Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (2): 223-228.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.02.02
Xiaoqing ZHU1,2( ), Yajun SHI3, Juan SHEN1, Qingsong WANG1,2,4, Tingting SONG1, Jiancheng XIU5, Tao CHEN1,2, Jun GUO1,2(
), Yajun SHI3, Juan SHEN1, Qingsong WANG1,2,4, Tingting SONG1, Jiancheng XIU5, Tao CHEN1,2, Jun GUO1,2( )
)
Received:2024-10-16
Online:2025-02-20
Published:2025-03-03
Contact:
Jun GUO
E-mail:zxq990715@163.com;guojun301@126.com
Xiaoqing ZHU, Yajun SHI, Juan SHEN, Qingsong WANG, Tingting SONG, Jiancheng XIU, Tao CHEN, Jun GUO. An atrial fibrillation prediction model based on quantitative features of electrocardiogram during sinus rhythm in the Chinese population[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 223-228.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.02.02
| Item | Non-AF group (n=29 013) | AF group (n=1370) | P |
| Age (year) | 50.0 (35.0, 61.0) | 70.0 (60.0, 78.0) | <0.001 |
| Gender (male) | 14648 (50.5) | 868 (63.4) | <0.001 |
Tab.1 Comparison of baseline characteristics between non-AF group and AF group
| Item | Non-AF group (n=29 013) | AF group (n=1370) | P |
