南方医科大学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (6): 1198-1208.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.06.22
收稿日期:2023-12-25
出版日期:2024-06-20
发布日期:2024-07-01
通讯作者:
马建华
E-mail:lzy313@smu.edu.cn;jhma@smu.edu.cn
作者简介:林宗悦,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: lzy313@smu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Zongyue LIN( ), Yongbo WANG, Zhaoying BIAN, Jianhua MA(
), Yongbo WANG, Zhaoying BIAN, Jianhua MA( )
)
Received:2023-12-25
Online:2024-06-20
Published:2024-07-01
Contact:
Jianhua MA
E-mail:lzy313@smu.edu.cn;jhma@smu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
目的 针对牙科CBCT扫描中患者不自主运动导致的重建图像运动伪影问题,提出了一种基于深度模糊学习的牙科CBCT运动伪影校正算法(DMBL),以提升牙科CBCT的成像质量。 方法 首先使用模糊编码模块提取运动退化特征,从而对运动导致的退化过程进行建模,然后将得到的运动退化特征输入伪影校正模块进行运动伪影去除。其中,伪影校正模块采用了图像模糊去除和图像模糊仿真的联合学习框架,可有效处理空间变化且随机的运动模式。为验证所提方法的有效性,本文分别在仿真运动数据集和临床数据集上进行对比实验。 结果 仿真数据集实验结果表明,本文方法峰值信噪比提升了2.88%,结构相似性(SSIM)提升了0.89%,均方根误差(RMSE)减少了10.58%;临床数据集实验结果表明,本文方法取得了最高的专家主观图像质量评分4.417(5分制),且与对比方法结果的评分具有显著性差异(P<0.001)。 结论 本文提出的DMBL算法,通过构建深度模糊联合学习网络结构,能够有效地去除牙科CBCT图像中的运动伪影,实现高质量的图像恢复。
林宗悦, 王永波, 边兆英, 马建华. 基于深度模糊学习的牙科CBCT运动伪影校正算法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(6): 1198-1208.
Zongyue LIN, Yongbo WANG, Zhaoying BIAN, Jianhua MA. A deep blur learning-based motion artifact reduction algorithm for dental cone-beam computed tomography images[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(6): 1198-1208.
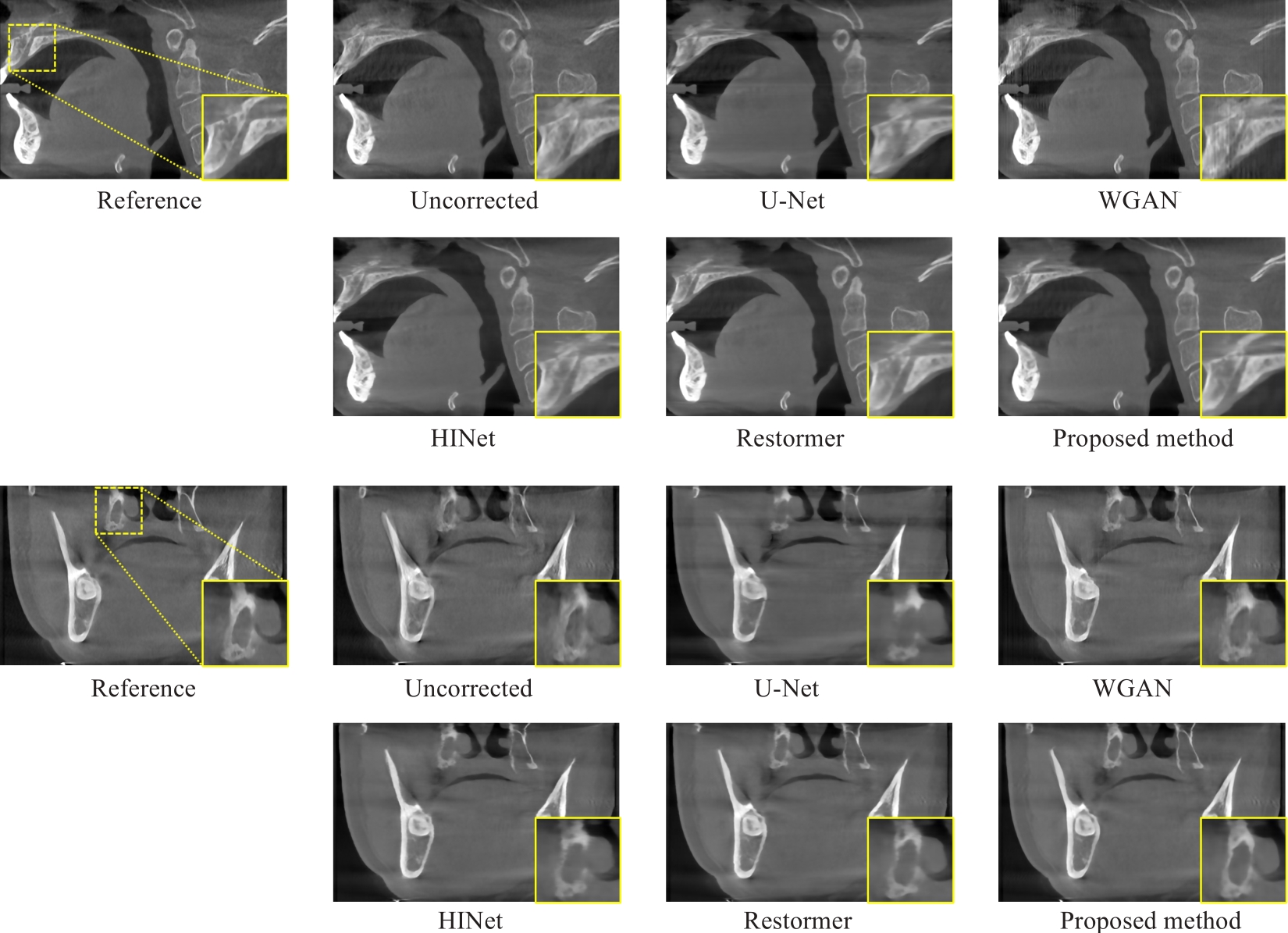
图8 仿真数据冠状面和矢状面校正结果
Fig.8 Coronal and sagittal plane results of motion artifact reduction for the simulated data. Display windows: C=400 HU, W=3000 HU.
| Methods | Uncorrected | U-net | WGAN | HINet | Restormer | Ours |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | 7.7350 | 9.5548 | 7.7357 | 6.2869 | 5.5503 | 4.9629 |
| PSNR | 30.4728 | 28.8756 | 30.4767 | 32.2988 | 33.3387 | 34.2981 |
| SSIM | 0.9130 | 0.9176 | 0.9017 | 0.9391 | 0.9476 | 0.9560 |
表1 仿真运动数据恢复结果定量比较
Tab.1 Quantitative comparison of restoration of simulated motion data using different methods
| Methods | Uncorrected | U-net | WGAN | HINet | Restormer | Ours |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | 7.7350 | 9.5548 | 7.7357 | 6.2869 | 5.5503 | 4.9629 |
| PSNR | 30.4728 | 28.8756 | 30.4767 | 32.2988 | 33.3387 | 34.2981 |
| SSIM | 0.9130 | 0.9176 | 0.9017 | 0.9391 | 0.9476 | 0.9560 |
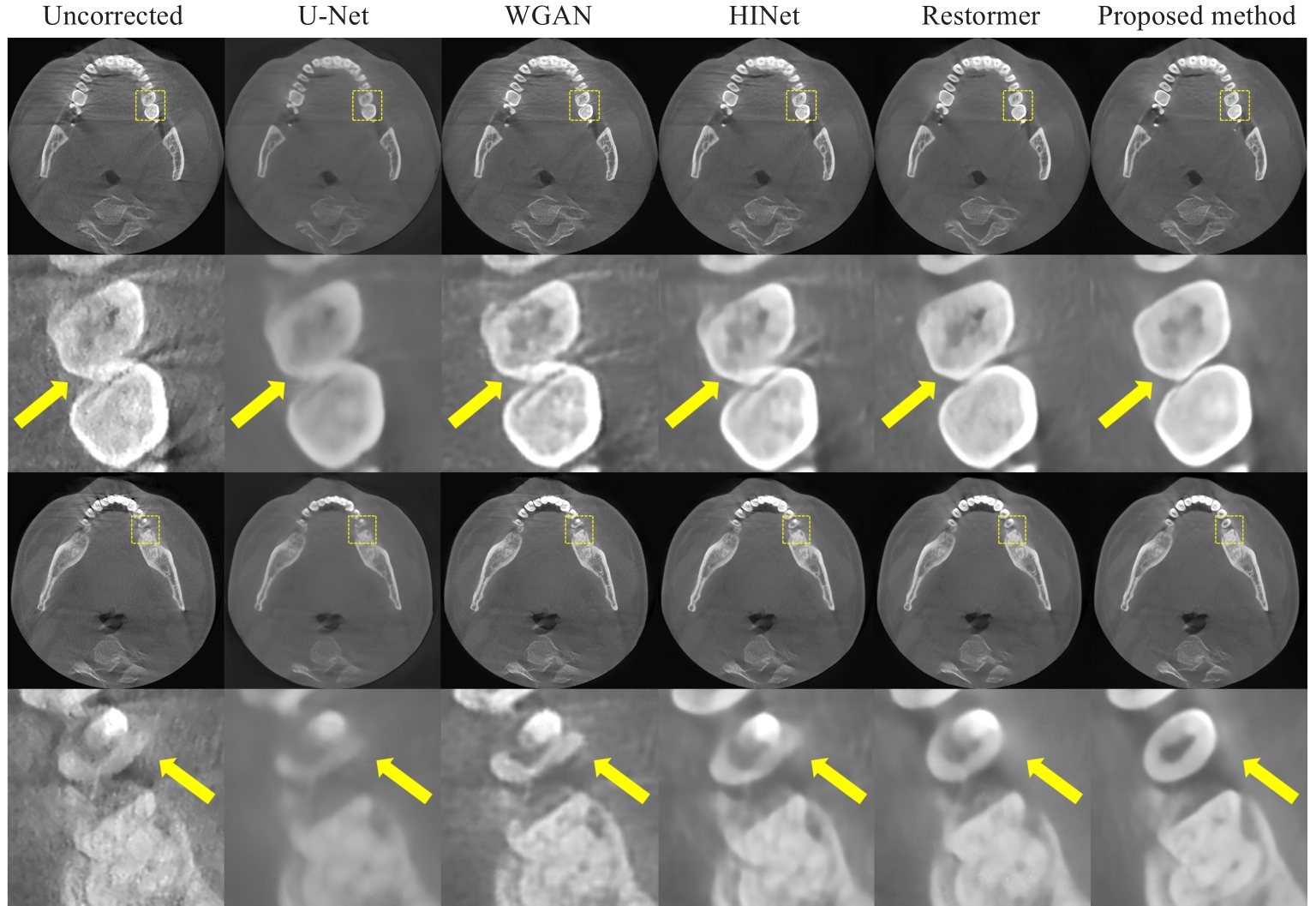
