Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (12): 2607-2615.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.12.08
Shanshan DING1( ), Ying LIAO1, Xue BAI1, Jiaoyang HUANG1, Tetsuya ASAKAWA1,2
), Ying LIAO1, Xue BAI1, Jiaoyang HUANG1, Tetsuya ASAKAWA1,2
Received:2025-07-22
Online:2025-12-20
Published:2025-12-22
Contact:
Shanshan DING
E-mail:ding123shan@163.com
Supported by:Shanshan DING, Ying LIAO, Xue BAI, Jiaoyang HUANG, Tetsuya ASAKAWA. Knockdown of Cav1 inhibits mitochondrial function and mRNA m6A modification and expression of key genes in mouse hepatocytes[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(12): 2607-2615.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.12.08
| Gene | Forward primers sequences | Reverse primers sequences |
|---|---|---|
| Usp15 | CCGTGGATGAAAACCTGAGTAG | TTCTCTTAGGCAGACAGGGATAA |
| Suclg2 | CCAGCGAACTTCTTGGACCT | CACAGTTGACGATCCCACCA |
| Ppa2 | CGGTGGACAAATGCCAAGATG | TTCGGTGTGTAGCGTAGCTT |
| Gapdh | CACTGAGCAAGAGAGGCCCTAT | GCAGCGAACTTTATTGATGGTATT |
Tab.1 Primer sequences for MeRIP-qPCR
| Gene | Forward primers sequences | Reverse primers sequences |
|---|---|---|
| Usp15 | CCGTGGATGAAAACCTGAGTAG | TTCTCTTAGGCAGACAGGGATAA |
| Suclg2 | CCAGCGAACTTCTTGGACCT | CACAGTTGACGATCCCACCA |
| Ppa2 | CGGTGGACAAATGCCAAGATG | TTCGGTGTGTAGCGTAGCTT |
| Gapdh | CACTGAGCAAGAGAGGCCCTAT | GCAGCGAACTTTATTGATGGTATT |
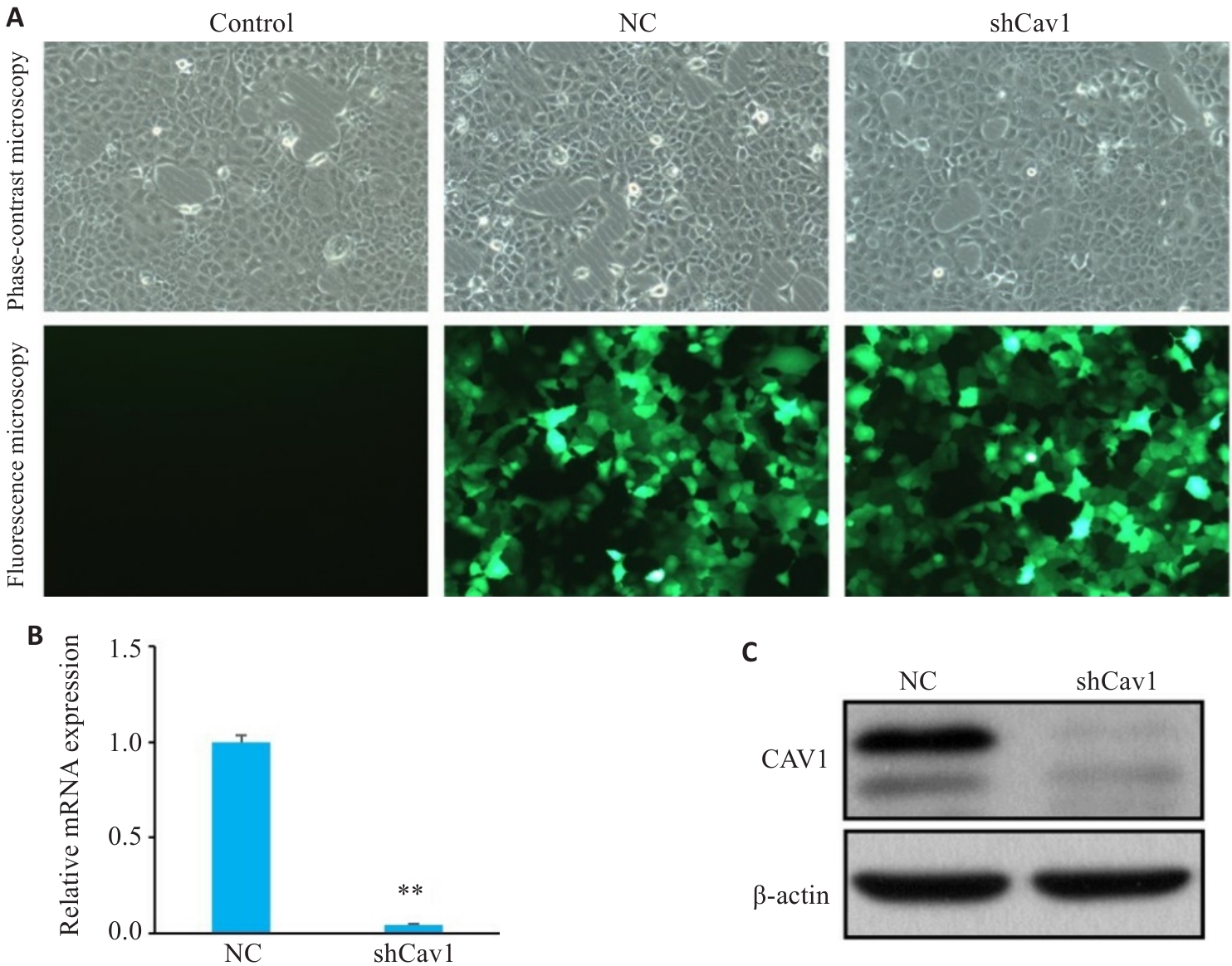
Fig.1 Knockdown of Cav1 by lentivirus-mediated transfection with shCav1 in AML12 cells. A: Phase-contrast and fluorescence microscopy of the cells under bright-field conditions (GFP, Original magnification: ×100). B: Real-time PCR analysis of Cav1 mRNA expression levels. C: Western blotting of Cav1 protein expression. Control : Untreated control; NC: Control shRNA; shCav1: Cav1 shRNA. **P<0.01 vs NC group.
