南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (6): 1297-1306.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.06.19
牛民主1,4,5( ), 殷丽霞2, 乔通4, 尹林2, 张可妮2, 胡建国1,2, 宋传旺4, 耿志军1,3, 李静1,2(
), 殷丽霞2, 乔通4, 尹林2, 张可妮2, 胡建国1,2, 宋传旺4, 耿志军1,3, 李静1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2025-01-20
出版日期:2025-06-20
发布日期:2025-06-27
通讯作者:
李静
E-mail:nmz8033@163.com;lijingbyfy@bbmc.edu.cn
作者简介:牛民主,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: nmz8033@163.com
基金资助:
Minzhu NIU1,4,5( ), Lixia YIN2, Tong QIAO4, Lin YIN2, Keni ZHANG2, Jianguo HU1,2, Chuanwang SONG4, Zhijun GENG1,3, Jing LI1,2(
), Lixia YIN2, Tong QIAO4, Lin YIN2, Keni ZHANG2, Jianguo HU1,2, Chuanwang SONG4, Zhijun GENG1,3, Jing LI1,2( )
)
Received:2025-01-20
Online:2025-06-20
Published:2025-06-27
Contact:
Jing LI
E-mail:nmz8033@163.com;lijingbyfy@bbmc.edu.cn
摘要:
目的 探讨旱莲苷A(ESA)对葡聚糖硫酸钠(DSS)诱导的小鼠炎症性肠病(IBD)模型的影响及其对巨噬细胞极化的作用机制。 方法 体内实验采用24只8~10周龄雄性C57BL/6小鼠,随机分成对照组(WT组)、2.5% DSS诱导模型组(DSS组)、ESA治疗组(DSS+ESA组,50 mg/kg),8只/组。每日记录小鼠体质量,观察粪便性状,通过DAI评分、结肠长度、脾指数、结肠组织HE染色及组织炎症评分、ELISA和RT-qPCR检测的肠黏膜炎症介质(TNF-α、IL-6和iNOS)水平评估ESA对小鼠肠炎症状的影响;采用AB-PAS染色标记杯状细胞,免疫荧光和Western blotting检测紧密连接蛋白水平(ZO-1和Claudin-1),评估ESA对小鼠肠道屏障的作用。体外培养小鼠单核巨噬细胞白血病细胞RAW264.7,分为Control组(M0组)、LPS(1 μg/mL)+IFN-γ(20 ng/mL)诱导组(M1组)和ESA治疗组(ESA组,50 μmol/L),采用流式细胞术评估ESA对小鼠肠系膜淋巴结及体外模型M1型极化标志物(CD86)比例的影响。Western blotting检测JAK2/STAT3通路关键蛋白表达,并使用信号通路激活剂RO8191(20 μmol/L)干预,分析ESA调控巨噬细胞极化的分子机制。 结果 体内实验显示,ESA可明显缓解DSS诱导的小鼠体质量下降、结肠长度缩短及DAI评分、脾指数、组织炎症评分的升高(P<0.05);HE结果显示,ESA可保护肠道固有层,减轻肠道炎症细胞浸润;ELISA和RT-qPCR显示,ESA可抑制DSS诱导的小鼠肠黏膜组织相关炎症介质(TNF-α、IL-6和iNOS)的高表达(P<0.05);AB-PAS和免疫荧光结果显示,ESA可保护结肠组织杯状细胞、黏液屏障和机械屏障的损伤。流式细胞术结果发现,ESA可降低DSS诱导的小鼠肠系膜淋巴结和体外诱导的M1型巨噬细胞极化标志物(CD86)的阳性比例(P<0.05)。Western blotting结果显示,体内外ESA治疗组p-JAK2和p-STAT3水平低于诱导组(P<0.05);体外经JAK2/STAT3激活剂RO8191干预后显示,ESA药物治疗未能抑制JAK2/STAT3信号通路活化,同时M1型极化标志物CD86阳性比例增加(P<0.05)。 结论 ESA可靶向拮抗JAK2/STAT3通路活化介导的M1型巨噬细胞极化,抑制炎症因子导致的肠道屏障的损伤,从而缓解DSS诱导的小鼠结肠炎。
牛民主, 殷丽霞, 乔通, 尹林, 张可妮, 胡建国, 宋传旺, 耿志军, 李静. 旱莲苷A通过调控JAK2/STAT3通路抑制M1型巨噬细胞极化改善葡聚糖硫酸钠诱导的小鼠结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1297-1306.
Minzhu NIU, Lixia YIN, Tong QIAO, Lin YIN, Keni ZHANG, Jianguo HU, Chuanwang SONG, Zhijun GENG, Jing LI. Ecliptasaponin A ameliorates DSS-induced colitis in mice by suppressing M1 macrophage polarization via inhibiting the JAK2/STAT3 pathway[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1297-1306.

图1 ESA显著降低体外模型M1型巨噬细胞的比例
Fig.1 ESA significantly reduces percentage of M1-type macrophages in RAW264.7 cells induced by LPS and IFN-γ. A: Morphology of macrophages from each group (scale bar=50 μm). B: Percentages of F4/80+CD86+ macrophages detected by flow cytometry. *P<0.05 vs M0 group. #P<0.05 vs M1 group.
