | Kumari R, Jat P. Mechanisms of cellular senescence: cell cycle arrest and senescence associated secretory phenotype[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2021, 9: 645593. doi:10.3389/fcell.2021.645593 |
| [15] | Zhang WJ, Frei B. Astragaloside IV inhibits NF‑κB activation and inflammatory gene expression in LPS-treated mice[J]. Mediators Inflamm, 2015, 2015: 274314. doi:10.1155/2015/274314 |
| [16] | Xu CH, Tang FT, Lu ML, et al. Pretreatment with Astragaloside IV protects human umbilical vein endothelial cells from hydrogen peroxide induced oxidative stress and cell dysfunction via inhibiting ENOS uncoupling and NADPH oxidase-ROS-NF‑κB pathway[J]. Can J Physiol Pharmacol, 2016, 94(11): 1132-40. doi:10.1139/cjpp-2015-0572 |
| [17] | Sun YX, Ma YH, Sun FY, et al. Astragaloside IV attenuates lipopolysaccharide induced liver injury by modulating Nrf2-mediated oxidative stress and NLRP3-mediated inflammation[J]. Heliyon, 2023, 9(4): e15436. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e15436 |
| [18] | Xiao XL, Zheng YL, Mo Y, et al. Astragaloside IV alleviates oxidative stress-related damage via inhibiting NLRP3 infla-mmasome in a MAPK signaling dependent pathway in human lens epithelial cells[J]. Drug Dev Res, 2022, 83(4): 1016-23. doi:10.1002/ddr.21929 |
| [19] | Qu CY, Tan XY, Hu QC, et al. A systematic review of astragaloside IV effects on animal models of diabetes mellitus and its complications[J]. Heliyon, 2024, 10(5): e26863. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26863 |
| [20] | Cheng SY, Zhang XX, Feng Q, et al. Astragaloside IV exerts angiogenesis and cardioprotection after myocardial infarction via regulating PTEN/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway[J]. Life Sci, 2019, 227: 82-93. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2019.04.040 |
| [21] | Shen Q, Fang J, Guo HJ, et al. Astragaloside IV attenuates podocyte apoptosis through ameliorating mitochondrial dysfunction by up-regulated Nrf2-ARE/TFAM signaling in diabetic kidney disease[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2023, 203: 45-57. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2023.03.022 |
| [22] | Liang YT, Chen BQ, Liang D, et al. Pharmacological effects of astragaloside IV: a review[J]. Molecules, 2023, 28(16): 6118. doi:10.3390/molecules28166118 |
| [23] | Wang SL, Long HJ, Hou LJ, et al. The mitophagy pathway and its implications in human diseases[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2023, 8(1): 304. doi:10.1038/s41392-023-01503-7 |
| [24] | Ajoolabady A, Chiong M, Lavandero S, et al. Mitophagy in cardiovascular diseases: molecular mechanisms, pathogenesis, and treatment[J]. Trends Mol Med, 2022, 28(10): 836-49. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2022.06.007 |
| [25] | Xue A, Zhao DP, Zhao CY, et al. Study on the neuroprotective effect of Zhimu-Huangbo extract on mitochondrial dysfunction in HT22 cells induced by D-galactose by promoting mitochondrial autophagy[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2024, 318: 117012. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.117012 |
| [26] | Zhou XH, Tan BW, Gui WW, et al. IGF2 deficiency promotes liver aging through mitochondrial dysfunction and upregulated CEBPB signaling in D-galactose-induced aging mice[J]. Mol Med, 2023, 29(1): 161. doi:10.1186/s10020-023-00752-0 |
| [27] | Li H, Guan KF, Wang RC, et al. Synergistic effects of MFG-E8 and whey protein on mitigating d-galactose-induced sarcopenia through PI3K/AKT/PGC-1α and MAPK/ERK signaling pathways[J]. J Dairy Sci, 2024, 107(1): 9-23. doi:10.3168/jds.2023-23637 |
| [28] | Yang L, Shi J, Wang XW, et al. Curcumin alleviates D-galactose-induced cardiomyocyte senescence by promoting autophagy via the SIRT1/AMPK/mTOR pathway[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2022, 2022: 2990843. doi:10.1155/2022/2990843 |
| [29] | Li HJ, Xu JL, Zhang YN, et al. Astragaloside IV alleviates senescence of vascular smooth muscle cells through activating Parkin-mediated mitophagy[J]. Hum Cell, 2022, 35(6): 1684-96. doi:10.1007/s13577-022-00758-6 |
| [30] | Li J, Yang DM, Li ZP, et al. PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy in neurodegenerative diseases[J]. Ageing Res Rev, 2023, 84: 101817. doi:10.1016/j.arr.2022.101817 |
| [31] | Cao YH, Chen X, Pan FQ, et al. Xinmaikang-mediated mitophagy attenuates atherosclerosis via the PINK1/Parkin signaling pathway[J]. Phytomedicine, 2023, 119: 154955. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154955 |
| [32] | Zhao XP, Wang Z, Wang LJ, et al. The PINK1/Parkin signaling pathway-mediated mitophagy: a forgotten protagonist in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2024, 209: 107466. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2024.107466 |
| [33] | He HL, Huang WY, Xiong LD, et al. FUNDC1-mediated mitophagy regulates photodamage independently of the PINK1/Parkin-dependent pathway[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2024, 225: 630-40. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2024.10.272 |
| [34] | Chen CY, Bu XL, Deng LP, et al. Astragaloside IV as a promising therapeutic agent for liver diseases: current landscape and future perspectives[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2025, 16: 1574154. doi:10.3389/fphar.2025.1574154 |
