Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (10): 1881-1886.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.10.06
Previous Articles Next Articles
Huagen MA1,2( ), Yan HUANG2, Yingxin YANG2, Haiqin LIU3, Yuanyu TANG4(
), Yan HUANG2, Yingxin YANG2, Haiqin LIU3, Yuanyu TANG4( ), Weihong CONG1(
), Weihong CONG1( )
)
Received:2024-03-11
Online:2024-10-20
Published:2024-10-31
Contact:
Yuanyu TANG, Weihong CONG
E-mail:mahuagen123666@163.com;2422198977@qq.com;congcao@188.com
Supported by:Huagen MA, Yan HUANG, Yingxin YANG, Haiqin LIU, Yuanyu TANG, Weihong CONG. Expansion and identification of primary rat aortic vascular stem cells in vitro[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(10): 1881-1886.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.10.06
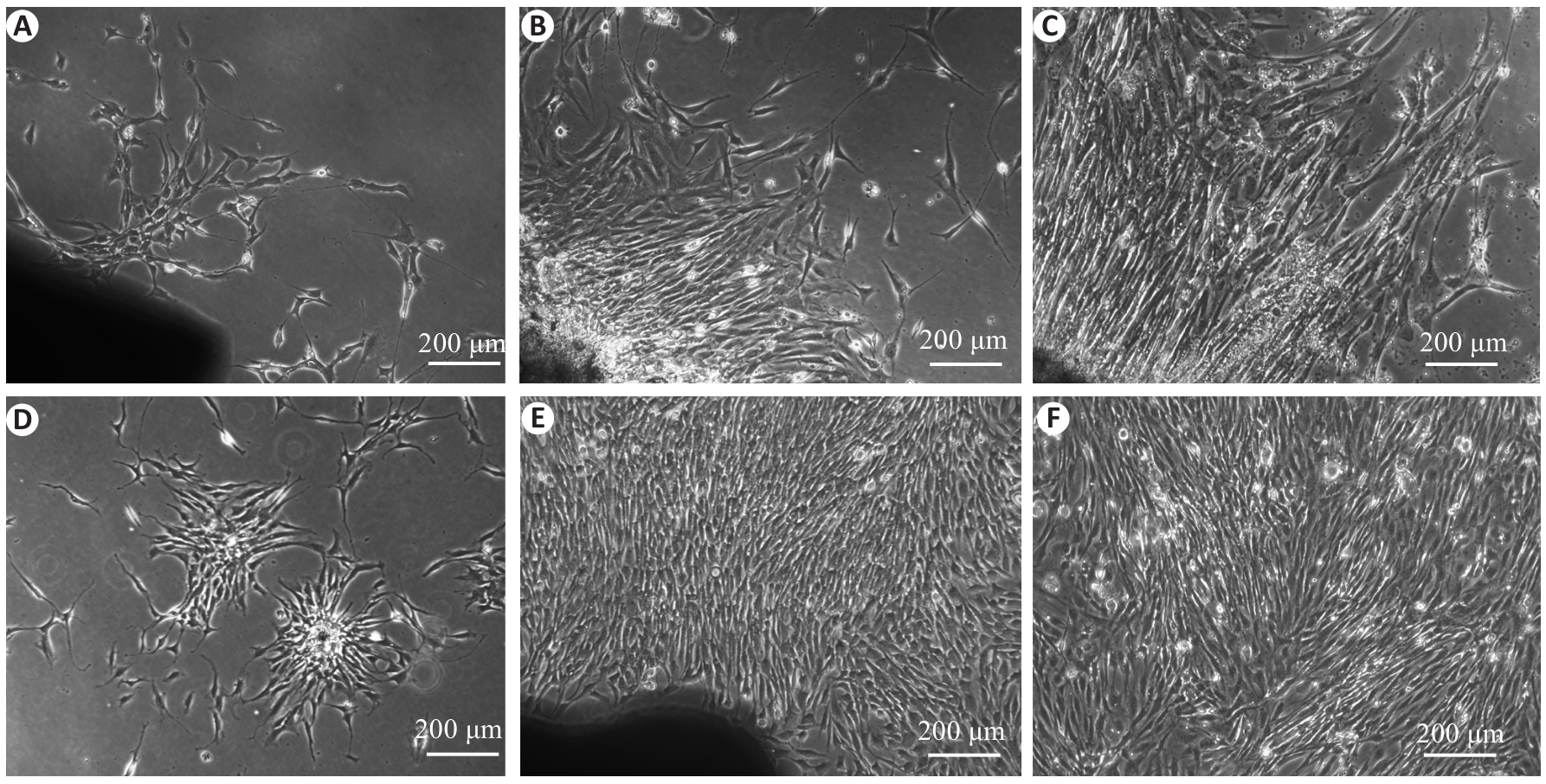
Fig.1 Morphological observation of rat aortic vascular stem cells (VSCs) in primary culture. A: Spindle-shaped, star-shaped or polygonal cells emerging from the peripheral of the vascular segments after 3 days of culture. B, C: After 5-6 days of culture, island-like cell colonies occurred and extended outward rapidly in a radial pattern. D: Cell cloning in the cell culture. E, F: After 7-8 days of culture, the cell density further increased, the cell colonies merged to exhibit a vortex-like distribution, and the cells formed a monolayer with adherent growth.
