Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (8): 1620-1630.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.08.22
Hongli YANG1,3( ), Yayun XIANG2, Tingting TAN2, Yang LEI2(
), Yayun XIANG2, Tingting TAN2, Yang LEI2( )
)
Received:2024-04-03
Online:2024-08-20
Published:2024-09-06
Contact:
Yang LEI
E-mail:2021110163@stu.cqmu.edu.cn;leiyang339@hospital.cqmu.edu.cn
Hongli YANG, Yayun XIANG, Tingting TAN, Yang LEI. ORY-1001 inhibits glioblastoma cell growth by downregulating the Notch/HES1 pathway via suppressing lysine-specific demethylase 1 expression[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1620-1630.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.08.22
| Primer | Sequences 5'-3' | |
|---|---|---|
| Notch1 | Forward Reverse | CTGAAGAACGGGGCTAACAA CAGGTTGTACTCGTCCAGCA |
| HES1 | Forward Reverse | GCAGATGACGGCTGCGCTGA AAGCGGGTCACCTCGTTCATGC |
| HES4 | Forward Reverse | GCTCAGCTCAAAACCCTCATC TTCACCTCCGCCAGACACTCG |
| HEY1 | Forward Reverse | TGCATACGGC AGGAGGGAAAG AGTCGAACTCGAAGCGGGTCA |
| HEY2 | Forward Reverse | AGGCGTCGGGATCGGATAAAT AAGAGCGTGTGCGTCAAAGTA |
| GAPDH | Forward Reverse | GGAGTCCACTGGCGTCTTCACC GAGGAGTGGGTGTCGCTGTTG |
| LSD1 | Forward Reverse | AGACGACAGTTCTGGAGGGTA TCTTGAGAAGTCATCCGGTCA |
Tab.1 Sequence of primers used for qRT-PCR
| Primer | Sequences 5'-3' | |
|---|---|---|
| Notch1 | Forward Reverse | CTGAAGAACGGGGCTAACAA CAGGTTGTACTCGTCCAGCA |
| HES1 | Forward Reverse | GCAGATGACGGCTGCGCTGA AAGCGGGTCACCTCGTTCATGC |
| HES4 | Forward Reverse | GCTCAGCTCAAAACCCTCATC TTCACCTCCGCCAGACACTCG |
| HEY1 | Forward Reverse | TGCATACGGC AGGAGGGAAAG AGTCGAACTCGAAGCGGGTCA |
| HEY2 | Forward Reverse | AGGCGTCGGGATCGGATAAAT AAGAGCGTGTGCGTCAAAGTA |
| GAPDH | Forward Reverse | GGAGTCCACTGGCGTCTTCACC GAGGAGTGGGTGTCGCTGTTG |
| LSD1 | Forward Reverse | AGACGACAGTTCTGGAGGGTA TCTTGAGAAGTCATCCGGTCA |
| Primer n | Sequences 5'-3' | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| HES1 | -2200 -2200 | Forward Reverse | AGG TCA CCC AGA GTC AGG AA CCA GCG TCT TGT TTG ATG TG |
| HES1 | TSS TSS | Forward Reverse | CGT GTC TCC TCC TCC CAT T GAG AGG TAG ACG GGG GAT TC |
