Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (7): 1527-1534.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.07.20
Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2025-03-11
Online:2025-07-20
Published:2025-07-17
Contact:
Li ZHAO
E-mail:1206635637@qq.com;lilily_333@sina.com
Tingting YANG, Li ZHAO. A stable mouse model of chronic liver fibrosis induced by vitamin A deficiency and intraperitoneal CCl4 injection[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1527-1534.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.07.20
| Index | Unmodeling group | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
VAN group (n=6) | VAD group 1 (n=6) | VAD group 2 (n=6) | VAN group (n=6) | VAD group 1 (n=6) | VAD group 2 (n=4) | |
| Serum retinol (μmol/L) | 1.313±0.09 | 0.76±0.111b | 0.592±0.042bc | 1.278±0.073 | 0.695±0.095b | 0.514±0.034abc |
| Liver index (%) | 4.25±0.658 | 4.07±0.175 | 4.41±0.969 | 6.05±0.802a | 6.37±0.195a | 6.19±0.337a |
| ALT (U/L) | 42.03±8.576 | 45.22±9.212 | 53.17±6.61bc | 70.73±8.663a | 75.73±9.886ab | 86.38±10.34abc |
| AST (U/L) | 76.13±7.81 | 113.33±11.72b | 111.01±23.73bc | 136.20±13.12a | 158.72±24.34ab | 182.74±19.49abc |
| Degree of fibrosis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
