Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (11): 2320-2329.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.11.04
Previous Articles Next Articles
Chen JIN( ), Jingping LIU, Bo LIU, Xiyun FEI, Yuxiang LIAO(
), Jingping LIU, Bo LIU, Xiyun FEI, Yuxiang LIAO( )
)
Received:2025-04-02
Online:2025-11-20
Published:2025-11-28
Contact:
Yuxiang LIAO
E-mail:Jinchen@csu.edu.cn;lyxxysw@126.com
Chen JIN, Jingping LIU, Bo LIU, Xiyun FEI, Yuxiang LIAO. circ_EPHB4 synergizes with YTHDF3 to promote glioma progression via m6A-dependent stabilization of Wnt3[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(11): 2320-2329.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.11.04
| Gene | Forward Primer (5'-3') | Reverse Primer (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| circ_EPHB4 | CAGAGAGCGCATCCGCAATTT | AAAGAAGGTGCGCCCACGGTT |
| Zeb1 | AACAGTGAGCGACCTTCATT | AGAGCGCAGAGAAGGAGAGTT |
| GAPDH | AGAGCGCAGAGAAGGAGAUTT | AAAGAGCGAGAGAAGGAGAT |
Tab.1 Primer sequences for RT-qPCR of the target and housekeeping genes
| Gene | Forward Primer (5'-3') | Reverse Primer (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| circ_EPHB4 | CAGAGAGCGCATCCGCAATTT | AAAGAAGGTGCGCCCACGGTT |
| Zeb1 | AACAGTGAGCGACCTTCATT | AGAGCGCAGAGAAGGAGAGTT |
| GAPDH | AGAGCGCAGAGAAGGAGAUTT | AAAGAGCGAGAGAAGGAGAT |
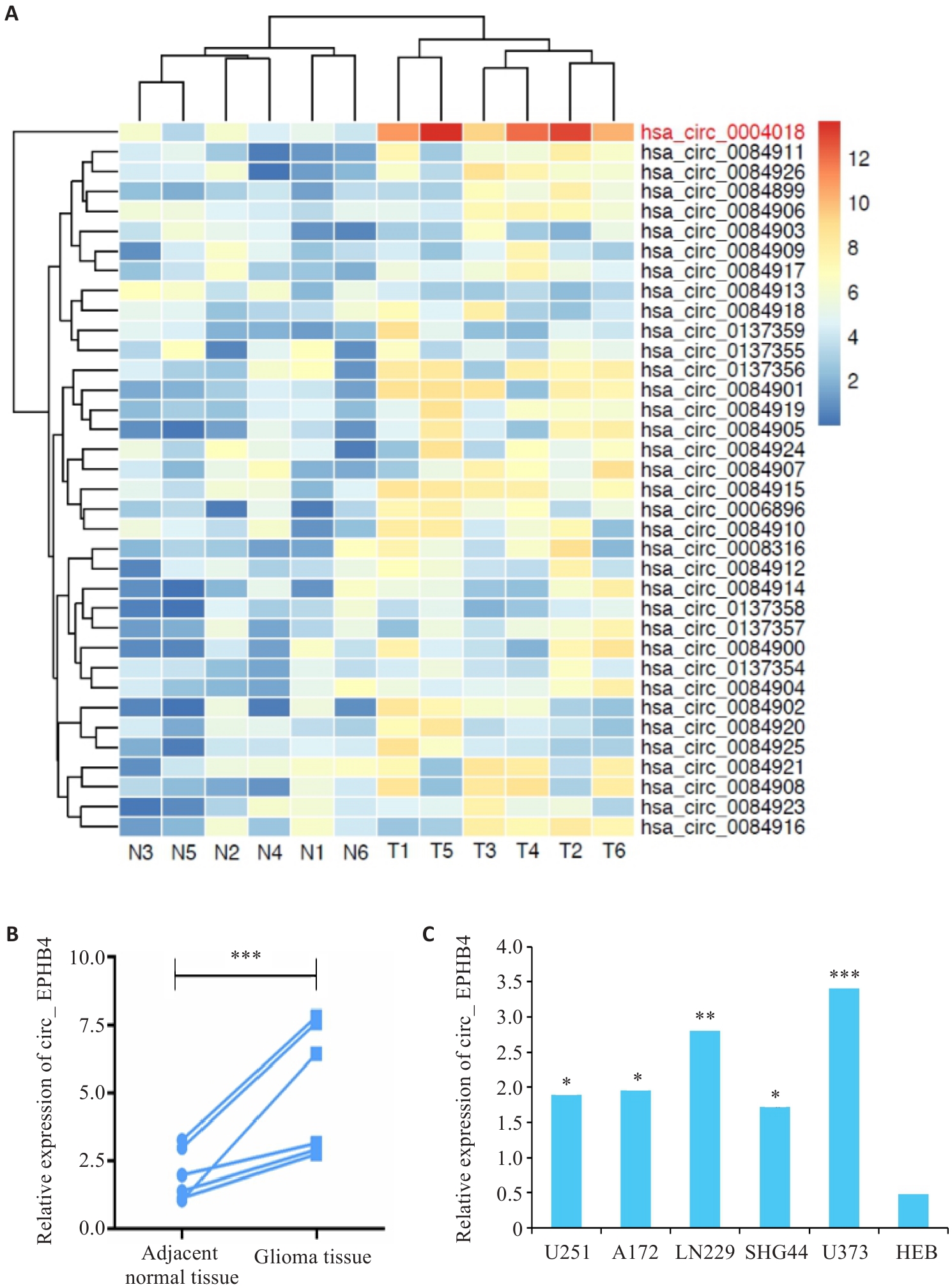
Fig.1 circ_EPHB4 is upregulated in glioma. A: Differential RNA expression analysis shows increased circ_EPHB4 expression in glioma. B: qRT-PCR confirms increased expression of circ_EPHB4 in glioma (***P<0.001). C: circ_EPHB4 expressions are significantly higher in glioma cell lines U251, A172, SHG44, LN229, and U373 than in normal human brain astrocyte HEB cells. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs HEB.