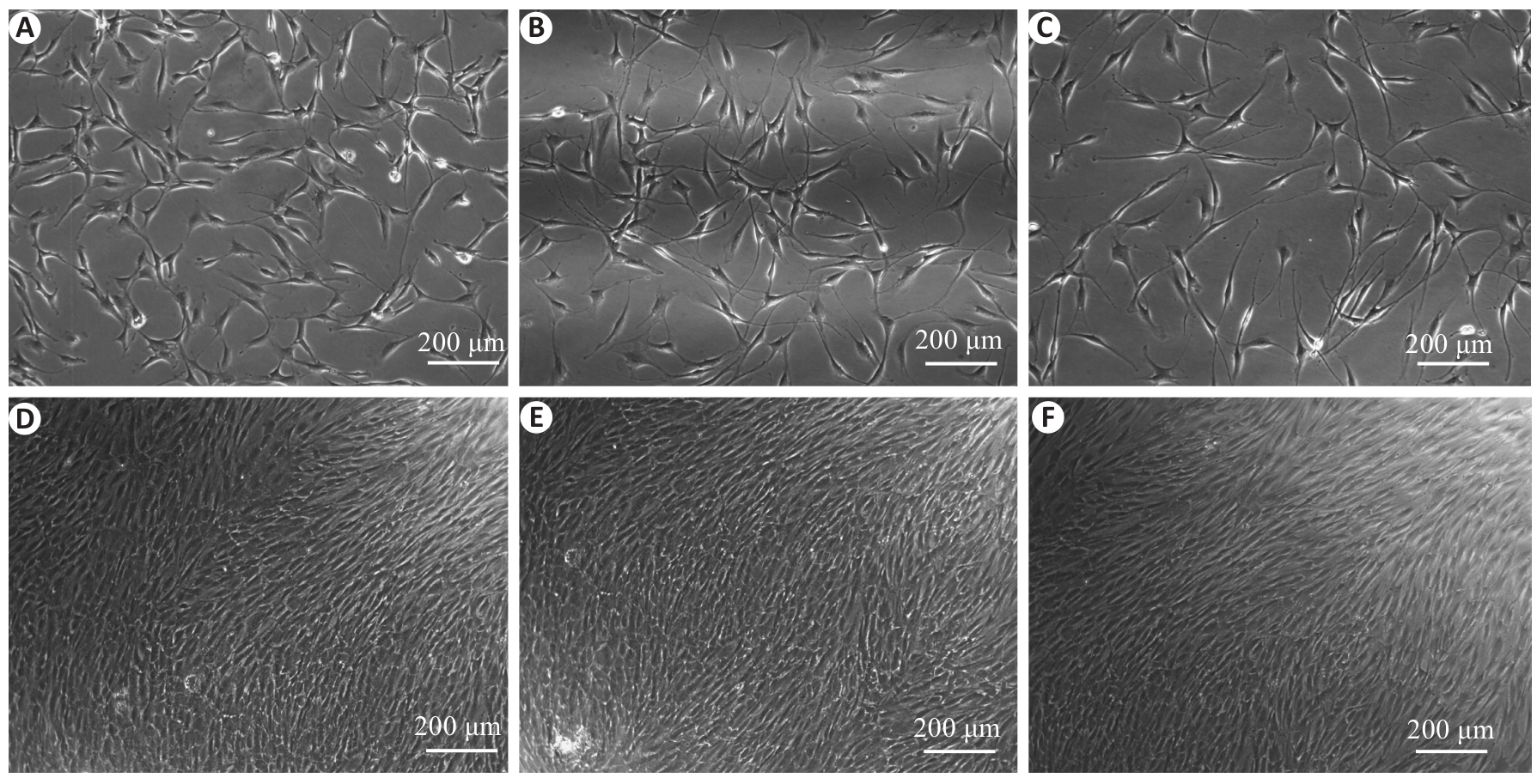
Fig.2 Morphological observation of rat aortic VSCs in the third to eighth passages. A-C: After passaging for 4-6 h, the cells became adherent and spread uniformly, exhibiting a consistent morphology. The individual cells displayed a typical fibroblast-like appearance with pseudopodia extending from both poles of the cells. D-F: After 36-48 h, the passaged cells aligned tightly along the longitudinal axis, forming a spiral pattern with a clear orientation.
