南方医科大学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (12): 2449-2460.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.12.22
曾佑琴1( ), 陈思雨1(
), 陈思雨1( ), 刘燕1, 刘奕彤1, 张玲1, 夏姣1, 吴心语1, 魏常友2, 冷平1(
), 刘燕1, 刘奕彤1, 张玲1, 夏姣1, 吴心语1, 魏常友2, 冷平1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-07-24
出版日期:2024-12-20
发布日期:2024-12-26
通讯作者:
冷平
E-mail:zengyouqin@163.com;chensiyu2@stu.cdutcm.edu.cn;lengping@cdutcm.edu.cn
作者简介:曾佑琴,实验师,E-mail: zengyouqin@163.com基金资助:
Youqin ZENG1( ), Siyu CHEN1(
), Siyu CHEN1( ), Yan LIU1, Yitong LIU1, Ling ZHANG1, Jiao XIA1, Xinyu WU1, Changyou WEI2, Ping LENG1(
), Yan LIU1, Yitong LIU1, Ling ZHANG1, Jiao XIA1, Xinyu WU1, Changyou WEI2, Ping LENG1( )
)
Received:2024-07-24
Online:2024-12-20
Published:2024-12-26
Contact:
Ping LENG
E-mail:zengyouqin@163.com;chensiyu2@stu.cdutcm.edu.cn;lengping@cdutcm.edu.cn
摘要:
目的 探究AKBA联合阿霉素对三阴性乳腺癌细胞MDA-MB-231在增殖、迁移、侵袭和凋亡上的协同抑制作用,并通过网络药理学分析AKBA作用乳腺癌的下游信号通路。 方法 MDA-MB-231细胞体外培养,CCK-8法分别检测AKBA和阿霉素(ADR)作用MDA-MB-231细胞48 h的半抑制浓度(IC50),SynergyFinder在线网站(
曾佑琴, 陈思雨, 刘燕, 刘奕彤, 张玲, 夏姣, 吴心语, 魏常友, 冷平. AKBA联合阿霉素抑制三阴性乳腺癌细胞MDA-MB-231的增殖、迁移和裸鼠移植瘤生长[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(12): 2449-2460.
Youqin ZENG, Siyu CHEN, Yan LIU, Yitong LIU, Ling ZHANG, Jiao XIA, Xinyu WU, Changyou WEI, Ping LENG. AKBA combined with doxorubicin inhibits proliferation and metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells and xenograft growth in nude mice[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(12): 2449-2460.
| Gene | Primer sequence 5'-3' |
|---|---|