Fig.2 circ_EPHB4 promotes glioma cell migration, invasion, and EMT. A: qRT-PCR of circ_EPHB4 expression in glioma cells after transfection with circ_EPHB4-overexpressing plasmids or circ_EPHB4 siRNA (**P<0.01). B: Scratch wound healing assay for evaluating glioma cell migration ability following circ_EPHB4 overexpression or knockdown (scale bar=100 μm). C: Transwell invasion assay for assessing glioma cell invasion ability after transfection (scale bar=50 μm). D: Western blotting of EMT-related proteins (E-cadherin, N-cadherin and vimentin) in glioma cells following circ_EPHB4 overexpression or knockdown. Data are presented as Mean±SD from 3 independent experiments. *P<0.05 vs siRNA NC; #P<0.05 vs pcDNA3.1 NC.

Fig.3 circ_EPHB4 promotes tumorigenesis and metastasis of glioma cells in nude mice. A: Number of pulmonary metastatic nodules in each group. B: Subcutaneous tumor volume at different time points in each group. C: Subcutaneous tumor weight in each group (*P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001). D: qRT-PCR analysis of mRNA expressions of E-cadherin, N-cadherin, vimentin) in subcutaneous tumors. E: Immunohistochemicalanalysis of protein expressions of E-cadherin, N-cadherin, and vimentin in subcutaneous tumors from each group. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs siRNA NC group; ##P<0.01, ### P<0.001 vs pcDNA3.1 NC group.