Tab.1 Effects of CCl4 treatment for 8 weeks on serum levels of retinol, ALT/AST and liver fibrosis in mice (Mean±SD)
| Index | Unmodeling group | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
VAN group (n=6) | VAD group 1 (n=6) | VAD group 2 (n=6) | VAN group (n=6) | VAD group 1 (n=6) | VAD group 2 (n=4) | |
| Serum retinol (μmol/L) | 1.313±0.09 | 0.76±0.111b | 0.592±0.042bc | 1.278±0.073 | 0.695±0.095b | 0.514±0.034abc |
| Liver index (%) | 4.25±0.658 | 4.07±0.175 | 4.41±0.969 | 6.05±0.802a | 6.37±0.195a | 6.19±0.337a |
| ALT (U/L) | 42.03±8.576 | 45.22±9.212 | 53.17±6.61bc | 70.73±8.663a | 75.73±9.886ab | 86.38±10.34abc |
| AST (U/L) | 76.13±7.81 | 113.33±11.72b | 111.01±23.73bc | 136.20±13.12a | 158.72±24.34ab | 182.74±19.49abc |
| Degree of fibrosis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
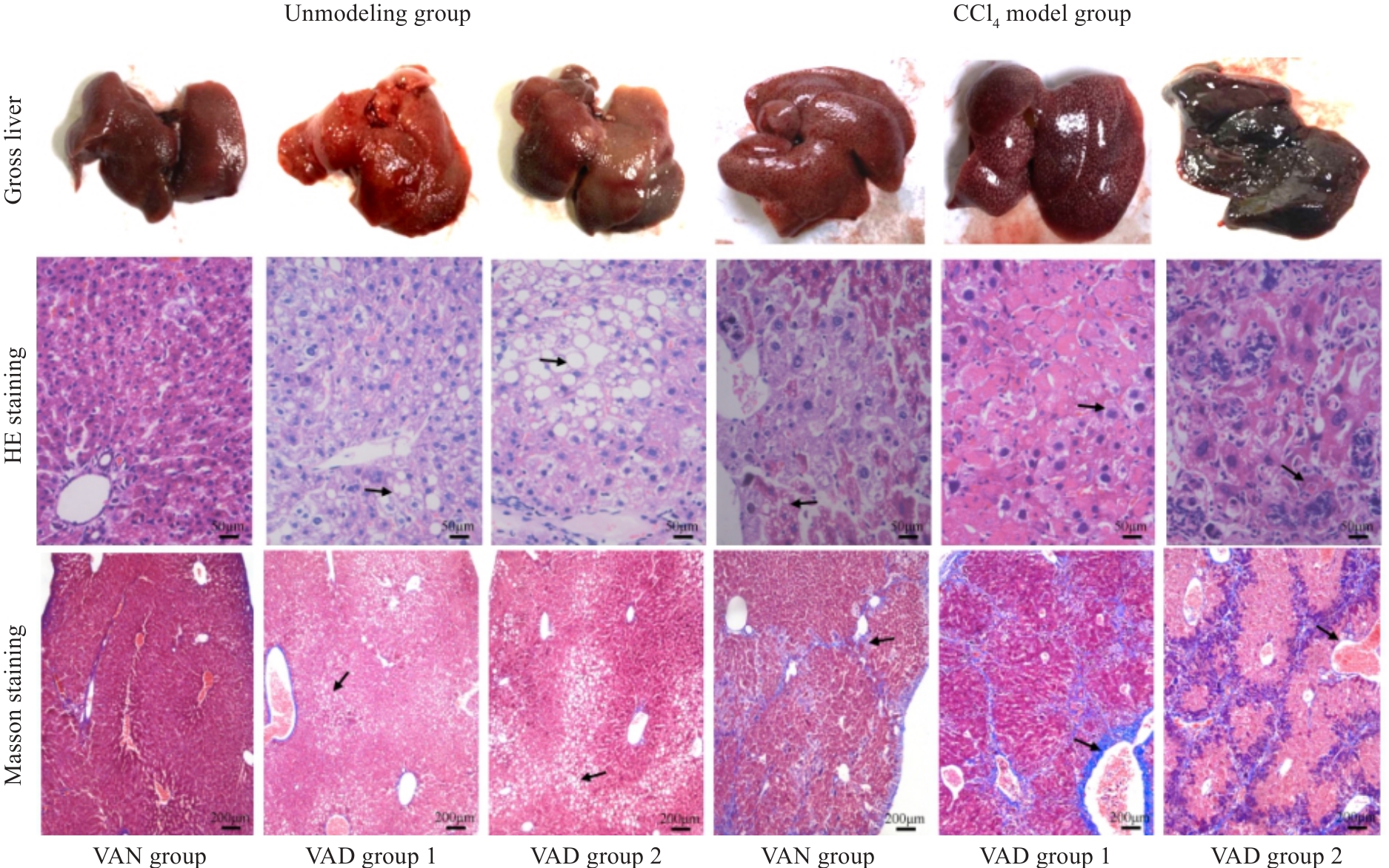
Fig.1 Gross observation of mouse livers and HE staining (Original magnification: ×400) and Masson staining (×100) of the liver tissues in each group after 8 weeks of CCl4 modeling. The arrows from "Unmodeled group" to "CCl4 model group" respectively point to: The cytoplasm is lightly stained and presents a vacuolar phenomenon,The phenomenon of inflammatory cell infiltration and the formation of blue stained fibrous tissue.
