Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (4): 880-892.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.04.24
Yutong LI1,2( ), Xingyu SONG1,2, Ruixu SUN1,2, Xuan DONG1,2, Hongwei LIU1,2(
), Xingyu SONG1,2, Ruixu SUN1,2, Xuan DONG1,2, Hongwei LIU1,2( )
)
Received:2025-02-17
Online:2025-04-20
Published:2025-04-28
Contact:
Hongwei LIU
E-mail:liyutong@gdmu.edu.cn;lhwhongwei@gdmu.edu.cn
Yutong LI, Xingyu SONG, Ruixu SUN, Xuan DONG, Hongwei LIU. A pan-cancer analysis of PYCR1 and its predictive value for chemotherapy and immunotherapy responses in bladder cancer[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 880-892.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.04.24
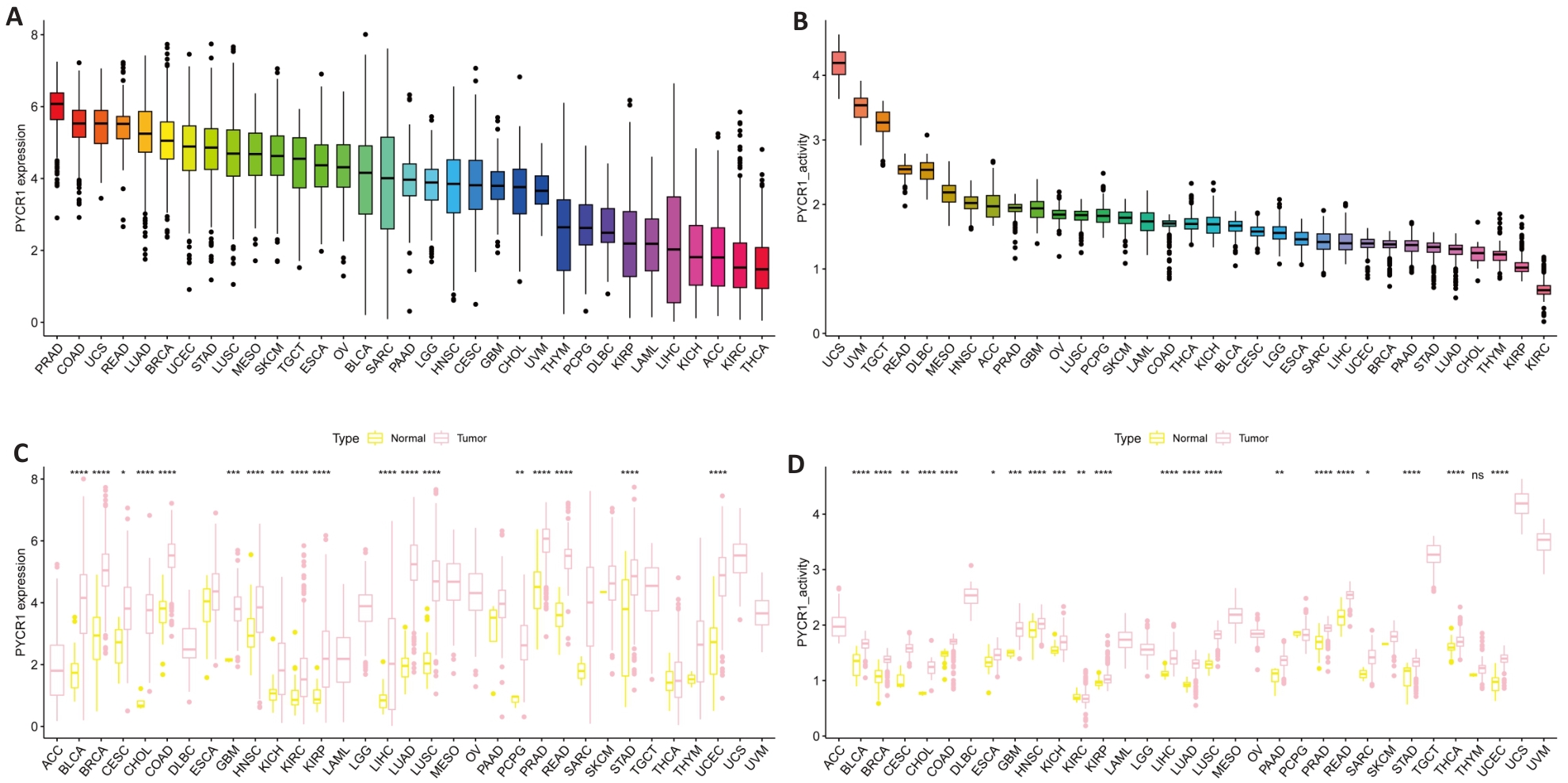
Fig.1 Expression of PYCR1 in pan-cancer. A, B: mRNA and protein expression levels of PYCR1 in UCSC Xena and GTEx pan-cancer data. C, D: Differences in mRNA and protein expression levels of PYCR1 between cancer and adjacent tissues in 33 cancers. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001 vs control group.