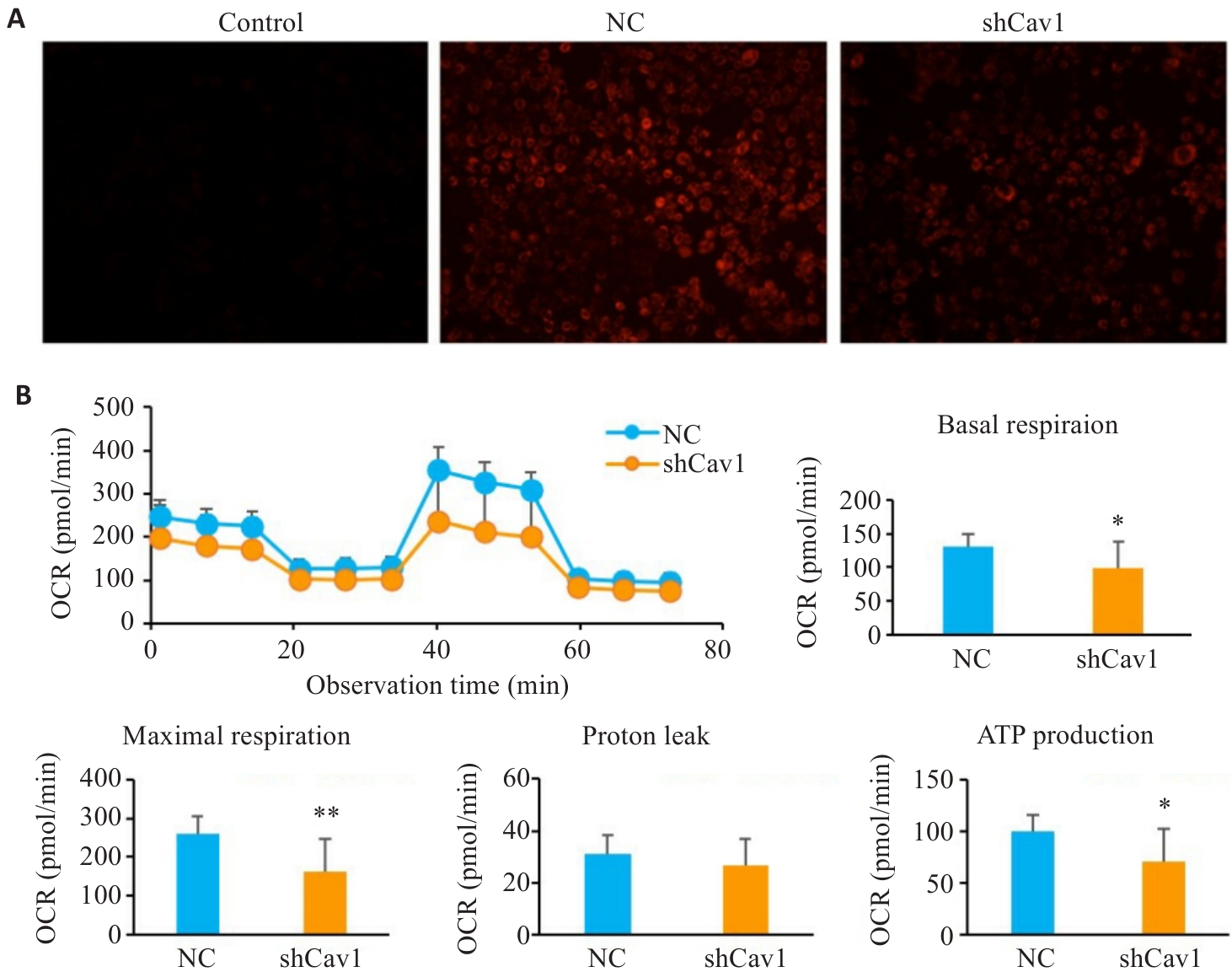
Fig.2 Cav1 knockdown impairs mitochondrial membrane potential and respiratory function in AML12 cells. A: TMRE staining for analysis of mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm) (×100). B: Seahorse XF metabolic analysis of basal respiration, maximal respiration and ATP production. CCCP: A mitochondrial uncoupler, used as a positive control to induce ΔΨm collapse (dim red fluorescence); OCR: Oxygen consumption rate. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs NC group.