图10 临床数据case 2 不同方法校正结果对比
Fig.10 Comparison of the results of motion artifact reduction for clinical data Case 2. Display windows: C=400 HU, W=3000 HU.
| Methods | Scores (Mean±SD) | P |
|---|---|---|
U-net WGAN HINet Restormer Ours | 2.250±0.778 2.208±0.762 3.083±0.759 3.667±0.687 4.417±0.571 | <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 - |
表2 临床数据图像质量主观评分统计
Tab.2 Overall image quality score statistics
| Methods | Scores (Mean±SD) | P |
|---|---|---|
U-net WGAN HINet Restormer Ours | 2.250±0.778 2.208±0.762 3.083±0.759 3.667±0.687 4.417±0.571 | <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 <0.001 - |
| Methods | Uncorrected | Restormer | Ours |
|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | 8.7842 | 6.5889 | 5.8347 |
| PSNR | 0.9052 | 0.9406 | 0.9498 |
| SSIM | 29.6934 | 32.2733 | 33.2851 |
表3 联合学习框架有效性验证实验定量比较
Tab.3 Quantitative comparison of verification experiment results of the joint learning framework
| Methods | Uncorrected | Restormer | Ours |
|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE | 8.7842 | 6.5889 | 5.8347 |
| PSNR | 0.9052 | 0.9406 | 0.9498 |
| SSIM | 29.6934 | 32.2733 | 33.2851 |
| 1 | Kaasalainen T, Ekholm M, Siiskonen T, et al. Dental cone beam CT: an updated review[J]. Phys Med, 2021, 88: 193-217. |
| 2 | Nemtoi A, Czink C, Haba D, et al. Cone beam CT: a current overview of devices[J]. Dentomaxillofac Radiol, 2013, 42(8): 20120443. |
| 3 | Spin-Neto R, Wenzel A. Patient movement and motion artefacts in cone beam computed tomography of the dentomaxillofacial region: a systematic literature review[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol, 2016, 121(4): 425-33. |
| 4 | Hanzelka T, Dusek J, Ocasek F, et al. Movement of the patient and the cone beam computed tomography scanner: objectives and possible solutions[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol, 2013, 116(6): 769-73. |
| 5 | Spin-Neto R, Costa C, Salgado DM, et al. Patient movement characteristics and the impact on CBCT image quality and interpretability[J]. Dentomaxillofac Radiol, 2018, 47(1): 20170216. |
| 6 | Weisenberger AG, Gleason SS, Goddard J, et al. A restraint-free small animal SPECT imaging system with motion tracking[J]. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci, 2005, 52(3): 638-44. |