| Index | Cancers | HR | 95% CI | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OS | SARC KIRP KIRC ESCA ACC LGG | 1.29 2.01 1.59 1.22 1.68 0.78 | 1.13-1.47 1.58-2.54 1.40-1.80 0.94-1.59 1.28-2.21 0.60-1.00 0.96-3.35 0.67-1.01 1.37-2.09 1.44-1.87 1.18-4.23 1.25-1.92 1.12-2.47 0.74-4.82 1.27-2.24 1.59-2.15 0.90-1.65 1.09-1.45 2.92-1003.87 2.27-4.20 | <0.001 <0.01 <0.01 0.022 0.022 0.017 |
| PFS | UVM LGG KIRP KIRC KICH ACC | 1.79 0.82 1.69 1.64 2.24 1.54 | 0.032 0.013 <0.01 <0.01 0.020 <0.01 | |
| DFS | ACC | 1.66 | 0.024 | |
| DSS | PCPG ACC KIRC ESCA SARC PRAD KIRP | 1.88 1.69 1.85 1.22 1.26 54.17 3.09 | 0.022 0.028 <0.01 0.043 0.047 0.030 <0.01 |
Tab.1 Prognostic significance of PYCR1 in pan-cancer
| Index | Cancers | HR | 95% CI | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OS | SARC KIRP KIRC ESCA ACC LGG | 1.29 2.01 1.59 1.22 1.68 0.78 | 1.13-1.47 1.58-2.54 1.40-1.80 0.94-1.59 1.28-2.21 0.60-1.00 0.96-3.35 0.67-1.01 1.37-2.09 1.44-1.87 1.18-4.23 1.25-1.92 1.12-2.47 0.74-4.82 1.27-2.24 1.59-2.15 0.90-1.65 1.09-1.45 2.92-1003.87 2.27-4.20 | <0.001 <0.01 <0.01 0.022 0.022 0.017 |
| PFS | UVM LGG KIRP KIRC KICH ACC | 1.79 0.82 1.69 1.64 2.24 1.54 | 0.032 0.013 <0.01 <0.01 0.020 <0.01 | |
| DFS | ACC | 1.66 | 0.024 | |
| DSS | PCPG ACC KIRC ESCA SARC PRAD KIRP | 1.88 1.69 1.85 1.22 1.26 54.17 3.09 | 0.022 0.028 <0.01 0.043 0.047 0.030 <0.01 |
| Cancers | Description |
|---|---|
| CESC | Maturity-onset diabetes of the young, Glutathione metabolism, Melanoma Olfactory Transduction, Maturity-onset diabetes of the young, Ascorbic Acid Metabolism Taurine and Hypotaurine Metabolism, Taste transduction, Hedgehog signaling pathway Ascorbic Acid Metabolism, Autophagy, Pentose and Glucuronate Interconversions Lysine Degradation, Arginine and Proline Metabolism, Basal Cell Carcinoma Folate biosynthesis, Autophagy, Cytosolic DNA sensing by cGAS Other glycan degradation, Autophagy, Butanoate Metabolism Primary immunodeficiency, Viral myocarditis, Graft-Versus-Host Disease Viral myocarditis, Maturity-onset diabetes of the young, Glutathione metabolism |
| LUSC | |
| LIHC | |
| THYM | |
| LAML | |
| CHOL | |
| UCS | |
| THCA | |
| KICH | |
| HNSC | Ascorbic Acid Metabolism, Porphyrin and Chlorophyll Metabolism, Metabolism of xenobiotics by cytochrome P450 |
| UCEC | Olfactory Transduction, Autophagy, Autoimmune thyroid disorders |
| STAD | Dilated cardiomyopathy, Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy, Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy |
| ACC | Glycosaminoglycan degradation, Hedgehog signaling pathway, Olfactory Transduction |
| SKCM | Primary immunodeficiency, Linoleic acid metabolism, Graft-Versus-Host Disease |
| LUAD | Olfactory Transduction, Autophagy, RIG-I-like Receptor signaling pathway |
| TGCT | Allograft rejection, Graft-Versus-Host Disease, Primary immunodeficiency |
| READ | Cytosolic DNA sensing by cGAS, Autoimmune thyroid disorders, Autophagy |
| LGG | Pentose and Glucuronate Interconversions, Ascorbic Acid Metabolism, Porphyrin and Chlorophyll Metabolism |
| BRCA | Olfactory Transduction, Cytosolic DNA sensing by cGAS, Autoimmune thyroid disorders |
