南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (8): 1732-1742.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.08.17
• • 上一篇
王子良1,2( ), 陈孝华1, 杨晶晶1, 严晨3, 张志郅3, 黄炳轶1,2, 赵萌1,2, 刘嵩1,2, 葛思堂2, 左芦根2, 陈德利2(
), 陈孝华1, 杨晶晶1, 严晨3, 张志郅3, 黄炳轶1,2, 赵萌1,2, 刘嵩1,2, 葛思堂2, 左芦根2, 陈德利2( )
)
收稿日期:2025-02-25
出版日期:2025-08-20
发布日期:2025-09-05
通讯作者:
陈德利
E-mail:wangziliang1115@163.com;13965295950@139.com
作者简介:王子良,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: wangziliang1115@163.com
基金资助:
Ziliang WANG1,2( ), Xiaohua CHEN1, Jingjing YANG1, Chen YAN3, Zhizhi ZHANG3, Bingyi HUANG1,2, Meng ZHAO1,2, Song LIU1,2, Sitang GE2, Lugen ZUO2, Deli CHEN2(
), Xiaohua CHEN1, Jingjing YANG1, Chen YAN3, Zhizhi ZHANG3, Bingyi HUANG1,2, Meng ZHAO1,2, Song LIU1,2, Sitang GE2, Lugen ZUO2, Deli CHEN2( )
)
Received:2025-02-25
Online:2025-08-20
Published:2025-09-05
Contact:
Deli CHEN
E-mail:wangziliang1115@163.com;13965295950@139.com
摘要:
目的 研究SURF4在胃癌中的表达情况及远期预后,进一步分析其影响胃癌细胞恶性生物学行为的可能作用途径。 方法 采用公共数据库初步验证SURF4在胃癌中表达高低及与不良预后之间的关系。回顾性分析蚌埠医科大学第一附属医院2016年1月~2019年10月共155例胃癌患者的信息,采用免疫组织化学方法检测癌和癌旁中SURF4表达水平,以SURF4表达量中位数(IOD=2.82)为界分为低表达组和高表达组,并分析与远期预后的关系。通过Cox比例风险模型筛选相关的独立预测因子,K-M生存曲线评估胃癌患者术后5年生存率。通过TISIBD数据库分析SURF4的表达水平与免疫细胞浸润方面的联系。采用GEO数据集筛选SURF4差异基因,利用GO和KEGG分析SURF4在胃癌中可能的分子机制及作用途径。在体外构建胃癌细胞系(HGC-27),并将SURF4分为上调组、下调组和2个对照组,采用CCK8、细胞划痕、Transwell、Western blotting实验证实对胃癌细胞增殖、迁移、侵袭和上皮间质转化(EMT)的影响。 结果 GEPIA数据集及免疫组化结果提示,SURF4在胃癌中表达水平升高(P<0.05)。K-M生存分析显示SURF4过表达组患者术后5年生存期缩短(Log-rank