| Caspase-3 | Forward: TATTCCACAGCACCTGGTTA Reverse: CAATACATGGAATCTGTTTCTT |
| Bax | Forward: CCTCAGGATGCGTCCACCAAGA Reverse: TGTGTCCACGGCGGCAATCA |
| Bcl-2 | Forward: GTGTGTGGAGAGCGTCAACC Reverse: TCTTCAGAGACAGCCAGGAGAA |
| GAPDH | Forward: GGAGCGAGATCCCTCCAAAAT Reverse: GGCTGTTGTCATACTTCTCATGG |
| PTGS2 | Forward: CTGGCGCTCAGCCATACAG Reverse: CGCACTTATACTGGTCAAATCCC |
表1 引物序列
Tab.1 Primer sequences for RT-qPCR
| Gene | Primer sequence 5'-3' |
|---|---|
| Caspase-3 | Forward: TATTCCACAGCACCTGGTTA Reverse: CAATACATGGAATCTGTTTCTT |
| Bax | Forward: CCTCAGGATGCGTCCACCAAGA Reverse: TGTGTCCACGGCGGCAATCA |
| Bcl-2 | Forward: GTGTGTGGAGAGCGTCAACC Reverse: TCTTCAGAGACAGCCAGGAGAA |
| GAPDH | Forward: GGAGCGAGATCCCTCCAAAAT Reverse: GGCTGTTGTCATACTTCTCATGG |
| PTGS2 | Forward: CTGGCGCTCAGCCATACAG Reverse: CGCACTTATACTGGTCAAATCCC |
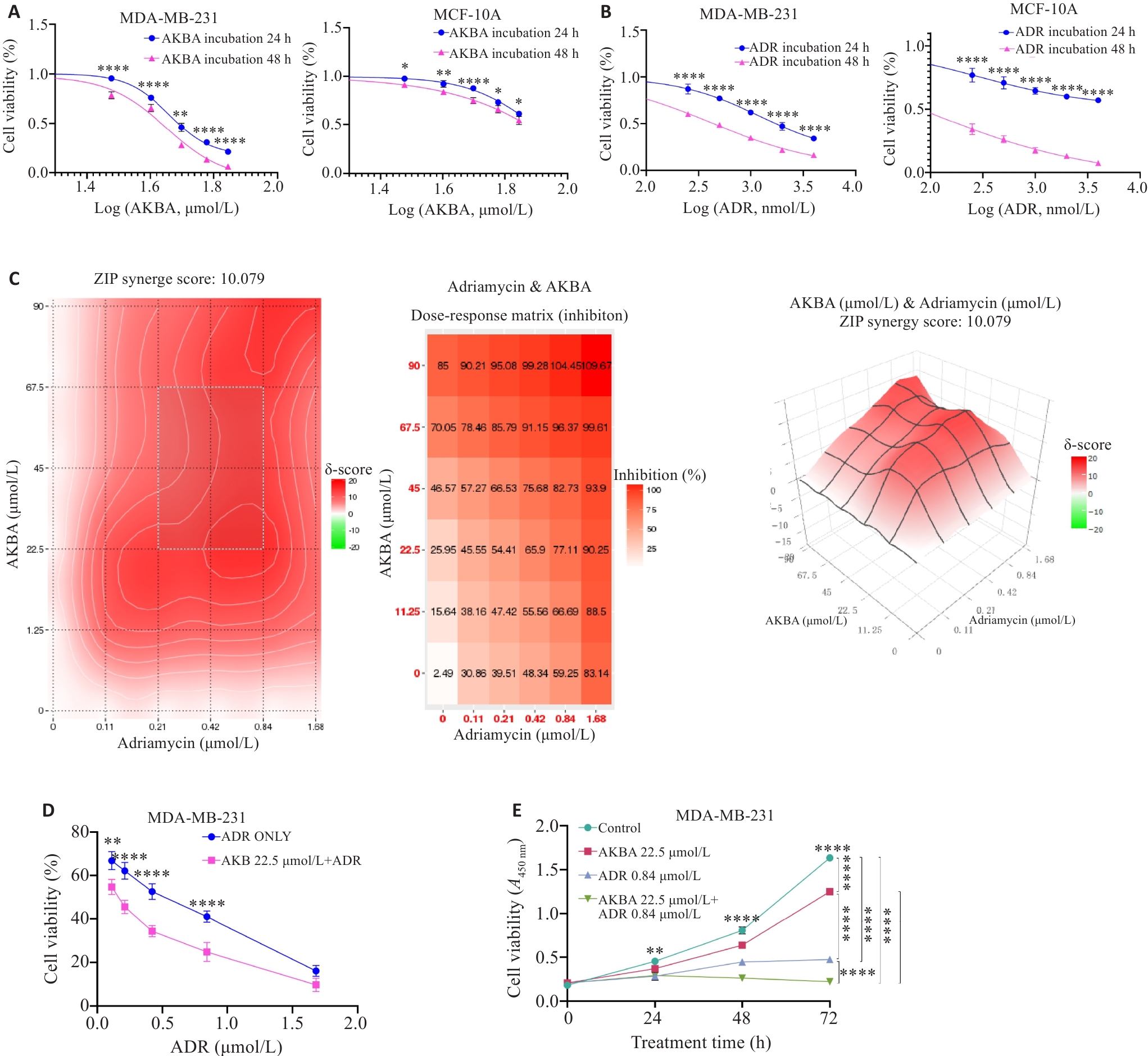
图1 CCK-8和Synergy Finder检测AKBA联合ADR对MDA-MB-231细胞增殖活性的影响以及药物联合协同指数
Fig.1 CCK-8 assay and SynergyFinder detection of the effect of AKBA combined with ADR on proliferation of MDA-MB-231 cells and drug combination synergy indices. A: Viability of AKBA-treated MDA-MB-231 and MCF-10A cells at 24 and 48 h. B: Viability of ADR-treated MDA-MB-231 and MCF-10A cells at 24 and 48 h. C: Synergistic indices of the combination of AKBA and ADR determined with Synergy Finder. D: Low concentrations of AKBA combined with different concentrations of ADR inhibit proliferation of MDA-MB-231 cells. E: Proliferation of MDA-MB-231 cells treated with saline, AKBA, ADR and AKBA+ADR for 72 h. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ****P<0.0001.