| COAD | Taste transduction, Olfactory Transduction, Cytosolic DNA sensing by cGAS |
| BLCA | Maturity-onset diabetes of the young, Valine, Leucine, and Isoleucine Degradation, Graft-Versus-Host Disease |
Tab.2 Top 3 molecular functions regulated by PYCR1 in pan-cancer
| Cancers | Description |
|---|---|
| CESC | Maturity-onset diabetes of the young, Glutathione metabolism, Melanoma Olfactory Transduction, Maturity-onset diabetes of the young, Ascorbic Acid Metabolism Taurine and Hypotaurine Metabolism, Taste transduction, Hedgehog signaling pathway Ascorbic Acid Metabolism, Autophagy, Pentose and Glucuronate Interconversions Lysine Degradation, Arginine and Proline Metabolism, Basal Cell Carcinoma Folate biosynthesis, Autophagy, Cytosolic DNA sensing by cGAS Other glycan degradation, Autophagy, Butanoate Metabolism Primary immunodeficiency, Viral myocarditis, Graft-Versus-Host Disease Viral myocarditis, Maturity-onset diabetes of the young, Glutathione metabolism |
| LUSC | |
| LIHC | |
| THYM | |
| LAML | |
| CHOL | |
| UCS | |
| THCA | |
| KICH | |
| HNSC | Ascorbic Acid Metabolism, Porphyrin and Chlorophyll Metabolism, Metabolism of xenobiotics by cytochrome P450 |
| UCEC | Olfactory Transduction, Autophagy, Autoimmune thyroid disorders |
| STAD | Dilated cardiomyopathy, Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy, Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy |
| ACC | Glycosaminoglycan degradation, Hedgehog signaling pathway, Olfactory Transduction |
| SKCM | Primary immunodeficiency, Linoleic acid metabolism, Graft-Versus-Host Disease |
| LUAD | Olfactory Transduction, Autophagy, RIG-I-like Receptor signaling pathway |
| TGCT | Allograft rejection, Graft-Versus-Host Disease, Primary immunodeficiency |
| READ | Cytosolic DNA sensing by cGAS, Autoimmune thyroid disorders, Autophagy |
| LGG | Pentose and Glucuronate Interconversions, Ascorbic Acid Metabolism, Porphyrin and Chlorophyll Metabolism |
| BRCA | Olfactory Transduction, Cytosolic DNA sensing by cGAS, Autoimmune thyroid disorders |
| COAD | Taste transduction, Olfactory Transduction, Cytosolic DNA sensing by cGAS |
| BLCA | Maturity-onset diabetes of the young, Valine, Leucine, and Isoleucine Degradation, Graft-Versus-Host Disease |
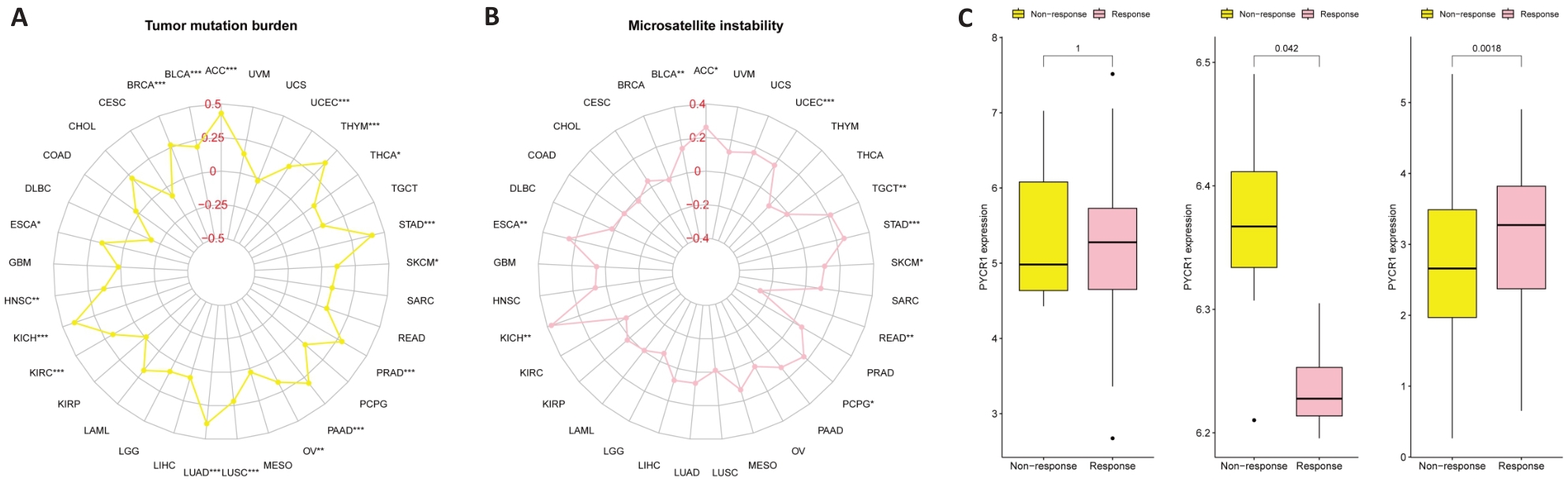
Fig.4 Potential of PYCR1 for assessing tumor mutation burden (TMB), microsatellite instability (MSI) and immune therapy benefits in pan-cancer. A: Correlation of PYCR1 with TMB and MSI. B: Correlation of PYCR1 with benefits of anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in SKCM patients in the SKCM immunotherapy cohort. C: Correlation of PYCR1 with benefits of anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy in RCC patients in the metastatic RCC immunotherapy cohort. D: Correlation of PYCR1 with immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy benefit in patients with BLCA in the IMvigor210 cohort.
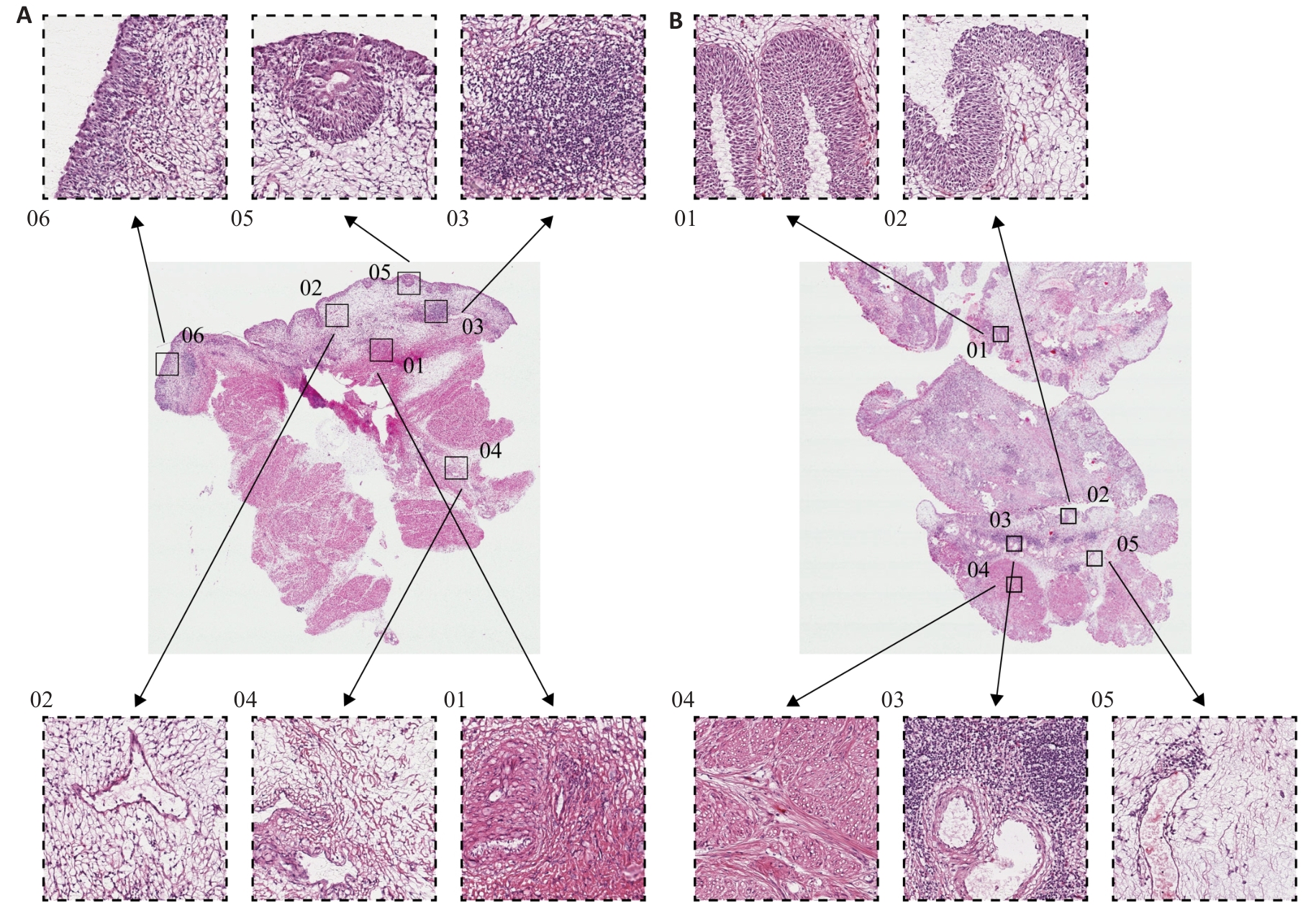
Fig.6 Histological features of BLCA with high and low PYCR1 expressions. A: HE staining profile of BLCA tissue with high PYCR1 expression level (Original magnification: ×1000). B: HE staining profile of BLCA tissue with low PYCR1 expression level (×1000).

