南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (9): 1927-1937.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.09.12
• • 上一篇
何榕茂1( ), 方泽扬1, 张芸芸1, 吴友谅1, 梁世秀2, 计涛3, 陈科全1, 王斯琪1(
), 方泽扬1, 张芸芸1, 吴友谅1, 梁世秀2, 计涛3, 陈科全1, 王斯琪1( )
)
收稿日期:2025-02-23
出版日期:2025-09-20
发布日期:2025-09-28
通讯作者:
王斯琪
E-mail:hrm715821@163.com;2023681011@gzhmu.edu.cn
作者简介:何榕茂,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: hrm715821@163.com
基金资助:
Rongmao HE1( ), Zeyang FANG1, Yunyun ZHANG1, Youliang WU1, Shixiu LIANG2, Tao JI3, Kequan CHEN1, Siqi WANG1(
), Zeyang FANG1, Yunyun ZHANG1, Youliang WU1, Shixiu LIANG2, Tao JI3, Kequan CHEN1, Siqi WANG1( )
)
Received:2025-02-23
Online:2025-09-20
Published:2025-09-28
Contact:
Siqi WANG
E-mail:hrm715821@163.com;2023681011@gzhmu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
目的 探讨铁死亡相关基因在溃疡性结肠炎 (UC)诊断和预测中的的价值。 方法 本研究从GEO数据库中选择UC数据集,筛选差异表达基因(DEGs),进一步从“FerrDb“数据库中筛选与铁死亡相关的DEGs并进行功能分析。通过构建蛋白-蛋白相互作用网络(PPI)筛选枢纽基因,采用CIBERSORT评估UC与对照组的免疫浸润水平差异,以及利用训练集验证枢纽基因在UC诊断中的价值。进一步通过构建UC小鼠模型,利用实时荧光定量PCR (qPCR)检测小鼠结肠中枢纽基因的表达情况。 结果 筛选到76个与铁死亡相关的差异表达基因。功能富集分析显示铁死亡和缺氧途径显著富集。蛋白相互作用网络确定了10个枢纽基因,经数据库验证有9个枢纽基因在UC中高表达。经免疫细胞浸润分析显示,27种细胞类型在UC中明显升高(P<0.05),免疫检查点相关基因均与枢纽基因PPARG相关性最强(P<0.05)。进一步通过训练集验证P4HB、PPARG、STAT3在疾病中预测价值最佳(P<0.05)。通过构建小鼠UC模型验证结肠组织中枢纽基因的表达水平,RT-PCR显示与对照组相比,UC模型中PPARG表达明显降低,P4HB、STAT3表达明显升高(P<0.05)。 结论 铁死亡相关基因在UC的诊断预测中具有重要价值。
何榕茂, 方泽扬, 张芸芸, 吴友谅, 梁世秀, 计涛, 陈科全, 王斯琪. 铁死亡相关基因对溃疡性结肠炎具有诊断预测价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1927-1937.
Rongmao HE, Zeyang FANG, Yunyun ZHANG, Youliang WU, Shixiu LIANG, Tao JI, Kequan CHEN, Siqi WANG. Diagnostic and predictive value of ferroptosis-related genes in patients with ulcerative colitis[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(9): 1927-1937.
| Primer | Sequence |
|---|---|
| GPX4-F | GATGGAGCCCATTCCTGAACC |
| GPX4-R | CCCTGTACTTATCCAGGCAGA |
| NOX1-F | GGTTGGGGCTGAACATTTTTC |
| NOX1-R | TCGACACACAGGAATCAGGAT |
| CYBB-F | TGTGGTTGGGGCTGAATGTC |
| CYBB-R | CTGAGAAAGGAGAGCAGATTTCG |
| PTGS2-F | TTCAACACACTCTATCACTGGC |
| PTGS2-R | AGAAGCGTTTGCGGTACTCAT |
