Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (11): 2235-2242.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.11.21
Liqiang LI1( ), Yuanyuan GUO1, Chengyong WANG1, Rui CHANG1, Wei SUN1, Wuyue GAO1, Chao WANG2, Beibei LIU1(
), Yuanyuan GUO1, Chengyong WANG1, Rui CHANG1, Wei SUN1, Wuyue GAO1, Chao WANG2, Beibei LIU1( )
)
Received:2024-01-15
Online:2024-11-20
Published:2024-11-29
Contact:
Beibei LIU
E-mail:348544730@qq.com;bb_dynasty@qq.com
Liqiang LI, Yuanyuan GUO, Chengyong WANG, Rui CHANG, Wei SUN, Wuyue GAO, Chao WANG, Beibei LIU. High expression of miR-204-5p promotes malignant behaviors of bladder cancer cells by negatively regulating RAB22A[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(11): 2235-2242.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.11.21
| Gene | Primer sequence (5'-3') |
|---|---|
| miR-204-5p-F | GCTACAGTCTTTCTTCATGTG |
| U6-F | CGCTTCGGCAGCACATATACTAA |
| Micro-R | AGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATT |
| RAB22A-F | GTCCCTTAGCACCAATGTACTATC |
| RAB22A-R | AATGGCAACTACAATATTAGGTGG |
| GAPDH-F | GGAGCGAGATCCCTCCAAAAT |
| GAPDH-R | GGCTGTTGTCATACTTCTCATGG |
Tab.1 Primer sequences for RT-qPCR
| Gene | Primer sequence (5'-3') |
|---|---|
| miR-204-5p-F | GCTACAGTCTTTCTTCATGTG |
| U6-F | CGCTTCGGCAGCACATATACTAA |
| Micro-R | AGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATT |
| RAB22A-F | GTCCCTTAGCACCAATGTACTATC |
| RAB22A-R | AATGGCAACTACAATATTAGGTGG |
| GAPDH-F | GGAGCGAGATCCCTCCAAAAT |
| GAPDH-R | GGCTGTTGTCATACTTCTCATGG |
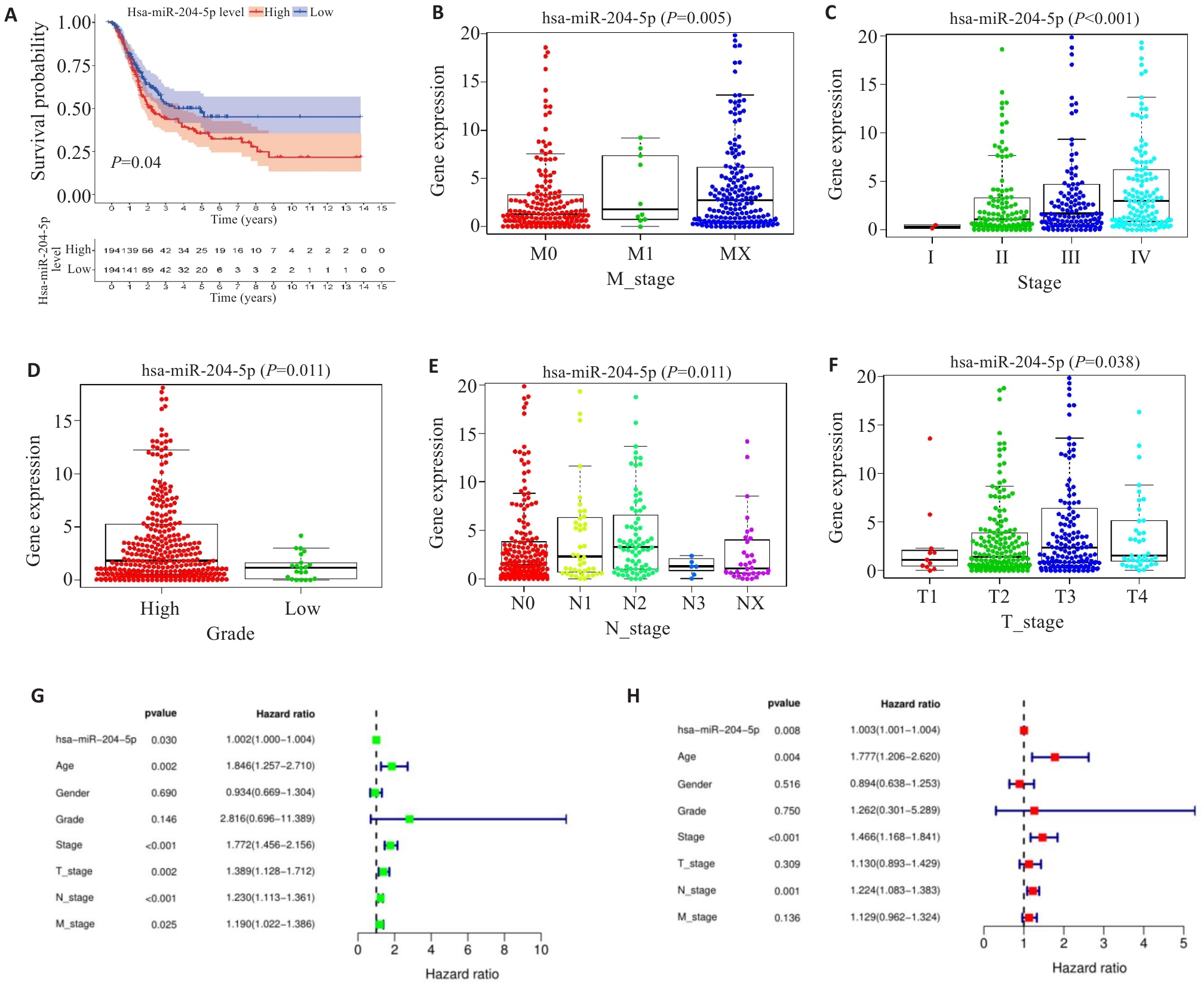
Fig.1 High expression of miR-204-5p is associated with poor prognosis of patients with bladder cancer. A: Kaplan-Meier plotter curves of patients with high and low expression of miR-204-5p. B-F: Correlation of miR-204-5p expression with clinical grade, stage, T-stage, N-stage and M-stage of the patients. G: Forest plot showing the results of the univariate Cox regression analysis. H: Forest plot showing the results of the multivariate Cox regression analysis.