| Age (year) | 50.0 (35.0, 61.0) | 70.0 (60.0, 78.0) | <0.001 |
| Gender (male) | 14648 (50.5) | 868 (63.4) | <0.001 |
| Item | Training set (n=21268) | Test set (n=9115) | P |
| Age (years) | 51.0 (36.0, 62.0) | 51.0 (35.0, 62.0) | 0.603 |
| Gender (male) | 10895 (51.2) | 4621 (50.7) | 0.397 |
| Incidence of AF | 956 (4.5%) | 414 (4.5%) | 0.857 |
Tab.2 Comparison of baseline characteristics between the training set and test set
| Item | Training set (n=21268) | Test set (n=9115) | P |
| Age (years) | 51.0 (36.0, 62.0) | 51.0 (35.0, 62.0) | 0.603 |
| Gender (male) | 10895 (51.2) | 4621 (50.7) | 0.397 |
| Incidence of AF | 956 (4.5%) | 414 (4.5%) | 0.857 |
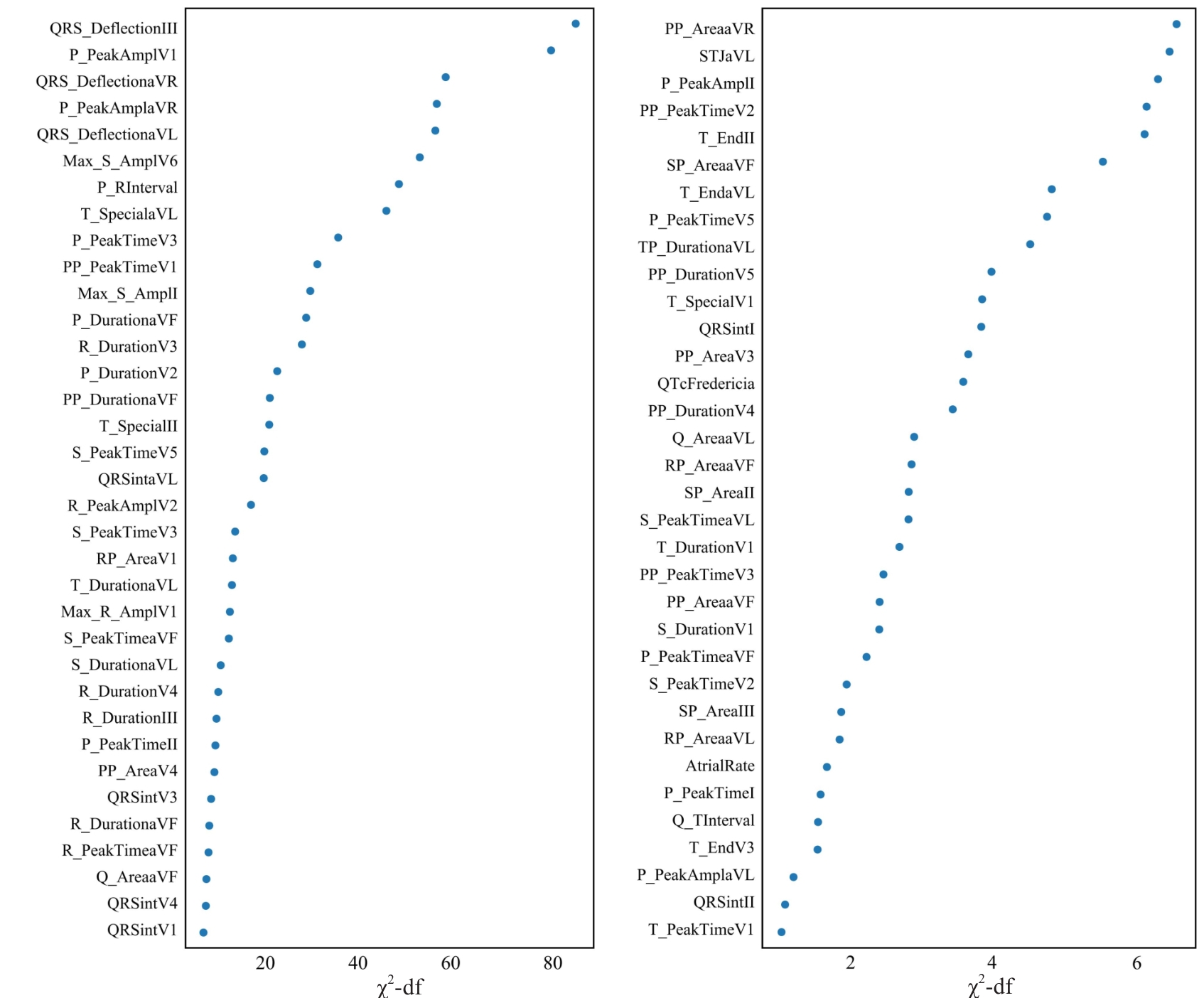
Fig.1 Relative importance of the variables included in the ECG model for predicting atrial fibrillation measured by chi-squared statistic minus predictor degrees of freedom (df).
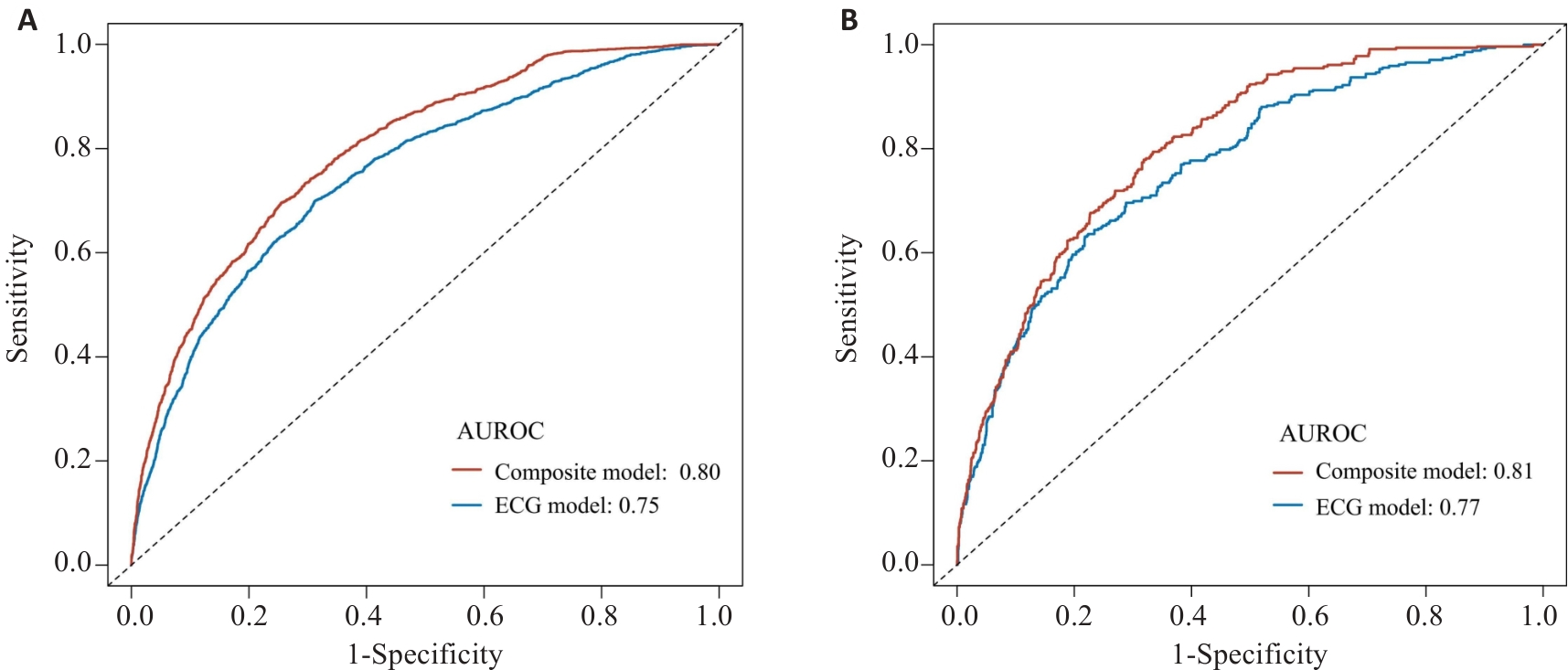
Fig.2 ROC curves of the ECG model and the composite model for predicting 5-year atrial fibrillation risk. A: ROC curves in the training set. B: ROC curves in the test set.