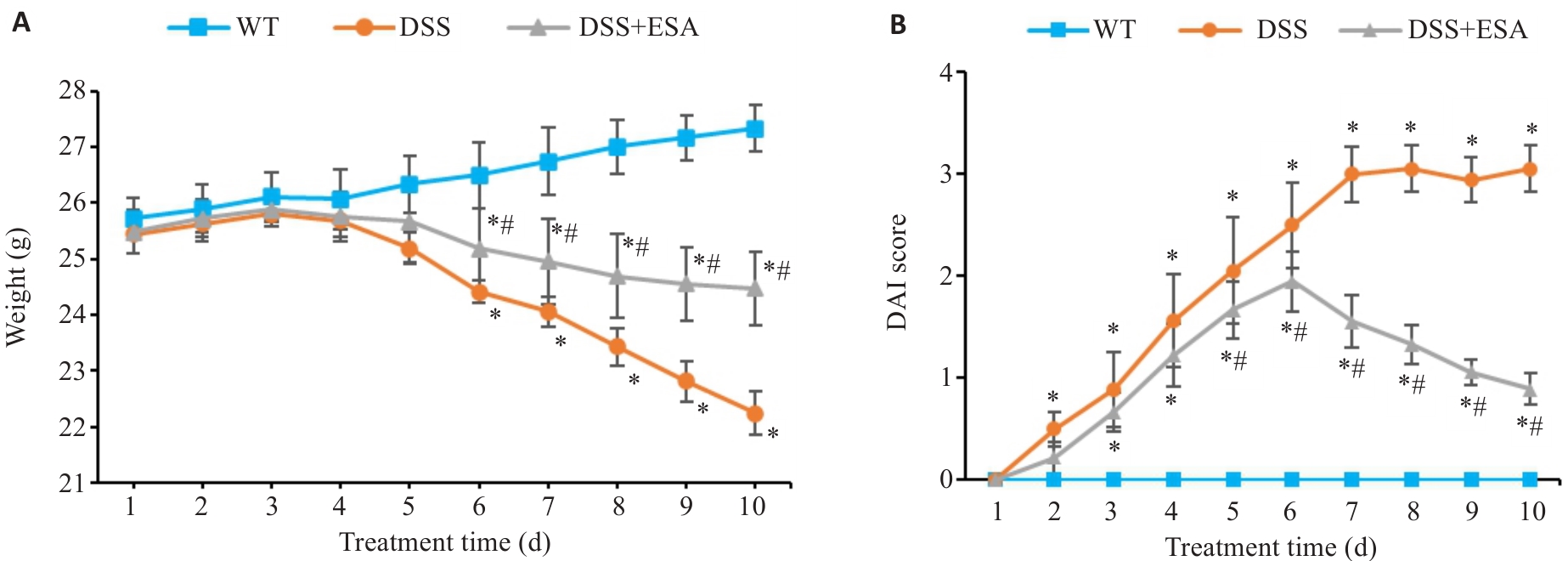
图2 ESA对DSS模型小鼠疾病状态的影响
Fig.2 Effect of ESA on the disease status of DSS model mice. A: Changes of body weight. B: Changes of DAI scores. WT: Control group; DSS: DSS-induced model group; DSS+ESA: ESA treatment group. *P<0.05 vs WT group. #P<0.05 vs DSS group.
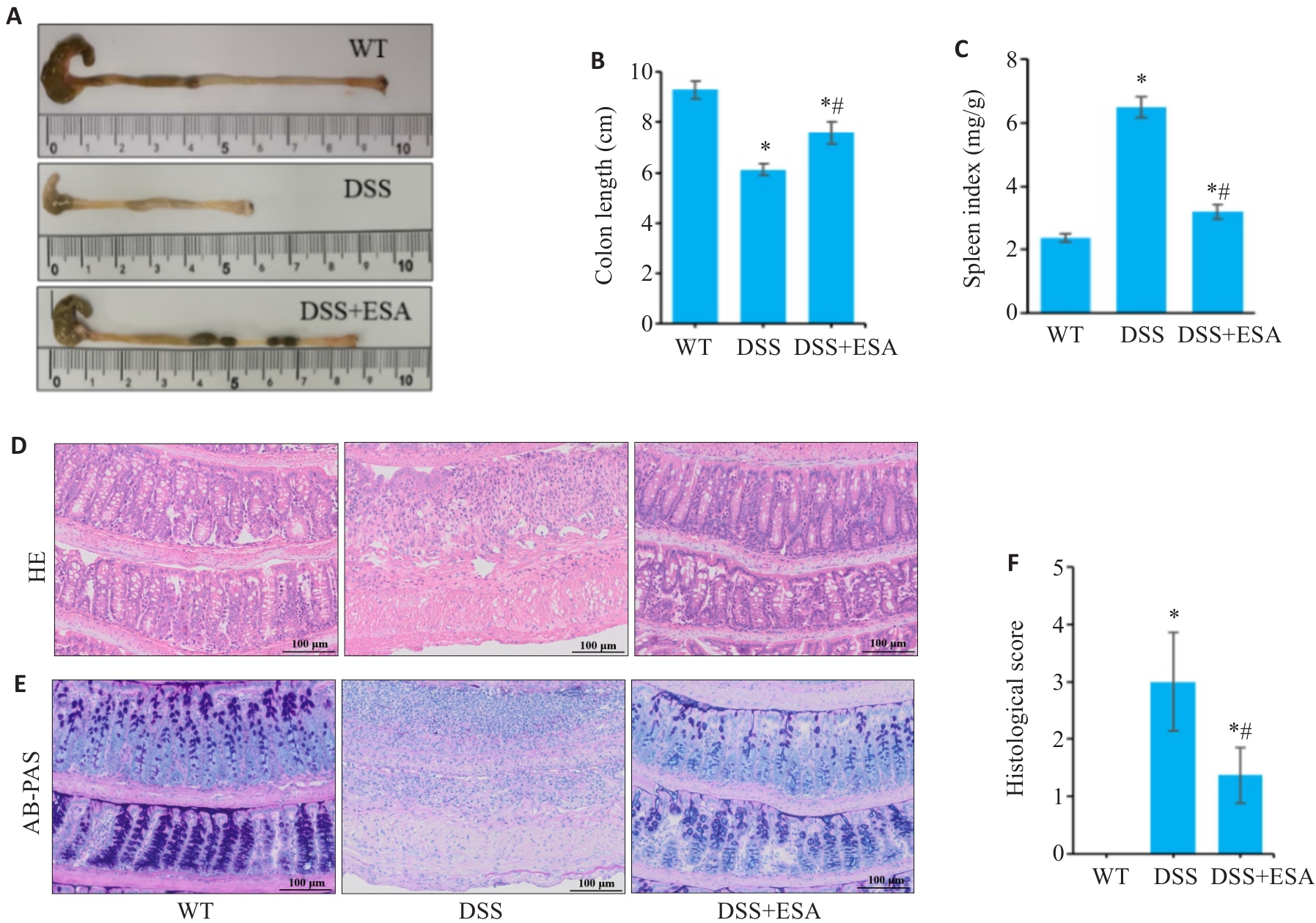
图3 ESA改善DSS诱导的结肠炎的病理表型
Fig.3 ESA improves pathological phenotype of DSS-induced colitis in mice. A, B: Representative images of mouse colons in each group. C: Changes of spleen index. D: HE staining of the colon tissues. E: AB-PAS staining of colon tissue from each groups. F: Histopathological scores in different groups. *P<0.05 vs WT group. #P<0.05 vs DSS group. (scale bar=100 μm).
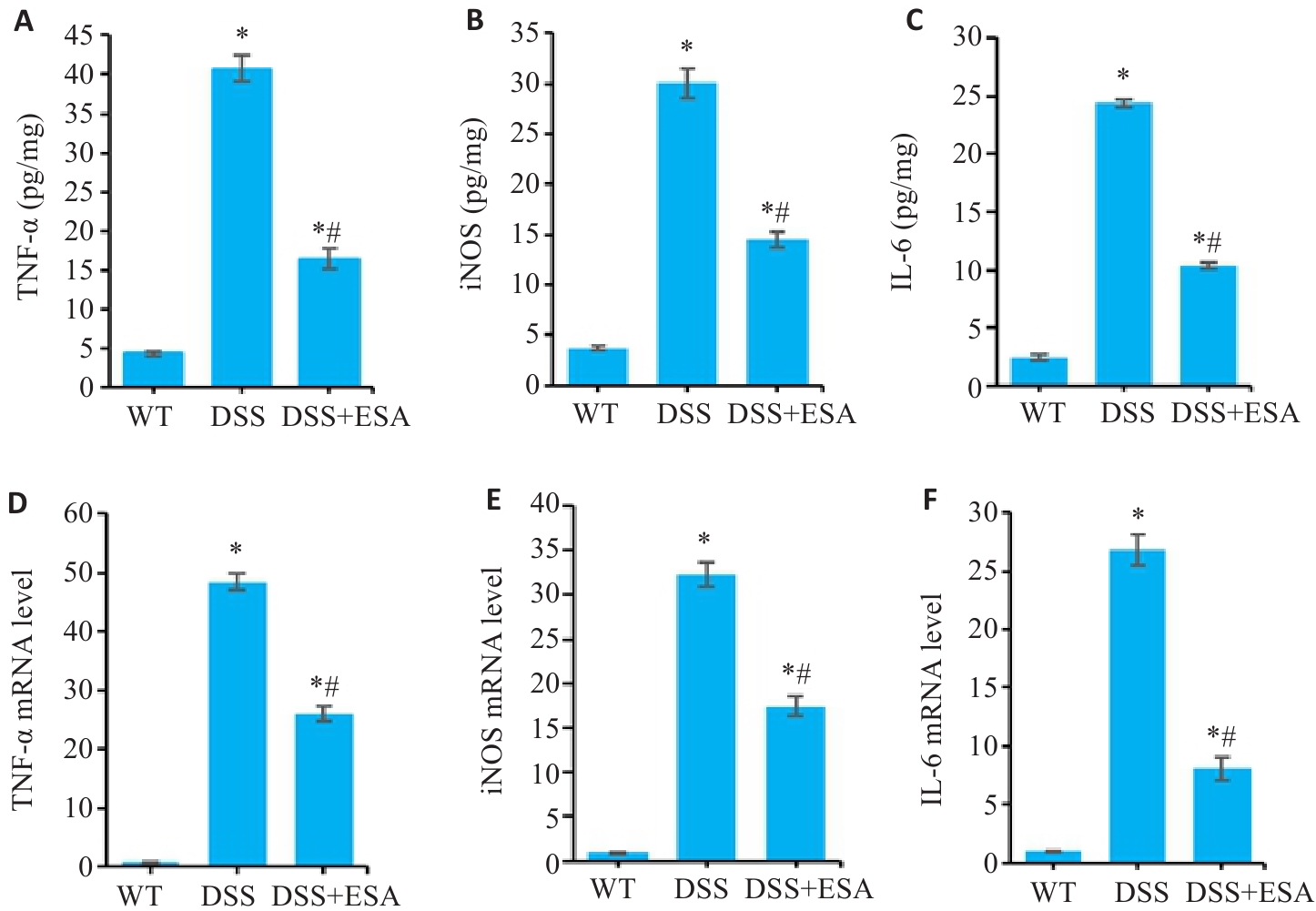
图4 ESA对DSS模型小鼠肠黏膜炎症介质的影响
Fig.4 Effect of ESA on intestinal mucosal inflammatory mediators in DSS model mice. A-C: Concentrations of proinflammatory cytokines TNF-α, iNOS and IL-6 in the colon tissues detected by ELISA. D-F: The mRNA levels of proinflammatory cytokines TNF-α, iNOS and IL-6 in different groups. *P<0.05 vs WT group. #P<0.05 vs DSS group.