| Index | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
VAN group (n=6) | VAD group 1 (n=6) | VAD group 2 (n=6) | VAN group (n=6) | VAD group 1 (n=6) | VAD group 2 (n=4) | |
| Serum retinol (μmol/L) | 1.325±0.073 | 0.733±0.122b | 0.587±0.053bc | 1.29±0.073 | 0.707±0.083b | 0.534±0.068abc |
| Liver index (%) | 4.10±0.748 | 3.98±0.226 | 4.28±0.859 | 6.32±1.228a | 6.08±0.585a | 5.85±0.947a |
| ALT (U/L) | 44.32±4.36 | 47.88±11.10 | 49.33±7.32 | 57.7±12.95a | 70.92±12.73ab | 90.33±20.40abc |
| AST (U/L) | 78.27±411.24 | 110.43±12.34b | 129.95±17.85bc | 101.43±17.53a | 147.92±22.29ab | 173.15±31.25abc |
| Degree of fibrosis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
Tab.2 Effects of CCl4 on serum levels of retinol, ALT/AST and liver fibrosis in mice 4 weeks after CCl4 discontinuation (Mean±SD)
| Index | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
VAN group (n=6) | VAD group 1 (n=6) | VAD group 2 (n=6) | VAN group (n=6) | VAD group 1 (n=6) | VAD group 2 (n=4) | |
| Serum retinol (μmol/L) | 1.325±0.073 | 0.733±0.122b | 0.587±0.053bc | 1.29±0.073 | 0.707±0.083b | 0.534±0.068abc |
| Liver index (%) | 4.10±0.748 | 3.98±0.226 | 4.28±0.859 | 6.32±1.228a | 6.08±0.585a | 5.85±0.947a |
| ALT (U/L) | 44.32±4.36 | 47.88±11.10 | 49.33±7.32 | 57.7±12.95a | 70.92±12.73ab | 90.33±20.40abc |
