Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (1): 72-79.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.01.10
Previous Articles Next Articles
Chunfei JI( ), Zongchao ZUO, Jun WANG, Miaonan LI(
), Zongchao ZUO, Jun WANG, Miaonan LI( )
)
Received:2024-05-06
Online:2025-01-20
Published:2025-01-20
Contact:
Miaonan LI
E-mail:1492160124@qq.com;13855265385@163.com
Chunfei JI, Zongchao ZUO, Jun WANG, Miaonan LI. N-acetylneuraminic acid promotes ferroptosis of H9C2 cardiomyocytes with hypoxia/reoxygenation injury by inhibiting the Nrf2 axis[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 72-79.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.01.10
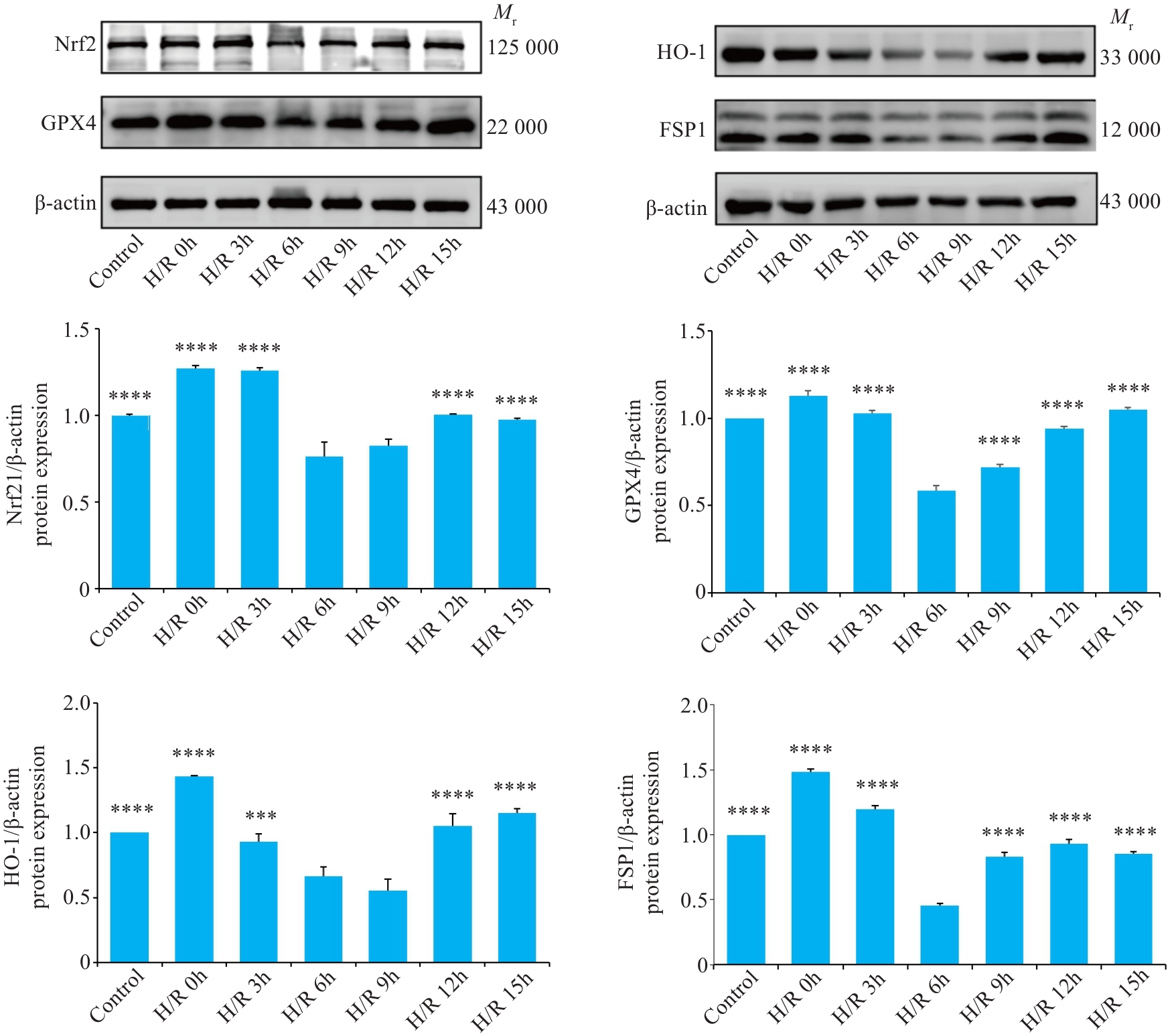
Fig.1 Western blotting of the expression of Nrf2, GPX4, HO-1, and FSP1 in H9C2 cells with hypoxia and glucose deprivation for 8 h, followed by reoxygenation with normal glucose supplementation for 0, 3, 6, 9, 12, and 15 h.***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001 vs H/R 6h group.
