Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (9): 1850-1858.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.09.05
Aili YAN1( ), Mengyao LUO2(
), Mengyao LUO2( ), Jinrui CHANG1, Xinhua LI1, Juanxia ZHU1(
), Jinrui CHANG1, Xinhua LI1, Juanxia ZHU1( )
)
Received:2025-02-02
Online:2025-09-20
Published:2025-09-28
Contact:
Juanxia ZHU
E-mail:1342748096@qq.com;1657238862@qq.com;1120270539@qq.com
Aili YAN, Mengyao LUO, Jinrui CHANG, Xinhua LI, Juanxia ZHU. Hesperetin alleviates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by regulating the AMPK/NLRP3 pathway[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(9): 1850-1858.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.09.05
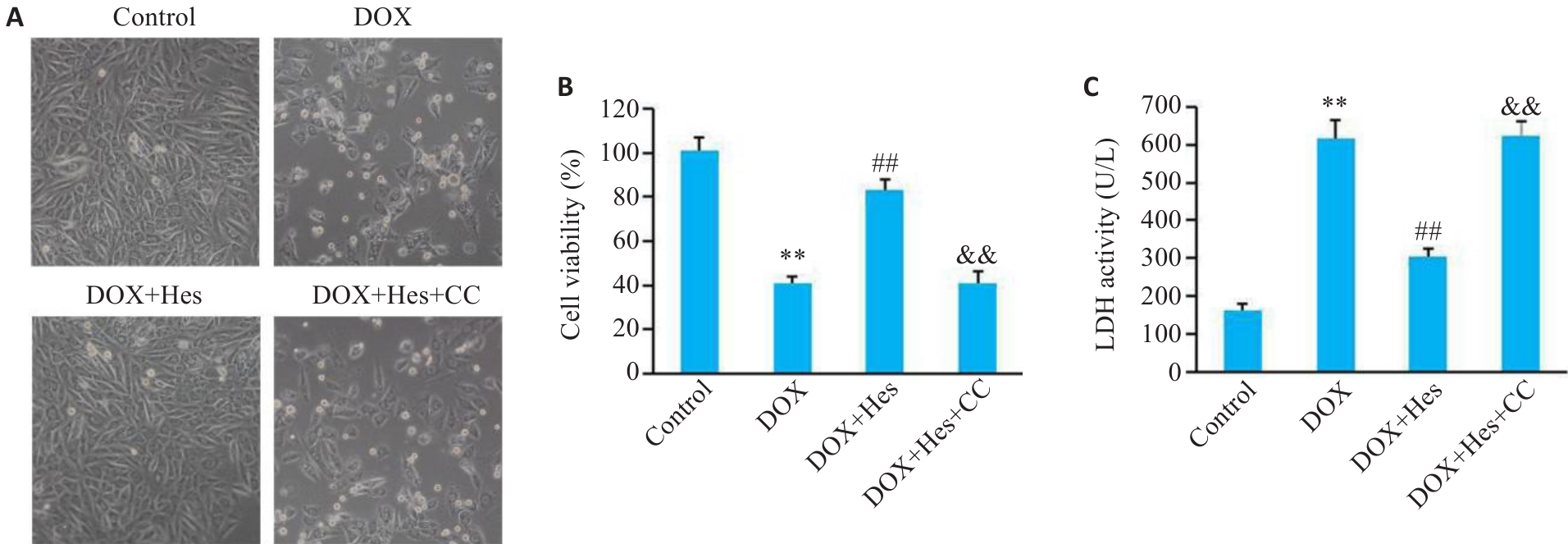
Fig.1 Compound C blocks the protective effects of Hes against DOX-induced cell injury in H9c2 cells. A: Cell morphology in each group (Original magnification: ×100). B: Comparison of cell viability among the 4 groups. C: LDH activity in the cells in the 4 groups. **P<0.01 vs Control group; ##P<0.01 vs DOX group; &&P<0.01 vs DOX+Hes group (n=6).