| AST (U/L) | 78.27±411.24 | 110.43±12.34b | 129.95±17.85bc | 101.43±17.53a | 147.92±22.29ab | 173.15±31.25abc |
| Degree of fibrosis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
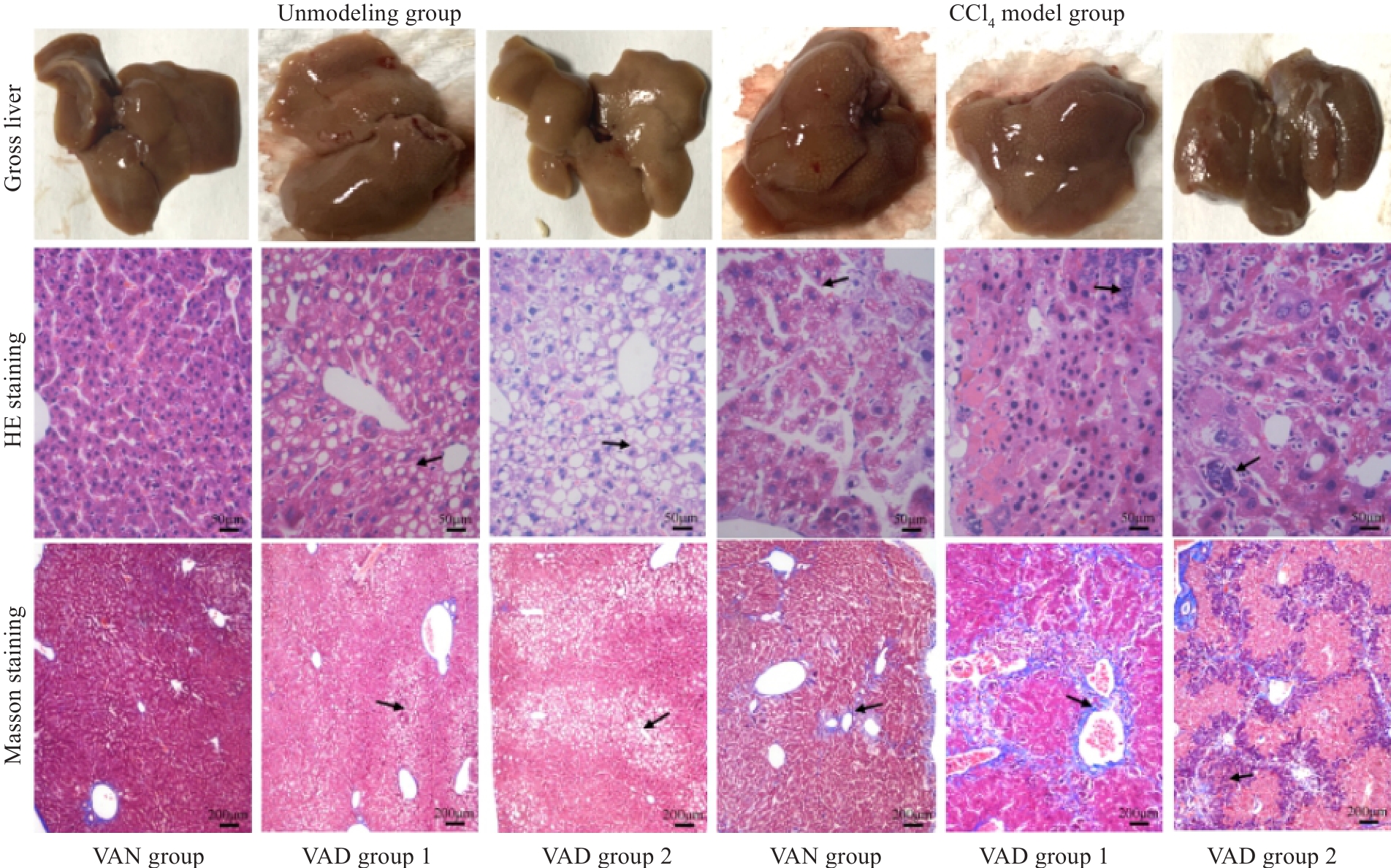
Fig.2 Gross observation of mouse livers and HE staining (×400) and Masson staining (×100) of the liver tissues in each group 4 weeks after CCl4 discontinuation. The arrows from "Unmodeled group" to "CCl4 model group" respectively point to: The cytoplasm is lightly stained and presents a vacuolar phenomenon,The phenomenon of inflammatory cell infiltration and formation of pseudolobules.
| Index | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
VAN group (n=6) | VAD group 1 (n=6) | VAD group 2 (n=6) | VAN group (n=6) | VAD group 1 (n=6) | VAD group2 (n=3) | |
| Serum retinol (μmol/L) | 1.37±0.08 | 0.78±0.13b | 0.60±0.10bc | 1.31±0.09 | 0.73±0.09bc | 0.55±0.10abc |
| Liver index (%) | 4.06±0.472 | 4.20±0.0.85 | 4.34±0.78 | 5.68±1.01a | 6.02±0.445a | 5.87±1.63a |
| ALT (U/L) | 45.1±8.95 | 48.67±7.86 | 49.52±10.58 | 49.33±0.09 | 72.78±0.09ab | 86.57±13.91abc |
| AST (U/L) | 76.40±12.19 | 114.85±9.84b | 123.0±25.21bc | 84.47±12.32 | 141.45±16.06ab | 197.4±67.92abc |
