Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (3): 650-660.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.03.23
Previous Articles Next Articles
Yong HONG( ), Xin ZHANG, Mingjun LIN, Qiucen WU, Chaomin CHEN(
), Xin ZHANG, Mingjun LIN, Qiucen WU, Chaomin CHEN( )
)
Received:2024-12-04
Online:2025-03-20
Published:2025-03-28
Contact:
Chaomin CHEN
E-mail:3547475276@qq.com;571611621@qq.com
Yong HONG, Xin ZHANG, Mingjun LIN, Qiucen WU, Chaomin CHEN. A lightweight classification network for single-lead atrial fibrillation based on depthwise separable convolution and attention mechanism[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 650-660.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.03.23
| Method | Input | Dataset | Task | Acc | Sen | Spe | Pre | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MGNN[ | 32 RR | AFDB | AF vs Non-AF | 97.07 | 94.95 | 97.77 | - | 93.91 |
| MT-DCNN[ | 30 s ECG | LTAFDB | AF vs Non-AF | 97.1 | 96.5 | 97.9 | - | 97.5 |
| LDSNet[ | 15 s ECG | AFDB | AF vs Non-AF | 94.57 | 99.15 | 93.03 | - | - |
| IMC-ResNet[ | 15 s ECG | AFDB | AF vs NSR | 96.18 | 99.97 | 94.36 | 89.51 | 94.45 |
| ResNet18 | 30 s ECG | LTAFDB | AF vs NSR | 94.82 | 94.27 | 95.29 | 95.94 | 94.60 |
| MobileNetV1 | 30 s ECG | LTAFDB | AF vs NSR | 95.64 | 97.86 | 97.80 | 94.17 | 95.80 |
| EfficientNetB0 | 30 s ECG | LTAFDB | AF vs NSR | 95.64 | 97.94 | 97.95 | 94.40 | 95.92 |
| DSC-AttNet,2024 | 30 s ECG | LTAFDB | AF vs NSR | 97.33 | 97.50 | 97.63 | 97.30 | 97.31 |
Tab.1 Comparison of classification performance among different models (%)
| Method | Input | Dataset | Task | Acc | Sen | Spe | Pre | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MGNN[ | 32 RR | AFDB | AF vs Non-AF | 97.07 | 94.95 | 97.77 | - | 93.91 |
| MT-DCNN[ | 30 s ECG | LTAFDB | AF vs Non-AF | 97.1 | 96.5 | 97.9 | - | 97.5 |
| LDSNet[ | 15 s ECG | AFDB | AF vs Non-AF | 94.57 | 99.15 | 93.03 | - | - |
| IMC-ResNet[ | 15 s ECG | AFDB | AF vs NSR | 96.18 | 99.97 | 94.36 | 89.51 | 94.45 |
| ResNet18 | 30 s ECG | LTAFDB | AF vs NSR | 94.82 | 94.27 | 95.29 | 95.94 | 94.60 |
| MobileNetV1 | 30 s ECG | LTAFDB | AF vs NSR | 95.64 | 97.86 | 97.80 | 94.17 | 95.80 |
| EfficientNetB0 | 30 s ECG | LTAFDB | AF vs NSR | 95.64 | 97.94 | 97.95 | 94.40 | 95.92 |
| DSC-AttNet,2024 | 30 s ECG | LTAFDB | AF vs NSR | 97.33 | 97.50 | 97.63 | 97.30 | 97.31 |
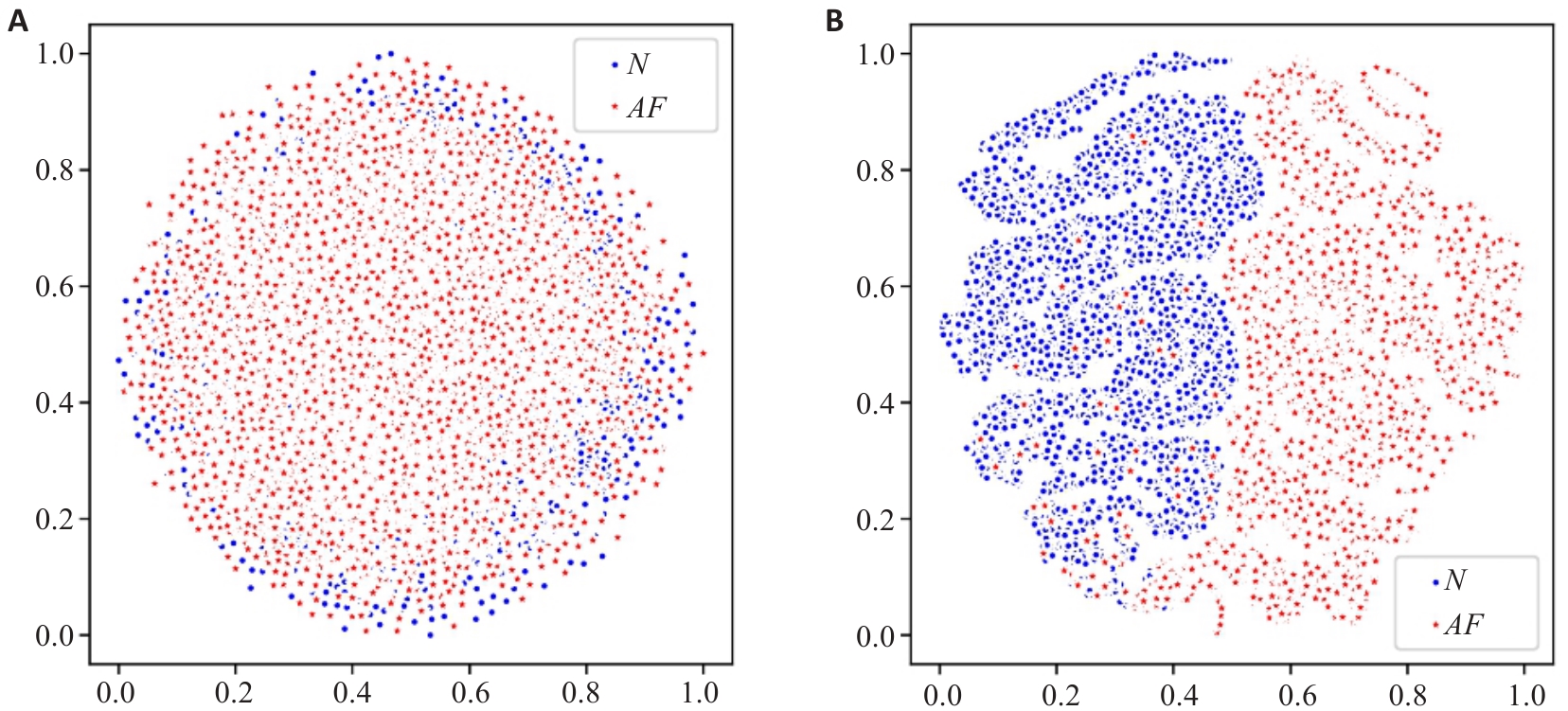
Fig.9 Evolution process of NSR-class features and AF-class features. A: Visualization of the output features from the first standard convolution layer. B: Visualization of the output features from the global attention module.
| Method | Acc | Sen | Spe | Pre | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ResNet18 | 87.24 | 83.97 | 91.90 | 78.62 | 81.21 |
| MobileNetV1 | 91.27 | 96.74 | 98.24 | 80.56 | 87.91 |
| EfficientNetB0 | 90.15 | 83.88 | 92.21 | 85.81 | 84.84 |
| DSC-AttNet | 92.78 | 89.98 | 95.05 | 88.26 | 89.11 |
Tab.2 Comparison of classification performance among different models on external test set AFDB (%)
| Method | Acc | Sen | Spe | Pre | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ResNet18 | 87.24 | 83.97 | 91.90 | 78.62 | 81.21 |
| MobileNetV1 | 91.27 | 96.74 | 98.24 | 80.56 | 87.91 |
