南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (1): 162-169.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.01.19
唐诗洲1( ), 苏若兰1, 李淑婷1, 赖珍珍1, 黄进红1,2, 牛善洲1,2(
), 苏若兰1, 李淑婷1, 赖珍珍1, 黄进红1,2, 牛善洲1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2024-09-12
出版日期:2025-01-20
发布日期:2025-01-20
通讯作者:
牛善洲
E-mail:206976182@qq.com;szniu@gnnu.edu.cn
作者简介:唐诗洲,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: 206976182@qq.com
基金资助:
Shizhou TANG1( ), Ruolan SU1, Shuting LI1, Zhenzhen LAI1, Jinhong HUANG1,2, Shanzhou NIU1,2(
), Ruolan SU1, Shuting LI1, Zhenzhen LAI1, Jinhong HUANG1,2, Shanzhou NIU1,2( )
)
Received:2024-09-12
Online:2025-01-20
Published:2025-01-20
Contact:
Shanzhou NIU
E-mail:206976182@qq.com;szniu@gnnu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
目的 提出一种基于亚像素各项异性扩散的低剂量CT重建方法。 方法 通过线性插值技术计算亚像素单元强度值及其二阶差分后,将计算得到的新的梯度信息引入到各项异性扩散过程中,并结合惩罚加权最小二乘模型对低剂量CT投影数据进行滤波,最后使用滤波反投影算法将恢复后的投影数据重建出CT图像。 结果 在Shepp-Logan体模实验中,与FBP、PWLS-Gibbs和PWLS-TV方法相比,新方法滤波后重建的CT图像在结构相似指数上分别提升了28.13%、5.49%和0.91%,在特征相似指数上分别提升了21.08%、1.78%和1.36%,并且在均方根误差上分别降低了69.59%、18.96%和3.90%。在XCAT体模实验中,与FBP、PWLS-Gibbs和PWLS-TV方法相比,新方法在结构相似指数上分别提高了14.24%、1.43%及7.89%,在特征相似指数上分别提高了9.61%、1.78%及5.66%,同时在均方根误差上分别降低了26.88%、9.41%及18.39%。在临床数据实验中,与FBP、PWLS-Gibbs和PWLS-TV方法重建的CT图像相比,新方法在结构相似指数上分别提升了19.24%、15.63%和3.68%,在特征相似指数上分别提升了4.30%、2.92%和0.43%,同时在均方根误差上分别降低了44.60%、36.84%和15.22%,并且在峰值信噪比上提升至28.39。 结论 本文提出的新方法可以有效去除低剂量CT图像的噪声和伪影,并可以保持结构细节信息。
唐诗洲, 苏若兰, 李淑婷, 赖珍珍, 黄进红, 牛善洲. 基于亚像素各向异性扩散的低剂量CT重建方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 162-169.
Shizhou TANG, Ruolan SU, Shuting LI, Zhenzhen LAI, Jinhong HUANG, Shanzhou NIU. A low-dose CT reconstruction method using sub-pixel anisotropic diffusion[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 162-169.
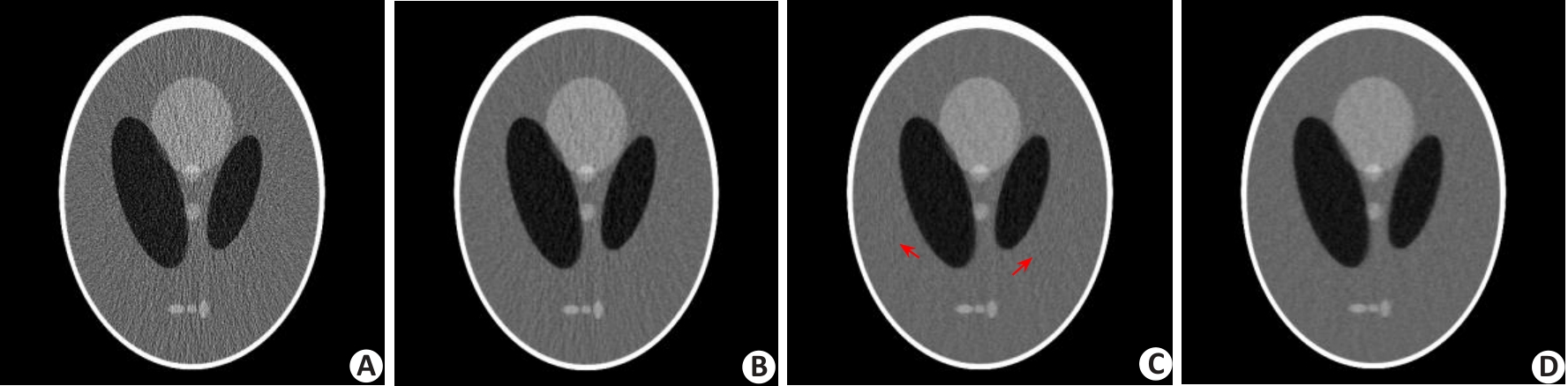
图3 不同方法重建的Shepp-Logan体模图像
Fig.3 Shepp-Logan images reconstructed by FBP method (A), PWLS-Gibbs method (B), PWLS-TV method (C) and the proposed PWLS-SPAD method (D).