| HES1 | +500 +500 | Forward Reverse | TCA ACA CGA CAC CGG ATA AA TCA GCT GGC TCA GAC TTT CA |
| HES1 | +2600 +2600 | Forward Reverse | GGC TTT TGG TGG AAT TTG AA TCA TGG AGG ATT GGT GAA AAG |
| Notch3 | -5000 -5000 | Forward Reverse | TAG CCC CTG GTC AGT CAT TC GGT GCA TCG TAT CAG GAG GT |
| Notch3 | TSS TSS | Forward Reverse | TGG CCT CAG TTT CCA GAG TT CAC ACC CAA CCT CGT GAA C |
| Notch3 | +3000 +3000 | Forward Reverse | GTC TCA GCA CAC CCC ATT CT AAC CAC AAA GCA GGG GAA G |
| Notch3 | +28600 +28600 | Forward Reverse | GGG GGC TAA AGA CAC AAA CA GTT CCT TCT CTC CCC ACT CC |
| DTX1 | -1700 -1700 | Forward Reverse | TGT GAA TGA CAT GGC AGA GG TGA ATC TCC TGC CAG TAC CC |
| DTX1 | +30000 +30000 | Forward Reverse | ACA TGC CAG ACA GCA GAA CA AAC CTT CCA GAC CCT GTG TG |
| CR2 | +5000 +5000 | Forward Reverse | GCC GGA AGG ATG TTC TTG TA CAG GGA AGG CCA TGA AAA TA |
| CR2 | +21000 +21000 | Forward Reverse | CCC CAC AGT GCT TAC GAT CT AAG CCA GGA TTG CAG TCA AC |
Tab.2 Primer sequences of Notch target gene promoters used for ChIP
| Primer n | Sequences 5'-3' | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| HES1 | -2200 -2200 | Forward Reverse | AGG TCA CCC AGA GTC AGG AA CCA GCG TCT TGT TTG ATG TG |
| HES1 | TSS TSS | Forward Reverse | CGT GTC TCC TCC TCC CAT T GAG AGG TAG ACG GGG GAT TC |
| HES1 | +500 +500 | Forward Reverse | TCA ACA CGA CAC CGG ATA AA TCA GCT GGC TCA GAC TTT CA |
| HES1 | +2600 +2600 | Forward Reverse | GGC TTT TGG TGG AAT TTG AA TCA TGG AGG ATT GGT GAA AAG |
| Notch3 | -5000 -5000 | Forward Reverse | TAG CCC CTG GTC AGT CAT TC GGT GCA TCG TAT CAG GAG GT |
| Notch3 | TSS TSS | Forward Reverse | TGG CCT CAG TTT CCA GAG TT CAC ACC CAA CCT CGT GAA C |
| Notch3 | +3000 +3000 | Forward Reverse | GTC TCA GCA CAC CCC ATT CT AAC CAC AAA GCA GGG GAA G |
| Notch3 | +28600 +28600 | Forward Reverse | GGG GGC TAA AGA CAC AAA CA GTT CCT TCT CTC CCC ACT CC |
| DTX1 | -1700 -1700 | Forward Reverse | TGT GAA TGA CAT GGC AGA GG TGA ATC TCC TGC CAG TAC CC |
| DTX1 | +30000 +30000 | Forward Reverse | ACA TGC CAG ACA GCA GAA CA AAC CTT CCA GAC CCT GTG TG |
| CR2 | +5000 +5000 | Forward Reverse | GCC GGA AGG ATG TTC TTG TA CAG GGA AGG CCA TGA AAA TA |