| Degree of fibrosis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 3 |
Tab.3 Serum levels of retinol, ALT/AST and liver fibrosis in mice 8 weeks after CCl4 discontinuation (Mean±SD)
| Index | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
VAN group (n=6) | VAD group 1 (n=6) | VAD group 2 (n=6) | VAN group (n=6) | VAD group 1 (n=6) | VAD group2 (n=3) | |
| Serum retinol (μmol/L) | 1.37±0.08 | 0.78±0.13b | 0.60±0.10bc | 1.31±0.09 | 0.73±0.09bc | 0.55±0.10abc |
| Liver index (%) | 4.06±0.472 | 4.20±0.0.85 | 4.34±0.78 | 5.68±1.01a | 6.02±0.445a | 5.87±1.63a |
| ALT (U/L) | 45.1±8.95 | 48.67±7.86 | 49.52±10.58 | 49.33±0.09 | 72.78±0.09ab | 86.57±13.91abc |
| AST (U/L) | 76.40±12.19 | 114.85±9.84b | 123.0±25.21bc | 84.47±12.32 | 141.45±16.06ab | 197.4±67.92abc |
| Degree of fibrosis | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 3 |
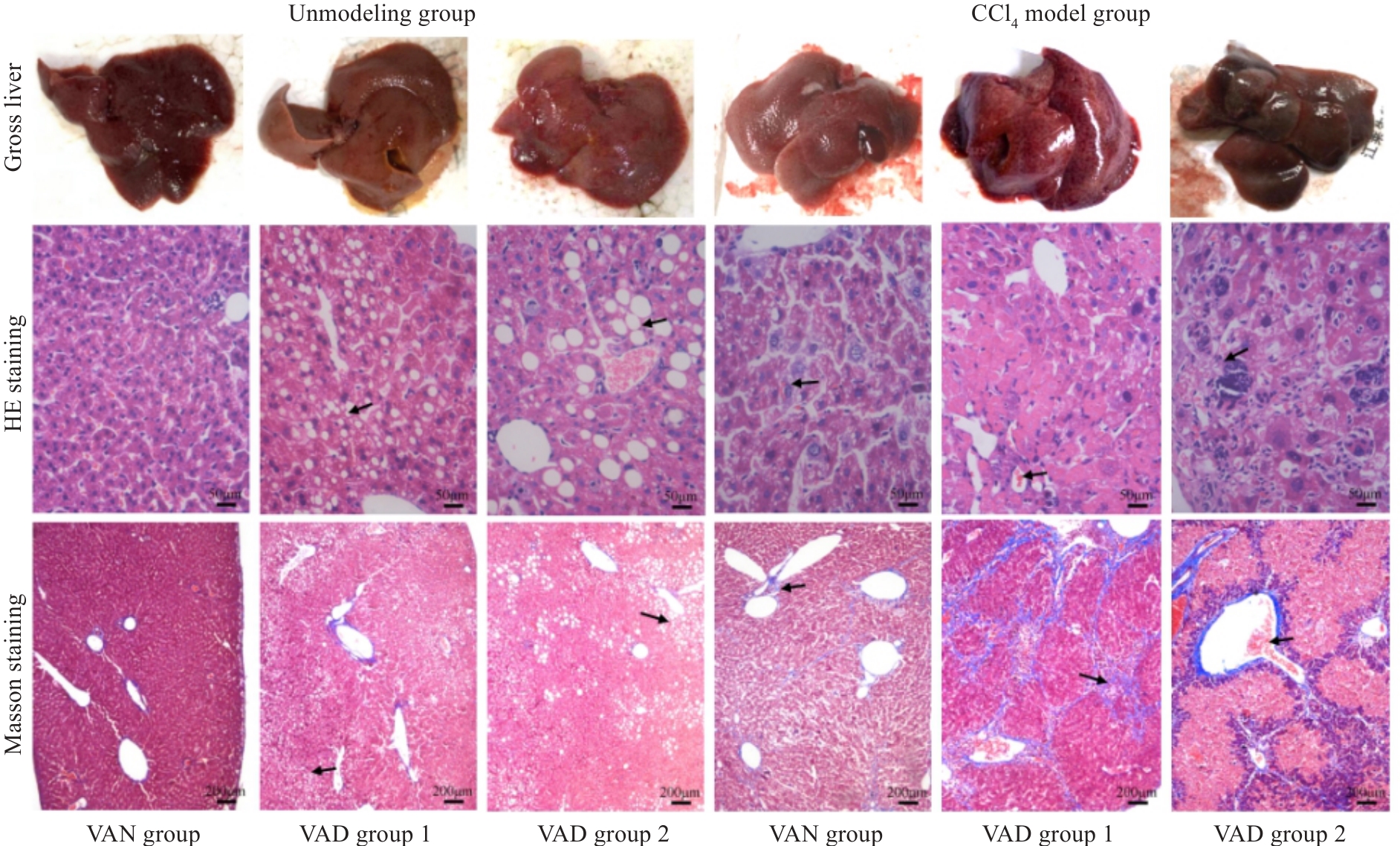
Fig.3 Gross observation of mouse livers and HE staining (×400) and Masson staining (×100) of the liver tissues in each group 8 weeks after CCl4 discontinuation. The arrows from "Unmodeled group" to "CCl4 model group" respectively point to: The cytoplasm is lightly stained and presents a vacuolar phenomenon,Disorder of hepatic cord structure and formation of pseudolobules.