王子良, 陈孝华, 杨晶晶, 严晨, 张志郅, 黄炳轶, 赵萌, 刘嵩, 葛思堂, 左芦根, 陈德利. 高表达SURF4通过抑制紧密连接蛋白表达促进胃癌细胞的恶性生物学行为[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(8): 1732-1742.
Ziliang WANG, Xiaohua CHEN, Jingjing YANG, Chen YAN, Zhizhi ZHANG, Bingyi HUANG, Meng ZHAO, Song LIU, Sitang GE, Lugen ZUO, Deli CHEN. High expression of SURF4 promotes migration, invasion and proliferation of gastric cancer cells by inhibiting tight junction proteins[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(8): 1732-1742.
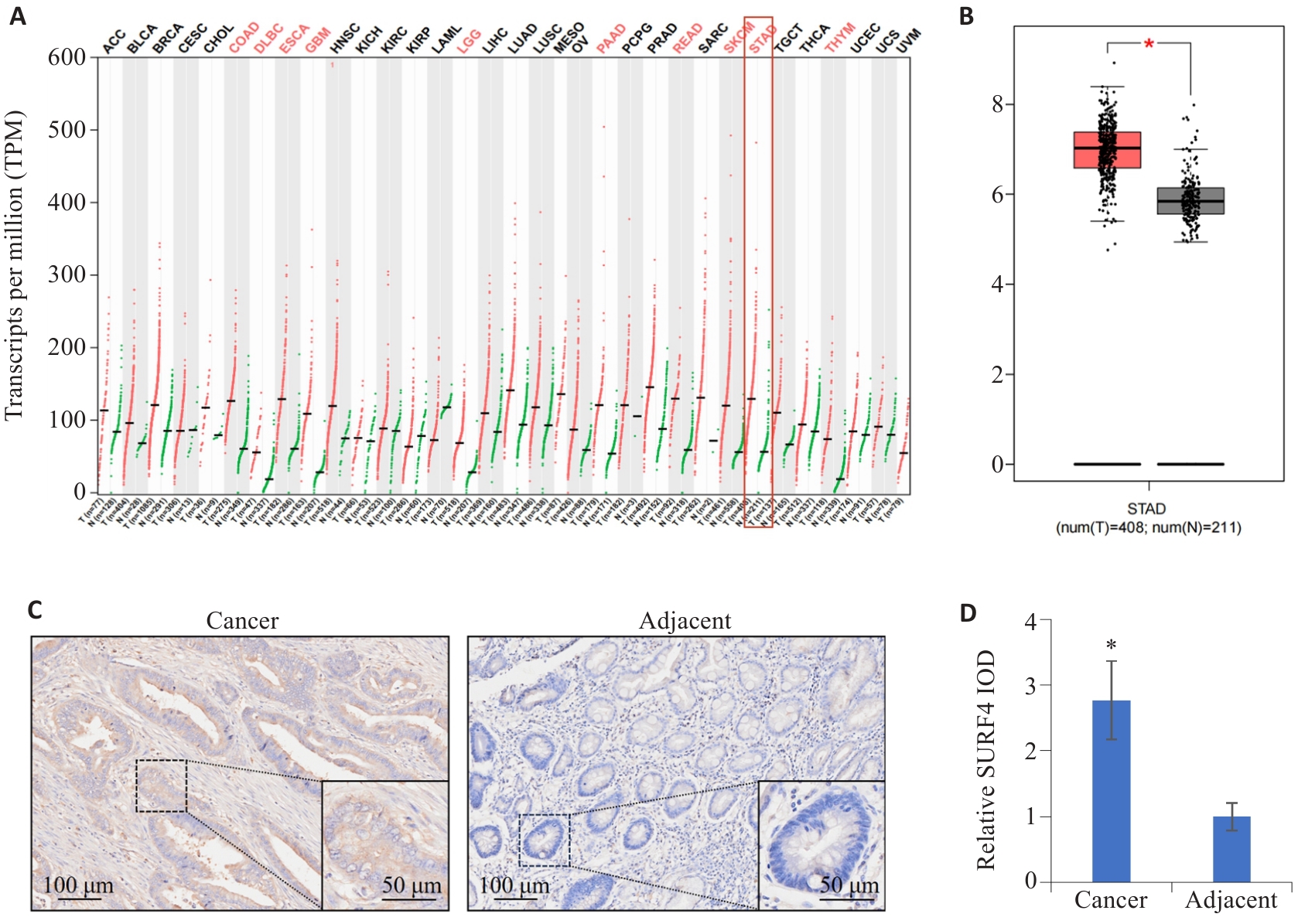
图1 SURF4在肿瘤中的分布特征
Fig.1 Distribution characteristics of SURF4 in different cancers. A: Expression of SURF4 in different human cancers. B: Expression of SURF4 in gastric cancer. *P<0.05. C: Distribution characteristics of SURF4 in gastric cancer and adjacent tissues detected by immunohistochemistry. D: Relative IOD value of SURF4. n=155. *P<0.05 vs adjacent.
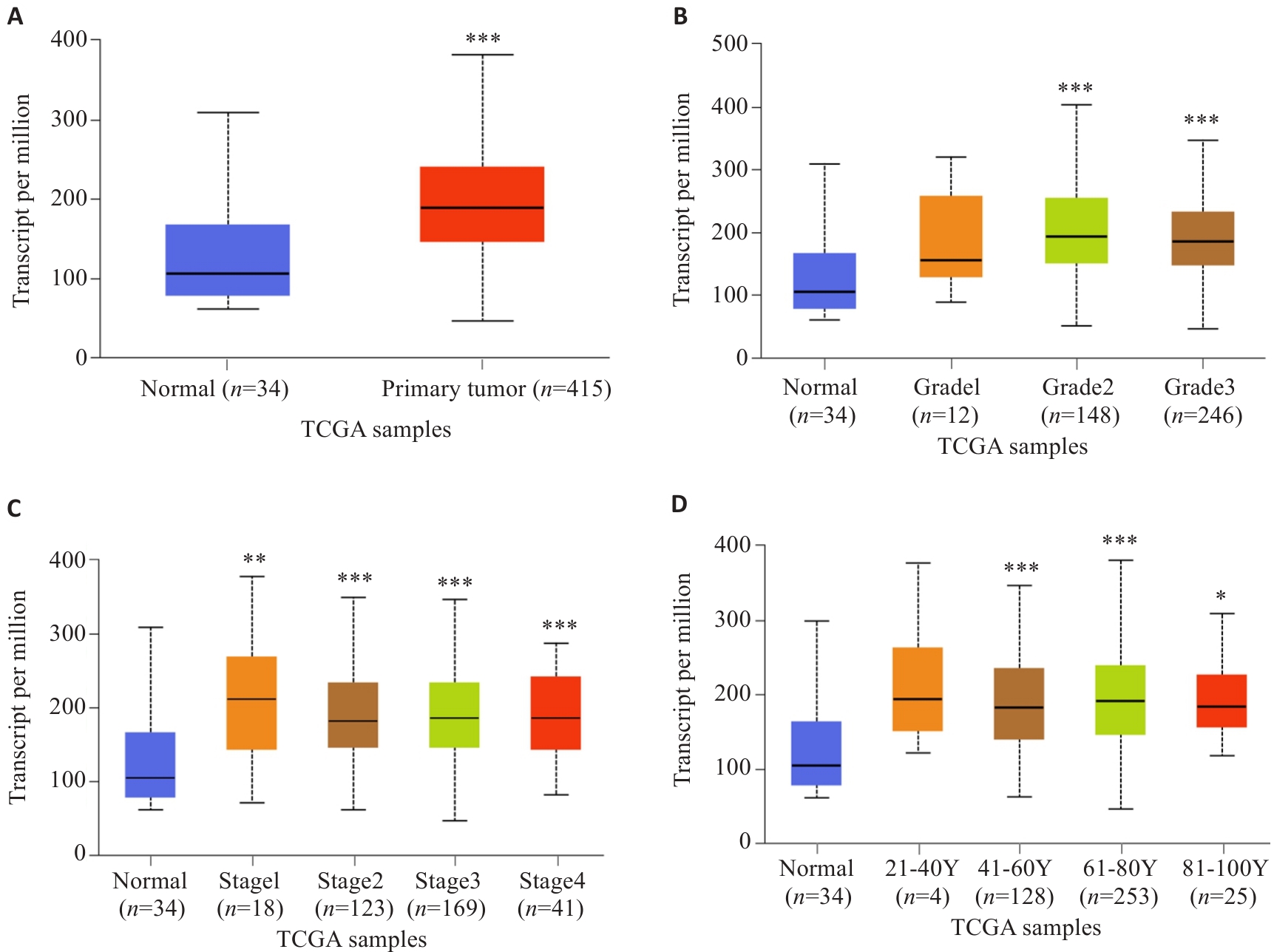
图2 UALCAN数据库分析不同病理参数下SURF4表达水平
Fig.2 Analysis of expression levels of SURF4 in gastric cancer patients with different pathological parameters based on UALCAN database. A: Sample type. B: Tumor grading. C: Cancer staging. D: Age. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs Normal.