| CR2 | +21000 +21000 | Forward Reverse | CCC CAC AGT GCT TAC GAT CT AAG CCA GGA TTG CAG TCA AC |
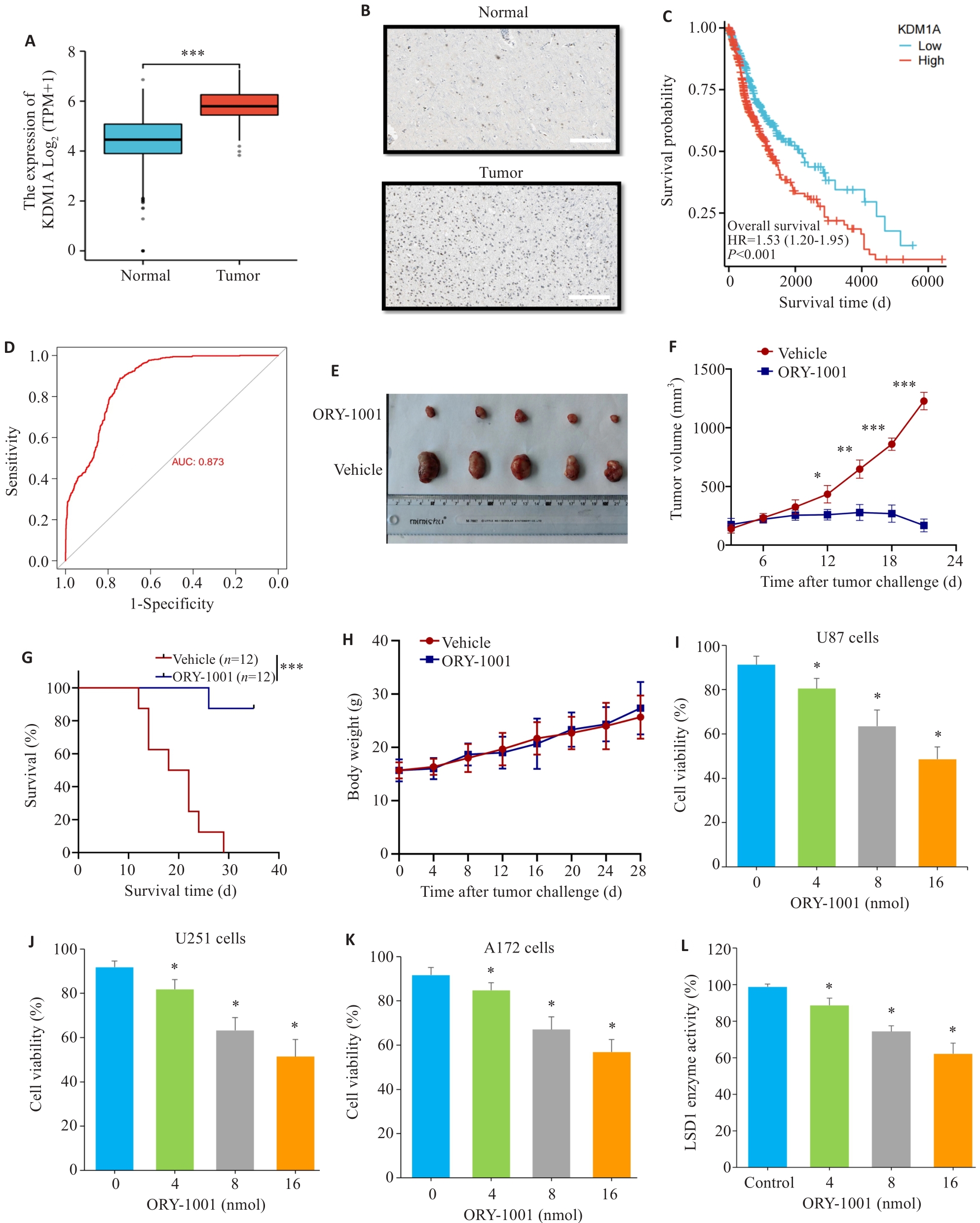
Fig.1 LSD1 inhibition prolongs the survival of GBM-bearing mice. A: LSD1 mRNA expression in glioblastoma and normal brain tissues. B: Expression of LSD1 in glioblastoma and normal brain tissues (Scale bar=200 μm). C: Kaplan-Meier survival analysis showing negative correlation between LSD1 expression and patient survival. D: ROC analysis of specificity and sensitivity of LSD1 expression for predicting GBM. E: General comparison of subcutaneous tumors in treated group and control group on day 21 after tumor cell engraftment. F: Tumor growth in the treated and control group (n=12). G: Survival curves of treated group and control group. H: Body weight curves of ORY-1001-treated group and control group. I: Cell viability of U87 cells treated with ORY-1001. J: Cell viability of U251 treated with ORY-1001. K: Cell viability of A172 treated with ORY-1001. L: Changes of LSD1 enzyme activity. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs the control group, vehicle.

Fig.2 Genetic targeting of LSD1 mirrors LSD1 pharmacological inhibition in GBM. A, B: Western blotting of the expression of LSD1 in ORY-1001-treated U87 cells. C, D: Western blotting of H3K4me2 expression in in ORY-1001-treated U87 cells with H3 expression as the internal reference. E: qPCR for detecting relative expression of LSD1 mRNA in sh-LSD1 and sh-NC cells. F: LSD1 expression of sh-LSD1 and sh-NC cells verified by Western blotting. G: Quantification of LSD1 expression. H: Cell viability of sh-LSD1-U87 cells compared with sh-NC-U87 cells. I, J: Cleaved caspase-3 expression upon LSD1 silencing. K: Effect of different ORY-1001 concentrations on sh-LSD1 and sh-NC cells. L: The subcutaneous tumor growth curves of LSD1-silenced group and control group. M: Survival curves of mice injected with LSD1-silenced and control GBM cells. N: Relative expression of LSD1 mRNA in LSD1-silenced group and control group at the time of death. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs 0 nmol, sh-NC.