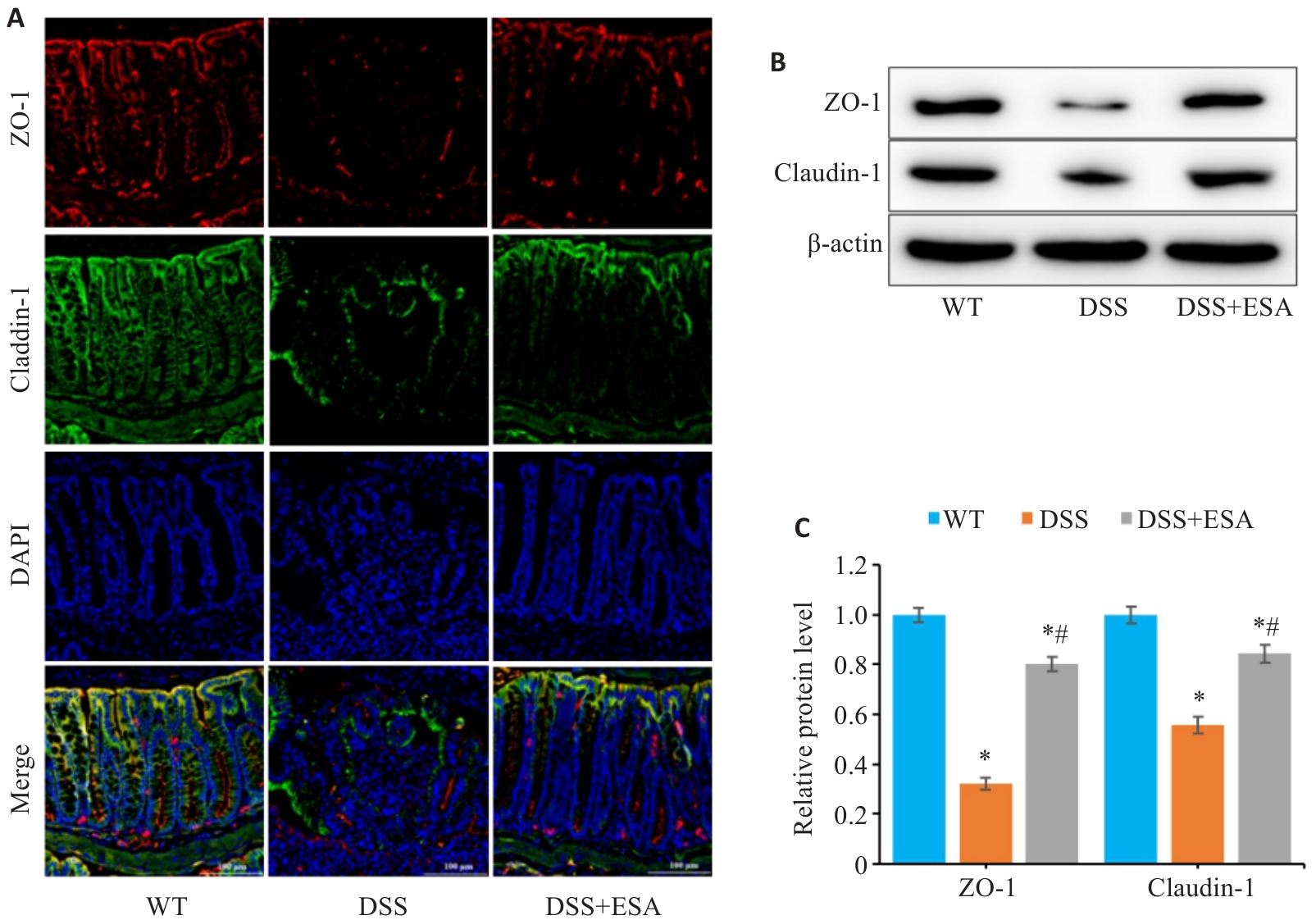
图5 ESA减轻DSS诱导的结肠炎的肠道屏障破坏
Fig.5 ESA improves gut barrier disruption in mice with DSS-induced colitis. A: Immunofluorescence staining showing expression of ZO-1 and claudin-1 proteins in the colon tissues. B, C: Relative expression levels of ZO-1 and claudin-1 proteins in colon mucosa detected by Western blotting. *P<0.05 vs WT group. #P<0.05 vs DSS group (scale bar=100 μm).

图6 ESA对DSS模型小鼠肠系膜淋巴结中M1型巨噬细胞的影响
Fig.6 Effect of ESA on M1 macrophages in the mesenteric lymph nodes of DSS model mice. The percentages of F4/80+CD86+ macrophages in mesenteric lymph nodes were detected by flow cytometry. *P<0.05 vs WT group. #P<0.05 vs DSS group.