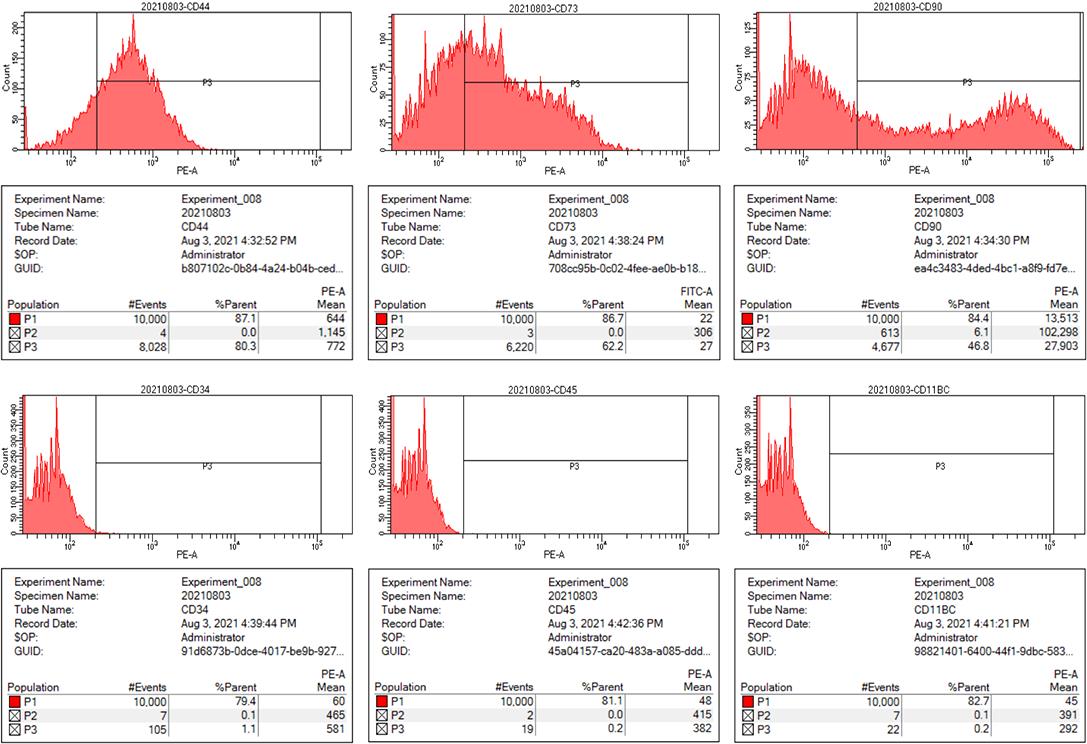
Fig.3 Expression of surface marker CD molecules on cultured rat aortic VSCs. The positive rates of CD44, CD73, CD90, CD34, CD45 and CD11b/c were 80.3%, 62.2%, 46.8%, 1.1%, 0.2% and 0.2%, respectively.