| Index | FBP | PWLS-Gibbs | PWLS-TV | PWLS-SPAD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSIM | 0.752083 | 0.913535 | 0.954934 | 0.963646 |
| FSIM | 0.767575 | 0.913088 | 0.916857 | 0.929354 |
| RMSE | 0.111569 | 0.041859 | 0.035302 | 0.033924 |
表1 Shepp-Logan体模实验的评估指数
Tab.1 Evaluation indexes of the reconstructed Shepp-Logan images by different methods
| Index | FBP | PWLS-Gibbs | PWLS-TV | PWLS-SPAD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSIM | 0.752083 | 0.913535 | 0.954934 | 0.963646 |
| FSIM | 0.767575 | 0.913088 | 0.916857 | 0.929354 |
| RMSE | 0.111569 | 0.041859 | 0.035302 | 0.033924 |
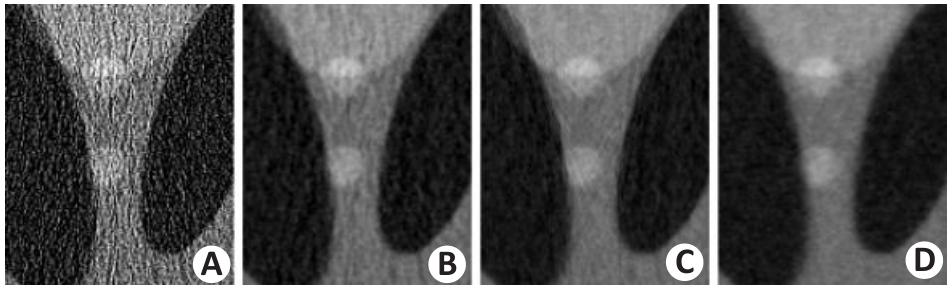
图4 Shepp-Logan体模的局部放大图
Fig.4 Zoomed-in views of the reconstructed Shepp-Logan phantom images by FBP method (A), PWLS-Gibbs method (B), PWLS-TV method (C) and the proposed PWLS-SPAD method (D).
| Index | FBP | PWLS-Gibbs | PWLS-TV | PWLS-SPAD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSIM | 0.203666 | 0.813477 | 0.850652 | 0.888047 |
| FSIM | 0.399392 | 0.790398 | 0.827324 | 0.853895 |
表2 图4中ROI的评估指数
Tab.2 Evaluation indexes of the region-of-interest (ROI) in Fig.4
| Index | FBP | PWLS-Gibbs | PWLS-TV | PWLS-SPAD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSIM | 0.203666 | 0.813477 | 0.850652 | 0.888047 |
| FSIM | 0.399392 | 0.790398 | 0.827324 | 0.853895 |
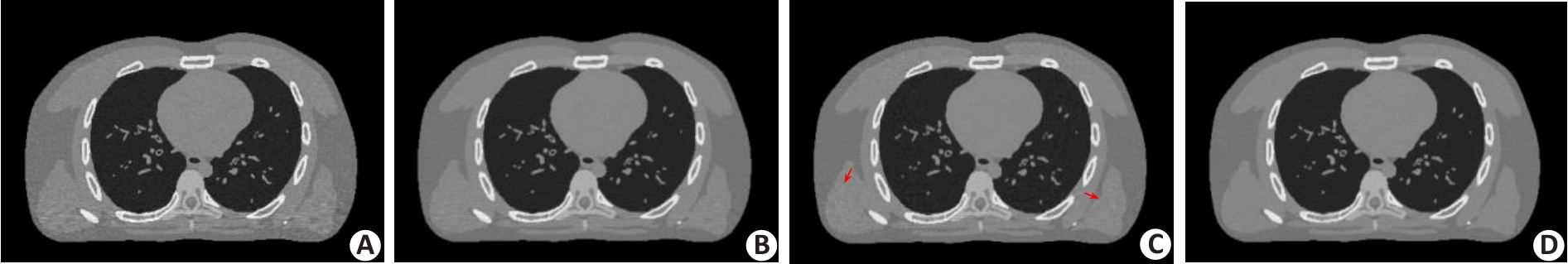
图5 不同方法重建的XCAT体模图像
Fig.5 XCAT phantom images reconstructed by FBP method (A), PWLS-Gibbs method (B), PWLS-TV method (C) and the proposed PWLS-SPAD method (D).
