Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (6): 1079-1087.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.06.08
Previous Articles Next Articles
Jie CHEN1,2( ), Chenxu LIU1,2, Chun WANG2,3, Li LI1,2, Weiting TAO1,2, Jingru XUN4, Honghui TANG4, Li HUANG1,2(
), Chenxu LIU1,2, Chun WANG2,3, Li LI1,2, Weiting TAO1,2, Jingru XUN4, Honghui TANG4, Li HUANG1,2( )
)
Received:2023-07-14
Online:2024-06-20
Published:2024-07-01
Contact:
Li HUANG
E-mail:cj332022@163.com;zi05@163.com
Jie CHEN, Chenxu LIU, Chun WANG, Li LI, Weiting TAO, Jingru XUN, Honghui TANG, Li HUANG. Exogenous leptin improves cerebral ischemia-reperfusion-induced glutamate excitotoxic injury in mice by up-regulating GLT-1 and GLAST expression in astrocytes[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(6): 1079-1087.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.06.08
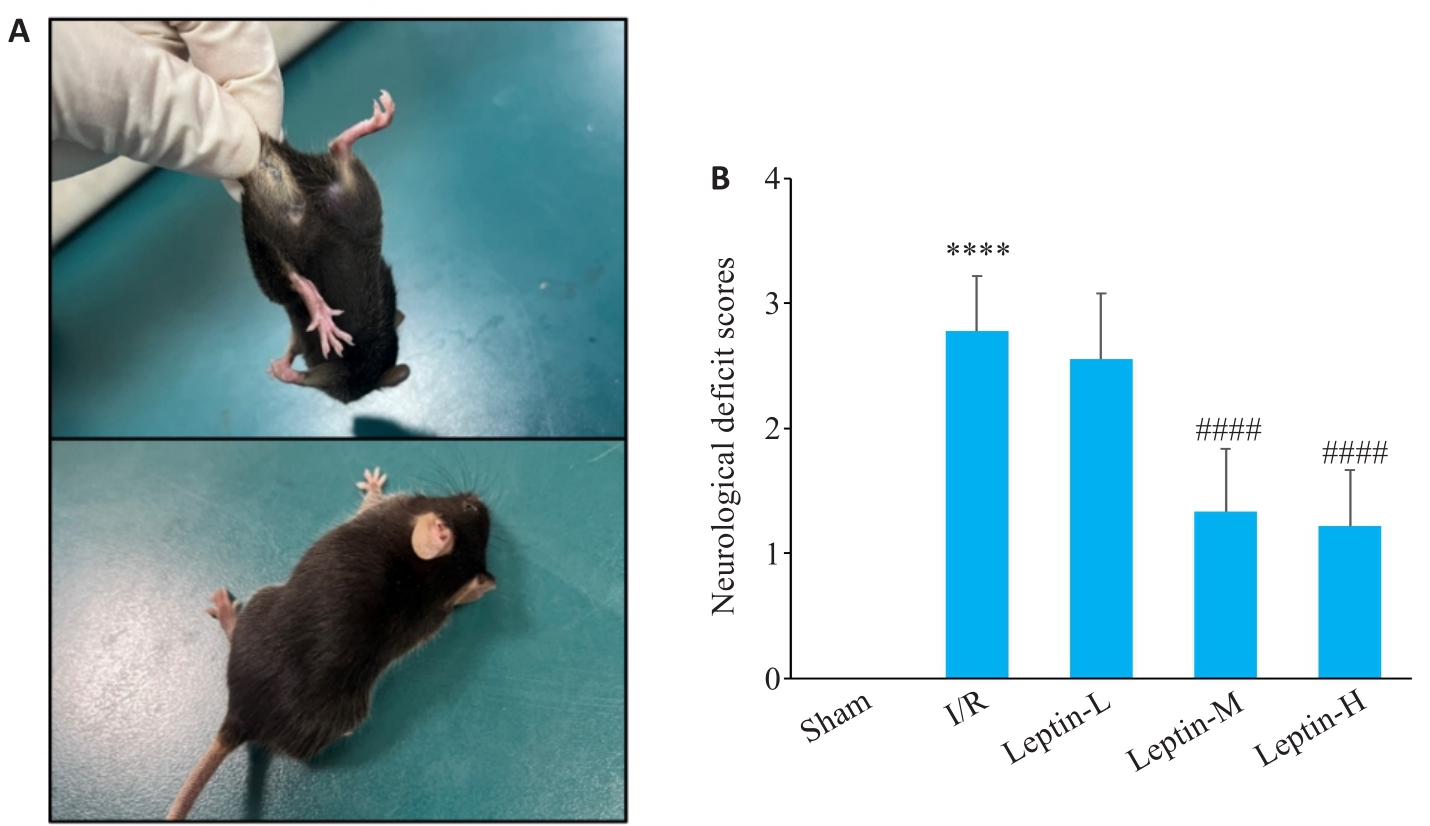
Fig.2 Posture of the mice following brain I/R modeling (A) and neurological deficit scores of the mice in different groups (B), n=9. ****P<0.0001 vs Sham group; ####P<0.0001 vs I/R group.