| [1] | Li T, Liu HB, Hu WY, et al. Role of inflammation hepatic fibrosis[J]. J Clin Exp Hepatol, 2022, 38(10): 2368-72. |
| [2] | Roehlen N, Crouchet E, Baumert TF. Liver fibrosis: mechanistic concepts and therapeutic perspectives[J]. Cells, 2020, 9(4): E875. doi:10.3390/cells9040875 |
| [3] | Parola M, Pinzani M. Liver fibrosis: Pathophysiology, pathogenetic targets and clinical issues[J]. Mol Aspects Med, 2019, 65: 37-55. doi:10.1016/j.mam.2018.09.002 |
| [4] | Fan W, Liu T, Chen W, et al. ECM1 prevents activation of transforming growth factor β, hepatic stellate cells, and fibrogenesis in mice[J]. Gastroenterology, 2019, 157(5): 1352-67.e13. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2019.07.036 |
| [5] | 王 娟, 杨晶晶, 周仁鹏, 等. 肝纤维化小鼠模型研究现状[J]. 中国比较医学杂志, 2022, 32(2): 105-10. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-7856.2022.02.016 |
| [6] | 王丽春, 赵连三. 肝纤维化的实验动物模型[J]. 中国实验动物学报, 2004, 12(4): 56-60. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1005-4847.2004.04.015 |
| [7] | Kim YO, Popov Y, Schuppan D. Optimized mouse models for liver fibrosis[J]. Methods Mol Biol, 2017, 1559: 279-96. doi:10.1007/978-1-4939-6786-5_19 |
| [8] | Yoneda A, Sakai-Sawada K, Niitsu Y, et al. Vitamin A and insulin are required for the maintenance of hepatic stellate cell quiescence[J]. Exp Cell Res, 2016, 341(1): 8-17. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2016.01.012 |
| [9] | Lee YS, Jeong WI. Retinoic acids and hepatic stellate cells in liver disease[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2012, 27(): 75-9. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1746.2011.07007.x |
| [10] | Haaker MW, Vaandrager AB, Helms JB. Retinoids in health and disease: a role for hepatic stellate cells in affecting retinoid levels[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta BBA Mol Cell Biol Lipds, 2020, 1865(6): 158674. doi:10.1016/j.bbalip.2020.158674 |
| [11] | 重庆医科大学附属儿童医院.一种肝纤维化动物模型的构建方法:CN202210011928.4[P]. 2022-04-22. |
| [12] | Li JP, Gao Y, Chu SF, et al. Nrf2 pathway activation contributes to anti-fibrosis effects of ginsenoside Rg1 in a rat model of alcohol- and CCl4-induced hepatic fibrosis[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2014, 35(8): 1031-44. doi:10.1038/aps.2014.41 |
| [13] | Li J, Deng X, Wang S, et al. Resolvin D1 attenuates CCl4 Induced Liver Fibrosis by Inhibiting Autophagy-Mediated HSC activation via AKT/mTOR Pathway[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2021, 12: 792414. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.792414 |
| [14] | 吕艳杭, 吴姗姗, 王振常, 等. 肝纤维化动物模型造模方法的研究进展[J]. 广西医学, 2020, 42(7): 875-8. |
| [15] | Crespo Yanguas S, Cogliati B, Willebrords J, et al. Experimental models of liver fibrosis[J]. Arch Toxicol, 2016, 90(5): 1025-48. doi:10.1007/s00204-015-1543-4 |