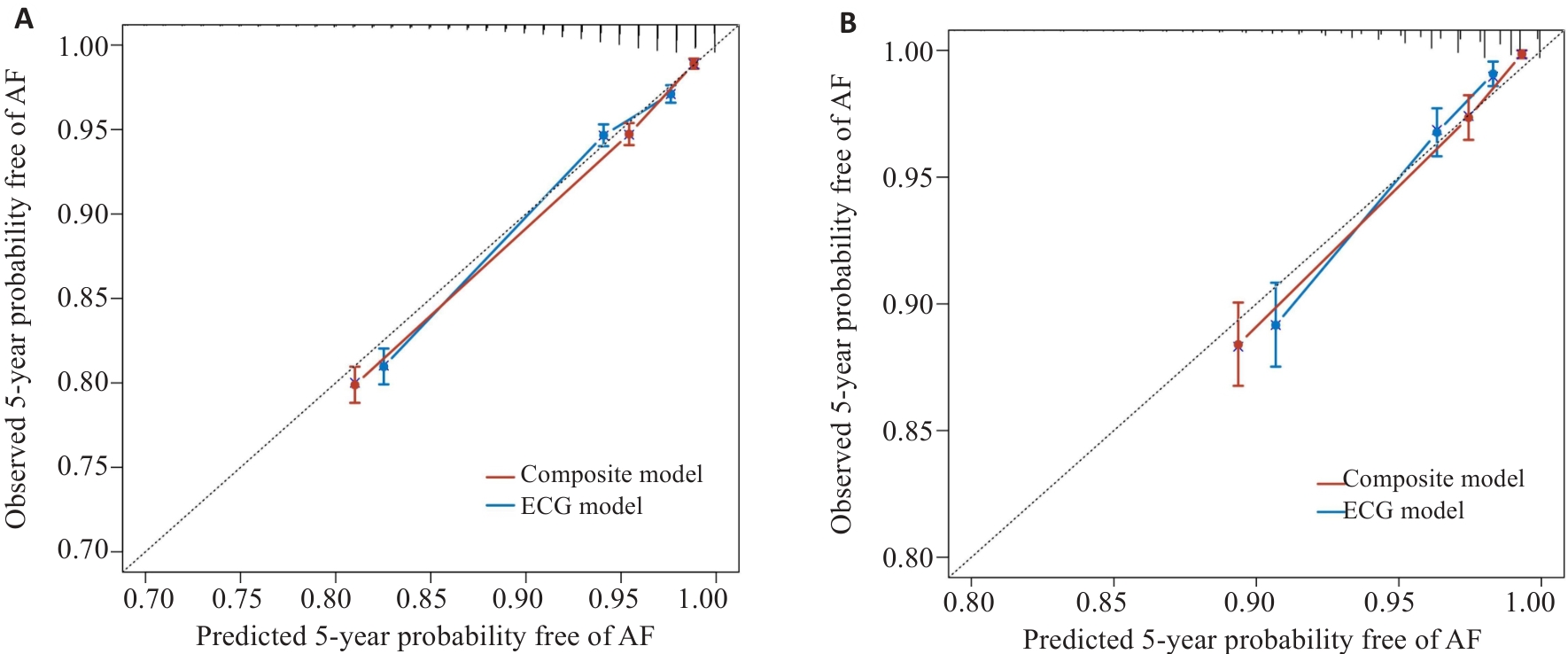
Fig.3 Calibration of the ECG model and the composite model for predicting 5-year atrial fibrillation risk. A: Calibration curves in the training set. B: Calibration curves in the test set.