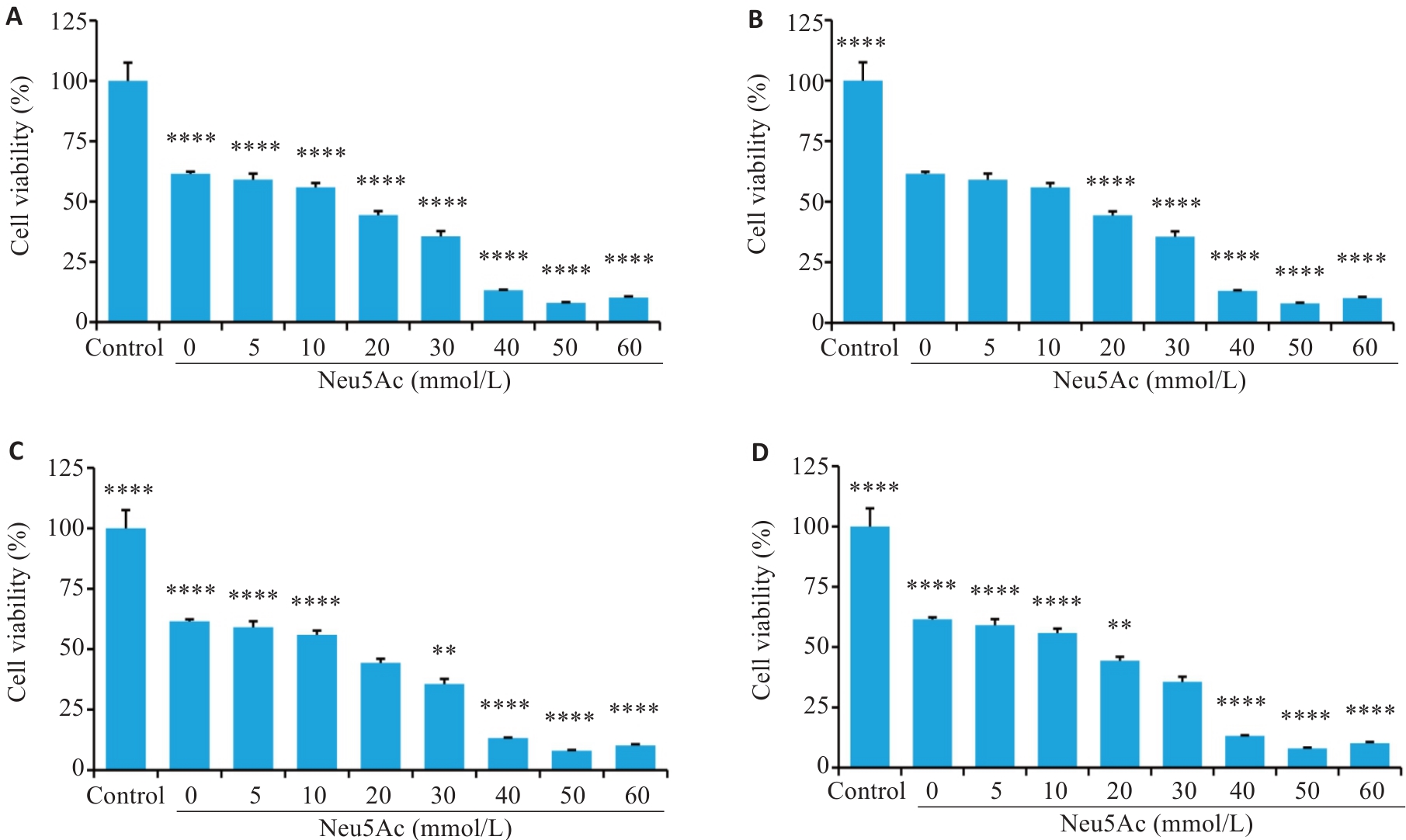
Fig.2 Effect of different Neu5Ac concentrations on survival rate of H9C2 cells with H/R injury at 3 h during reoxygenation (Mean±SD, n=3). A-D: Other groups were compared with Control Group, 10 mmol/L group, 20 mmol/L group and 30 mmol/L group separately. **P<0.01, ****P<0.0001, ****P<0.0001.
