Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (6): 1336-1342.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.06.23
Previous Articles Next Articles
Zhenxiang DONG1,2( ), Yihao GUO1,2, Qiang LIU1,2, Yizhe ZHANG1,2, Qianyi QIU3, Xiaodong ZHANG3, Yanqiu FENG1,2(
), Yihao GUO1,2, Qiang LIU1,2, Yizhe ZHANG1,2, Qianyi QIU3, Xiaodong ZHANG3, Yanqiu FENG1,2( )
)
Received:2025-03-13
Online:2025-06-20
Published:2025-06-27
Contact:
Yanqiu FENG
E-mail:3464737526@qq.com;foree@163.com
Supported by:Zhenxiang DONG, Yihao GUO, Qiang LIU, Yizhe ZHANG, Qianyi QIU, Xiaodong ZHANG, Yanqiu FENG. A single repetition time quantitative magnetic susceptibility imaging method for the lumbar spine using bipolar readout gradient[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1336-1342.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.06.23
| MR scan sequence | Dual TR gradient echo sequence | Single TR gradient echo sequence |
|---|---|---|
| Field of view | 256×184×152 mm3 | 256×184×152 mm3 |
| Voxel size | 2 mm isotropic | 2 mm isotropic |
| Flip angle | 15° | 15° |
| Echo time | TE1=1.54 ms, TE2=2.3 ms, | TE1=1.2 ms, NTE =6 |
| Bandwidth | 996 hz/pixel | 996 hz/pixel |
| TR | 25 ms | 25 ms |
| Scan time | 9 min10 s | 4 min35 s |
| SENSE | SENSE=1 | SENSE=1 |
Tab.1 MR scan parameters of dual TR and single TR gradient echo sequences
| MR scan sequence | Dual TR gradient echo sequence | Single TR gradient echo sequence |
|---|---|---|
| Field of view | 256×184×152 mm3 | 256×184×152 mm3 |
| Voxel size | 2 mm isotropic | 2 mm isotropic |
| Flip angle | 15° | 15° |
| Echo time | TE1=1.54 ms, TE2=2.3 ms, | TE1=1.2 ms, NTE =6 |
| Bandwidth | 996 hz/pixel | 996 hz/pixel |
| TR | 25 ms | 25 ms |
| Scan time | 9 min10 s | 4 min35 s |
| SENSE | SENSE=1 | SENSE=1 |
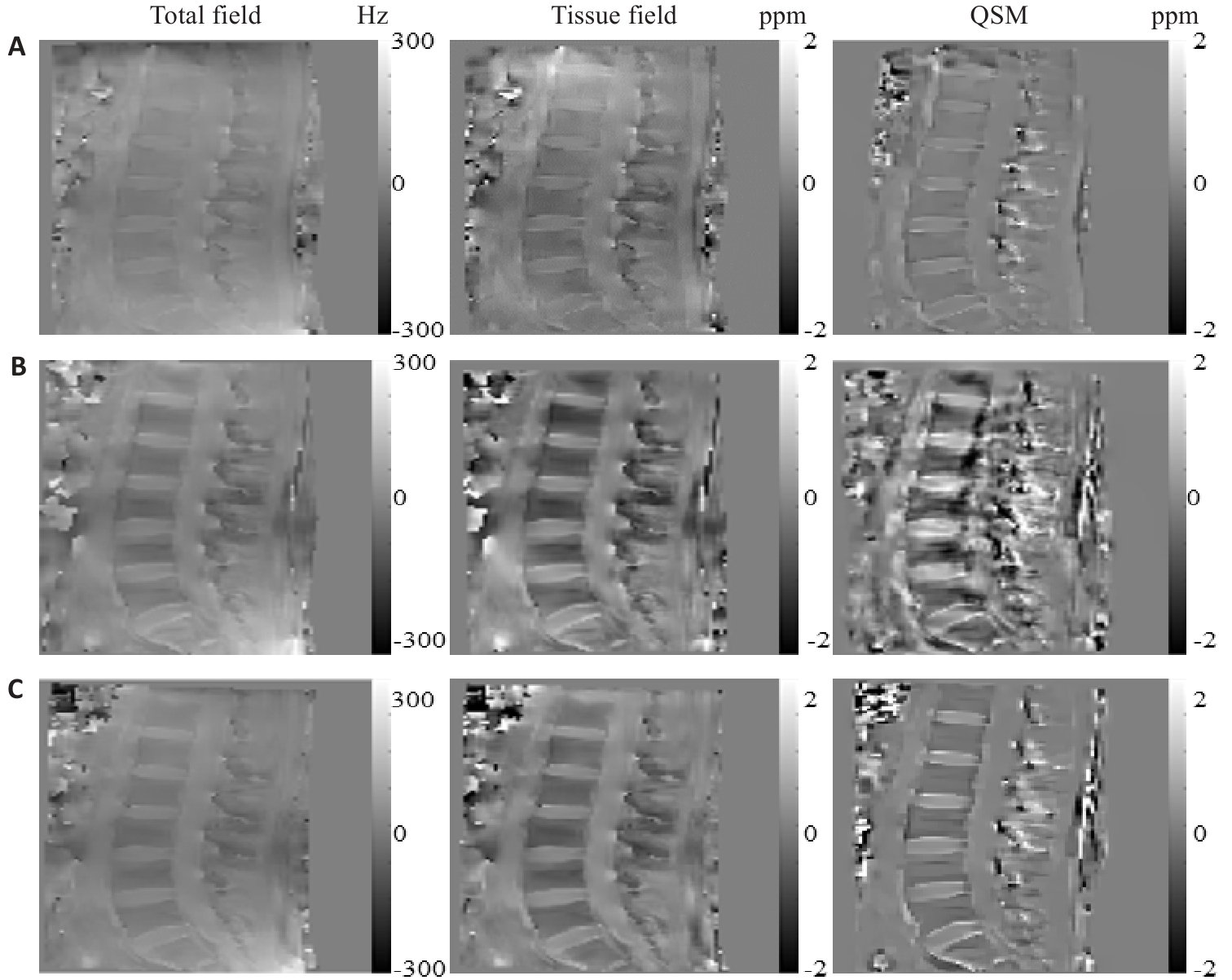
Fig.4 Total field map, tissue field map, and QSM results of the lumbar spine of normal volunteers.A: Dual TR method fitting results. B: Single TR method fitting results before calibration. C: Single TR method fitting results after calibration.
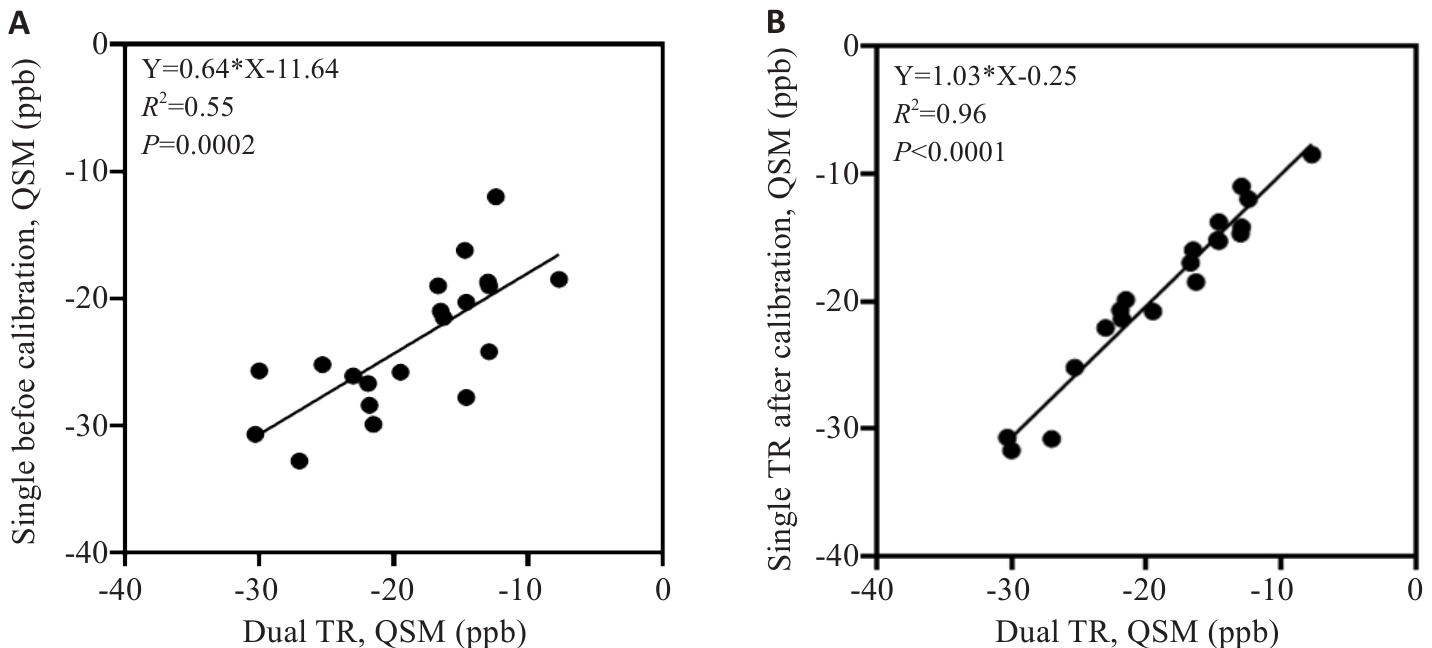
Fig.5 Comparison of quantitative results between dual TR lumbar spine QSM and single TR. A: Comparison of dual TR and single TR before calibration. B: Comparison of dual TR and single TR after calibration.
| 1 | Wang Y, Liu T. Quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM): decoding MRI data for a tissue magnetic biomarker[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2015, 73(1): 82-101. doi:10.1002/mrm.25358 |