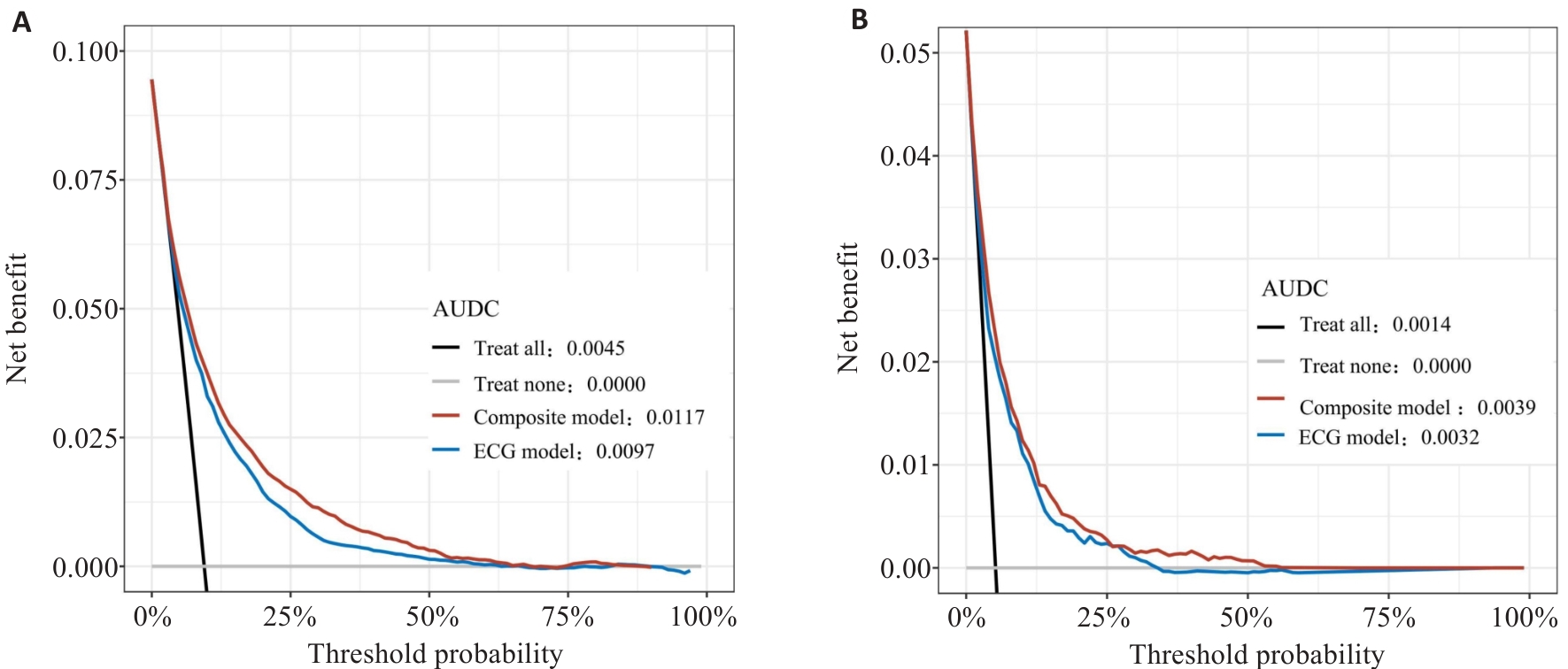
Fig.4 Decision curves of the ECG model and the composite model for predicting 5-year atrial fibrillation risk. A: Decision curves in the training set. B: Decision curves in in the test set.