| HIF-1A-F | ACCTTCATCGGAAACTCCAAAG |
| HIF-1A-R | CTGTTAGGCTGGGAAAAGTTAGG |
| ACSL1-F | TGCCAGAGCTGATTGACATTC |
| ACSL1-R | GGCATACCAGAAGGTGGTGAG |
| SMAD7-F | GGCCGGATCTCAGGCATTC |
| SMAD7-R | TTGGGTATCTGGAGTAAGGAGG |
| CD44-F | TCGATTTGAATGTAACCTGCCG |
| CD44-R | CAGTCCGGGAGATACTGTAGC |
| PPARG-F | GGAAGACCACTCGCATTCCTT |
| PPARG-R | GTAATCAGCAACCATTGGGTCA |
表1 引物序列
Tab.1 Primers sequences for qPCR
| Primer | Sequence |
|---|---|
| GPX4-F | GATGGAGCCCATTCCTGAACC |
| GPX4-R | CCCTGTACTTATCCAGGCAGA |
| NOX1-F | GGTTGGGGCTGAACATTTTTC |
| NOX1-R | TCGACACACAGGAATCAGGAT |
| CYBB-F | TGTGGTTGGGGCTGAATGTC |
| CYBB-R | CTGAGAAAGGAGAGCAGATTTCG |
| PTGS2-F | TTCAACACACTCTATCACTGGC |
| PTGS2-R | AGAAGCGTTTGCGGTACTCAT |
| HIF-1A-F | ACCTTCATCGGAAACTCCAAAG |
| HIF-1A-R | CTGTTAGGCTGGGAAAAGTTAGG |
| ACSL1-F | TGCCAGAGCTGATTGACATTC |
| ACSL1-R | GGCATACCAGAAGGTGGTGAG |
| SMAD7-F | GGCCGGATCTCAGGCATTC |
| SMAD7-R | TTGGGTATCTGGAGTAAGGAGG |
| CD44-F | TCGATTTGAATGTAACCTGCCG |
| CD44-R | CAGTCCGGGAGATACTGTAGC |
| PPARG-F | GGAAGACCACTCGCATTCCTT |
| PPARG-R | GTAATCAGCAACCATTGGGTCA |
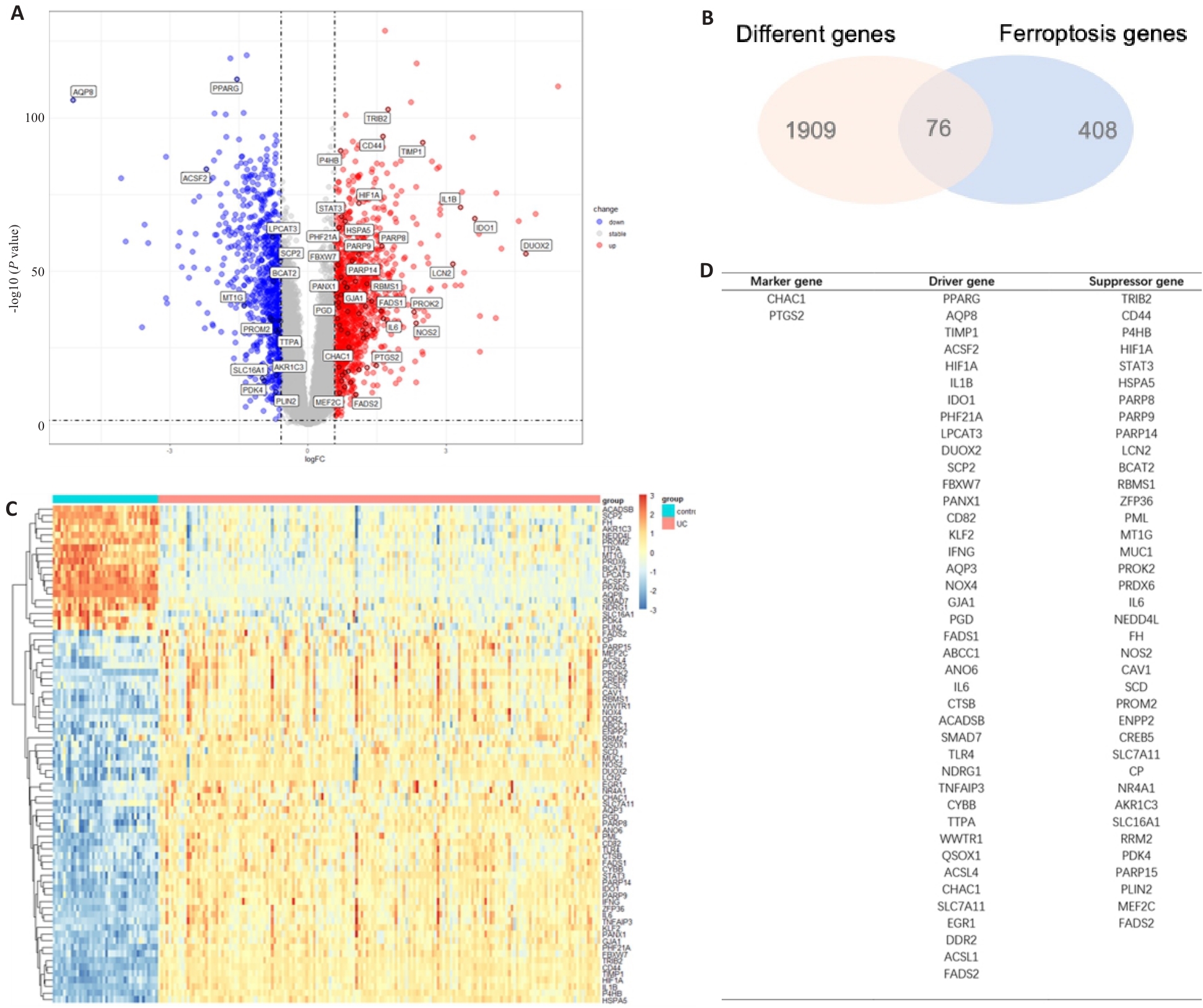
图1 UC患者与对照组铁死亡相关差异基因分析
Fig.1 Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) associated with iron death in UC patients and control subjects. A: Volcano maps of differential gene expressions in UC and control groups. B: Intersection of the DEGs and the genes associated with ferroptosis in UC and control groups. C: Heat maps of the DEGs associated with ferroptosis in UC and control groups. D: Classification of the 76 DEGs associated with ferroptosis, including 41 driver genes, 38 suppressor genes, and 2 marker genes.
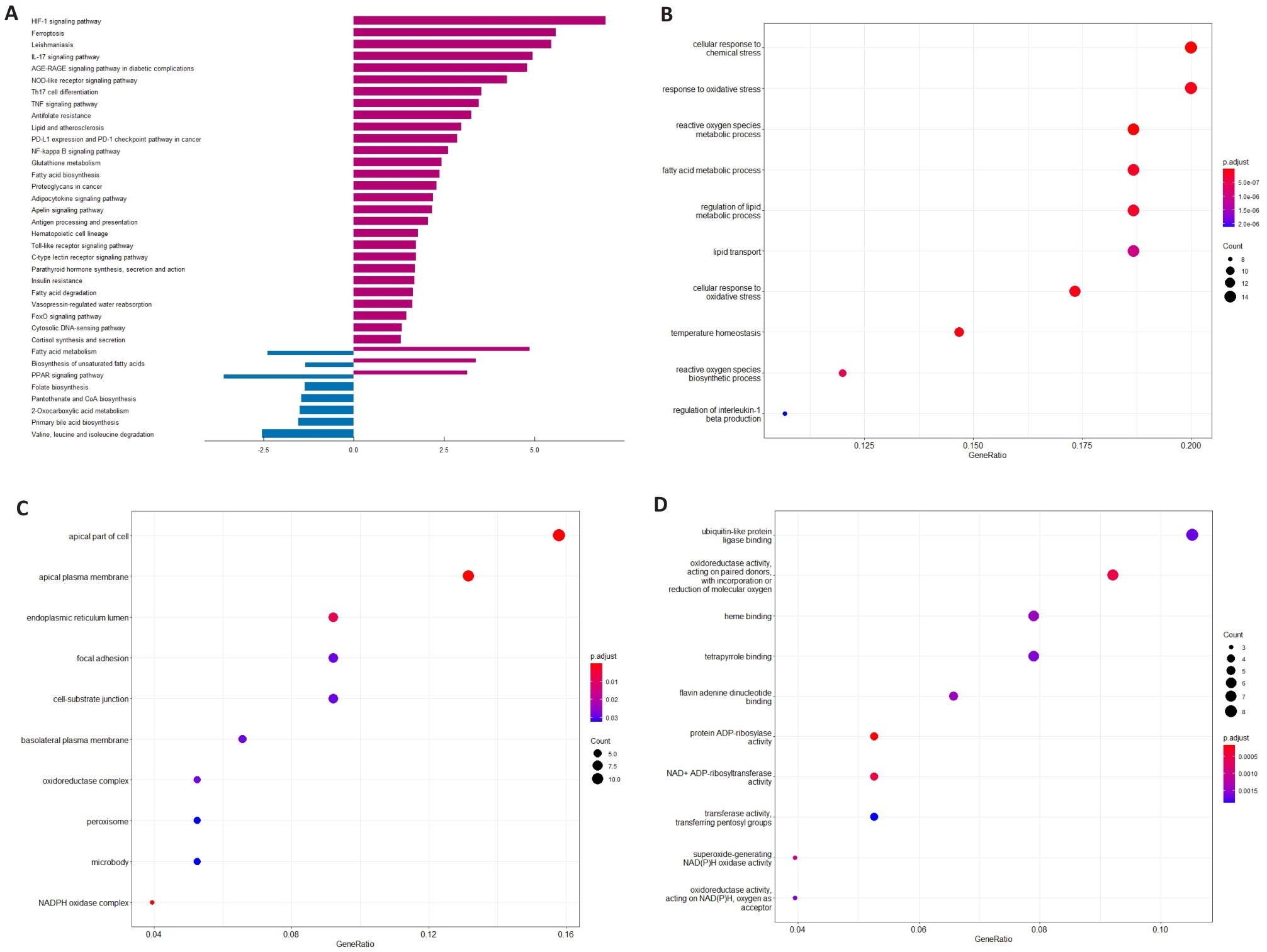
图2 UC患者和对照组中铁死亡相关DEGs富集分析
Fig.2 Analysis of DEGs enrichment in relation to ferroptosis in UC and control groups. A: KEGG path in UC and control groups. B: Main biological processes of the DEGs in UC patients and control group. C: Main cell components of the DEGs in UC patients and control group. D: Main molecular functions of the DEGs in UC patients and control group.