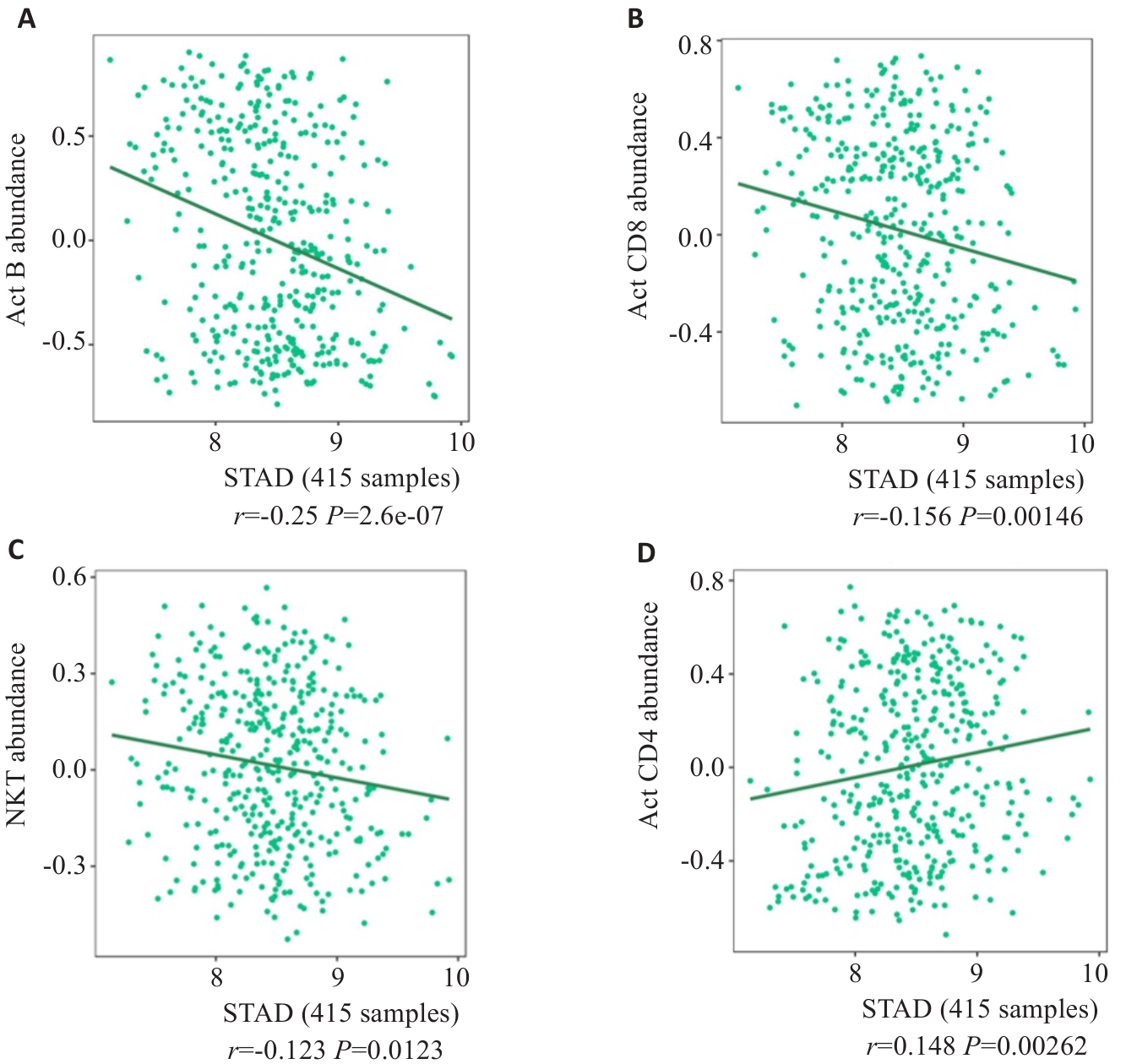
图3 TISIBD数据平台分析SURF4的表达特征与免疫微环境的联系
Fig.3 Relationship between SURF4 expression level and immune microenvironment of gastric cancer analyzed using TISIBD data platform. A: Activated B cells. B: CD8+ effector memory T cells. C: NK cells. D: CD4+ thymocytes.