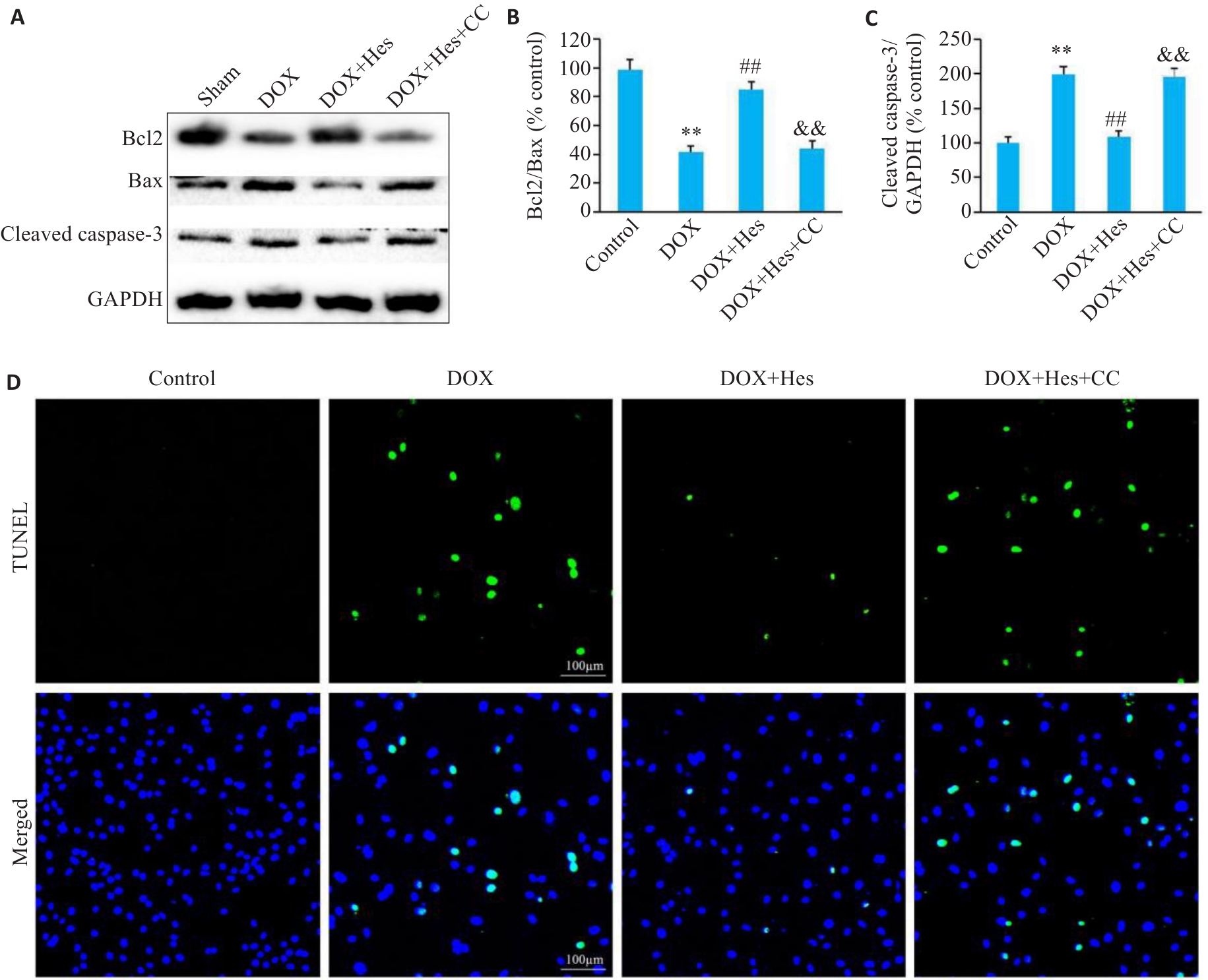
Fig.2 Compound C reduces the protective effect of Hes against DOX-induced cell apoptosis.A: Representative Western blots of Bcl2, Bax, cleaved caspase-3 and GAPDH in each group. B: Bcl2/Bax ratios in each group. C: Cleaved caspase-3 expression levels in each group. D: TUNEL staining of the cells in each group (Scale bar=100 μm). **P<0.01 vs Control group; ##P<0.01 vs DOX group; &&P<0.01 vs DOX+Hes group (n=6).
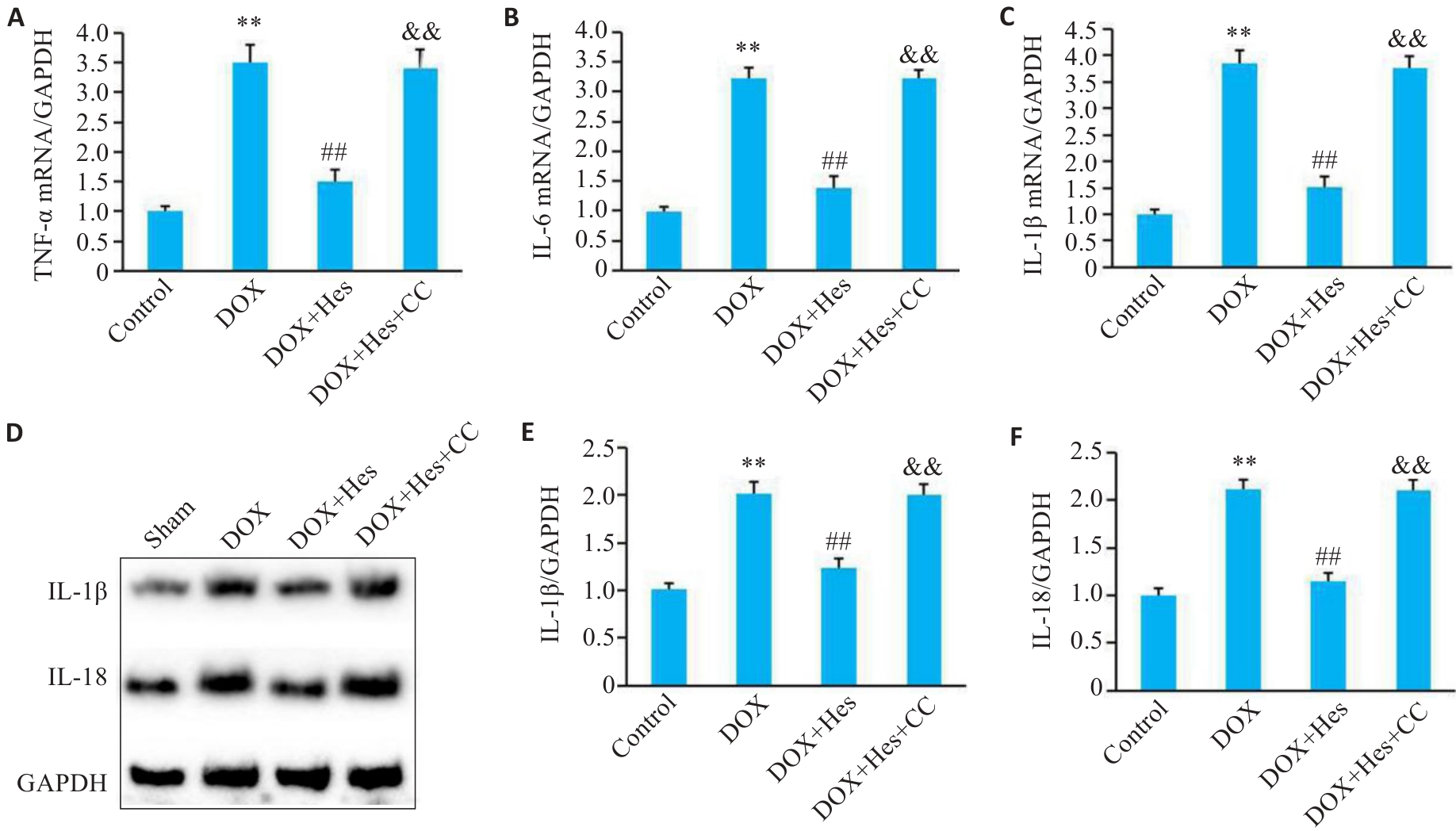
Fig.3 Compound C attenuates the protective effect of Hes against DOX-induced inflammation. A-C: Relative mRNA expressions of TNF‑α, IL-6 and IL-1β in each group. D: Representative