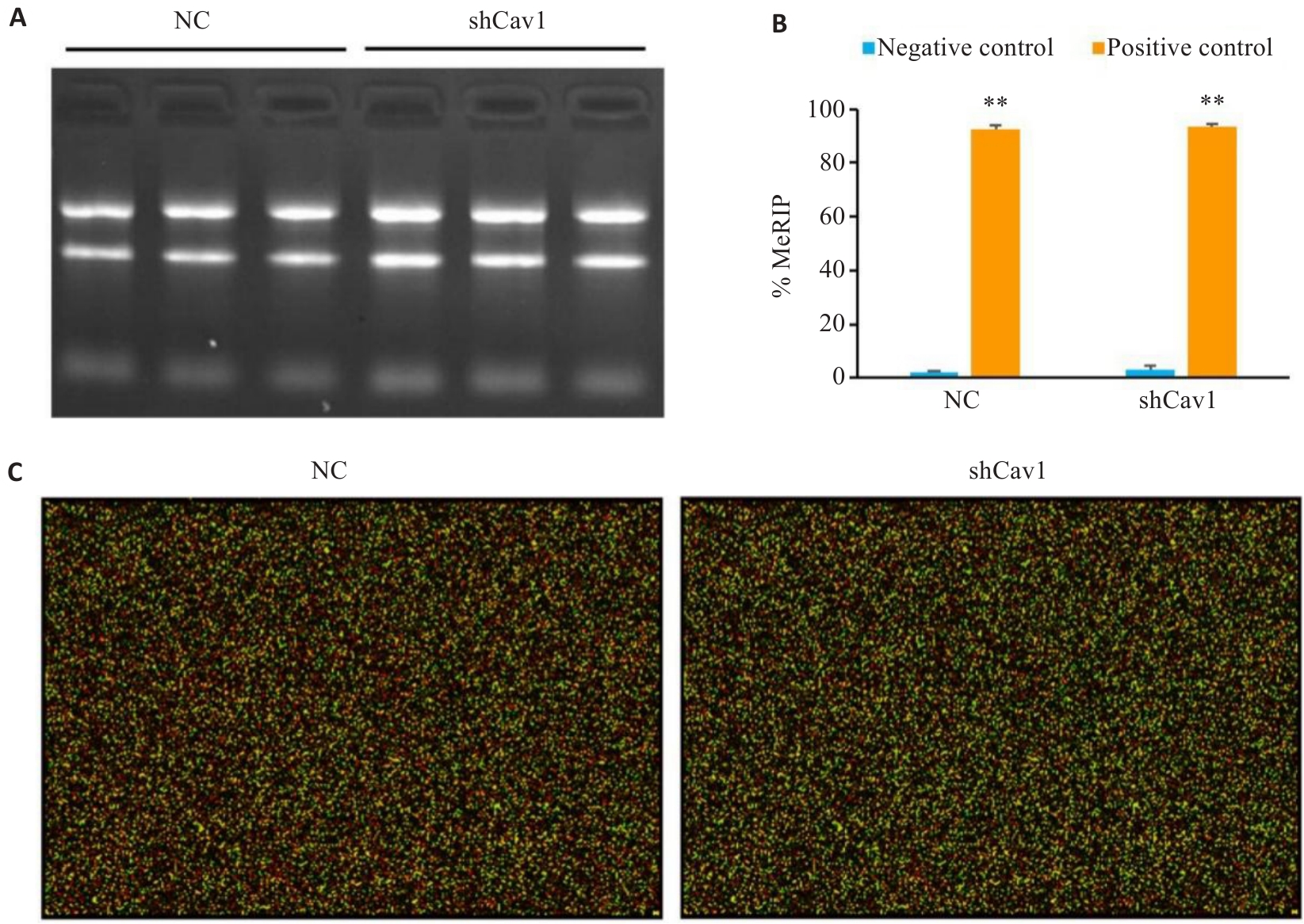
Fig.3 Quality control of MeRIP and reliability of microarray. A: Agarose gel electrophoresis of the total RNA to confirm RNA integrity. B: MeRIP quality control demonstrating efficient m6A enrichment (%MeRIP confirming assay specificity). C: Representative RNA microarray hybridization image (Cy5 and Cy3). Positive controls: m6A-modified RNAs; Negative controls: Non-methylated RNAs. **P<0.01 vs negative control.
