Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (11): 2297-2308.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.11.02
Lili CHENG1( ), Zhongfu TANG1, Ming LI1,2, Junjie CHEN3, Shuangshuang SHANG1, Sidi LIU1, Chuanbing HUANG1,2(
), Zhongfu TANG1, Ming LI1,2, Junjie CHEN3, Shuangshuang SHANG1, Sidi LIU1, Chuanbing HUANG1,2( )
)
Received:2025-06-13
Online:2025-11-20
Published:2025-11-28
Contact:
Chuanbing HUANG
E-mail:3265544980@qq.com;chuanbinh@163.com
Supported by:Lili CHENG, Zhongfu TANG, Ming LI, Junjie CHEN, Shuangshuang SHANG, Sidi LIU, Chuanbing HUANG. Qihuang Jianpi Zishen Granules improves renal damage in MRL/lpr mice by inhibiting B cell differentiation via the AIM2/Blimp-1/Bcl-6 axis[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(11): 2297-2308.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.11.02
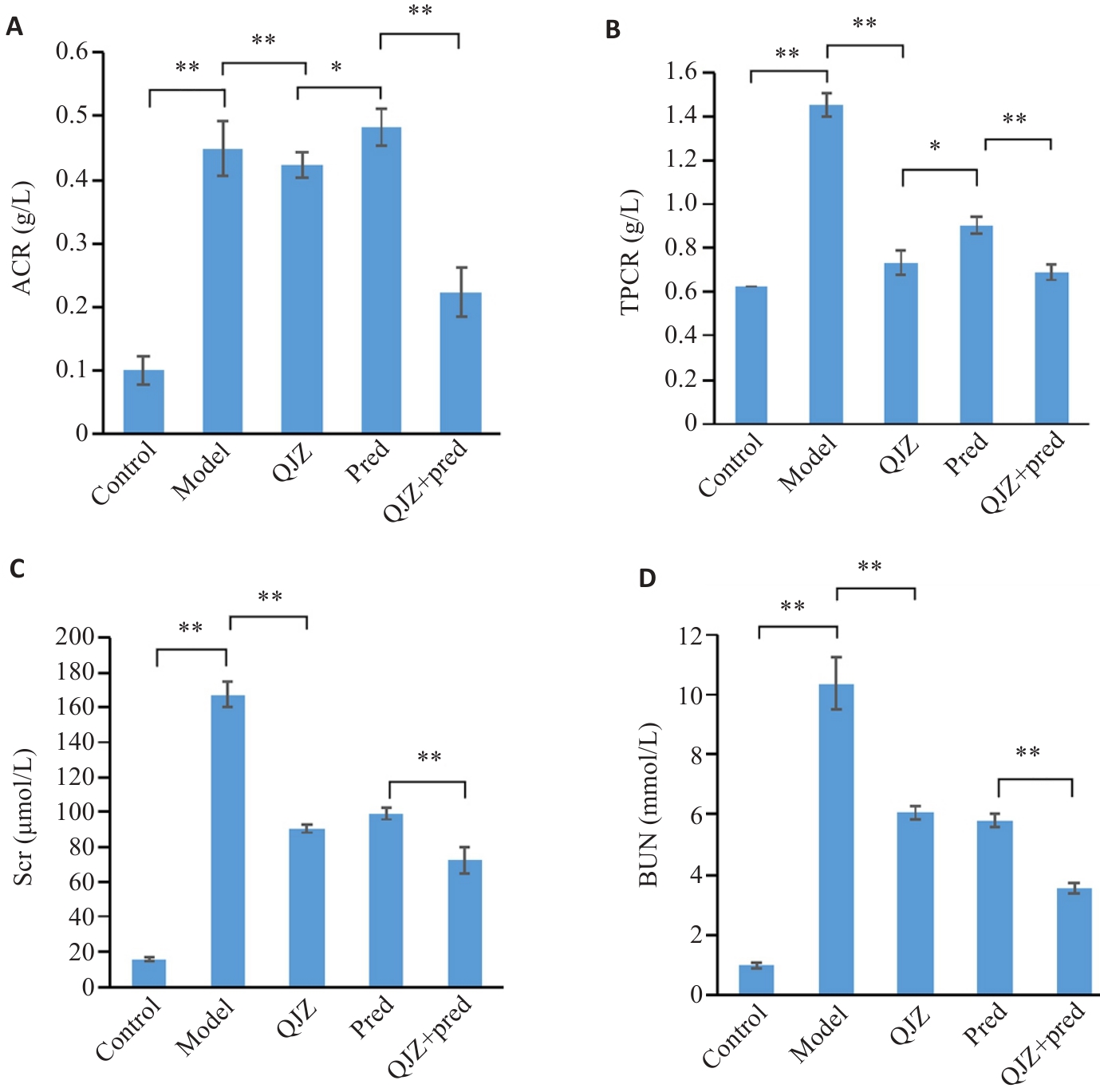
Fig.1 Comparison of renal function among different groups of MRL/lpr mice. A: Expression levels of ACR in MRL/lpr mice in each group. B: Expression levels of TPCR in each group. C: Expression levels of Scr in each group. D: Expression levels of BUN in each group. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
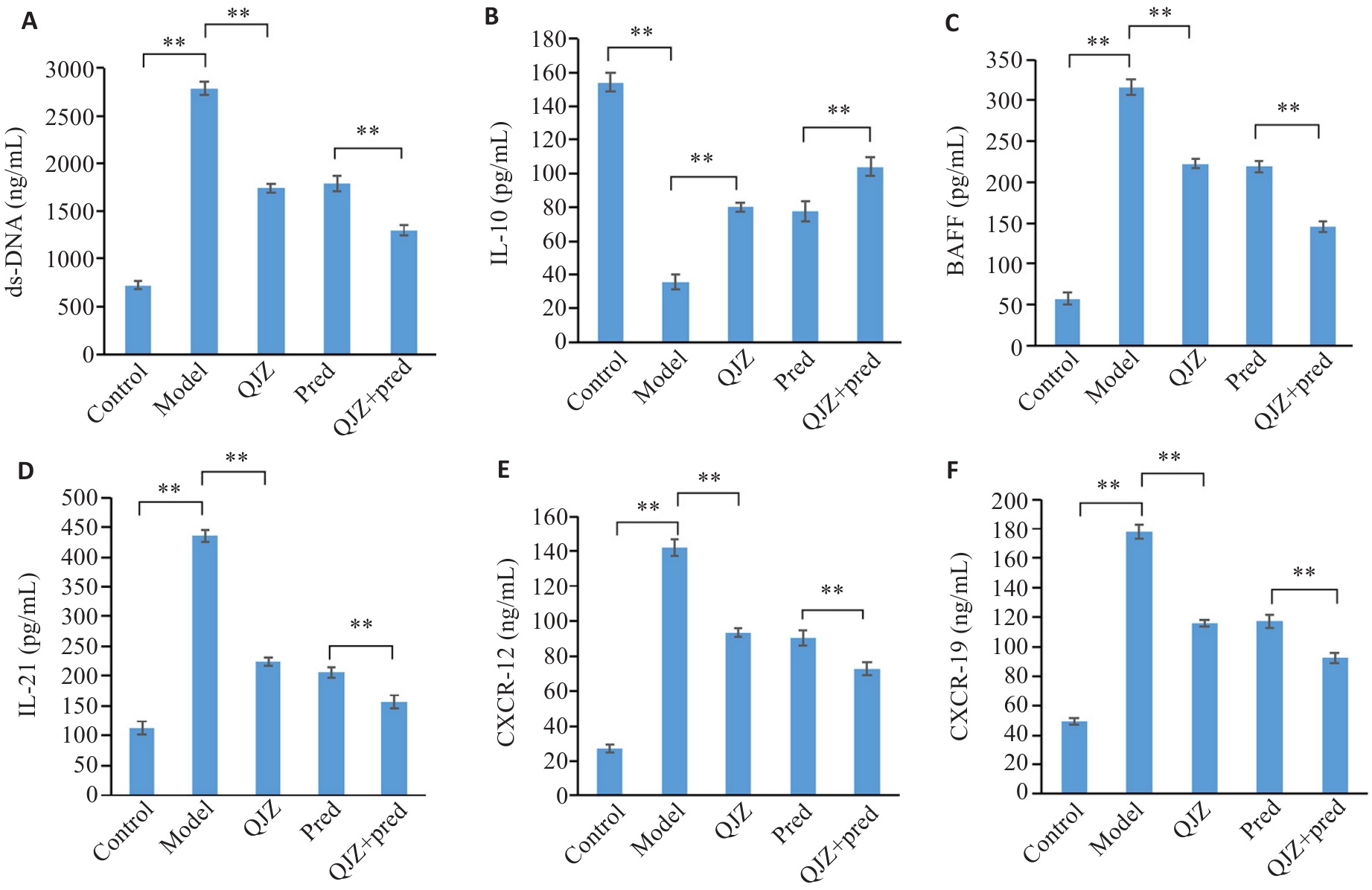
Fig.2 Comparison of ds-DNA antibody, cytokine and chemokine levels in MRL/lpr mice in each group. A: Levels of ds-DNA in each group. B: Levels of IL-10 in each group. C: Levels of BAFF in each group. D: Levels of IL-21 in each group. E: Levels of CXCR-12 in each group. F: Levels of CXCR-19 in each group. **P<0.01.

