Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (8): 1508-1517.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.08.09
Previous Articles Next Articles
Xingmei CHEN1( ), Qinwen LIU2,3, Yi LI2,3, Xiaoyu ZHONG1, Qiling FAN2,3, Ke MA1, Liuting LUO1, Daogang GUAN2,3, Zhibo ZHU1(
), Qinwen LIU2,3, Yi LI2,3, Xiaoyu ZHONG1, Qiling FAN2,3, Ke MA1, Liuting LUO1, Daogang GUAN2,3, Zhibo ZHU1( )
)
Received:2024-03-21
Online:2024-08-20
Published:2024-09-06
Contact:
Zhibo ZHU
E-mail:1842578607@qq.com;zhuzb676@smu.edu.cn
Xingmei CHEN, Qinwen LIU, Yi LI, Xiaoyu ZHONG, Qiling FAN, Ke MA, Liuting LUO, Daogang GUAN, Zhibo ZHU. Analysis of core functional components in Yinchenhao Decoction and their pathways for treating liver fibrosis[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1508-1517.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.08.09
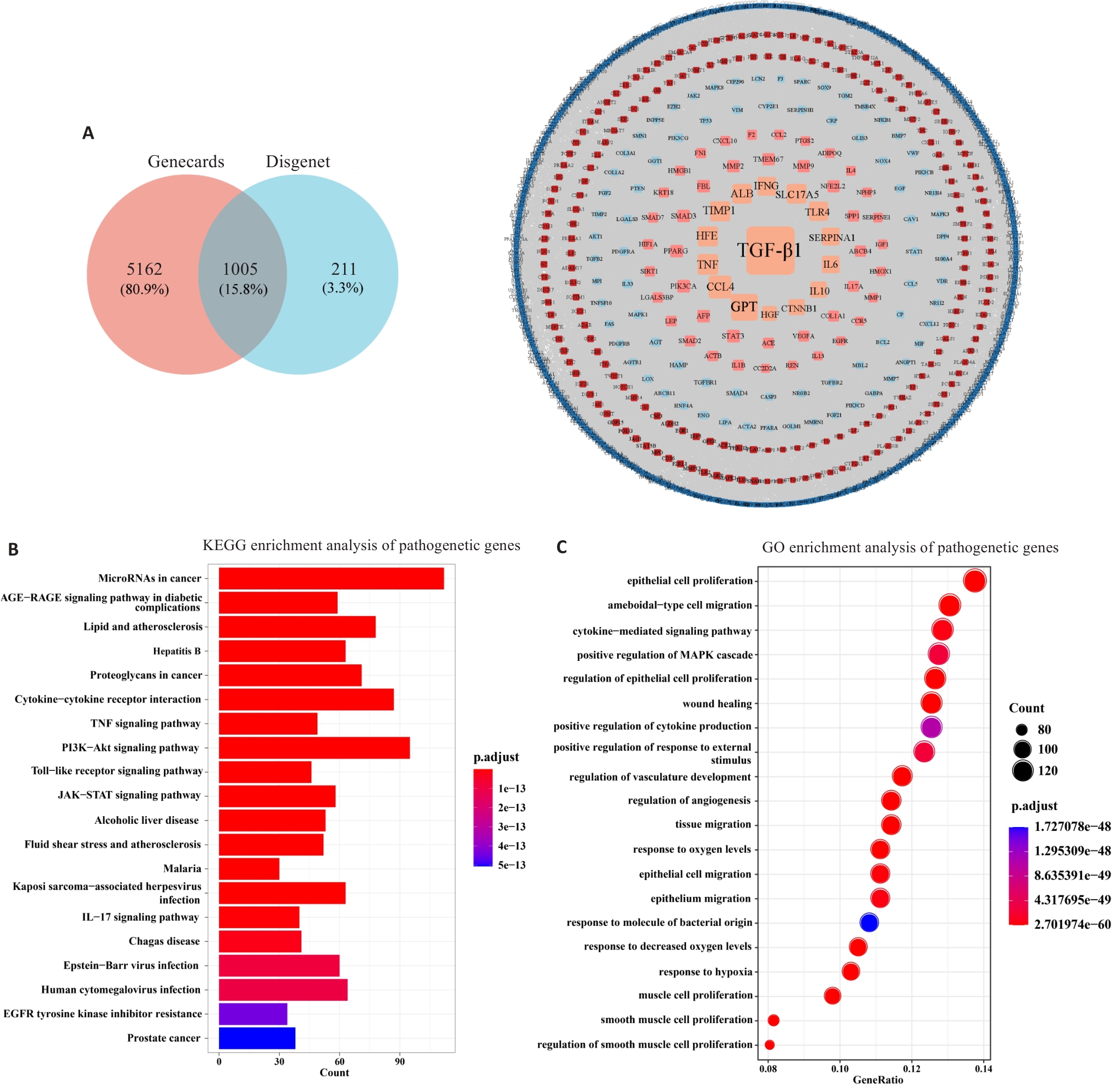
Fig.1 Weighted network and functional analysis of the pathogenic genes. A: Gene selection and PPI network for hepatic fibrosis (HF) based on Genescards and Disease databases. B: KEGG enrichment analysis of the pathogenic genes. C: GO enrichment analysis of the pathogenic genes.