Fig.5 ORY-1001 affects the binding of LSD1 to the Notch target gene promoter regions in GBM. ChIP analysis was performed on the chromatin from GBM U87 cells treated with ORY-1001 (16 nmol/L) for 24 h. A: LSD1 binds to the promoter sequence of the Notch target gene (red). B: Changes of LSD1 occupancy in Notch target gene promoter region after ORY-1001treatment. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs Vehicle group.
| 1 | Schaff LR, Mellinghoff IK. Glioblastoma and other primary brain malignancies in adults: a review[J]. JAMA, 2023, 329(7): 574-87. |
| 2 | Ma RC, Taphoorn MJB, Plaha P. Advances in the management of glioblastoma[J]. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry, 2021, 92(10): 1103-11. |
| 3 | Oraiopoulou ME, Tzamali E, Papamatheakis J, et al. Phenocopying glioblastoma: a review[J]. IEEE Rev Biomed Eng, 2023, 16: 456-71. |
| 4 | Rong L, Li N, Zhang ZZ. Emerging therapies for glioblastoma: current state and future directions[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2022, 41(1): 142. |
| 5 | Guo MZ, Niu Y, Xie M, et al. Notch signaling, hypoxia, and cancer[J]. Front Oncol, 2023, 13: 1078768. |
| 6 | Yi L, Zhou XC, Li T, et al. Notch1 signaling pathway promotes invasion, self-renewal and growth of glioma initiating cells via modulating chemokine system CXCL12/CXCR4[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2019, 38(1): 339. |
| 7 | Sarkar S, Mirzaei R, Zemp FJ, et al. Activation of NOTCH signaling by tenascin-C promotes growth of human brain tumor-initiating cells[J]. Cancer Res, 2017, 77(12): 3231-43. |
| 8 | Sun Z, Wang L, Zhou YL, et al. Glioblastoma stem cell-derived exosomes enhance stemness and tumorigenicity of glioma cells by transferring Notch1 protein[J]. Cell Mol Neurobiol, 2020, 40(5): 767-84. |
| 9 | Shabani M, Javanshir HT, Bereimipour A, et al. Contradictory effect of Notch1 and Notch2 on phosphatase and tensin homolog and its influence on glioblastoma angiogenesis[J]. Galen Med J, 2021, 10: e2091. |
| 10 | Wang JL, Wakeman TP, Lathia JD, et al. Notch promotes radioresistance of glioma stem cells[J]. Stem Cells, 2010, 28(1): 17-28. |
| 11 | Eyler CE, Matsunaga H, Hovestadt V, et al. Single-cell lineage analysis reveals genetic and epigenetic interplay in glioblastoma drug resistance[J]. Genome Biol, 2020, 21(1): 174. |
| 12 | Yu JB, Jiang H, Zhan RY. Aberrant Notch signaling in glioblastoma stem cells contributes to tumor recurrence and invasion[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2016, 14(2): 1263-8. |
| 13 | Lv YX, Tian S, Zhang ZD, et al. LSD1 inhibitors for anticancer therapy: a patent review (2017-present)[J]. Expert Opin Ther Pat, 2022, 32(9): 1027-42. |
| 14 | Karakaidos P, Verigos J, Magklara A. LSD1/KDM1A, a gate-keeper of cancer stemness and a promising therapeutic target[J]. Cancers, 2019, 11(12): 1821. |
| 15 | Yang GJ, Liu YJ, Ding LJ, et al. A state-of-the-art review on LSD1 and its inhibitors in breast cancer: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic significance[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2022, 13: 989575. |
| 16 | Noce B, di Bello E, Fioravanti R, et al. LSD1 inhibitors for cancer treatment: focus on multi-target agents and compounds in clinical trials[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2023, 14: 1120911. |
| 17 | Fang Y, Yang C, Yu ZQ, et al. Natural products as LSD1 inhibitors for cancer therapy[J]. Acta Pharm Sin B, 2020, 11(3): 621-31. |