Fig.3 Effect of QJZ on renal pathology in MRL/lpr lupus mice. A: Results of HE, PAS and Masson staining of the kidneys in each group (Scale bar=50 μm). B: Comparison of pathological AI scores of the kidneys in each group. C: Comparison of pathological CI scores of the kidneys in each group. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.

Fig.5 Comparison of C3 and C4 deposition levels in the kidneys of MRL/lpr mice among the groups. A: Immunohistochemistry for detecting expressions of C3 and C4 in the kidneys in each group (×100). B: Average fluorescence intensity of C3 in the kidneys in each group. C: Average fluorescence intensity of C4 in each group. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
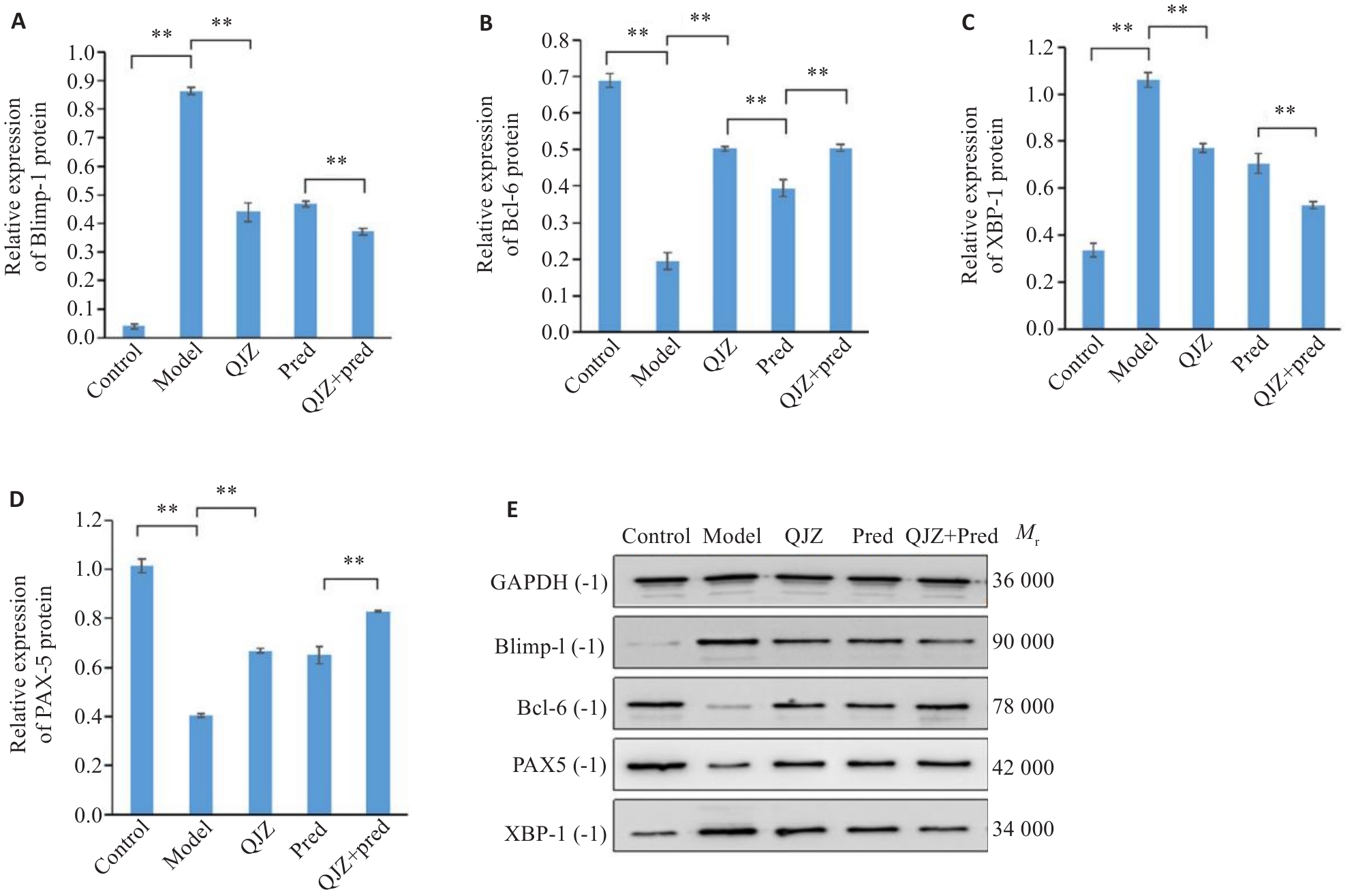
Fig.6 Comparison of expression levels of key transcriptional proteins involved in B-cell differentiation in each group. A: Relative protein expression levels of Blimp-1 in each group. B: Relative protein expression levels of Bcl-6 in each group. C: Relative protein expression levels of XBP-1 in each group. D: Relative protein expression levels of PAX-5 in each group. E: Protein bands in Western blotting in each group. **P<0.01.
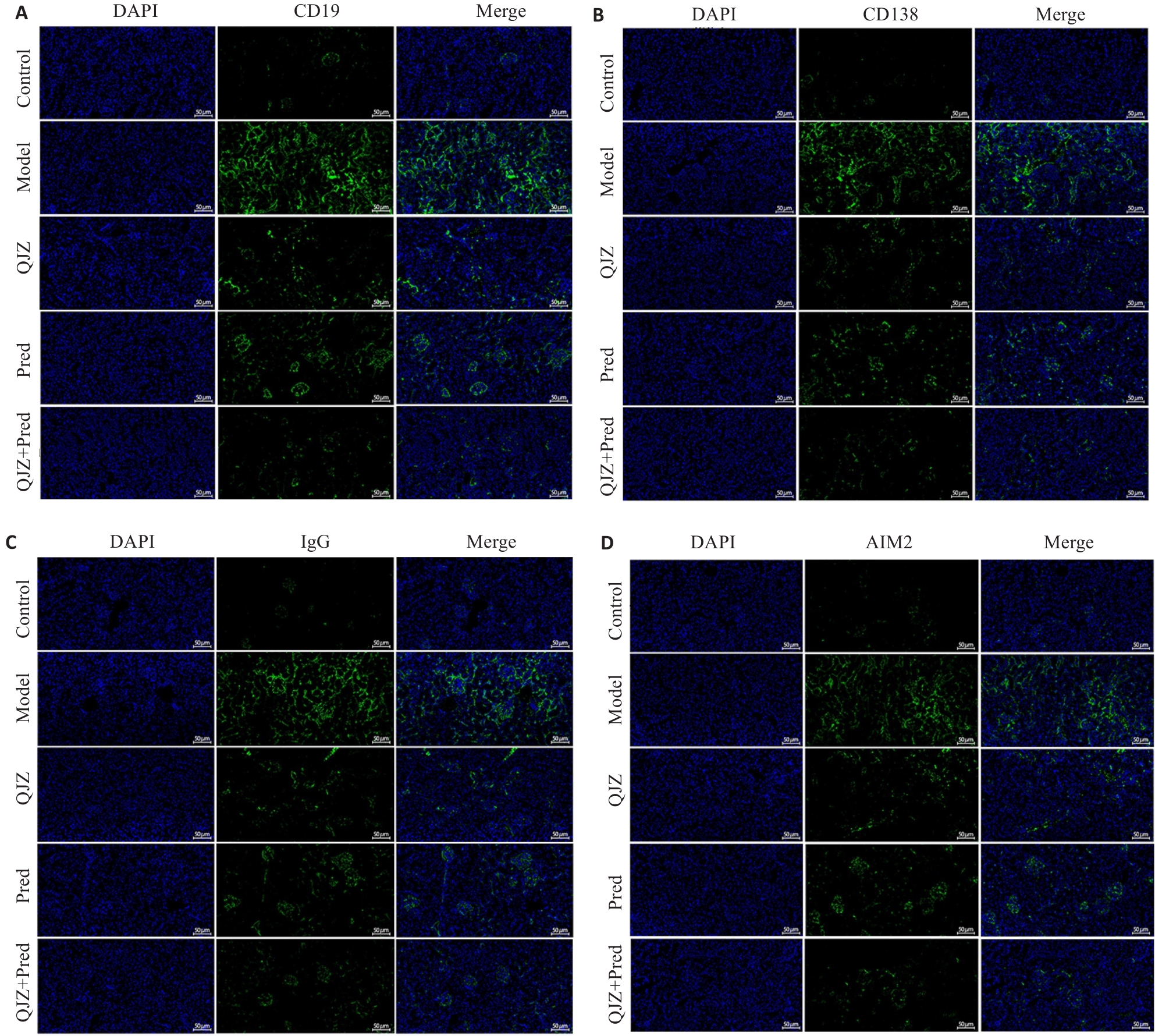
Fig.9 Expression levels of CD19, CD138, IgG and AIM2 in the renal tissues of MRL/lpr mice in each group (Immunofluorescence staining; Scale bar=50 μm). A: CD19 expression levels in each group. B: CD138 expression levels in each group. C: IgG expression levels in each group. D: AIM2 expression levels in each group.