| Formula/Herbs | Component | Content (mg/g) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rheum palmatumL. | Catechin | 0.015-11.66 | |
| Chrysophanol | 0.17-4.36 | ||
| (-)-epicatechin | 0.98-6.33 | ||
| Gallic acid | 0.041-4.21 | ||
| Isolindleyin | 0.056-4.37 | ||
| Lindleyin | 0.40-4.02 | ||
| Phenylbutanone-glucoside | 0.36 | ||
| Physcion | 0.09-0.15 | ||
| 4,3,5'-trihydroxystilbene-4-(6"-galloyl-glucoside) | 0.14-0.20 | ||
| Emodin | 0.058-4.15 | ||
| Rhein | 0.08-4.97 | ||
| Physcione | 0.056-1.66 | ||
| Sennoside B | 0.47-1.59 | ||
| 3,4,3',5'-tetrahydroxystilbene-3-glucoside | 0.05 | ||
| (-)-Epicatechin gallate | 0.37-0.045 | ||
| (+)-catechin | 0.07-0.79 | ||
| 1,6-digalloyl-2-cinnamoyi-glucose | 0.07-0.30 | ||
| 1-galloyl-2-cinnamoyl-glucose | 0.63-1.48 | ||
| 2-cinnamoyl-glucose | 0.13-0.42 | ||
| 4-4-HydroxyphenylButan-2-One | 0.48 | ||
| Aloe-emodin-8-glucoside | 0.31-0.46 | ||
| Chrysophanol-8-glucoside | 0.52-1.08 | ||
| Emodin-8-glucoside | 0.10-1.16 | ||
| Epicatechin | 0.28-0.70 | ||
| Musizin-glucoside | 0.06-0.82 | ||
| Physcion-8-glucoside | 0.20-0.78 | ||
| Sennosides | 0.40-2.20 | ||
| Torachrysone-8-glucoside | 0.12-0.25 | ||
| Trans-cinnamic acid | 1.05 | ||
| Artemisia capillaris Thunb. | Caffeic acid | 0.31 | |
| Chlorogenic acid | 0.49-25.09 | ||
| P-hydroxyacetophenone | 0.03 | ||
| Oleanolic acid | 4.03 | ||
| Rutin | 0.045 | ||
| Isoquercitrin | 0.0094 | ||
| 4,5-Dicaffeoylquinic acid | 0.92 | ||
| Hyperin | 0.0129 | ||
| Isorhamnetin-3-o-glucoside | 0.0039 | ||
| 3, 5-Dicaffeoylquinic acid | 4.21 | ||
| 4,5-O-dicaffeoyl quinic acid | 4.55 | ||
| Hyperoside | 0.52-7.81 | ||
| Yinchenhao Decoction | Catechin | 0.09-1.29 | |
| Chlorogenic acid | 0.43-18.12 | ||
| Gallic acid | 0.58 | ||
| Genipin | 0.0053 | ||
| Geniposide | 0.033-23.07 | ||
| p-Hydroxyacetophenone | 0.69 | ||
| Physcion | 0.004-1.20 | ||
| Quercetin | 0.041 | ||
| Scoparone | 0.15 | ||
| Scopoletin | 0.0087 | ||
| Emodin | 0.0083-1.39 | ||
| Crocin I | 1.38 | ||
| Crocin II | 0.15 | ||
| Rhein | 0.15-13.04 | ||
| Esculetin | 0.024 | ||
| Aloe-emodin | 0.041-6.26 | ||
| Aloe-emodin-8-O-β-D-glucoside | 0.20 | ||
| Chrysophanol-1-O-β-D-glucoside | 0.17 | ||
| deacetyl asperulosidic acid methylester | 0.67 | ||
| Hyperoside | 0.065 | ||
| Gardenia jasminoides Ellis | Chlorogenic acid | 0.12-0.27 | |
| Geniposide | 2.13-74.65 | ||
| Geniposidic acid | 1.04-1.99 | ||
| Neochlorogenic acid | 0.43 | ||
| Picrocrocin | 1.30 | ||
| Crocin I | 1.27-19.16 | ||
| Crocin II | 0.96-1.18 | ||
| 4-Dicaffeoylquinic Acid | 2.14 | ||
| Crocin III | 0.44 | ||
| Deacetyl asperulosidic acid methylester | 0.44-3.36 | ||
| Genipin 1-gentiobioside | 0.56-17.94 | ||
| Rutinum | 1.03 |
Tab.1 Collection of experimentally validated key components of the formula by HPLC
