南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (9): 1938-1945.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.09.13
• • 上一篇
马倩倩1( ), 牛钰琪2, 左铭钰1, 李鑫1, 符竣轲1, 王瑾瑾2(
), 牛钰琪2, 左铭钰1, 李鑫1, 符竣轲1, 王瑾瑾2( )
)
收稿日期:2025-02-13
出版日期:2025-09-20
发布日期:2025-09-28
通讯作者:
王瑾瑾
E-mail:wtt01232024@163.com;wangjinjin@hactcm.edu.cn
作者简介:马倩倩,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: wtt01232024@163.com
基金资助:
Qianqian MA1( ), Yuqi NIU2, Mingyu ZUO1, Xin LI1, Junke FU1, Jinjin WANG2(
), Yuqi NIU2, Mingyu ZUO1, Xin LI1, Junke FU1, Jinjin WANG2( )
)
Received:2025-02-13
Online:2025-09-20
Published:2025-09-28
Contact:
Jinjin WANG
E-mail:wtt01232024@163.com;wangjinjin@hactcm.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
目的 观察鬼箭羽对晚期糖基化终末产物(AGEs)刺激的小鼠肾足细胞(MPC-5)AGEs-晚期糖基化终末产物受体(RAGE)信号转导通路及下游靶点的影响,并阐明鬼箭羽改善糖尿病肾脏疾病(DKD)足细胞损伤的机制。 方法 鬼箭羽干预糖尿病肾脏疾病动物模型,利用透射电镜观察肾脏形态与结构;实时荧光定量-聚合酶链反应(RT-qPCR)、免疫组化检测相关基因与核心蛋白的表达情况。体外培养MPC-5,采用浓度为50 mg/L糖基化终末期产物-牛血清白蛋白(AGEs-BSA)培养液孵育24 h,诱导建立糖尿病细胞模型。利用CCK-8法检测技术,评价造模后的细胞成活率。将对数生长期的MPC-5随机分为正常组、模型组、鬼箭羽组、RAGE激动剂(D-Ribose)组、鬼箭羽+RAGE激动剂(D-Ribose)组,利用CCK-8法筛选不同浓度鬼箭羽对MPC-5细胞活力的影响。蛋白免疫印迹法检测各组细胞RAGE、VEGFA、TNF-α、NF-κB(p65)、IL-6、Caspase-3蛋白表达;RT-qPCR检测RAGE、NF-κB(p65)、VEGFA、IL-6mRNA表达。 结果 体内结果表明,鬼箭羽干预后,与模型组相比,干预组动物模型肾脏组织足细胞病理变化有所改善。免疫组化结果显示,与模型组比较,鬼箭羽高剂量组RAGE、VEGFA、NF-κB(p65)、IL-6蛋白表达降低(P<0.05);RT-qPCR结果显示,与模型组比较,鬼箭羽高剂量组RAGE、NF-κB、IL-6mRNA表达降低(P<0.05)。体外结果表明,与正常组相比,模型组细胞活力显著降低(P<0.05),RAGE、NF-κB(p65)、VEGFA、TNF-α、IL-6和Caspase-3蛋白表达升高(P<0.05),RAGE、NF-κB(p65)、VEGFA和IL-6 mRNA表达升高(P<0.05);与模型组比较,浓度为550 mg/L的鬼箭羽干预成模后的MPC-5,24 h提高细胞活力最为显著(P<0.05),降低RAGE、NF-κB(p65)、VEGFA、TNF-α、IL-6和Caspase-3蛋白表达(P<0.05);而鬼箭羽+RAGE激动剂可逆转RAGE激动剂对MPC-5模型中RAGE、VEGFA、TNF-α、IL-6和Caspase-3蛋白表达的改变(P<0.05),同时与RAGE激动剂组比较,鬼箭羽+RAGE激动剂组RAGE、NF-κB(p65)、IL-6、VEGFAmRNA表达显著降低(P<0.01)。 结论 鬼箭羽可以通过抑制AGEs-RAGE信号转导通路的激活,减少下游促炎细胞因子和血管内皮生长因子的表达,进而发挥改善AGEs诱导糖尿病肾脏疾病MPC-5损伤的作用。
马倩倩, 牛钰琪, 左铭钰, 李鑫, 符竣轲, 王瑾瑾. 鬼箭羽通过抑制AGEs-RAGE信号转导通路改善晚期糖基化终末产物诱导的小鼠肾足细胞损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1938-1945.