Western blots of TNF‑α, IL-6, IL-1β and GAPDH in each group. E, F: Relative expression levels of IL-1β and IL-18 in the cells in each group. **P<0.01 vs Control group; ##P<0.01 vs DOX group; &&P<0.01 vs DOX+Hes group (n=6).
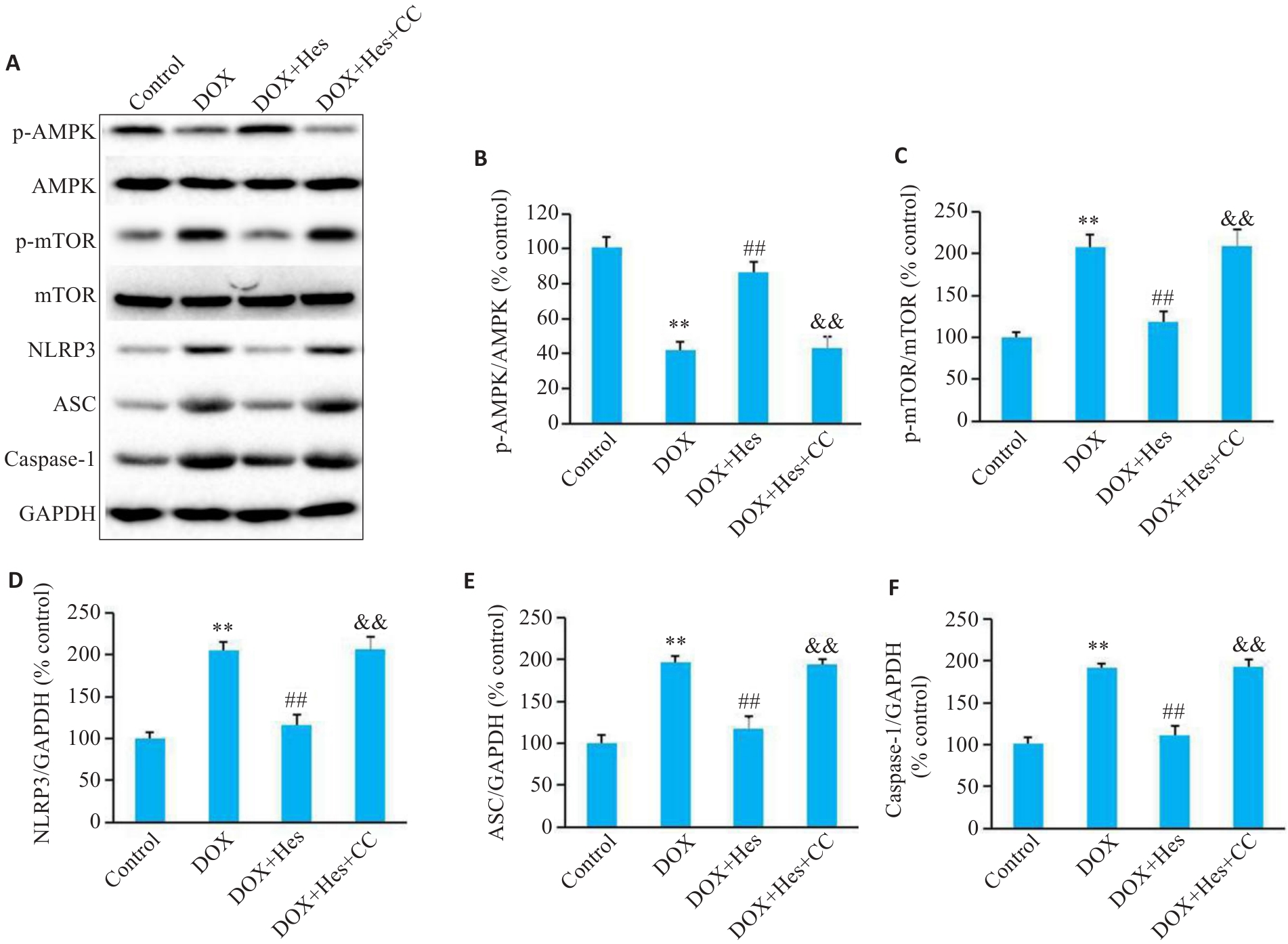
Fig.4 Compound C blocks the effect of Hes against DOX-induced changes in protein expressions of AMPK/NLRP3 signaling. A: Representative Western blots of p-AMPK, AMPK, p-mTOR, mTOR, NLRP3, ASC, caspase-1 and GAPDH in each group. B-F: Relative expression levels of p-AMPK, p-mTOR, NLRP3, ASC, and caspase-1 in each group. **P<0.01 vs Control group; ##P<0.01 vs DOX group; &&P<0.01 vs DOX+Hes group (n=6).