Fig.10 Effect of AIM2 inhibitor on renal damage in MRL/lpr mice. A: Relative protein expression levels of Blimp-1 in each group. B: Relative protein expression levels of Bcl-6 in each group. C: Relative protein expression levels of PAX-5 in each group. D: Relative protein expression levels of XBP-1 in each group. E: Western blotting bands in each group. F: Results of HE, Masson, and PAS staining in each group (×200). G: Expression of IgG in each group (×200). H: Level of B cells in each group. I: Expression of C3 and C4 in each group (×200). **P<0.01.
| [1] | Lou HT, Ling GS, Cao XT. Autoantibodies in systemic lupus erythematosus: From immunopathology to therapeutic target[J]. J Autoimmun, 2022, 132: 102861. doi:10.1016/j.jaut.2022.102861 |
| [2] | Rahman A, Isenberg DA. Systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. N Engl J Med, 2008, 358(9): 929-39. doi:10.1056/nejmra071297 |
| [3] | Canny SP, Jackson SW. B cells in systemic lupus erythematosus: from disease mechanisms to targeted therapies[J]. Rheum Dis Clin North Am, 2021, 47(3): 395-413. doi:10.1016/j.rdc.2021.04.006 |
| [4] | Arbitman L, Furie R, Vashistha H. B cell-targeted therapies in systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. J Autoimmun, 2022, 132: 102873. doi:10.1016/j.jaut.2022.102873 |
| [5] | Ma KY, Du WH, Wang XH, et al. Multiple functions of B cells in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(23): 6021. doi:10.3390/ijms20236021 |
| [6] | Choubey D, Panchanathan R. Absent in melanoma 2 proteins in SLE[J]. Clin Immunol, 2017, 176: 42-8. doi:10.1016/j.clim.2016.12.011 |