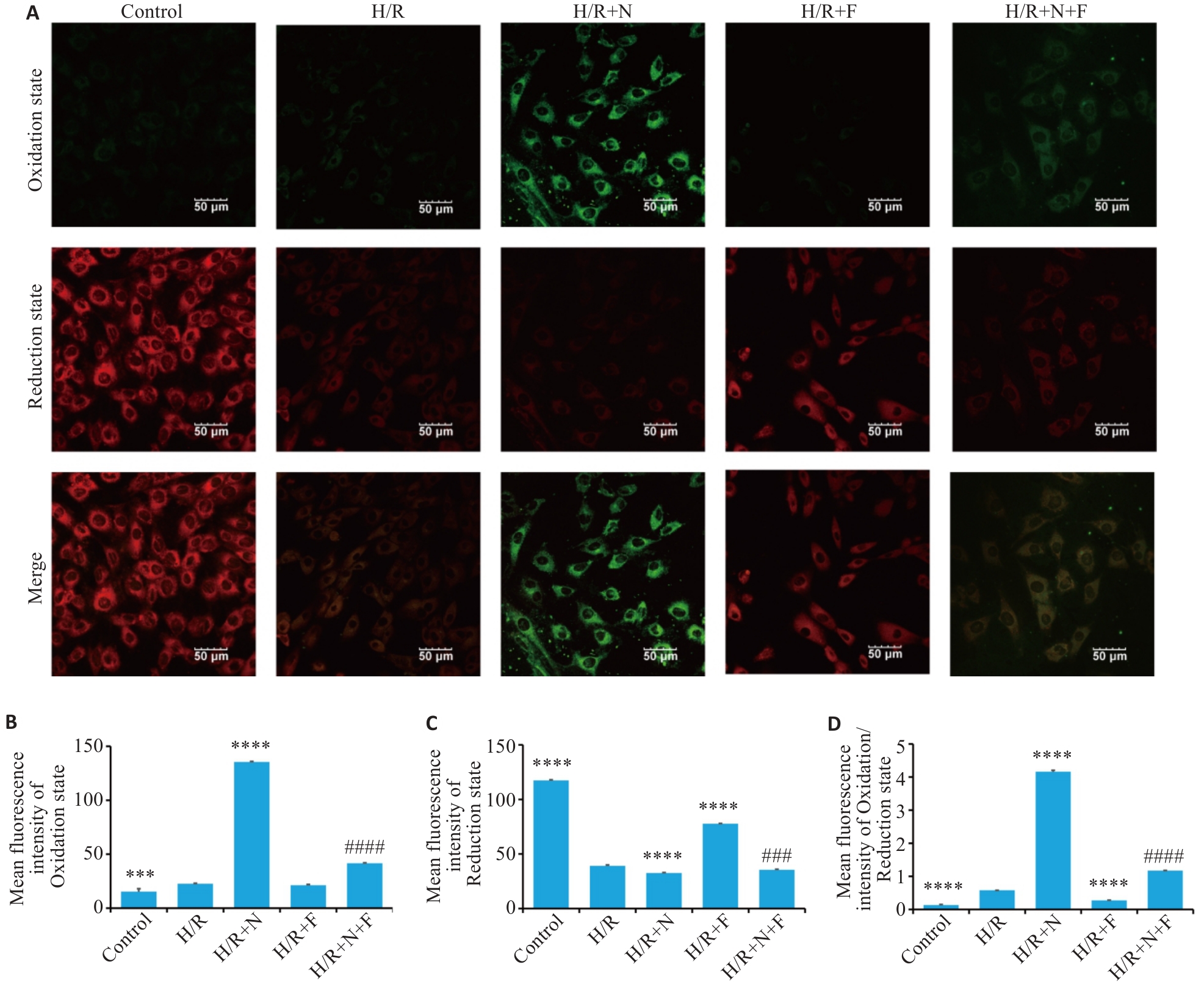
Fig.5 Effect of Neu5Ac on the production of lipid ROS in H9C2 cells with H/R injury. A: Fluorescence images of the 5 groups of cells in Oxidation state, Reduction state, and Merge. B: Mean fluorescence intensity of the 5 groups of cells in the oxidized state. C: Mean fluorescence intensity of the 5 groups of cells in the reduced state. D: Ratio of the mean fluorescence intensity in the oxidized and reduced states in the 5 groups. ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001 vs H/R group, ###P<0.001, ####P<0.0001 vs H/R+N group.