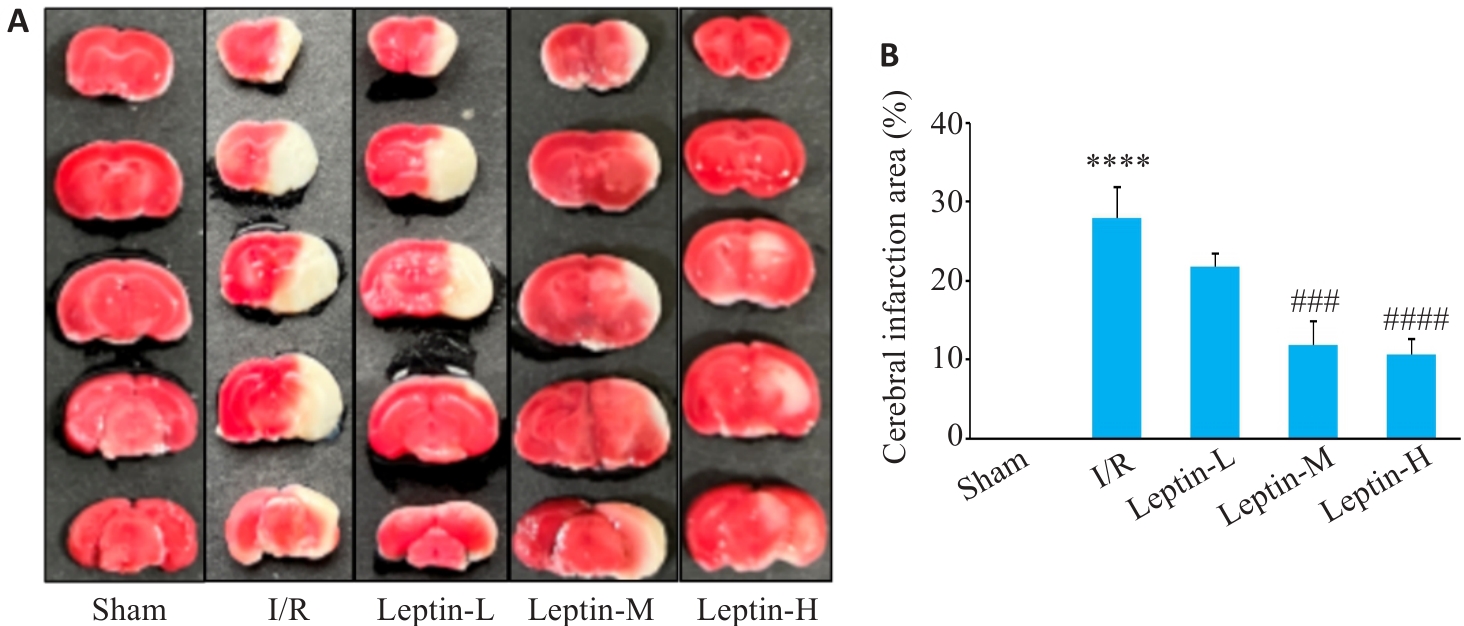
Fig.3 TTC staining for determining the size of cerebral infarct area of the mice. A: TTC staining of the brain tissue sections. B: Quantitative analysis of brain infarct area (n=3). ****P<0.0001 vs Sham group; ###P<0.001, ####P<0.0001 vs I/R group.