| [7] | Zhu H, Zhao M, Chang C, et al. The complex role of AIM2 in autoimmune diseases and cancers[J]. Immun Inflamm Dis, 2021, 9(3): 649-65. doi:10.1002/iid3.443 |
| [8] | Yi P, Cao PP, Yang M, et al. Overexpressed CD44 is associated with B-cell activation via the HA-CD44-AIM2 pathway in lupus B cells[J]. Clin Immunol, 2023, 255: 109710. doi:10.1016/j.clim.2023.109710 |
| [9] | Yang M, Long D, Hu LY, et al. AIM2 deficiency in B cells ameliorates systemic lupus erythematosus by regulating Blimp-1-Bcl-6 axis-mediated B-cell differentiation[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2021, 6(1): 341. doi:10.1038/s41392-021-00725-x |
| [10] | Shang SS, Li M, Jiang H, et al. The protective effects of qihuang Jianpi zishen decoction on mrl/lpr mice and its mechanism[J]. Pak J Pharm Sci, 2022, 35(6): 1627-35. |
| [11] | 李云飞, 庞利君, 束龙武, 等. 芪黄健脾滋肾颗粒可改善小鼠系统性红斑狼疮血小板减少: 基于Ca2+/CaMKK2/AMPK/mTOR信号通路介导的自噬[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(12): 2327-34. |
| [12] | 陈君洁, 黄传兵, 程丽丽, 等. 芪黄健脾滋肾颗粒调控JAK1/STAT1信号通路对MRL/lpr狼疮小鼠足细胞凋亡的影响[J]. 中成药, 2024, 46(12): 4145-50. |
| [13] | 尚双双, 李 明, 黄传兵. 芪黄健脾滋肾颗粒改善MRL/lpr小鼠肾脏损害机制研究[J]. 中国中西医结合杂志, 2025, 45(3): 321-9. |
| [14] | 陈君洁, 黄传兵, 李 明. 健脾滋肾方抑制系统性红斑狼疮患者的足细胞自噬: 基于网络药理学和临床研究[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 465-73. |
| [15] | 汤忠富, 黄传兵, 李 明, 等. 芪黄健脾滋肾颗粒通过抑制MyD88/NF-κB通路减轻MRL/lpr小鼠肾损害[J/OL]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45 (8): 1625-32. |
| [16] | Dobrowolski C, Lao SM, Kharouf F, et al. Lupus nephritis: biomarkers[J]. Adv Clin Chem, 2025, 124: 87-122. doi:10.1016/bs.acc.2024.10.002 |