Fig.2 Verification of miR-204-5p expression level in bladder cancer tissue and cells. A: miR-204-5p expressions in normal tissues and bladder cancer tissues. B: miR-204-5p expression in bladder cancer cell lines T24, J82, 5637 and EJ and normal SV-HUC-1 cells (n=3, **P<0.01).

Fig.3 Effects of miR-204-5p knockdown and over-expression on proliferation, migration, invasion and apoptosis of bladder cancer cells. A: CCK8 assay for assessing proliferation ability of T24 cells with miR-204-5p knockdown or overexpression. B: Flow cytometry for analyzing apoptosis of T24 cells with miR-204-5p knockdown or overexpression. C: Transwell assay for assessing migration and invasion abilities of T24 cells with miR-204-5p knockdown or overexpression (Original magnification: ×100). *P<0.05, **P<0.01 (n=3).

Fig.4 Targeting relationship between miR-204-5p and RAB22A. A: Result of transcriptome sequencing. B: Wayne diagram of the 3 major databases. C: Binding site between miR-204-5p and RAB22A. D: Overexpression of miR-204-5p reduces mRNA expression level of RAB22A as detected by qRT-PCR. E, F: Overexpression of miR-204-5p reduces protein expression level of RAB22A as detected by Western blotting (n=3, **P<0.01).

Fig.6 Rescue experiment confirms that miR-204-5p targets RAB22A to regulate proliferation, migration, invasion and apoptosis of bladder cancer cells. A: Overexpression of RAB22A partially reverses the effect of miR-204-5p overexpression on migration and invasion of T24 cells. B: Overexpression of RAB22A partially reverses the effect of miR-204-5p overexpression on apoptosis of T24 cells. C: Overexpression of RAB22A partially reverses the effect of miR-204-5p overexpression on the proliferation of T24 cells (×100). *P<0.05, **P<0.01 (n=3).
