Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (5): 941-949.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.05.16
• Clinical Research • Previous Articles Next Articles
Bei PEI1( ), Yi ZHANG1, Siyuan WEI1, Yu MEI1, Biao SONG1, Gang DONG1, Ziang WEN2, Xuejun LI1(
), Yi ZHANG1, Siyuan WEI1, Yu MEI1, Biao SONG1, Gang DONG1, Ziang WEN2, Xuejun LI1( )
)
Received:2023-09-25
Online:2024-05-20
Published:2024-06-06
Contact:
Xuejun LI
E-mail:18356051572@163.com;lixujun0308@126.com
Bei PEI, Yi ZHANG, Siyuan WEI, Yu MEI, Biao SONG, Gang DONG, Ziang WEN, Xuejun LI. Identification of potential pathogenic genes of intestinal metaplasia based on transcriptomic sequencing and bioinformatics analysis[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(5): 941-949.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.05.16
| Name | Forward primer | Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| AGMAT | 5′-CTCACTCCTAGTCAGGCTC-3′ | 5′-TGAAACTTCGACAAGATCACAG-3′ |
| CCL25 | 5′-CACCCAAGGTGTCTTTGAG-3′ | 5′-CTGGATCCGGTAAGTCCAG-3′ |
| FABP1 | 5′-CATGAAGGCAATCGGTCTG-3′ | 5′-CCATTCTGCACGATTTCCG-3′ |
| SPINK4 | 5′-TCAAGAATGCCCATCTGTG-3′ | 5′-ATATGTGAGCCCATCAGTG-3′ |
| CDX1 | 5′-TCGGACCAAGGACAAGTACC-3′ | 5′-AGATCTTCACCTGCCGTTCA-3′ |
| MUC2 | 5′-GCTGTCCCTTCTACTGGTGT-3′ | 5′-GTTGAGCAGGGTGTTGTTGT-3′ |
Tab.1 PCR primer sequences of the target genes
| Name | Forward primer | Reverse primer |
|---|---|---|
| AGMAT | 5′-CTCACTCCTAGTCAGGCTC-3′ | 5′-TGAAACTTCGACAAGATCACAG-3′ |
| CCL25 | 5′-CACCCAAGGTGTCTTTGAG-3′ | 5′-CTGGATCCGGTAAGTCCAG-3′ |
| FABP1 | 5′-CATGAAGGCAATCGGTCTG-3′ | 5′-CCATTCTGCACGATTTCCG-3′ |
| SPINK4 | 5′-TCAAGAATGCCCATCTGTG-3′ | 5′-ATATGTGAGCCCATCAGTG-3′ |
| CDX1 | 5′-TCGGACCAAGGACAAGTACC-3′ | 5′-AGATCTTCACCTGCCGTTCA-3′ |
| MUC2 | 5′-GCTGTCCCTTCTACTGGTGT-3′ | 5′-GTTGAGCAGGGTGTTGTTGT-3′ |
| Indexes | Control group | IM group | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | 56.76±10.64 | 60.62±9.02 | 0.2124 |
| Gender | 0.7579 | ||
| Male | 10 | 12 | |
| Female | 11 | 9 | |
| Smoking history | 0.6965 | ||
| Yes | 3 | 5 | |
| No | 18 | 16 | |
| Drinking history | 0.4841 | ||
| Yes | 4 | 7 | |
| No | 17 | 14 | |
| Diet | 0.6060 | ||
| Irregular | 1 | 3 | |
| Regular | 20 | 18 | |
| Diabetes | 0.9999 | ||
| Yes | 0 | 1 | |
| No | 21 | 20 | |
| Hypertension | 0.6965 | ||
| Yes | 3 | 5 | |
| No | 18 | 16 | |
| Hyperlipidemia | 0.7186 | ||
| Yes | 4 | 6 | |
| No | 17 | 15 | |
| Family history of tumors | 0.6060 | ||
| Yes | 1 | 3 | |
| No | 20 | 18 | |
| H. pylori infection | 0.9999 | ||
| Yes | 0 | 0 | |
| No | 21 | 21 |
Tab.2 Demographic and clinical characteristics of the 21 patients with intestinal metaplasia (IM) and the control subjects
| Indexes | Control group | IM group | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | 56.76±10.64 | 60.62±9.02 | 0.2124 |
| Gender | 0.7579 | ||
| Male | 10 | 12 | |
| Female | 11 | 9 | |