| 2 | Wisnieff C, Ramanan S, Olesik J, et al. Quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) of white matter multiple sclerosis lesions: Interpreting positive susceptibility and the presence of iron[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2015, 74(2): 564-70. doi:10.1002/mrm.25420 |
| 3 | Ravanfar P, Loi SM, Syeda WT, et al. Systematic review: quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) of brain iron profile in neurodegenerative diseases[J]. Front Neurosci, 2021, 15: 618435. doi:10.3389/fnins.2021.618435 |
| 4 | Yang J, Lv M, Han L, et al. Evaluation of brain iron deposition in different cerebral arteries of acute ischaemic stroke patients using quantitative susceptibility mapping[J]. Clin Radiol, 2024, 79(4): e592-8. doi:10.1016/j.crad.2024.01.007 |
| 5 | Guo W, Zhang D, Sun J, et al. Quantitative susceptibility mapping of subcortical iron deposition in Parkinson disease and multiple system atrophy: clinical correlations and diagnostic implications[J]. Quant Imaging Med Surg, 2024, 14(7): 4464-74. doi:10.21037/qims-24-168 |
| 6 | Carpenter KLH, Li W, Wei HJ, et al. Magnetic susceptibility of brain iron is associated with childhood spatial IQ[J]. NeuroImage, 2016, 132: 167-74. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.02.028 |
| 7 | Li X, Allen RP, Earley CJ, et al. Brain iron deficiency in idiopathic restless legs syndrome measured by quantitative magnetic susceptibility at 7 tesla[J]. Sleep Med, 2016, 22: 75-82. doi:10.1016/j.sleep.2016.05.001 |
| 8 | Kataike VM, Desmond PM, Steward C, et al. Iron changes within infarct tissue in ischemic stroke patients after successful reperfusion quantified using QSM[J]. Neuroradiology, 2024, 66(12): 2233-42. doi:10.1007/s00234-024-03444-6 |
| 9 | Sharma SD, Hernando D, Horng DE, et al. Quantitative susceptibility mapping in the abdomen as an imaging biomarker of hepatic iron overload[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2015, 74(3): 673-83. doi:10.1002/mrm.25448 |
| 10 | Lin HM, Wei HJ, He NY, et al. Quantitative susceptibility mapping in combination with water-fat separation for simultaneous liver iron and fat fraction quantification[J]. Eur Radiol, 2018, 28(8): 3494-504. doi:10.1007/s00330-017-5263-4 |
| 11 | Jafari R, Sheth S, Spincemaille P, et al. Rapid automated liver quantitative susceptibility mapping[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2019, 50(3): 725-32. doi:10.1002/jmri.26632 |
| 12 | Buelo CJ, Velikina J, Mao L, et al. Multicenter, multivendor validation of liver quantitative susceptibility mapping in patients with iron overload at 1.5 T and 3 T[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2025, 93(1): 330-40. doi:10.1002/mrm.30251 |