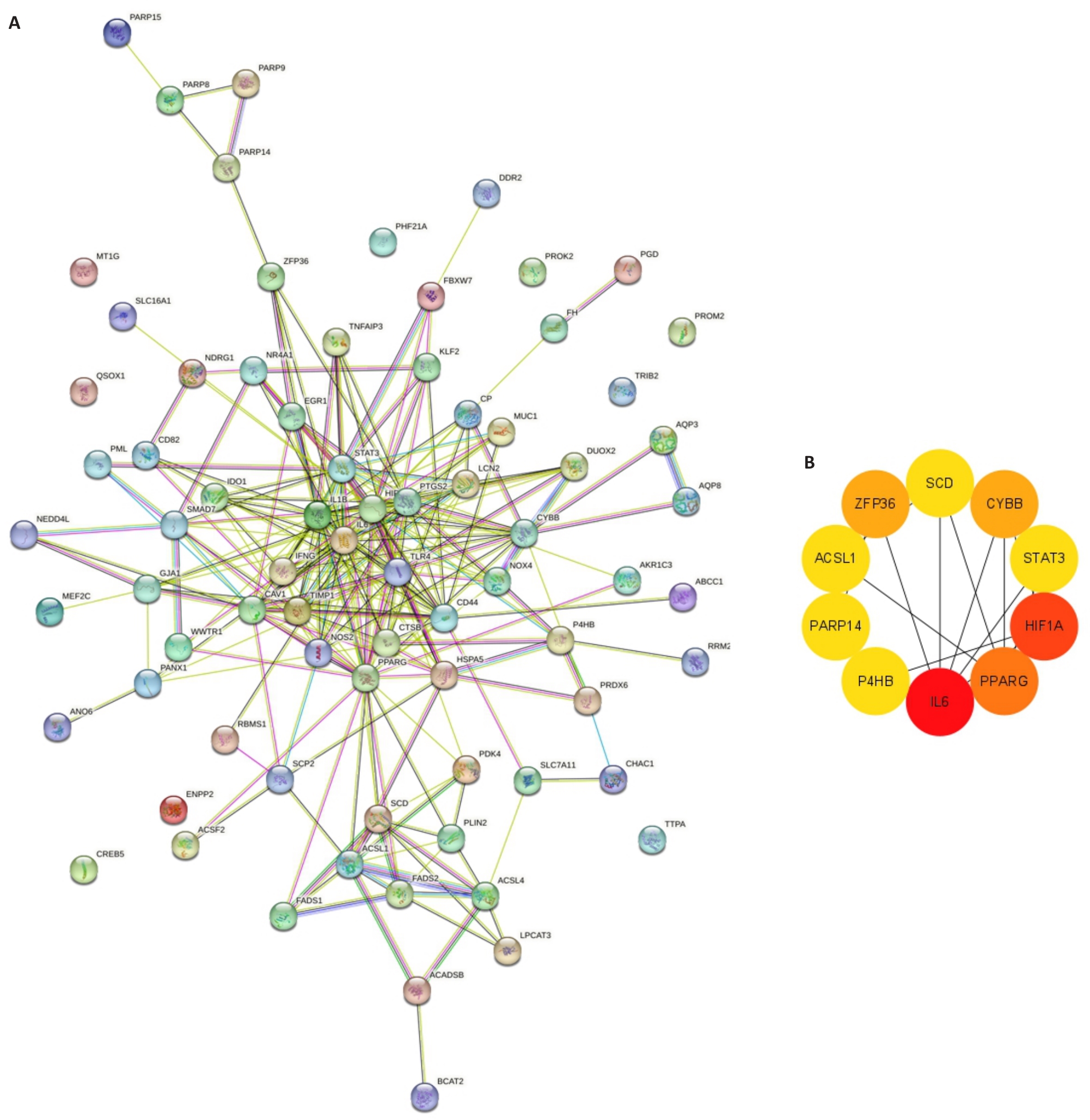
图3 UC患者和对照组与铁死亡相关DEGs PPI分析
Fig.3 PPI analysis of the DEGs associated with ferroptosis in UC and controls. A: PPI network of the DEGs associated with ferroptosis in UC and controls. B: MCC algorithm for screening the main hub gene network.