| Formula/Herbs | Component | Content (mg/g) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rheum palmatumL. | Catechin | 0.015-11.66 | |
| Chrysophanol | 0.17-4.36 | ||
| (-)-epicatechin | 0.98-6.33 | ||
| Gallic acid | 0.041-4.21 | ||
| Isolindleyin | 0.056-4.37 | ||
| Lindleyin | 0.40-4.02 | ||
| Phenylbutanone-glucoside | 0.36 | ||
| Physcion | 0.09-0.15 | ||
| 4,3,5'-trihydroxystilbene-4-(6"-galloyl-glucoside) | 0.14-0.20 | ||
| Emodin | 0.058-4.15 | ||
| Rhein | 0.08-4.97 | ||
| Physcione | 0.056-1.66 | ||
| Sennoside B | 0.47-1.59 | ||
| 3,4,3',5'-tetrahydroxystilbene-3-glucoside | 0.05 | ||
| (-)-Epicatechin gallate | 0.37-0.045 | ||
| (+)-catechin | 0.07-0.79 | ||
| 1,6-digalloyl-2-cinnamoyi-glucose | 0.07-0.30 | ||
| 1-galloyl-2-cinnamoyl-glucose | 0.63-1.48 | ||
| 2-cinnamoyl-glucose | 0.13-0.42 | ||
| 4-4-HydroxyphenylButan-2-One | 0.48 | ||
| Aloe-emodin-8-glucoside | 0.31-0.46 | ||
| Chrysophanol-8-glucoside | 0.52-1.08 | ||
| Emodin-8-glucoside | 0.10-1.16 | ||
| Epicatechin | 0.28-0.70 | ||
| Musizin-glucoside | 0.06-0.82 | ||
| Physcion-8-glucoside | 0.20-0.78 | ||
| Sennosides | 0.40-2.20 | ||
| Torachrysone-8-glucoside | 0.12-0.25 | ||
| Trans-cinnamic acid | 1.05 | ||
| Artemisia capillaris Thunb. | Caffeic acid | 0.31 | |
| Chlorogenic acid | 0.49-25.09 | ||
| P-hydroxyacetophenone | 0.03 | ||
| Oleanolic acid | 4.03 | ||
| Rutin | 0.045 | ||
| Isoquercitrin | 0.0094 | ||
| 4,5-Dicaffeoylquinic acid | 0.92 | ||
| Hyperin | 0.0129 | ||
| Isorhamnetin-3-o-glucoside | 0.0039 | ||
| 3, 5-Dicaffeoylquinic acid | 4.21 | ||
| 4,5-O-dicaffeoyl quinic acid | 4.55 | ||
| Hyperoside | 0.52-7.81 | ||
| Yinchenhao Decoction | Catechin | 0.09-1.29 | |
| Chlorogenic acid | 0.43-18.12 | ||
| Gallic acid | 0.58 | ||
| Genipin | 0.0053 | ||
| Geniposide | 0.033-23.07 | ||
| p-Hydroxyacetophenone | 0.69 | ||
| Physcion | 0.004-1.20 | ||
| Quercetin | 0.041 | ||
| Scoparone | 0.15 | ||
| Scopoletin | 0.0087 | ||
| Emodin | 0.0083-1.39 | ||
| Crocin I | 1.38 | ||
| Crocin II | 0.15 | ||
| Rhein | 0.15-13.04 | ||
| Esculetin | 0.024 | ||
| Aloe-emodin | 0.041-6.26 | ||
| Aloe-emodin-8-O-β-D-glucoside | 0.20 | ||
| Chrysophanol-1-O-β-D-glucoside | 0.17 | ||
| deacetyl asperulosidic acid methylester | 0.67 | ||
| Hyperoside | 0.065 | ||
| Gardenia jasminoides Ellis | Chlorogenic acid | 0.12-0.27 | |
| Geniposide | 2.13-74.65 | ||
| Geniposidic acid | 1.04-1.99 | ||
| Neochlorogenic acid | 0.43 | ||
| Picrocrocin | 1.30 | ||
| Crocin I | 1.27-19.16 | ||
| Crocin II | 0.96-1.18 | ||
| 4-Dicaffeoylquinic Acid | 2.14 | ||
| Crocin III | 0.44 | ||
| Deacetyl asperulosidic acid methylester | 0.44-3.36 | ||
| Genipin 1-gentiobioside | 0.56-17.94 | ||
| Rutinum | 1.03 |
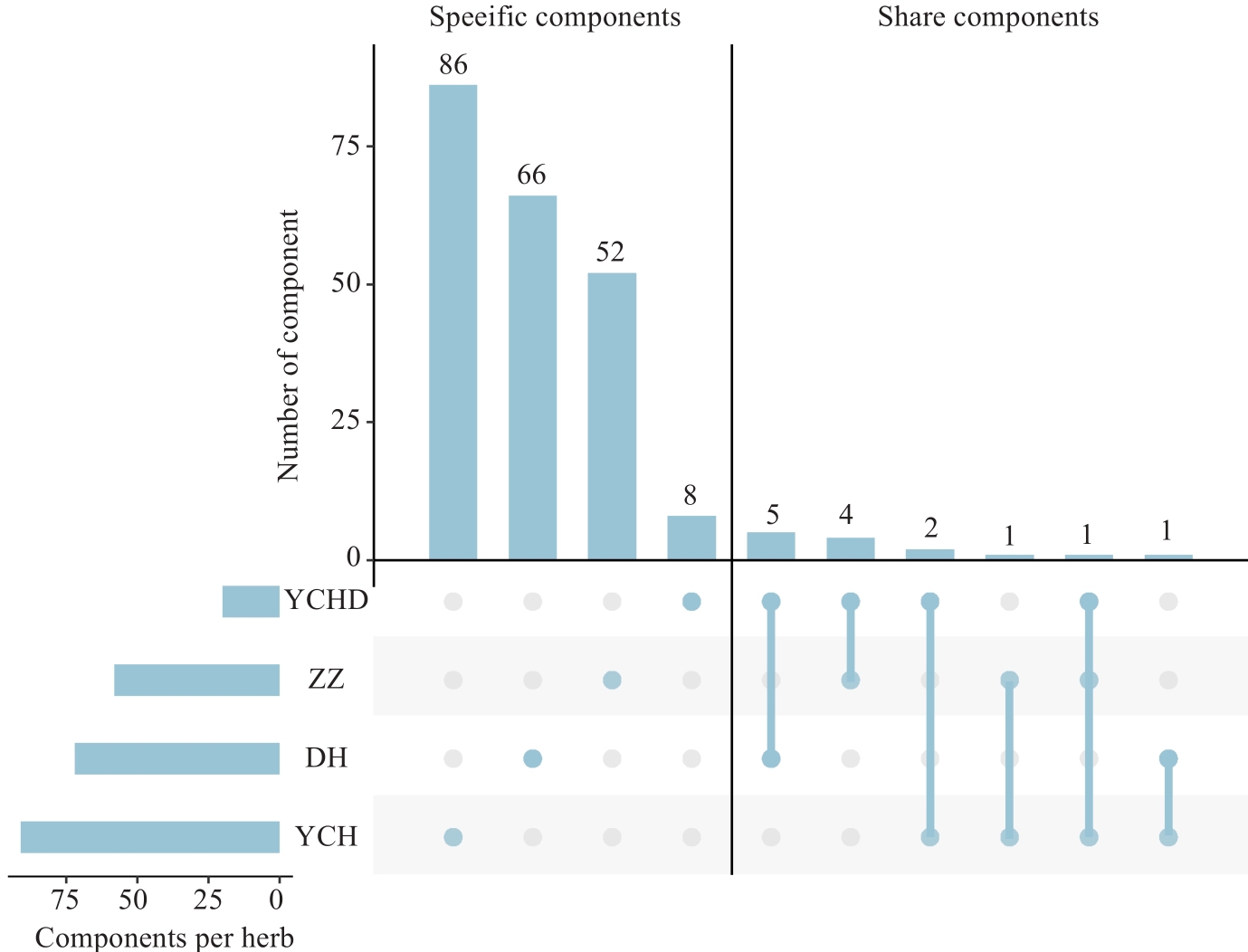
Fig.2 Distribution of sepecific and common chemical components in 3 medicinal plants and prescriptions in YCHD (ZZ, DH and YCH refer to Zhizi, Dahuang and Yinchenhao).