| Factors | n | SURF4 expression | χ2 | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (n=77) | High (n=78) | ||||
| Gender | 0.919 | 0.338 | |||
| Male | 114 | 54 (47.4) | 60 (52.6) | ||
| Female | 41 | 23 (56.1) | 18 (43.9) | ||
| Age (year) | 1.459 | 0.227 | |||
| <60 | 65 | 36 (55.4) | 29 (44.6) | ||
| ≥60 | 90 | 41 (45.6) | 49 (54.4) | ||
| CEA (μg/L) | 10.874 | <0.001 | |||
| <5 | 80 | 50 (62.5) | 30 (37.5) | ||
| ≥5 | 75 | 27 (36.0) | 48 (64.0) | ||
| CA19-9 (kU/L) | 8.080 | 0.004 | |||
| <37 | 87 | 52 (59.8) | 35 (40.2) | ||
| ≥37 | 68 | 25 (36.8) | 43 (63.2) | ||
| Tumor size (cm) | 0.156 | 0.693 | |||
| <5 | 87 | 42 (48.3) | 45 (51.7) | ||
| ≥5 | 68 | 35 (51.5) | 33 (48.5) | ||
| Histological type | 1.455 | 0.228 | |||
| Adenocarcinoma | 112 | 59 (52.7) | 53 (47.3) | ||
| Other | 43 | 18 (41.9) | 25 (58.1) | ||
| T stage | 8.836 | 0.003 | |||
| 1-2 | 78 | 48 (61.5) | 30 (38.5) | ||
| 3-4 | 77 | 29 (37.7) | 48 (62.3) | ||
| N stage | 5.441 | 0.020 | |||
| 0-1 | 70 | 42 (60.0) | 28 (40.0) | ||
| 2-3 | 85 | 35 (41.2) | 80 (58.8) | ||
表1 胃癌SURF4表达水平与临床病理参数的联系
Tab.1 Relationship between SURF4 expression levels and clinicopathological parameters in 155 patients with gastric cancer [n(%)]
| Factors | n | SURF4 expression | χ2 | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (n=77) | High (n=78) | ||||
| Gender | 0.919 | 0.338 | |||
| Male | 114 | 54 (47.4) | 60 (52.6) | ||
| Female | 41 | 23 (56.1) | 18 (43.9) | ||
| Age (year) | 1.459 | 0.227 | |||
| <60 | 65 | 36 (55.4) | 29 (44.6) | ||
| ≥60 | 90 | 41 (45.6) | 49 (54.4) | ||
| CEA (μg/L) | 10.874 | <0.001 | |||
| <5 | 80 | 50 (62.5) | 30 (37.5) | ||
| ≥5 | 75 | 27 (36.0) | 48 (64.0) | ||
| CA19-9 (kU/L) | 8.080 | 0.004 | |||
| <37 | 87 | 52 (59.8) | 35 (40.2) | ||
| ≥37 | 68 | 25 (36.8) | 43 (63.2) | ||
| Tumor size (cm) | 0.156 | 0.693 | |||
| <5 | 87 | 42 (48.3) | 45 (51.7) | ||
| ≥5 | 68 | 35 (51.5) | 33 (48.5) | ||
| Histological type | 1.455 | 0.228 | |||
| Adenocarcinoma | 112 | 59 (52.7) | 53 (47.3) | ||
| Other | 43 | 18 (41.9) | 25 (58.1) | ||
| T stage | 8.836 | 0.003 | |||
| 1-2 | 78 | 48 (61.5) | 30 (38.5) | ||
| 3-4 | 77 | 29 (37.7) | 48 (62.3) | ||
| N stage | 5.441 | 0.020 | |||
| 0-1 | 70 | 42 (60.0) | 28 (40.0) | ||
| 2-3 | 85 | 35 (41.2) | 80 (58.8) | ||
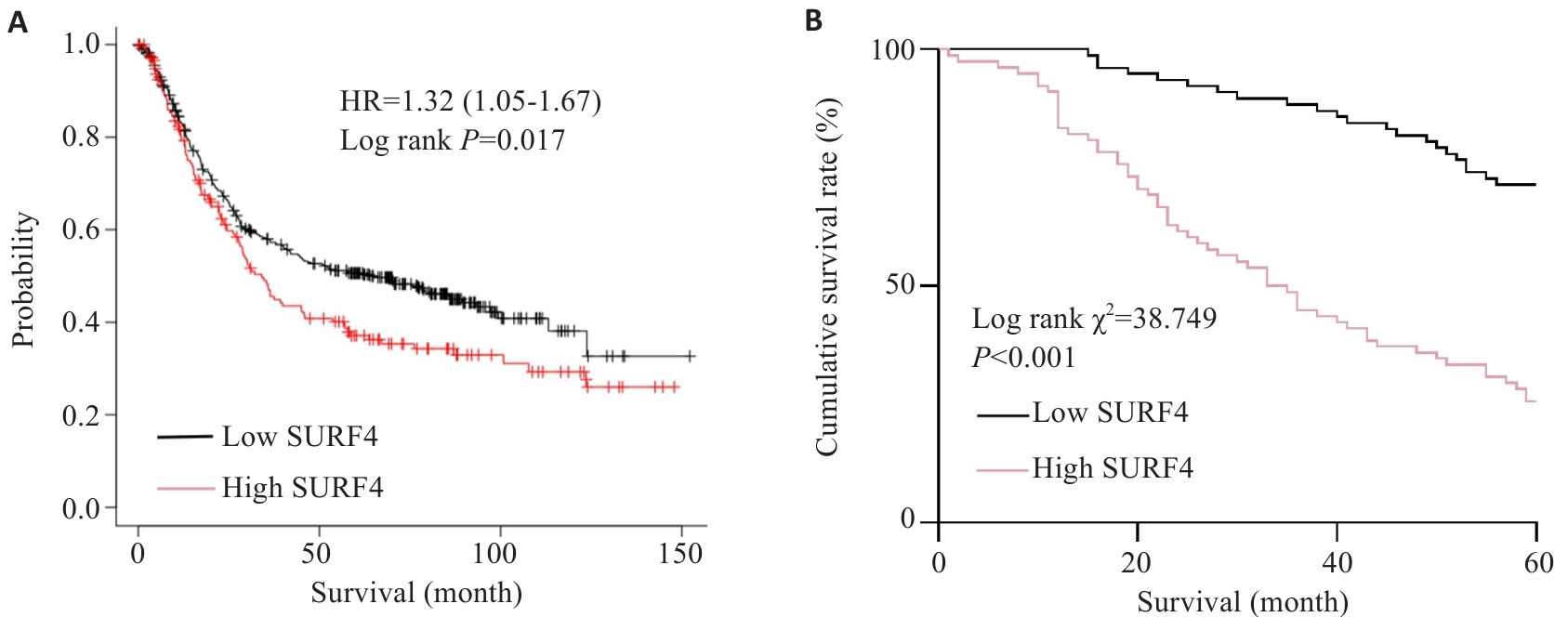
图4 SURF4表达量与胃癌根治术后5年生存期的关系
Fig.4 Relationship between SURF4 expression and 5-year survival of the patients after radical gastrectomy for gastric cancer. A: Relationship between SURF4 expression and overall survival. B: Postoperative survival of patients in high expression group and low expression group.