| 7 | Herzog H, Tellmann L, Fulton R, et al. Motion artifact reduction on parametric PET images of neuroreceptor binding[J]. J Nucl Med, 2005, 46(6): 1059-65. |
| 8 | Kim JH, Nuyts J, Kyme A, et al. A rigid motion correction method for helical computed tomography (CT)[J]. Phys Med Biol, 2015, 60(5): 2047-73. |
| 9 | Kyme AZ, Se S, Meikle SR, et al. Markerless motion estimation for motion-compensated clinical brain imaging[J]. Phys Med Biol, 2018, 63(10): 105018. |
| 10 | Sisniega A, Stayman JW, Yorkston J, et al. Motion compensation in extremity cone-beam CT using a penalized image sharpness criterion[J]. Phys Med Biol, 2017, 62(9): 3712-34. |
| 11 | Maur S, Stsepankou D, Hesser J. Auto-calibration by locally consistent contours for dental CBCT[J]. Phys Med Biol, 2018, 63(21): 215018. |
| 12 | Huang H, Siewerdsen JH, Zbijewski W, et al. Reference-free learning-based similarity metric for motion compensation in cone-beam CT[J]. Phys Med Biol, 2022, 67(12): 10.1088/1361-6560/ac749a. |
| 13 | Hahn J, Bruder H, Rohkohl C, et al. Motion compensation in the region of the coronary arteries based on partial angle reconstructions from short-scan CT data[J]. Med Phys, 2017, 44(11): 5795-813. |
| 14 | Berger M, Xia Y, Aichinger W, et al. Motion compensation for cone-beam CT using Fourier consistency conditions[J]. Phys Med Biol, 2017, 62(17): 7181-215. |
| 15 | Preuhs A, Maier A, Manhart M, et al. Symmetry prior for epipolar consistency[J]. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg, 2019, 14(9): 1541-51. |
| 16 | Ouadah S, Jacobson M, Stayman JW, et al. Correction of patient motion in cone-beam CT using 3D-2D registration[J]. Phys Med Biol, 2017, 62(23): 8813-31. |
| 17 | Niebler S, Schömer E, Tjaden H, et al. Projection-based improvement of 3D reconstructions from motion-impaired dental cone beam CT data[J]. Med Phys, 2019, 46(10): 4470-80. |
| 18 | Hu ZL, Jiang CH, Zhang QY, et al. Wasserstein generative adversarial networks for motion artifact removal in dental CT imaging[C]//Medical Imaging 2019: Physics of Medical Imaging. February 16-21, 2019. San Diego, USA. SPIE, 2019: 1094836. |
| 19 | Su B, Wen YT, Liu YY, et al. A deep learning method for eliminating head motion artifacts in computed tomography[J]. Med Phys, 2022, 49(1): 411-9. |
| 20 | Ko Y, Moon S, Baek J, et al. Rigid and non-rigid motion artifact reduction in X-ray CT using attention module[J]. Med Image Anal, 2021, 67: 101883. |