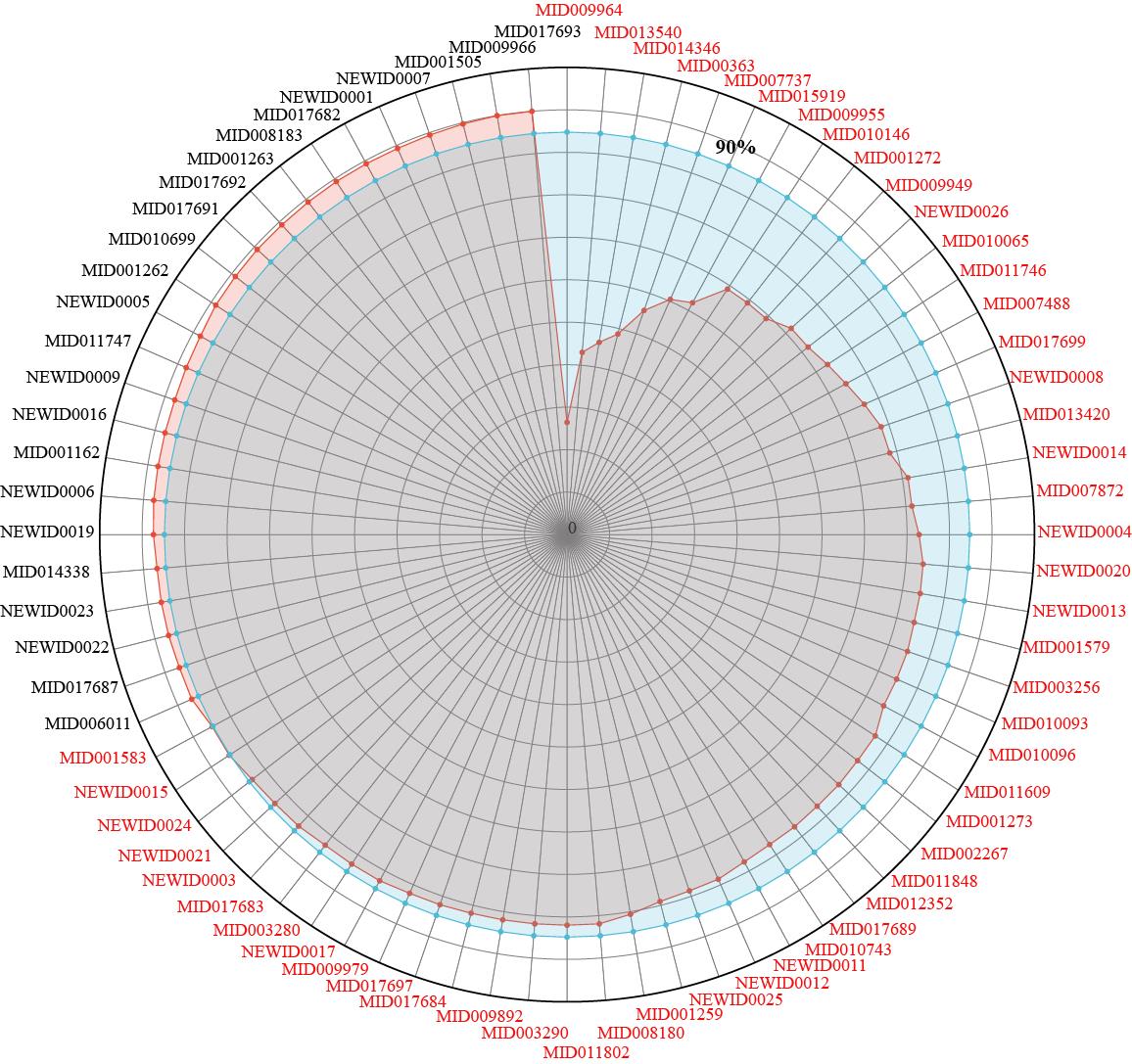
Fig.3 Core functional component groups (CFCG) in YCHD and its distribution rate. MID and NEWID represent the ID of the active ingredients; the red line represents the coverage of active ingredients from 0 to 100%; the blue line represents 90% coverage; the contribution rate of 52 components of labeled red was less than 90%, which was defined as the CFCG of YCHD.