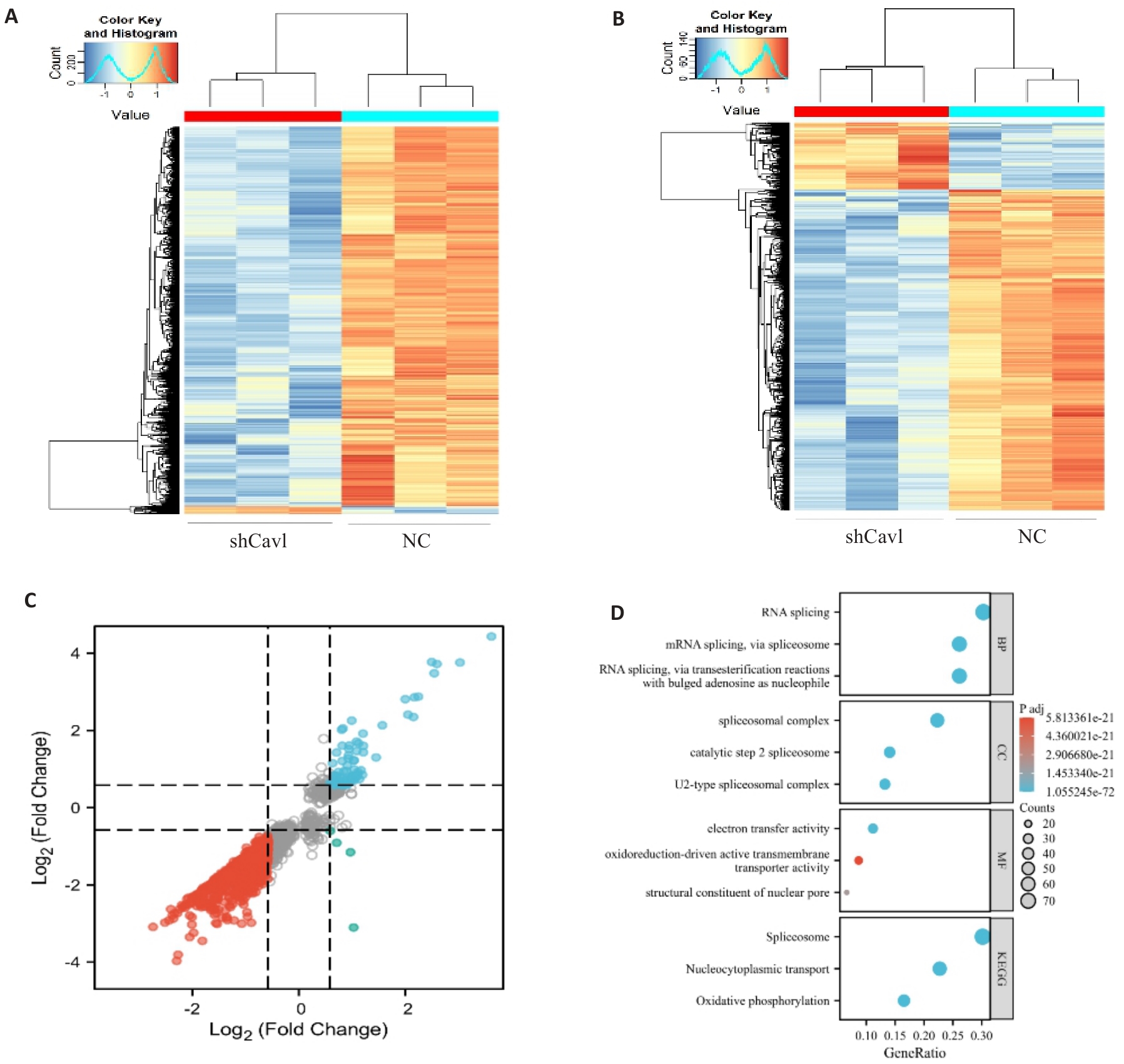
Fig.4 Cav1 knockdown alters mRNA m6A modification and expression profiles in AML12 cells. A: Heatmap of differentially methylated mRNAs. B: Heatmap of differentially expressed mRNAs. C: Nine-quadrant analysis of coordinated m6A methylation and mRNA expression changes. D: Gene Ontology and KEGG pathway enrichment analysis of genes with concurrent m6A and expression changes. |log2 fold change|>0.58, P<0.05.
| Gene | FC | P | Reg | %m6A | Gene | FC | P | Reg | %m6A | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ifrd1 | 0.07 | 0.002 | Down | -55% | Olfr175-ps1 | 19.55 | 0.001 | Up | 54% | |
| Zfp934 | 0.08 | 0.000 | Down | -54% | Crhr2 | 13.70 | 0.000 | Up | 52% | |
| Kif18a | 0.06 | 0.001 | Down | -54% | Glis1 | 13.21 | 0.008 | Up | 49% | |
| Kif20b | 0.07 | 0.000 | Down | -51% | Olfr175-ps1 | 21.62 | 0.000 | Up | 47% | |
| Tcaf1 | 0.12 | 0.001 | Down | -51% | Fam19a2 | 2.14 | 0.045 | Up | 40% | |
| Zufsp | 0.08 | 0.004 | Down | -50% | Gss | 11.18 | 0.001 | Up | 37% | |
| Zfp932 | 0.09 | 0.000 | Down | -50% | Slc13a4 | 7.35 | 0.000 | Up | 36% | |
| Klhl32 | 0.13 | 0.000 | Down | -49% | Elavl2 | 4.16 | 0.003 | Up | 33% | |
| Slc35d1 | 0.15 | 0.003 | Down | -49% | Crlf1 | 4.78 | 0.032 | Up | 33% | |
| Mis18bp1 | 0.12 | 0.028 | Down | -47% | Mdc1 | 2.62 | 0.042 | Up | 32% | |
| Samd9l | 0.14 | 0.002 | Down | -46% | Grm2 | 7.02 | 0.004 | Up | 32% | |
| Smek1 | 0.13 | 0.001 | Down | -45% | Tulp2 | 4.39 | 0.001 | Up | 31% | |
| Fastkd2 | 0.19 | 0.000 | Down | -45% | Dynap | 2.69 | 0.020 | Up | 28% | |
| Zfp280d | 0.13 | 0.001 | Down | -45% | Adamtsl1 | 3.05 | 0.008 | Up | 26% | |
| Sema6d | 0.10 | 0.002 | Down | -44% | Txnip | 2.68 | 0.005 | Up | 26% | |
| Pole4 | 0.15 | 0.006 | Down | -44% | Dpp4 | 13.55 | 0.000 | Up | 26% | |
| Kif20b | 0.10 | 0.000 | Down | -43% | Il5ra | 7.25 | 0.000 | Up | 25% | |
| Pcdhb18 | 0.14 | 0.000 | Down | -42% | Klrc1 | 3.28 | 0.001 | Up | 24% | |
| Wac | 0.14 | 0.005 | Down | -42% | Txnip | 3.17 | 0.004 | Up | 24% | |
| Cdadc1 | 0.15 | 0.015 | Down | -42% | Kcne3 | 2.70 | 0.048 | Up | 23% |
Tab.2 Top 20 upregulated and downregulated m6A-modified mRNAs in AML12 cells with Cav1 knockdown
| Gene | FC | P | Reg | %m6A | Gene | FC | P | Reg | %m6A | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ifrd1 | 0.07 | 0.002 | Down | -55% | Olfr175-ps1 | 19.55 | 0.001 | Up | 54% | |
| Zfp934 | 0.08 | 0.000 | Down | -54% | Crhr2 | 13.70 | 0.000 | Up | 52% | |
| Kif18a | 0.06 | 0.001 | Down | -54% | Glis1 | 13.21 | 0.008 | Up | 49% | |
| Kif20b | 0.07 | 0.000 | Down | -51% | Olfr175-ps1 | 21.62 | 0.000 | Up | 47% | |
