Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (5): 930-940.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.05.15
• Clinical Research • Previous Articles Next Articles
Ruibo LI( ), Ge GAO, Xi XIE(
), Ge GAO, Xi XIE( ), Haibin LUO(
), Haibin LUO( )
)
Received:2024-01-17
Online:2024-05-20
Published:2024-06-04
Contact:
Xi XIE, Haibin LUO
E-mail:21211007000005@hainanu.edu.cn;xiexi@hainanu.edu.cn;hbluo@hainanu.edu.cn
Supported by:Ruibo LI, Ge GAO, Xi XIE, Haibin LUO. Oral submucosal fibrosis induced by active components in areca nut: a network pharmacology-based analysis and validation of the mechanism[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(5): 930-940.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.05.15
| NO. | Molecule | Molecular formula | QD (ppm) | Mw | RT (min) | Matching score | Peak area | Relative content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Arecoline | C8H13NO2 | -5.75 | 155.09374 | 3.758 | 90.9 | 68518632210 | 45.473 |
| 2 | Quinic acid | C7H12O6 | -2.88 | 192.06283 | 1.539 | 92.6 | 22692914797 | 15.060 |
| 3 | Epicatechin | C15H14O6 | -3.42 | 290.07805 | 18.93 | 94.7 | 14748028849 | 9.788 |
| 4 | Trigonelline HCl | C7H7NO2 | -5.85 | 137.04688 | 1.547 | 87.3 | 12273994597 | 8.146 |
| 5 | Citric acid | C6H8O7 | -2.05 | 192.02661 | 1.672 | 85.3 | 11231967076 | 7.454 |
| 6 | Procyanidin B1 | C30H26O12 | -4.2 | 578.14 | 18.324 | 92.4 | 7264204843 | 4.821 |
| 7 | p-Coumaric acid | C9H8O3 | -5.71 | 164.04641 | 4.772 | 85 | 3213100960 | 2.132 |
| 8 | (+)-Catechin hydrate | C15H14O6 | -3.73 | 290.07796 | 19.914 | 95.2 | 857006365.1 | 0.569 |
| 9 | Uridine | C9H12N2O6 | -2.72 | 244.06887 | 4.959 | 93.6 | 835052793.2 | 0.566 |
| 10 | Isorhamnetin-3-O-nehesperidine | C28H32O16 | -3.49 | 624.16686 | 22.33 | 92.2 | 760984003.5 | 0.505 |
| 11 | Sucrose | C12H22O11 | -3.26 | 342.1151 | 1.575 | 93.4 | 721956624 | 0.479 |
| 12 | 4'-O-Glucosylvitexin | C27H30O15 | -4.08 | 594.15604 | 20.961 | 87 | 608955062.8 | 0.404 |
| 13 | Procyanidin B2 | C30H28O10 | -5.78 | 578.13909 | 19.473 | 90.1 | 563763212.9 | 0.374 |
| 14 | Rosarin | C20H28O10 | -2.75 | 428.16707 | 22.833 | 79.7 | 480609598 | 0319 |
| 15 | Isoguanosine | C10H13N5O5 | -2.41 | 283.09099 | 10.894 | 83.8 | 44491969.7 | 0.295 |
| 16 | Nicotinic acid | C6H5NO2 | -4.82 | 123.03143 | 2.533 | 78 | 432658200.9 | 0.287 |
| 17 | 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural | C6H6O3 | -5.63 | 126.03098 | 1.912 | 73.9 | 431787858.3 | 0.287 |
| 18 | 2-Pyrrolidinecarboxylic acid | C5H9NO2 | -5.99 | 115.06264 | 1.547 | 74.7 | 397002912.3 | 0.263 |
| 19 | L-Tyrosine | C9H11NO3 | -2.26 | 181.07348 | 4.815 | 88.5 | 373792777.1 | 0.248 |
| 20 | Benzoic acid | C7H6O2 | -6.16 | 122.03603 | 18.932 | 88.4 | 277514777.6 | 0.184 |