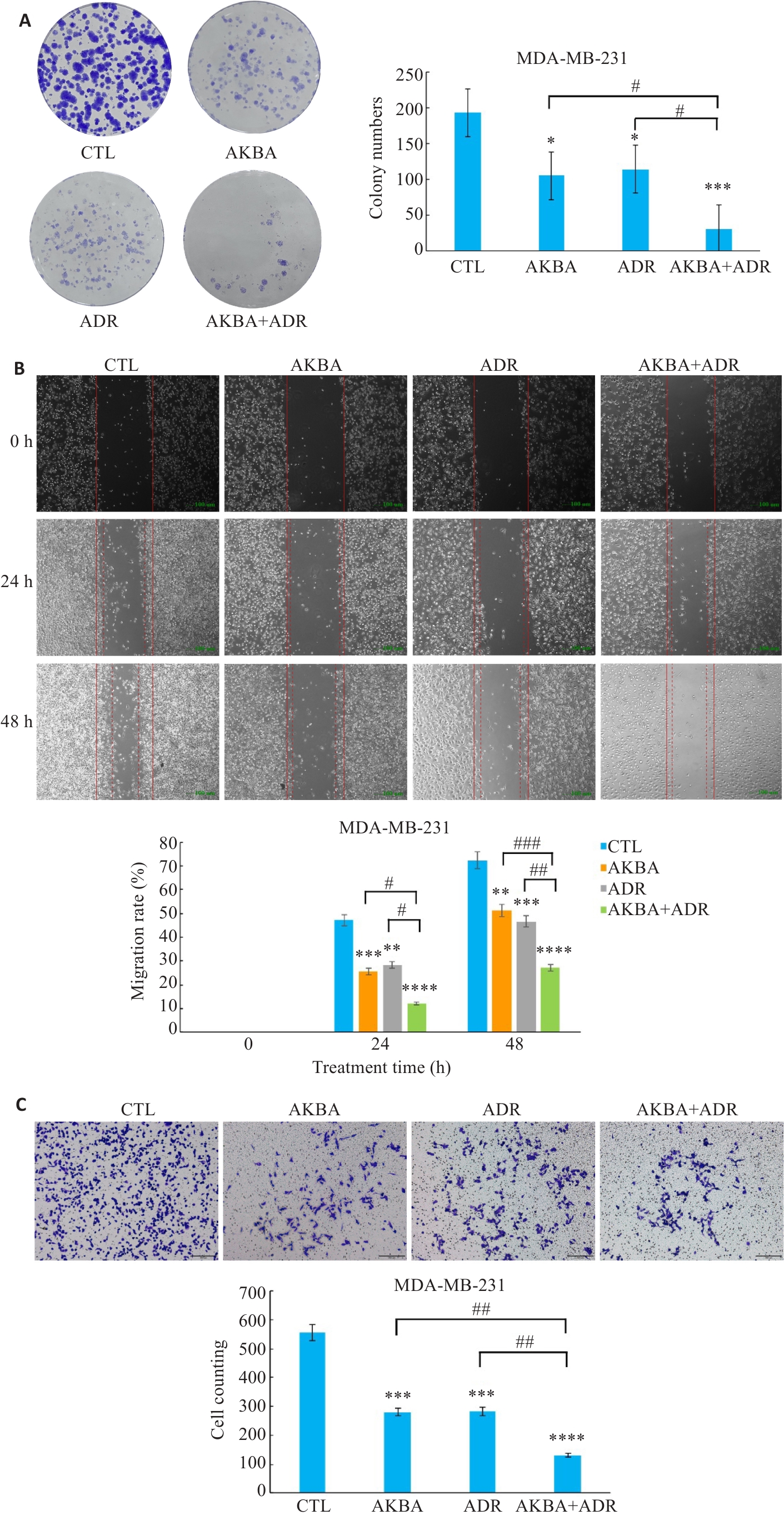
图2 AKBA联合ADR对TNBC细胞增殖和迁移的影响
Fig.2 Effect of AKBA combined with ADR on TNBC cell proliferation and migration. A: Clone formation assay in each group. B: Scratch assay for assessing migration ability of TNBC cells (Original magnification: ×40). C: Transwell migration assay of TNBC cells treated with AKBA combined with ADR (×100). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001 vs CTL; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001.
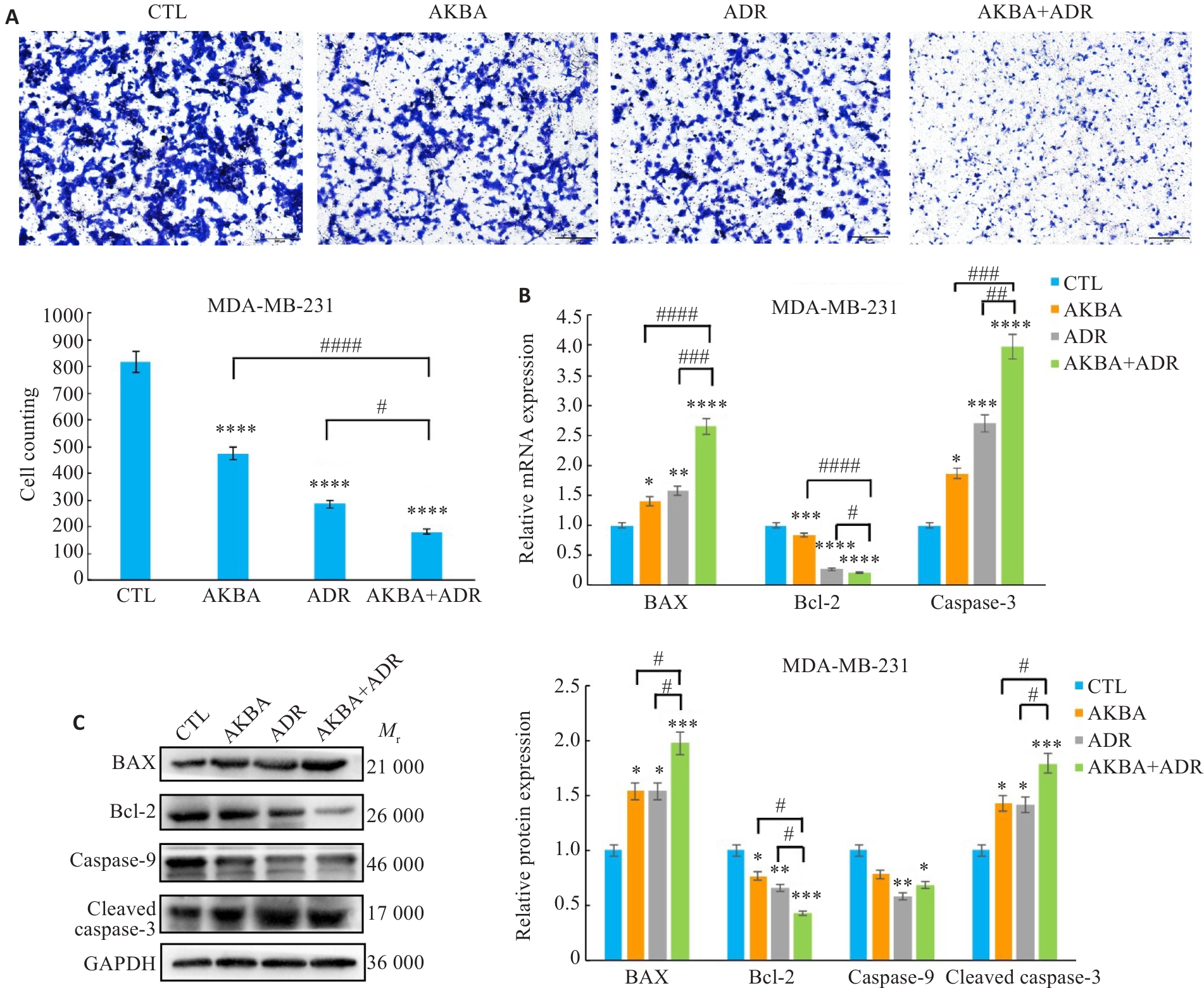
图3 AKBA联合ADR对TNBC细胞侵袭和凋亡的影响
Fig.3 Effect of AKBA combined with ADR on TNBC cell invasion and apoptosis. A: Transwell invasion assay for assessing the ability of TNBC cells to invade stromal gel (×100). B: RT-qPCR for detecting mRNA expressions of apoptosis-related genes in TNBC cells. C: Western blotting for detecting expressions of apoptosis-related proteins in TNBC cells. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001 vs CTL; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001, ####P<0.0001.
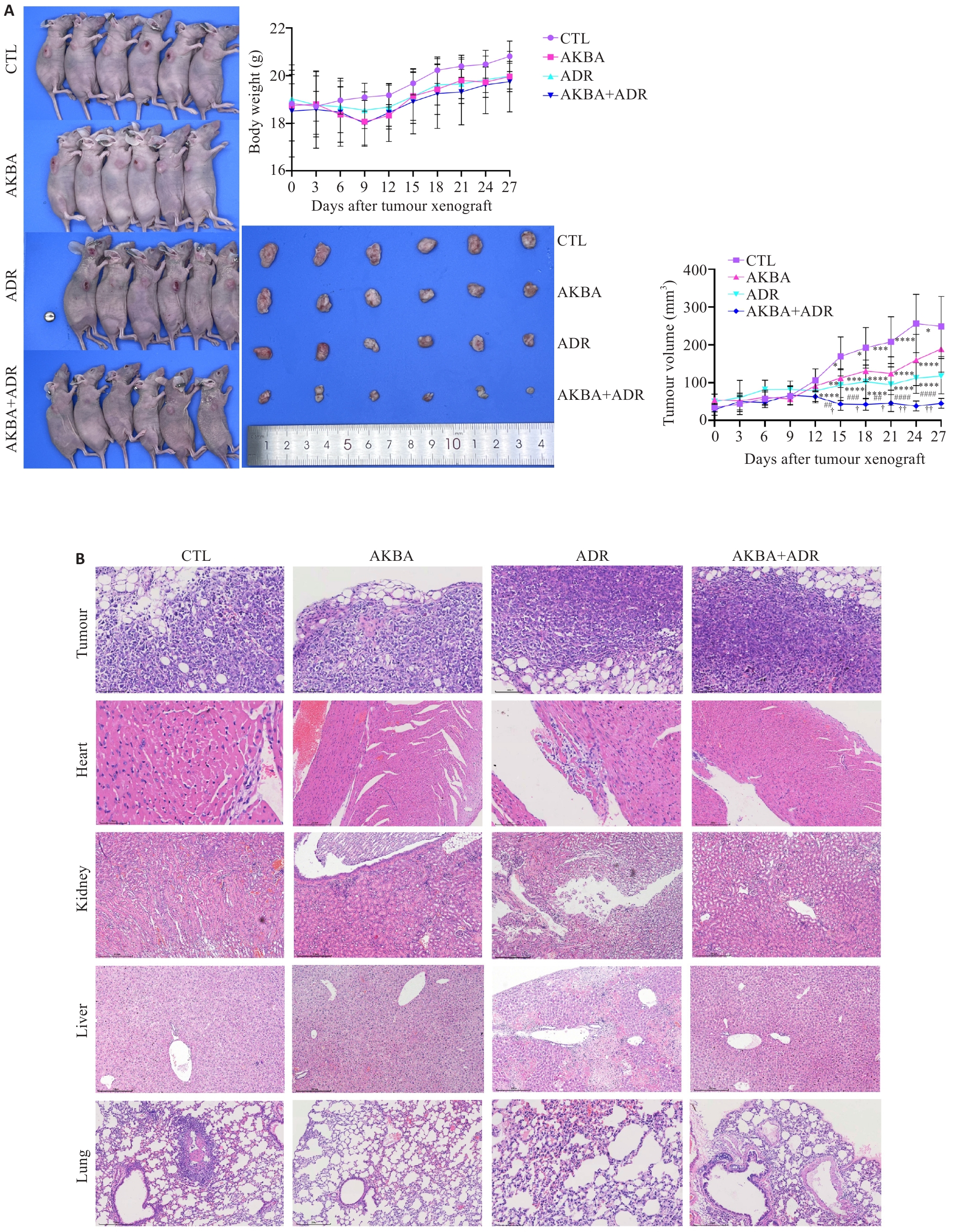
图4 AKBA联合ADR对TNBC细胞裸鼠移植瘤生长的影响以及脏器毒性作用
Fig.4 Effect of AKBA combined with ADR on TNBC xenograft growth and its organ toxicity in nude mice. A: Observation of the tumor-bearing mice and the dissected tumors on day 27 and changes of body weight of the mice and tumor volume over time (black arrows indicate the time points of drug administration). B: HE staining for examining tumor histopathology and evaluating toxic effects of AKBA combined with ADR in the heart, liver, kidney, and lungs of the nude mice (×10). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001 vs CTL; ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001, ####P<0.0001 vs AKBA group; †P<0.05, ††P<0.01 vs ADR group
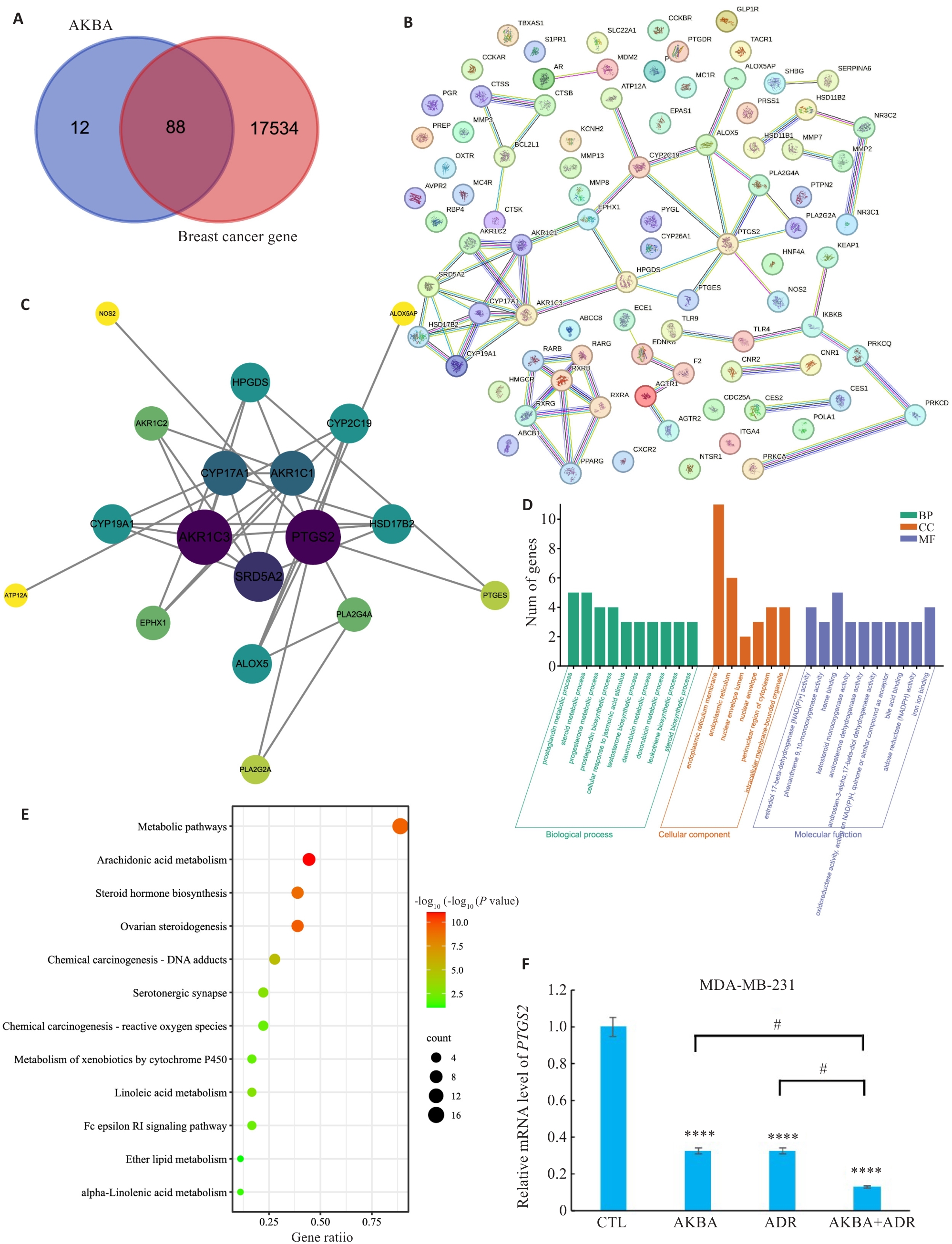
图5 网络药理学分析筛选AKBA作用乳腺癌的下游通路和靶点