| Tcaf1 | 0.12 | 0.001 | Down | -51% | Fam19a2 | 2.14 | 0.045 | Up | 40% | |
| Zufsp | 0.08 | 0.004 | Down | -50% | Gss | 11.18 | 0.001 | Up | 37% | |
| Zfp932 | 0.09 | 0.000 | Down | -50% | Slc13a4 | 7.35 | 0.000 | Up | 36% | |
| Klhl32 | 0.13 | 0.000 | Down | -49% | Elavl2 | 4.16 | 0.003 | Up | 33% | |
| Slc35d1 | 0.15 | 0.003 | Down | -49% | Crlf1 | 4.78 | 0.032 | Up | 33% | |
| Mis18bp1 | 0.12 | 0.028 | Down | -47% | Mdc1 | 2.62 | 0.042 | Up | 32% | |
| Samd9l | 0.14 | 0.002 | Down | -46% | Grm2 | 7.02 | 0.004 | Up | 32% | |
| Smek1 | 0.13 | 0.001 | Down | -45% | Tulp2 | 4.39 | 0.001 | Up | 31% | |
| Fastkd2 | 0.19 | 0.000 | Down | -45% | Dynap | 2.69 | 0.020 | Up | 28% | |
| Zfp280d | 0.13 | 0.001 | Down | -45% | Adamtsl1 | 3.05 | 0.008 | Up | 26% | |
| Sema6d | 0.10 | 0.002 | Down | -44% | Txnip | 2.68 | 0.005 | Up | 26% | |
| Pole4 | 0.15 | 0.006 | Down | -44% | Dpp4 | 13.55 | 0.000 | Up | 26% | |
| Kif20b | 0.10 | 0.000 | Down | -43% | Il5ra | 7.25 | 0.000 | Up | 25% | |
| Pcdhb18 | 0.14 | 0.000 | Down | -42% | Klrc1 | 3.28 | 0.001 | Up | 24% | |
| Wac | 0.14 | 0.005 | Down | -42% | Txnip | 3.17 | 0.004 | Up | 24% | |
| Cdadc1 | 0.15 | 0.015 | Down | -42% | Kcne3 | 2.70 | 0.048 | Up | 23% |
| Gene | FC | P | Reg | Gene | FC | P | Reg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cav1 | 0.05 | 0.000 | Down | Olfr175-ps1 | 12.25 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Dek | 0.14 | 0.000 | Down | Olfr175-ps1 | 8.42 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Dek | 0.15 | 0.000 | Down | Dpp4 | 8.14 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Upf3b | 0.16 | 0.000 | Down | Glis1 | 6.03 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Tpr | 0.18 | 0.000 | Down | Gss | 5.82 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Arid4b | 0.19 | 0.000 | Down | Crhr2 | 5.64 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Dtnbp1 | 0.19 | 0.000 | Down | Slc13a4 | 4.73 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Hells | 0.20 | 0.010 | Down | Il5ra | 4.49 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Zfml | 0.20 | 0.000 | Down | Slc45a4 | 4.44 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Kif18a | 0.20 | 0.000 | Down | Pdzd2 | 4.14 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Ccl2 | 0.21 | 0.000 | Down | Grm2 | 3.99 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Dek | 0.21 | 0.000 | Down | Cdh26 | 3.73 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Kif20b | 0.21 | 0.000 | Down | Ube2i | 3.13 | 0.040 | Up | |
| Thoc2 | 0.21 | 0.000 | Down | Tulp2 | 2.96 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Ccar1 | 0.22 | 0.000 | Down | Olfr70 | 2.81 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Zfml | 0.22 | 0.000 | Down | Chpf2 | 2.73 | 0.000 | Up | |