Tab.1 Identification of the top 20 components of areca extract from Hainan areca nut
| NO. | Molecule | Molecular formula | QD (ppm) | Mw | RT (min) | Matching score | Peak area | Relative content (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Arecoline | C8H13NO2 | -5.75 | 155.09374 | 3.758 | 90.9 | 68518632210 | 45.473 |
| 2 | Quinic acid | C7H12O6 | -2.88 | 192.06283 | 1.539 | 92.6 | 22692914797 | 15.060 |
| 3 | Epicatechin | C15H14O6 | -3.42 | 290.07805 | 18.93 | 94.7 | 14748028849 | 9.788 |
| 4 | Trigonelline HCl | C7H7NO2 | -5.85 | 137.04688 | 1.547 | 87.3 | 12273994597 | 8.146 |
| 5 | Citric acid | C6H8O7 | -2.05 | 192.02661 | 1.672 | 85.3 | 11231967076 | 7.454 |
| 6 | Procyanidin B1 | C30H26O12 | -4.2 | 578.14 | 18.324 | 92.4 | 7264204843 | 4.821 |
| 7 | p-Coumaric acid | C9H8O3 | -5.71 | 164.04641 | 4.772 | 85 | 3213100960 | 2.132 |
| 8 | (+)-Catechin hydrate | C15H14O6 | -3.73 | 290.07796 | 19.914 | 95.2 | 857006365.1 | 0.569 |
| 9 | Uridine | C9H12N2O6 | -2.72 | 244.06887 | 4.959 | 93.6 | 835052793.2 | 0.566 |
| 10 | Isorhamnetin-3-O-nehesperidine | C28H32O16 | -3.49 | 624.16686 | 22.33 | 92.2 | 760984003.5 | 0.505 |
| 11 | Sucrose | C12H22O11 | -3.26 | 342.1151 | 1.575 | 93.4 | 721956624 | 0.479 |
| 12 | 4'-O-Glucosylvitexin | C27H30O15 | -4.08 | 594.15604 | 20.961 | 87 | 608955062.8 | 0.404 |
| 13 | Procyanidin B2 | C30H28O10 | -5.78 | 578.13909 | 19.473 | 90.1 | 563763212.9 | 0.374 |
| 14 | Rosarin | C20H28O10 | -2.75 | 428.16707 | 22.833 | 79.7 | 480609598 | 0319 |
| 15 | Isoguanosine | C10H13N5O5 | -2.41 | 283.09099 | 10.894 | 83.8 | 44491969.7 | 0.295 |
| 16 | Nicotinic acid | C6H5NO2 | -4.82 | 123.03143 | 2.533 | 78 | 432658200.9 | 0.287 |
| 17 | 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural | C6H6O3 | -5.63 | 126.03098 | 1.912 | 73.9 | 431787858.3 | 0.287 |
| 18 | 2-Pyrrolidinecarboxylic acid | C5H9NO2 | -5.99 | 115.06264 | 1.547 | 74.7 | 397002912.3 | 0.263 |
| 19 | L-Tyrosine | C9H11NO3 | -2.26 | 181.07348 | 4.815 | 88.5 | 373792777.1 | 0.248 |
| 20 | Benzoic acid | C7H6O2 | -6.16 | 122.03603 | 18.932 | 88.4 | 277514777.6 | 0.184 |

Fig.2 Network pharmacological analysis of the components of areca nut. A: Network pharmacology technology flow chart. B: Areca nut active ingredient-disease target for oral submucous fibrosis (OSF). C: Protein-protein interaction. D: Core target acquisition map. E: Intersection of the core target genes of the active ingredients of areca nut and OSF. F: Areca nut-component-target-OSF target interaction map. G: Effect of areca nut active ingredients on GO enrichment of OSF targets. H: KEGG pathway enrichment analysis of the effects of areca nut active ingredients on OSF targets. I: KEGG pathway secondary classification analysis. J: Molecular docking binding energy heat map.