Qianqian MA, Yuqi NIU, Mingyu ZUO, Xin LI, Junke FU, Jinjin WANG. Guijianyu alleviates advanced glycation endproducts-induced mouse renal podocyte injury by inhibiting the AGEs-RAGE signaling pathway[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(9): 1938-1945.
| Gene | Forward 5'-3' | Reverse 5'-3' |
|---|---|---|
| RAGE | CCACTGGAATTGTCGATGAGG | CTCGGACTCGGTAGTTGGACT |
| NF-κB | GCAGAAAGAAGACATTGAGGTGTAT | GCGATCATCTGTGTCTGGCA |
| IL-6 | CCCCAATTTCCAATGCTCTCC | CGCACTAGGTTTGCCGAGTA |
| VEGFA | TAACGATGAAGCCCTGGAGTG | CACAGTGAACGCTCCAGGATTTA |
| β-actin | GTGACGTTGACATCCGTAAAGA | GTAACAGTCCGCCTAGAAGCAC |
表1 RT-qPCR引物序列
Tab.1 Primer sequences for RT-qPCR
| Gene | Forward 5'-3' | Reverse 5'-3' |
|---|---|---|
| RAGE | CCACTGGAATTGTCGATGAGG | CTCGGACTCGGTAGTTGGACT |
| NF-κB | GCAGAAAGAAGACATTGAGGTGTAT | GCGATCATCTGTGTCTGGCA |
| IL-6 | CCCCAATTTCCAATGCTCTCC | CGCACTAGGTTTGCCGAGTA |
| VEGFA | TAACGATGAAGCCCTGGAGTG | CACAGTGAACGCTCCAGGATTTA |
| β-actin | GTGACGTTGACATCCGTAAAGA | GTAACAGTCCGCCTAGAAGCAC |
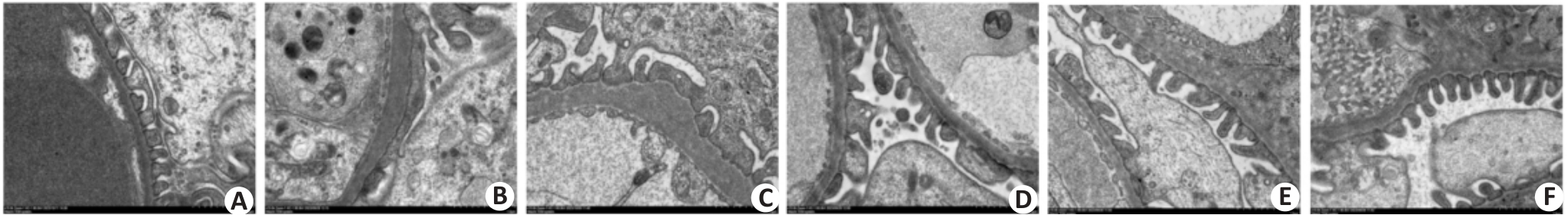
图1 电镜下db/db小鼠足细胞超微结构
Fig.1 Ultrastructure of podocytes of db/db mice under electron microscope (Original magnification: ×15 000). A: Normal group. B: Model group. C: Guijianyu low-dose group. D: Guijianyu medium-dose group. E: Guijianyu high-dose group. F: Irbesartan group.
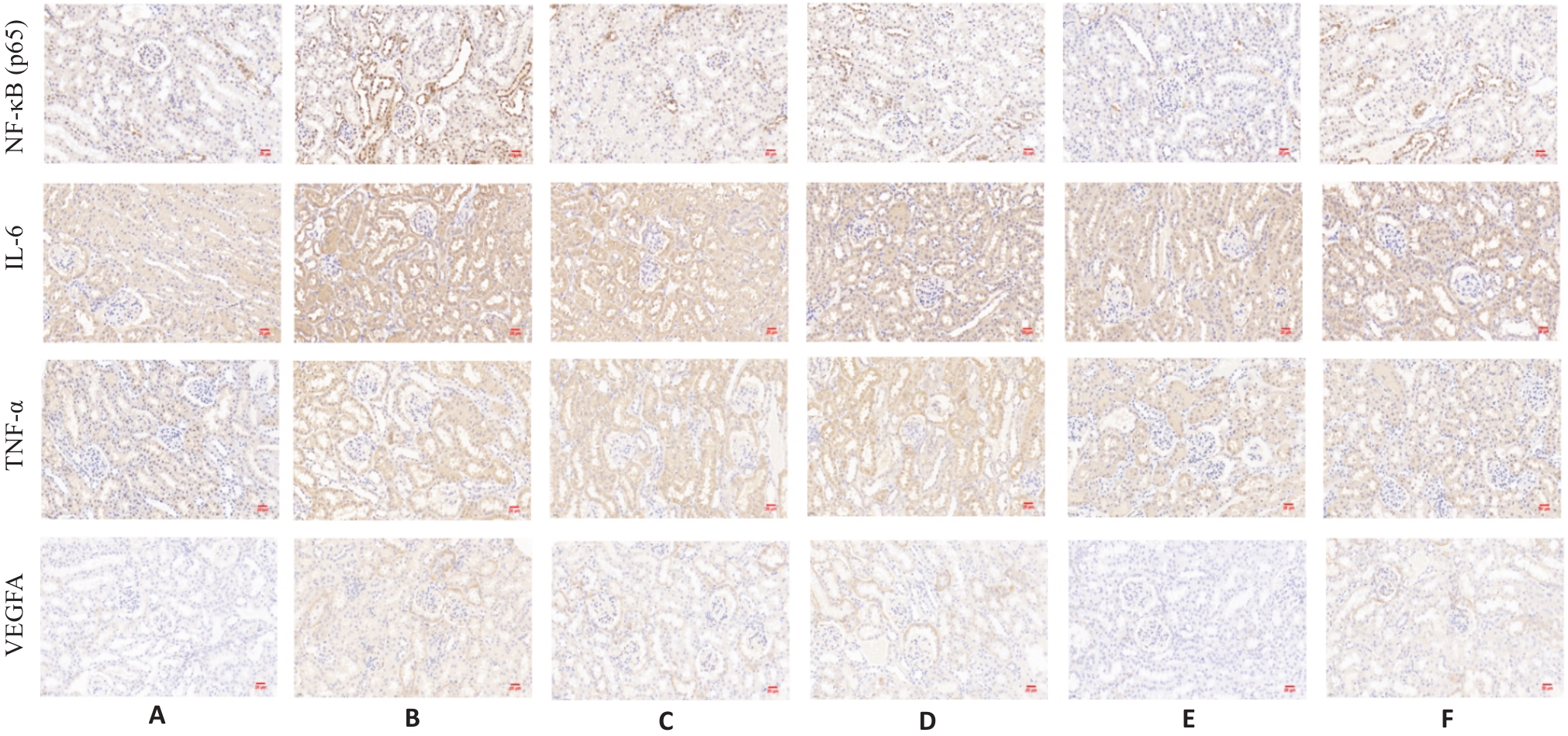
图2 各组肾脏NF-κB、IL-6、VEGFA、TNF-α的免疫组化结果
Fig.2 Immunohistochemistry for NF-κB, IL-6, VEGFA, and TNF-α in mouse renal tissues in each group (×400). A: Normal group. B: Model group. C: Guijianyu low-dose group. D: Guijianyu medium-dose group. E: Guijianyu high-dose group. F: Irbesartan group.
| Group | NF-κB (p65) | VEGFA | TNF-α | IL-6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0.120±0.036 | 0.067±0.015 | 0.085±0.017 | 0.102±0.011 |
| B | 0.210±0.010 | 0.123±0.005* | 0.121±0.007* | 0.143±0.015* |
| C | 0.173±0.023* | 0.097±0.015 | 0.112±0.001 | 0.123±0.012 |
| D | 0.146±0.015 | 0.087±0.012# | 0.108±0.004 | 0.117±0.015# |
E F | 0.130±0.010# 0.137±0.006# | 0.067±0.006# 0.063±0.015# | 0.102±0.002# 0.099±0.006# | 0.103±0.015# 0.103±0.006# |
| P | <0.001 | 0.013 | 0.003 | 0.012 |
表2 DKD模型小鼠肾脏NF-κB(p65)、VEGFA、TNF-α、IL-6阳性表达情况
Tab.2 Expression levels of NF-κB (p65), VEGFA, TNF-α and IL-6 proteins in the kidney of DKD mouse models in each group (Mean±SD, n=3)
| Group | NF-κB (p65) | VEGFA | TNF-α | IL-6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0.120±0.036 | 0.067±0.015 | 0.085±0.017 | 0.102±0.011 |