| Smoking history | 0.6965 | ||
| Yes | 3 | 5 | |
| No | 18 | 16 | |
| Drinking history | 0.4841 | ||
| Yes | 4 | 7 | |
| No | 17 | 14 | |
| Diet | 0.6060 | ||
| Irregular | 1 | 3 | |
| Regular | 20 | 18 | |
| Diabetes | 0.9999 | ||
| Yes | 0 | 1 | |
| No | 21 | 20 | |
| Hypertension | 0.6965 | ||
| Yes | 3 | 5 | |
| No | 18 | 16 | |
| Hyperlipidemia | 0.7186 | ||
| Yes | 4 | 6 | |
| No | 17 | 15 | |
| Family history of tumors | 0.6060 | ||
| Yes | 1 | 3 | |
| No | 20 | 18 | |
| H. pylori infection | 0.9999 | ||
| Yes | 0 | 0 | |
| No | 21 | 21 |
| Name | Description | P |
|---|---|---|
| AGMAT | Agmatinase | 3.51×10-13 |
| CCL25 | C-C motif chemokine ligand 25 | 8.86×10-13 |
| FABP1 | Fatty acid binding protein 1 | 6.22×10-11 |
| MUC2 | Mucin 2 | 1.95×10-10 |
| SPINK4 | Serine peptidase inhibitor Kazal type 4 | 1.04×10-9 |
| ANXA13 | Annexin A13 | 1.24×10-9 |
| GIP | Gastric inhibitory polypeptide | 2.01×10-9 |
| KCP | Kielin cysteine rich BMP regulator | 2.48×10-9 |
| DEFA5 | Defensin alpha 5 | 2.55×10-9 |
| ZG16 | Zymogen granule protein 16 | 4.38×10-9 |
| CDX1 | Caudal type homeobox 1 | 9.33×10-9 |
| RAB3B | RAB3B, member RAS oncogene family | 1.35×10-8 |
| PTAFR | Platelet activating factor receptor | 2.37×10-8 |
| RBP2 | Retinol binding protein 2 | 4.19×10-8 |
| OLFM4 | Olfactomedin 4 | 4.19×10-8 |
| ALPI | Alkaline phosphatase, intestinal | 6.04×10-8 |
| MOCOS | Molybdenum cofactor sulfurase | 8.81×10-8 |
| SLC6A20 | Solute carrier family 6 member 20 | 1.18×10-7 |
| HOXB9 | Homeobox B9 | 2.88×10-7 |
| CPS1 | Carbamoyl-phosphate synthase 1 | 3.00×10-7 |
Tab.3 Top 20 upregulated genes in intestinal metaplasia
| Name | Description | P |
|---|---|---|
| AGMAT | Agmatinase | 3.51×10-13 |
| CCL25 | C-C motif chemokine ligand 25 | 8.86×10-13 |
| FABP1 | Fatty acid binding protein 1 | 6.22×10-11 |
| MUC2 | Mucin 2 | 1.95×10-10 |
| SPINK4 | Serine peptidase inhibitor Kazal type 4 | 1.04×10-9 |
| ANXA13 | Annexin A13 | 1.24×10-9 |
| GIP | Gastric inhibitory polypeptide | 2.01×10-9 |
| KCP | Kielin cysteine rich BMP regulator | 2.48×10-9 |
| DEFA5 | Defensin alpha 5 | 2.55×10-9 |
| ZG16 | Zymogen granule protein 16 | 4.38×10-9 |
| CDX1 | Caudal type homeobox 1 | 9.33×10-9 |
| RAB3B | RAB3B, member RAS oncogene family | 1.35×10-8 |
| PTAFR | Platelet activating factor receptor | 2.37×10-8 |
| RBP2 | Retinol binding protein 2 | 4.19×10-8 |
| OLFM4 | Olfactomedin 4 | 4.19×10-8 |
| ALPI | Alkaline phosphatase, intestinal | 6.04×10-8 |
| MOCOS | Molybdenum cofactor sulfurase | 8.81×10-8 |
| SLC6A20 | Solute carrier family 6 member 20 | 1.18×10-7 |
| HOXB9 | Homeobox B9 | 2.88×10-7 |
| CPS1 | Carbamoyl-phosphate synthase 1 | 3.00×10-7 |
| Name | Description | P |
|---|---|---|
| CARNS1 | Carnosine synthase 1 | 2.38×10-13 |
| SH3GL2 | SH3 domain containing GRB2 like 2, endophilin A1FT | 3.08×10-13 |
| RGMB | Repulsive guidance molecule BMP co-receptor bFT | 2.28×10-10 |