Fig.5 Network pharmacological analysis of downstream pathways and targets of AKBA in breast cancer. A: Venn diagram of intersected targets of AKBA and breast cancer. B: Protein interaction network obtained by STRING analysis of the intersected targets. C: Protein-protein interaction (PPI) network created was by Cytoscape for identifying the key targets of AKBA in breast cancer. D, E: Bubble diagram of KEGG pathway enrichment analysis of the biological process (BP), cellular composition (CC), molecular function (MF), GeneRatio, ratio of differential genes in KEGG pathway to the total differential genes. F: RT-qPCR of mRNA expression of the predicted target PTGS2 in each group. ****P<0.0001 vs CTL; #P<0.05.
| 1 | Asleh K, Riaz N, Nielsen TO. Heterogeneity of triple negative breast cancer: current advances in subtyping and treatment implications[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2022, 41(1): 265. |
| 2 | Abu-Khalaf M, Wang C, Zhang ZC, et al. Genomic aberrations in circulating tumor DNAs from palbociclib-treated metastatic breast cancer patients reveal a novel resistance mechanism[J]. Cancers, 2022, 14(12): 2872. |
| 3 | Keenan TE, Tolaney SM. Role of immunotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer[J]. J Natl Compr Canc Netw, 2020, 18(4): 479-89. |
| 4 | Kwakman JJM, Bond MJG, Demichelis RM, et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with clinically node-negative but pathologically node-positive rectal cancer in the Netherlands: a retrospective analysis[J]. Eur J Cancer, 2024, 197: 113466. |
| 5 | Kciuk M, Gielecińska A, Mujwar S, et al. Doxorubicin-an agent with multiple mechanisms of anticancer activity[J]. Cells, 2023, 12(4): 659. |
| 6 | Yu J, Wang CX, Kong Q, et al. Recent progress in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity and protective potential of natural products[J]. Phytomedicine, 2018, 40: 125-39. |
| 7 | Pugazhendhi A, Edison TNJI, Velmurugan BK, et al. Toxicity of Doxorubicin (Dox) to different experimental organ systems[J]. Life Sci, 2018, 200: 26-30. |
| 8 | 孙春萌, 王雅恬. 中国药科大学高质量完成药用辅料标准相关研究课题[J]. 中国药科大学学报, 2020, 51(2): 137. |
| 9 | 刘 迪, 张冰洋, 姚 铁, 等. 乳香化学成分及药理作用研究进展[J]. 中草药, 2020, 51(22): 5900-14. |
| 10 | 哈瑞雯, 周海燕, 詹志来, 等. 乳香化学成分、药理作用研究进展及质量标志物的预测分析[J]. 中华中医药学刊, 2021, 39(11): 94-107. |