| mt-Nd1 | 0.22 | 0.000 | Down | Slc6a20b | 2.66 | 0.040 | Up | |
| Zfp950 | 0.22 | 0.000 | Down | Msantd3 | 2.61 | 0.020 | Up | |
| Zfp960 | 0.22 | 0.000 | Down | Atp2c1 | 2.59 | 0.010 | Up | |
| Ccar1 | 0.23 | 0.010 | Down | Fam32a | 2.58 | 0.050 | Up |
Tab.3 Top 20 upregulated and downregulated mRNAs in AML12 cells with Cav1 knockdown
| Gene | FC | P | Reg | Gene | FC | P | Reg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cav1 | 0.05 | 0.000 | Down | Olfr175-ps1 | 12.25 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Dek | 0.14 | 0.000 | Down | Olfr175-ps1 | 8.42 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Dek | 0.15 | 0.000 | Down | Dpp4 | 8.14 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Upf3b | 0.16 | 0.000 | Down | Glis1 | 6.03 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Tpr | 0.18 | 0.000 | Down | Gss | 5.82 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Arid4b | 0.19 | 0.000 | Down | Crhr2 | 5.64 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Dtnbp1 | 0.19 | 0.000 | Down | Slc13a4 | 4.73 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Hells | 0.20 | 0.010 | Down | Il5ra | 4.49 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Zfml | 0.20 | 0.000 | Down | Slc45a4 | 4.44 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Kif18a | 0.20 | 0.000 | Down | Pdzd2 | 4.14 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Ccl2 | 0.21 | 0.000 | Down | Grm2 | 3.99 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Dek | 0.21 | 0.000 | Down | Cdh26 | 3.73 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Kif20b | 0.21 | 0.000 | Down | Ube2i | 3.13 | 0.040 | Up | |
| Thoc2 | 0.21 | 0.000 | Down | Tulp2 | 2.96 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Ccar1 | 0.22 | 0.000 | Down | Olfr70 | 2.81 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Zfml | 0.22 | 0.000 | Down | Chpf2 | 2.73 | 0.000 | Up | |
| mt-Nd1 | 0.22 | 0.000 | Down | Slc6a20b | 2.66 | 0.040 | Up | |
| Zfp950 | 0.22 | 0.000 | Down | Msantd3 | 2.61 | 0.020 | Up | |
| Zfp960 | 0.22 | 0.000 | Down | Atp2c1 | 2.59 | 0.010 | Up | |
| Ccar1 | 0.23 | 0.010 | Down | Fam32a | 2.58 | 0.050 | Up |
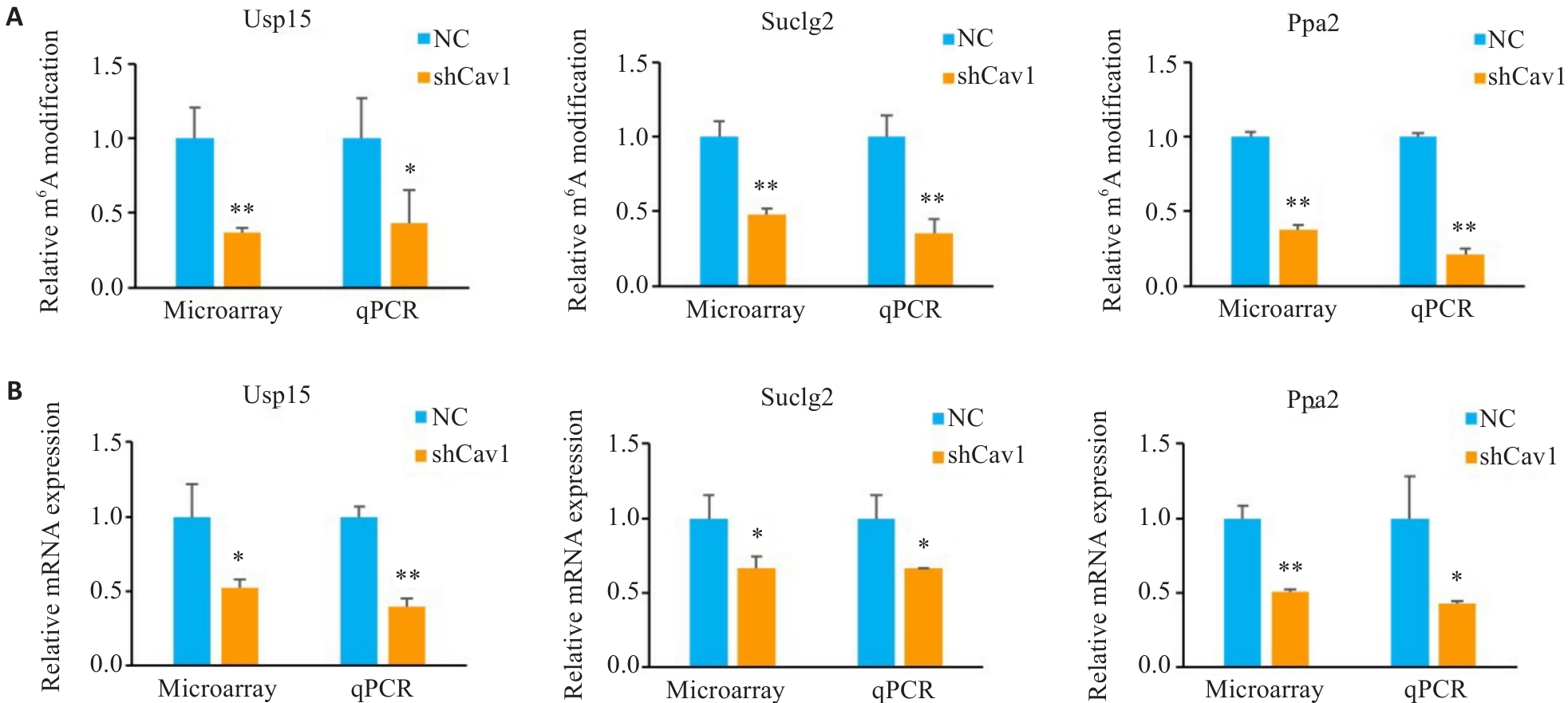
Fig.5 m6A modification and relative expression levels of mitochondrial function-associated mRNAs in AML12 cells. A: Microarray and qPCR analysis of relative m6A modification of Usp15, Suclg2 and Ppa2 mRNA. B: Microarray and qPCR analysis of relative mRNA expression of Usp15, Suclg2 and Ppa2. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs NC group.