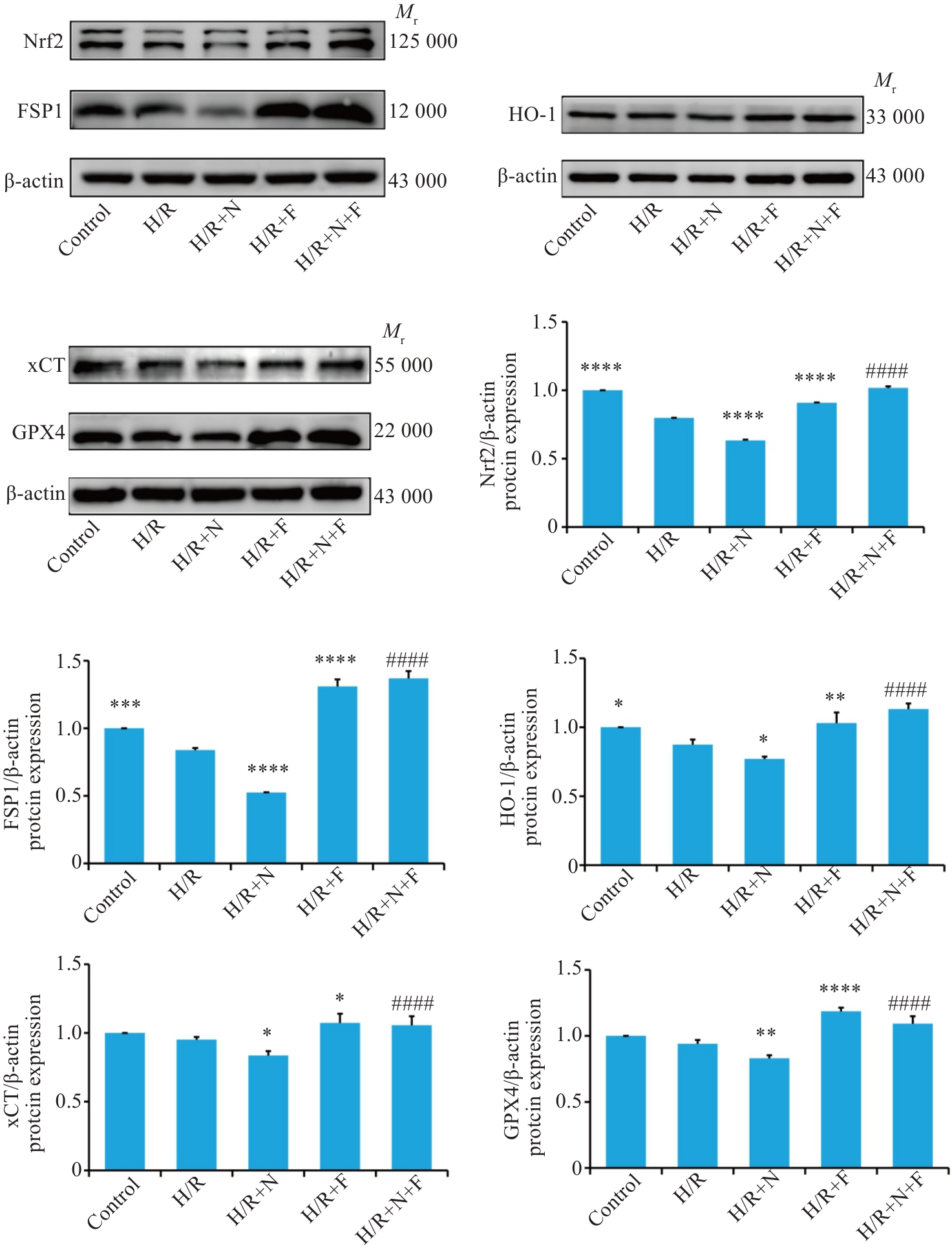
Fig.6 Effect of Neu5Ac on expression of ferroptosis related proteins in H9C2 cells with H/R injury. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001,****P<0.0001 vs H/R group,####P<0.0001 vs H/R+N group.