| Factor | Univariate analysis | Multivariate analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Log rank χ2 | P | HR | 95% CI | P | |
| Gender (Male vs female) | 2.023 | 0.155 | - | - | - |
| Age (≥60 years vs <60 years) | 2.691 | 0.101 | - | - | - |
| SURF4 expression (low vs high) | 38.749 | <0.001 | 3.106 | 1.853-5.206 | <0.001 |
| CEA (≥5 μg/L vs <5 μg/L) | 34.667 | <0.001 | 1.853 | 1.092-3.146 | 0.022 |
| CA19-9 (≥37kU/L vs <37kU/L) | 35.752 | <0.001 | 1.949 | 1.125-3.378 | 0.017 |
| Tumor size (≥5 cm vs <5 cm) | 0.044 | 0.833 | - | - | - |
| Histological type (Adenocarcinoma vs other) | 0.013 | 0.910 | - | - | - |
| T stage (T3-T4 vs T1-T2) | 31.071 | <0.001 | 2.774 | 1.661-4.635 | <0.001 |
| N stage (N2-N3 vs N0-N1) | 28.779 | <0.001 | 2.641 | 1.515-4.604 | <0.001 |
表2 Cox回归分析胃癌根治术后5年生存期的预后因子
Tab.2 Cox regression analysis of prognostic factors for 5-year survival after radical gastrectomy for gastric cancer
| Factor | Univariate analysis | Multivariate analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Log rank χ2 | P | HR | 95% CI | P | |
| Gender (Male vs female) | 2.023 | 0.155 | - | - | - |
| Age (≥60 years vs <60 years) | 2.691 | 0.101 | - | - | - |
| SURF4 expression (low vs high) | 38.749 | <0.001 | 3.106 | 1.853-5.206 | <0.001 |
| CEA (≥5 μg/L vs <5 μg/L) | 34.667 | <0.001 | 1.853 | 1.092-3.146 | 0.022 |
| CA19-9 (≥37kU/L vs <37kU/L) | 35.752 | <0.001 | 1.949 | 1.125-3.378 | 0.017 |
| Tumor size (≥5 cm vs <5 cm) | 0.044 | 0.833 | - | - | - |
| Histological type (Adenocarcinoma vs other) | 0.013 | 0.910 | - | - | - |
| T stage (T3-T4 vs T1-T2) | 31.071 | <0.001 | 2.774 | 1.661-4.635 | <0.001 |
| N stage (N2-N3 vs N0-N1) | 28.779 | <0.001 | 2.641 | 1.515-4.604 | <0.001 |
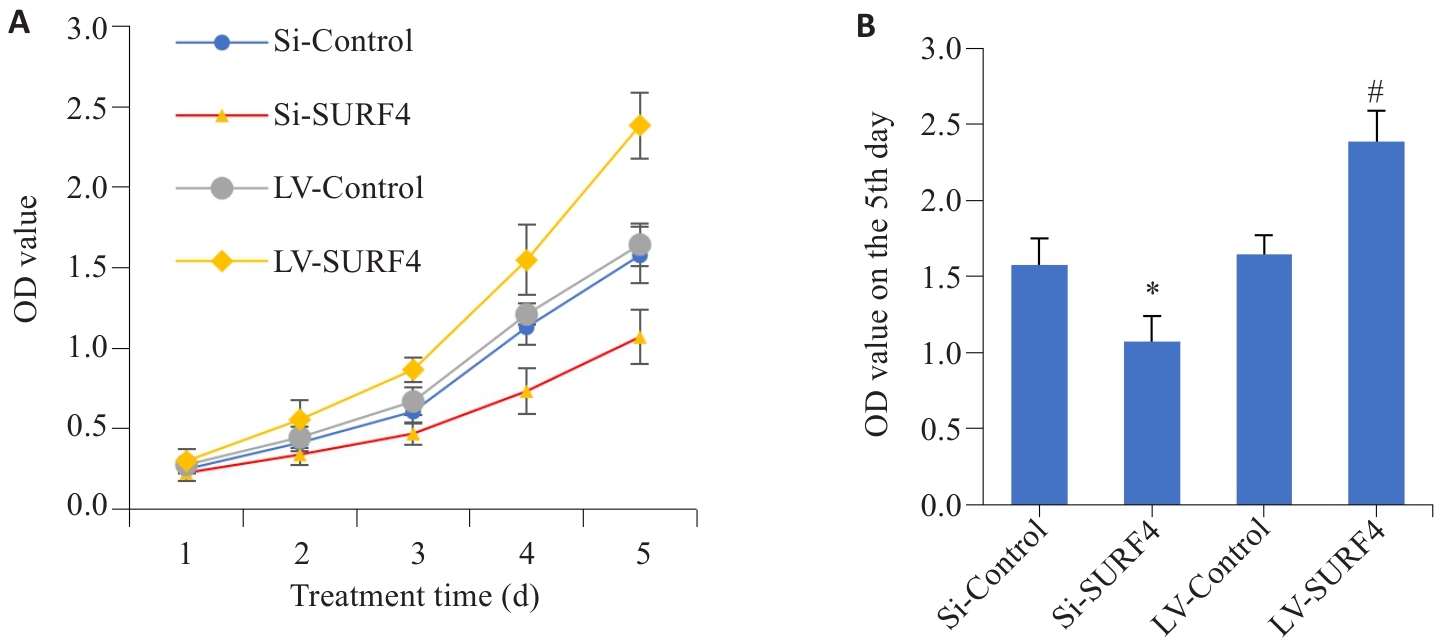
图7 SURF4对胃癌细胞增殖能力的影响
Fig.7 Effect of SURF4 expression level on proliferation of gastric cancer HGC-27 cells. A: Cell proliferation from day 1 to day 5. B: Comparison of cell proliferation on day 5 (n=4). LV: overexpression; Si: SiRNA. *P<0.05 vs Si-Control; #P<0.05 vs LV-Control.