| 1 | Dyrskjøt L, Hansel DE, Efstathiou JA, et al. Bladder cancer[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2023, 9(1): 58. |
| 2 | Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2018, 68(6): 394-424. |
| 3 | Kamat AM, Hahn NM, Efstathiou JA, et al. Bladder cancer[J]. Lancet, 2016, 388(10061): 2796-810. |
| 4 | Andreassen BK, Grimsrud TK, Haug ES. Bladder cancer survival: women better off in the long Run[J]. Eur J Cancer, 2018, 95: 52-8. |
| 5 | Cumberbatch MGK, Jubber I, Black PC, et al. Epidemiology of bladder cancer: a systematic review and contemporary update of risk factors in 2018[J]. Eur Urol, 2018, 74(6): 784-95. |
| 6 | Choi W, Ochoa A, McConkey DJ, et al. Genetic alterations in the molecular subtypes of bladder cancer: illustration in the cancer genome atlas dataset[J]. Eur Urol, 2017, 72(3): 354-65. |
| 7 | Li HT, Duymich CE, Weisenberger DJ, et al. Genetic and epigenetic alterations in bladder cancer[J]. Int Neurourol J, 2016, 20(): S84-S94. |
| 8 | Fabian MR, Sonenberg N. The mechanics of miRNA-mediated gene silencing: a look under the hood of miRISC[J]. Nat Struct Mol Biol, 2012, 19(6): 586-93. |
| 9 | Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions[J]. Cell, 2009, 136(2): 215-33. |
| 10 | 邹震海, 程 琪, 李 中, 等. MiR-let-7g-3p靶向HMGB2调控膀胱癌细胞的增殖、迁移、侵袭和和凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(9): 1335-43. |
| 11 | 郭晓波, 赵宇峰, 赵 波, 等. BRD4抑制剂JQ1及miR-141对膀胱癌细胞增殖和凋亡的影响及其机制[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2022, 42(22): 5621-5. |
| 12 | McLoughlin LC, O'Halloran S, Tjong M, et al. The prognostic value of urinary cytology after trimodal therapy (TMT) for muscle-invasive bladder cancer[J]. Urol Oncol, 2022, 40(7): 346. e9-16. |
| 13 | Hong BS, Ryu HS, Kim N, et al. Tumor suppressor miRNA-204-5p regulates growth, metastasis, and immune microenvironment remodeling in breast cancer[J]. Cancer Res, 2019, 79(7): 1520-34. |
| 14 | 薛无涯. MiR-204-5p对结直肠癌细胞增殖、迁移及侵袭的作用及机制的初步探讨[D]. 泸州: 西南医科大学, 2018. |
| 15 | Yin Y, Zhang BB, Wang WL, et al. MiR-204-5p inhibits proliferation and invasion and enhances chemotherapeutic sensitivity of colorectal cancer cells by downregulating RAB22A[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2014, 20(23): 6187-99. |
| 16 | He HH, Chen K, Wang F, et al. MiR-204-5p promotes the adipogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells by modulating DVL3 expression and suppressing Wnt/β-catenin signaling[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2015, 35(6): 1587-95. |
| 17 | Antoni S, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, et al. Bladder cancer incidence and mortality: a global overview and recent trends[J]. Eur Urol, 2017, 71(1): 96-108. |
| 18 | 刘晨溪, 赵红娟, 田 伟, 等. MiR-199b-3p对肾癌细胞增殖、凋亡、侵袭的影响及其机制探讨[J]. 山东医药, 2022, 62(4): 26-30, 35. |
| 19 | Yang S, Chen BN, Zhang BG, et al. MiR-204-5p promotes apoptosis and inhibits migration of gastric cancer cells by targeting HER-2[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2020, 22(4): 2645-54. |
| 20 | Cai KT, Liu AG, Wang ZF, et al. Expression and potential molecular mechanisms of miR-204-5p in breast cancer, based on bioinformatics and a meta-analysis of 2, 306cases[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2019, 19(2): 1168-84. |
| 21 | He M, Shen LH, Jiang CW, et al. Rab22a is a novel prognostic marker for cell progression in breast cancer[J]. Int J Mol Med, 2020, 45(4): 1037-46. |
| 22 | Zhou Y, Wu B, Li JH, et al. Rab22a enhances CD147 recycling and is required for lung cancer cell migration and invasion[J]. Exp Cell Res, 2017, 357(1): 9-16. |
| 23 | Magadán JG, Barbieri MA, Mesa R, et al. Rab22a regulates the sorting of transferrin to recycling endosomes[J]. Mol Cell Biol, 2006, 26(7): 2595-614. |
| 24 | Mosesson Y, Mills GB, Yarden Y. Derailed endocytosis: an emerging feature of cancer[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2008, 8(11): 835-50. |
| 25 | Abella JV, Park M. Breakdown of endocytosis in the oncogenic activation of receptor tyrosine kinases[J]. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, 2009, 296(5): E973-84. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||