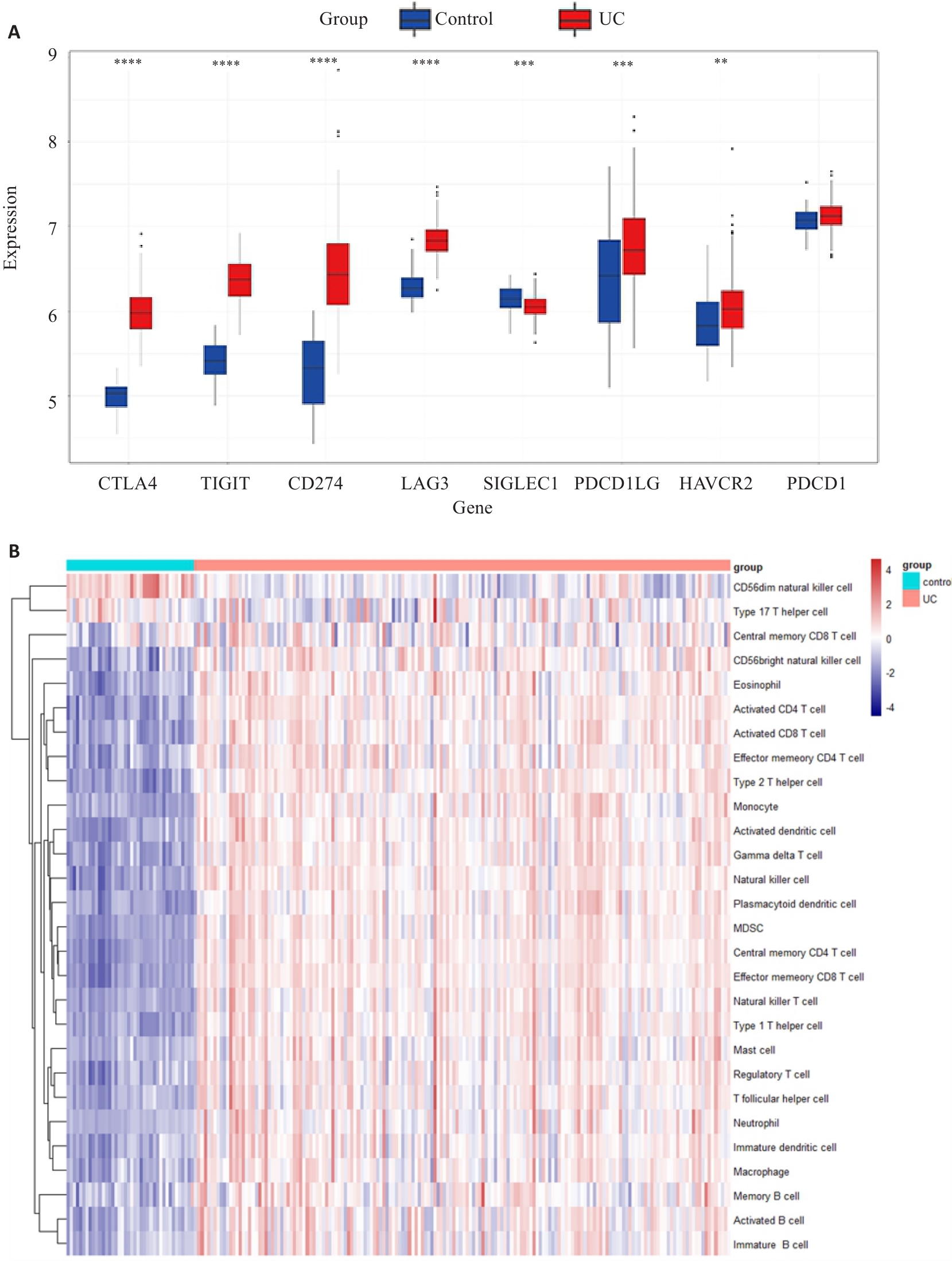
图4 UC与对照组之间的免疫检查点和免疫浸润差异分析
Fig.4 Analysis of the differences in immune checkpoint and immune infiltration between UC and control groups in the dataset. A: Differential expression of 8 immune checkpoint genes between UC and control group. **P<0.01,***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001 (Control group vs UC group). B: Differences in 28 different types of immune cells between UC patients and controls.
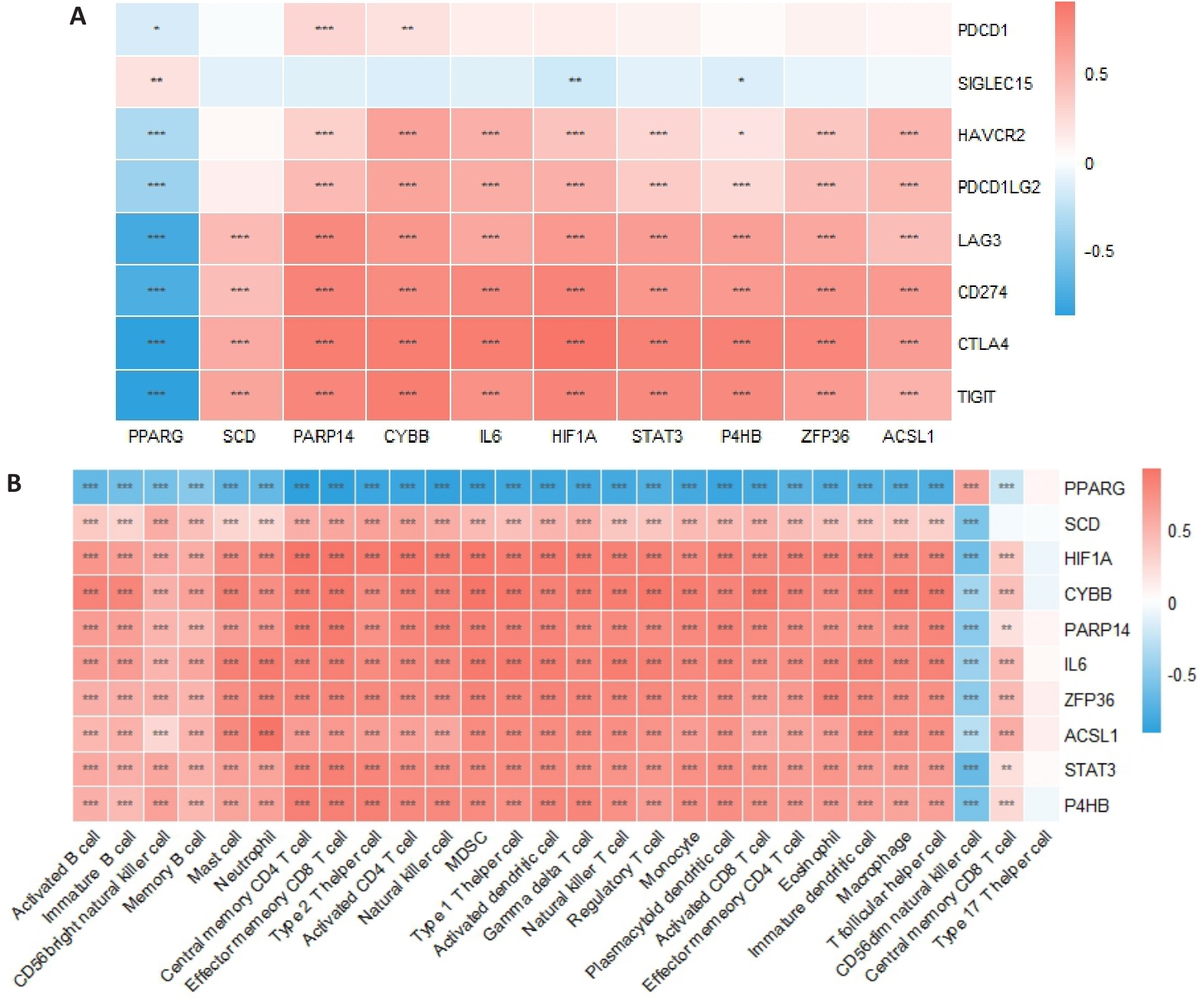
图5 枢纽基因与免疫检查点基因及免疫细胞的关系