| [1] | 范建高, 徐小元, 南月敏, 等. 代谢相关(非酒精性)脂肪性肝病防治指南(2024年版)[J]. 实用肝脏病杂志, 2024, 27(4): 494-510. |
| [2] | Eslam M, Sarin SK, Wong VW, et al. The Asian Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of metabolic associated fatty liver disease[J]. Hepatol Int, 2020, 14(6): 889-919. doi:10.1007/s12072-020-10094-2 |
| [3] | Radosavljevic T, Brankovic M, Samardzic J, et al. Altered mitochondrial function in MASLD: key features and promising therapeutic approaches[J]. Antioxidants (Basel), 2024, 13(8): 906. doi:10.3390/antiox13080906 |
| [4] | Shin S, Kim J, Lee JY, et al. Mitochondrial quality control: its role in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD)[J]. J Obes Metab Syndr, 2023, 32(4): 289-302. doi:10.7570/jomes23054 |
| [5] | Bhowmick S, Biswas T, Ahmed M, et al. Caveolin-1 and lipids: association and their dualism in oncogenic regulation[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer, 2023, 1878(6): 189002. doi:10.1016/j.bbcan.2023.189002 |
| [6] | Jiang Y, Krantz S, Qin X, et al. Caveolin-1 controls mitochondrial damage and ROS production by regulating fission - fusion dynamics and mitophagy[J]. Redox Biol, 2022, 52: 102304. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2022.102304 |
| [7] | Fu DD, Wu S, Jiang XF, et al. Caveolin-1 alleviates acetaminophen-induced vascular oxidative stress and inflammation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2023, 195: 245-57. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.12.095 |
| [8] | Tang WX, Li YS, Li Y, et al. Caveolin-1, a novel player in cognitive decline[J]. Neurosci Biobehav Rev, 2021, 129: 95-106. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.06.044 |
| [9] | Timmins LR, Ortiz-Silva M, Joshi B, et al. Caveolin-1 promotes mitochondrial health and limits mitochondrial ROS through ROCK/AMPK regulation of basal mitophagic flux[J]. FASEB J, 2024, 38: e23343. doi:10.1096/fj.202201872rr |
| [10] | You TY, Li Y, Li BW, et al. Caveolin-1 protects against liver damage exacerbated by acetaminophen in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by inhibiting the ERK/HIF-1α pathway[J]. Mol Immunol, 2023, 163: 104-15. doi:10.1016/j.molimm.2023.09.003 |
| [11] | Deng GH, Wu CF, Li YJ, et al. Caveolin-1 is critical for hepatic iron storage capacity in the development of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Mil Med Res, 2023, 10(1): 53. doi:10.1186/s40779-023-00487-3 |
| [12] | Ćorović M, Hoch-Kraft P, Zhou Y, et al. m6A in the coding sequence: linking deposition, translation, and decay[J]. Trends Genet, 2025: S0168-9525(25)00132-5. doi:10.1016/j.tig.2025.06.002 |
| [13] | Xie XZ, Fang Z, Zhang HY, et al. The role of N(6)-methyladenosine (m6a) modification in cancer: recent advances and future directions[J]. EXCLI J, 2025, 24: 113-50. |
| [14] | Ming XY, Chen SR, Li HJ, et al. m6A RNA methylation and implications for hepatic lipid metabolism[J]. DNA Cell Biol, 2024, 43(6): 271-8. doi:10.1089/dna.2023.0410 |
| [15] | Yan W, Saqirile, Li K, et al. The role of N6-methyladenosine in mitochondrial dysfunction and pathology[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2025, 26(8): 3624. doi:10.3390/ijms26083624 |
| [16] | Fan JH, You JB, Liu ZY, et al. Novel landscapes of N6-methyladenosine modification of mitochondrial oxidative stress in organ fibrosis[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2025, 1003: 177888. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2025.177888 |
| [17] | Fromenty B, Roden M. Mitochondrial alterations in fatty liver diseases[J]. J Hepatol, 2023, 78(2): 415-29. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2022.09.020 |
| [18] | 丁珊珊, 庄 妍, 廖 颖, 等. 二陈汤通过抑制mTORC1/SREBP1/CAV1通路改善高脂饮食小鼠肝脏线粒体功能的作用研究[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2024, 49(3): 763-9. |
| [19] | Xu HL, Li Y, Guo N, et al. Caveolin-1 mitigates the advancement of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease by reducing endoplasmic reticulum stress and pyroptosis through the restoration of cholesterol homeostasis[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2025, 21(2): 490-506. doi:10.7150/ijbs.100794 |
| [20] | Razani B, Combs TP, Wang XB, et al. Caveolin-1-deficient mice are lean, resistant to diet-induced obesity, and show hypertriglyc-eridemia with adipocyte abnormalities[J]. J Biol Chem, 2002, 277(10): 8635-47. doi:10.1074/jbc.m110970200 |
| [21] | Xu YQ, Chen BW, Yi J, et al. Buyang Huanwu Decoction alleviates cerebral ischemic injury through modulating caveolin-1-mediated mitochondrial quality control[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2023, 14: 1137609. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1137609 |