Fig.7 Effect of PYCR1 silencing on proliferative capacity of BLCA cell lines. A: mRNA expression levels of PYCR1 in BLCA cell lines and SV-HUC-1. **P<0.01 vs SV-HUC-1. B: Verification of PYCR1 silencing efficiency. C: Effect of PYCR1 silencing on proliferation of T24 and UM-UC-3 cells. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs si-NC.
| Characteristics | HR | 95% CI | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | 1.05 | 1.02-1.07 | <0.001 |
| Tumor classification | 1.25 | 1.04-1.49 | 0.016 |
| Copy number variation | 0.97 | 0.79-1.19 | 0.764 |
| Gender | 0.95 | 0.55-1.65 | 0.858 |
| Grade | 2.02 | 0.49-8.29 | 0.327 |
| Hypermethylation | 0.93 | 0.79-1.09 | 0.377 |
| Hypomethylation | 0.92 | 0.78-1.08 | 0.044 |
| Tumor mutation burden | 1.10 | 0.85-1.44 | 0.457 |
| PYCR1 | 1.23 | 0.99-1.87 | 0.032 |
| Race | 0.91 | 0.67-1.24 | 0.544 |
| Single nucleotide variation | 1.00 | 0.99-1.01 | 0.027 |
| Stage | 1.60 | 1.19-2.15 | 0.002 |
Tab.3 Univariate analysis for identifying prognostic risk factors for BLCA
| Characteristics | HR | 95% CI | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | 1.05 | 1.02-1.07 | <0.001 |
| Tumor classification | 1.25 | 1.04-1.49 | 0.016 |
| Copy number variation | 0.97 | 0.79-1.19 | 0.764 |
| Gender | 0.95 | 0.55-1.65 | 0.858 |
| Grade | 2.02 | 0.49-8.29 | 0.327 |
| Hypermethylation | 0.93 | 0.79-1.09 | 0.377 |
| Hypomethylation | 0.92 | 0.78-1.08 | 0.044 |
| Tumor mutation burden | 1.10 | 0.85-1.44 | 0.457 |
| PYCR1 | 1.23 | 0.99-1.87 | 0.032 |
| Race | 0.91 | 0.67-1.24 | 0.544 |
| Single nucleotide variation | 1.00 | 0.99-1.01 | 0.027 |
| Stage | 1.60 | 1.19-2.15 | 0.002 |
| Characteristics | HR | 95% CI | Assignment and Attributes | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | 1.04 | 1.02-1.07 | Continuous variable | 0.001 |
| Tumor classification | 1.16 | 0.95-1.41 | 0= LumP,1= LumNS,2= LumU,3= Stroma-rich,4= Ba/Sq,5= NE-like | 0.135 |
| Hypomethylation | 0.89 | 0.75-1.05 | Continuous variable | 0.162 |
| PYCR1 | 1.14 | 1.02-1.68 | Continuous variable | 0.006 |
| Single nucleotide variation | 1.00 | 0.99-1.01 | Continuous variable | 0.019 |
| Stage | 1.49 | 1.10-2.04 | 0= I-II,1= III-IV | 0.011 |
Tab.4 Multivariate analysis for identifying independent prognostic risk factors for BLCA
| Characteristics | HR | 95% CI | Assignment and Attributes | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | 1.04 | 1.02-1.07 | Continuous variable | 0.001 |
| Tumor classification | 1.16 | 0.95-1.41 | 0= LumP,1= LumNS,2= LumU,3= Stroma-rich,4= Ba/Sq,5= NE-like | 0.135 |
| Hypomethylation | 0.89 | 0.75-1.05 | Continuous variable | 0.162 |
| PYCR1 | 1.14 | 1.02-1.68 | Continuous variable | 0.006 |
| Single nucleotide variation | 1.00 | 0.99-1.01 | Continuous variable | 0.019 |
| Stage | 1.49 | 1.10-2.04 | 0= I-II,1= III-IV | 0.011 |
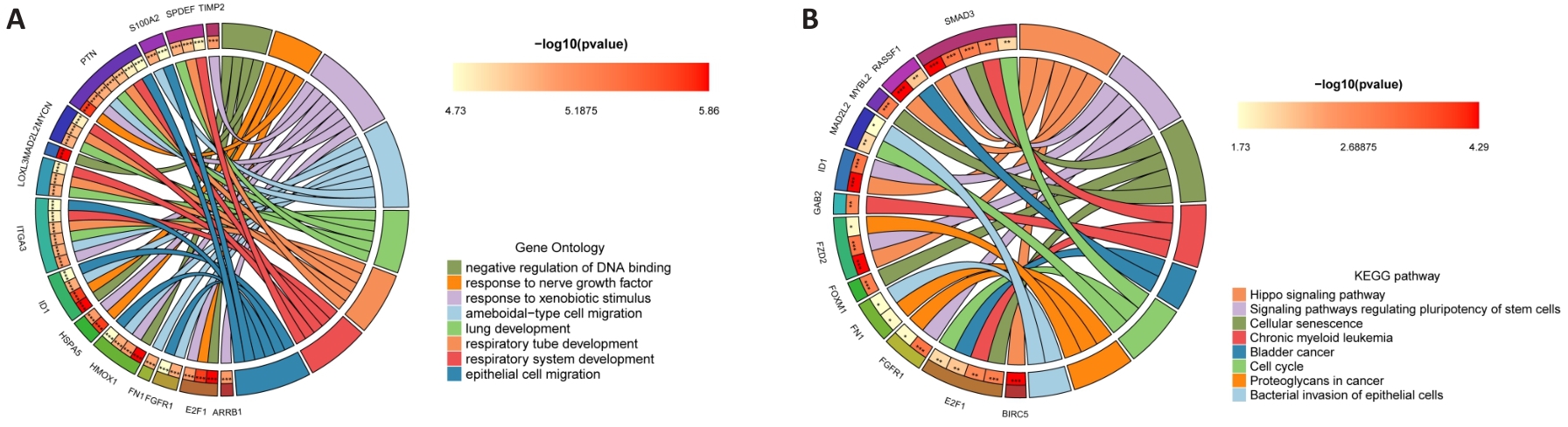
Fig.10 Molecular mechanism of PYCR1 for promoting BLCA progression. A, B: GO and KEGG signaling pathway enrichment analysis circle diagram of PYCR1 co-expressed genes.