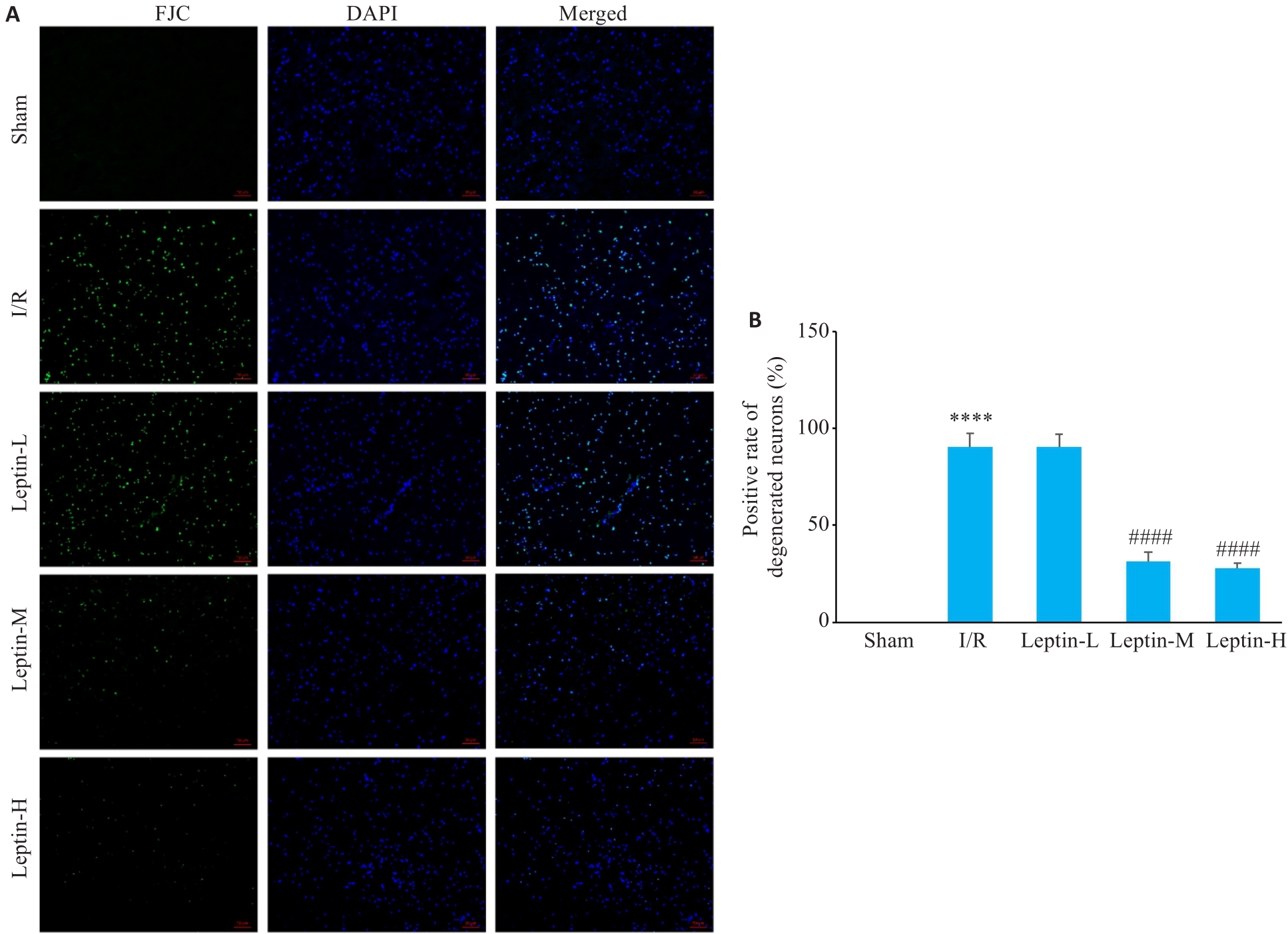
Fig.5 FJC staining for assessing cortical neuronal degenerative damage. A: FJC staining iamges (scale bar=20 μm). B: Positive rate of the degenerated neurons. ****P<0.0001 vs Sham group; ####P<0.0001 vs I/R group.