| 11 | Li W, Liu JY, Fu WQ, et al. 3-O-acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid exerts anti-tumor effects in glioblastoma by arresting cell cycle at G2/M phase[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2018, 37(1): 132. |
| 12 | Verma M, Fatima S, Saeed M, et al. Anti-proliferative, pro-apoptotic, and chemosensitizing potential of 3-acetyl-11-keto‑β-boswellic acid (AKBA) against prostate cancer cells[J]. Mol Biotechnol, 2024. DOI: 10.1007/s12033-024-01089-7 . |
| 13 | Yang YT, Guo YL, Luo H, et al. Metabolomics-based discovery of XHP as a CYP3A4 inhibitor against pancreatic cancer[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2023, 14: 1164827. |
| 14 | Gong C, Li W, Wu J, et al. AKBA inhibits radiotherapy resistance in lung cancer by inhibiting maspin methylation and regulating the AKT/FOXO1/p21 axis[J]. J Radiat Res, 2023, 64(1): 33-43. |
| 15 | Sun MX, He XP, Huang PY, et al. Acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of gastric cancer cells through the phosphatase and tensin homolog/Akt/cyclooxygenase-2 signaling pathway[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2020, 26(38): 5822-35. |
| 16 | Takada Y, Ichikawa H, Badmaev V, et al. Acetyl-11-keto-beta-boswellic acid potentiates apoptosis, inhibits invasion, and abolishes osteoclastogenesis by suppressing NF-kappa B and NF-kappa B-regulated gene expression[J]. J Immunol, 2006, 176(5): 3127-40. |
| 17 | Xue X, Chen F, Liu AX, et al. Reversal of the multidrug resistance of human ileocecal adenocarcinoma cells by acetyl-11-keto‑β-boswellic acid via downregulation of P-glycoprotein signals[J]. Biosci Trends, 2016, 10(5): 392-9. |
| 18 | Lu J, Wang YC, Shi ZJ, et al. 3-acetyl-11-keto-beta-boswellic acid decreases the malignancy of taxol resistant human ovarian cancer by inhibiting multidrug resistance (MDR) proteins function[J]. Biomedecine Pharmacother, 2019, 116: 108992. |
| 19 | Jiang XF, Liu YS, Zhang GJ, et al. Acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid inhibits precancerous breast lesion MCF-10AT cells via regulation of LINC00707/miR-206 that reduces estrogen receptor‑Α[J]. Cancer Manag Res, 2020, 12: 2301-14. |