| [22] | Wu S, Guo N, Xu HL, et al. Caveolin-1 ameliorates hepatic injury in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by inhibiting ferroptosis via the NOX4/ROS/GPX4 pathway[J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2024, 230(Pt 2): 116594. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2024.116594 |
| [23] | Kahl M, Xu ZF, Arumugam S, et al. m6A RNA methylation regulates mitochondrial function[J]. Hum Mol Genet, 2024, 33(11): 969-80. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddae029 |
| [24] | Wang SW, Zhang WY, Wang ZJ, et al. Mettl3-m6A-YTHDF1 axis promotion of mitochondrial dysfunction in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease[J]. Cell Signal, 2024, 121: 111303. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2024.111303 |
| [25] | Huangfu LT, Zhu HB, Wang GJ, et al. The deubiquitinase USP15 drives malignant progression of gastric cancer through glucose metabolism remodeling[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2024, 43(1): 235. doi:10.1186/s13046-024-03152-2 |
| [26] | Fang RH, Jia ZG, Xin YH, et al. N6-methyladenosine-modification of USP15 regulates chemotherapy resistance by inhibiting LGALS3 ubiquitin-mediated degradation via AKT/mTOR signaling activation pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cell Death Discov, 2025, 11(1): 3. doi:10.1038/s41420-024-02282-y |
| [27] | Wu BW, Qiu JT, Zhao TV, et al. Succinyl-CoA ligase deficiency in pro-inflammatory and tissue-invasive T cells[J]. Cell Metab, 2020, 32(6): 967-80.e5. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2020.10.025 |
| [28] | Zhang XM, Liu J, Cheng YJ, et al. Metabolic enzyme Suclg2 maintains tolerogenicity of regulatory dendritic cells diffDCs by suppressing Lactb succinylation[J]. J Autoimmun, 2023, 138: 103048. doi:10.1016/j.jaut.2023.103048 |
| [29] | Hu QF, Xu J, Wang L, et al. SUCLG2 regulates mitochondrial dysfunction through succinylation in lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Adv Sci (Weinh), 2023, 10(35): e2303535. doi:10.1002/advs.202303535 |
| [30] | Yu HF, Zeng QR, Xiao PY, et al. Hippo-YAP signaling alleviates copper-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative damage via the ATOX1-PPA2 pathway[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2025, 290: 138908. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.138908 |
| [31] | Zhang X, Di YQ, Wang YP, et al. SIRT5-mediated desuccinylation of PPA2 enhances HIF-1alpha-dependent adaptation to hypoxic stress and colorectal cancer metastasis[J]. EMBO J, 2025, 44(9): 2514-40. doi:10.1038/s44318-025-00416-1 |
| [32] | Zhou Y, Wang Q, Deng HF, et al. N6-methyladenosine demethylase FTO promotes growth and metastasis of gastric cancer via m6A modification of caveolin-1 and metabolic regulation of mitochondrial dynamics[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2022, 13(1): 72. doi:10.1038/s41419-022-04503-7 |
| [33] | Golubeva VA, Das AS, Rabolli CP, et al. YTHDF1 is pivotal for maintenance of cardiac homeostasis[J]. J Mol Cell Cardiol, 2024, 193: 25-35. doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2024.05.008 |
| [1] | . Effects of bisphenol A on apoptosis of ovarian preantral follicular granulosa cells and ovarian development in mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2021, 41(1): 93-99. |
| [2] | . Chromomycin A2 induces apoptosis of HepG2 cells in vitro [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2014, 34(10): 1449-. |
| [3] | . Relationship between heroin spongiform leucoencephalopathy and respiratory chain complex I deficiency [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2013, 33(09): 1357-. |
| [4] | MA Xiao-dong, YAN Fang, MA An-de, WANG Hui-jun Central Laboratory, Department of Histology and Embryology, Department of Forensic Medicine, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, China. Resveratrol induces HepG2 cell apoptosis by depolarizing mitochondrial membrane [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2006, 26(04): 406-. |
| [5] | JI Xi-qing, LI Chao-long, YANG Jin-cheng, LIU Xing-guo, WANG Meng-long, LIU Zhi-qi, LIN Jian-hua. Application of ischemic preconditioning before hepatic vascular exclusion for resection of hepatocellular carcinoma [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2004, 24(01): 66-68,71. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||