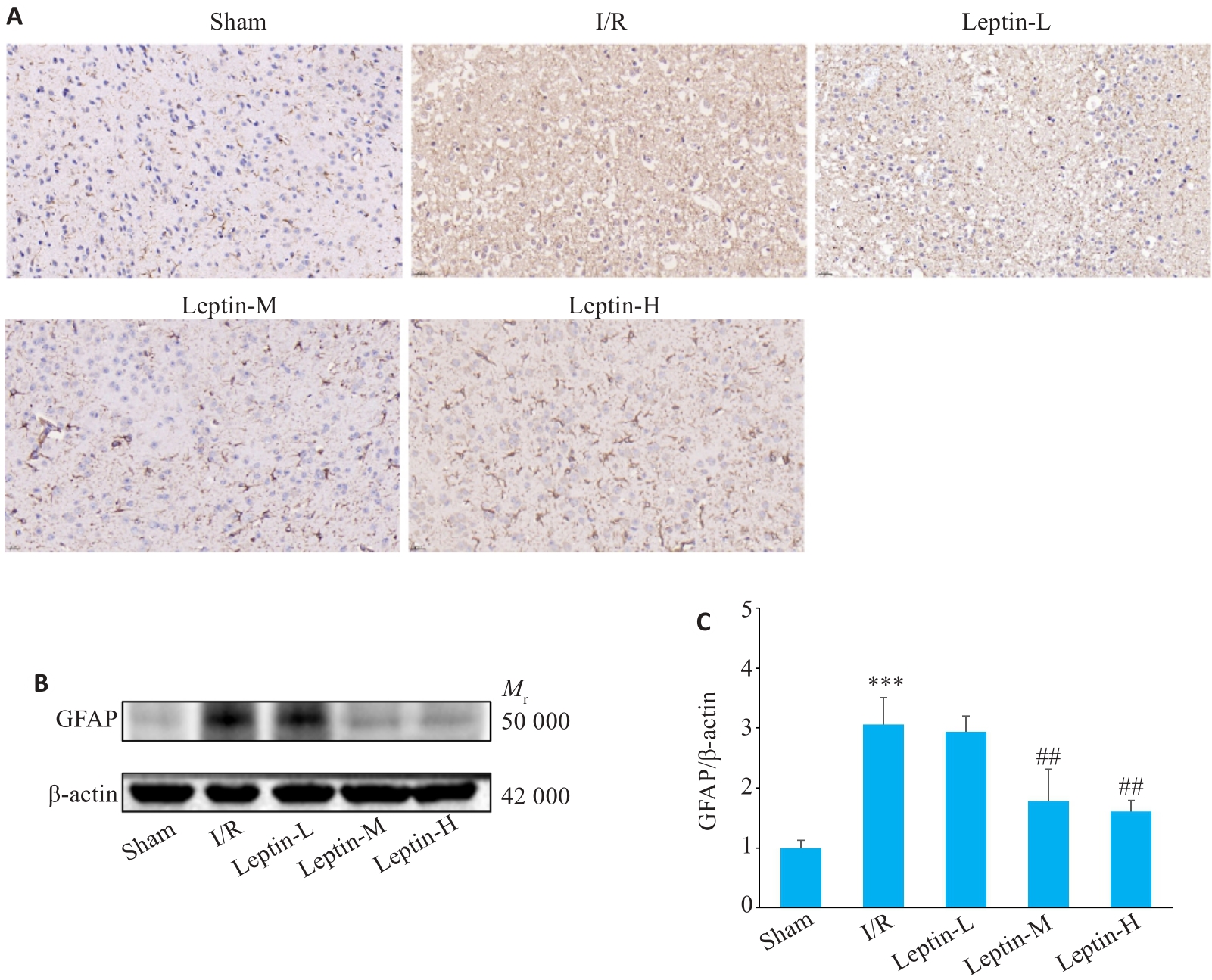
Fig.6 Expression of GFAP protein in mouse cortical brain tissue. A: Expression of GFAP detected by immunohistochemistry (Original magnification: ×40). B: Expression of GFAP detected by Western blotting (n=3). C: Quantitative analysis of GFAP expression. ***P<0.001 vs Sham group; ##P<0.01 vs I/R group.