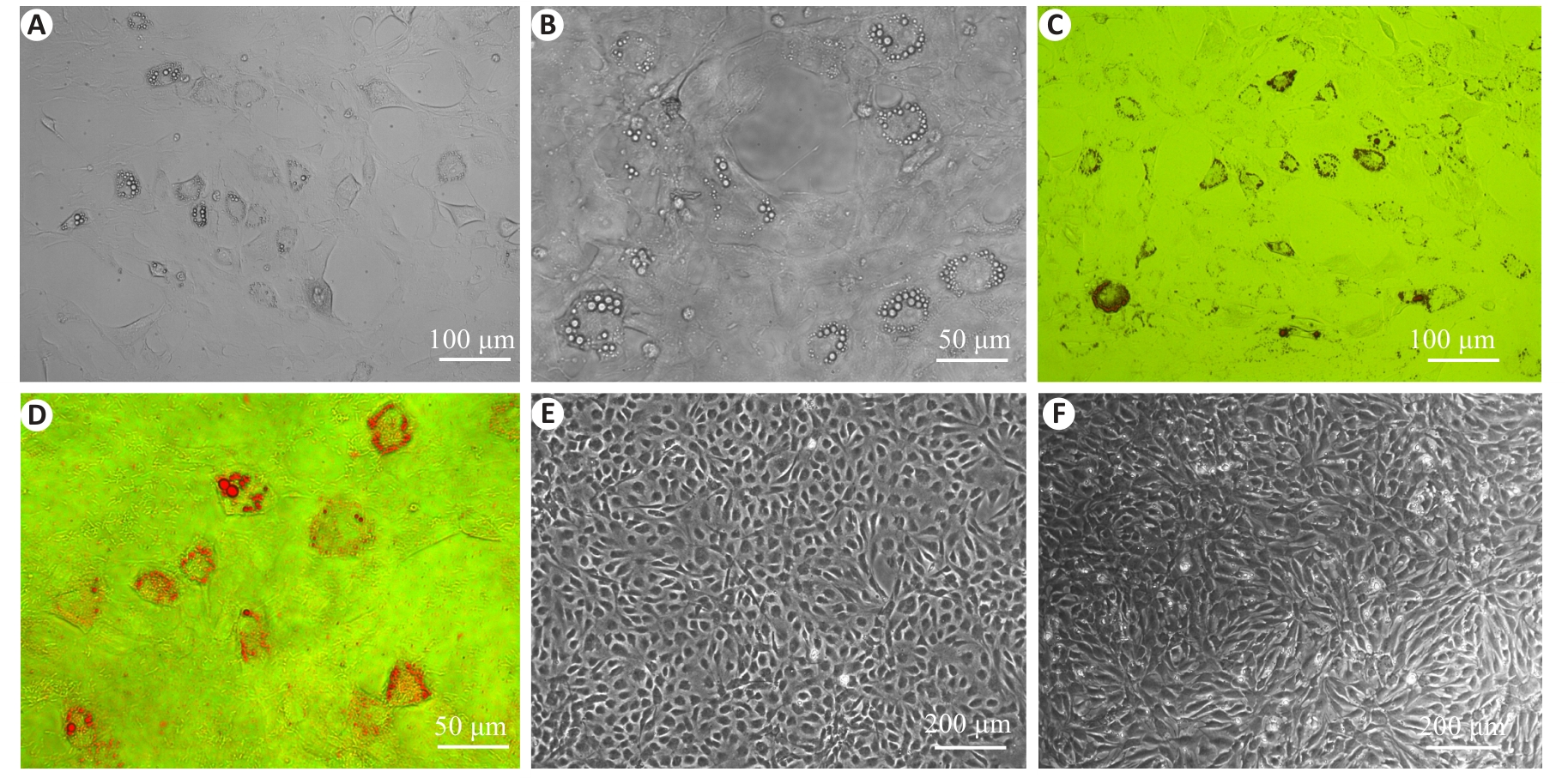
Fig.4 Observation of induced adipogenesis of cultured rat aortic VSCs and oil red O staining of the cells. A, B: After 14 days of adipogenic induction, translucent lipid droplets appeared in the cytoplasm. C, D: Oil red O staining highlighting the bright red lipid droplets. E, F: Absence of translucent lipid droplets in the negative control cells before and after induction.