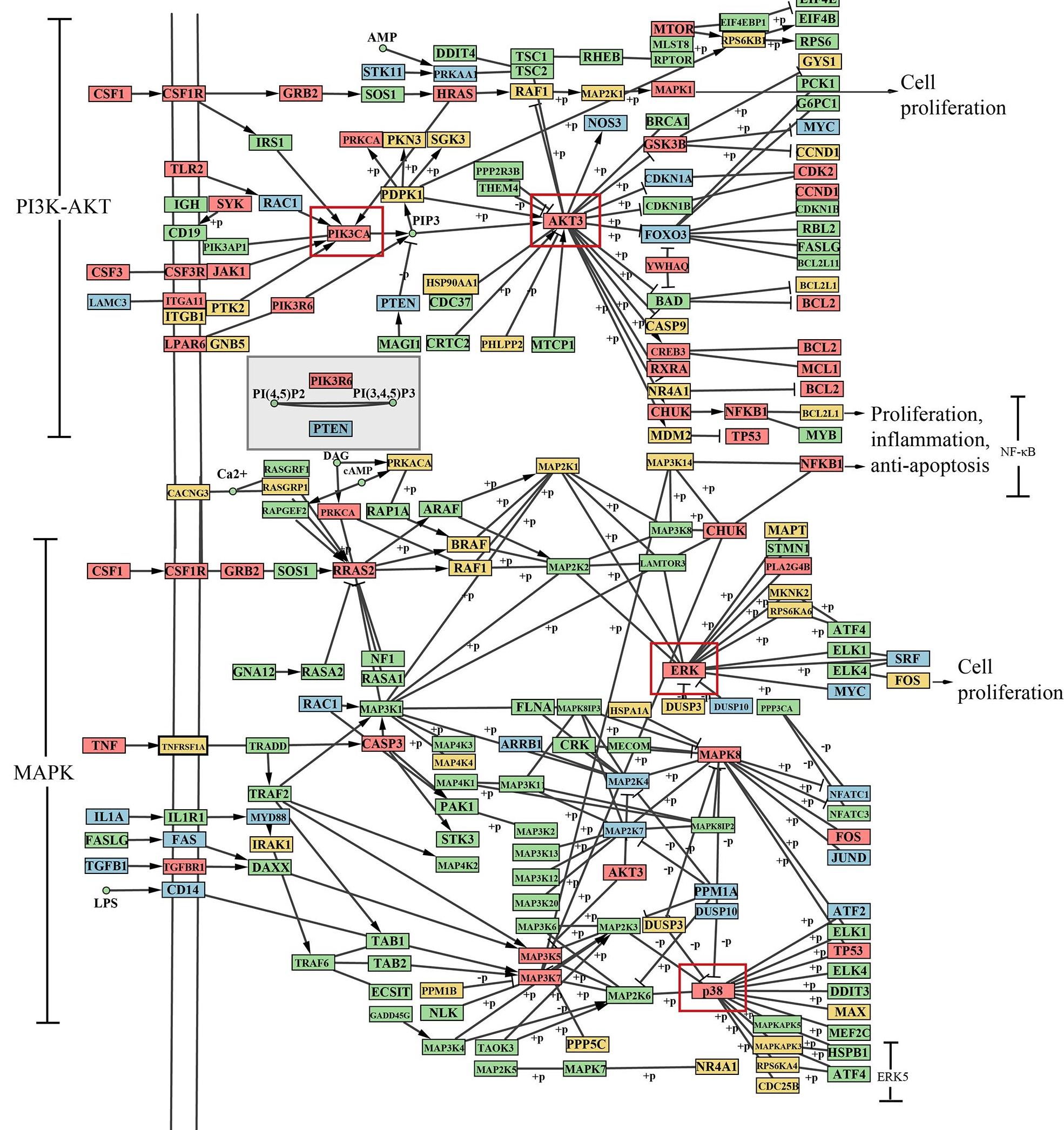
Fig.5 Distribution of CFCG targets and pathogenic genes in the integrated pathway. The blue, orange and pink frames represent pathogenic genes, CFCG targets and their common genes, respectively.