Fig.5 Relationship between pivot genes, immune checkpoint genes and immune cells. A: Pearson correlation analysis of the correlations of the hub gene with immune checkpoint gene in UC and control groups. B: CIBERSORT algorithm for assessing the correlation between the key genes and 28 immune cell types in UC and control group. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
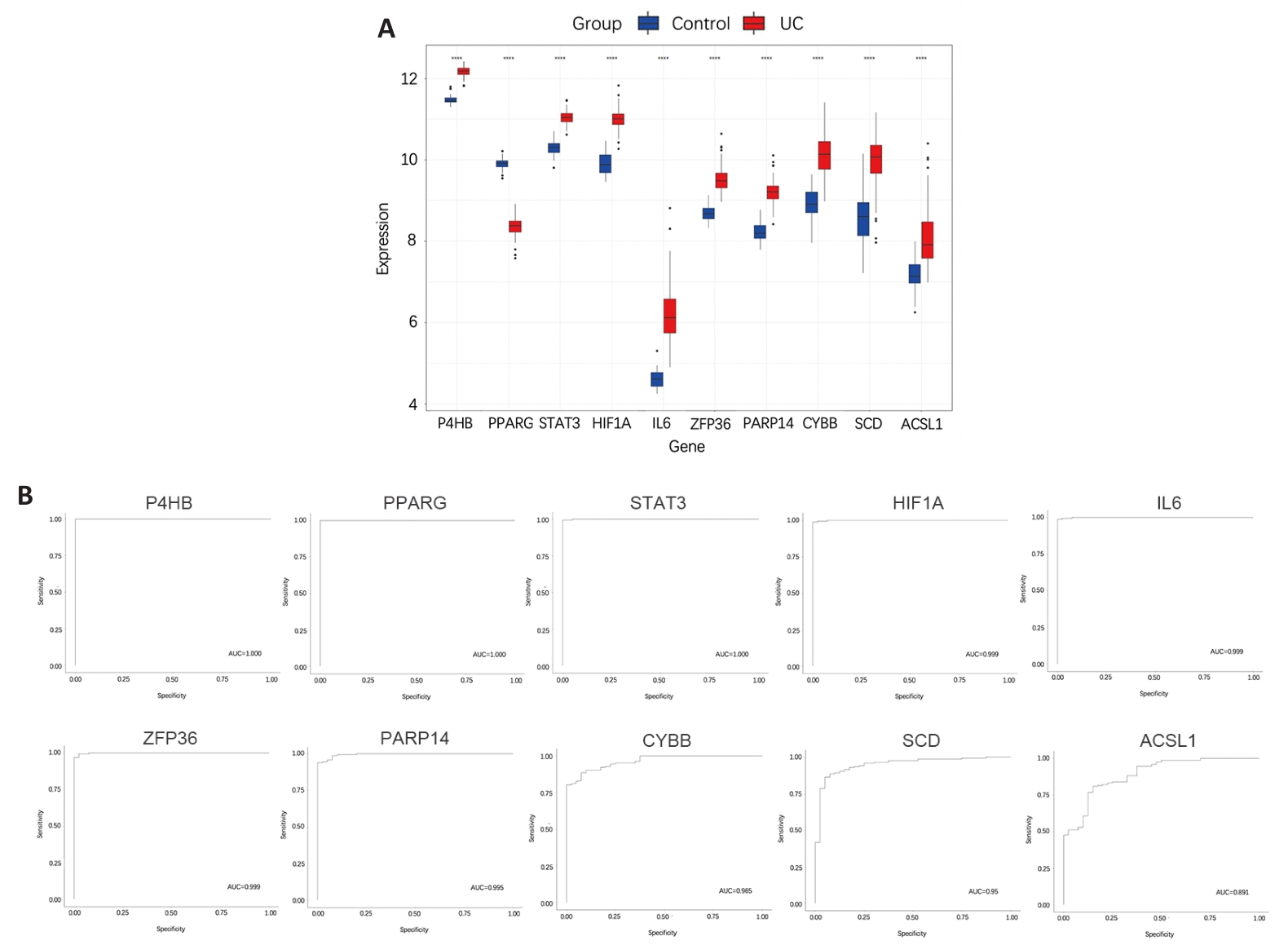
图6 UC训练集中10个枢纽基因诊断价值
Fig.6 Analysis of the diagnostic values of the hub genes for UC using the training set. A: Expression differences of 10 hub genes between UC group and control group. ****P<0.0001, Control group vs UC group. B: ROC curves of the 10 hub genes for UC diagnosis.