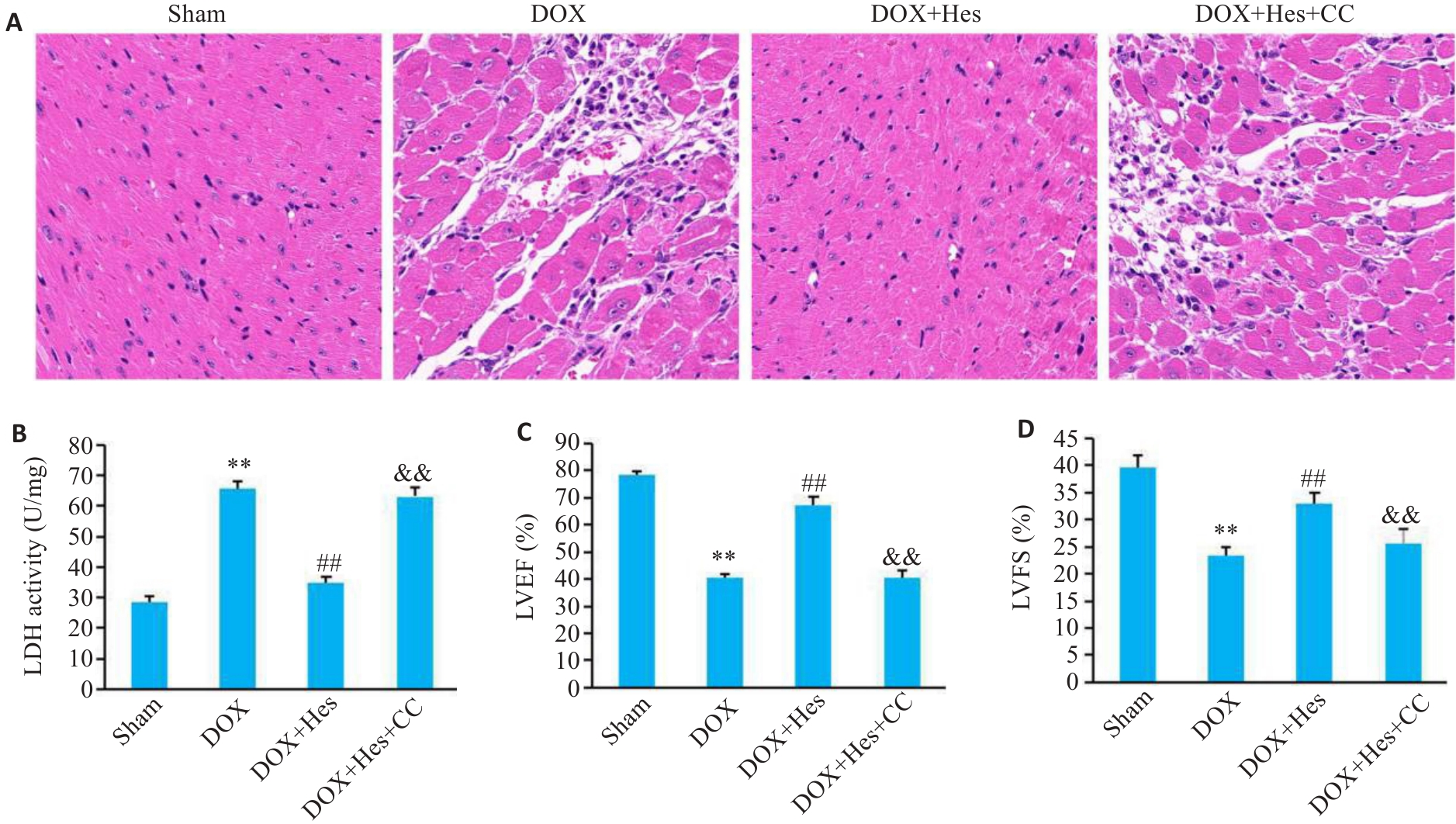
Fig.5 Compound C blocks the protective effect of Hes against DOX-induced myocardial injury in mice. A: HE staining of the myocardial tissues in each group (×200). B: Myocardial LDH activity in each group. C: LVEF in each group. D: LVFS in each group. **P<0.01 vs Sham group; ##P<0.01 vs DOX group; &&P<0.01 vs DOX+Hes group (n=6).