| Index | FBP | PWLS-Gibbs | PWLS-TV | PWLS-SPAD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSIM | 0.793550 | 0.893789 | 0.840232 | 0.906532 |
| FSIM | 0.814784 | 0.877465 | 0.845212 | 0.893061 |
| RMSE | 0.073716 | 0.059505 | 0.066048 | 0.053903 |
表3 XCAT体模实验的评估指数
Tab.3 Evaluation indexes of reconstructed XCAT results by different methods
| Index | FBP | PWLS-Gibbs | PWLS-TV | PWLS-SPAD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSIM | 0.793550 | 0.893789 | 0.840232 | 0.906532 |
| FSIM | 0.814784 | 0.877465 | 0.845212 | 0.893061 |
| RMSE | 0.073716 | 0.059505 | 0.066048 | 0.053903 |
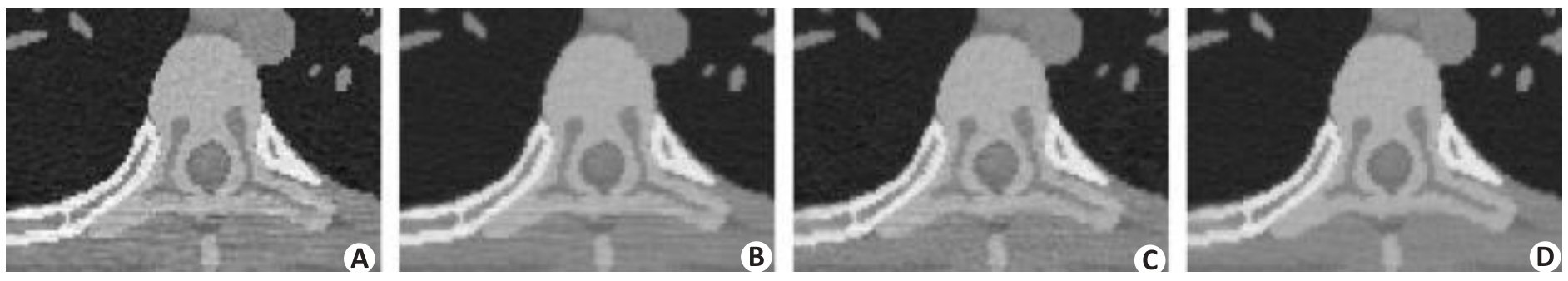
图6 XCAT体模的局部放大图
Fig.6 Zoomed-in views of the reconstructed XCAT phantom images by FBP method (A), PWLS-Gibbs method (B), PWLS-TV method (C) and the proposed PWLS-SPAD method (D).