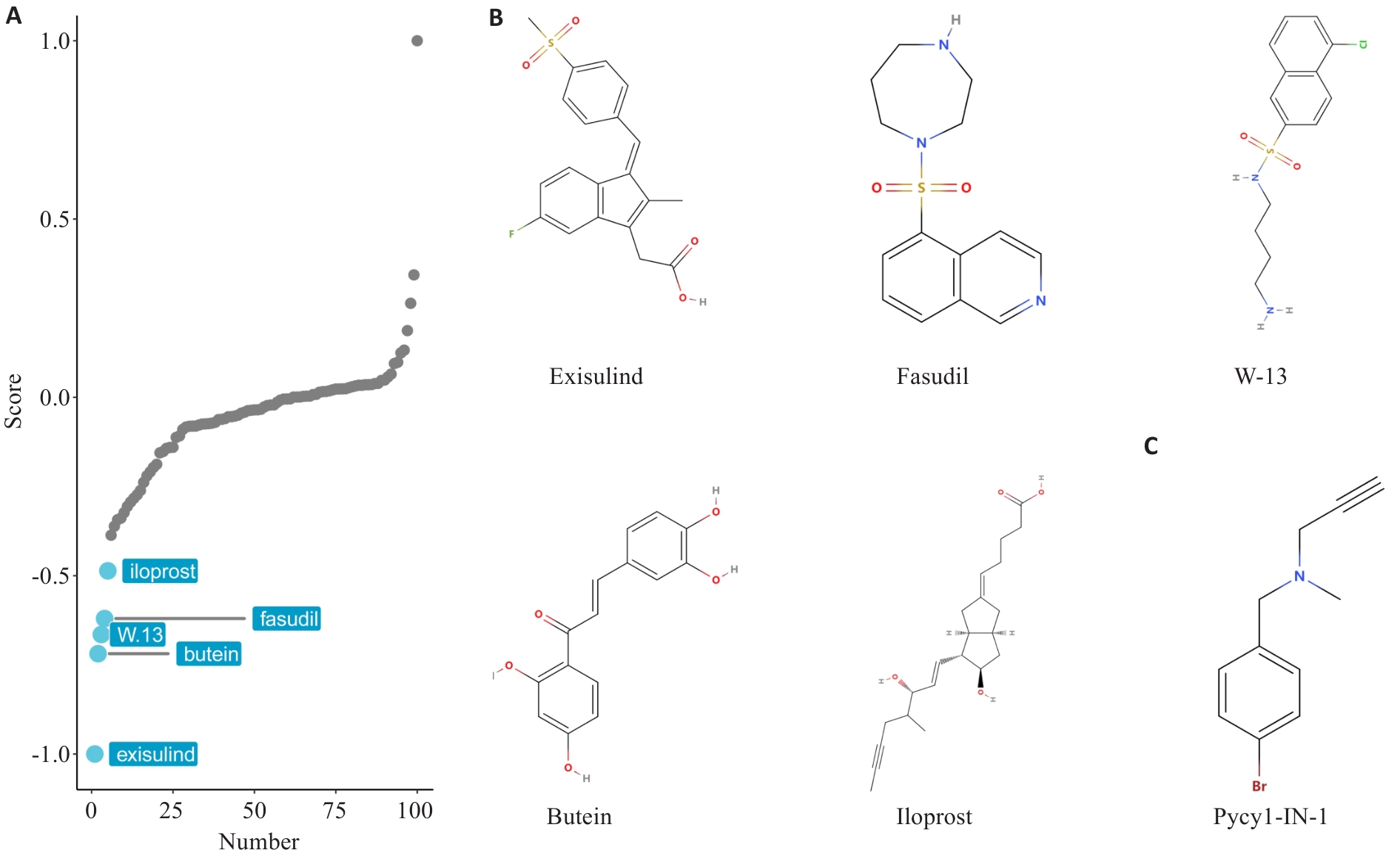
Fig.12 Virtual screening of small molecule drugs based on PYCR1 expression profiling. A: Screening for small molecule drugs in BLCA patients based on PYCR1 expression profile using XSum algorithm. B: Likely compound structures of candidate small molecule inhibitors of PYCR1. C: Known PYCR1 inhibitor Pycr1-IN-1 is used as the positive control.