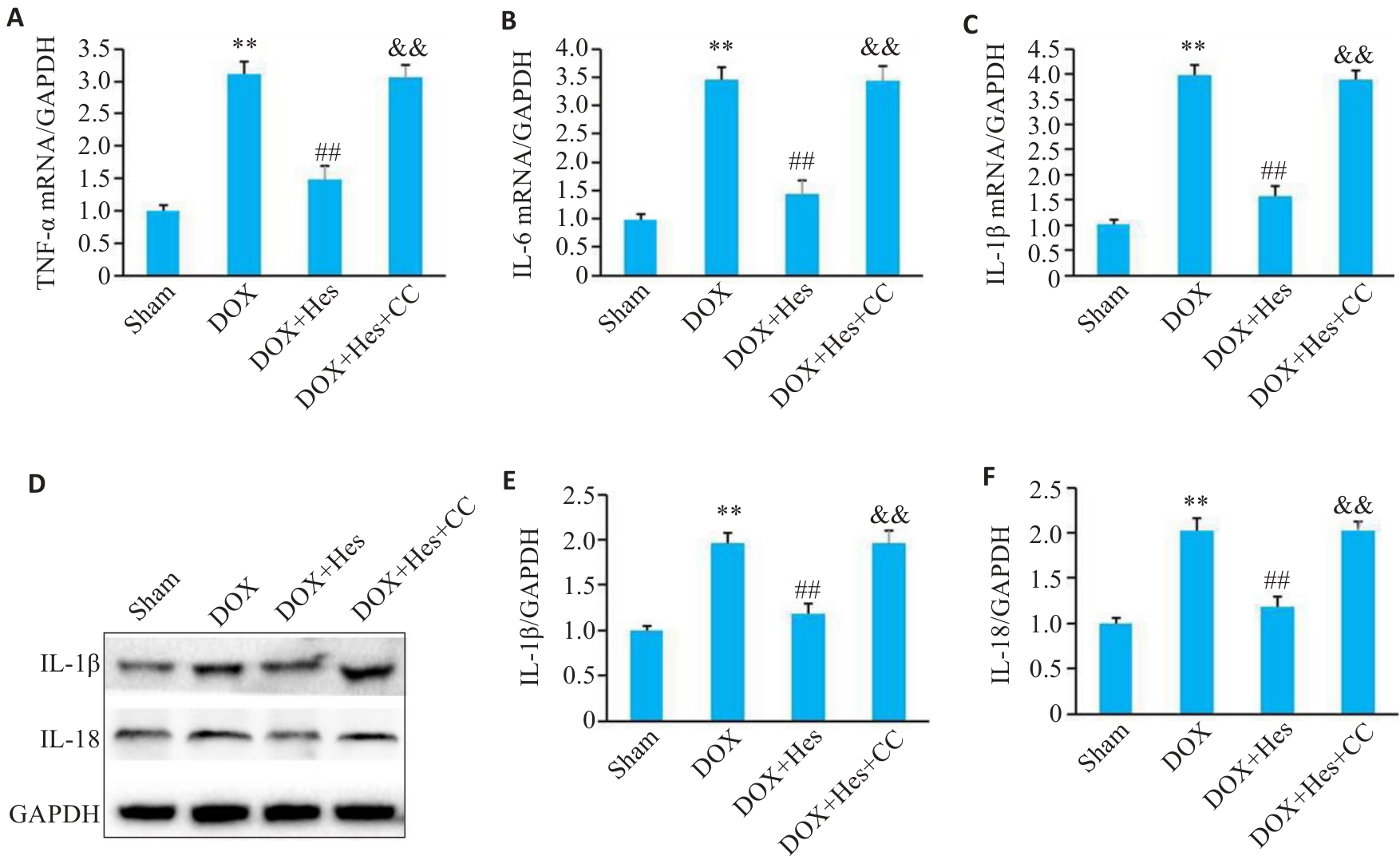
Fig.6 Compound C attenuates the protective effect of Hes against DOX-induced inflammation in the myocardial tissues of the mice. A-C: Relative mRNA expressions of TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β in each group. D: Representative Western blots of IL-1β, IL-18 and GAPDH. E, F: Relative expression levels of IL-1β and IL-18 in each group. **P<0.01 vs Sham group; ##P<0.01 vs DOX group; &&P<0.01 vs DOX+Hes group (n=6).