| [17] | 庞利君, 黄传兵, 李 明, 等. 应用LC-MS/MS技术研究健脾滋肾方对系统性红斑狼疮鼠血清代谢物及代谢通路的影响[J]. 中国医院药学杂志, 2025, 45(4): 368-77. |
| [18] | 熊 峰. 槲皮素治疗系统性红斑狼疮模型MRL/Lpr鼠的疗效观察及机制研究[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2023. |
| [19] | 燕红梅. 中药狼疮方及其活性成分槲皮素对系统性红斑狼疮的治疗作用及可能机制的探索[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2023. |
| [20] | 王 蕊, 刘 茜, 李 丽. 槲皮素对系统性红斑狼疮模型小鼠肾脏的保护作用及对其免疫功能的影响研究[J]. 临床和实验医学杂志, 2021, 20(21): 2252-6. |
| [21] | 王俊青, 余惠凡, 黄林生, 等. 金丝桃苷通过抑制YAP改善肾小管间质纤维化[J]. 华中科技大学学报: 医学版, 2025, 54(2): 190-7. |
| [22] | 王 超, 魏翠婷, 李 润, 等. 山柰酚通过改善肾小管上皮细胞的氧化应激与炎症反应减轻1型糖尿病小鼠肾损伤[J]. 解放军医学院学报, 2024, 45(3): 261-9. |
| [23] | 杨 亿. 芍药苷调控肠道菌群和Th17/Treg免疫平衡治疗系统性红斑狼疮[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2024. |
| [24] | Dörner T, Szelinski F, Lino AC, et al. Therapeutic implications of the anergic/postactivated status of B cells in systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. RMD Open, 2020, 6(2): e001258. doi:10.1136/rmdopen-2020-001258 |
| [25] | Gao YN, Zhou JW, Huang Y, et al. Jiedu-Quyu-Ziyin Fang (JQZF) inhibits the proliferation and activation of B cells in MRL/lpr mice via modulating the AKT/mTOR/c-Myc signaling pathway[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2023, 315: 116625. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2023.116625 |
| [26] | Choubey D, Panchanathan R. Interferon (IFN)-inducible Absent in Melanoma 2 proteins in the negative regulation of the type I IFN response: Implications for lupus nephritis[J]. Cytokine, 2020, 132: 154682. doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2019.03.008 |