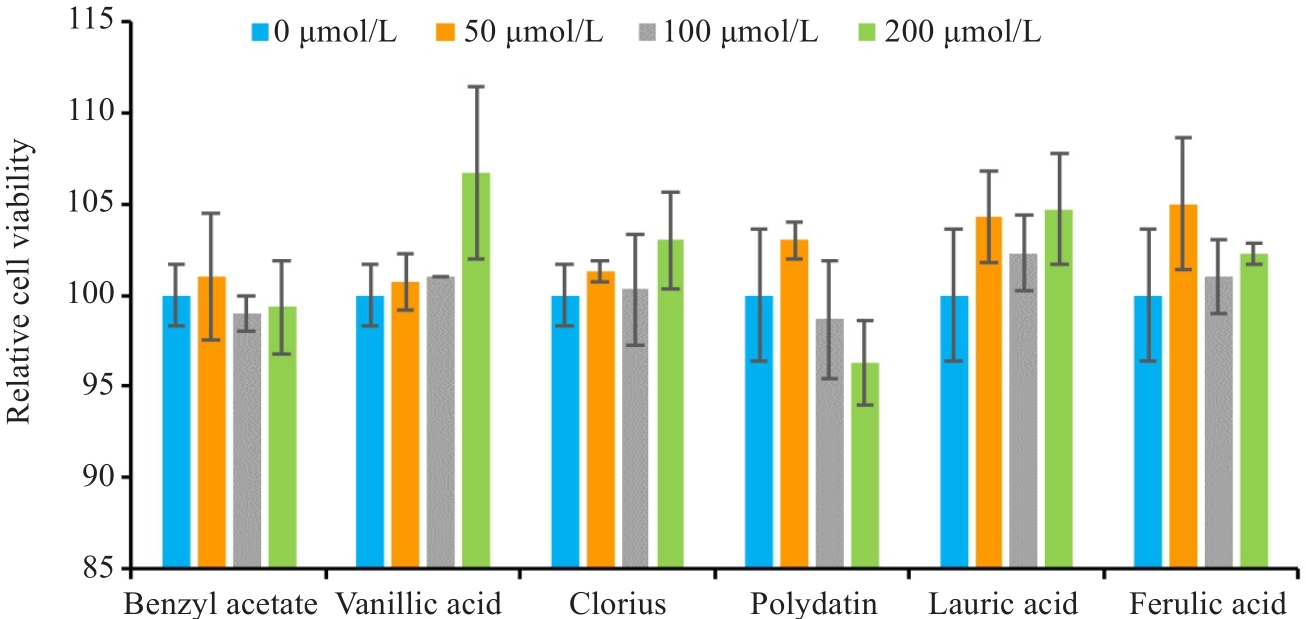
Fig.6 CCK-8 assay of LX-2 cells treated with benzyl acetate, vanillic acid, clorius, polydatin, lauric acid or ferulic acid (drug concentration: 0-200 μmol/L).
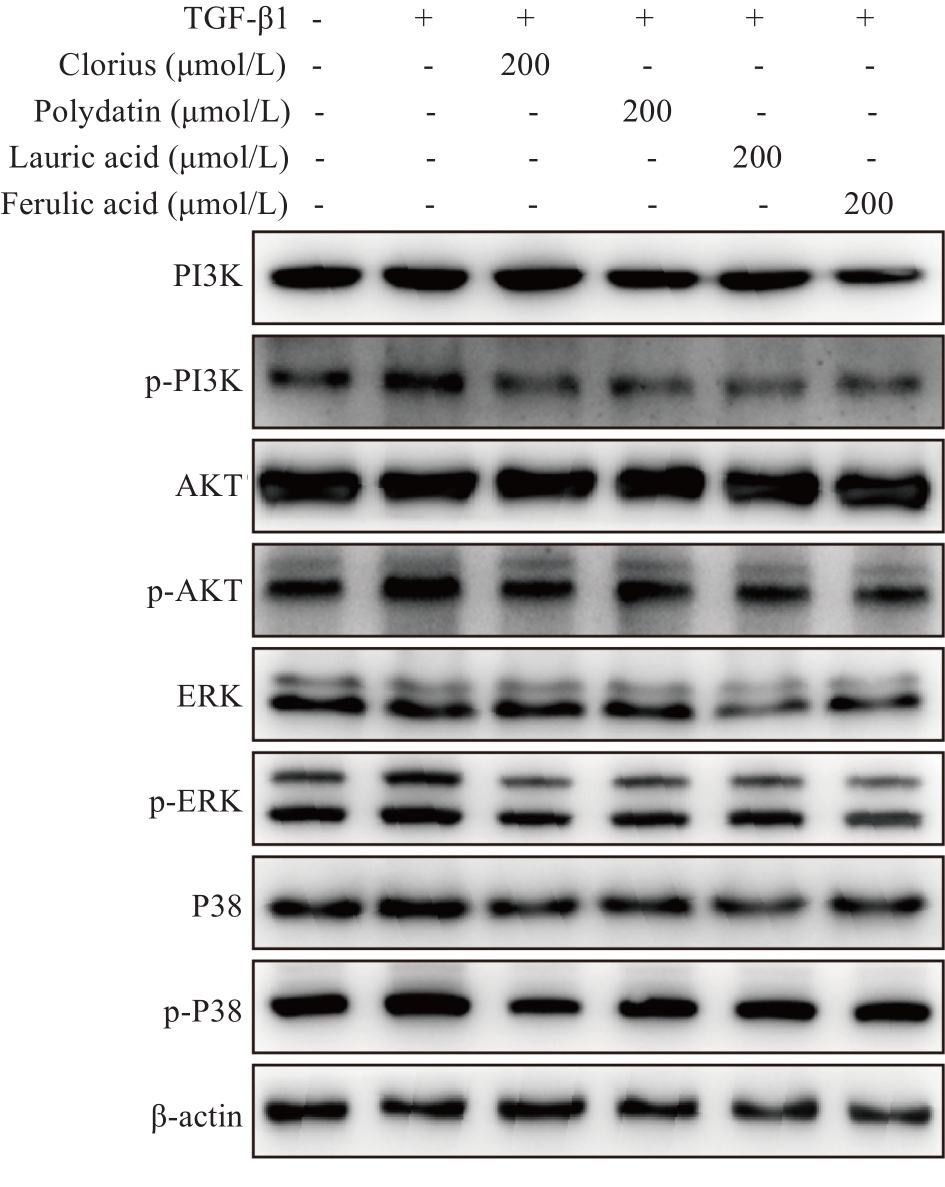
Fig.8 Western blotting of PI3K, AKT and MAPK expressions in TGF‑β1-induced LX-2 cells treated with clorius, polydatin, lauric acid and ferulic acid (Mean±SD, n=3).