| NO. | Molecule ID | Molecule name | OB/% | PubChem ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | MOL005835 | Guvacine | 98.35 | 40468028 |
| A2 | MOL005833 | Arecaine | 84.34 | 6971195 |
| A3 | MOL005838 | isoguvacine | 72.17 | 7059534 |
| A4 | MOL010481 | WLN: GR DSWR DG | 70.57 | 6625 |
| A5 | MOL000004 | Procyanidin B1 | 67.87 | 11250133 |
| A6 | MOL000676 | DBP | 64.54 | 3026 |
| A7 | MOL004544 | Quinic acid | 63.53 | 37439 |
| A8 | MOL001456 | citric acid | 56.22 | 19782904 |
| A9 | MOL004365 | Isomenthol | 55.30 | 19244 |
| A10 | MOL000492 | Catechin | 54.83 | 9064 |
| A11 | MOL002095 | DEP | 52.19 | 6781 |
| A12 | MOL000555 | Homoarecoline | 52.03 | 34167 |
| A13 | MOL010483 | dehydeoacetic acid | 52.02 | 1712264 |
| A14 | MOL000635 | vanilline | 52.00 | 1183 |
| A15 | MOL000073 | ent-Epicatechin | 48.96 | 1822932 |
| A16 | MOL010485 | EPA | 45.66 | 446284 |
| A17 | MOL010482 | WLN: 6OVR BVO6 | 43.74 | 6786 |
| A18 | MOL001749 | ZINC03860434 | 43.59 | 7057921 |
| A19 | MOL000131 | EIC | 41.90 | 5280450 |
| A20 | MOL004454 | ODD | 41.70 | 5282800 |
| A21 | MOL000041 | PHA | 41.62 | 6925665 |
| A22 | MOL010492 | Arecoline | 40.70 | 2230 |
| A23 | MOL002032 | DNOP | 40.59 | 8346 |
| A24 | MOL002850 | butylated hydroxytoluene | 40.02 | 31404 |
| A25 | MOL000198 | (R)-linalool | 39.80 | 443158 |
| A26 | MOL000234 | L-Limonen | 38.09 | 439250 |
| A27 | MOL001739 | zoomaric acid | 35.78 | 445638 |
| A28 | MOL010488 | 10Z-heptadecenoic acid | 34.42 | 5312435 |
| A29 | MOL002372 | (6Z,10E,14E,18E)-2,6,10,15,19,23-hexamethyltetracosa-2,6,10,14,18,22-hexaene | 33.55 | 11975273 |
| A30 | MOL000675 | oleic acid | 33.13 | 445639 |
| A31 | MOL010487 | Guvacoline | 32.67 | 160492 |
| A32 | MOL000301 | 2-lauroleic acid | 31.42 | 5282729 |
| A33 | MOL010489 | Resivit | 30.84 | 71629 |
| A34 | MOL003505 | Panosorb | 30.82 | 643460 |
Tab.2 Screening of active ingredients in areca nut
| NO. | Molecule ID | Molecule name | OB/% | PubChem ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | MOL005835 | Guvacine | 98.35 | 40468028 |