| EfficientNetB0 | 90.15 | 83.88 | 92.21 | 85.81 | 84.84 |
| DSC-AttNet | 92.78 | 89.98 | 95.05 | 88.26 | 89.11 |
| Method | Acc | Sen | Spe | Pre | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ResNet18 | 99.80 | - | 1.0 | - | - |
| MobileNetV1 | 99.94 | - | 1.0 | - | - |
| EfficientNetB0 | 99.77 | - | 1.0 | - | - |
| DSC-AttNet | 99.97 | - | 1.0 | - | - |
Tab.3 Comparison of classification performance among different models on external test set NSRDB (%)
| Method | Acc | Sen | Spe | Pre | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ResNet18 | 99.80 | - | 1.0 | - | - |
| MobileNetV1 | 99.94 | - | 1.0 | - | - |
| EfficientNetB0 | 99.77 | - | 1.0 | - | - |
| DSC-AttNet | 99.97 | - | 1.0 | - | - |
| Method | Input size | MACs (G) | Params (M) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MGNN[ | 1*32 | 0.02 | 1.49 |
| LDSNet[ | 1*3000 | 0.33 | 0.2 |
| ResNet18 | 1*3840 | 183.65 | 4.20 |
| MobileNetV1 | 1*3840 | 39.46 | 3.19 |
| EfficientNetB0 | 1*3840 | 31.68 | 7.00 |
| DSC-AttNet, 2024 | 1*3840 | 27.19 | 1.01 |
Tab.4 Comparison of complexity among different models
| Method | Input size | MACs (G) | Params (M) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MGNN[ | 1*32 | 0.02 | 1.49 |
| LDSNet[ | 1*3000 | 0.33 | 0.2 |
| ResNet18 | 1*3840 | 183.65 | 4.20 |
| MobileNetV1 | 1*3840 | 39.46 | 3.19 |
| EfficientNetB0 | 1*3840 | 31.68 | 7.00 |
| DSC-AttNet, 2024 | 1*3840 | 27.19 | 1.01 |
| Method | Acc | Sen | Spe | Pre | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 97.13 | 97.70 | 97.80 | 96.89 | 97.15 |
| +CBAM | 97.21 | 96.30 | 96.77 | 98.07 | 97.04 |
| +Global Attention | 95.90 | 96.19 | 96.64 | 96.08 | 95.87 |
| DSC-AttNet | 97.33 | 97.50 | 97.63 | 97.30 | 97.31 |
Tab.5 Results of ablation study (%)
| Method | Acc | Sen | Spe | Pre | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 97.13 | 97.70 | 97.80 | 96.89 | 97.15 |
| +CBAM | 97.21 | 96.30 | 96.77 | 98.07 | 97.04 |
| +Global Attention | 95.90 | 96.19 | 96.64 | 96.08 | 95.87 |
| DSC-AttNet | 97.33 | 97.50 | 97.63 | 97.30 | 97.31 |
| Method | Data input | Acc | Sen | Spe | Pre | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ResNet18 | 10s ECG | 61.97 | 55.29 | 90.41 | 60.30 | 54.23 |
| MobileNetV1 | 10s ECG | 75.65 | 65.57 | 93.69 | 66.80 | 64.18 |
| EfficientNetB0 | 10s ECG | 81.38 | 70.25 | 95.19 | 69.09 | 68.62 |
| DSC-AttNet | 10s ECG | 71.20 | 60.98 | 92.44 | 77.13 | 59.19 |
Tab.6 Comparison of the performance of different models for 5 classification tasks on LTAFDB (%)
| Method | Data input | Acc | Sen | Spe | Pre | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ResNet18 | 10s ECG | 61.97 | 55.29 | 90.41 | 60.30 | 54.23 |
| MobileNetV1 | 10s ECG | 75.65 | 65.57 | 93.69 | 66.80 | 64.18 |
| EfficientNetB0 | 10s ECG | 81.38 | 70.25 | 95.19 | 69.09 | 68.62 |
| DSC-AttNet | 10s ECG | 71.20 | 60.98 | 92.44 | 77.13 | 59.19 |
| 1 | Shi SB, Tang YH, Zhao QY, et al. Prevalence and risk of atrial fibrillation in China: a national cross-sectional epidemiological study[J]. Lancet Reg Health West Pac, 2022, 23: 100439. |
| 2 | 苏 晞, 张劲林, 韩宏伟, 等. 单导联心电图记录系统进行心房颤动机会性筛查的首个国内经验[J]. 中华心律失常学杂志, 2017, 21(6): 485-8. |