| 1 | 刘明波, 王增武, 樊 静, 等. 《中国心血管健康与疾病报告2023》要点解读[J]. 中国心血管病研究, 2024, 22(7): 577-93. |
| 2 | Szczeklik W, Fronczek J. Myocardial injury after noncardiac surgery ‑an update[J]. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol, 2021, 34(3): 381-6. |
| 3 | Shi XJ, Li MN, Xuan L, et al. Clinical characteristics of patients with premature acute coronary syndrome and adverse cardiovascular events after PCI[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2019, 18(1): 793-801. |
| 4 | Gunata M, Parlakpinar H. A review of myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion injury: Pathophysiology, experimental models, biomarkers, genetics and pharmacological treatment[J]. Cell Biochem Funct, 2021, 39(2): 190-217. |
| 5 | Chen H, Zhu J, Le YF, et al. Salidroside inhibits doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy by modulating a ferroptosis-dependent pathway[J]. Phytomedicine, 2022, 99: 153964. |
| 6 | Ding SY, Duanmu XY, Xu LS, et al. Ozone pretreatment alleviates ischemiareperfusion injury-induced myocardial ferroptosis by activating the Nrf2/Slc7a11/Gpx4 axis[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2023, 165: 115185. |
| 7 | Qian SE, Long Y, Tan GL, et al. Programmed cell death: molecular mechanisms, biological functions, diseases, and therapeutic targets[J]. MedComm, 2024, 5(12): e70024. |
| 8 | Heimerl M, Sieve I, Ricke-Hoch M, et al. Neuraminidase-1 promotes heart failure after ischemia/reperfusion injury by affecting cardiomyocytes and invading monocytes/macrophages[J]. Basic Res Cardiol, 2020, 115(6): 62. |
| 9 | Varki A. Sialic acids in human health and disease[J]. Trends Mol Med, 2008, 14(8): 351-60. |
| 10 | Heimerl M, Gausepohl T, Mueller JH, et al. Neuraminidases-key players in the inflammatory response after pathophysiological cardiac stress and potential new therapeutic targets in cardiac disease[J]. Biology, 2022, 11(8): 1229. |
| 11 | Liu ZH, Xiang P, Zeng SM, et al. N-Acetylneuraminic acid triggers endothelial pyroptosis and promotes atherosclerosis progression via GLS2-mediated glutaminolysis pathway[J]. Cell Death Discov, 2024, 10(1): 467. |
| 12 | Xiang P, Chen QQ, Chen L, et al. Metabolite Neu5Ac triggers SLC3A2 degradation promoting vascular endothelial ferroptosis and aggravates atherosclerosis progression in ApoE-/- mice[J]. Theranostics, 2023, 13(14): 4993-5016. |
| 13 | Zhang L, Wei TT, Li Y, et al. Functional metabolomics characterizes a key role for N-acetylneuraminic acid in coronary artery diseases[J]. Circulation, 2018, 137(13): 1374-90. |
| 14 | Gayral S, Garnotel R, Castaing-Berthou A, et al. Elastin-derived peptides potentiate atherosclerosis through the immune Neu1-PI3Kγ pathway[J]. Cardiovasc Res, 2014, 102(1): 118-27. |
| 15 | Hu XM, Li YY, Chen QY, et al. Sialic acids promote macrophage M1 polarization and atherosclerosis by upregulating ROS and autophagy blockage[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2023, 120: 110410. |
| 16 | Chen L, Qiu HM, Chen QQ, et al. N-acetylneuraminic acid modulates SQSTM1/p62 sialyation-mediated ubiquitination degradation contributing to vascular endothelium dysfunction in experimental atherosclerosis mice[J]. IUBMB Life, 2024, 76(3): 161-78. |
| 17 | Li MN, Qian SH, Yao ZY, et al. Correlation of serum N-Acetylneuraminic acid with the risk and prognosis of acute coronary syndrome: a prospective cohort study[J]. BMC Cardiovasc Disord, 2020, 20(1): 404. |