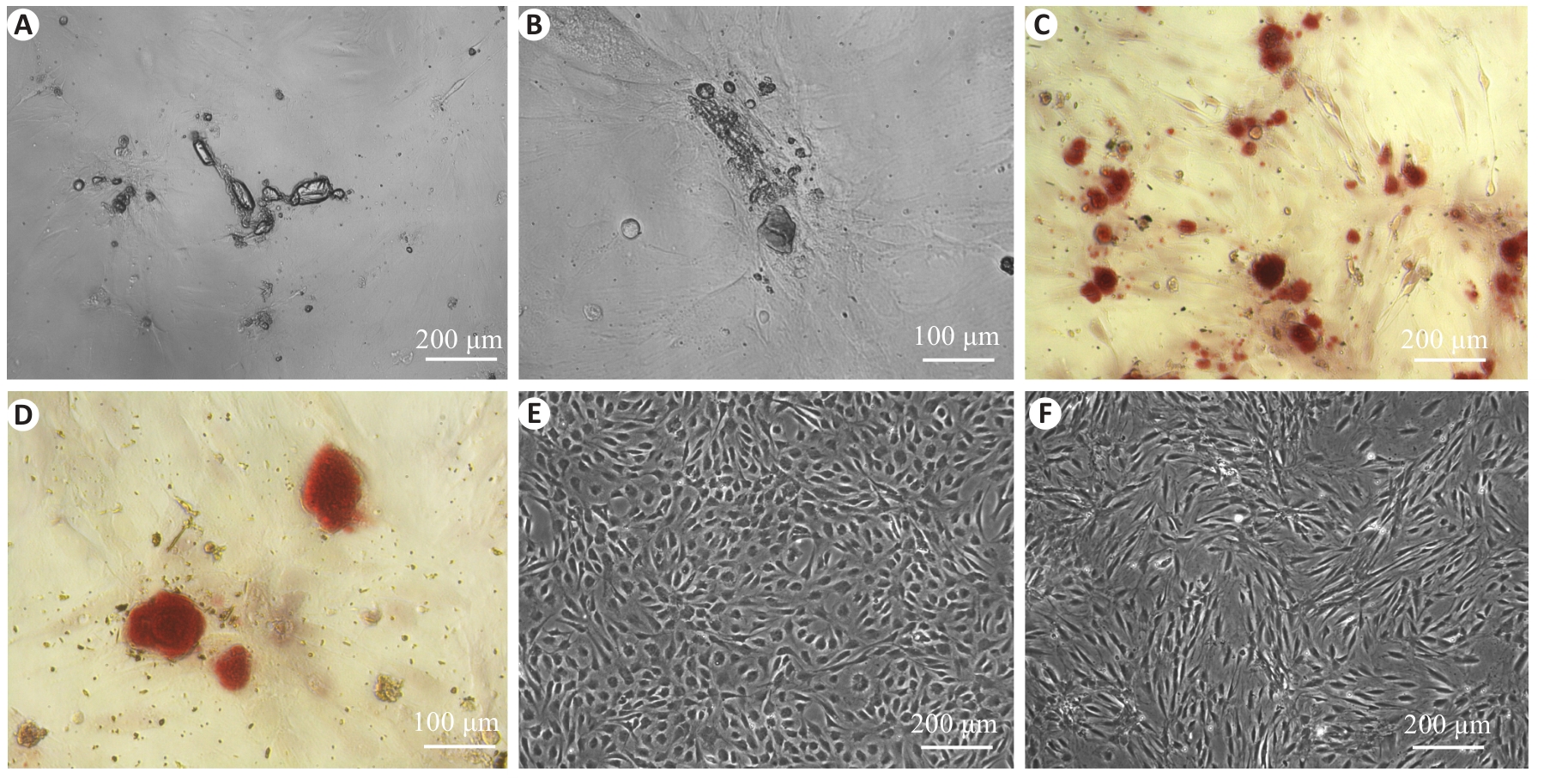
Fig.5 Observation of induced osteogenesis of cultured rat aortic VSCs and alizarin red staining of the cells. A, B: After 21 days of osteogenic induction, irregular dense mineralized nodules occurred at the cell aggregations. C, D: Alizarin red staining showing bright red nodules. E, F: Absence of mineralized nodules in the negative control cells before and after induction.