| [35] | Liu T, Ai L, Jiang AB, et al. Astragaloside IV suppresses the proliferation and inflammatory response of human epidermal keratinocytes and ameliorates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin damage in mice[J]. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr), 2024, 52(5): 44-50. doi:10.15586/aei.v52i5.1140 |
| [36] | Xia DQ, Li WJ, Tang C, et al. Astragaloside IV, as a potential anticancer agent[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2023, 14: 1065505. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1065505 |
| [37] | Deng LL. Astragaloside IV as potential antioxidant against diabetic ketoacidosis in juvenile mice through activating JNK/Nrf2 signaling pathway[J]. Arch Med Res, 2020, 51(7): 654-63. doi:10.1016/j.arcmed.2020.06.013 |
| [1] | Yu ZHANG, Yinqi HU, Peipei LI, Xiao SHI, Wei XU, Jianpeng HU. Naoluo Xintong Decoction promotes proliferation of rat brain microvascular endothelial cells after oxygen-glucose deprivation by activating the HIF-1α/VEGF signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(9): 1980-1988. |
| [2] | Xiaoyu CHANG, Hanwen ZHANG, Hongting CAO, Ling HOU, Xin MENG, Hong TAO, Yan LUO, Guanghua LI. Heat stress affects expression levels of circadian clock gene Bmal1 and cyclins in rat thoracic aortic endothelial cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1353-1362. |
| [3] | Yanyan DONG, Kejing ZHANG, Jun CHU, Quangen CHU. Didang Decoction-medicated serum enhances autophagy in high glucose-induced rat glomerular endothelial cells via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 461-469. |
| [4] | Ming LIAO, Wenhua ZHONG, Ran ZHANG, Juan LIANG, Wentaorui XU, Wenjun WAN, Chao LI Shu WU. Protein C activator derived from snake venom protects human umbilical vein endothelial cells against hypoxia-reoxygenation injury by suppressing ROS via upregulating HIF-1α and BNIP3 [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 614-621. |
| [5] | Kelei GUO, Yingli LI, Chenguang XUAN, Zijun HOU, Songshan YE, Linyun LI, Liping CHEN, Li HAN, Hua BIAN. Yiqi Yangyin Huazhuo Tongluo Formula alleviates diabetic podocyte injury by regulating miR-21a-5p/FoxO1/PINK1-mediated mitochondrial autophagy [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 27-34. |
| [6] | Junping ZHAN, Shuo HUANG, Qingliang MENG, Wei FAN, Huimin GU, Jiakang CUI, Huilian WANG. Buyang Huanwu Decoction reduces mitochondrial autophagy in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts in hypoxic culture by inhibiting the BNIP3-PI3K/Akt pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 35-42. |
| [7] | Yao CHENG, Yuanying WANG, Feiyang YAO, Pan HU, Mingxian CHEN, Ning WU. Baicalin suppresses type 2 dengue virus-induced autophagy of human umbilical vein endothelial cells by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1272-1283. |
| [8] | Chengcheng JIANG, Yangyang LI, Kexin DUAN, Tingting ZHAN, Zilong CHEN, Yongxue WANG, Rui ZHAO, Caiyun MA, Yu GUO, Changqing LIU. Parkin deletion affects PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitochondrial autophagy to exacerbate neuroinflammation and accelerate progression of Parkinson's disease in mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(12): 2359-2366. |
| [9] | Xiaofei SU, Lin LI, Jingrong DAI, Bao XIAO, Ziqi JIN, Bin LIU. GSK484, a PAD4 inhibitor, improves endothelial dysfunction in mice with sepsis-induced lung injury by inhibiting H3Cit expression [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(12): 2396-2403. |
| [10] | LUO Rui, TIAN Longhai, YANG Yongyao. Galangin inhibits oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced angiogenic activity in human aortic endothelial cells by downregulating lncRNA H19 [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(1): 52-59. |
| [11] | YU Jiachi, LI Ruibing, XIA Tian, WANG Jianan, JIN Jiacheng, YUAN Manqiu, LI Mianyang. PDCD4 knockdown ameliorates lipopolysaccharide- induced endothelial cell damage by improving mitochondrial dynamics [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(1): 25-35. |
| [12] | LI Peipei, HU Yinqi, LIU Jia, WANG Lina, WU Yuanjie, HU Jianpeng. Naoluo Xintong Decoction activates caspase-1/Gasdermin D pathway to promote angiogenesis of rat brain microvascular endothelial cells after oxygen glucose deprivation/reperfusion injury [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(7): 1093-1101. |
| [13] | JIANG Yong, GE Wenting, ZHAO Ying, WU Yuge, HUO Yiming, PAN Lanting, CAO Shuang. LINC00926 promotes pyroptosis of hypoxia-induced human umbilical vein vascular endothelial cells by recruiting ELAVL1 [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(5): 807-814. |
| [14] | ZENG Jiao, LI Xinzhu, YIN Linying, CHEN Ting, HOU Jin. Porphyromonas gingivalis infection causes umbilical vein endothelial barrier dysfunction in vitro by down-regulating ZO-1, occludin and VE-cadherin expression [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(2): 287-293. |
| [15] | HU Pan, CHENG Yao, WANG Yuanying, GOU Xiaoqin, LIU Hua, ZUO Li, WU Ning. Phosphoproteomic analysis of human umbilical venous endothelial cells with DENV-2 infection [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(1): 29-38. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||