| ZNF334 | Zinc finger protein 334 | 8.71×10-10 |
| WIPF3 | WAS/WASL interacting protein family member 3FT | 4.81×10-9 |
| PM20D1 | Peptidase M20 domain containing 1 | 5.08×10-9 |
| KLHDC8A | Kelch domain containing 8A | 1.34×10-8 |
| RGS7 | Regulator of G protein signaling 7 | 1.50×10-8 |
| RGN | Regucalcin | 2.75×10-8 |
| RPS6KA6 | Ribosomal protein S6 kinase A6 | 5.64×10-8 |
| NCMAP | Non-compact myelin associated protein | 5.99×10-8 |
| EDARADD | EDAR associated death domain | 7.13×10-8 |
| GPC3 | Glypican 3 | 7.53×10-8 |
| TMEM151A | Transmembrane protein 151A | 1.07×10-7 |
| PER3 | Period circadian regulator 3 | 1.20×10-7 |
| ZNF677 | Zinc finger protein 677 | 1.55×10-7 |
| RNF217 | Ring finger protein 217 | 1.75×10-7 |
| PWWP3B | PWWP domain containing 3B | 1.79×10-7 |
| ZFP28 | ZFP28 zinc finger protein | 1.91×10-7 |
| CYB5R1 | Cytochrome b5 reductase 1 | 2.74×10-7 |
Tab.4 Top 20 downregulated genes in intestinal metaplasia
| Name | Description | P |
|---|---|---|
| CARNS1 | Carnosine synthase 1 | 2.38×10-13 |
| SH3GL2 | SH3 domain containing GRB2 like 2, endophilin A1FT | 3.08×10-13 |
| RGMB | Repulsive guidance molecule BMP co-receptor bFT | 2.28×10-10 |
| ZNF334 | Zinc finger protein 334 | 8.71×10-10 |
| WIPF3 | WAS/WASL interacting protein family member 3FT | 4.81×10-9 |
| PM20D1 | Peptidase M20 domain containing 1 | 5.08×10-9 |
| KLHDC8A | Kelch domain containing 8A | 1.34×10-8 |
| RGS7 | Regulator of G protein signaling 7 | 1.50×10-8 |
| RGN | Regucalcin | 2.75×10-8 |
| RPS6KA6 | Ribosomal protein S6 kinase A6 | 5.64×10-8 |
| NCMAP | Non-compact myelin associated protein | 5.99×10-8 |
| EDARADD | EDAR associated death domain | 7.13×10-8 |
| GPC3 | Glypican 3 | 7.53×10-8 |
| TMEM151A | Transmembrane protein 151A | 1.07×10-7 |
| PER3 | Period circadian regulator 3 | 1.20×10-7 |
| ZNF677 | Zinc finger protein 677 | 1.55×10-7 |
| RNF217 | Ring finger protein 217 | 1.75×10-7 |
| PWWP3B | PWWP domain containing 3B | 1.79×10-7 |
| ZFP28 | ZFP28 zinc finger protein | 1.91×10-7 |
| CYB5R1 | Cytochrome b5 reductase 1 | 2.74×10-7 |
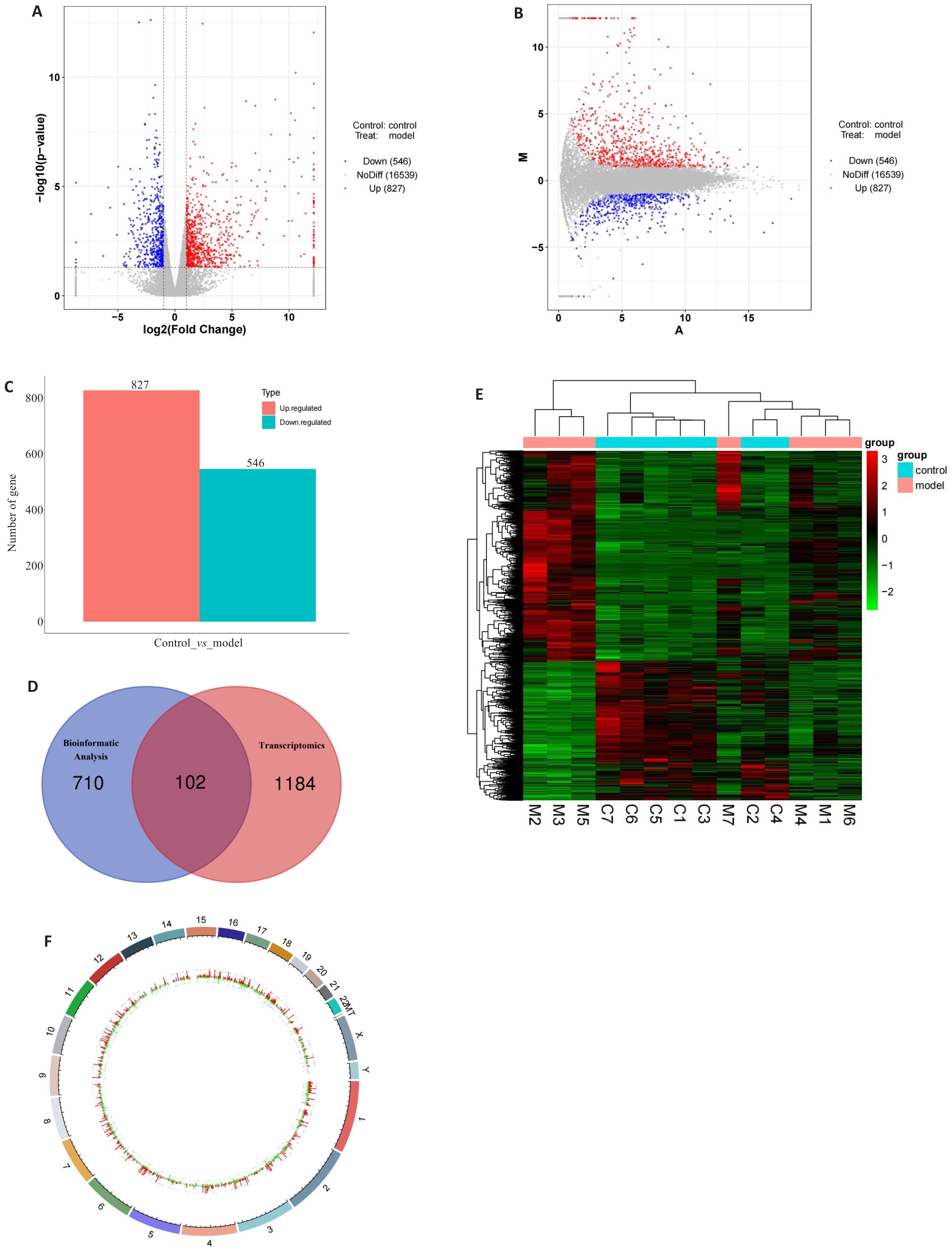
Fig.1 Screening and analysis of the differentially expressed genes in intestinal metaplasia. A: Volcano plot of the differentially expressed genes. B: MA volcano plot of the differentially expressed genes. C: Histogram of the number of the differentially expressed genes. D: Venn diagram of the differentially expressed genes in transcriptomics sequencing group and the bioinformatic analysis group. E: Heatmap of the distribution of the differentially expressed genes in gastric tissues between the experimental and control groups. F: Genomic circle plot of the differentially expressed genes.
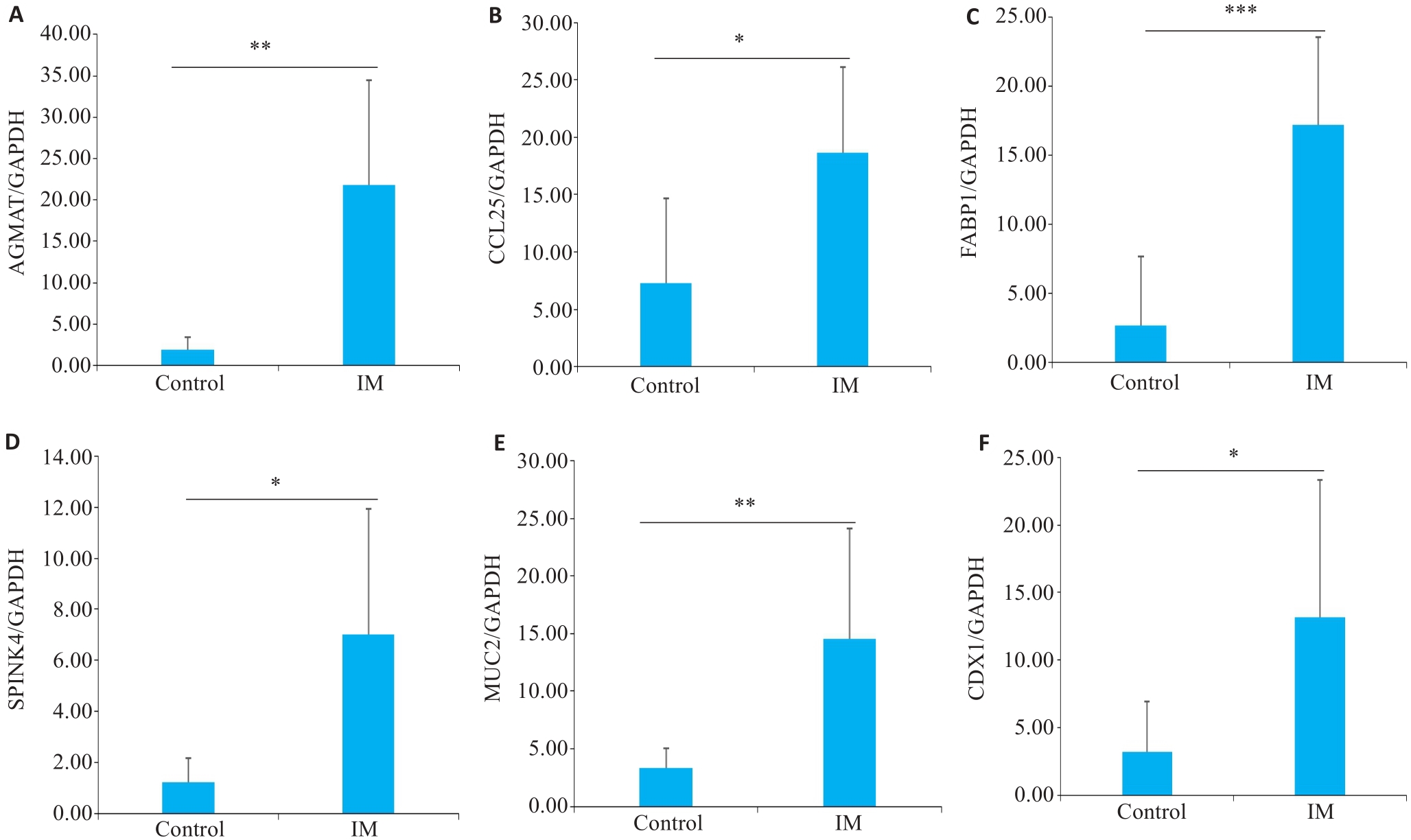