| 1 | Martin SS, Aday AW, Almarzooq ZI, et al. 2024 heart disease and stroke statistics: a report of US and global data from the American heart association[J]. Circulation, 2024, 149(8): e347-913. |
| 2 | Vinding NE, Kristensen SL, Rørth R, et al. Ischemic stroke severity and mortality in patients with and without atrial fibrillation[J]. J Am Heart Assoc, 2022, 11(4): e022638. |
| 3 | Staerk L, Sherer JA, Ko D, et al. Atrial fibrillation: epidemiology, pathophysiology, and clinical outcomes[J]. Circ Res, 2017, 120(9): 1501-17. |
| 4 | Shi SB, Tang YH, Zhao QY, et al. Prevalence and risk of atrial fibrillation in China: a national cross-sectional epidemiological study[J]. Lancet Reg Health West Pac, 2022, 23: 100439. |
| 5 | van den Berg NWE, Neefs J, Kawasaki M, et al. Extracellular matrix remodeling precedes atrial fibrillation: Results of the PREDICT-AF trial[J]. Heart Rhythm, 2021, 18(12): 2115-25. |
| 6 | Kashou AH, Adedinsewo DA, Siontis KC, et al. Artificial intelligence-enabled ECG: physiologic and pathophysiologic insights and implications[J]. Compr Physiol, 2022, 12(3): 3417-24. |
| 7 | Christopoulos G, Graff-Radford J, Lopez CL, et al. Artificial intelligence-electrocardiography to predict incident atrial fibrillation: a population-based study[J]. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol, 2020, 13(12): e009355. |
| 8 | Khurshid S, Friedman S, Reeder C, et al. ECG-based deep learning and clinical risk factors to predict atrial fibrillation[J]. Circulation, 2022, 145(2): 122-33. |
| 9 | Noseworthy PA, Attia ZI, Brewer LC, et al. Assessing and mitigating bias in medical artificial intelligence: the effects of race and ethnicity on a deep learning model for ECG analysis[J]. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol, 2020, 13(3): e007988. |
| 10 | 李盼盼, 韩宇臣, 李 峰, 等. 阵发性心房颤动发作风险的人工智能预测模型[J]. 中国心血管病研究, 2024, 22(3): 196-202. |
| 11 | 奚丽婧, 郭昭艳, 杨雪珂, 等. LASSO及其拓展方法在回归分析变量筛选中的应用[J]. 中华预防医学杂志, 2023, 57(1): 107-11. |
| 12 | Manigault AW, Sheinkopf SJ, Silverman HF, et al. Newborn cry acoustics in the assessment of neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome using machine learning[J]. JAMA Netw Open, 2022, 5(10): e2238783. |
| 13 | Lindholm D, Lindbäck J, Armstrong PW, et al. Biomarker-based risk model to predict cardiovascular mortality in patients with stable coronary disease[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2017, 70(7): 813-26. |
| 14 | Siontis KC, Noseworthy PA, Attia ZI, et al. Artificial intelligence-enhanced electrocardiography in cardiovascular disease management[J]. Nat Rev Cardiol, 2021, 18: 465-78. |
| 15 | MacFarlane PW, Katibi IA, Hamde ST, et al. Racial differences in the ECG: selected aspects[J]. J Electrocardiol, 2014, 47(6): 809-14. |
| 16 | Schnabel RB, Sullivan LM, Levy D, et al. Development of a risk score for atrial fibrillation (Framingham Heart Study): a community-based cohort study[J]. Lancet, 2009, 373(9665): 739-45. |
| 17 | Alonso A, Krijthe BP, Aspelund T, et al. Simple risk model predicts incidence of atrial fibrillation in a racially and geographically diverse population: the CHARGE-AF consortium[J]. J Am Heart Assoc, 2013, 2(2): e000102. |
| 18 | Li YG, Pastori D, Farcomeni A, et al. A simple clinical risk score (C2HEST) for predicting incident atrial fibrillation in Asian subjects derivation in 471, 446 Chinese subjects, with internal validation and external application in 451, 199 Korean subjects[J]. Chest, 2019, 155(3): 510-8. |
| 19 | Alexander B, Milden J, Hazim B, et al. New electrocardiographic score for the prediction of atrial fibrillation: The MVP ECG risk score (morphology-voltage-P-wave duration)[J]. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol, 2019, 24(6): e12669. |
| 20 | Kreimer F, Aweimer A, Pflaumbaum A, et al. Impact of P-wave indices in prediction of atrial fibrillation-Insight from loop recorder analysis[J]. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol, 2021, 26(5): e12854. |
| 21 | Rasmussen MU, Kumarathurai P, Fabricius-Bjerre A, et al. P-wave indices as predictors of atrial fibrillation[J]. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol, 2020, 25(5): e12751. |
| 22 | Chen LY, Ribeiro ALP, Platonov PG, et al. P wave parameters and indices: a critical appraisal of clinical utility, challenges, and future research-a consensus document endorsed by the international society of electrocardiology and the international society for holter and noninvasive electrocardiology[J]. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol, 2022, 15(4): e010435. |