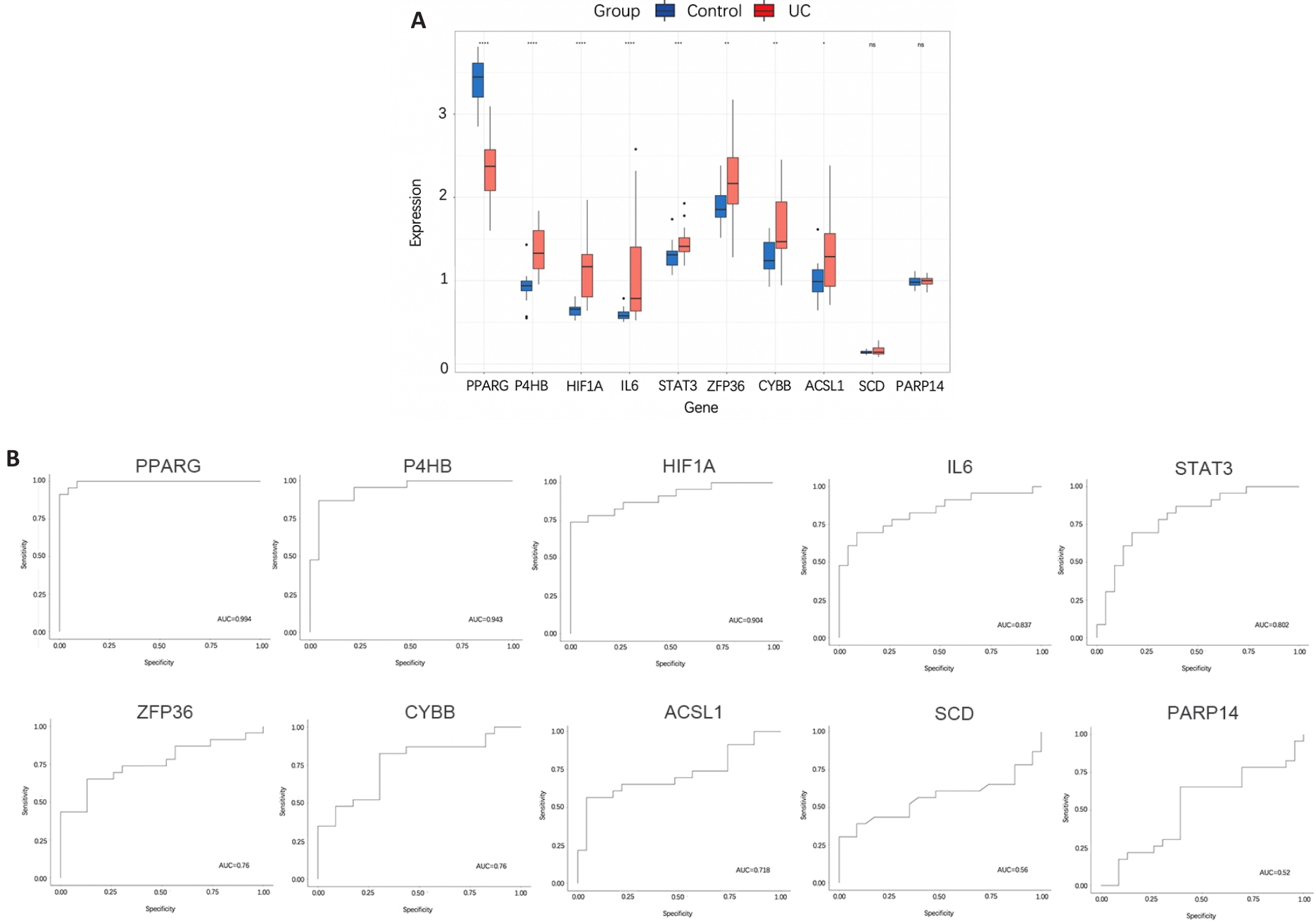
图7 验证集中10个枢纽基因预测UC价值
Fig.7 Verification of the value of the 10 hub genes for predicting UC. A: Differences in the expression of 10 hub genes between UC group and control group. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001 (Control group vs UC group). B: ROC curve of the 10 hub genes for predicting UC.
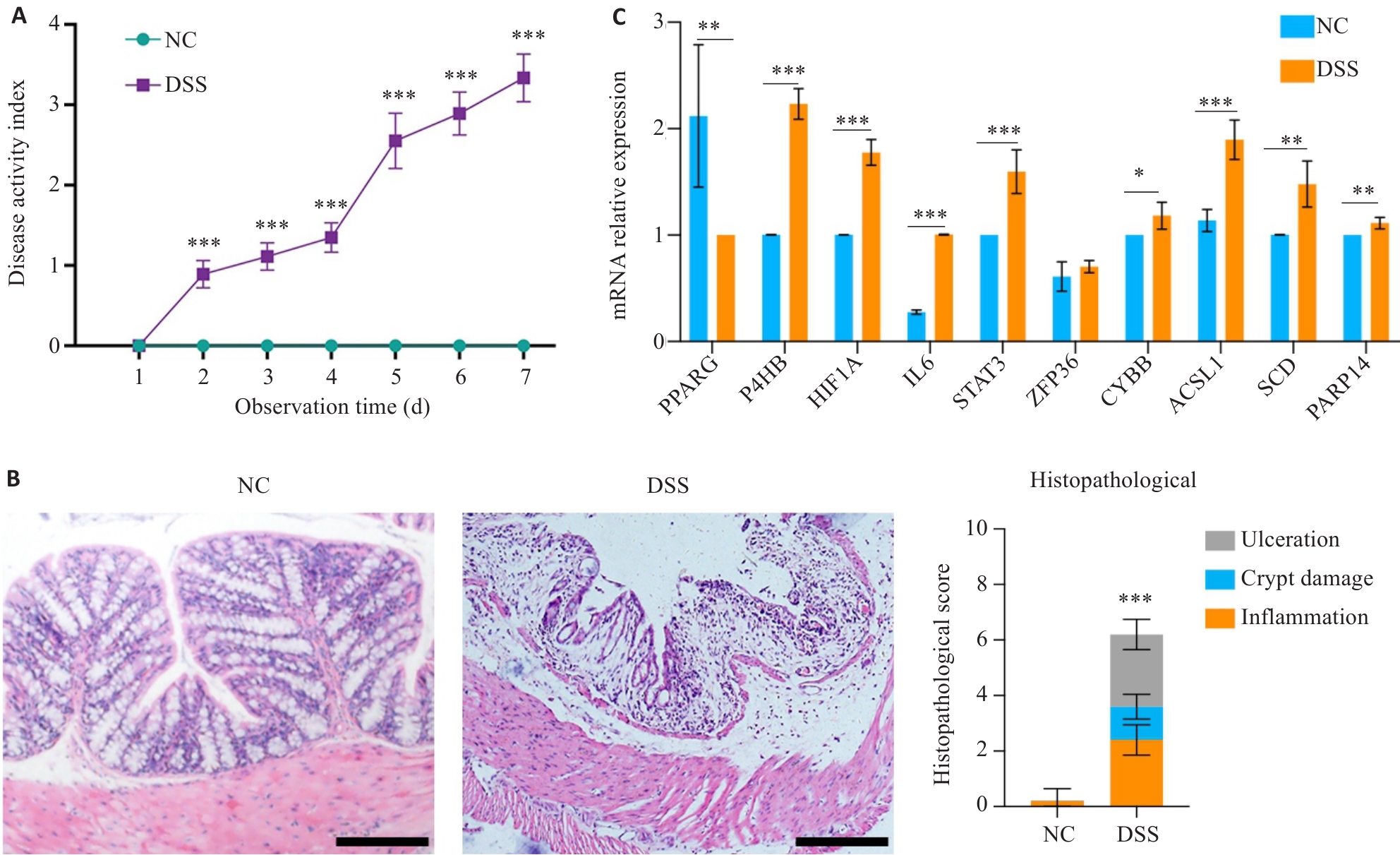
图8 对照组UC模型小鼠模型结肠枢纽基因表达情况
Fig.8 Hub gene expressions in the colon tissues of the UC mouse model. A: Comparison of disease activity index (DAI) between control and UC mice. B: HE staining of the colon tissue in control and UC mice (Scale bar=50 μm). C: Comparison of the expression levels of the 10 hub genes in the colon tissues between control and UC mice. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs NC group.