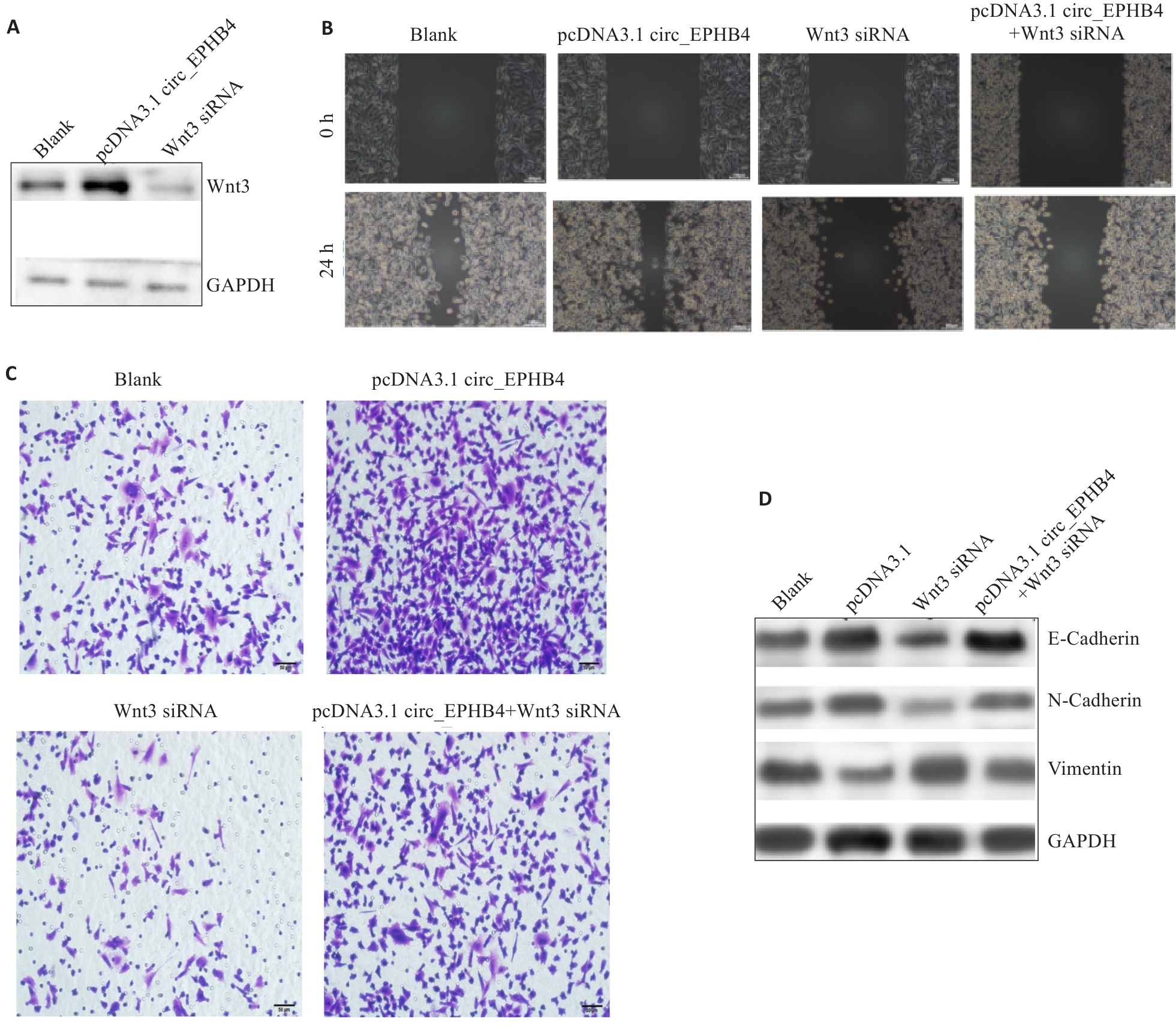
Fig.4 circ_EPHB4 promotes glioma cell metastasis by upregulating Wnt3 expression. A: Overexpression of circ_EPHB4 enhances Wnt3 expression, and circ_EPHB4 knockdown suppresses Wnt3 expression. B: Scratch wound healing assay for evaluating the effect of Wnt3 knockdown on glioma cell migration following circ_EPHB4 overexpression (scale bar=50 μm). C: Transwell invasion assay for assessing the impact of Wnt3 knockdown on invasion ability of circ_EPHB4-overexpressing glioma cells (scale bar=50 μm). D: Western blotting for evaluating the effects of Wnt3 knockdown on expressions of E-cadherin, N-cadherin and vimentin in circ_EPHB4-overexpressing glioma cells.