| B | 0.210±0.010 | 0.123±0.005* | 0.121±0.007* | 0.143±0.015* |
| C | 0.173±0.023* | 0.097±0.015 | 0.112±0.001 | 0.123±0.012 |
| D | 0.146±0.015 | 0.087±0.012# | 0.108±0.004 | 0.117±0.015# |
E F | 0.130±0.010# 0.137±0.006# | 0.067±0.006# 0.063±0.015# | 0.102±0.002# 0.099±0.006# | 0.103±0.015# 0.103±0.006# |
| P | <0.001 | 0.013 | 0.003 | 0.012 |
| Group | RAGE | NF-κB(p65) | IL-6 |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 1.00±0.09 | 1.00±0.03 | 1.00±0.14 |
| B | 1.83±0.15* | 1.71±0.16* | 1.42±0.08* |
| C | 1.25±0.11# | 1.22±0.26# | 1.21±0.07# |
| D | 1.13±0.06# | 1.10±0.18# | 1.18±0.05# |
E F | 1.10±0.38# 1.12±0.02# | 1.05±0.34# 1.09±0.16# | 1.06±0.04# 1.04±0.14# |
| P | <0.001 | 0.013 | 0.002 |
表3 DKD模型小鼠肾脏RAGE、NF-κB(p65)、IL-6mRNA表达的影响
Tab.3 Expression levels of RAGE, NF-κB (p65) and IL-6 mRNA in the kidney of DKD mouse models in each group (Mean±SD, n=3)
| Group | RAGE | NF-κB(p65) | IL-6 |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 1.00±0.09 | 1.00±0.03 | 1.00±0.14 |
| B | 1.83±0.15* | 1.71±0.16* | 1.42±0.08* |
| C | 1.25±0.11# | 1.22±0.26# | 1.21±0.07# |
| D | 1.13±0.06# | 1.10±0.18# | 1.18±0.05# |
E F | 1.10±0.38# 1.12±0.02# | 1.05±0.34# 1.09±0.16# | 1.06±0.04# 1.04±0.14# |
| P | <0.001 | 0.013 | 0.002 |
| Group | Cell viability |
|---|---|
| Normal | 100.00±3.45 |
| Model | 67.86±0.93* |
| 150 mg/L Guijianyu | 84.33±8.45# |
| 350 mg/L Guijianyu | 88.00±4.84# |
| 550 mg/L Guijianyu | 96.28±2.94# |
| 750 mg/L Guijianyu | 86.01±4.89# |
| P | <0.001 |
表4 鬼箭羽对AGEs诱导的MPC-5细胞活性的影响
Tab.4 Effect of Guijianyu on AGEs-induced MPC-5 cell viability (%, Mean±SD, n=3)
| Group | Cell viability |
|---|---|
| Normal | 100.00±3.45 |
| Model | 67.86±0.93* |
| 150 mg/L Guijianyu | 84.33±8.45# |
| 350 mg/L Guijianyu | 88.00±4.84# |
| 550 mg/L Guijianyu | 96.28±2.94# |
| 750 mg/L Guijianyu | 86.01±4.89# |
| P | <0.001 |
| Group | Cell viability |
|---|---|
| Normal | 100±1.32 |
| Model | 67.78±5.06* |
| Guijianyu | 88.66±2.39# |
| RAGE agonist | 48.38±7.00## |
| Guijianyu+RAGE agonist | 76.40±2.85** |
| P | <0.001 |
表5 各给药组对AGEs诱导的MPC-5细胞活性的影响
Tab.5 Effect of Guijianyu on AGes-induced MPC-5 cell viability (%, Mean±SD, n=3)
| Group | Cell viability |
|---|---|
| Normal | 100±1.32 |
| Model | 67.78±5.06* |
| Guijianyu | 88.66±2.39# |
| RAGE agonist | 48.38±7.00## |
| Guijianyu+RAGE agonist | 76.40±2.85** |
| P | <0.001 |
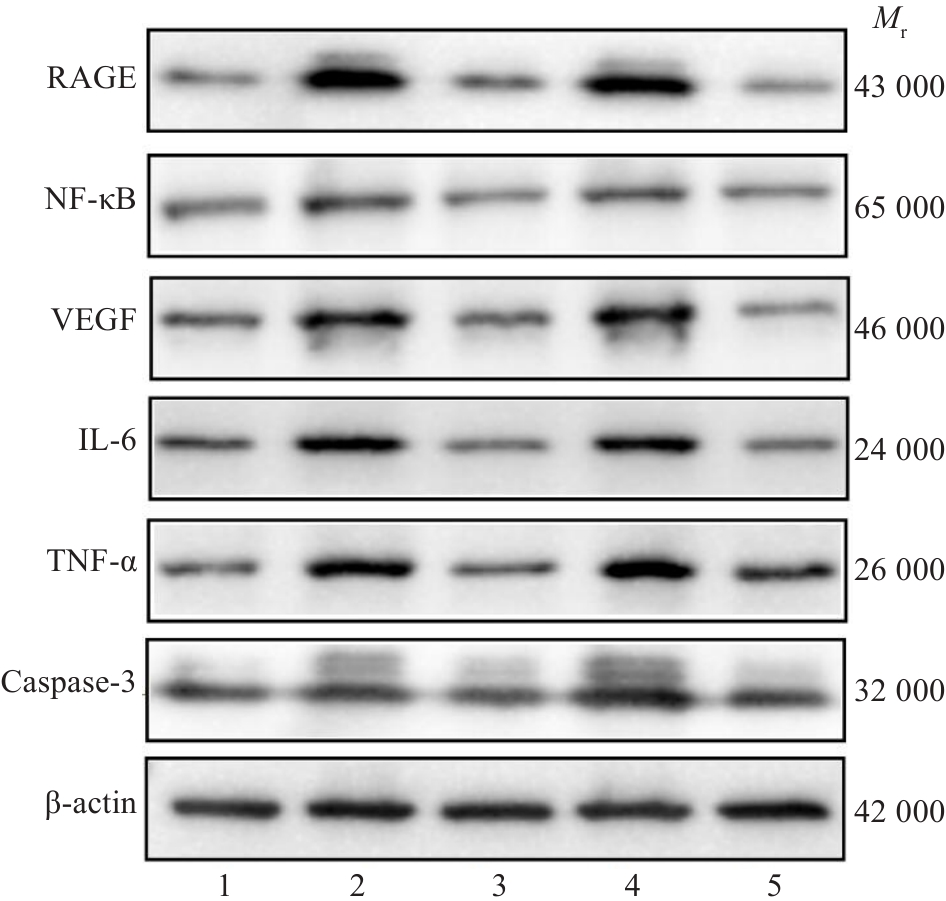
图3 各组细胞RAGE、NF-κB(p65)、VEGFA、TNF-α、IL-6、Caspase-3蛋白表达情况