Fig.5 Results of qRT-PCR for detecting mRNA expressions of AGMAT, CCL25, FABP1, SPINK4, MUC2 and CDX1 (A-F, respectively) in the gastric tissues of patients with intestinal metaplasia (IM) and the control subjects. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
| 1 | Jonaitis P, Kupcinskas L, Kupcinskas J. Molecular alterations in gastric intestinal Metaplasia [J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(11): 5758. DOI: 10.3390/ijms22115758 |
| 2 | Aumpan N, Vilaichone RK, Pornthisarn B, et al. Predictors for regression and progression of intestinal metaplasia (IM): a large population-based study from low prevalence area of gastric cancer (IM-predictor trial)[J]. PLoS One, 2021, 16(8): e0255601. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0255601 |
| 3 | Lee JWJ, Zhu F, Srivastava S, et al. Severity of gastric intestinal metaplasia predicts the risk of gastric cancer: a prospective multicentre cohort study (GCEP)[J]. Gut, 2022, 71(5): 854-63. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2021-324057 |
| 4 | Gawron AJ, Shah SC, Altayar O, et al. AGA technical review on gastric intestinal Metaplasia-natural history and clinical outcomes[J]. Gastroenterology, 2020, 158(3): 705-31. e5. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.12.001 |
| 5 | Hrdlickova R, Toloue M, Tian B. RNA-Seq methods for transcriptome analysis[J]. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA, 2017, 8(1): 10.1002/wrna.1364. DOI: 10.1002/wrna.1364 |
| 6 | Wang Z, Gerstein M, Snyder M. RNA-Seq: a revolutionary tool for transcriptomics[J]. Nat Rev Genet, 2009, 10(1): 57-63. DOI: 10.1038/nrg2484 |
| 7 | Saeidian AH, Youssefian L, Vahidnezhad H, et al. Research techniques made simple: whole-transcriptome sequencing by RNA-seq forDiagnosis of monogenic disorders[J]. J Investig Dermatol, 2020, 140(6): 1117-26. e1. DOI: 10.1016/j.jid.2020.02.032 |
| 8 | Safran M, Dalah I, Alexander J, et al. GeneCards Version 3: the human gene integrator[J]. Database, 2010, 2010: baq020. DOI: 10.1093/database/baq020 |
| 9 | Piñero J, Ramírez-Anguita JM, Saüch-Pitarch J, et al. The DisGeNET knowledge platform for disease genomics: 2019 update[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2020, 48(D1): D845-55. |
| 10 | Tjandra D, Busuttil RA, Boussioutas A. Gastric intestinal Metaplasia: challenges and the opportunity for precision prevention[J]. Cancers, 2023, 15(15): 3913. DOI: 10.3390/cancers15153913 |
| 11 | Akbari M, Tabrizi R, Kardeh S, et al. Gastric cancer in patients with gastric atrophy and intestinal metaplasia: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. PLoS One, 2019, 14(7): e0219865. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0219865 |
| 12 | Shin SY, Kim JH, Chun J, et al. Chronic atrophic gastritis and intestinal metaplasia surrounding diffuse-type gastric cancer: are they just bystanders in the process of carcinogenesisJ]PLoS One?, 2019, 14(12): e0226427. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0226427 |