| 18 | Li MN, Bao BW, Ding SY, et al. Correlation between plasma glutathione peroxidase 4 and N-acetylneuraminic acid levels with clinical risk stratification and prognosis of patients with acute coronary syndrome[J]. Saudi Med J, 2022, 43(10): 1103-10. |
| 19 | Chen XC, Sun T, Qi YX, et al. Paeoniflorin ameliorates reperfusion injury in H9C2 cells through SIRT1-PINK1/parkin-mediated mitochondrial autophagy[J]. Mol Immunol, 2024, 177: 32-43. |
| 20 | Gao Y, Song LL, Xu JT, et al. The role of exosomes in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury[J]. Cardiology, 2024: 1-17. |
| 21 | Shi PL, Sha YT, Wang XR, et al. Targeted delivery and ROS-responsive release of lutein nanoassemblies inhibit myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by improving mitochondrial function[J]. Int J Nanomedicine, 2024, 19: 11973-96. |
| 22 | Zavadovsky KV, Ryabov VV, Vyshlov EV, et al. Intra-myocardial hemorrhage and cardiac microvascular injury in ischemia/reperfusion. A systematic review of current evidences[J]. Curr Probl Cardiol, 2025, 50(1): 102918. |
| 23 | Brown AR, Hirschhorn T, Stockwell BR. Ferroptosis-disease perils and therapeutic promise[J]. Science, 2024, 386(6724): 848-9. |
| 24 | Zhong CN, Dong H, Ma YT, et al. Single-cell sequencing combined with transcriptomics and invivo and invitro analysis reveals the landscape offerroptosis in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury[J]. FASEB J, 2024, 38(21): e70164. |
| 25 | Schauer R. Sialic acids: fascinating sugars in higher animals and man[J]. Zoology, 2004, 107(1): 49-64. |
| 26 | He ML, Li XY, Guo YQ, et al. Nerol attenuates doxorubicin-induced heart failure by inhibiting cardiomyocyte apoptosis in rats[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2024, 987: 177203. |
| 27 | Abdelmawgood IA, Kotb MA, Hassan HS, et al. Gentisic acid attenuates ovalbumin-induced airway inflammation, oxidative stress, and ferroptosis through the modulation of Nrf2/HO-1 and NF-κB signaling pathways[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2024, 146: 113764. |
| 28 | Yang F, Smith MJ. Metal profiling in coronary ischemia-reperfusion injury: implications for KEAP1/NRF2 regulated redox signaling[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2024, 210: 158-71. |
| 29 | Liu DH, Zhu YZ. Unveiling smyd-2's role in cytoplasmic nrf-2 sequestration and ferroptosis induction in hippocampal neurons after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion[J]. Cells, 2024, 13(23): 1969. |
| 30 | Ibanez B, James S, Agewall S, et al. 2017 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation: the Task Force for the management of acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment elevation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC)[J]. Eur Heart J, 2018, 39(2): 119-77. |
| [1] | Xinyuan CHEN, Chengting WU, Ruidi LI, Xueqin PAN, Yaodan ZHANG, Junyu TAO, Caizhi LIN. Shuangshu Decoction inhibits growth of gastric cancer cell xenografts by promoting cell ferroptosis via the P53/SLC7A11/GPX4 axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1363-1371. |
| [2] | Mengying ZHANG, Chenling ZHAO, Liwei TIAN, Guofang YU, Wenming YANG, Ting DONG. Gandou Fumu Decoction improves liver steatosis by inhibiting hepatocyte ferroptosis in mice with Wilson's disease through the GPX4/ACSL4/ALOX15 signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1471-1478. |