Fig.3 Protein expressions of RAGE, NF-κB(p65), VEGFA, TNF-α, IL-6, and caspase-3 in MPC-5 cells in each group. 1: Normal group; 2: Model group; 3: Guijianyu group; 4: RAGE agonist group; 5: Guijianyu+RAGE agonist group.
| Group | RAGE | NF-κB(p65) | VEGFA | TNF-α | IL-6 | Caspase-3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.00±0.05 | 1.00±0.05 | 1.00±0.05 | 1.00±0.05 | 1.00±0.05 | 1.00±0.05 |
| 2 | 2.01±0.17* | 1.41±0.19* | 1.55±0.27* | 1.51±0.12** | 1.53±0.14* | 1.64±0.24* |
| 3 | 1.14±0.31# | 0.91±0.14# | 1.15±0.16# | 1.06±0.14# | 1.16±0.14# | 1.20±0.25# |
| 4 | 2.11±0.29 | 1.17±0.13 | 1.57±0.29 | 1.37±0.23 | 1.37±0.07 | 1.81±0.13 |
| 5 | 0.96±0.56## | 0.99±0.24 | 1.11±0.12## | 0.96±0.39## | 1.01±0.20## | 1.13±0.14## |
| P | 0.002 | 0.023 | 0.015 | 0.039 | 0.002 | 0.001 |
表6 鬼箭羽对DKD模型MPC-5细胞中RAGE、VEGFA、TNF-α、NF-κB(p65)、IL-和Caspase-3蛋白表达的影响
Tab.6 Effects of Guijianyu on the protein expressions of RAGE, VEGFA, TNF-α, NF-κB (p65), IL-6 and Caspase-3 in MPC-5 cells in each group (Mean±SD, n=3)
| Group | RAGE | NF-κB(p65) | VEGFA | TNF-α | IL-6 | Caspase-3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.00±0.05 | 1.00±0.05 | 1.00±0.05 | 1.00±0.05 | 1.00±0.05 | 1.00±0.05 |
| 2 | 2.01±0.17* | 1.41±0.19* | 1.55±0.27* | 1.51±0.12** | 1.53±0.14* | 1.64±0.24* |
| 3 | 1.14±0.31# | 0.91±0.14# | 1.15±0.16# | 1.06±0.14# | 1.16±0.14# | 1.20±0.25# |
| 4 | 2.11±0.29 | 1.17±0.13 | 1.57±0.29 | 1.37±0.23 | 1.37±0.07 | 1.81±0.13 |
| 5 | 0.96±0.56## | 0.99±0.24 | 1.11±0.12## | 0.96±0.39## | 1.01±0.20## | 1.13±0.14## |
| P | 0.002 | 0.023 | 0.015 | 0.039 | 0.002 | 0.001 |
| Group | RAGE | NF-κB (p65) | VEGFA | IL-6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.00±0.07 | 1.00±0.05 | 1.00±0.11 | 1.00±0.11 |
| 2 | 4.44±0.40* | 2.49±0.21* | 1.68±0.11* | 2.09±0.12* |
| 3 | 1.30±0.20# | 1.15±0.07# | 1.13±0.30# | 1.11±0.05# |
| 4 | 5.04±0.88 | 2.64±0.15 | 2.77±0.08 | 3.62±1.19 |
| 5 | 1.48±0.40## | 1.36±0.24## | 1.31±0.27## | 1.34±0.25## |
| P | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.001 |
表7 鬼箭羽对DKD模型MPC-5细胞中RAGE、NF-κB(p65)、IL-6、VEGFA mRNA表达的影响
Tab.7 Effect of Guijianyu on mRNA expressions of RAGE, NF-κB (p65), IL-6 and VEGFA in MPC-5 cells in each group (Mean±SD, n=3)
| Group | RAGE | NF-κB (p65) | VEGFA | IL-6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.00±0.07 | 1.00±0.05 | 1.00±0.11 | 1.00±0.11 |
| 2 | 4.44±0.40* | 2.49±0.21* | 1.68±0.11* | 2.09±0.12* |
| 3 | 1.30±0.20# | 1.15±0.07# | 1.13±0.30# | 1.11±0.05# |