| 13 | Correa P. Human gastric carcinogenesis: a multistep and multifactorial process: first American Cancer Society Award Lecture on Cancer Epidemiology and Prevention[J]. Cancer Res, 1992, 52(24): 6735-40. |
| 14 | Pei B, Wen ZA, Yang Q, et al. Risk factors analysis and prediction model establishment of intestinal Metaplasia or dysplasia in patients with chronic atrophic gastritis: a multi-center retrospective study[J]. Front Med, 2022, 9: 912331. DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.912331 |
| 15 | Ogutmen Koc D, Bektas S. Serum pepsinogen levels and OLGA/OLGIM staging in the assessment of atrophic gastritis types[J]. Postgrad Med J, 2022, 98(1160): 441-5. DOI: 10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-139183 |
| 16 | 李娜娜, 齐 涛, 朱黎明. 血清胃蛋白酶原、胃泌素17和幽门螺杆菌IgG抗体在胃部疾病初筛中的临床价值[J]. 诊断学理论与实践, 2022, 21(4): 509-13. |
| 17 | Zhang Y, Cao LJ, Xie YY, et al. Agmatinase facilitates the tumorigenesis of pancreatic adenocarcinoma through the TGFβ/Smad pathway[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2022, 24(2): 490. DOI: 10.3892/etm.2022.11417 |
| 18 | Zhu HE, Yin JY, Chen DX, et al. Agmatinase promotes the lung adenocarcinoma tumorigenesis by activating the NO-MAPKs-PI3K/Akt pathway[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2019, 10(11): 854. DOI: 10.1038/s41419-019-2082-3 |
| 19 | Xie YY, Zhang Y, Liu XJ, et al. MiR-151a-5p promotes the proliferation and metastasis of colorectal carcinoma cells by targeting AGMAT[J]. Oncol Rep, 2023, 49(3): 50. DOI: 10.3892/or.2023.8487 |
| 20 | Wang DL, Su Q, Qu Q, et al. Adeno-associated virus-mediated knockdown of agmatinase attenuates inflammation and tumorigenesis in a mouse model of colitis-associated colorectal cancer[J]. Hum Gene Ther, 2023, 34(11/12): 518-29. DOI: 10.1089/hum.2022.191 |
| 21 | Jarade A, Garcia Z, Marie S, et al. Inflammation triggers ILC3 patrolling of the intestinal barrier[J]. Nat Immunol, 2022, 23(9): 1317-23. DOI: 10.1038/s41590-022-01284-1 |
| 22 | Wu X, Sun M, Yang Z, et al. The roles of CCR9/CCL25 in inflammation and inflammation-associated diseases[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2021, 9: 686548. DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.686548 |
| 23 | Yu H, Mei Y, Dong Y, et al. CCR9-CCL25 mediated plasmacytoid dendritic cell homing and contributed the immunosuppressive microenvironment in gastric cancer[J]. Transl Oncol, 2023, 33: 101682. DOI: 10.1016/j.tranon.2023.101682 |
| 24 | Niu YX, Tang DF, Fan LW, et al. CCL25 promotes the migration and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer cells by regulating VEGF and MMPs in a CCR9-dependent manner[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2020, 19(6): 3571-80. |
| 25 | Du DY, Liu C, Qin MY, et al. Metabolic dysregulation and emerging therapeutical targets for hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Acta Pharm Sin B, 2022, 12(2): 558-80. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.09.019 |