| Index | FBP | PWLS-Gibbs | PWLS-TV | PWLS-SPAD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSIM | 0.748943 | 0.852549 | 0.798578 | 0.873204 |
| FSIM | 0.806244 | 0.862104 | 0.832281 | 0.867679 |
表4 图6中ROI的评估指数
Tab.4 Evaluation indexes of ROI in Fig.6
| Index | FBP | PWLS-Gibbs | PWLS-TV | PWLS-SPAD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSIM | 0.748943 | 0.852549 | 0.798578 | 0.873204 |
| FSIM | 0.806244 | 0.862104 | 0.832281 | 0.867679 |
| Index | FBP | PWLS-Gibbs | PWLS-TV | PWLS-SPAD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSIM | 0.795249 | 0.820050 | 0.914574 | 0.948223 |
| FSIM | 0.936031 | 0.948504 | 0.972051 | 0.976237 |
| RMSE | 0.068670 | 0.060228 | 0.044872 | 0.038042 |
| PSNR | 23.26 | 24.40 | 26.96 | 28.39 |
表5 低剂量临床数据重建CT图像的评估指数
Tab.5 Evaluation indexes of the reconstructed low-dose clinical CT images by different methods
| Index | FBP | PWLS-Gibbs | PWLS-TV | PWLS-SPAD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSIM | 0.795249 | 0.820050 | 0.914574 | 0.948223 |
| FSIM | 0.936031 | 0.948504 | 0.972051 | 0.976237 |
| RMSE | 0.068670 | 0.060228 | 0.044872 | 0.038042 |
| PSNR | 23.26 | 24.40 | 26.96 | 28.39 |
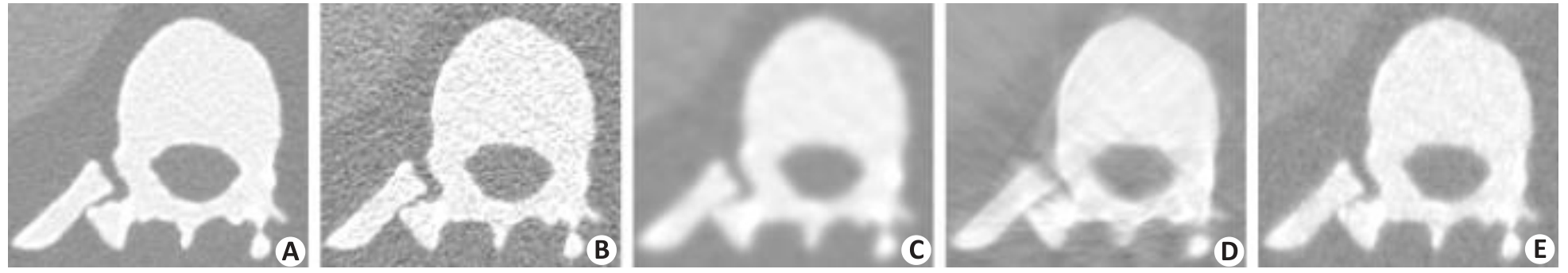
图8 临床数据重建CT图像的ROI放大图
Fig.8 Zoomed-in views of the ROI in the reconstructed images by FBP method at 400 mAs (A) and 50 mAs (B), by PWLS-Gibbs at 50 mAs (C), by PWLS-TV at 50 mAs (D), and by the proposed PWLS-SPAD method at 50 mAs (E).
| Index | FBP | PWLS-Gibbs | PWLS-TV | PWLS-SPAD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSIM | 0.622500 | 0.786073 | 0.783700 | 0.810993 |
| FSIM | 0.840642 | 0.865528 | 0.882331 | 0.919254 |
表6 图8中ROI的评估指数
Tab.6 Evaluation indexes of ROI in Fig.8
| Index | FBP | PWLS-Gibbs | PWLS-TV | PWLS-SPAD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSIM | 0.622500 | 0.786073 | 0.783700 | 0.810993 |
| FSIM | 0.840642 | 0.865528 | 0.882331 | 0.919254 |
| 1 | Vliegenthart R, Fouras A, Jacobs C, et al. Innovations in thoracic imaging: CT, radiomics, AI and X-ray velocimetry[J]. Respirology, 2022, 27(10): 818-33. |
| 2 | Bonney A, Malouf R, Marchal C, et al. Impact of low-dose computed tomography (LDCT) screening on lung cancer-related mortality[J]. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2022, 8(8): CD013829. |
| 3 | Gillies RJ, Schabath MB. Radiomics improves cancer screening and early detection[J]. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev, 2020, 29(12): 2556-67. |
| 4 | 牛善洲, 唐诗洲, 黄舒彦, et al. 基于高维PDE投影恢复的低剂量CT重建方法 [J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(4): 682-8. |
| 5 | Zhang H, Wang J, Zeng D, et al. Regularization strategies in statistical image reconstruction of low-dose X-ray CT: a review[J]. Med Phys, 2018, 45(10): e886-e907. |
| 6 | 邸江磊, et al. 基于深度学习的稀疏或有限角度CT重建方法研究综述 [J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2023, 60(8): 42-79. |
| 7 | 牛善洲, 梁礼境, 李 硕, et al. 基于低维流形先验的低剂量CT重建方法[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2023, 59(18): 242-8. |
| 8 | 李进丹, 陈 龙, 杨聪慧, et al. 低剂量PET/CT及PET/MRI临床研究进展[J]. 中国医学影像技术, 2021, 37(11): 1740-3. |