| 13 | Jung M, Bresson X, Chan TF, et al. Nonlocal Mumford-Shah regularizers for color image restoration[J]. IEEE Trans Image Process, 2011, 20(6): 1583-98. doi:10.1109/tip.2010.2092433 |
| 14 | Lebenatus A, Kuster J, Straub S, et al. In-vitro detection of intramammary-like macrocalcifications using susceptibility-weighted MR imaging techniques at 1.5T[J]. Magn Reson Med Sci, 2024: mp. 2024-75. doi:10.2463/mrms.mp.2024-0075 |
| 15 | Boehm C, Sollmann N, Meineke J, et al. Preconditioned water-fat total field inversion: Application to spine quantitative susceptibility mapping[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2022, 87(1): 417-30. doi:10.1002/mrm.28903 |
| 16 | Diefenbach MN, Meineke J, Ruschke S, et al. On the sensitivity of quantitative susceptibility mapping for measuring trabecular bone density[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2019, 81(3): 1739-54. doi:10.1002/mrm.27531 |
| 17 | Guo Y, Chen Y, Zhang X, et al. Magnetic susceptibility and fat content in the lumbar spine of postmenopausal women with varying bone mineral density[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2019, 49(4): 1020-8. doi:10.1002/jmri.26279 |
| 18 | Guo Y, Liu Z, Wen Y, et al. Quantitative susceptibility mapping of the spine using in-phase echoes to initialize inhomogeneous field and R2* for the nonconvex optimization problem of fat-water separation[J]. NMR Biomed, 2019, 32(11): e4156. doi:10.1002/nbm.4156 |
| 19 | Jerban S, Ma Y, Jang H, et al. MRI-based bone biomarkers; proceedings of the Seminars in musculoskeletal. Radiology, F, 2024 [C]. doi:10.1055/s-0040-1710355 |
| 20 | Li N, Li XM, Xu L, et al. Comparison of QCT and DXA: osteoporosis detection rates in postmenopausal women[J]. Int J Endocrinol, 2013, 2013: 895474. doi:10.1155/2013/895474 |
| 21 | Wáng YXJ, Yu W, Leung JCS, et al. More evidence to support a lower quantitative computed tomography (QCT) lumbar spine bone mineral density (BMD) cutpoint value for classifying osteoporosis among older East Asian women than for Caucasians[J]. Quant Imaging Med Surg, 2024, 14(5): 3239-47. doi:10.21037/qims-24-429 |
| 22 | Liu C, Li W, Tong KA, et al. Susceptibility-weighted imaging and quantitative susceptibility mapping in the brain[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2015, 42(1): 23-41. doi:10.1002/jmri.24768 |
| 23 | Hopkins JA, Wehrli FW. Magnetic susceptibility measurement of insoluble solids by NMR: magnetic susceptibility of bone[J]. Magn Reson Med, 1997, 37(4): 494-500. doi:10.1002/mrm.1910370404 |