| [27] | Wortmann M, Xiao XH, Wabnitz G, et al. AIM2 levels and DNA-triggered inflammasome response are increased in peripheral leukocytes of patients with abdominal aortic aneurysm[J]. Inflamm Res, 2019, 68(4): 337-45. doi:10.1007/s00011-019-01212-4 |
| [28] | Ke PF, Zhu YT, Cao SL, et al. Identification of pattern recognition receptor genes in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and monocytes as biomarkers for the diagnosis of lupus nephritis[J]. Clin Chim Acta, 2024, 554: 117785. doi:10.1016/j.cca.2024.117785 |
| [29] | Sharma BR, Karki R, Kanneganti TD. Role of AIM2 inflammasome in inflammatory diseases, cancer and infection[J]. Eur J Immunol, 2019, 49(11): 1998-2011. doi:10.1002/eji.201848070 |
| [30] | Svensson A, Patzi Churqui M, Schlüter K, et al. Maturation-dependent expression of AIM2 in human B-cells[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(8): e0183268. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0183268 |
| [31] | Uresti-Rivera EE, García-Hernández MH. AIM2-inflammasome role in systemic lupus erythematous and rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Autoimmunity, 2022, 55(7): 443-54. doi:10.1080/08916934.2022.2103802 |
| [32] | Javierre BM, Fernandez AF, Richter J, et al. Changes in the pattern of DNA methylation associate with twin discordance in systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Genome Res, 2010, 20(2): 170-9. doi:10.1101/gr.100289.109 |
| [33] | Leite JA, Menezes L, Martins E, et al. AIM2 promotes TH17 cells differentiation by regulating RORγt transcription activity[J]. iScience, 2023, 26(11): 108134. doi:10.1016/j.isci.2023.108134 |