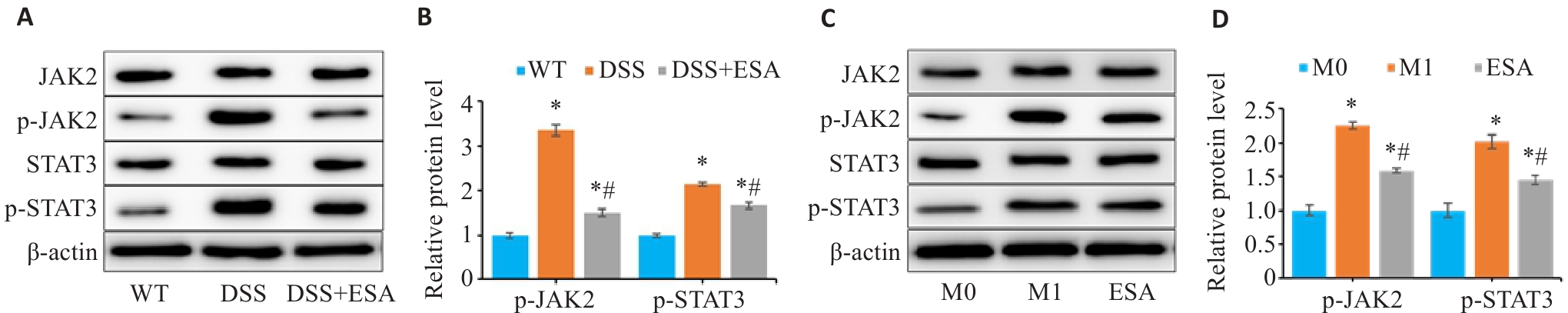
图7 ESA可抑制体内外JAK2/STAT3信号通路的磷酸化
Fig.7 ESA suppresses JAK2/STAT3 pathway activation by blocking its phosphorylation in vitro and in vivo. A, B: Relative expression levels of JAK2, p-JAK2, STAT3, and p-STAT3 proteins in mouse colon tissue detected by Western blotting (*P<0.05 vs WT group; #P<0.05 vs DSS group). C, D: Relative expression levels of JAK2, p-JAK2, STAT3, p-STAT3 proteins in RAW264.7 cells detected by Western blotting (*P<0.05 vs M0 group. #P<0.05 vs M1 group).
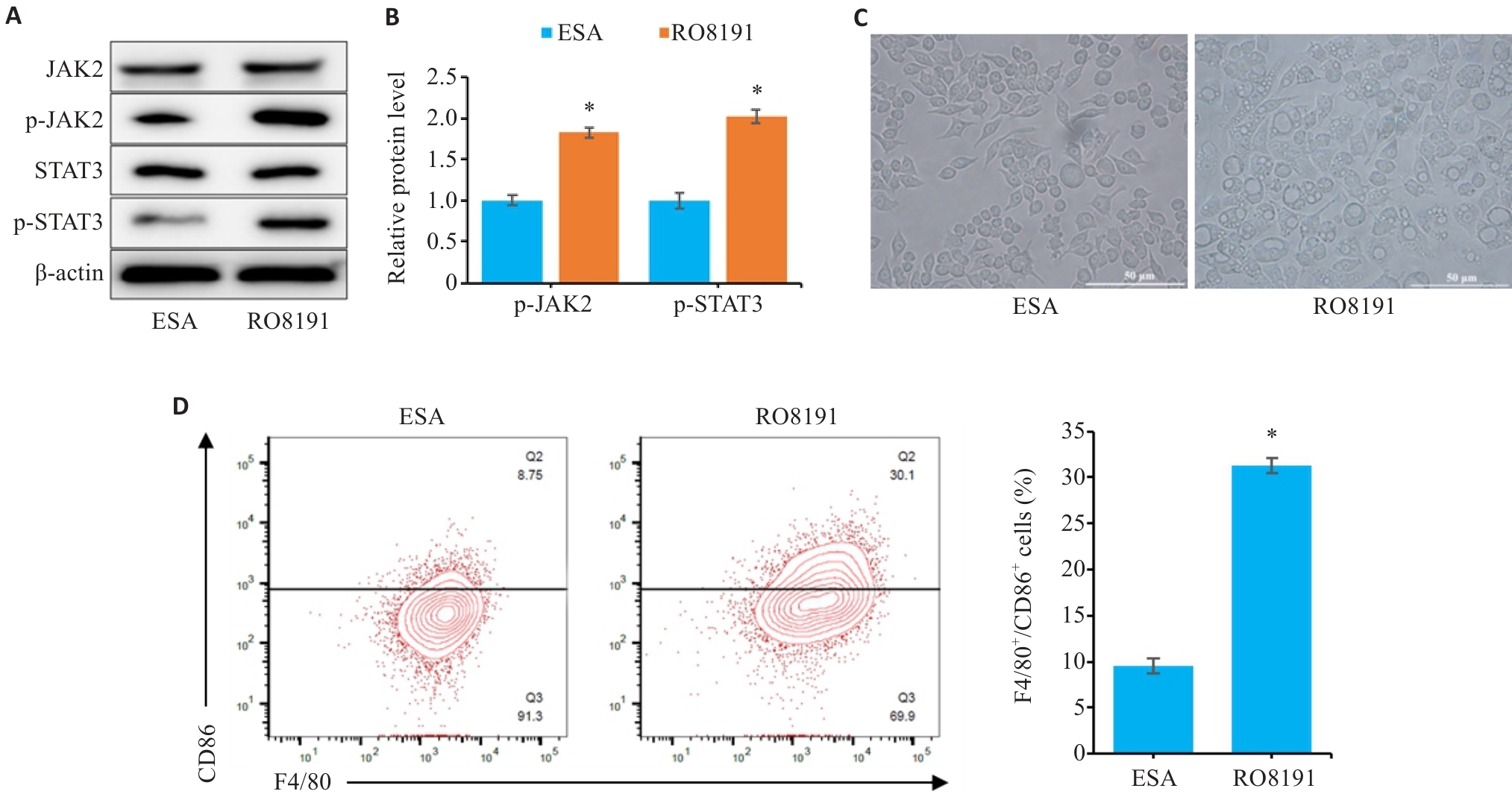
图8 JAK2/STAT3信号通路参与ESA抑制M1型巨噬细胞极化
Fig.8 JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway is involved in ESA-mediated inhibition of M1-type macrophage polarization of RAW264.7 cells. A, B: Relative expressions of JAK2, p-JAK2, STAT3 and p-STAT3 proteins detected by Western blotting in RAW264.7 cells. C: Morphology of the macrophages (×400). D: Proportion of F4/80+CD86+ cells in each group. *P<0.05 vs ESA group (Scale bar=50 μm).