| 4 | 5.04±0.88 | 2.64±0.15 | 2.77±0.08 | 3.62±1.19 |
| 5 | 1.48±0.40## | 1.36±0.24## | 1.31±0.27## | 1.34±0.25## |
| P | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.001 |
| [1] | Audzeyenka I, Bierżyńska A, Lay AC. Podocyte bioenergetics in the development of diabetic nephropathy: the role of mitochondria[J]. Endocrinology, 2022, 163(1): bqab234. doi:10.1210/endocr/bqab234 |
| [2] | Zhang L, Wen Z, Han L, et al. Research progress on the pathological mechanisms of podocytes in diabetic nephropathy[J]. J Diabetes Res, 2020, 2020: 7504798. doi:10.1155/2020/7504798 |
| [3] | Fedulovs A, Janevica J, Kruzmane L, et al. Glucose control and variability assessed by continuous glucose monitoring in patients with type 1 diabetes and diabetic kidney disease[J]. Biomed Rep, 2025, 22(2): 23. doi:10.3892/br.2024.1901 |
| [4] | Li YJ, Duan YQ, Chu QQ, et al. G-protein coupled receptor GPR124 protects against podocyte senescence and injury in diabetic kidney disease[J]. Kidney Int, 2025, 107(4): 652-65. doi:10.1016/j.kint.2024.12.013 |
| [5] | 徐 洋, 王 敏, 张恒璐, 等. 达格列净通过Rffl抑制STAT1/TGF-β1信号通路改善糖尿病肾病肾小管上皮细胞EMT和纤维化[J]. 南京医科大学学报: 自然科学版, 2023, 43(9): 1201-7. |
| [6] | 陆钰婷, 高常柏, 张童燕, 等. 鬼箭羽的本草学研究[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2020, 31(7): 1632-4. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1008-0805.2020.07.028 |
| [7] | 郭延秀, 席少阳, 马 毅, 等. 鬼箭羽化学成分及药理活性研究进展[J]. 中国现代应用药学, 2021, 38(18): 2305-16. |
| [8] | 陈明环, 王咏兰, 李相国, 等. 鬼箭羽醇提取物通过阻止氧化应激和抑制TNF-α-NF-κB及TβR1-Smad2/3通路减轻兔肾缺血再灌注损伤[J]. 中国病理生理杂志, 2022, 38(4): 688-97. |
| [9] | 杜雨璇, 谢治深, 徐江雁, 等. 鬼箭羽化学成分和药理作用的研究进展及其质量标志物预测[J]. 天然产物研究与开发, 2024, 36(6): 1064-81, 1044. |
| [10] | Chen YP, Chen J, Jiang M, et al. Loganin and catalpol exert cooperative ameliorating effects on podocyte apoptosis upon diabetic nephropathy by targeting AGEs-RAGE signaling[J]. Life Sci, 2020, 252: 117653. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117653 |
| [11] | Nishad R, Meshram P, Singh AK, et al. Activation of Notch1 signaling in podocytes by glucose-derived AGEs contributes to proteinuria[J]. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care, 2020, 8(1): e001203. doi:10.1136/bmjdrc-2020-001203 |
| [12] | Zhuang GD, Deng SM, Chen MD, et al. Huang-Lian-Jie-Du Decoction alleviates diabetic encephalopathy by regulating inflammation and pyroptosis via suppression of AGEs/RAGE/NF-κB pathways[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2025, 337: 118787. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.118787 |