| [34] | Zhao JJ, Miller-Little W, Li XX. Inflammasome-independent functions of AIM2[J]. J Exp Med, 2021, 218(5): e20210273. doi:10.1084/jem.20210273 |
| [35] | Luu M, Krause FF, Monning H, et al. Dissecting the metabolic signaling pathways by which microbial molecules drive the differentiation of regulatory B cells[J]. Mucosal Immunol, 2025, 18(1): 66-75. doi:10.1016/j.mucimm.2024.09.003 |
| [36] | Faliti CE, Mesina M, Choi J, et al. Interleukin-2-secreting T helper cells promote extra-follicular B cell maturation via intrinsic regulation of a B cell mTOR-AKT-Blimp-1 axis[J]. Immunity, 2024, 57(12): 2772-89.e8. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2024.11.006 |
| [37] | Qian GJ, Jiang WX, Sun DL, et al. B-cell-derived IL-10 promotes allergic sensitization in asthma regulated by Bcl-3[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2023, 20(11): 1313-27. doi:10.1038/s41423-023-01079-w |
| [38] | Caneparo V, Landolfo S, Gariglio M, et al. The absent in melanoma 2-like receptor IFN-inducible protein 16 as an inflammasome regulator in systemic lupus erythematosus: the dark side of sensing microbes[J]. Front Immunol, 2018, 9: 1180. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2018.01180 |
| [39] | Nakou M, Papadimitraki ED, Fanouriakis A, et al. Interleukin-21 is increased in active systemic lupus erythematosus patients and contributes to the generation of plasma B cells[J]. Clin Exp Rheumatol, 2013, 31(2): 172-9. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||