| [3] | Anbang ZHANG, Xiuqi SUN, Bo PANG, Yuanhua WU, Jingyu SHI, Ning ZHANG, Tao YE. Electroacupuncture pretreatment alleviates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by inhibiting ferroptosis through the gut-brain axis and the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 911-920. |
| [4] | Linluo ZHANG, Changqing LI, Lingling HUANG, Xueping ZHOU, Yuanyuan LOU. Catalpol reduces liver toxicity of triptolide in mice by inhibiting hepatocyte ferroptosis through the SLC7A11/GPX4 pathway: testing the Fuzheng Zhidu theory for detoxification [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 810-818. |
| [5] | Kai CHEN, Zhaofei MENG, Jingting MIN, Jiahui WANG, Zhenghong LI, Qin GAO, Junfeng HU. Curcumin alleviates septic lung injury in mice by inhibiting TXNIP/TRX-1/GPX4-mediated ferroptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1805-1813. |
| [6] | Mingzi OUYANG, Jiaqi CUI, Hui WANG, Zheng LIANG, Dajin PI, Liguo CHEN, Qianjun CHEN, Yingchao WU. Kaixinsan alleviates adriamycin-induced depression-like behaviors in mice by reducing ferroptosis in the prefrontal cortex [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1441-1449. |
| [7] | Yinliang ZHANG, Zetan LUO, Rui ZHAO, Na ZHAO, Zhidong XU, Di AO, Guyi CONG, Xinyu LIU, Hailun ZHENG. Sanguinarine induces ferroptosis of colorectal cancer cells by upregulating STUB1 and downregulating GPX4 [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1537-1544. |
| [8] | Yuanguo WANG, Peng ZHANG. Ferroptosis suppressor genes are highly expressed in esophageal cancer to inhibit tumor cell ferroptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1389-1396. |
| [9] | Huaxing HE, Lulin LIU, Yingyin LIU, Nachuan CHEN, Suxia SUN. Sodium butyrate and sorafenib synergistically inhibit hepatocellular carcinoma cells possibly by inducing ferroptosis through inhibiting YAP [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1425-1430. |
| [10] | Zhixian REN, Beixian ZHOU, Linxin WANG, Jing LI, Rongping ZHANG, Xiping PAN. Inhibitory effect of 5-hydroxy-6,7-dimethoxyflavone on H1N1 influenza virus-induced ferroptosis and inflammation in A549 cells and its possible mechanisms [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(6): 1070-1078. |
| [11] | Fangyuan ZHANG, Gang LIU. Dexmedetomidine inhibits ferroptosis of human renal tubular epithelial cells by activating the Nrf2/HO-1/GPX4 pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(6): 1135-1140. |
| [12] | Nan WANG, Bin SHI, Xiaolan MAN, Weichao WU, Jia CAO. High expression of fragile X mental retardation protein inhibits ferroptosis of colorectal tumor cells by activating the RAS/MAPK signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(5): 885-893. |
| [13] | LI Shuxian, YU Shuping, MU Yaming, WANG Kai, LIU Yu, ZHANG Meihua. Metformin ameliorates PM2.5- induced functional impairment of placental trophoblasts by inhibiting ferroptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(3): 437-446. |
| [14] | Hong KUANG, Wenhan CAI, Yiming LIU, Jiaxin WEN, Shuo TIAN, Zhiqiang XUE. High expression of SLC2A1 inhibits ferroptosis and promotes proliferation and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(12): 2404-2411. |
| [15] | Qi ZHANG, Zezhao JI, Abai JIASHAER∙, Youda WANG, ABUDUXUKUER∙Abulimiti. FER-1 inhibits methylglyoxal-induced ferroptosis in mouse alveolar macrophages in vitro [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(12): 2443-2448. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||