| 1 | Lin CS, Lue TF. Defining vascular stem cells[J]. Stem Cells Dev, 2013, 22(7): 1018-26. |
| 2 | 李诗媛, 周 敏, 丁利军. 血管周围干细胞在组织纤维化和损伤修复中的作用[J]. 中国细胞生物学学报, 2023, 45(8): 1248-56. |
| 3 | Wörsdörfer P, Mekala SR, Bauer J, et al. The vascular adventitia: an endogenous, omnipresent source of stem cells in the body[J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2017, 171: 13-29. |
| 4 | Tang J, Wang HX, Huang XZ, et al. Arterial Sca1+ vascular stem cells generate de novo smooth muscle for artery repair and regeneration[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2020, 26(1): 81-96. e4. |
| 5 | Zhang L, Issa Bhaloo S, Chen T, et al. Role of resident stem cells in vessel formation and arteriosclerosis[J]. Circ Res, 2018, 122(11): 1608-24. |
| 6 | Wang D, Li LK, Dai T, et al. Adult stem cells in vascular remodeling[J]. Theranostics, 2018, 8(3): 815-29. |
| 7 | Jiang LJ, Sun XL, Deng JC, et al. Different roles of stem/progenitor cells in vascular remodeling[J]. Antioxid Redox Signal, 2021, 35(3): 192-203. |
| 8 | Klein D, Weisshardt P, Kleff V, et al. Vascular wall-resident CD44+ multipotent stem cells give rise to pericytes and smooth muscle cells and contribute to new vessel maturation[J]. PLoS One, 2011, 6(5): e20540. |
| 9 | 郭 虹, 刘杰文, 杨少光, 等. 地塞米松促进胎儿主动脉血管CD105+间充质干细胞向脂肪细胞分化[J]. 中国病理生理杂志, 2004, 20(10): 1786-9. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4718.2004.10.010 |
| 10 | 刘煜昊, 房佰俊, 史明霞, 等. 自发性高血压大鼠间充质干细胞生物学特性变化的研究[J]. 中国生物工程杂志, 2004, 24(04): 49-53. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-8135.2004.04.011 |
| 11 | 凌思英, 张柏杨, 滕 勇, 等. 人大隐静脉干细胞原代培养方法的改良[J]. 生物工程学报, 2018, 34(6): 973-82. DOI: 10.13345/j.cjb.170459 |
| 12 | 杨礼菊, 马 颖, 李 源, 等. 小鼠血管壁CD34+干细胞的分离、培养及鉴定[J]. 生理学报, 2023, 75(2): 205-15. |
| 13 | Han CT, Xie C, Dang QY, et al. Immunomagnetic isolation of the vascular wall-resident CD34+ stem cells from mice[J]. J Vis Exp, 2023(202): e66193. |
| 14 | Wu Y, Zhang RN, Sen-Zhao, et al. Isolation and culture of vascular wall-resident CD34+ stem/progenitor cells[J]. Cardiology Plus, 2019, 4(4): 116-20. |
| 15 | 唐元瑜, 刘海琴, 马华根. 原代SD大鼠主动脉内皮细胞培养方法的建立及其鉴定[J]. 吉林大学学报 (医学版), 2021, 47(04): 1038-42. |
| 16 | Lin SG, Lin RR, Zhang HK, et al. Peripheral vascular remodeling during ischemia[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2022, 13: 1078047. |
| 17 | Ye C, Zheng F, Wu N, et al. Extracellular vesicles in vascular remodeling[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2022, 43(9): 2191-201. |
| 18 | Hu Y, Zhang Z, Torsney E, et al. Abundant progenitor cells in the adventitia contribute to atherosclerosis of vein grafts in ApoE-deficient mice[J]. J Clin Invest, 2004, 113(9): 1258-65. |
| 19 | 李伟慷, 崔清卓, 郑玉光, 等. 基于TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3通路的羟基红花黄色素A抑制血管紧张素II诱导的血管外膜成纤维细胞迁移研究[J]. 中草药, 2023, 54 (05): 1478-86. DOI: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2023.05.014 |
| 20 | Klein D. Vascular wall-resident multipotent stem cells of mesenchymal nature within the process of vascular remodeling: cellular basis, clinical relevance, and implications for stem cell therapy[J]. Stem Cells Int, 2016, 2016: 1905846. |
| 21 | Tyurin-Kuzmin PA, Hayashi Y, Kulebyakin K. Editorial: functional heterogeneity of stem cells[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2023, 11: 1179911. |
| 22 | Orekhov AN, Bobryshev YV, Chistiakov DA. The complexity of cell composition of the intima of large arteries: focus on pericyte-like cells[J]. Cardiovasc Res, 2014, 103(4): 438-51. |
| 23 | Narbonne P. The effect of age on stem cell function and utility for therapy[J]. Cell Med, 2018, 10: 2155179018773756. |
| 24 | 李 媛, 钟海英, 董世访, 等. 不同年龄小鼠骨来源间充质干细胞衰老相关特性与成骨分化能力的比较研究[J]. 陆军军医大学学报, 2024, 46 (13): 1512-22. |
| 25 | Greuel S, Hanci G, Böhme M, et al. Effect of inoculum density on human-induced pluripotent stem cell expansion in 3D bioreactors[J]. Cell Prolif, 2019, 52(4): e12604. |