| 1 | Caligiuri A, Gentilini A, Pastore M, et al. Cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying liver fibrosis regression[J]. Cells, 2021, 10(10): 2759. |
| 2 | Li Z, Zhu JF, Ouyang H. Research progress of traditional Chinese medicine in improving hepatic fibrosis based on inhibiting pathological angiogenesis[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2023, 14: 1303012. |
| 3 | Li H. Advances in anti hepatic fibrotic therapy with Traditional Chinese Medicine herbal formula[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2020, 251: 112442. |
| 4 | Xu FP, Zhang H, Chen JM, et al. Recent progress on the application of compound formulas of traditional Chinese medicine in clinical trials and basic research in vivo for chronic liver disease[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2024, 321: 117514. |
| 5 | Ma Z, Zhang B, Fan YQ, et al. Traditional Chinese medicine combined with hepatic targeted drug delivery systems: a new strategy for the treatment of liver diseases[J]. Biomedecine Pharmacother, 2019, 117: 109128. |
| 6 | He ZW, Chen SY, Pan TT, et al. Ginsenoside Rg2 ameliorating CDAHFD-induced hepatic fibrosis by regulating AKT/mTOR-mediated autophagy[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2022, 70(6): 1911-22. |
| 7 | Cai YJ, Zheng Q, Sun R, et al. Recent progress in the study of Artemisiae Scopariae Herba (Yin Chen), a promising medicinal herb for liver diseases[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2020, 130: 110513. |
| 8 | Wei CL, Qiu J, Wu YY, et al. Promising traditional Chinese medicine for the treatment of cholestatic liver disease process (cholestasis, hepatitis, liver fibrosis, liver cirrhosis)[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2022, 297: 115550. |
| 9 | Liu JJ, Xu Y, Chen S, et al. The mechanism of Yinchenhao Decoction in treating obstructive-jaundice-induced liver injury based on Nrf2 signaling pathway[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2022, 28(32): 4635-48. |
| 10 | Xu L, Xie T, Shen T, et al. Yinchenhao decoction for chronic hepatitis B: Protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Medicine, 2019, 98(8): e14648. |
| 11 | Zhang P, Zhang DF, Zhou WA, et al. Network pharmacology: towards the artificial intelligence-based precision traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Brief Bioinform, 2023, 25(1): bbad518. |
| 12 | Nogales C, Mamdouh ZM, List M, et al. Network pharmacology: curing causal mechanisms instead of treating symptoms[J]. Trends Pharmacol Sci, 2022, 43(2): 136-50. |
| 13 | Wu Q, Yin CH, Li Y, et al. Detecting critical functional ingredients group and mechanism of xuebijing injection in treating sepsis[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2021, 12: 769190. |
| 14 | Cai FF, Bian YQ, Wu R, et al. Yinchenhao decoction suppresses rat liver fibrosis involved in an apoptosis regulation mechanism based on network pharmacology and transcriptomic analysis[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2019, 114: 108863. |
| 15 | Huang L, Xie DL, Yu YR, et al. TCMID 2.0: a comprehensive resource for TCM[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2018, 46(D1): D1117-D1120. |
| 16 | Wu Y, Zhang FL, Yang K, et al. SymMap: an integrative database of traditional Chinese medicine enhanced by symptom mapping[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2019, 47(D1): D1110-D1117. |
| 17 | Xu HY, Zhang YQ, Liu ZM, et al. ETCM: an encyclopaedia of traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2019, 47(D1): D976-D982. |
| 18 | Khan HU, Aamir K, Jusuf PR, et al. Lauric acid ameliorates lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced liver inflammation by mediating TLR4/MyD88 pathway in Sprague Dawley (SD) rats[J]. Life Sci, 2021, 265: 118750. |
| 19 | Shan L, Wang FL, Xue WJ, et al. New insights into fibrotic signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Front Oncol, 2023, 13: 1196298. |
| 20 | Mu M, Zuo S, Wu RM, et al. Ferulic acid attenuates liver fibrosis and hepatic stellate cell activation via inhibition of TGF‑β/Smad signaling pathway[J]. Drug Des Devel Ther, 2018, 12: 4107-15. |
| 21 | Zhao XM, Zhang J, Liang YN, et al. Astragaloside IV synergizes with ferulic acid to alleviate hepatic fibrosis in bile duct-ligated cirrhotic rats[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2020, 65(10): 2925-36. |
| 22 | Tang DD, Zhang Q, Duan H, et al. Polydatin: a critical promising natural agent for liver protection via antioxidative stress[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2022, 2022: 9218738. |
| 23 | Cheng K, Niu JY, Zheng XT, et al. Aflatoxin-B1-exposure-induced hepatic injury could be alleviated by polydatin through reducing oxidative stress, inhibiting inflammation and improving mitophagy[J]. Toxics, 2023, 11(4): 309. |
| 24 | Peng RQ, Wang SZ, Wang R, et al. Antifibrotic effects of tanshinol in experimental hepatic fibrosis by targeting PI3K/AKT/mTOR/p70S6K1 signaling pathways[J]. Discov Med, 2017, 23(125): 81-94. |
| 25 | Lei Y, Wang QL, Shen L, et al. MicroRNA-101 suppresses liver fibrosis by downregulating PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway[J]. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol, 2019, 43(5): 575-84. |