图8 过表达SURF4与HGC-27胃癌细胞迁移和侵袭能力及EMT之间的关系
Fig.8 Effect of SURF4 knockdown and overexpression on migration, invasion and EMT of HGC-27 gastric cancer cells. A, D: Results of scratch assay. B, E: Effect of SURF4 knockdown and overexpression on migration ability of HGC-27 cells. C, F: Invasion ability of HGC-27 cells with SURF4 knockdown and overexpression. G-I: Expressions of E-cadherin and N-cadherin protein in HGC-27 cells with SURF4 knockdown and overexpression. *P<0.05 vs Si-Control; #P<0.05 vs LV-Control(n=4).
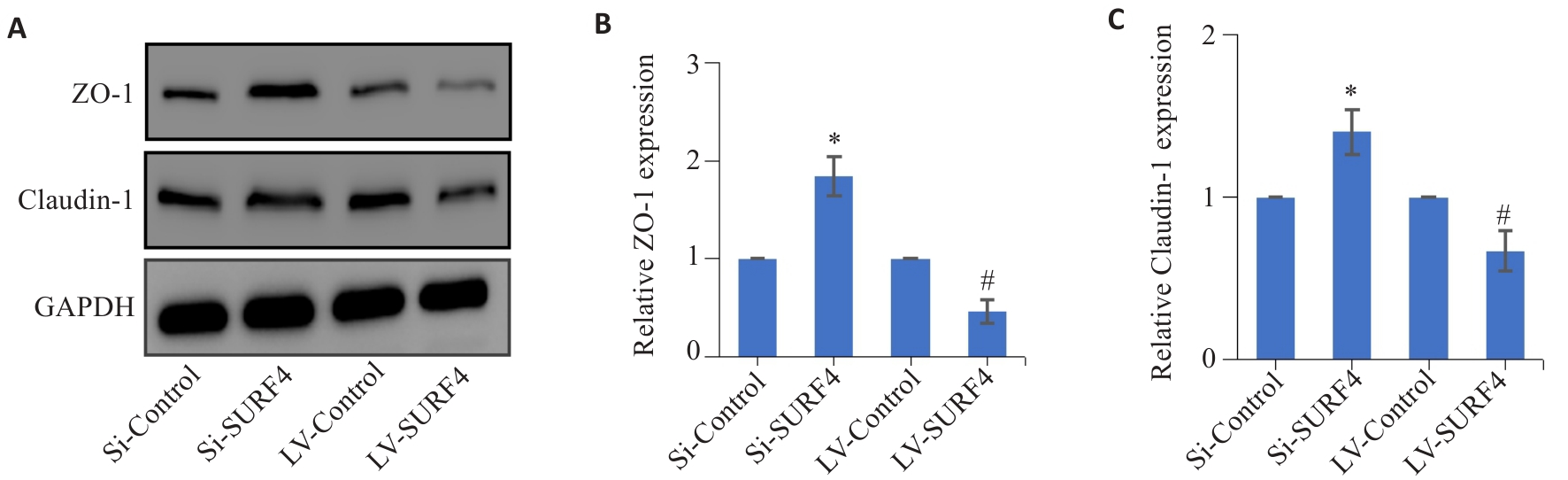
图9 高表达SURF4与紧密连接蛋白表达的关系
Fig.9 Effect of SURF4 knockdown and overexpression on tight junction protein expression in HGC-27 cells detected by Western blotting. A-C: Expressions of ZO-1 and Caudin-1 protein in HGC-27 gastric cancer cells. *P<0.05 vs Si-Control; #P<0.05 vs LV-Control (n=4).