| 3 | Halcox JPJ, Wareham K, Cardew A, et al. Assessment of remote heart rhythm sampling using the AliveCor heart monitor to screen for atrial fibrillation: the REHEARSE-AF study[J]. Circulation, 2017, 136(19): 1784-94. |
| 4 | Daqrouq K, Alkhateeb A, Ajour MN, et al. Neural network and wavelet average framing percentage energy for atrial fibrillation classification[J]. Comput Methods Programs Biomed, 2014, 113(3): 919-26. |
| 5 | Fuadah YN, Lim KM. Optimal classification of atrial fibrillation and congestive heart failure using machine learning[J]. Front Physiol, 2022, 12: 761013. |
| 6 | Bashar SK, Hossain MB, Ding E, et al. Atrial fibrillation detection during sepsis: study on mimic iii icu data[J]. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform, 2020, 24(11): 3124-35. |
| 7 | Bashar SK, Han D, Zieneddin F, et al. Novel density poincaré plot based machine learning method to detect atrial fibrillation from premature atrial/ventricular contractions[J]. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng, 2021, 68(2): 448-60. |
| 8 | García-Isla G, Mainardi L, Corino VDA. A detector for premature atrial and ventricular complexes[J]. Front Physiol, 2021, 12: 678558. |
| 9 | Gupta K, Bajaj V, Ahmad Ansari I. Atrial fibrillation detection using electrocardiogram signal input to LMD and ensemble classifier[J]. IEEE Sens Lett, 2023, 7(6): 7002904. |
| 10 | Asgari S, Mehrnia A, Moussavi M. Automatic detection of atrial fibrillation using stationary wavelet transform and support vector machine[J]. Comput Biol Med, 2015, 60: 132-42. |
| 11 | Abdul-Kadir NA, Mat Safri N, Othman MA. Dynamic ECG features for atrial fibrillation recognition[J]. Comput Methods Programs Biomed, 2016, 136: 143-50. |
| 12 | Luongo G, Rees F, Nairn D, et al. Machine learning using a single-lead ECG to identify patients with atrial fibrillation-induced heart failure[J]. Front Cardiovasc Med, 2022, 9: 812719. |
| 13 | Kalidas V, Tamil LS. Detection of atrial fibrillation using discrete-state Markov models and Random Forests[J]. Comput Biol Med, 2019, 113: 103386. |
| 14 | Li XY, Shi XL, Handa BS, et al. Classification of fibrillation organisation using electrocardiograms to guide mechanism-directed treatments[J]. Front Physiol, 2021, 12: 712454. |
| 15 | Mateo J, Joaquín Rieta J. Radial basis function neural networks applied to efficient QRST cancellation in atrial fibrillation[J]. Comput Biol Med, 2013, 43(2): 154-63. |
| 16 | Chen B, Maslove DM, Curran JD, et al. A deep learning model for the classification of atrial fibrillation in critically ill patients[J]. Intensive Care Med Exp, 2023, 11(1): 2. |
| 17 | Pourbabaee B, Roshtkhari MJ, Khorasani K. Deep convolutional neural networks and learning ECG features for screening paroxysmal atrial fibrillation patients[J]. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst, 2017, 48(12): 2095-104. |
| 18 | Faust O, Shenfield A, Kareem M, et al. Automated detection of atrial fibrillation using long short-term memory network with RR interval signals[J]. Comput Biol Med, 2018, 102: 327-35. |
| 19 | Kumar D, Peimankar A, Sharma K, et al. Deepaware: a hybrid deep learning and context-aware heuristics-based model for atrial fibrillation detection[J]. Comput Methods Programs Biomed, 2022, 221: 106899. |