| 20 | Ahmed SA, Al-Shanon AF, Al-Saffar AZ, et al. Antiproliferative and cell cycle arrest potentials of 3-O-acetyl-11-keto‑β‑boswellic acid against MCF-7 cells in vitro [J]. J Genet Eng Biotechnol, 2023, 21(1): 75. |
| 21 | Siegel R, Miller KD, Wagle NS, et al. Cancer statistics, 2023[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2023, 73(1):17-48. |
| 22 | Lauß J, Kappacher C, Isser O, et al. Species-Specific quantification of bioactive boswellic acids in Boswellia resin using NIR spectroscopy, HPLC and Multivariate data analysis[J]. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc, 2024, 316: 124384. |
| 23 | Ammon HPT. Boswellic extracts and 11-keto‑β‑boswellic acids prevent type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus by suppressing the expression of proinflammatory cytokines[J]. Phytomedicine, 2019, 63: 153002. |
| 24 | Pan D, Wang Q, Tang SY, et al. Acetyl-11-keto-beta-boswellic acid inhibits cell proliferation and growth of oral squamous cell carcinoma via RAB7B-mediated autophagy[J]. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol, 2024, 485: 116906. |
| 25 | Park YS, Lee JH, Bondar J, et al. Cytotoxic action of acetyl-11-keto-beta-boswellic acid (AKBA) on meningioma cells[J]. Planta Med, 2002, 68(5): 397-401. |
| 26 | Sparger CC, Hernandez AE, Rojas KE, et al. Axillary management and long-term oncologic outcomes in breast cancer patients with clinical N1 disease treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy[J]. World J Surg Oncol, 2024, 22(1): 199. |
| 27 | Lin XX, Wu GM, Wang S, et al. Bibliometric and visual analysis of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2023, 14: 1255158. |
| 28 | Moon JY, Manh Hung LV, Unno T, et al. Nobiletin enhances chemosensitivity to adriamycin through modulation of the akt/GSK3β/β⁻Catenin/MYCN/MRP1 signaling pathway in A549 human non-small-cell lung cancer cells[J]. Nutrients, 2018, 10(12): 1829. |
| 29 | Li YX, Zhai ZH, Li H, et al. Guajadial reverses multidrug resistance by inhibiting ABC transporter expression and suppressing the PI3K/Akt pathway in drug-resistant breast cancer cells[J]. Chem Biol Interact, 2019, 305: 98-104. |