| [1] | Yang WJ, Zhao HP, Yu Y, et al. Updates on global epidemiology, risk and prognostic factors of gastric cancer[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2023, 29(16): 2452-68. doi:10.3748/wjg.v29.i16.2452 |
| [2] | Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2024[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2024, 74(1): 12-49. doi:10.3322/caac.21820 |
| [3] | Zheng RS, Chen R, Han BF, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2022[J]. Chin J Oncol, 2024, 46(3): 221-31. |
| [4] | Huang CM, Liu H, Hu YF, et al. Laparoscopic vs open distal gastrectomy for locally advanced gastric cancer: five-year outcomes from the CLASS-01 randomized clinical trial[J]. JAMA Surg, 2022, 157(1): 9-17. doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2021.7583 |
| [5] | Li GZ, Doherty GM, Wang JP. Surgical management of gastric cancer: a review[J]. JAMA Surg, 2022, 157(5): 446-54. doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2022.0182 |
| [6] | Joshi SS, Badgwell BD. Current treatment and recent progress in gastric cancer[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 264-79. doi:10.3322/caac.21657 |
| [7] | Kelly RJ, Ajani JA, Kuzdzal J, et al. Adjuvant nivolumab in resected esophageal or gastroesophageal junction cancer[J]. N Engl J Med, 2021, 384(13): 1191-203. doi:10.1056/nejmoa2032125 |
| [8] | 史佳炜. 胃癌D2根治术后淋巴结阳性患者辅助免疫联合化疗对比单纯辅助化疗的临床疗效和安全性分析[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2024. |
| [9] | Ward ZJ, Gaba Q, Atun R. Cancer incidence and survival for 11 cancers in the commonwealth: a simulation-based modelling study[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2024, 25(9): 1127-34. doi:10.1016/s1470-2045(24)00336-x |
| [10] | Wu ZH, Qu BC, Yuan MX, et al. CRIP1 reshapes the gastric cancer microenvironment to facilitate development of lymphatic metastasis[J]. Adv Sci (Weinh), 2023, 10(26): e2303246. doi:10.1002/advs.202303246 |
| [11] | Xiao J, Cao SQ, Wang JW, et al. Leptin-mediated suppression of lipoprotein lipase cleavage enhances lipid uptake and facilitates lymph node metastasis in gastric cancer[J]. Cancer Commun (Lond), 2024, 44(8): 855-78. doi:10.1002/cac2.12583 |
| [12] | Won Y, Jang B, Lee SH, et al. Oncogenic fatty acid metabolism rewires energy supply chain in gastric carcinogenesis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2024, 166(5): 772-86.e14. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2024.01.027 |
| [13] | Augustin JE, Soussan P, Bass AJ. Targeting the complexity of ERBB2 biology in gastroesophageal carcinoma[J]. Ann Oncol, 2022, 33(11): 1134-48. doi:10.1016/j.annonc.2022.08.001 |
| [14] | 赵 燕, 于 鸿. 管家基因SURF4的生理功能及其与肿瘤的关系[J]. 中华生物医学工程杂志, 2022, 28(6): 704-8. |
| [15] | Zhai JT, Han JS, Li C, et al. High SURF4 expression is associated with poor prognosis of breast cancer[J]. Aging (Albany NY), 2022, 14(22): 9317-37. doi:10.18632/aging.204409 |
| [16] | Yue YF, Xia LL, Xu SS, et al. SURF4 maintains stem-like properties via BIRC3 in ovarian cancer cells[J]. J Gynecol Oncol, 2020, 31(4): e46. doi:10.3802/jgo.2020.31.e46 |
| [17] | Kim J, Lee HS, Hong CM, et al. Novel endogenous endoplasmic reticulum transmembrane protein SURF4 suppresses cell death by negatively regulating the STING-STAT6 axis in myeloid leukemia[J]. Cancer Commun (Lond), 2023, 43(3): 395-9. doi:10.1002/cac2.12390 |
| [18] | Yu J, Meng SB, Xuan TT, et al. Identification of hsa-miR-193a-5p-SURF4 axis related to the gut microbiota-metabolites- cytokines in lung cancer based on Mendelian randomization study and bioinformatics analysis[J]. Discov Oncol, 2024, 15(1): 475. doi:10.1007/s12672-024-01359-5 |
| [19] | Yang WS, Cui XH, Sun DP, et al. POU5F1 promotes the proliferation, migration, and invasion of gastric cancer cells by reducing the ubiquitination level of TRAF6[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2023, 14(12): 802. doi:10.1038/s41419-023-06332-8 |
| [20] | Kim J, Hong CM, Park SM, et al. SURF4 has oncogenic potential in NIH3T3 cells[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2018, 502(1): 43-7. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.05.116 |
| [21] | Thrift AP, Wenker TN, El-Serag HB. Global burden of gastric cancer: epidemiological trends, risk factors, screening and prevention[J]. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 2023, 20(5): 338-49. doi:10.1038/s41571-023-00747-0 |
| [22] | Huang JJ, Lucero-Prisno DE, Zhang L, et al. Updated epidemiology of gastrointestinal cancers in east Asia[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2023, 20(5): 271-87. doi:10.1038/s41575-022-00726-3 |