| 23 | Eranti A, Carlson J, Kenttä T, et al. Orthogonal P-wave morphology, conventional P-wave indices, and the risk of atrial fibrillation in the general population using data from the Finnish Hospital Discharge Register[J]. Europace, 2020, 22(8): 1173-81. |
| 24 | Cheng S, Keyes MJ, Larson MG, et al. Long-term outcomes in individuals with prolonged PR interval or first-degree atrioventricular block[J]. JAMA, 2009, 301(24): 2571-7. |
| 25 | Macfarlane PW. The influence of age and sex on the electrocardiogram[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2018, 1065: 93-106. |
| 26 | Joglar JA, Chung MK, Armbruster AL, et al. 2023 ACC/AHA/ACCP/HRS guideline for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation: a report of the American college of cardiology/American heart association joint committee on clinical practice guidelines[J]. Circulation, 2024, 149(1): e1-156. |
| [1] | Hongsen WANG, Lijie MI, Yue ZHANG, Lan GE, Jiewei LAI, Tao CHEN, Jian LI, Xiangmin SHI, Jiancheng XIU, Min TANG, Wei YANG, Jun GUO. An intelligent model for classifying supraventricular tachycardia mechanisms based on 12-lead wearable electrocardiogram devices [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(5): 851-858. |
| [2] | Jiaxin JIN, Pengzhen MA, Eryu WANG, Yingzhen XIE. Risk factors of recurrence of acute ischemic stroke and construction of a nomogram model for predicting the recurrence risk based on Lasso Regression [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(12): 2375-2381. |
| [3] | HE Yong, LIU Siyun, LUO Yongjin, WU Hongkun, YU Yang, CHEN Hao. Elevation of C-reactive protein early after cardiopulmonary bypass surgery is associated with occurrence of postoperative atrial fibrillation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42(3): 443-447. |
| [4] | GAO Qi, GENG Jiayi, DING Yangyang, YAO Zhuoya, MENG Jinjin, WANG Cong, ZHANG Heng, KANG Pinfang, TANG Bi. Serum levels of endothelin-1 and connective tissue growth factor are elevated in patients with atrial fibrillation and correlated with relapse following radiofrequency ablation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42(11): 1689-1696. |
| [5] | CAO Shi, GONG Gao, XIAO Hui, FANG Weiyang, QUE Yuqing, CHEN Chaomin. Fetal ECG extraction using temporal convolutional encoder-decoder network [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42(11): 1672-1680. |
| [6] | ZHOU Mengmeng, CHEN Jindong, WANG Hao, XI Siqi, GAN Tian, ZHAO Liang. Independent risk factors of atrial thrombosis in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation and low CHA2DS2-VASc scores [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2021, 41(8): 1243-1249. |
| [7] | . Success rate of one-stop procedure for atrial fibrillation ablation and its impact on cardiac function: a propensity-matched study [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2020, 40(10): 1415-1421. |
| [8] | . Clinical value of detecting serum soluble CD163 level in patients with atrial fibrillation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2016, 36(10): 1406-. |
| [9] |
.
CHADS2 versus CHA2DS2-VASc scoring systems for predicting left atrial thrombus in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2014, 34(11): 1601-. |
| [10] | . [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2014, 34(04): 448-. |
| [11] | . Association of T393C single nucleotide polymorphism of GNAS1 gene with non-valvular atrial fibrillation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2013, 33(10): 1508-. |
| [12] | ZHAO Fu, FENG Shao-xian, ZHAO Ping, MA Hong Department of Cardiology, First Municipal Hospital of Guangzhou, Guangzhou 510080, China;Department of Cardiology, First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, China. Effect of oral cordarone in reversing persistent atrial fibrillation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2006, 26(04): 521-522. |
| [13] | SUN Zhong-bo1, ZHANG Qin1, YANG Xia-fang2. Changes in myocardial enzyme spectrum and electrocardiogram after Salmonella food poisoning [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2004, 24(11): 1311-1312,1315. |
| [14] | HUANG Zou-qin1, LI Huo-xia1, WANG Jia-li1, WAN Song-guo2. Clinical observation of electrocardiographic changes in response to taxotere combined with adriamycin treatment for breast cancer [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2004, 24(05): 582-583. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||