| [16] | Chow AM, Tan M, Gao DS, et al. Molecular MRI of liver fibrosis by a peptide-targeted contrast agent in an experimental mouse model[J]. Invest Radiol, 2013, 48(1): 46-54. doi:10.1097/rli.0b013e3182749c0b |
| [17] | 郑 虹, 肖 海, 吴雄健. 肝纤维化的发病机制及治疗的最新进展[J]. 赣南医学院学报, 2019, 39(3): 298-302, 308. |
| [18] | 刘甦苏, 霍桂桃, 王辰飞, 等. 四氯化碳诱导近交系C57BL/6小鼠建立肝纤维化模型[J]. 实验动物科学, 2019, 36(4): 28-30, 34. |
| [19] | 史丛晶, 邓雅方, 张志宏, 等.胆南星对四氯化碳致小鼠急性肝损伤的保护作用及机制研究[J]. 中国药房, 2022, 33(23): 2835-9. doi:10.6039/j.issn.1001-0408.2022.23.04 |
| [20] | 平大冰, 齐婧姝, 孙 鑫, 等. 全反式维甲酸对肝纤维化氧化应激损伤自然杀伤细胞的保护作用[J]. 中国免疫学杂志, 2024, 40(7): 1359-63. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1000-484X.2024.07.003 |
| [21] | 汪 辛. VA修饰PEG-PCL纳米胶束载喜树碱选择性抑制活化态肝星状细胞糖酵解行为及小鼠肝纤维化的研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2017. |
| [22] | 翁飞鸿, 周一平, 伊思敏, 等. 肝纤维化的病理学发生机制及诊疗研究进展[J]. 天津医科大学学报, 2023, 29(5): 559-63. |
| [23] | 合肥博太医药生物技术发展有限公司. 视黄酸及其衍生物在制备治疗肝纤维化药物中的应用:CN201210029865.1[P]. 2012-07-04. |
| [24] | 周 哲. 维生素A缺乏对免疫性肝炎肝损伤影响的实验研究[D]. 天津医科大学, 2018, 11-78. |
| [25] | 杨怡静, 王雨青, 刘 杰. 辛酸癸酸聚乙二醇甘油酯在口服制剂中的应用及促吸机理[J]. 药学与临床研究, 2021, 29(6): 449-53. |
| [26] | Aasheim ET, Hofsø D, Hjelmesæth J, et al. Vitamin status in morbidly obese patients: a cross-sectional study 2[J]. Am J Clin Nutr, 2008, 87(2): 362-9. doi:10.1093/ajcn/87.2.362 |
| [27] | Jeyakumar SM, Vajreswari A, Sesikeran B, et al. Vitamin A supplementation induces adipose tissue loss through apoptosis in lean but not in obese rats of the WNIN/Ob strain[J]. J Mol Endocrinol, 2005, 35(2): 391-8. doi:10.1677/jme.1.01838 |
| [28] | Prashanth A, Jeyakumar SM, Giridharan NV, et al. Vitamin A-enriched diet modulates reverse cholesterol transport in hypercholesterolemic obese rats of the WNIN/ob strain[J]. J Atheroscler Thromb, 2014, 21(11): 1197-207. doi:10.5551/jat.22186 |
| [29] | Ravichandra A, Schwabe RF. Mouse models of liver fibrosis[J]. Methods Mol Biol, 2021, 2299: 339-56. doi:10.1007/978-1-0716-1382-5_23 |
| [30] | Hisamori S, Tabata C, Kadokawa Y, et al. All-trans-retinoic acid ameliorates carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis in mice through modulating cytokine production[J]. Liver Int, 2008, 28(9): 1217-25. doi:10.1111/j.1478-3231.2008.01745.x |
| [31] | 庄子锐, 王明亮, 张 婷, 等. 肝肾纤维化动物模型的研究进展及评价[J]. 中国实验动物学报, 2020, 28(6): 845-52. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1005-4847.2020.06.016 |
| [32] | Luangmonkong T, Suriguga S, Mutsaers HAM, et al. Targeting oxidative stress for the treatment of liver fibrosis[J]. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol, 2018, 175: 71-102. doi:10.1007/112_2018_10 |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