| 18 | Zhang XY, Wang XR, Wu TX, et al. Therapeutic potential of targeting LSD1/KDM1A in cancers[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2022, 175: 105958. |
| 19 | Mohammad HP, Smitheman KN, Kamat CD, et al. A DNA hypomethylation signature predicts antitumor activity of LSD1 inhibitors in SCLC[J]. Cancer Cell, 2015, 28(1): 57-69. |
| 20 | Maes T, Mascaró C, Tirapu I, et al. ORY-1001, a potent and selective covalent KDM1A inhibitor, for the treatment of acute leukemia[J]. Cancer Cell, 2018, 33(3): 495-511.e12. |
| 21 | Zhao JX, Jin WL, Yi KK, et al. Combination LSD1 and HOTAIR-EZH2 inhibition disrupts cell cycle processes and induces apoptosis in glioblastoma cells [J]. Pharmacol Res, 2021, 171. |
| 22 | Rodríguez-Camacho A, Flores-Vázquez JG, Moscardini-Martelli J, et al. Glioblastoma treatment: state-of-the-art and future perspectives[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(13): 7207. |
| 23 | Nagata S. Apoptosis and clearance of apoptotic cells[J]. Annu Rev Immunol, 2018, 36: 489-517. |
| 24 | Bazzoni R, Bentivegna A. Role of Notch signaling pathway in glioblastoma pathogenesis[J]. Cancers, 2019, 11(3): 292. |
| 25 | Kipper FC, Kieran MW, Thomas A, et al. Notch signaling in malignant gliomas: supporting tumor growth and the vascular environment[J]. Cancer Metastasis Rev, 2022, 41(3): 737-47. |
| 26 | Hai L, Zhang C, Li T, et al. Notch1 is a prognostic factor that is distinctly activated in the classical and proneural subtype of glioblastoma and that promotes glioma cell survival via the NF-κB(p65) pathway[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2018, 9: 158. |
| 27 | Guelfi S, Orsetti B, Deleuze V, et al. SLUG and truncated TAL1 reduce glioblastoma stem cell growth downstream of Notch1 and define distinct vascular subpopulations in glioblastoma multiforme[J]. Cancers, 2021, 13(21): 5393. |
| 28 | Lin Y, Wei L, Hu BQ, et al. RBM8A promotes glioblastoma growth and invasion through the notch/STAT3 pathway[J]. Front Oncol, 2021, 11: 736941. |
| 29 | Yuan Y, Wang LH, Zhao XX, et al. The E3 ubiquitin ligase HUWE1 acts through the N-Myc-DLL1-NOTCH1 signaling axis to suppress glioblastoma progression[J]. Cancer Commun, 2022, 42(9): 868-86. |
| 30 | Aster JC, Pear WS, Blacklow SC. The varied roles of Notch in cancer[J]. Annu Rev Pathol, 2017, 12: 245-75. |
| 31 | Canova S, Trevisan B, Abbate MI, et al. Novel therapeutic options for small cell lung cancer[J]. Curr Oncol Rep, 2023, 25(11): 1277-94. |
| 32 | Lu ZM, Ren YD, Zhang MY, et al. FLI-06 suppresses proliferation, induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest by targeting LSD1 and Notch pathway in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells[J]. Biomedecine Pharmacother, 2018, 107: 1370-6. |
| 33 | Fang Y, Liao GC, Yu B. LSD1/KDM1A inhibitors in clinical trials: advances and prospects[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2019, 12(1): 129. |
| 34 | Chen L, Sun X, Chen DD, et al. LSD1 for the targeted regulation of adipose tissue[J]. Curr Issues Mol Biol, 2022, 45(1): 151-63. |
| 35 | Li Y, Zhao YY, Li XN, et al. Biological and therapeutic role of LSD1 in Alzheimer’s diseases[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2022, 13: 1020556. |
| 36 | Gu FY, Lin YX, Wang Z, et al. Biological roles of LSD1 beyond its demethylase activity[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2020, 77(17): 3341-50. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||