| 26 | Liu SY, Ni CX, Li YZ, et al. The involvement of TRIB3 and FABP1 and their potential functions in the dynamic process of gastric cancer[J]. Front Mol Biosci, 2021, 8: 790433. DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.790433 |
| 27 | Hashimoto T, Kusakabe T, Watanabe K, et al. Liver-type fatty acid-binding protein is highly expressed in intestinal metaplasia and in a subset of carcinomas of the stomach without association with the fatty acid synthase status in the carcinoma[J]. Pathobiology, 2004, 71(3): 115-22. DOI: 10.1159/000076465 |
| 28 | Wang XJ, Yu Q, Ghareeb WM, et al. Downregulated SPINK4 is associated with poor survival in colorectal cancer[J]. BMC Cancer, 2019, 19(1): 1258. DOI: 10.1186/s12885-019-6484-5 |
| 29 | Chen TJ, Tian YF, Chou CL, et al. High SPINK4 expression predicts poor outcomes among rectal cancer patients receiving CCRT[J]. Curr Oncol, 2021, 28(4): 2373-84. DOI: 10.3390/curroncol28040218 |
| 30 | Owen RP, White MJ, Severson DT, et al. Single cell RNA-seq reveals profound transcriptional similarity between Barrett’s oesophagus and oesophageal submucosal glands[J]. Nat Commun, 2018, 9(1): 4261. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-06796-9 |
| 31 | Brenna Ø, Furnes MW, Drozdov I, et al. Relevance of TNBS-colitis in rats: a methodological study with endoscopic, histologic and Transcriptomic characterization and correlation to IBD[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(1): e54543. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054543 |
| 32 | Häsler R, Feng Z, Bäckdahl L, et al. A functional methylome map of ulcerative colitis[J]. Genome Res, 2012, 22(11): 2130-7. DOI: 10.1101/gr.138347.112 |
| 33 | Liu Y, Yu XJ, Zhao JX, et al. The role of MUC2 mucin in intestinal homeostasis and the impact of dietary components on MUC2 expression[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2020, 164: 884-91. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.07.191 |
| 34 | Kerckhoffs KGP, Liu DHW, Saragoni L, et al. Mucin expression in gastric- and gastro-oesophageal signet-ring cell cancer: results from a comprehensive literature review and a large cohort study of Caucasian and Asian gastric cancer[J]. Gastric Cancer, 2020, 23(5): 765-79. DOI: 10.1007/s10120-020-01086-0 |
| 35 | Yokoyama S, Hamada T, Higashi M, et al. Predicted prognosis of patients with pancreatic cancer by machine learning[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2020, 26(10): 2411-21. DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-19-1247 |
| 36 | Astashchanka A, Shroka TM, Jacobsen BM. Mucin 2 (MUC2) modulates the aggressiveness of breast cancer[J]. Breast Cancer Res Treat, 2019, 173(2): 289-99. DOI: 10.1007/s10549-018-4989-2 |