| [13] | Shi Q, Zhou T, Hou W, et al. Isoliquiritigenin protects against diabetic nephropathy in db/db mice by inhibiting advanced glycation end product-receptor for advanced glycation end product axis[J]. Drug Dev Res, 2025, 86(1): e70051. doi:10.1002/ddr.70051 |
| [14] | Wang WT, Zhao WS, Song XX, et al. Zhongfeng decoction attenuates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting autophagy via regulating the AGE-RAGE signaling pathway[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2025, 336: 118718. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.118718 |
| [15] | 王瑾瑾, 牛钰琪, 马倩倩, 等. 基于AGEs-RAGE信号转导通路的鬼箭羽干预糖尿病肾病小鼠作用机制研究 [J]. 中国慢性病预防与控制, 2025, 33(2): 126-34. |
| [16] | 樊俐慧, 王志刚, 杨 霞. 基于网络药理学与细胞实验探讨葛连调糖丸对2型糖尿病的预防作用 [J]. 中成药,47(5): 1-10. |
| [17] | Shen S, Zhong H, Zhou X, et al. Advances in Traditional Chinese Medicine research in diabetic kidney disease treatment[J]. Pharm Biol, 2024, 62(1): 222-32. doi:10.1080/13880209.2024.2314705 |
| [18] | Benzing T, Salant D. Insights into glomerular filtration and albuminuria[J]. N Engl J Med, 2021, 384(15): 1437-46. doi:10.1056/nejmra1808786 |
| [19] | Tomita I, Kume S, Sugahara S, et al. SGLT2 inhibition mediates protection from diabetic kidney disease by promoting ketone body-induced mTORC1 inhibition[J]. Cell Metab, 2020, 32(3): 404-19.e6. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2020.06.020 |
| [20] | 卢 昭, 闫 镛. 闫镛教授治疗糖尿病肾病经验; proceedings of the 中华中医药学会糖尿病分会全国中医药糖尿病大会(第十九次), 中国安徽合肥, F, 2018 [C]. |
| [21] | 洑晓哲, 张耀夫, 赵进喜, 等. 赵进喜应用鬼箭羽、牛蒡子对药治疗糖尿病肾脏病经验探析 [J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2021, 36(8): 4742-4. |
| [22] | 张娉娜, 包 能, 孔 薇. 孔薇治疗糖尿病肾病经验举隅[J]. 中国中医基础医学杂志, 2020, 26(9): 1384-6. |
| [23] | 陆 跃, 陈仁寿. 鬼箭羽的本草考证[J]. 中药材, 2020, 43(4): 1007-11. |
| [24] | 王瑾瑾, 牛钰琪, 马倩倩, 等. 鬼箭羽对糖尿病肾病小鼠肾脏结构及功能的影响[J]. 郑州大学学报: 医学版, 2024, 59(4): 454-8. |
| [25] | Lehtonen S, Meri S. Podocyte-mediated protection from kidney injury[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2025, 36(2): 166-8. doi:10.1681/asn.0000000594 |
| [26] | Lv C, Qiao XH, Shi Z, et al. Dihuangzicao granules regulate the AGE/RAGE/NF‑κB signaling pathway to inhibit inflammation in psoriatic mice via network pharmacologyand experimental validation[J]. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen, 2024, 27: doi: 10.2174/0113862073313333240912080819. Online ahead of print. doi:10.2174/0113862073313333240912080819 |