| 26 | Xiao Q, Yu HB, Zhu X. The associations of hub gene polymorphisms in PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and Schistosomiasis Japonica infection and hepatic fibrosis[J]. Infect Genet Evol, 2020, 85: 104423. |
| 27 | Su GY, Li ZY, Wang R, et al. Signaling pathways involved in p38-ERK and inflammatory factors mediated the anti-fibrosis effect of AD-2 on thioacetamide-induced liver injury in mice[J]. Food Funct, 2019, 10(7): 3992-4000. |
| 28 | Wang Y, Song JY, Bian HY, et al. Apelin promotes hepatic fibrosis through ERK signaling in LX-2 cells[J]. Mol Cell Biochem, 2019, 460(1/2): 205-15. |
| 29 | Huang Y, Wang ZL, He Y, et al. Jiawei Taohe Chengqi Decoction attenuates hepatic fibrosis by preventing activation of HSCs through regulating Src/ERK/Smad3 signal pathway[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2023, 305: 116059. |
| 30 | Wang R, Zhang H, Wang YY, et al. Inhibitory effects of quercetin on the progression of liver fibrosis through the regulation of NF-кB/IкBα, p38 MAPK, and Bcl-2/Bax signaling[J]. Int Immuno-pharmacol, 2017, 47: 126-33. |
| [1] | Xinyuan CHEN, Chengting WU, Ruidi LI, Xueqin PAN, Yaodan ZHANG, Junyu TAO, Caizhi LIN. Shuangshu Decoction inhibits growth of gastric cancer cell xenografts by promoting cell ferroptosis via the P53/SLC7A11/GPX4 axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1363-1371. |
| [2] | Liming WANG, Hongrui CHEN, Yan DU, Peng ZHAO, Yujie WANG, Yange TIAN, Xinguang LIU, Jiansheng LI. Yiqi Zishen Formula ameliorates inflammation in mice with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1409-1422. |
| [3] | Yinfu ZHU, Yiran LI, Yi WANG, Yinger HUANG, Kunxiang GONG, Wenbo HAO, Lingling SUN. Therapeutic mechanism of hederagenin, an active component in Guizhi Fuling Pellets, against cervical cancer in nude mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1423-1433. |
| [4] | Lijun HE, Xiaofei CHEN, Chenxin YAN, Lin SHI. Inhibitory effect of Fuzheng Huaji Decoction against non-small cell lung cancer cells in vitro and the possible molecular mechanism [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1143-1152. |
| [5] | Guoyong LI, Renling LI, Yiting LIU, Hongxia KE, Jing LI, Xinhua WANG. Therapeutic mechanism of Arctium lappa extract for post-viral pneumonia pulmonary fibrosis: a metabolomics, network pharmacology analysis and experimental verification [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1185-1199. |
| [6] | Liping GUAN, Yan YAN, Xinyi LU, Zhifeng LI, Hui GAO, Dong CAO, Chenxi HOU, Jingyu ZENG, Xinyi LI, Yang ZHAO, Junjie WANG, Huilong FANG. Compound Centella asiatica formula alleviates Schistosoma japonicum-induced liver fibrosis in mice by inhibiting the inflammation-fibrosis cascade via regulating the TLR4/MyD88 pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1307-1316. |
| [7] | Peipei TANG, Yong TAN, Yanyun YIN, Xiaowei NIE, Jingyu HUANG, Wenting ZUO, Yuling LI. Tiaozhou Ziyin recipe for treatment of premature ovarian insufficiency: efficacy, safety and mechanism [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 929-941. |
| [8] | Xiaotao LIANG, Yifan XIONG, Xueqi LIU, Xiaoshan LIANG, Xiaoyu ZHU, Wei XIE. Huoxue Shufeng Granule alleviates central sensitization in chronic migraine mice via TLR4/NF-κB inflammatory pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 986-994. |
| [9] | Niandong RAN, Jie LIU, Jian XU, Yongping ZHANG, Jiangtao GUO. n-butanol fraction of ethanol extract of Periploca forrestii Schltr.: its active components, targets and pathways for treating Alcheimer's disease in rats [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 785-798. |
| [10] | Haonan¹ XU, Fang³ ZHANG, Yuying² HUANG, Qisheng⁴ YAO, Yueqin⁴ GUAN, Hao CHEN. Thesium chinense Turcz. alleviates antibiotic-associated diarrhea in mice by modulating gut microbiota structure and regulating the EGFR/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 285-295. |
| [11] | Junjie GAO, Kai YE, Jing WU. Quercetin inhibits proliferation and migration of clear cell renal cell carcinoma cells by regulating TP53 gene [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 313-321. |
| [12] | Ying LIU, Borui LI, Yongcai LI, Lubo CHANG, Jiao WANG, Lin YANG, Yonggang YAN, Kai QV, Jiping LIU, Gang ZHANG, Xia SHEN. Jiawei Xiaoyao Pills improves depression-like behavior in rats by regulating neurotransmitters, inhibiting inflammation and oxidation and modulating intestinal flora [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 347-358. |
| [13] | Qiao CHU, Xiaona WANG, Jiaying XU, Huilin PENG, Yulin ZHAO, Jing ZHANG, Guoyu LU, Kai WANG. Pulsatilla saponin D inhibits invasion and metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer cells through multiple targets and pathways [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 150-161. |
| [14] | Xiupeng LONG, Shun TAO, Shen YANG, Suyun LI, Libing RAO, Li LI, Zhe ZHANG. Quercetin improves heart failure by inhibiting cardiomyocyte apoptosis via suppressing the MAPK signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 187-196. |
| [15] | Meng XU, Lina CHEN, Jinyu WU, Lili LIU, Mei SHI, Hao ZHOU, Guoliang ZHANG. Mechanism of Hedyotis diffusa-Scutellaria barbata D. Don for treatment of primary liver cancer: analysis with network pharmacology, molecular docking and in vitro validation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 80-89. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||