| [23] | Lei ZN, Teng QX, Tian Q, et al. Signaling pathways and therapeutic interventions in gastric cancer[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2022, 7(1): 358. doi:10.1038/s41392-022-01190-w |
| [24] | 左芦根, 王 炼, 杨 子, 等. 高表达CAMSAP2通过上调TGF-β信号促进胃癌细胞的侵袭和转移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(9): 1460-8. doi:10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2023.09.02 |
| [25] | Carter P, Kang YB. Tumor heterogeneity and cooperating cancer hallmarks driven by divergent EMT programs[J]. Cancer Res, 2025, 85(1): 12-4. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-24-4309 |
| [26] | Verstappe J, Berx G. A role for partial epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in enabling stemness in homeostasis and cancer[J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 2023, 90: 15-28. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2023.02.001 |
| [27] | Ang HL, Mohan CD, Shanmugam MK, et al. Mechanism of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer and its regulation by natural compounds[J]. Med Res Rev, 2023, 43(4): 1141-200. doi:10.1002/med.21948 |
| [28] | Yu S, He J, Xie KP. Zonula occludens proteins signaling in inflammation and tumorigenesis[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2023, 19(12): 3804-15. doi:10.7150/ijbs.85765 |
| [29] | 丛 馨, 张 艳, 俞光岩, 等. 上皮细胞间紧密连接功能的研究进展[J]. 生理学报, 2016, 68(4): 492-504. doi:10.13294/j.aps.2016.0057 |
| [30] | 谭眉灵, 龙春姣, 蒋 旺, 等. 呼吸系统中上皮-间质转化的研究进展及细胞黏附连接调控机制[J]. 生理学报, 2020, 72(5): 605-16. doi:10.13294/j.aps.2020.0043 |
| [31] | Du FQ, Xie YW, Wu SZ, et al. Expression and targeted application of claudins family in hepatobiliary and pancreatic diseases[J]. J Hepatocell Carcinoma, 2024, 11: 1801-21. doi:10.2147/jhc.s483861 |
| [32] | Kim HS, Lee SI, Choi YR, et al. GNAQ-regulated ZO-1 and ZO-2 act as tumor suppressors by modulating EMT potential and tumor-repressive microenvironment in lung cancer[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(10): 8801. doi:10.3390/ijms24108801 |
| [33] | Tsuboi T, Matsuzaki T, Takekoshi S, et al. Significance of ZO-1, an intercellular adhesion molecule, as a prognostic marker in lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Tokai J Exp Clin Med, 2024, 49(1): 1-8. |
| [34] | García-García CA, Cruz-Gregorio A, Pedraza-Chaverri J, et al. NDMA enhances claudin-1 and-6 expression viaCYP2E1/ROS in AGS cells[J]. Toxicol In Vitro, 2025, 102: 105952. doi:10.1016/j.tiv.2024.105952 |
| [1] | 马思源, 张博超, 浦春. Circ_0000437通过靶向let-7b-5p/CTPS1轴促进乳腺癌细胞的增殖、侵袭、迁移及上皮间质转化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(8): 1682-1696. |
| [2] | 陈鑫源, 吴成挺, 李瑞迪, 潘雪芹, 张耀丹, 陶俊宇, 林才志. 双术汤通过P53/SLC7A11/GPX4通路诱导胃癌细胞铁死亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1363-1371. |
| [3] | 庞金龙, 赵新丽, 张振, 王豪杰, 周星琦, 杨玉梅, 李姗姗, 常小强, 李锋, 李娴. 皮肤黑色素瘤中MMRN2高表达促进肿瘤细胞的侵袭和迁移并与不良预后相关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1479-1489. |
| [4] | 吴璇, 方家敏, 韩玮玮, 陈琳, 孙菁, 金齐力. 高表达PRELID1促进胃癌细胞上皮间质转化并与不良预后相关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1535-1542. |
| [5] | 王康, 李海宾, 余靖, 孟源, 张虹丽. ELFN1高表达是结肠癌的预后生物标志物并促进结肠癌细胞的增殖转移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1543-1553. |
| [6] | 侯鑫睿, 张振东, 曹明远, 杜予心, 王小平. 红景天苷靶向miR-1343-3p-OGDHL/PDHB糖代谢轴抑制胃癌细胞的体内外增殖[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1226-1239. |
| [7] | 马振南, 刘福全, 赵雪峰, 张晓微. DTX2促进奥沙利铂耐药的结直肠癌细胞增殖、侵袭和上皮间质转化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 829-836. |
| [8] | 张毅, 沈昱, 万志强, 陶嵩, 柳亚魁, 王栓虎. CDKN3高表达促进胃癌细胞的迁移和侵袭:基于调控p53/NF-κB信号通路和抑制胃癌细胞凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 853-861. |
| [9] | 陶露, 韦卓利, 王月月, 项平. CEACAM6通过调控上皮间质转化抑制鼻咽癌细胞的增殖和迁移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 566-576. |
| [10] | 黄晴晴, 张文静, 张小凤, 王炼, 宋雪, 耿志军, 左芦根, 王月月, 李静, 胡建国. 高表达MYO1B促进胃癌细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭并与患者的不良预后有关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 622-631. |
| [11] | 李华莉, 宋婷, 刘嘉雯, 李永宝, 姜兆静, 窦文, 周凌宏. 预后导向的肺癌调强放疗计划优化新方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 643-649. |
| [12] | 宋雪, 陈悦, 张敏, 张诺, 左芦根, 李静, 耿志军, 张小凤, 王月月, 王炼, 胡建国. GPSM2在胃癌组织中高表达并通过促进肿瘤细胞的增殖影响患者预后[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 229-238. |
| [13] | 唐天威, 李路安, 陈源汉, 张丽, 徐丽霞, 李志莲, 冯仲林, 张辉林, 华瑞芳, 叶智明, 梁馨苓, 李锐钊. 高血清胱抑素C水平是IgA肾病不良预后的独立危险因素[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 379-386. |
| [14] | 陈晓睿, 魏青政, 张宗亮, 原江水, 宋卫青. 过表达带电多泡体蛋白2B基因抑制肾透明细胞癌细胞的增殖[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 126-136. |
| [15] | 王耀彬, 陈柳燕, 罗伊凌, 申继清, 周素芳. NUF2对泛癌的预后和免疫治疗效果的预测价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 137-149. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||