| 24 | Berikol G, Ekşi MŞ, Aydın L, et al. Subcutaneous fat index: a reliable tool for lumbar spine studies[J]. Eur Radiol, 2022, 32(9): 6504-13. doi:10.1007/s00330-022-08775-7 |
| 25 | Boehm C, Schlaeger S, Meineke J, et al. On the water–fat in-phase assumption for quantitative susceptibility mapping[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2023, 89(3): 1068-82. doi:10.1002/mrm.29516 |
| 26 | Ruschke S, Eggers H, Kooijman H, et al. Correction of phase errors in quantitative water-fat imaging using a monopolar time-interleaved multi-echo gradient echo sequence[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2017, 78(3): 984-96. doi:10.1002/mrm.26485 |
| 27 | Walsh DO, Gmitro AF, Marcellin MW. Adaptive reconstruction of phased array MR imagery[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2000, 43(5): 682-90. doi:10.1002/(sici)1522-2594(200005)43:5<682::aid-mrm10>3.0.co;2-g |
| 28 | Yu H, Shimakawa A, McKenzie CA, et al. Multiecho water-fat separation and simultaneous R2* estimation with multifrequency fat spectrum modeling[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2008, 60(5): 1122-34. doi:10.1002/mrm.21737 |
| 29 | Zhou D, Liu T, Spincemaille P, et al. Background field removal by solving the Laplacian boundary value problem[J]. NMR Biomed, 2014, 27(3): 312-9. doi:10.1002/nbm.3064 |
| 30 | Liu J, Liu T, de Rochefort L, et al. Morphology enabled dipole inversion for quantitative susceptibility mapping using structural consistency between the magnitude image and the susceptibility map[J]. NeuroImage, 2012, 59(3): 2560-8. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.08.082 |
| 31 | Feng W, Neelavalli J, Haacke EM. Catalytic multiecho phase unwrapping scheme (CAMPUS) in multiecho gradient echo imaging: removing phase wraps on a voxel-by-voxel basis[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2013, 70(1): 117-26. doi:10.1002/mrm.24457 |
| 32 | Peterson P, Månsson S. Fat quantification using multiecho sequences with bipolar gradients: investigation of accuracy and noise performance[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2014, 71(1): 219-29. doi:10.1002/mrm.24657 |
| 33 | Yu H, Shimakawa A, McKenzie CA, et al. Phase and amplitude correction for multi-echo water-fat separation with bipolar acquisitions[J]. J Magn Reson Imaging, 2010, 31(5): 1264-71. doi:10.1002/jmri.22111 |
| 34 | QSM Consensus Organization Committee, Bilgic B, Costagli M, et al. Recommended implementation of quantitative susceptibility mapping for clinical research in the brain: a consensus of the ISMRM electro-magnetic tissue properties study group[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2024, 91(5): 1834-62. doi:10.1002/mrm.30006 |