| Ligands | ID | Cavity volume (Å3) | Vina score (kcal/mol) | Center (x, y, z) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pycr1-IN-1 | C1 | 436 | -5.2 | 34, 58, 14 |
| C2 | 377 | -4.5 | 31, 63, 1 | |
| C3 | 316 | -4.7 | 9, 60, -6 | |
| Exisulind | C2 | 377 | -7.1 | 31, 63, 1 |
| C4 | 232 | -7.1 | 1, 66, -5 | |
| C3 | 316 | -6.8 | 9, 60, -6 | |
| Fasudil | C1 | 436 | -7 | 34, 58, 14 |
| C4 | 232 | -6.5 | 1, 66, -5 | |
| C5 | 142 | -6.4 | 40, 83, -2 | |
| Butein | C4 | 232 | -6.6 | 1, 66, -5 |
| C2 | 377 | -6.5 | 31, 63, 1 | |
| C1 | 436 | -6.3 | 34, 58, 14 | |
| Iloprost | C1 | 436 | -6.3 | 34, 58, 14 |
| C2 | 377 | -6.2 | 31, 63, 1 | |
| C4 | 232 | -6.1 | 1, 66, -5 | |
| W-13 | C1 | 436 | -6.2 | 34, 58, 14 |
| C2 | 377 | -6 | 31, 63, 1 | |
| C4 | 232 | -5.9 | 1, 66, -5 |
Tab.5 Conformational binding energies of small molecule inhibitor-PYCR1 protein complexes (Top 3)
| Ligands | ID | Cavity volume (Å3) | Vina score (kcal/mol) | Center (x, y, z) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pycr1-IN-1 | C1 | 436 | -5.2 | 34, 58, 14 |
| C2 | 377 | -4.5 | 31, 63, 1 | |
| C3 | 316 | -4.7 | 9, 60, -6 | |
| Exisulind | C2 | 377 | -7.1 | 31, 63, 1 |
| C4 | 232 | -7.1 | 1, 66, -5 | |
| C3 | 316 | -6.8 | 9, 60, -6 | |
| Fasudil | C1 | 436 | -7 | 34, 58, 14 |
| C4 | 232 | -6.5 | 1, 66, -5 | |
| C5 | 142 | -6.4 | 40, 83, -2 | |
| Butein | C4 | 232 | -6.6 | 1, 66, -5 |
| C2 | 377 | -6.5 | 31, 63, 1 | |
| C1 | 436 | -6.3 | 34, 58, 14 | |
| Iloprost | C1 | 436 | -6.3 | 34, 58, 14 |
| C2 | 377 | -6.2 | 31, 63, 1 | |
| C4 | 232 | -6.1 | 1, 66, -5 | |
| W-13 | C1 | 436 | -6.2 | 34, 58, 14 |
| C2 | 377 | -6 | 31, 63, 1 | |
| C4 | 232 | -5.9 | 1, 66, -5 |
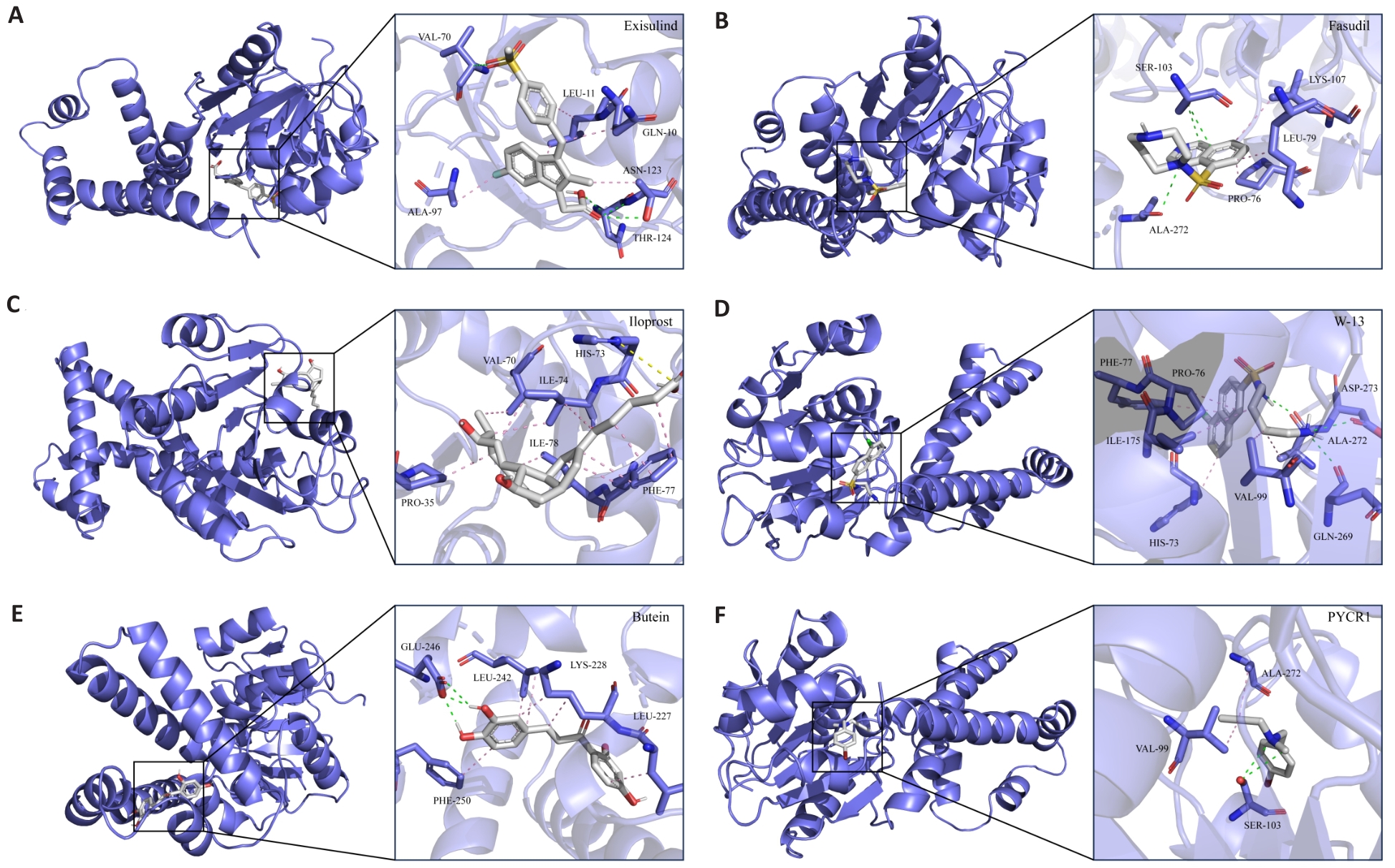
Fig.13 Interaction pattern of candidate compounds with protein receptors. A-F: 3D interaction pattern diagram between candidate small molecule inhibitors and receptor protein PYCR1. Gray stick model represents subsequent small molecule inhibitors, the blue stick model represents PYCR1 side chain amino acid residues, the pink dashed line represents hydrophobic interactions, the green dashed line represents hydrogen bonding interactions, and the yellow dashed line represents alkyl interactions.