| 37 | Ribeirinho-Soares S, Pádua D, Amaral AL, et al. Prognostic significance of MUC2, CDX2 and SOX2 in stage II colorectal cancer patients[J]. BMC Cancer, 2021, 21(1): 359. DOI: 10.1186/s12885-021-08070-6 |
| 38 | Li YX, Jiang LB, Li ZC, et al. Differences in gastric microbiota and mucosal function between patients with chronic superficial gastritis and intestinal metaplasia[J]. Front Microbiol, 2022, 13: 950325. DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.950325 |
| 39 | Battista S, Ambrosio MR, Limarzi F, et al. Molecular alterations in gastric preneoplastic lesions and early gastric cancer[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(13): 6652. DOI: 10.3390/ijms22136652 |
| 40 | Grainger S, Hryniuk A, Lohnes D. Cdx1 and Cdx2 exhibit transcriptional specificity in the intestine[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(1): e54757. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054757 |
| 41 | Almeida R, Silva E, Santos-Silva F, et al. Expression of intestine-specific transcription factors, CDX1 and CDX2, in intestinal metaplasia and gastric carcinomas[J]. J Pathol, 2003, 199(1): 36-40. DOI: 10.1002/path.1246 |
| 42 | Kang JM, Lee BH, Kim N, et al. CDX1 and CDX2 expression in intestinal metaplasia, dysplasia and gastric cancer[J]. J Korean Med Sci, 2011, 26(5): 647-53. DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2011.26.5.647 |
| 43 | Wong NA, Wilding J, Bartlett S, et al. CDX1 is an important molecular mediator of Barrett’s metaplasia[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2005, 102(21): 7565-70. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0502031102 |
| 44 | Rau TT, Rogler A, Frischauf M, et al. Methylation-dependent activation of CDX1 through NF-κB[J]. Am J Pathol, 2012, 181(2): 487-98. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.04.028 |
| [1] | Xinyuan CHEN, Chengting WU, Ruidi LI, Xueqin PAN, Yaodan ZHANG, Junyu TAO, Caizhi LIN. Shuangshu Decoction inhibits growth of gastric cancer cell xenografts by promoting cell ferroptosis via the P53/SLC7A11/GPX4 axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1363-1371. |
| [2] | Kang WANG, Haibin LI, Jing YU, Yuan MENG, Hongli ZHANG. High expression of ELFN1 is a prognostic biomarker and promotes proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1543-1553. |
| [3] | Zhi GAO, Ao WU, Zhongxiang HU, Peiyang SUN. Bioinformatics analysis of oxidative stress and immune infiltration in rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 862-870. |
| [4] | Huaiwen XU, Li WENG, Hong XUE. CXCL12 is a potential therapeutic target for type 2 diabetes mellitus complicated by chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 100-109. |
| [5] | Mengnan YE, Hongmei WU, Yan MEI, Qingling ZHANG. High expression of CREM is associated with poor prognosis in gastric cancer patients [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1776-1782. |