| A2 | MOL005833 | Arecaine | 84.34 | 6971195 |
| A3 | MOL005838 | isoguvacine | 72.17 | 7059534 |
| A4 | MOL010481 | WLN: GR DSWR DG | 70.57 | 6625 |
| A5 | MOL000004 | Procyanidin B1 | 67.87 | 11250133 |
| A6 | MOL000676 | DBP | 64.54 | 3026 |
| A7 | MOL004544 | Quinic acid | 63.53 | 37439 |
| A8 | MOL001456 | citric acid | 56.22 | 19782904 |
| A9 | MOL004365 | Isomenthol | 55.30 | 19244 |
| A10 | MOL000492 | Catechin | 54.83 | 9064 |
| A11 | MOL002095 | DEP | 52.19 | 6781 |
| A12 | MOL000555 | Homoarecoline | 52.03 | 34167 |
| A13 | MOL010483 | dehydeoacetic acid | 52.02 | 1712264 |
| A14 | MOL000635 | vanilline | 52.00 | 1183 |
| A15 | MOL000073 | ent-Epicatechin | 48.96 | 1822932 |
| A16 | MOL010485 | EPA | 45.66 | 446284 |
| A17 | MOL010482 | WLN: 6OVR BVO6 | 43.74 | 6786 |
| A18 | MOL001749 | ZINC03860434 | 43.59 | 7057921 |
| A19 | MOL000131 | EIC | 41.90 | 5280450 |
| A20 | MOL004454 | ODD | 41.70 | 5282800 |
| A21 | MOL000041 | PHA | 41.62 | 6925665 |
| A22 | MOL010492 | Arecoline | 40.70 | 2230 |
| A23 | MOL002032 | DNOP | 40.59 | 8346 |
| A24 | MOL002850 | butylated hydroxytoluene | 40.02 | 31404 |
| A25 | MOL000198 | (R)-linalool | 39.80 | 443158 |
| A26 | MOL000234 | L-Limonen | 38.09 | 439250 |
| A27 | MOL001739 | zoomaric acid | 35.78 | 445638 |
| A28 | MOL010488 | 10Z-heptadecenoic acid | 34.42 | 5312435 |
| A29 | MOL002372 | (6Z,10E,14E,18E)-2,6,10,15,19,23-hexamethyltetracosa-2,6,10,14,18,22-hexaene | 33.55 | 11975273 |
| A30 | MOL000675 | oleic acid | 33.13 | 445639 |
| A31 | MOL010487 | Guvacoline | 32.67 | 160492 |
| A32 | MOL000301 | 2-lauroleic acid | 31.42 | 5282729 |
| A33 | MOL010489 | Resivit | 30.84 | 71629 |
| A34 | MOL003505 | Panosorb | 30.82 | 643460 |
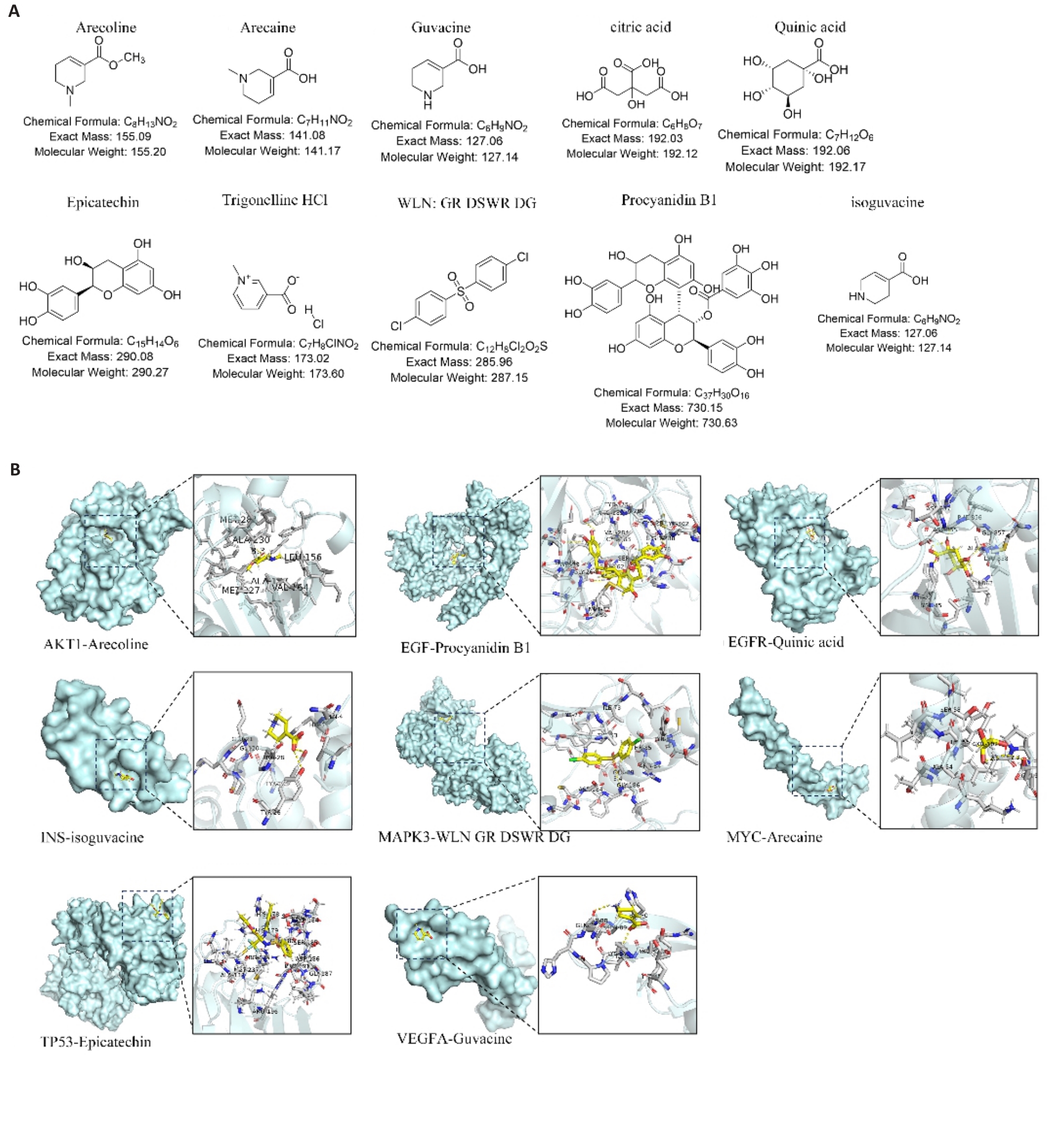
Fig.3 Molecular docking of areca nut components. A: Chemical structures of 10 areca nut active ingredients. B: Visualization of molecular docking of some active ingredients of areca nut with the core targets.