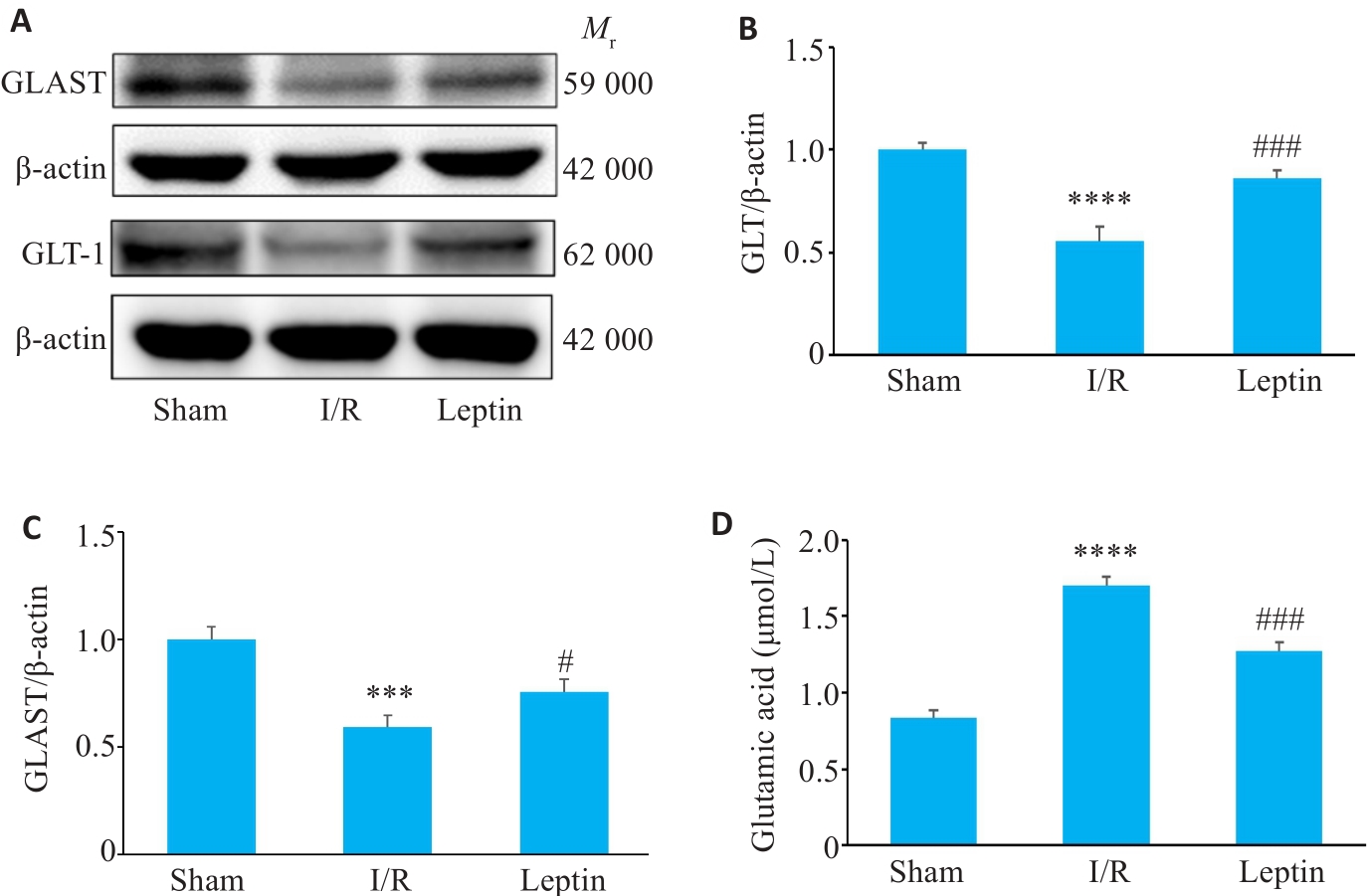
Fig.8 Changes in the expression of GLT-1 and GLAST proteins and Glu content in mouse cortical brain tissue. A: Expression of GLT-1 and GLAST detected by Western blotting (n=3). B: Quantitative analysis of GLT-1 expression. C: Quantitative analysis of GLAST expression; D: Content of Glu (n=3). ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001 vs Sham group; #P<0.01, ###P<0.001 vs I/R group.