| 1 | Li Y, Xu J, Bao P, et al. Survival and clinicopathological significance of PYCR1 expression in cancer: A meta-analysis[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12: 985613. |
| 2 | Luo Y, Yu J, Lin Z, et al. Metabolic characterization of sphere-derived prostate cancer stem cells reveals aberrant urea cycle in stemness maintenance[J]. Int J Cancer, 2024, 155(4): 742-55. |
| 3 | Kay EJ, Paterson K, Riera-Domingo C, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts require proline synthesis by PYCR1 for the deposition of pro-tumorigenic extracellular matrix[J]. Nat Metab, 2022, 4(6): 693-710. |
| 4 | Zhou P, Du X, Jia W, et al. Engineered extracellular vesicles for targeted reprogramming of cancer-associated fibroblasts to potentiate therapy of pancreatic cancer[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2024, 9(1): 151. |
| 5 | Fang K, Sun M, Leng Z, et al. Targeting IGF1R signaling enhances the sensitivity of cisplatin by inhibiting proline and arginine metabolism in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma under hypoxia [J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2023, 42(1): 73. |
| 6 | Li F, Zheng Z, Chen W, et al. Regulation of cisplatin resistance in bladder cancer by epigenetic mechanisms[J]. Drug Resist Updat, 2023, 68: 100938. |
| 7 | Lopez-Beltran A, Cookson M S, Guercio B J, et al. Advances in dia-gnosis and treatment of bladder cancer[J]. Bmj, 2024, 384: e076743. |
| 8 | Rouanne M, Adam J, Radulescu C, et al. BCG therapy down-regulates HLA-I on malignant cells to subvert antitumor immune responses in bladder cancer[J]. J Clin Invest, 2022, 132(12). |
| 9 | Al Hussein Al Awamlh B, Chang SS. Novel Therapies for High-Risk Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer[J]. Curr Oncol Rep, 2023, 25(2): 83-91. |
| 10 | Xu X, Wang Y, Hu X, et al. Effects of PYCR1 on prognosis and immunotherapy plus tyrosine kinase inhibition responsiveness in metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients[J]. Neoplasia, 2023, 43: 100919. |
| 11 | Fan G, Yu B, Tang L, et al. TSPAN8(+) myofibroblastic cancer-associated fibroblasts promote chemoresistance in patients with breast cancer[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2024, 16(741): eadj5705. |
| 12 | Li Z, Jiang Y, Liu J, et al. Exosomes from PYCR1 knockdown bone marrow mesenchymal stem inhibits aerobic glycolysis and the growth of bladder cancer cells via regulation of the EGFR/PI3K/AKT pathway[J]. Int J Oncol, 2023, 63(1). |
| 13 | Zhang J, Yuan S, Cao W, et al. Signature Search Polestar: a comprehensive drug repurposing method evaluation assistant for customized oncogenic signature[J]. Bioinformatics, 2024, 40(9). |
| 14 | Huang X, Tan J, Chen M, et al. Prognostic, Immunological, and Mutational Analysis of MTA2 in Pan-Cancer and Drug Screening for Hepatocellular Carcinoma[J]. Biomolecules, 2023, 13(6). |
| 15 | Huang J, Zhang J L, Ang L, et al. Proposing a novel molecular subtyping scheme for predicting distant recurrence-free survival in breast cancer post-neoadjuvant chemotherapy with close correlation to metabolism and senescence[J]. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2023, 14: 1265520. |
| 16 | Geeleher P, Cox NJ, Huang RS. Clinical drug response can be predicted using baseline gene expression levels and in vitro drug sensitivity in cell lines[J]. Genome Biol, 2014, 15(3): R47. |
| 17 | Yoshihara K, Shahmoradgoli M, Martínez E, et al. Inferring tumour purity and stromal and immune cell admixture from expression data [J]. Nat Commun, 2013, 4: 2612. |
| 18 | Van Calster B, Wynants L, Verbeek JFM, et al. Reporting and Interpreting Decision Curve Analysis: A Guide for Investigators[J]. Eur Urol, 2018, 74(6): 796-804. |
| 19 | Yang C, Zhang H, Chen M, et al. A survey of optimal strategy for signature-based drug repositioning and an application to liver cancer [J]. Elife, 2022, 11. |
| 20 | Subramanian A, Narayan R, Corsello SM, et al. A Next Generation Connectivity Map: L1000 Platform and the First 1,000,000 Profiles [J]. Cell, 2017, 171(6): 1437-52.e17. |
| 21 | Christensen EM, Bogner AN, Vandekeere A, et al. In crystallo screening for proline analog inhibitors of the proline cycle enzyme PYCR1[J]. J Biol Chem, 2020, 295(52): 18316-27. |
| 22 | Liu Z, Sun T, Zhang Z, et al. An 18-gene signature based on glucose metabolism and DNA methylation improves prognostic prediction for urinary bladder cancer[J]. Genomics, 2021, 113(1 Pt 2): 896-907. |
| 23 | Xiao S, Chen J, Wei Y, et al. BHLHE41 inhibits bladder cancer progression via regulation of PYCR1 stability and thus inactivating PI3K/AKT signaling pathway[J]. Eur J Med Res, 2024, 29(1): 302. |
| 24 | Du S, Sui Y, Ren W, et al. PYCR1 promotes bladder cancer by affecting the Akt/Wnt/β‑catenin signaling[J]. J Bioenerg Biomembr, 2021, 53(2): 247-58. |
| 25 | Deng D, Liu F, Liu Z, et al. Robust pyroptosis risk score guides the treatment options and predicts the prognosis of bladder carcinoma [J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 965469. |
| 26 | Xiong S, Li S, Zeng J, et al. Deciphering the immunological and prognostic features of bladder cancer through platinum-resistance-related genes analysis and identifying potential therapeutic target P4HB[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14: 1253586. |
| 27 | Shenoy A, Belugali Nataraj N, Perry G, et al. Proteomic patterns associated with response to breast cancer neoadjuvant treatment[J]. Mol Syst Biol, 2020, 16(9): e9443. |
| 28 | Loriot Y, Petrylak DP, Rezazadeh Kalebasty A, et al. TROPHY-U-01, a phase II open-label study of sacituzumab govitecan in patients with metastatic urothelial carcinoma progressing after platinum-based chemotherapy and checkpoint inhibitors: updated safety and efficacy outcomes[J]. Ann Oncol, 2024, 35(4): 392-401. |
| 29 | Goldenberg DM, Sharkey RM. Antibody-drug conjugates targeting TROP-2 and incorporating SN-38: A case study of anti-TROP-2 sacituzumab govitecan[J]. MAbs, 2019, 11(6): 987-95. |