| 30 | Smoots SG, Schreiber AR, Jackson MM, et al. Overcoming doxorubicin resistance in triple-negative breast cancer using the class I-targeting HDAC inhibitor bocodepsin/OKI-179 to promote apoptosis[J]. Breast Cancer Res, 2024, 26(1): 35. |
| 31 | Zhou J, Li XY, Han ZY, et al. Acetyl-11-keto‑β‑boswellic acid restrains the progression of synovitis in osteoarthritis via the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway[J]. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin, 2024. DOI: 10.3724/abbs.2024102 . |
| 32 | Lv MH, Zhuang XB, Zhang Q, et al. Acetyl-11-keto-β‑boswellic acid enhances the cisplatin sensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer cells through cell cycle arrest, apoptosis induction, and autophagy suppression via p21-dependent signaling pathway[J]. Cell Biol Toxicol, 2021, 37(2): 209-28. |
| 33 | Yang YH, Li W, Ren LW, et al. S670, an amide derivative of 3-O-acetyl-11-keto‑β‑boswellic acid, induces ferroptosis in human glioblastoma cells by generating ROS and inhibiting STX17-mediated fusion of autophagosome and lysosome[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2024, 45(1): 209-22. |
| 34 | Zhang P, Jiang H. Acetyl-11-keto‑β‑boswellic acid confers protection in DSS-induced colitis via the JNK-p38 MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways[J]. Adv Biol, 2023, 7(6): e2200247. |
| 35 | Finetti F, Travelli C, Ercoli J, et al. Prostaglandin E2 and cancer: insight into tumor progression and immunity[J]. Biology, 2020, 9(12): 434. |
| 36 | Hashemi Goradel N, Najafi M, Salehi E, et al. Cyclooxygenase-2 in cancer: a review[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2019, 234(5): 5683-99. |
| 37 | Ganz PA, Goodwin PJ. Breast cancer survivorship: where are we today[J]? Adv Exp Med Biol, 2015, 862: 1-8. |
| 38 | Yuan CC, Dong XW, Xu SX, et al. AKBA alleviates experimental pancreatitis by inhibiting oxidative stress in Macrophages through the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2023, 121: 110501. |
| [1] | 陈镝, 吕莹, 郭怡欣, 张怡荣, 王蕊璇, 周小若, 陈雨欣, 武晓慧. 双氢青蒿素可显著增强阿霉素诱导的三阴性乳腺癌细胞凋亡:基于负向调控STAT3/HIF-1α通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 254-260. |