| Main active ingredients | Binding energy with target (kcal/mol) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecule name | PubChem ID | AKT1 (4GV1) | INS (1TYL) | EGF (1NQL) | EGFR (3W2S) | VEGFA (4KZN) | TP53 (3Q01) | MAPK3 (4QTB) | MYC (5I4Z) |
| Guvacine | 40468028 | -4.35 | -4.16 | 0.00 | -4.41 | -3.82 | 0.00 | 0.00 | -4.17 |
| Arecaine | 6971195 | -4.25 | -4.43 | 0.00 | -4.27 | -3.74 | 0.00 | 0.00 | -4.46 |
| isoguvacine | 7059534 | -4.38 | -4.06 | 0.00 | -4.01 | -3.78 | 0.00 | 0.00 | -3.85 |
| WLN: GR DSWR DG | 6625 | -5.66 | -4.89 | -5.32 | -4.73 | -4.38 | -4.76 | -5.71 | -4.54 |
| Procyanidin B1 | 11250133 | -6.86 | -6.42 | -6.70 | -6.68 | -5.45 | -6.02 | -6.60 | -5.94 |
| Quinic acid | 37439 | -4.78 | -4.45 | 0.00 | -5.28 | -4.11 | 0.00 | 0.00 | -4.14 |
| ent-Epicatechin | 1822932 | -6.54 | -5.61 | -5.72 | -6.15 | -4.91 | -5.51 | -6.54 | -5.16 |
| Arecoline | 2230 | -5.28 | -4.69 | 0.00 | 0.00 | -4.47 | -4.03 | 0.00 | -4.48 |
Tab.3 Molecular docking scoring list
| Main active ingredients | Binding energy with target (kcal/mol) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecule name | PubChem ID | AKT1 (4GV1) | INS (1TYL) | EGF (1NQL) | EGFR (3W2S) | VEGFA (4KZN) | TP53 (3Q01) | MAPK3 (4QTB) | MYC (5I4Z) |
| Guvacine | 40468028 | -4.35 | -4.16 | 0.00 | -4.41 | -3.82 | 0.00 | 0.00 | -4.17 |
| Arecaine | 6971195 | -4.25 | -4.43 | 0.00 | -4.27 | -3.74 | 0.00 | 0.00 | -4.46 |
| isoguvacine | 7059534 | -4.38 | -4.06 | 0.00 | -4.01 | -3.78 | 0.00 | 0.00 | -3.85 |
| WLN: GR DSWR DG | 6625 | -5.66 | -4.89 | -5.32 | -4.73 | -4.38 | -4.76 | -5.71 | -4.54 |
| Procyanidin B1 | 11250133 | -6.86 | -6.42 | -6.70 | -6.68 | -5.45 | -6.02 | -6.60 | -5.94 |
| Quinic acid | 37439 | -4.78 | -4.45 | 0.00 | -5.28 | -4.11 | 0.00 | 0.00 | -4.14 |
| ent-Epicatechin | 1822932 | -6.54 | -5.61 | -5.72 | -6.15 | -4.91 | -5.51 | -6.54 | -5.16 |
| Arecoline | 2230 | -5.28 | -4.69 | 0.00 | 0.00 | -4.47 | -4.03 | 0.00 | -4.48 |

Fig.4 Clinical validation. A: HE staining, Masson, SR staining (Original magnification: ×100 or ×200). B: Fibronectin immunohistochemistry and H-score semi-quantitative analysis (×100 or ×200; n≥5). C: SR staining and differentiation of COL I and COL III under polarized light (×100). Orange and red fluorescence indicate Col I. Green fluorescence indicates COL III. D: Immunohistochemical staining of PI3K-Akt pathway proteins (×100 or ×200; n≥5). E: Immunohistochemistry and H-score semi-quantitative analysis of PI3K-Akt pathway proteins (n≥5). F: Immunohistochemical staining of MAPK pathway protein (×100, ×200 or ×400; n≥5). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001.