Fig.5 YTHDF3 enhances Wnt3 mRNA stability in an m6A-dependent manner. A: Direct interaction between YTHDF3 and Wnt3 mRNA in U3T3 and SHG44 cells. B: Effect of YTHDF3 knockdown on Wnt3 expression. C: Positive correlation between YTHDF3 and Wnt3 expression in the StarBase database. D: Effect of circ_EPHB4 on the interaction between YTHDF3 and Wnt3 RNA. E: Effect of combined knockdown of circ_EPHB4 and YTHDF3 on Wnt3 mRNA expression. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
| [1] | Ludwig K, Kornblum HI. Molecular markers in glioma[J]. J Neurooncol, 2017, 134(3): 505-12. doi:10.1007/s11060-017-2379-y |
| [2] | 翟 贝, 魏 灯, 王 萍. tRNA修饰在胶质瘤中的研究进展[J]. 中国肿瘤临床, 2024,51(11): 567-71. |
| [3] | 贾金曦, 姚春旭, 刘 畅, 等. 脑胶质瘤患者术后远期预后影响因素分析[J]. 实用癌症杂志, 2024, 39(3): 514-7. |
| [4] | Liu ZX, Li LM, Sun HL, et al. Link between m6A modification and cancers[J]. Front Bioeng Biotechnol, 2018, 6: 89. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2018.00089 |
| [5] | Zhang G, Cheng C, Wang X, et al. N6-Methyladenosine methylation modification in breast cancer: current insights[J]. J Transl Med, 2024, 22(1): 971. doi:10.1186/s12967-024-05771-x |
| [6] | Rui Y, Zhang H, Yu K, et al. N6-methyladenosine regulates Cilia elongation in cancer cells by modulating HDAC6 expression[J]. Adv Sci: Weinh, 2025, 12(2): e2408488. doi:10.1002/advs.202408488 |
| [7] | Chen XH, Guo KX, Li J, et al. Regulations of m6A and other RNA modifications and their roles in cancer[J]. Front Med, 2024, 18(4): 622-48. doi:10.1007/s11684-024-1064-8 |
| [8] | Qin L, Zeng X, Qiu X, et al. The role of N6-methyladenosine modification in tumor angiogenesis[J]. Front Oncol, 2024, 14: 1467850. doi:10.3389/fonc.2024.1467850 |
| [9] | Saluja S, Ganguly S, Singh J, et al. Aberrant overexpression of m6A writer and reader genes in pediatric B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (B-ALL)[J]. Transl Oncol, 2025, 56: 102403. doi:10.1016/j.tranon.2025.102403 |
| [10] | Zhao Y, Feng F, Guo QH, et al. Role of succinate dehydrogenase deficiency and oncometabolites in gastrointestinal stromal tumors[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2020, 26(34): 5074-89. doi:10.3748/wjg.v26.i34.5074 |
| [11] | Li J, Han Y, Zhang HM, et al. The m6A demethylase FTO promotes the growth of lung cancer cells by regulating the m6A level of USP7 mRNA[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2019, 512(3): 479-85. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.03.093 |
| [12] | Dong J, Zeng Z, Huang Y, et al. Challenges and opportunities for circRNA identification and delivery[J]. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol, 2023, 58(1): 19-35. doi:10.1080/10409238.2023.2185764 |
| [13] | Chen X, Lu Y. Circular RNA: biosynthesis in vitro [J]. Front Bioeng Biotechnol, 2021, 9: 787881. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2021.787881 |
| [14] | Patop IL, Kadener S. circRNAs in cancer[J]. Curr Opin Genet Dev, 2018, 48: 121-7. doi:10.1016/j.gde.2017.11.007 |
| [15] | Hanan M, Soreq H, Kadener S. CircRNAs in the brain[J]. RNA Biol, 2017, 14(8): 1028-34. doi:10.1080/15476286.2016.1255398 |
| [16] | Chen M, Wei L, Law CT, et al. RNA N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase-like 3 promotes liver cancer progression through YTHDF2-dependent posttranscriptional silencing of SOCS2 [J]. Hepatology, 2018, 67(6): 2254-70. doi:10.1002/hep.29683 |
| [17] | Yin J, Ding F, Cheng Z, et al. METTL3-mediated m6A modification of LINC00839 maintains glioma stem cells and radiation resistance by activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2023, 14(7): 417. doi:10.1038/s41419-023-05933-7 |