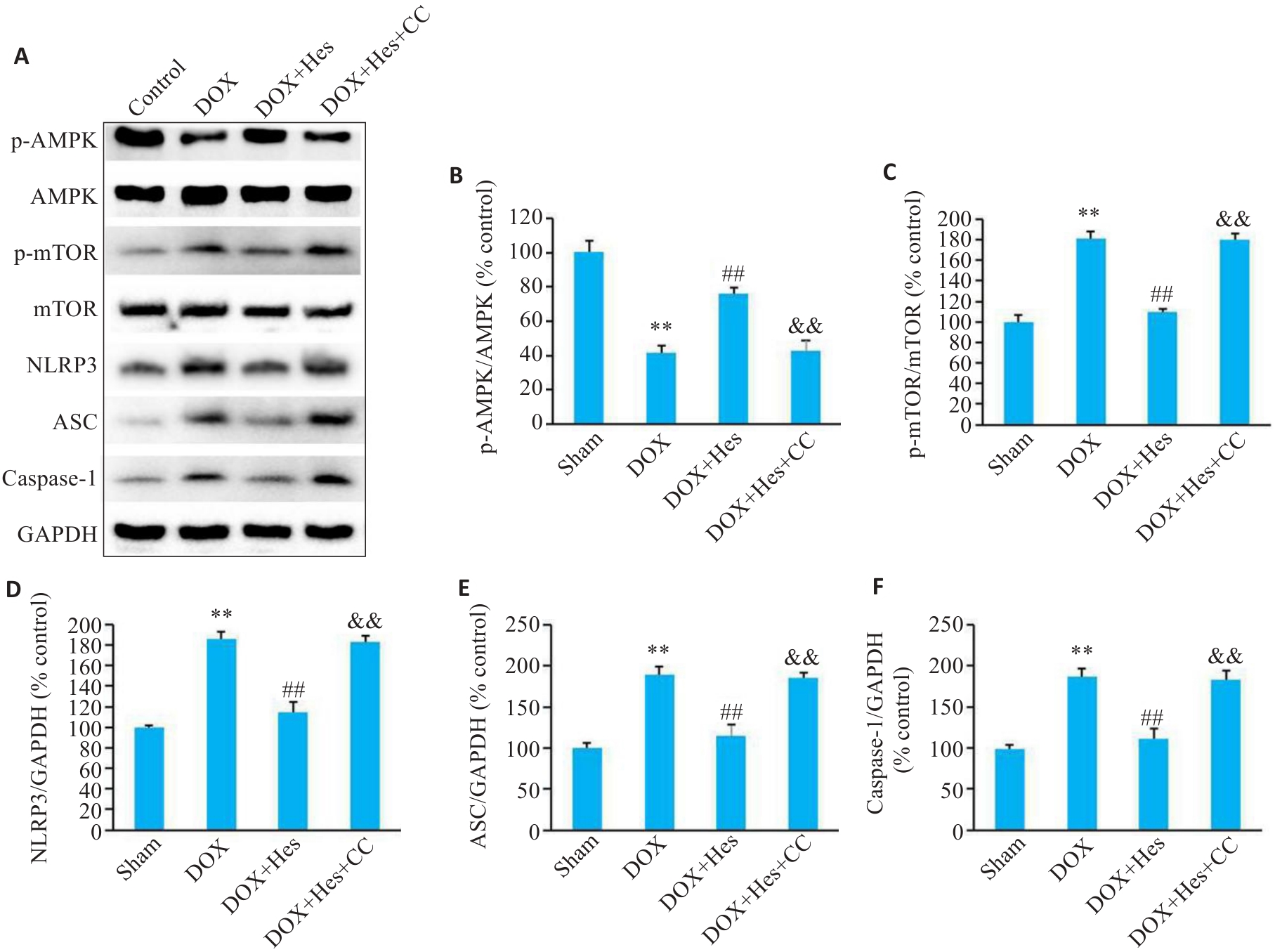
Fig.7 Compound C blocks the effect of Hes against DOX-induced changes in expression of AMPK/NLRP3 signaling in the mice. A: Representative Western blots of p-AMPK, AMPK, p-mTOR, mTOR, NLRP3, ASC, caspase-1 and GAPDH. B-F: Relative expression levels of p-AMPK, p-mTOR, NLRP3, ASC, and caspase-1 in the myocardial tissues of the mice in each group. **P<0.01 vs Sham group; ##P<0.01 vs DOX group; &&P<0.01 vs DOX+Hes group (n=6).
| [1] | Karlstaedt A, Taegtmeyer H. Cardio-Onco-Metabolism–Metabolic vulnerabilities in cancer and the heart[J]. J Mol Cell Cardiol, 2022, 171: 71-80. doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2022.06.008 |
| [2] | Sangweni NF, Gabuza K, Huisamen B, et al. Molecular insights into the pathophysiology of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity: a graphical representation[J]. Arch Toxicol, 2022, 96(6): 1541-50. doi:10.1007/s00204-022-03262-w |
| [3] | Hulst MB, Grocholski T, Neefjes JJC, et al. Anthracyclines: biosynthesis, engineering and clinical applications[J]. Nat Prod Rep, 2022, 39(4): 814-41. doi:10.1039/d1np00059d |
| [4] | Schmidt AF, Bourfiss M, Alasiri A, et al. Druggable proteins influencing cardiac structure and function: Implications for heart failure therapies and cancer cardiotoxicity[J]. Sci Adv, 2023, 9(17): eadd4984. doi:10.1126/sciadv.add4984 |
| [5] | Kong CY, Guo Z, Song P, et al. Underlying the mechanisms of doxorubicin-induced acute cardiotoxicity: oxidative stress and cell death[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2022, 18(2): 760-70. doi:10.7150/ijbs.65258 |
| [6] | Wu L, Wang LT, Du YX, et al. Mitochondrial quality control mechanisms as therapeutic targets in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity[J]. Trends Pharmacol Sci, 2023, 44(1): 34-49. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2022.10.003 |
| [7] | Vitale R, Marzocco S, Popolo A. Role of oxidative stress and inflammation in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity: a brief account[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2024, 25(13): 7477. doi:10.3390/ijms25137477 |
| [8] | Ji Z, Deng W, Chen D, et al. Recent understanding of the mechanisms of the biological activities of hesperidin and hesperetin and their therapeutic effects on diseases[J]. Heliyon, 2024, 10(5): e26862. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26862 |
| [9] | Zhang YX, Chen XJ, Wang XX, et al. Hesperetin ameliorates spinal cord injury in rats through suppressing apoptosis, oxidative stress and inflammatory response[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2024, 971: 176541. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2024.176541 |
| [10] | Liu PP, Li JH, Liu MM, et al. Hesperetin modulates the Sirt1/Nrf2 signaling pathway in counteracting myocardial ischemia through suppression of oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2021, 139: 111552. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111552 |
| [11] | Li X, Yan A, Chang J, et al. Hesperetin alleviates doxorubicin-induced cytotoxicity in H9c2 cells by activating SIRT1/NRF2 signaling[J]. Sichuan da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban, 2023, 54(5): 947-53. |
| [12] | Chen MC. Empagliflozin attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardioto-xicity by activating AMPK/SIRT-1/PGC-1α-mediated mitochondrial biogenesis[J]. Toxicol Res, 2023, 12(2): 216-23. doi:10.1093/toxres/tfad007 |
| [13] | Zhao XY, Ren JM, Liu HR, et al. DJ-1 activates the AMPK/mTOR pathway by binding RACK1 to induce autophagy and protect the myocardium from ischemia/hypoxia injury[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2022, 637: 276-85. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2022.10.100 |
| [14] | Zhu M, Hu J, Pan Y, et al. Magnoflorine attenuates Ang II-induced cardiac remodeling via promoting AMPK-regulated autophagy[J]. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther, 2024, 14(4): 576-88. doi:10.21037/cdt-24-130 |
| [15] | 魏 佳, 杨 强, 林 琳, 等. 二甲双胍减轻阿霉素诱导的心脏毒性:基于AMPK通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(10): 1682-8. |