| 20 | Laghari AA, Sun YQ, Alhussein M, et al. Deep residual-dense network based on bidirectional recurrent neural network for atrial fibrillation detection[J]. Sci Rep, 2023, 13(1): 15109. |
| 21 | Iandola FN, Han S, Moskewicz MW, et al. SqueezeNet: AlexNet-level accuracy with 50x fewer parameters and <0.5MB model size[EB/OL]. 2016: 1602.07360. . |
| 22 | Howard AG, Zhu ML, Chen B, et al. MobileNets: efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications[EB/OL]. 2017: 1704.04861. . |
| 23 | Li YJ, Chen M, Wang Y, et al. Diagnosis of atrial fibrillation based on lightweight detail-semantic network[J]. Biomed Signal Process Contr, 2023, 85: 105025. |
| 24 | Petrutiu S, Sahakian AV, Swiryn S. Abrupt changes in fibrillatory wave characteristics at the termination of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation in humans[J]. Europace, 2007, 9(7): 466-70. |
| 25 | Moody GB, Mark RR. New method for detecting atrial fibrillation using r-r intervals[J]. Comput Cardiol, 1983: 227-30. |
| 26 | Goldberger AL, Amaral LA, Glass L, et al. PhysioBank, PhysioToolkit, and PhysioNet: components of a new research resource for complex physiologic signals[J]. Circulation, 2000, 101(23): E215-20. |
| 27 | 谭 琛. 《2020 ECS/EACTS心房颤动诊断和管理指南》解读[J]. 中国循证心血管医学杂志, 2021, 13(2): 129-32. |
| 28 | Hamilton P. Open source ECG analysis[C]//Computers in Cardiology. September 22-25, 2002, Memphis, TN, USA. IEEE, 2002: 101-4. |
| 29 | Christov II. Real time electrocardiogram QRS detection using combined adaptive threshold[J]. Biomed Eng Online, 2004, 3(1): 28. |
| 30 | Woo S, Park J, Lee JY, et al. CBAM: convolutional block attention module[C]//Computer Vision-ECCV 2018. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2018: 3-19. |
| 31 | Liu S, Wang AG, Deng XT, et al. MGNN: a multiscale grouped convolutional neural network for efficient atrial fibrillation detection[J]. Comput Biol Med, 2022, 148: 105863. |
| 32 | Prabhakararao E, Dandapat S. Atrial fibrillation burden estimation using multi-task deep convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform, 2022, 26(12): 5992-6002. |
| 33 | Sun YH, Li YJ, Chen M, et al. IMC-ResNet: Atrial fibrillation detection method based on interlayer multiscale coupling[J]. Biomed Signal Process Contr, 2024, 97: 106683. |
| 34 | Mousavi SS, Afghah F, Razi A, et al. ECGNET: Learning where to attend for detection of atrial fibrillation with deep visual attention[J]. IEEE EMBS Int Conf Biomed Health Inform, 2019: 10.1109/BHI.2019.8834637. |
| 35 | Chollet F. Xception: deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions[C]//2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). July 21-26, 2017, Honolulu, HI, USA. IEEE, 2017: 1800-7. |
| 36 | Chen LC, Zhu YK, Papandreou G, et al. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation[C]// Computer Vision-ECCV 2018. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2018: 833-51. |
| [1] | Xiaoqing ZHU, Yajun SHI, Juan SHEN, Qingsong WANG, Tingting SONG, Jiancheng XIU, Tao CHEN, Jun GUO. An atrial fibrillation prediction model based on quantitative features of electrocardiogram during sinus rhythm in the Chinese population [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 223-228. |