| 1 | Mehrtash H, Duncan K, Parascandola M, et al. Defining a global research and policy agenda for betel quid and areca nut[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2017, 18(12): e767-75. DOI: 10.1016/s1470-2045(17)30460-6 |
| 2 | 周明玺, 郭亦晨, 李 珂, 等. 槟榔活性成分及药理毒理作用研究进展[J]. 中成药, 2022, 44(3): 878-83. |
| 3 | 周思安, 刘斯薇, 金力行, 等. 槟榔碱对生殖与泌尿系统的影响[J]. 国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志, 2019, 38(5): 413-7. |
| 4 | Kondaiah P, Pant I, Khan I. Molecular pathways regulated by areca nut in the etiopathogenesis of oral submucous fibrosis[J]. Periodontol 2000, 2019, 80(1): 213-24. DOI: 10.1111/prd.12266 |
| 5 | 中华口腔医学会, 口腔黏膜下纤维性变诊断与临床管理指南:T/ [S]. 2022. |
| 6 | Arakeri G, Rai KK, Hunasgi S, et al. Oral submucous fibrosis: an update on current theories of pathogenesis[J]. J Oral Pathology Medicine, 2017, 46(6): 406-12. DOI: 10.1111/jop.12581 |
| 7 | Gupta S, Jawanda MK. Oral submucous fibrosis: an overview of a challenging entity[J]. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol, 2021, 87: 768-77. DOI: 10.25259/ijdvl_371_20 |
| 8 | Hsieh PL, Yu CC. Oral fibrosis and oral cancer: from molecular targets to therapeutics[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(11): 6110. DOI: 10.3390/ijms23116110 |
| 9 | Shih YH, Wang TH, Shieh TM, et al. Oral submucous fibrosis: a review on etiopathogenesis, diagnosis, and therapy[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(12): 2940. DOI: 10.3390/ijms20122940 |
| 10 | Warnakulasuriya S, Tilakaratne WM, Kerr A. Oral submucous fibrosis[M]//Contemporary Oral Oncology. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2016: 329-53. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-14911-0_8 |
| 11 | Wang LP, Tang ZG. Immunopathogenesis of oral submucous fibrosis by chewing the areca nut[J]. J Leukoc Biol, 2022, 111(2): 469-76. DOI: 10.1002/jlb.3mr0521-763rr |
| 12 | Zhou BL, Zhu W, Ren CP. First steps to regulate advertising of areca nut in China[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2019, 20(5): 615-6. DOI: 10.1016/s1470-2045(19)30231-1 |
| 13 | Zhou LH, Tan J, Dai YZ, et al. Jiawei Danxuan Koukang alleviates arecoline induced oral mucosal lesions: network pharmacology and the combined ultra-high performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) and mass spectrometry (MS)[J]. Drug Des Devel Ther, 2023, 17: 3085-101. DOI: 10.2147/dddt.s413897 |
| 14 | Luo WF, Deng J, He JC, et al. Integration of molecular docking, molecular dynamics and network pharmacology to explore the multi-target pharmacology of fenugreek against diabetes[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2023, 27(14): 1959-74. DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.17787 |
| 15 | 欧海亚,叶小鹏,李舒 等.基于网络药理学及数据挖掘探讨中药调节铁死亡的用药规律研究[J]. 中国现代应用药,2019,36(18):2317-24 |
| 16 | Hou FF, Yu ZY, Cheng Y, et al. Deciphering the pharmacological mechanisms of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi on oral leukoplakia by combining network pharmacology, molecular docking and experimental evaluations[J]. Phytomedicine, 2022, 103: 154195. DOI: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154195 |
| 17 | Zhao JL, Lin FZ, Liang GH, et al. Exploration of the molecular mechanism of polygonati rhizoma in the treatment of osteoporosis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking[J]. Front Endocrinol, 2022, 12: 815891. DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2021.815891 |
| 18 | Gao P, Chang K, Yuan S, et al. Exploring the mechanism of hepatotoxicity induced by Dictamnus dasycarpus based on network pharmacology, molecular docking and experimental pharmacology[J]. Molecules, 2023, 28(13): 5045. DOI: 10.3390/molecules28135045 |