| 1 | Glassner KL, Abraham BP, Quigley EMM. The microbiome and inflammatory bowel disease[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2020, 145(1): 16-27. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2019.11.003 |
| 2 | Ordás I, Eckmann L, Talamini M, et al. Ulcerative colitis[J]. Lancet, 2012, 380(9853): 1606-19. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(12)60150-0 |
| 3 | Xu L, He B, Sun Y, et al. Incidence of inflammatory bowel disease in urban China: a nationwide population-based study[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2023, 21(13): 3379-86. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2023.08.013 |
| 4 | Wangchuk P, Yeshi K, Loukas A. Ulcerative colitis: clinical biomarkers, therapeutic targets, and emerging treatments[J]. Trends Pharmacol Sci, 2024, 45(10): 892-903. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2024.08.003 |
| 5 | Saez A, Herrero-Fernandez B, Gomez-Bris R, et al. Pathophysiology of inflammatory bowel disease: innate immune system[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(2): 1526. doi:10.3390/ijms24021526 |
| 6 | Zhou X, Li WY, Wang S, et al. YAP aggravates inflammatory bowel disease by regulating M1/M2 macrophage polarization and gut microbial homeostasis[J]. Cell Rep, 2019, 27(4): 1176-89. e5. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2019.03.028 |
| 7 | Krausgruber T, Blazek K, Smallie T, et al. IRF5 promotes inflammatory macrophage polarization and TH1-TH17 responses[J]. Nat Immunol, 2011, 12(3): 231-8. doi:10.1038/ni.1990 |
| 8 | Pan XH, Zhu Q, Pan LL, et al. Macrophage immunometabolism in inflammatory bowel diseases: From pathogenesis to therapy[J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2022, 238: 108176. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2022.108176 |
| 9 | Zhang K, Guo J, Yan W, et al. Macrophage polarization in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Cell Commun Signal, 2023, 21(1): 367. doi:10.1186/s12964-023-01386-9 |
| 10 | Ruan S, Xu L, Sheng Y, et al. Th1 promotes M1 polarization of intestinal macrophages to regulate colitis-related mucosal barrier damage[J]. Aging: Albany NY, 2023, 15(14): 6721-35. doi:10.18632/aging.204629 |
| 11 | Guo HR, Guo H, Xie Y, et al. Mo3Se4 nanoparticle with ROS scavenging and multi-enzyme activity for the treatment of DSS-induced colitis in mice[J]. Redox Biol, 2022, 56: 102441. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2022.102441 |
| 12 | Yang Y, Ma Q, Wang Q, et al. Mannose enhances intestinal immune barrier function and dextran sulfate sodium salt-induced colitis in mice by regulating intestinal microbiota[J]. Front Immunol, 2024, 15: 1365457. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2024.1365457 |
| 13 | You XY, Xue Q, Fang Y, et al. Preventive effects of Ecliptae Herba extract and its component, ecliptasaponin A, on bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2015, 175: 172-80. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2015.08.034 |
| 14 | Han J, Lv W, Sheng H, et al. Ecliptasaponin A induces apoptosis through the activation of ASK1/JNK pathway and autophagy in human lung cancer cells[J]. Ann Transl Med, 2019, 7(20): 539. doi:10.21037/atm.2019.10.07 |
| 15 | Xi FM, Li CT, Han J, et al. Thiophenes, polyacetylenes and terpenes from the aerial parts of Eclipata prostrata[J]. Bioorg Med Chem, 2014, 22(22): 6515-22. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2014.06.051 |
| 16 | Ge SM, Wu SH, Yin Q, et al. Ecliptasaponin A protects heart against acute ischemia-induced myocardial injury by inhibition of the HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB pathway[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2024, 335: 118612. doi:10.1016/j.jep.2024.118612 |
| 17 | Ge ST, Yang YT, Zuo LG, et al. Sotetsuflavone ameliorates Crohn’s disease-like colitis by inhibiting M1 macrophage-induced intestinal barrier damage via JNK and MAPK signalling[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2023, 940: 175464. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2022.175464 |
| 18 | Lei X, Zou F, Tang X, et al. CD3D silencing alleviates diabetic nephropathy via inhibition of JAK/STAT pathway[J]. FASEB J, 2024, 38(21): e70169. doi:10.1096/fj.202401879r |