| 9 | 陈世宣, 曾栋, 边兆英, et al. 基于联邦特征学习的多机型低剂量CT重建算法 [J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 333-43. |
| 10 | Yang SH, Pu Q, Lei CT, et al. Low-dose CT denoising with a high-level feature refinement and dynamic convolution network[J]. Med Phys, 2023, 50(6): 3597-611. |
| 11 | Wu DF, Kim K, El Fakhri G, et al. Iterative low-dose CT reconstruction with priors trained by artificial neural network[J]. IEEE Trans Med Imaging, 2017, 36(12): 2479-86. |
| 12 | Zhang H, Ma JH, Wang J, et al. Statistical image reconstruction for low-dose CT using nonlocal means-based regularization. Part II: an adaptive approach[J]. Comput Med Imaging Graph, 2015, 43: 26-35. |
| 13 | Zhang H, Ma JH, Wang J, et al. Statistical image reconstruction for low-dose CT using nonlocal means-based regularization. Part II: an adaptive approach[J]. Comput Med Imaging Graph, 2015, 43: 26-35. |
| 14 | Niu SZ, Liu H, Zhang MZ, et al. Iterative reconstruction for low-dose cerebral perfusion computed tomography using prior image induced diffusion tensor[J]. Phys Med Biol, 2021, 66(11): 1150-24. |
| 15 | Wang J, Li TF, Lu HB, et al. Penalized weighted least-squares approach to sinogram noise reduction and image reconstruction for low-dose X-ray computed tomography[J]. IEEE Trans Med Imaging, 2006, 25(10): 1272-83. |
| 16 | Wang J, Lu HB, Wen JH, et al. Multiscale penalized weighted least-squares sinogram restoration for low-dose X-ray computed tomography[J]. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng, 2008, 55(3): 1022-31. |
| 17 | 张心如, 周先春, 汪志飞, et al. 基于改进各向异性扩散的图像去噪算法 [J]. 电子测量技术, 2022, 45(17): 113-9. |
| 18 | Guo YH, Cheng HD. Image noise removal approach based on subpixel anisotropic diffusion[J]. J Electron Imaging, 2012, 21(3): 033026-1. |
| 19 | Zhang HJ, Zeng D, Lin JH, et al. Iterative reconstruction for dual energy CT with an average image-induced nonlocal means regularization[J]. Phys Med Biol, 2017, 62(13): 5556-74. |
| 20 | Huang J, Zhang YW, Ma JH, et al. Iterative image reconstruction for sparse-view CT using normal-dose image induced total variation prior[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(11): e79709. |
| 21 | Zhang HW, Zhang PC, Cheng WT, et al. Learnable PM diffusion coefficients and reformative coordinate attention network for low dose CT denoising[J]. Phys Med Biol, 2023, 68(24): Physicsinmedi-cineandbiologyvol.68, 2410.1088/1361-6560/aced33.11Dec.2023, . |
| 22 | Wang J, Guan HQ, Solberg T. Inverse determination of the penalty parameter in penalized weighted least-squares algorithm for noise reduction of low-dose CBCT[J]. Med Phys, 2011, 38(7): 4066-72. |
| 23 | Liu Y, Ma JH, Fan Y, et al. Adaptive-weighted total variation minimization for sparse data toward low-dose X-ray computed tomography image reconstruction[J]. Phys Med Biol, 2012, 57(23): 7923-56. |
| 24 | 牛善洲, 刘宏, 朱赟, et al. 基于广义惩罚加权最小二乘的低剂量CT重建方法 [J]. 数值计算与计算机应用, 2021, 42(3): 289-302. DOI: 10.12288/szjs.s2020-0671 |
| 25 | 牛善洲, 张梦真, 邱 洋, et al. 基于全广义变分约束加权最小二乘的低剂量计算机断层重建方法[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2023, 60(4): 3788/LOP212853. DOI: 10.3788/LOP212853 |