| 26 | Liang L, Xu L, Dong Q, et al. Low initial cell density promotes the differentiation and maturation of human pluripotent stem cells into erythrocytes[J]. Stem Cells Dev, 2024, 33(11-12): 321-31. |
| 27 | Yang GQ, Fan XH, Liu YC, et al. Immunomodulatory mechanisms and therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Stem Cell Rev Rep, 2023, 19(5): 1214-31. |
| 28 | Wan XX, Hu XM, Xiong K. Multiple pretreatments can effectively improve the functionality of mesenchymal stem cells[J]. World J Stem Cells, 2024, 16(2): 58-63. |
| [1] | LIU Jinjun, LI Qingqing, ZENG Chaochao, WANG Yuexiang, HU Qingtian, WANG Hongju, WU Shili. Role of myelin and lymphocyte protein in regulating pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell proliferation and apoptosis in pulmonary hypertension [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42(10): 1572-1577. |
| [2] | ZHONG Huilin, ZOU Qingjian, LIU Haixia, WANG Xiaomin, DU Shaoyin, LIANG Haiyan, WU Zhijun, YE Junjie, ZOU Qingyan. Construction and evaluation of dual-effect cord blood natural killer cells expressing high-affinity PD-1 and chimeric antigen CD19 receptor [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2021, 41(12): 1877-1884. |
| [3] | . Analysis of immunophenotypes and expressions of non-myeloid antigens in acute myeloid leukemia [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2020, 40(11): 1639-1644. |
| [4] | . Culture and identification of tumor stem cells from surgically resected colorectal cancer tissues [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2019, 39(04): 415-. |
| [5] | . Effects of serum starvation on cell cycle synchronization in primary human umbilical vein endothelial cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2016, 36(08): 1140-. |
| [6] |
.
Effect of cancer-associated fibroblasts on proliferation and invasion of gallbladder carcinoma cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2015, 35(08): 1149-. |
| [7] |
.
Simultaneous isolation and primary culture of rat hepatocytes, hepatic stellate cells, Kupffer’s cells and hepatic sinus endothelial cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2014, 34(04): 532-. |
| [8] |
.
Effect of exogenous hydrogen sulfide on BACE-1 enzyme expression and β-amyloid peptide metabolism in high-glucose primary neuronal culture [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2014, 34(04): 504-. |
| [9] |
.
Progress in research of molecular mechanisms of pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cell proliferation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2013, 33(12): 1852-. |
| [10] | . 滤泡性免疫母细胞淋巴瘤临床病理分析 [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2013, 33(06): 794-. |
| [11] | . Protective effect of maslinic acid preconditioning against oxygen-glucose deprivationinduced injuries in embryonic rat cortical neurons [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2013, 33(03): 322-. |
| [12] | JING Li1, 2, ZHANG Jian-zhong2, WANG Yi-li1, GUO Feng-ying2 1Institute of Immunopathology, School of Life Science and Technology, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710061, China; 2Department of Pathology, Ningxia Medical College, Yinchuan 750004, China. P21ras and phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase are highly expressed in vascular smooth muscle cells of hypertensive rats [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2006, 26(07): 895-900. |
| [13] | SHEN Ce1, LIU Hao1, ZUO Qiang2, ZHANG Jun-yi2, YANG Jin-xing2. Effects of short-term chemotherapy on the compliance of rabbit abdominal aorta [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2005, 25(11): 1443-1445. |
| [14] | HAN Yu-jing1, LAI Zhuo-sheng1, WANG Ya-dong1, JIANG Bo1, ZHOU Zhi-tao2, ZHOU Dian-yuan1. Electron microscopic observation of primary cultured laterally spreading tum or cell line [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2004, 24(01): 79-80,84. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||