| [16] | Liu D, Ma ZQ, Di SY, et al. AMPK/PGC1α activation by melatonin attenuates acute doxorubicin cardiotoxicity via alleviating mitochondrial oxidative damage and apoptosis[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2018, 129: 59-72. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.08.032 |
| [17] | Wang WL, Jiang JL, Huang Y, et al. Aconitine induces autophagy via activating oxidative DNA damage-mediated AMPK/ULK1 signaling pathway in H9c2 cells[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2022, 282: 114631. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2021.114631 |
| [18] | Ta N, Qu C, Wu H, et al. Mitochondrial outer membrane protein FUNDC2 promotes ferroptosis and contributes to doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2022, 119(36): e2117396119. doi:10.1073/pnas.2117396119 |
| [19] | Kitakata H, Endo J, Matsushima H, et al. MITOL/MARCH5 determines the susceptibility of cardiomyocytes to doxorubicin-induced ferroptosis by regulating GSH homeostasis[J]. J Mol Cell Cardiol, 2021, 161: 116-29. doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2021.08.006 |
| [20] | 熊凤梅, 刘瑞萍, 李 洋, 等. 和厚朴酚可体外减轻阿霉素诱导的心肌毒性: 基于激活AMPK/Nrf2信号通路抑制细胞焦亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(8): 1205-11. doi:10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2022.08.13 |
| [21] | Nakamura M, Sadoshima J. Mechanisms of physiological and pathological cardiac hypertrophy[J]. Nat Rev Cardiol, 2018, 15(7): 387-407. doi:10.1038/s41569-018-0007-y |
| [22] | Zaafar D, Khalil HMA, Rasheed RA, et al. Hesperetin mitigates sorafenib-induced cardiotoxicity in mice through inhibition of the TLR4/NLRP3 signaling pathway[J]. PLoS One, 2022, 17(8): e0271631. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0271631 |
| [23] | Zhang Z, Shen C, Wu N, et al. Gab1 overexpression alleviates doxorubicin-induced cardiac oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis through PI3K/Akt signaling pathway[J]. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol, 2022, 80(6): 804-12. doi:10.1097/fjc.0000000000001333 |
| [24] | Quagliariello V, De Laurentiis M, Rea D, et al. The SGLT-2 inhibitor empagliflozin improves myocardial strain, reduces cardiac fibrosis and pro-inflammatory cytokines in non-diabetic mice treated with doxorubicin[J]. Cardiovasc Diabetol, 2021, 20(1): 150. doi:10.1186/s12933-021-01346-y |
| [25] | Yildirim C, Cangi S, Orkmez M, et al. Sinapic acid attenuated cisplatin-induced cardiotoxicity by inhibiting oxidative stress and İnflammation with GPX4-mediated NF-kB modulation[J]. Cardiovasc Toxicol, 2023, 23(1): 10-22. doi:10.1007/s12012-022-09773-3 |
| [26] | Morsy MA, Abdel-Gaber SA, Mokhemer SA, et al. Pregnenolone inhibits doxorubicin-induced cardiac oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis-role of matrix metalloproteinase 2 and NADPH oxidase 1[J]. Pharmaceuticals: Basel, 2023, 16(5): 665. doi:10.3390/ph16050665 |
| [27] | Toldo S, Abbate A. The role of the NLRP3 inflammasome and pyroptosis in cardiovascular diseases[J]. Nat Rev Cardiol, 2024, 21(4): 219-37. doi:10.1038/s41569-023-00946-3 |
| [28] | Townsend LK, Steinberg GR. AMPK and the endocrine control of metabolism[J]. Endocr Rev, 2023, 44(5): 910-33. doi:10.1210/endrev/bnad012 |
| [29] | Steinberg GR, Hardie DG. New insights into activation and function of the AMPK[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2023, 24(4): 255-72. doi:10.1038/s41580-022-00547-x |
| [30] | Liu C, Guo X, Zhou Y, et al. AMPK signalling pathway: a potential strategy for the treatment of heart failure with Chinese medicine[J]. J Inflamm Res, 2023, 16: 5451-64. doi:10.2147/jir.s441597 |
| [1] | Bing XIA, Jin PENG, Jiuyang DING, Jie WANG, Guowei TANG, Guojie LIU, Yun WANG, Changwu WAN, Cuiyun LE. ATF3 regulates inflammatory response in atherosclerotic plaques in mice through the NF-κB signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1131-1142. |
| [2] | Yumeng YE, Bo YU, Shasha LU, Yu ZHOU, Meihong DING, Guilin CHENG. Design and inflammation-targeting efficiency assessment of an engineered liposome-based nanomedicine delivery system targeting E-selectin [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 1013-1022. |