| [1] | Aniwan S, Santiago P, Loftus EV Jr, et al. The epidemiology of inflammatory bowel disease in Asia and Asian immigrants to Western countries[J]. UEG J, 2022, 10(10): 1063-76. doi:10.1002/ueg2.12350 |
| [2] | Gros B, Kaplan GG. Ulcerative colitis in adults[J]. Jama, 2023, 330(10): 951. doi:10.1001/jama.2023.15389 |
| [3] | Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death[J]. Cell, 2012, 149(5): 1060-72. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.042 |
| [4] | Wang S, Liu W, Wang J, et al. Curculigoside inhibits ferroptosis in ulcerative colitis through the induction of GPX4[J]. Life Sci, 2020, 259: 118356. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118356 |
| [5] | Chen YJ, Yan WY, Chen YQ, et al. SLC6A14 facilitates epithelial cell ferroptosis via the C/EBPβ-PAK6 axis in ulcerative colitis[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2022, 79(11): 563. doi:10.1007/s00018-022-04594-7 |
| [6] | Xu M, Tao J, Yang Y, et al. Ferroptosis involves in intestinal epithelial cell death in ulcerative colitis[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2020, 11(2): 86. doi:10.1038/s41419-020-2299-1 |
| [7] | Deng L, He S, Li Y, et al. Identification of lipocalin 2 as a potential ferroptosis-related gene in ulcerative colitis[J]. Inflamm Bowel Dis, 2023, 29(9): 1446-57. doi:10.1093/ibd/izad050 |
| [8] | Chen YJ, Wang JY, Li JT, et al. Astragalus polysaccharide prevents ferroptosis in a murine model of experimental colitis and human Caco-2 cells via inhibiting NRF2/HO-1 pathway[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2021, 911: 174518. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174518 |
| [9] | Xu C, Liu Z, Xiao J. Ferroptosis: a double-edged sword in gastrointestinal disease[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(22): 12403. doi:10.3390/ijms222212403 |
| [10] | Ni JH, Zhang LJ, Feng GZ, et al. Vanillic acid restores homeostasis of intestinal epithelium in colitis through inhibiting CA9/STIM1-mediated ferroptosis[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2024, 202: 107128. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2024.107128 |
| [11] | Long D, Mao CH, Huang YT, et al. Ferroptosis in ulcerative colitis: Potential mechanisms and promising therapeutic targets[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2024, 175: 116722. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116722 |
| [12] | Ye Y, Liu L, Jing Y, et al. Ferroptosis: a therapeutic opportunity of inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Chin Med J: Engl, 2024, 137(7): 874-6. doi:10.1097/cm9.0000000000002998 |
| [13] | Rahman MS, Alam MB, Kim YK, et al. Activation of Nrf2/HO-1 by peptide YD1 attenuates inflammatory symptoms through suppression of TLR4/MYyD88/NF‑κB signaling cascade[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(10): 5161. doi:10.3390/ijms22105161 |
| [14] | Huang J, Zhang J, Ma J, et al. Inhibiting ferroptosis: a novel approach for ulcerative colitis therapeutics[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2022, 2022: 9678625. doi:10.1155/2022/9678625 |
| [15] | 黄柳芳, 吴 博, 王 莹. 儿童溃疡性结肠炎手术治疗的预测标志物分析[J]. 临床儿科杂志, 2025, 43(2): 120-7. doi:10.12372/jcp.2025.24e0051 |
| [16] | Fajas L, Auboeuf D, Raspé E, et al. The organization, promoter analysis, and expression of the human PPARγ gene[J]. J Biol Chem, 1997, 272(30): 18779-89. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.30.18779 |
| [17] | Saez E, Tontonoz P, Nelson MC, et al. Activators of the nuclear receptor PPARgamma enhance colon polyp formation[J]. Nat Med, 1998, 4(9): 1058-61. doi:10.1038/2042 |
| [18] | Braissant O. Differential expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-, -, and -during rat embryonic development[J]. Endocrinology, 1998, 139(6): 2748-54. doi:10.1210/en.139.6.2748 |
| [19] | Michalik L, Wahli W. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: three isotypes for a multitude of functions[J]. Curr Opin Biotechnol, 1999, 10(6): 564-70. doi:10.1016/s0958-1669(99)00030-0 |
| [20] | Zhang W, Gong M, Zhang W, et al. Thiostrepton induces ferroptosis in pancreatic cancer cells through STAT3/GPX4 signalling[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2022, 13(7): 630. doi:10.1038/s41419-022-05082-3 |
| [21] | Ouyang SM, Li HX, Lou LL, et al. Inhibition of STAT3-ferroptosis negative regulatory axis suppresses tumor growth and alleviates chemoresistance in gastric cancer[J]. Redox Biol, 2022, 52: 102317. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2022.102317 |
| [22] | Sugimoto K. Role of STAT3 in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2008, 14(33): 5110-4. doi:10.3748/wjg.14.5110 |