| 19 | Wirtz S, Popp V, Kindermann M, et al. Chemically induced mouse models of acute and chronic intestinal inflammation[J]. Nat Protoc, 2017, 12(7): 1295-309. doi:10.1038/nprot.2017.044 |
| 20 | Chougule PR, Sangaraju R, Patil PB, et al. Effect of ethyl gallate and propyl gallate on dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced ulcerative colitis in C57BL/6J mice: preventive and protective[J]. Inflammopharmacology, 2023, 31(4): 2103-20. doi:10.1007/s10787-023-01254-5 |
| 21 | Kobayashi T, Siegmund B, Le Berre C, et al. Ulcerative colitis[J]. Nat Rev Dis Primers, 2020, 6: 74. doi:10.1038/s41572-020-0205-x |
| 22 | Le Berre C, Honap S, Peyrin-Biroulet L. Ulcerative colitis[J]. Lancet, 2023, 402(10401): 571-84. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(23)00966-2 |
| 23 | Dai N, Haidar O, Askari A, et al. Colectomy rates in ulcerative colitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Dig Liver Dis, 2023, 55(1): 13-20. doi:10.1016/j.dld.2022.08.039 |
| 24 | Asano K, Takahashi N, Ushiki M, et al. Intestinal CD169+ macrophages initiate mucosal inflammation by secreting CCL8 that recruits inflammatory monocytes[J]. Nat Commun, 2015, 6: 7802. doi:10.1038/ncomms8802 |
| 25 | Goddard ZR, Searcey M, Osbourn A. Advances in triterpene drug discovery[J]. Trends Pharmacol Sci, 2024, 45(11): 964-8. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2024.10.003 |
| 26 | Martin LBB, Kikuchi S, Rejzek M, et al. Complete biosynthesis of the potent vaccine adjuvant QS-21[J]. Nat Chem Biol, 2024, 20(4): 493-502. doi:10.1038/s41589-023-01538-5 |
| 27 | Hirata K, Helal F, Hadgraft J, et al. Formulation of carbenoxolone for delivery to the skin[J]. Int J Pharm, 2013, 448(2): 360-5. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2013.03.045 |
| 28 | Chen Y, Hu Z, Li R, et al. The effects of carbenoxolone against experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in a mouse model[J]. Neuroimmunomodulation, 2020, 27(1): 19-27. doi:10.1159/000505333 |
| 29 | Kou RW, Li ZQ, Wang JL, et al. Ganoderic acid a mitigates inflammatory bowel disease through modulation of AhR activity by microbial tryptophan metabolism[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2024, 72(32): 17912-23. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.4c01166 |
| 30 | Stronati L, Palone F, Negroni A, et al. Dipotassium glycyrrhizate improves intestinal mucosal healing by modulating extracellular matrix remodeling genes and restoring epithelial barrier functions[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10: 939. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2019.00939 |
| 31 | Hong GU, Lee JY, Kang H, et al. Inhibition of osteoarthritis-related molecules by isomucronulatol 7-O-β-d-glucoside and ecliptasaponin a in IL-1β-stimulated chondrosarcoma cell model[J]. Molecules, 2018, 23(11): E2807. doi:10.3390/molecules23112807 |
| 32 | De Schepper S, Verheijden S, Aguilera-Lizarraga J, et al. Self-maintaining gut macrophages are essential for intestinal homeostasis[J]. Cell, 2019, 176(3): 676. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2019.01.010 |
| 33 | Tao Q, Liang Q, Fu Y, et al. Puerarin ameliorates colitis by direct suppression of macrophage M1 polarization in DSS mice[J]. Phytomedicine, 2024, 135: 156048. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.156048 |
| 34 | Westendorp BF, Büller NVJA, Karpus ON, et al. Indian hedgehog suppresses a stromal cell-driven intestinal immune response[J]. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2018, 5(1): 67-82.e1. doi:10.1016/j.jcmgh.2017.08.004 |
| 35 | Huang B, Chen Z, Geng L, et al. Mucosal profiling of pediatric-onset colitis and IBD reveals common pathogenics and therapeutic pathways[J]. Cell, 2019, 179(5): 1160-76.e24. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2019.10.027 |
| 36 | Xue C, Yao Q, Gu X, et al. Evolving cognition of the JAK-STAT signaling pathway: autoimmune disorders and cancer[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2023, 8(1): 204. doi:10.1038/s41392-023-01468-7 |
| 37 | Huang B, Lang X, Li X. The role of IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway in cancers[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12: 1023177. doi:10.3389/fonc.2022.1023177 |