| 30 | Elbadawy M, Sato Y, Mori T, et al. Anti-tumor effect of trametinib in bladder cancer organoid and the underlying mechanism[J]. Cancer Biol Ther, 2021, 22(5-6): 357-71. |
| 31 | Plumber SA, Tate T, Al-Ahmadie H, et al. Rosiglitazone and trametinib exhibit potent anti-tumor activity in a mouse model of muscle invasive bladder cancer[J]. Nat Commun, 2024, 15(1): 6538. |
| 32 | Wang Z, Li L, Chu C, et al. CUDC‑101 is a potential target inhibitor for the EGFR‑overexpression bladder cancer cells[J]. Int J Oncol, 2023, 63(6). |
| 33 | Vemula D, Jayasurya P, Sushmitha V, et al. CADD, AI and ML in drug discovery: A comprehensive review[J]. Eur J Pharm Sci, 2023, 181: 106324. |
| 34 | Zhang Y, Luo M, Wu P, et al. Application of Computational Biology and Artificial Intelligence in Drug Design[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(21). |
| 35 | Li Y, Miao J, Liu C, et al. Kushenol O Regulates GALNT7/NF-κB axis-Mediated M2 Macrophage Polarization and Efferocytosis in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma[J]. Phytomedicine, 2025: 156373. |
| 36 | Goluboff E T. Exisulind, a selective apoptotic antineoplastic drug [J]. Expert Opin Investig Drugs, 2001, 10(10): 1875-82. |
| 37 | Geng H, Huang C, Xu L, et al. Targeting cellular senescence as a therapeutic vulnerability in gastric cancer[J]. Life Sci, 2024, 346: 122631. |
| 38 | Huang Y, Wang S, Zhang X, et al. Identification of Fasudil as a collaborator to promote the anti-tumor effect of lenvatinib in hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting GLI2-mediated hedgehog signaling pathway[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2024, 200: 107082. |
| [1] | Hongbo ZHANG, Mengyu YAN, Jiandong ZHANG, Peiwang SUN, Rui WANG, Yuanyuan GUO. Pirfenidone inhibits bladder cancer xenograft growth in mice by regulating regulatory T cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1513-1518. |
| [2] | Wei SU, Houhua LAI, Xin TANG, Qun ZHOU, Yachun TANG, Hao FU, Xuancai CHEN. Apelin promotes proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis in bladder cancer by activating the FGF2/FGFR1 pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1289-1296. |
| [3] | Mingyang ZHU, Bokang WANG, Xiusen ZHANG, Kexu ZHOU, Zeyu MIAO, Jiangtao SUN. Assessment of baseline CCL19+ dendritic cell infiltration for predicting responses to immunotherapy in lung adenocarcinoma patients [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1529-1536. |
| [4] | CHEN Shoufeng, ZHANG Shuchao, FAN Weilin, SUN Wei, LIU Beibei, LIU Jianmin, GUO Yuanyuan. Efficacy of combined treatment with pirfenidone and PD-L1 inhibitor in mice bearing ectopic bladder cancer xenograft [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(2): 210-216. |
| [5] | Liqiang LI, Yuanyuan GUO, Chengyong WANG, Rui CHANG, Wei SUN, Wuyue GAO, Chao WANG, Beibei LIU. High expression of miR-204-5p promotes malignant behaviors of bladder cancer cells by negatively regulating RAB22A [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(11): 2235-2242. |
| [6] | YAN Qiuxia, ZENG Peng, HUANG Shuqiang, TAN Cuiyu, ZHOU Xiuqin, QIAO Jing, ZHAO Xiaoying, FENG Ling, ZHU Zhenjie, ZHANG Guozhi, HU Hong, CHEN Cairong. RBMX overexpression inhibits proliferation, migration, invasion and glycolysis of human bladder cancer cells by downregulating PKM2 [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(1): 9-16. |
| [7] | ZHANG Xiaolin, WU Haosong, WANG Sheng. SLC12A8 promotes proliferation, invasiveness, migration and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of bladder cancer cells by activating JAK/STAT singaling [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(9): 1613-1621. |
| [8] | ZHANG Ziran, TAN Jiale, YU Zihang, LIU Chengdong, WANG Jian, WU Dehua, BAI Xue. FARSB stratifies prognosis and cold tumor microenvironment across different cancer types: an integrated single cell and bulk RNA sequencing analysis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(5): 667-679. |
| [9] | CAI Taonong, LU Jiangli, LIN Zhijun, LUP Mingrui, LIANG Haitao, QIN Zike, YE Yunlin. Intravesical instillation of bacillus Calmette-Guerin for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer: outcomes of 421 patients in a single center [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(3): 488-494. |
| [10] | GONG Ying, AIMAITI Ailifeire, HE Zongzhong. ARL67156, a small-molecule CD39 inhibitor, enhances natural killer cell cytotoxicity against gastric cancer cells in vitro and in nude mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(12): 2006-2014. |
| [11] | ZOU Zhenhai, CHENG Qi, LI Zhong, GAO Wuyue, SUN Wei, LIU Beibei, GUO Yuanyuan, LIU Jianmin. microRNA let-7g-3p regulates proliferation, migration, invasion and apoptosis of bladder cancer cells by targeting HMGB2 [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42(9): 1335-1343. |
| [12] | LI Ruining, HUANG Chaoyi, HONG Chang, WANG Jiaren, LI Qimei, HU Chengyi, CUI Hao, DONG Zhongyi, ZHU Hongbo, LIU Li, XIAO Lushan. Impact of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on efficacy of anti-PD-1 therapy for primary liver cancer [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42(5): 698-704. |
| [13] | FU Xiaocong, YU Guangchuang, GUO Yanfang. Expression pattern of the histone lysine demethylase family and its potential role in bladder cancer: a multi-omics analysis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42(12): 1822-1831. |
| [14] | LIN Xuan, MAO Duo, BAI Ruixia. Comparison of three commercial photosensitizers for efficiency of inducing immunogenic cell death in anti-tumor immunotherapy [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42(12): 1791-1798. |
| [15] | . miR-let-7c-5p inhibits invasion and migration of bladder cancer cells by targeting HMGA2 [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2021, 41(7): 1022-1029. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||