| [2] | 褚乔, 王小娜, 续佳颖, 彭荟林, 赵裕琳, 张静, 陆国玉, 王恺. 白头翁皂苷D通过多靶点和多途径抑制三阴性乳腺癌侵袭转移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 150-161. |
| [3] | 张钰明, 夏士程, 张淋淋, 陈梦茜, 刘晓婧, 高琴, 叶红伟. 金银花提取物对小鼠阿霉素肝脏损伤的保护作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1571-1581. |
| [4] | 崔芝, 马萃娇, 王倩茹, 陈金豪, 严子阳, 杨建林, 吕亚丰, 曹春雨. 表达 TGF-βⅡ受体的腺相关病毒载体抑制小鼠三阴性乳腺癌4T1细胞的增殖和肺转移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 818-826. |
| [5] | 徐梦歧, 石宇彤, 刘俊平, 吴敏敏, 张凤梅, 何志强, 唐 敏. JAG1影响单核-巨噬细胞重塑三阴性乳腺癌转移前微环境:基于外泌体中的LncRNA MALAT1[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(9): 1525-1535. |
| [6] | 王 丽, 严志锐, 夏耀雄. 抑制RAB27a能够抑制三阴乳腺癌细胞的增殖、侵袭和粘附[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(4): 560-567. |
| [7] | 魏 佳, 杨 强, 林 琳, 朱参战, 魏 瑾. 二甲双胍减轻阿霉素诱导的心脏毒性:基于AMPK通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(10): 1682-1688. |
| [8] | 熊凤梅, 刘瑞萍, 李 洋, 孙 娜. 和厚朴酚可体外减轻阿霉素诱导的心肌毒性:基于激活AMPK/Nrf2信号通路抑制细胞焦亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(8): 1205-1211. |
| [9] | 刘俊平, 石宇彤, 吴敏敏, 徐梦岐, 张凤梅, 何志强, 唐 敏. JAG1影响血管生成并促进三阴性乳腺癌细胞的迁移、侵袭和粘附[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(7): 1100-1108. |
| [10] | 方雨潇, 王淑美, 杨 倩, 游松凡, 幸享玲. 柴胡桂枝汤加减方联合卡培他滨抑制三阴性乳腺癌裸鼠皮下移植瘤的生长:基于抑制IL-6/STAT3信号通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(6): 905-912. |
| [11] | 王 婷, 杨 铃, 谢雨涵, 程思宇, 熊 敏, 罗晓明. 持续释放CA4P和阿霉素的可注射水凝胶/短纤维复合物用于小鼠乳腺癌异种移植瘤联合化疗[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(5): 625-632. |
| [12] | 葛 钰, 卢林明, 田澍雨, 肖 雨, 谢尚富, 王 琪, 支 慧. 皖南蝮蛇毒抑瘤组分-Ⅰ通过MMP2抑制三阴性乳腺癌细胞体外血管生成拟态[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(3): 438-442. |
| [13] | 吕雪丽, 刘 媛, 祝瑶露, 赵博欣, 魏 理, 李国锋. 阿霉素-甘草酸分子复合物的制备及体外抗肿瘤活性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(4): 613-620. |
| [14] | 王 璐, 赵 琳, 张丽芬, 景 鑫, 张玉姣, 邵 珊, 赵新汉, 罗敏娜. VEGF通过激活ERK/MAPK通路促进三阴性乳腺癌肿瘤干细胞的形成[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(10): 1484-1491. |
| [15] | 罗东,汪威,陈俊林,刘宝茹,陈锦云,王嫣,陈文直. 低强度脉冲超声对阿霉素联合环磷酰胺化疗后大鼠造血功能的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2019, 39(07): 836-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||