| [6] | Kai JI, Guanyu YU, Leqi ZHOU, Tianshuai ZHANG, Qianlong LING, Wenjiang MAN, Bing ZHU, Wei ZHANG. HNRNPA1 gene is highly expressed in colorectal cancer: its prognostic implications and potential as a therapeutic target [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1685-1695. |
| [7] | Hongli YANG, Yayun XIANG, Tingting TAN, Yang LEI. ORY-1001 inhibits glioblastoma cell growth by downregulating the Notch/HES1 pathway via suppressing lysine-specific demethylase 1 expression [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1620-1630. |
| [8] | Wei ZHOU, Jun NIE, Jia HU, Yizhi JIANG, Dafa ZHANG. Differential expressions of endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated genes in aortic dissection and their correlation with immune cell infiltration [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(5): 859-866. |
| [9] | Qinzhi WANG, Bing SONG, Shirui HAO, Zhiyuan XIAO, Lianhui JIN, Tong ZHENG, Fang CHAI. Bioinformatic analysis of CCND2 expression in papillary thyroid carcinoma and its impact on immune infiltration [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(5): 981-988. |
| [10] | LIANG Yihao, LAI Yingjun, YUAN Yanwen, YUAN Wei, ZHANG Xibo, ZHANG Bashan, LU Zhifeng. Screening of differentially expressed genes in gastric cancer based on GEO database and function and pathway enrichment analysis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(3): 605-616. |
| [11] | Zijing REN, Peiyang ZHOU, Jing TIAN. Plasma long noncoding RNA expression profiles in patients with Parkinson's disease and the role of lnc-CTSD-5:1 in a PD cell model: a ceRNA microarray-based study [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(11): 2146-2155. |
| [12] | CHENG Jiacong, LI Zhihui, LIU Yao, LI Cheng, HUANG Xin, TIAN Yinxin, SHEN Fubing. Bioinformatics analysis and validation of the interaction between PML protein and TAB1 protein [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(1): 179-186. |
| [13] | WANG Qiusheng, ZHANG Zhen, WANG Lian, WANG Yu, YAO Xinyu, WANG Yueyue, ZHANG Xiaofeng, GE Sitang, ZUO Lugen. High expression of death-associated protein 5 promotes glucose metabolism in gastric cancer cells and correlates with poor survival outcomes [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(7): 1063-1070. |
| [14] | ZHANG Weijian, ZOU Zhuoyue, ZHU Yongna, WANG Min, MA Caiyun, WU Junjie, SHI Xin, LIU Xi. Expression of interleukin-34 in tongue squamous cell carcinoma and its clinical implications [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(12): 2111-2117. |
| [15] | XIN Baoshan, LIU Gang, ZHANG Chengxiong, WANG Bing, SHI Lianghui. LncRNA LINC00342 regulates gastric cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting miR-596 [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(10): 1761-1770. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||