| 1 | Collaborators G 2 N. Global, regional, and national burden of neurological disorders, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016[J]. Lancet Neurol, 2019, 18(5): 459-80. |
| 2 | Campbell BCV, Khatri P. Stroke[J]. Lancet, 2020, 396(10244): 129-42. |
| 3 | Ghosh M, Lane M, Krizman E, et al. The transcription factor Pax6 contributes to the induction of GLT-1 expression in astrocytes through an interaction with a distal enhancer element[J]. J Neurochem, 2016, 136(2): 262-75. |
| 4 | Kim K, Lee SG, Kegelman TP, et al. Role of excitatory amino acid transporter-2 (EAAT2) and glutamate in neurodegeneration: opportunities for developing novel therapeutics[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2011, 226(10): 2484-93. |
| 5 | Murphy-Royal C, Dupuis J, Groc L, et al. Astroglial glutamate transporters in the brain: regulating neurotransmitter homeostasis and synaptic transmission[J]. J Neurosci Res, 2017, 95(11): 2140-51. |
| 6 | Verkhratsky A, Nedergaard M. Physiology of astroglia[J]. Physiol Rev, 2018, 98(1): 239-389. |
| 7 | Danbolt NC, Furness DN, Zhou Y. Neuronal vs glial glutamate uptake: resolving the conundrum[J]. Neurochem Int, 2016, 98: 29-45. |
| 8 | Malik AR, Willnow TE. Excitatory amino acid transporters in physiology and disorders of the central nervous system[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(22): 5671. |
| 9 | Melone M, Ciriachi C, Pietrobon D, et al. Heterogeneity of astrocytic and neuronal GLT-1 at cortical excitatory synapses, as revealed by its colocalization with Na+/K+-ATPase α isoforms[J]. Cereb Cortex, 2019, 29(8): 3331-50. |
| 10 | Roberts RC, Roche JK, McCullumsmith RE. Localization of excitatory amino acid transporters EAAT1 and EAAT2 in human postmortem cortex: a light and electron microscopic study[J]. Neuroscience, 2014, 277: 522-40. |
| 11 | Kashem MA, Sultana N, Pow DV, et al. GLAST (GLutamate and ASpartate Transporter) in human prefrontal cortex; interactome in healthy brains and the expression of GLAST in brains of chronic alcoholics[J]. Neurochem Int, 2019, 125: 111-6. |
| 12 | Danbolt NC. Glutamate uptake[J]. Prog Neurobiol, 2001, 65(1): 1-105. |
| 13 | Suárez-Pozos E, Thomason EJ, Fuss B. Glutamate transporters: expression and function in oligodendrocytes[J]. Neurochem Res, 2020, 45(3): 551-60. |
| 14 | Pajarillo E, Rizor A, Lee J, et al. The role of astrocytic glutamate transporters GLT-1 and GLAST in neurological disorders: potential targets for neurotherapeutics[J]. Neuropharmacology, 2019, 161: 107559. |
| 15 | Banks WA, Kastin AJ, Huang W, et al. Leptin enters the brain by a saturable system independent of insulin[J]. Peptides, 1996, 17(2): 305-11. |
| 16 | Hu SJ, Cheng DB, Peng DT, et al. Leptin attenuates cerebral ischemic injury in rats by modulating the mitochondrial electron transport chain via the mitochondrial STAT3 pathway[J]. Brain Behav, 2019, 9(2): e01200. |
| 17 | Zhang WF, Jin YC, Wang D, et al. Neuroprotective effects of leptin on cerebral ischemia through JAK2/STAT3/PGC-1-mediated mitochondrial function modulation[J]. Brain Res Bull, 2020, 156: 118-30. |