| 26 | Zhang H, Capaldi D, Zeng D, et al. Prior-image-based CT reconstruction using attenuation-mismatched priors[J]. Phys Med Biol, 2021, 66(6): 064007. |
| 27 | Zhang L, Zhang L, Mou XQ, et al. FSIM: a feature similarity index for image quality assessment[J]. IEEE Trans Image Process, 2011, 20(8): 2378-86. |
| 28 | Tsai MY, Liang HL, Chuo CC, et al. A novel protocol for abdominal low-dose CT scans adapted with a model-based iterative reconstruction method[J]. J Xray Sci Technol, 2023, 31(3): 453-61. |
| 29 | Wilson DO. Is there more to low dose CT scans[J]? Chest, 2022, 161(4): 880-1. |
| 30 | Sun T, Sun NB, Wang J, et al. Iterative CBCT reconstruction using Hessian penalty[J]. Phys Med Biol, 2015, 60(5): 1965-87. |
| 31 | Niu S, Bian Z, Zeng D, et al. Total image constrained diffusion tensor for spectral computed tomography reconstruction[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2019, 68: 487-508. |
| 32 | Niu SZ, Zhang MZ, Qiu Y, et al. Evaluation of low-dose computed tomography reconstruction using spatial-radon domain total generalized variation regularization[J]. Phys Med Biol, 2024, 69(10): 1050-05. |
| [1] | 牛善洲, 唐诗洲, 黄舒彦, 梁礼境, 李 硕, 刘汉明. 基于高维PDE投影恢复的低剂量CT重建方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(4): 682-688. |
| [2] | 陈世宣, 曾 栋, 边兆英, 马建华. 基于联邦特征学习的多机型低剂量CT重建算法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 333-343. |
| [3] | 王海龙, 林国钦, 段晓曼, 亓孟科, 武王将, 马健晖, 徐 圆. 锥束CT系统几何校正的偏差因素敏感性分析方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(7): 1233-1240. |
| [4] | 符 帅, 李明强, 边兆英, 马建华. 低剂量CT图像重建算法对脑出血检测性能的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(2): 223-231. |
| [5] | 斯文彬, 冯衍秋. 定量磁化率成像中磁化率重建伪影的清除:基于多通道输入的卷积神经网络方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(12): 1799-1806. |
| [6] | 黄进红, 周根娇, 喻泽峰, 胡文玉. 基于复值损失函数的并行MRI的深度重建[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(12): 1755-1764. |
| [7] | 王正策,赵凯旋,徐中标,冯衍秋. 基于局部亚像素移位和隔行局部变差消除Gibbs 伪影[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2019, 39(05): 603-. |
| [8] | 吴洋洋,杨丰,黄靖,刘娅琴. 生成对抗网络的血管内超声图像超分辨率重建[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2019, 39(01): 82-. |
| [9] | 马昆,李明强,陶熙,曾栋,王永波,边兆英,韦子权,谌高峰,冯前进,马建华,黄静. 四肢成像专用锥束CT方法的设计与优化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2018, 38(11): 1331-. |
| [10] | 牛善洲,吴恒,喻泽峰,郑子君,喻高航. 基于投影数据全广义变分最小化的低剂量CT重建[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2017, 37(12): 1585-. |
| [11] | 肖珊,王婷婷,吕庆文,张煜. 基于快速亚像素运动估计的肺4D-CT图像超分辨率重建[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2015, 35(07): 1034-. |
| [12] | 张善立,张华,胡德斌,曾栋,边兆英,路利军,马建华,黄静. 基于边缘检测算子的Huber正则化阈值选择方法在低剂量CT重建中的应用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2015, 35(03): 375-. |
| [13] | 杨柳,齐宏亮,徐圆,甄鑫,卢文婷,周凌宏. 一种基于分裂Bregman方法求解的锥束CT图像迭代重建[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2014, 34(06): 783-. |
| [14] | 张喜乐,田玲玲,黄静,马建华,张华,冯前进,陈武凡. 基于非局部权值先验和GPU加速的3D低剂量CT成像[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2011, 31(12): 1974-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||