| [18] | Xiao L, Li X, Mu Z, et al. FTO inhibition enhances the anti-tumor effect of temozolomide by targeting MYC-miR-155/23a cluster-MXI1 feedback circuit in glioma. Cancer Res. 2020. 80(18): canres.0132.2020. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-20-0132 |
| [19] | Zheng W, Li J, Zhou X, et al. The lncRNA XIST promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells by targeting miR-337[J]. Arab J Gastroenterol, 2020, 21(3): 199-206. doi:10.1016/j.ajg.2020.07.010 |
| [20] | Patop IL, Wüst S, Kadener S. Past, present, and future of circRNAs[J]. EMBO J, 2019, 38(16): e100836. doi:10.15252/embj.2018100836 |
| [21] | Yu T, Wang Y, Fan Y, et al. CircRNAs in cancer metabolism: a review[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2019, 12(1): 90. doi:10.1186/s13045-019-0776-8 |
| [22] | Yang R, Cui J. Advances and applications of RNA vaccines in tumor treatment[J]. Mol Cancer, 2024, 23(1): 226. doi:10.1186/s12943-024-02141-5 |
| [23] | Yi Q, Feng JG, Lan WW, et al. CircRNA and lncRNA-encoded peptide in diseases, an update review[J]. Mol Cancer, 2024, 23(1): 214. doi:10.1186/s12943-024-02131-7 |
| [24] | Zhang S, Zhang P, Wu A, et al. Downregulated M6A modification and expression of circRNA_103239 promoted the progression of glioma by regulating the miR-182-5p/MTSS1 signalling pathway[J]. J Cancer, 2023, 14(18): 3508-20. doi:10.7150/jca.85320 |
| [25] | Dai YH, Zhao SH, Chen HL, et al. RNA methylation and breast cancer: insights into m6A, m7G and m5C[J]. Mol Biol Rep, 2024, 52(1): 27. doi:10.1007/s11033-024-10138-y |
| [26] | Lin ZY, Wan AH, Sun L, et al. N6-methyladenosine demethylase FTO enhances chemo-resistance in colorectal cancer through SIVA1-mediated apoptosis[J]. Mol Ther, 2023, 31(2): 517-34. doi:10.1016/j.ymthe.2022.10.012 |
| [27] | Zhang C, Huang S, Zhuang H, et al. YTHDF2 promotes the liver cancer stem cell phenotype and cancer metastasis by regulating OCT4 expression via m6A RNA methylation[J]. Oncogene, 2020, 39(23): 4507-18. doi:10.1038/s41388-020-1303-7 |
| [28] | Chang H, Yang J, Wang Q, et al. Role of N6-methyladenosine modification in pathogenesis of ischemic stroke[J]. Expert Rev Mol Diagn, 2022, 22(3): 295-303. doi:10.1080/14737159.2022.2049246 |
| [29] | Li L, Zhang T, Xiao M, et al. Brain macrophage senescence in glioma[J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 2024, 104/105: 46-60. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2024.07.005 |
| [30] | Davidson CL, Vengoji R, Jain M, et al. Biological, diagnostic and therapeutic implications of exosomes in glioma[J]. Cancer Lett, 2024, 582: 216592. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2023.216592 |
| [31] | Yin JL, Liu G, Zhang Y, et al. Gender differences in gliomas: From epidemiological trends to changes at the hormonal and molecular levels[J]. Cancer Lett, 2024, 598: 217114. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2024.217114 |
| [1] | Yanpeng PU, Zhen WANG, Haoran CHU. Eye acupuncture improves neural function in rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by promoting angiogenesis via upregulating METTL3-mediated m6A methylation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 921-928. |
| [2] | Yuxiang LIAO, Jingping LIU, Bo LIU, Xiyun FEI, Chen JIN. Circ_EPHB4 regulates temozolomide sensitivity in glioma cells through the miR-424-5p/Wnt3 axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 942-953. |