| 38 | Lu MN, Xie KG, Lu XZ, et al. Notoginsenoside R1 counteracts mesenchymal stem cell-evoked oncogenesis and doxorubicin resistance in osteosarcoma cells by blocking IL-6 secretion-induced JAK2/STAT3 signaling[J]. Investig New Drugs, 2021, 39(2): 416-25. doi:10.1007/s10637-020-01027-9 |
| 39 | Salas A, Hernandez-Rocha C, Duijvestein M, et al. JAK-STAT pathway targeting for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 17(6): 323-37. doi:10.1038/s41575-020-0273-0 |
| 40 | Huang XL, Lin R, Liu H, et al. Resatorvid (TAK-242) ameliorates ulcerative colitis by modulating macrophage polarization and T helper cell balance via TLR4/JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway[J]. Inflammation, 2024, 47(6): 2108-28. doi:10.1007/s10753-024-02028-z |
| 41 | Wang Y, Song X, Xia Y, et al. Complanatuside A ameliorates 2, 4, 6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced colitis in mice by regulating the Th17/Treg balance via the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway[J]. FASEB J, 2024, 38(10): e23667. doi:10.1096/fj.202301127rr |
| 42 | 罗雪菲, 王 伟, 赵晓芳, 等. 基于网络药理学探讨桃莲绞复方增强全成分肿瘤细胞疫苗抗结直肠癌作用分子机制[J]. 中草药, 2021, 52(2): 459-68. doi:10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2021.02.020 |
| 43 | Xiao QP, Luo L, Zhu XY, et al. Formononetin alleviates ulcerative colitis via reshaping the balance of M1/M2 macrophage polarization in a gut microbiota-dependent manner[J]. Phytomedicine, 2024, 135: 156153. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.156153 |
| 44 | Xiao QP, Huang JQ, Zhu XY, et al. Formononetin ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis via enhancing antioxidant capacity, promoting tight junction protein expression and reshaping M1/M2 macrophage polarization balance[J]. Int Immuno-pharmacol, 2024, 142: 113174. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113174 |
| [1] | 涂舒谕, 陈祥宇, 李程辉, 黄丹萍, 张莉. 补阳还五汤通过调控外泌体miR-590-5p介导的巨噬细胞极化延缓大鼠血管衰老[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1251-1259. |
| [2] | 俞佳雯, 周薏, 钱春美, 穆蓝, 阙任烨. 铁过载诱导的小鼠肝纤维化过程影响巨噬细胞M2极化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 684-691. |
| [3] | 储菲, 陈孝华, 宋博文, 杨晶晶, 左芦根. 苏荠宁黄酮通过抑制PI3K/AKT信号通路拮抗肠上皮细胞凋亡改善小鼠实验性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 819-828. |
| [4] | 殷丽霞, 牛民主, 张可妮, 耿志军, 胡建国, 李江艳, 李静. 升麻素抑制MAPK通路调节辅助性T细胞免疫平衡改善小鼠克罗恩病样结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 595-602. |
| [5] | 宾禹, 李子雯, 左素微, 孙思诺, 李敏, 宋佳茵, 林旭, 薛刚, 吴靖芳. 载脂蛋白C1高表达通过激活JAK2/STAT3信号通路促进甲状腺乳头状癌细胞的增殖并抑制凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 359-370. |
| [6] | 刘硕, 李静, 吴兴旺. Swertiamarin通过抑制肠上皮细胞细胞凋亡改善TNBS诱导的实验性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1545-1552. |
| [7] | 席 进, 张 敏, 张永玉, 张 晨, 张雨路, 王 锐, 申 林, 李 静, 宋 雪. 上调KLF11可改善结肠炎模型小鼠的肠道炎症:基于抑制JAK2/STAT3信号通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(4): 765-772. |
| [8] | 牛民主, 殷丽霞, 段婷, 黄菊, 李静, 耿志军, 胡建国, 宋传旺. 川续断皂苷VI通过抑制PI3K/AKT/NF-κB通路拮抗肠上皮细胞凋亡缓解TNBS诱导的小鼠克罗恩病样结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(12): 2335-2346. |
| [9] | 邵荣瑢, 杨 子, 张文静, 张 诺, 赵雅静, 张小凤, 左芦根, 葛思堂. 茯苓酸缓解小鼠克罗恩病:基于抑制PI3K/AKT信号通路拮抗肠上皮细胞凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(6): 935-942. |
| [10] | 李敬怡, 杨思圆, 韩 振, 江天乐, 朱 耀, 周子航, 周静萍. Akt2抑制剂促进大鼠根尖周炎症微环境中巨噬细胞的极化:基于降低miR-155-5p的表达[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(4): 568-576. |
| [11] | 张梦莹, 李 志, 裴纬亚, 李雪琴, 杨 辉, 朱小龙, 吕 坤. M2型巨噬细胞来源的外泌体lncRNA NR_028113.1通过激活JAK2/STAT3通路促进巨噬细胞的极化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(3): 393-399. |
| [12] | 赵佳琳, 陈 萍, 徐广立, 孙建华, 阮媛媛, 薛苗苗, 吴悦靓. 补肾活血方通过下调JAK2/STAT3通路改善小鼠的复发性流产[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(2): 265-270. |
| [13] | 肖姝喆, 成燕玲, 朱 云, 唐 芮, 古建标, 兰 林, 何志华, 刘丹琼, 耿岚岚, 程 旸, 龚四堂. WNT2b高表达的成纤维细胞破坏肠道黏膜屏障[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(2): 206-212. |
| [14] | 王 杰, 刘 健, 文建庭, 王 馨. 雷公藤甲素抑制类风湿关节炎患者的成纤维样滑膜细胞的炎症和迁移: 基于circRNA 0003353/JAK2/STAT3信号通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(3): 367-374. |
| [15] | 王 冰, 黄启林, 李 帅, 吴 俊, 原小惠, 孙红玉, 汤礼军. 鸟苷酸环化酶C在重症急性胰腺炎大鼠相关性肠损伤中的变化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(3): 376-383. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||