| [23] | Alhouayek M, Buisseret B, Paquot A, et al. The endogenous bioactive lipid prostaglandin D2-glycerol ester reduces murine colitisviaDP1 and PPARγ receptors[J]. FASEB J, 2018, 32(9): 5000-11. doi:10.1096/fj.201701205r |
| [24] | Farrokhyar F, Swarbrick ET, Irvine EJ. A critical review of epidemiological studies in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Scand J Gastroenterol, 2001, 36(1): 2-15. doi:10.1080/00365520150218002 |
| [25] | Cox DG, Crusius JB, Peeters PH, et al. Haplotype of prostaglandin synthase 2/cyclooxygenase 2 is involved in the susceptibility to inflammatory bowel disease[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2005, 11(38): 6003-8. doi:10.3748/wjg.v11.i38.6003 |
| [26] | Wallace JL. Prostaglandin biology in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Gastroenterol Clin North Am, 2001, 30(4): 971-80. doi:10.1016/s0889-8553(05)70223-5 |
| [27] | Feng D, Wang J, Li D, et al. Targeting prolyl 4-hydroxylase subunit beta (P4HB) in cancer: new roads to travel[J]. Aging Dis, 2023, 15(6): 2369-80. |
| [28] | Feng D, Li L, Li D, et al. Prolyl 4-hydroxylase subunit beta (P4HB) could serve as a prognostic and radiosensitivity biomarker for prostate cancer patients[J]. Eur J Med Res, 2023, 28(1): 245. doi:10.1186/s40001-023-01215-2 |
| [29] | Butturini E, Carcereri de Prati A, Mariotto S. Redox regulation of STAT1 and STAT3 signaling[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(19): E7034. doi:10.3390/ijms21197034 |
| [30] | Thuya WL, Cao Y, Ho PC, et al. Insights into IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signaling in the tumor microenvironment: Implications for cancer therapy[J]. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev, 2025, doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2025.01.003 . Online ahead of print. |
| [31] | Zhang W, Gong M, Zhang W, et al. Thiostrepton induces ferroptosis in pancreatic cancer cells through STAT3/GPX4 signalling[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2022, 13(7): 630. doi:10.1038/s41419-022-05082-3 |
| [32] | Ouyang SM, Li HX, Lou LL, et al. Inhibition of STAT3-ferroptosis negative regulatory axis suppresses tumor growth and alleviates chemoresistance in gastric cancer[J]. Redox Biol, 2022, 52: 102317. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2022.102317 |
| [33] | Huang F, Zhang S, Li X, et al. STAT3-mediated ferroptosis is involved in ulcerative colitis[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2022, 188: 375-85. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.06.242 |
| [1] | 刘辰菲, 张玮, 曾尧, 梁艳, 王梦婷, 张明芳, 李新元, 王凤超, 杨燕青. 2,6-二甲氧基-1,4-苯醌通过抑制NLRP3炎症小体活化改善葡聚糖硫酸钠诱导的小鼠溃疡性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(8): 1654-1662. |
| [2] | 欧泽金, 李瀛, 陈诗, 王梓译, 何美仪, 陈志成, 唐侍豪, 孟晓静, 王致. 抑制铁死亡减轻敌草快引起的斑马鱼急性肾损伤的机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(8): 1743-1750. |
| [3] | 李军仪, 陈思源, 谢力遥, 王劲, 程奥, 张绍伟, 林继瑜, 方志涵, 潘一锐, 崔翀鹤, 陈庚鑫, 张超, 李栎. 益智仁提取物谷甾醇通过抑制铁死亡中的ETS-5基因表达延长秀丽隐杆线虫的寿命[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(8): 1751-1757. |
| [4] | 陈鑫源, 吴成挺, 李瑞迪, 潘雪芹, 张耀丹, 陶俊宇, 林才志. 双术汤通过P53/SLC7A11/GPX4通路诱导胃癌细胞铁死亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1363-1371. |
| [5] | 张梦影, 赵晨玲, 田丽伟, 余郭芳, 杨文明, 董婷. 肝豆扶木汤通过GPX4/ACSL4/ALOX15通路抑制铁死亡改善Wilson病小鼠的肝脏脂肪变性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1471-1478. |
| [6] | 庞金龙, 赵新丽, 张振, 王豪杰, 周星琦, 杨玉梅, 李姗姗, 常小强, 李锋, 李娴. 皮肤黑色素瘤中MMRN2高表达促进肿瘤细胞的侵袭和迁移并与不良预后相关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1479-1489. |
| [7] | 张宏博, 闫梦宇, 张建东, 孙培旺, 汪蕊, 郭园园. 吡非尼酮抑制调节性T细胞延缓小鼠膀胱癌进展[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1513-1518. |
| [8] | 郭晓娟, 杜瑞娟, 陈丽平, 郭克磊, 周彪, 卞华, 韩立. WW结构域E3泛素连接酶1调控卵巢癌肿瘤微环境中的免疫浸润[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(5): 1063-1073. |
| [9] | 张安邦, 孙秀颀, 庞博, 吴远华, 时靖宇, 张宁, 叶涛. 电针预处理通过调节肠道-大脑轴及Nrf2/HO-1信号通路抑制铁死亡减轻大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(5): 911-920. |
| [10] | 张林落, 李长青, 皇玲玲, 周学平, 娄媛媛. 梓醇扶正制毒配伍从SLC7A11/GPX4通路抑制铁死亡减轻雷公藤甲素肝毒性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 810-818. |
| [11] | 高志, 吴傲, 胡仲翔, 孙培养. 类风湿性关节炎中氧化应激与免疫浸润的生物信息学分析[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 862-870. |
| [12] | 申琳, 宋翠豪, 王聪敏, 高西, 安俊红, 李承新, 梁斌, 李霞. 溃疡性结肠炎并发坏疽性脓皮病患者发生营养风险的因素及预测模型[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 514-521. |
| [13] | 殷丽霞, 牛民主, 张可妮, 耿志军, 胡建国, 李江艳, 李静. 升麻素抑制MAPK通路调节辅助性T细胞免疫平衡改善小鼠克罗恩病样结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 595-602. |
| [14] | 王耀彬, 陈柳燕, 罗伊凌, 申继清, 周素芳. NUF2对泛癌的预后和免疫治疗效果的预测价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 137-149. |
| [15] | 季春斐, 左宗超, 王钧, 李妙男. N-乙酰神经氨酸中通过抑制Nrf2轴促进缺氧/复氧损伤的H9C2心肌细胞发生铁死亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 72-79. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||