| [3] | Di CHEN, Ying LÜ, Yixin GUO, Yirong ZHANG, Ruixuan WANG, Xiaoruo ZHOU, Yuxin CHEN, Xiaohui WU. Dihydroartemisinin enhances doxorubicin-induced apoptosis of triple negative breast cancer cells by negatively regulating the STAT3/HIF-1α pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 254-260. |
| [4] | Hanjun ZUO, Zhaoda DUAN, Zhao WANG, Tao GUO, Jinsha SHI, Haolong SHI, Juanjuan LI. Gastrodin improves microglia-mediated inflammatory response after hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in neonatal rats via PI3K/AKT pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1712-1719. |
| [5] | Yuming ZHANG, Shicheng XIA, Linlin ZHANG, Mengxi CHEN, Xiaojing LIU, Qin GAO, Hongwei YE. Protective effect of Lonicerae japonicae flos extract against doxorubicin-induced liver injury in mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1571-1581. |
| [6] | Lingjun LU, Xiaodi YANG, Huaping ZHANG, Yuan LIANG, Xiulan SHI, Xin ZHOU. Recombinant Schistosoma japonicum cystatin alleviates acute liver injury in mice by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress, inflammation and hepatocyte apoptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(6): 1126-1134. |
| [7] | HE Cheng, CHEN Wei, ZHANG Nianzhi, LUAN Jun, WANG Sanfeng, ZHANG You. Shenqi Chongcao Formula ameliorates inflammatory response in rats with pulmonary fibrosis by activating the ASS1/src/STAT3 signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(4): 644-651. |
| [8] | BAO Hansheng, WANG Sutong, LÜ Mujie, WANG Yongcheng, JIANG Ping, LI Xiao. Activation of α7 nAChR improves white fat homeostasis and promotes beige adipogenesis and thermogenesis in obese mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(3): 499-506. |
| [9] | Youqin ZENG, Siyu CHEN, Yan LIU, Yitong LIU, Ling ZHANG, Jiao XIA, Xinyu WU, Changyou WEI, Ping LENG. AKBA combined with doxorubicin inhibits proliferation and metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells and xenograft growth in nude mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(12): 2449-2460. |
| [10] | Xiuqi SUN, Jing CAI, Anbang ZHANG, Bo PANG, Chunyan CHENG, Qiqi CHA, Fei QUAN, Tao YE. Electroacupuncture pretreatment alleviates post-stroke spasticity in rats by inhibiting NF‑κB/NLRP3 signaling pathway-mediated inflammation and neuronal apoptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(11): 2102-2109. |
| [11] | Hong YAO, Kedi LIU, Chengzhao LIU, Weihong LI, Qi DAI, Shi ZHAO, Ziheng DING, Hefei WANG, Xiaojing GE, Peifeng WEI, Jialin DUAN, Miaomiao XI. Maggot alleviates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin lesions in mice by inhibiting immune stress and complement activation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(11): 2121-2130. |
| [12] | Mengmeng CHENG, Xinguang LIU, Yanxin WEI, Xiaoxiang XING, Lan LIU, Nan XIN, Peng ZHAO. Tongsai Granules inhibit autophagy and macrophage-mediated inflammatory response to improve acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in rats [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(10): 1995-2003. |
| [13] | LI Shai, LI Li, MIN Simin, LIU Saisai, QIN Zhiwen, XIONG Zhishang, XU Jianguo, WANG Bowen, DING Dushan, ZHAO Shidi. Soybean isoflavones alleviate cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats by inhibiting ferroptosis and inflammatory cascade reaction [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(2): 323-330. |
| [14] | WEI Jia, YANG Qiang, LIN Lin, ZHU Canzhan, WEI Jin. Metformin mitigates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity via the AMPK pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(10): 1682-1688. |
| [15] | XIONG Fengmei, LIU Ruiping, LI Yang, SUN Na. Honokiol reduces doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in vitro by inhibiting pyroptosis via activating AMPK/Nrf2 signaling [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42(8): 1205-1211. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||