| [27] | Zhang XM, Min XR, Xie HX, et al. Piperazine ferulate inhibits diabetic nephropathy by suppressing AGE/RAGE-mediated inflammatory signaling in rats and podocytes[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2024, 15: 1394369. doi:10.3389/fphar.2024.1394369 |
| [28] | Li Z, Zhao Z, Chen S, et al. Ge-Gen-Qin-Lian decoction alleviates the symptoms of type 2 diabetes mellitus with inflammatory bowel disease via regulating the AGE-RAGE pathway[J]. BMC Complement Med Ther, 2024, 24(1): 225. doi:10.1186/s12906-024-04526-x |
| [29] | Li S, Fan C, Li X, et al. Cannabidiol ameliorates inflammatory response partly by AGE-RAGE pathway in diabetic mice[J]. Drug Dev Res, 2023, 84(7): 1427-36. doi:10.1002/ddr.22093 |
| [30] | Ma X, Hao C, Yu M, et al. Investigating the molecular mechanism of quercetin protecting against podocyte injury to attenuate diabetic nephropathy through network pharmacology, MicroarrayData analysis, and molecular docking[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2022, 2022: 7291434. doi:10.1155/2022/7291434 |
| [31] | Fatima N, Khan MI, Jawed H, et al. Cinnamaldehyde ameliorates diabetes-induced biochemical impairments and AGEs macromo-lecules in a pre-clinical model of diabetic nephropathy[J]. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol, 2024, 25(1): 85. doi:10.1186/s40360-024-00811-0 |
| [32] | Jahan H, Tufail P, Shamim S, et al. 1, 2, 4-Triazine derivatives as agents for the prevention of AGE-RAGE-mediated inflammatory cascade in THP-1 monocytes: an approach to prevent inflammation-induced late diabetic complications[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2024, 142(pt b): 113145. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113145 |
| [33] | Wang BJ, Jiang TD, Qi YY, et al. AGE-RAGE axis and cardiovascular diseases: pathophysiologic mechanisms and prospects for clinical applications[J]. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther, 2024: doi: 10.1007/s10557-024-07639-0 . Online ahead of print. |
| [34] | Fang Y, Zhang Y, Jia C, et al. Niaoduqing alleviates podocyte injury in high glucose model via regulating multiple targets and AGE/RAGE pathway: Network pharmacology and experimental validation[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2023, 14: 1047184. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1047184 |
| [35] | Tufro A, Veron D. VEGF and podocytes in diabetic nephropathy[J]. Semin Nephrol, 2012, 32(4): 385-93. doi:10.1016/j.semnephrol.2012.06.010 |