| 35 | Jerban S, Ma YJ, Chang EY, et al. A UTE-based biomarker panel in osteoporosis [M]. MRI of Short-and Ultrashort-T2 Tissues: Making the Invisible Visible. Springer. 2024: 427-39. doi:10.1007/978-3-031-35197-6_34 |
| 36 | Shin SH, Chae HD, Suprana A, et al. UTE MRI technical developments and applications in osteoporosis: a review [J]. Frontiers in Endocrinology, 2025, 16: 1510010. doi:10.3389/fendo.2025.1510010 |
| 37 | Streichenberger B, Santin M, Roche S, et al. Quantitative susceptibility mapping of the cervical spinal cord for MS monitoring; proceedings of the 2025-20th MRI Workshop: MS lesions imaging: update on chronic active lesion and the central vein sign, F, 2025 [C]. |
| [1] | Yuancheng CHEN, Wen WU, Ling XU, Haiou DENG, Ruixue WANG, Qianwen HUANG, Liping XUAN, Xueying CHEN, Ximei ZHI. Changes in circulating levels of calcium and bone metabolism biochemical markers in patients receiving denosumab treatment [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 760-764. |
| [2] | Ying ZHOU, Danyang ZHANG, Lifan WU, Guishan WANG, Jiedan MU, Chengwen CUI, Xiuxiu SHI, Jige DONG, Yu WANG, Wangli XU, Xiao LI. Epidemiological survey of osteoporosis in Beijing over the past decade: a single-center analysis of dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry scans from 30 599 individuals [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 443-452. |
| [3] | Weiyang FANG, Hui XIAO, Shuang WANG, Xiaoming LIN, Chaomin CHEN. A deep learning model based on magnetic resonance imaging and clinical feature fusion for predicting preoperative cytokeratin 19 status in hepatocellular carcinoma [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1738-1751. |
| [4] | LUO Caizhu, CHEN Jinxiang, ZHANG Qun, YU Xuezhao, ZHANG Shuqin. A polylactic acid/hydroxyapatite/scholzite composite scaffold for promoting healing of osteoporotic bone defects in rats [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(2): 370-380. |
| [5] | Xiaoyin HUANG, Fenglian CHEN, Yu ZHANG, Shujun LIANG. A predictive model for survival outcomes of glioma patients based on multi-parametric, multi-regional MRI radiomics features and clinical features [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(10): 2004-2014. |
| [6] | HE Huishan, GUO Erjia, MENG Wenyi, WANG Yu, WANG Wen, HE Wenle, WU Yuankui, YANG Wei. Predicting cerebral glioma enhancement pattern using a machine learning-based magnetic resonance imaging radiomics model [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(1): 194-200. |