| 19 | Luo WF, Deng J, He JC, et al. Integration of molecular docking, molecular dynamics and network pharmacology to explore the multi-target pharmacology of fenugreek against diabetes[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2023, 27(14): 1959-74. DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.17787 |
| 20 | He JH, Han DB, Jia CL, et al. Integrating network pharmacology, molecular docking and pharmacological evaluation for exploring the Polyrhachis vicina Rogers in ameliorating depression[J]. Drug Des Devel Ther, 2023, 17: 717-35. DOI: 10.2147/dddt.s399183 |
| 21 | Zhan QX, Zhao JN, Liu L, et al. Integrated network pharmacology and molecular docking analyses of the mechanisms underlying the antihypertensive effects of lotusine[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2023, 945: 175622. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2023.175622 |
| 22 | Torres PHM, Sodero ACR, Jofily P, et al. Key topics in molecular docking for drug design[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(18): 4574. DOI: 10.3390/ijms20184574 |
| 23 | Liao F, Yousif M, Huang RY, et al. Network pharmacology- and molecular docking-based analyses of the antihypertensive mechanism of Ilex kudingcha [J]. Front Endocrinol, 2023, 14: 1216086. DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1216086 |
| 24 | Di-Luoffo M, Ben-Meriem Z, Lefebvre P, et al. PI3K functions as a hub in mechanotransduction[J]. Trends Biochem Sci, 2021, 46(11): 878-88. DOI: 10.1016/j.tibs.2021.05.005 |
| 25 | Fruman DA, Chiu H, Hopkins BD, et al. The PI3K pathway in human disease[J]. Cell, 2017, 170(4): 605-35. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.07.029 |
| 26 | Wang JC, Hu KL, Cai XY, et al. Targeting PI3K/AKT signaling for treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis[J]. Acta Pharm Sin B, 2022, 12(1): 18-32. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.07.023 |
| 27 | de Oliveira RP, de Andrade JS, Spina M, et al. Clozapine prevented social interaction deficits and reduced c-Fos immunoreactivity expression in several brain areas of rats exposed to acute restraint stress[J]. PLoS One, 2022, 17(3): e0262728. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0262728 |
| 28 | Yang Y, Gong WY, Jin CX, et al. Naringin ameliorates experimental diabetic renal fibrosis by inhibiting the ERK1/2 and JNK MAPK signaling pathways[J]. J Funct Foods, 2018, 50: 53-62. DOI: 10.1016/j.jff.2018.09.020 |
| 29 | Pant I, Rao SG, Kondaiah P. Role of areca nut induced JNK/ATF2/Jun axis in the activation of TGF-β pathway in precancerous Oral Submucous Fibrosis[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 34314. DOI: 10.1038/srep34314 |
| 30 | Carleton M, Zhou M, De Henau O, et al. Serum interleukin 8 (IL-8) may serve as a biomarker of response to immuno-oncology (I-O) therapy[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2018, 36(): 3025. DOI: 10.1200/jco.2018.36.15_suppl.3025 |
| 31 | Bucur M, Dinca O, Vladan C, et al. Variation in expression of inflammation-related signaling molecules with profibrotic and antifibrotic effects in cutaneous and oral mucosa scars[J]. J Immunol Res, 2018, 2018: 5196023. DOI: 10.1155/2018/5196023 |
| [1] | Xinyuan CHEN, Chengting WU, Ruidi LI, Xueqin PAN, Yaodan ZHANG, Junyu TAO, Caizhi LIN. Shuangshu Decoction inhibits growth of gastric cancer cell xenografts by promoting cell ferroptosis via the P53/SLC7A11/GPX4 axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1363-1371. |
| [2] | Liming WANG, Hongrui CHEN, Yan DU, Peng ZHAO, Yujie WANG, Yange TIAN, Xinguang LIU, Jiansheng LI. Yiqi Zishen Formula ameliorates inflammation in mice with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1409-1422. |