| 21 | Spin-Neto R, Matzen LH, Schropp LW, et al. An ex vivo study of automated motion artefact correction and the impact on cone beam CT image quality and interpretability[J]. Dentomaxillofacial Radiol, 2018: 20180013. |
| 22 | Kim JH, Sun T, Alcheikh AR, et al. Correction for human head motion in helical X-ray CT[J]. Phys Med Biol, 2016, 61(4): 1416-38. |
| 23 | Li XH, Da Z, Liu B. A generic geometric calibration method for tomographic imaging systems with flat-panel detectors: a detailed implementation guide[J]. Med Phys, 2010, 37(7): 3844-54. |
| 24 | Li DS, Zhang Y, Cheung KC, et al. Learning degradation representations for image deblurring[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. Cham: Springer, 2022: 736-753. |
| 25 | Park T, Liu MY, Wang TC, et al. Semantic image synthesis with spatially-adaptive normalization[C]//2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Long Beach, CA, USA. IEEE, 2019: 2332-41. |
| 26 | Mechrez R, Talmi I, Shama F, et al. Maintaining natural image statistics with the contextual loss[C]//Asian Conference on Computer Vision. Cham: Springer, 2019: 427-443. |
| 27 | Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[M]//Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2015: 234-41. |
| 28 | Gulrajani I, Ahmed F, Arjovsky M, et al. Improved training of Wasserstein GANs[C]//Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. December 4 ‑9, 2017, Long Beach, California, USA. ACM, 2017: 5769-79. |
| 29 | Chen LY, Lu X, Zhang J, et al. HINet: half instance normalization network for image restoration[C]//2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW). Nashville, TN, USA. IEEE, 2021: 182-92. |
| 30 | Zamir SW, Arora A, Khan S, et al. Restormer: efficient transformer for high-resolution image restoration[C]//2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans, LA, USA. IEEE, 2022: 5718-29. |
| 31 | Sun T, Jacobs R, Pauwels R, et al. A motion correction approach for oral and maxillofacial cone-beam CT imaging[J]. Phys Med Biol, 2021, 66(12): 125008. |
| 32 | Wang ZH, Chen J, Hoi SCH. Deep learning for image super-resolution: a survey[J]. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 2021, 43(10): 3365-87. |
| [1] | 曾智雄, 王永波, 林宗悦, 边兆英, 马建华. 基于分段反投影张量退化特征编码的牙科锥形束计算机断层扫描运动伪影校正[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 422-436. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||