| [36] | Mohebi R, Liu Y, Hansen MK, et al. Associations of angiopoietin 2 and vascular endothelial growth factor-a concentrations with clinical end points[J]. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol, 2024, 19(4): 429-37. doi:10.2215/cjn.0000000000000389 |
| [1] | 李天宏, 覃新芳, 韦丽丽, 毕慧欣. 终末期肾病患者血清晚期糖基化终末产物水平是首次动静脉内瘘术后狭窄的危险因素[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(8): 1663-1671. |
| [2] | 郭克磊, 李颖利, 宣晨光, 侯紫君, 叶松山, 李林运, 陈丽平, 韩立, 卞华. 益气养阴化浊通络方通过调控miR-21a-5p/FoxO1/PINK1介导的线粒体自噬减轻糖尿病肾病小鼠的足细胞损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 27-34. |
| [3] | 刘本菊, 王业磊, 任海文, 欧丽雯, 邓轩, 黄梦欣, 吴鑫, 龚权. 3-甲基腺嘌呤通过抑制AKT信号减轻糖尿病小鼠的早期肾损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1236-1242. |
| [4] | 王瑾瑾, 崔文飞, 窦雪伟, 尹冰磊, 牛钰琪, 牛羚, 闫国立. 鬼箭羽通过调节EGFR酪氨酸激酶抑制剂耐药信号通路延缓糖尿病肾病的进展[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1243-1255. |
| [5] | 陈君洁, 黄传兵, 李 明. 健脾滋肾方抑制系统性红斑狼疮患者的足细胞自噬:基于网络药理学和临床研究[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 465-473. |
| [6] | 万 璐, 钱宇池, 倪文静, 卢宇欣, 李 巍, 潘 艳, 陈卫东. 利格列汀通过激活AMPK/PGC-1α/TFAM通路改善糖尿病肾脏疾病线粒体生物合成[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(12): 2053-2060. |
| [7] | 王欢岚, 刘 红, 张燕敏, 陈伟栋. miR-34a通过靶向抑制Notch信号通路减轻糖尿病肾病小鼠的足细胞损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(12): 1839-1845. |
| [8] | 丁晓倩,胡 赟,罗 丹,唐 宇,李彩玉,郑雷蕾. 晚期糖基化终末产物对破骨细胞分化不同阶段的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2020, 40(04): 573-579. |
| [9] | 何朝生,史伟,李锐钊,张丽. NFAT2参与高糖诱导的大鼠足细胞凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2018, 38(10): 1270-. |
| [10] | 朱晓娜,王玉环,吴娟娟,董鹏,张敏. VEGF及TRPC6的表达与糖尿病肾病大鼠足细胞损伤的相关机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2018, 38(03): 296-. |
| [11] | 庞若宇,关美萍,郑宗基,薛耀明. 二甲双胍对糖基化终末产物诱导的成纤维细胞凋亡及相关蛋白caspase-3、Bax及Bcl-2表达的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2015, 35(06): 898-. |
| [12] | 何朝生,章斌,谢少庭,杨芸,马娟,史伟. 阿米洛利抑制尿激酶受体表达及减少蛋白尿的机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2014, 34(11): 1654-. |
| [13] | 赵艳,王建成,李红瑜,贾倩倩,陈斯佳,许兆忠,杜晓燕,陈晓雯,鲁路,黄波,龙海波. 肾康丸通过p38/NF-κB通路抑制AOPP诱导的足细胞炎症因子MCP-1的表达[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2014, 34(09): 1265-. |
| [14] | 冯仲林,刘双信,史 伟,肖厚勤,梁馨苓,刘晓颖,叶智明,王素霞,梁永正,章 斌,王文健,刘艳辉,梅 平,徐丽霞,马建超,夏运风. 嘌呤霉素氨基核苷肾病肾脏中RANK-RANKL的表达[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2014, 34(01): 65-. |
| [15] | 孔卫娜,张佳,高维娟,刘清涛,周利明,柴锡庆. β淀粉样蛋白通过升高ROS水平上调晚期糖基化终末产物受体的表达[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2013, 33(08): 1132-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||