| [3] | Yinfu ZHU, Yiran LI, Yi WANG, Yinger HUANG, Kunxiang GONG, Wenbo HAO, Lingling SUN. Therapeutic mechanism of hederagenin, an active component in Guizhi Fuling Pellets, against cervical cancer in nude mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1423-1433. |
| [4] | Lijun HE, Xiaofei CHEN, Chenxin YAN, Lin SHI. Inhibitory effect of Fuzheng Huaji Decoction against non-small cell lung cancer cells in vitro and the possible molecular mechanism [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1143-1152. |
| [5] | Guoyong LI, Renling LI, Yiting LIU, Hongxia KE, Jing LI, Xinhua WANG. Therapeutic mechanism of Arctium lappa extract for post-viral pneumonia pulmonary fibrosis: a metabolomics, network pharmacology analysis and experimental verification [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1185-1199. |
| [6] | Liping GUAN, Yan YAN, Xinyi LU, Zhifeng LI, Hui GAO, Dong CAO, Chenxi HOU, Jingyu ZENG, Xinyi LI, Yang ZHAO, Junjie WANG, Huilong FANG. Compound Centella asiatica formula alleviates Schistosoma japonicum-induced liver fibrosis in mice by inhibiting the inflammation-fibrosis cascade via regulating the TLR4/MyD88 pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1307-1316. |
| [7] | Peipei TANG, Yong TAN, Yanyun YIN, Xiaowei NIE, Jingyu HUANG, Wenting ZUO, Yuling LI. Tiaozhou Ziyin recipe for treatment of premature ovarian insufficiency: efficacy, safety and mechanism [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 929-941. |
| [8] | Xiaotao LIANG, Yifan XIONG, Xueqi LIU, Xiaoshan LIANG, Xiaoyu ZHU, Wei XIE. Huoxue Shufeng Granule alleviates central sensitization in chronic migraine mice via TLR4/NF-κB inflammatory pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 986-994. |
| [9] | Niandong RAN, Jie LIU, Jian XU, Yongping ZHANG, Jiangtao GUO. n-butanol fraction of ethanol extract of Periploca forrestii Schltr.: its active components, targets and pathways for treating Alcheimer's disease in rats [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 785-798. |
| [10] | Haonan¹ XU, Fang³ ZHANG, Yuying² HUANG, Qisheng⁴ YAO, Yueqin⁴ GUAN, Hao CHEN. Thesium chinense Turcz. alleviates antibiotic-associated diarrhea in mice by modulating gut microbiota structure and regulating the EGFR/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 285-295. |
| [11] | Junjie GAO, Kai YE, Jing WU. Quercetin inhibits proliferation and migration of clear cell renal cell carcinoma cells by regulating TP53 gene [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 313-321. |
| [12] | Ying LIU, Borui LI, Yongcai LI, Lubo CHANG, Jiao WANG, Lin YANG, Yonggang YAN, Kai QV, Jiping LIU, Gang ZHANG, Xia SHEN. Jiawei Xiaoyao Pills improves depression-like behavior in rats by regulating neurotransmitters, inhibiting inflammation and oxidation and modulating intestinal flora [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 347-358. |
| [13] | Qiao CHU, Xiaona WANG, Jiaying XU, Huilin PENG, Yulin ZHAO, Jing ZHANG, Guoyu LU, Kai WANG. Pulsatilla saponin D inhibits invasion and metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer cells through multiple targets and pathways [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 150-161. |
| [14] | Xiupeng LONG, Shun TAO, Shen YANG, Suyun LI, Libing RAO, Li LI, Zhe ZHANG. Quercetin improves heart failure by inhibiting cardiomyocyte apoptosis via suppressing the MAPK signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 187-196. |
| [15] | Meng XU, Lina CHEN, Jinyu WU, Lili LIU, Mei SHI, Hao ZHOU, Guoliang ZHANG. Mechanism of Hedyotis diffusa-Scutellaria barbata D. Don for treatment of primary liver cancer: analysis with network pharmacology, molecular docking and in vitro validation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 80-89. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||