| [3] | Chuixing WU, Weixiong ZHONG, Jincheng XIE, Ruimeng YANG, Yuankui WU, Yikai XU, Linjing WANG, Xin ZHEN. An MRI multi-sequence feature imputation and fusion mutual-aid model based on sequence deletion for differentiation of high-grade from low-grade glioma [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1561-1570. |
| [4] | Ze YANG, Xiusen ZHANG, Xudong ZHANG, Ying LIU, Jiacheng ZHANG, Xiang YUAN. Porphyromonas gingivalis infection facilitates immune escape of esophageal cancer by enhancing YTHDF2-mediated Fas degradation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(6): 1159-1165. |
| [5] | HUANG Qiuhu, ZHOU Jian, WANG Zizhen, YANG Kun, CHEN Zhenggang. MiR-26-3p regulates proliferation, migration, invasion and apoptosis of glioma cells by targeting CREB1 [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(3): 578-584. |
| [6] | Xiaoyin HUANG, Fenglian CHEN, Yu ZHANG, Shujun LIANG. A predictive model for survival outcomes of glioma patients based on multi-parametric, multi-regional MRI radiomics features and clinical features [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(10): 2004-2014. |
| [7] | ZHANG Zhenyang, XIE Jincheng, ZHONG Weixiong, LIANG Fangrong, YANG Ruimeng, ZHEN Xin. A multi-modal feature fusion classification model based on distance matching and discriminative representation learning for differentiation of high-grade glioma from solitary brain metastasis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(1): 138-145. |
| [8] | YU Zhengtao, LI Jiameng, JIANG Junwen, LI You, LIN Long, XIA Ying, WANG Lei. miRNA-128-3p inhibits malignant behavior of glioma cells by downregulating KLHDC8A expression [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(9): 1447-1459. |
| [9] | CHU Zhiqin, QU Yaoming, ZHONG Tao, LIANG Shujun, WEN Zhibo, ZHANG Yu. A Dual-Aware deep learning framework for identification of glioma isocitrate dehydrogenase genotype using magnetic resonance amide proton transfer modalities [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(8): 1379-1387. |
| [10] | YE Jingjing, XU Wenqin, XI Bangsheng, WANG Nengqian, CHEN Tianbing. Lactate-induced up-regulation of PLEKHA4 promotes proliferation and apoptosis of human glioma cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(7): 1071-1080. |
| [11] | LU Mingjun, QU Yaoming, MA Andong, ZHU Jianbin, ZOU Xia, LIN Gengyun, LI Yuxin, LIU Xinzi, WEN Zhibo. Prediction of 1p/19q codeletion status in diffuse lower-grade glioma using multimodal MRI radiomics [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(6): 1023-1028. |
| [12] | XU Wenqin, YE Jingjing, WANG Fei, CHEN Tianbing. Piroctone olamine disrupts mitochondrial dynamics in glioma cells through the PI3K/AKT pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(5): 764-771. |
| [13] | SUN Jiangchuan, XING Jiaheng, TAN Ruxue, QIAN Ying, TIAN Nan. Curcumol reverses temozolomide resistance in glioma cells by regulating the UTX/MGMT axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(10): 1697-1705. |
| [14] | CUI Ying, FAN Shuizhi, PAN Didi, CHAO Qing. Atorvastatin inhibits malignant behaviors and induces apoptosis in human glioma cells by up-regulating miR-146a and inhibiting the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42(6): 899-904. |
| [15] | YANG Xuezhi, SHEN Hong, LI Qun, DAI Zichao, YANG Rongqiang, HUANG Guobin, CHEN Rui, WANG Fang, SONG Jingling, HUA Hairong. Interference of P2X4 receptor expression in tumor-associated macrophages suppresses migration and invasion of glioma cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42(5): 658-664. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||