| 18 | Zhang Y, Cheng DB, Jie CX, et al. Leptin alleviates endoplasmic reticulum stress induced by cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway[J]. Biosci Rep, 2022, 42(12): BSR20221443. |
| 19 | Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, et al. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats[J]. Stroke, 1989, 20(1): 84-91. |
| 20 | Jiwaji Z, Hardingham GE. Good, bad, and neglectful: Astrocyte changes in neurodegenerative disease[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2022, 182: 93-9. |
| 21 | Liu ZW, AstrocytesChopp M., therapeutic targets for neuroprotection and neurorestoration in ischemic stroke[J]. Prog Neurobiol, 2016, 144: 103-20. |
| 22 | Pekny M, Wilhelmsson U, Pekna M. The dual role of astrocyte activation and reactive gliosis[J]. Neurosci Lett, 2014, 565: 30-8. |
| 23 | Michinaga S, Koyama Y. Pathophysiological responses and roles of astrocytes in traumatic brain injury[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(12): 6418. |
| 24 | Zhang SF, Shang DS, Shi H, et al. Function of astrocytes in neuroprotection and repair after ischemic stroke[J]. Eur Neurol, 2021, 84(6): 426-34. |
| 25 | Mahmoud S, Gharagozloo M, Simard C, et al. Astrocytes maintain glutamate homeostasis in the CNS by controlling the balance between glutamate uptake and release[J]. Cells, 2019, 8(2): 184. |
| 26 | Yeh TH, Hwang HM, Chen JJ, et al. Glutamate transporter function of rat hippocampal astrocytes is impaired following the global ischemia[J]. Neurobiol Dis, 2005, 18(3): 476-83. |
| 27 | Fontana AC. Current approaches to enhance glutamate transporter function and expression[J]. J Neurochem, 2015, 134(6): 982-1007. |
| 28 | Roettger V, Lipton P. Mechanism of glutamate release from rat hippocampal slices during in vitro ischemia[J]. Neuroscience, 1996, 75(3): 677-85. |
| 29 | Rossi DJ, Oshima T, Attwell D. Glutamate release in severe brain ischaemia is mainly by reversed uptake[J]. Nature, 2000, 403(6767): 316-21. |
| 30 | Shen YL, Lu HL, Xu RN, et al. The expression of GLAST and GLT1 in a transient cerebral ischemia Mongolian gerbil model[J]. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat, 2020, 16: 789-800. |
| 31 | Rao VL, Dogan A, Bowen KK, et al. Antisense knockdown of the glial glutamate transporter GLT-1 exacerbates hippocampal neuronal damage following traumatic injury to rat brain[J]. Eur J Neurosci, 2001, 13(1): 119-28. |
| 32 | Naranjo V, Contreras A, Merino B, et al. Specific deletion of the astrocyte leptin receptor induces changes in hippocampus glutamate metabolism, synaptic transmission and plasticity[J]. Neuroscience, 2020, 447: 182-90. |
| 33 | Zhang J, Deng Z, Liao J, et al. Leptin attenuates cerebral ischemia injury through the promotion of energy metabolism via the PI3K/Akt pathway[J]. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab, 2013, 33(4): 567-74. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||