| [2] | Hongsen WANG, Lijie MI, Yue ZHANG, Lan GE, Jiewei LAI, Tao CHEN, Jian LI, Xiangmin SHI, Jiancheng XIU, Min TANG, Wei YANG, Jun GUO. An intelligent model for classifying supraventricular tachycardia mechanisms based on 12-lead wearable electrocardiogram devices [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(5): 851-858. |
| [3] | HE Yong, LIU Siyun, LUO Yongjin, WU Hongkun, YU Yang, CHEN Hao. Elevation of C-reactive protein early after cardiopulmonary bypass surgery is associated with occurrence of postoperative atrial fibrillation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42(3): 443-447. |
| [4] | GAO Qi, GENG Jiayi, DING Yangyang, YAO Zhuoya, MENG Jinjin, WANG Cong, ZHANG Heng, KANG Pinfang, TANG Bi. Serum levels of endothelin-1 and connective tissue growth factor are elevated in patients with atrial fibrillation and correlated with relapse following radiofrequency ablation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42(11): 1689-1696. |
| [5] | CAO Shi, GONG Gao, XIAO Hui, FANG Weiyang, QUE Yuqing, CHEN Chaomin. Fetal ECG extraction using temporal convolutional encoder-decoder network [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42(11): 1672-1680. |
| [6] | ZHOU Mengmeng, CHEN Jindong, WANG Hao, XI Siqi, GAN Tian, ZHAO Liang. Independent risk factors of atrial thrombosis in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation and low CHA2DS2-VASc scores [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2021, 41(8): 1243-1249. |
| [7] | . Success rate of one-stop procedure for atrial fibrillation ablation and its impact on cardiac function: a propensity-matched study [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2020, 40(10): 1415-1421. |
| [8] | . Clinical value of detecting serum soluble CD163 level in patients with atrial fibrillation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2016, 36(10): 1406-. |
| [9] |
.
CHADS2 versus CHA2DS2-VASc scoring systems for predicting left atrial thrombus in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2014, 34(11): 1601-. |
| [10] | . [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2014, 34(04): 448-. |
| [11] | . Association of T393C single nucleotide polymorphism of GNAS1 gene with non-valvular atrial fibrillation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2013, 33(10): 1508-. |
| [12] | ZHAO Fu, FENG Shao-xian, ZHAO Ping, MA Hong Department of Cardiology, First Municipal Hospital of Guangzhou, Guangzhou 510080, China;Department of Cardiology, First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, China. Effect of oral cordarone in reversing persistent atrial fibrillation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2006, 26(04): 521-522. |
| [13] | SUN Zhong-bo1, ZHANG Qin1, YANG Xia-fang2. Changes in myocardial enzyme spectrum and electrocardiogram after Salmonella food poisoning [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2004, 24(11): 1311-1312,1315. |
| [14] | HUANG Zou-qin1, LI Huo-xia1, WANG Jia-li1, WAN Song-guo2. Clinical observation of electrocardiographic changes in response to taxotere combined with adriamycin treatment for breast cancer [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2004, 24(05): 582-583. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||