| [7] | CHEN Zifeng, LI Shengfa, ZHANG Youming, YANG Wanwen, WANG Ting. Lipocalin 2 induces self- limited inhibition of osteoblast differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(8): 1339-1344. |
| [8] | LIU Yuxuan, CHU Zhiqin, ZHANG Yu. Physical model-based cascaded generative adversarial networks for accelerating quantitative multi-parametric magnetic resonance imaging [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(8): 1402-1409. |
| [9] | WU Xiuhua, FAN Yingjing, YE Yongnong, LI Ping, ZHU Qing'an, CHEN Zesen, LI Bo, WANG Wen, ZHENG Lei. A transcriptomic study of osteoporosis induced by ketogenic diet in mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(8): 1440-1446. |
| [10] | LU Mingjun, QU Yaoming, MA Andong, ZHU Jianbin, ZOU Xia, LIN Gengyun, LI Yuxin, LIU Xinzi, WEN Zhibo. Prediction of 1p/19q codeletion status in diffuse lower-grade glioma using multimodal MRI radiomics [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(6): 1023-1028. |
| [11] | GONG Gao, CAO Shi, XIAO Hui, FANG Weiyang, QUE Yuqing, LIU Ziwei, CHEN Chaomin. Prediction of microvascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma with magnetic resonance imaging using models combining deep attention mechanism with clinical features [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(5): 839-851. |
| [12] | HAO Yuwei, GAO Sheng, ZHANG Xiaoyue, CUI Mengqiu, DING Xiaohui, WANG He, YANG Dawei, YE Huiyi, WANG Haiyi. Comparison of diagnostic performance of Clear Cell Likelihood Score v1.0 and v2.0 for clear renal cell carcinoma [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(5): 800-806. |
| [13] | YU Jingwen, YANG Meijie, JIANG Li, XIAO Zhibo, LI Shuang, CHEN Jinyun. Preoperative MR T2WI signal characteristics of adenomyosis are closely related with the outcome of high-intensity focused ultrasound ablation: a propensity score-matched cohort study [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(4): 597-603. |
| [14] | RUAN Hongliang, SHE Dongmei, SUN Shaoqiu. Liuwei Dihuang Pills alleviates postmenopausal osteoporosis and fatigue in rats by inhibiting the epigenetic regulatory molecule BRD4 pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(12): 1998-2005. |
| [15] | WU Xueyang, ZHANG Yu, ZHANG Hua, ZHONG Tao. Whole-brain parcellation for macaque brain magnetic resonance images based on attention mechanism and multi-modality feature fusion [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(12): 2118-2125. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||