南方医科大学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (12): 2367-2374.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.12.12
收稿日期:2024-07-19
出版日期:2024-12-20
发布日期:2024-12-26
通讯作者:
王允
E-mail:3395103897@qq.com;wy_sunnyday@126.com
作者简介:李 欢,硕士,E-mail: 3395103897@qq.com
基金资助:
Huan LI( ), Zixin QIU, Wenjie XU, Xue CHEN, Diandian WEI, Yun WANG(
), Zixin QIU, Wenjie XU, Xue CHEN, Diandian WEI, Yun WANG( )
)
Received:2024-07-19
Online:2024-12-20
Published:2024-12-26
Contact:
Yun WANG
E-mail:3395103897@qq.com;wy_sunnyday@126.com
摘要:
目的 探究木犀草素(Lut)对肺癌A549细胞增殖的抑制作用及其内在机制。 方法 用不同浓度的Lut处理A549细胞48 h,通过MTT法检测细胞活性,通过平板克隆和EdU染色检测细胞增殖,通过DCFH-DA法检测细胞活性氧(ROS)水平,通过Hoechst33258 染色法检测细胞凋亡水平,通过MDC染色法检测细胞自噬水平,通过Western blotting实验检测细胞凋亡相关蛋白Bax、Bcl-2、Cleaved caspase-9,自噬相关蛋白LC3B、Beclin1、P62,AKT/mTOR通路蛋白以及HO-1蛋白的表达。 结果 Lut剂量依赖性的抑制A549细胞的活力和增殖能力(P<0.05),引发细胞内ROS水平增加(P<0.05),上调凋亡相关蛋白Bax、Cleaved caspase-9和自噬相关蛋白Beclin1的表达,增加LC3B-II/LC3B-I的比值,下调抗凋亡蛋白Bcl-2和自噬相关蛋白P62的表达,诱导细胞凋亡和自噬(P<0.001)。此外,Lut可显著抑制AKT和mTOR的磷酸化,下调HO-1蛋白的表达(P<0.05)。 结论 Lut通过增加细胞内ROS的产生,抑制AKT/mTOR通路以及下调HO-1蛋白水平诱导A549细胞的凋亡和自噬。
李欢, 邱紫欣, 徐文洁, 陈雪, 魏典典, 王允. 木犀草素通过增加ROS的产生和下调AKT/mTOR通路及HO-1蛋白表达抑制肺癌A549细胞增殖[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(12): 2367-2374.
Huan LI, Zixin QIU, Wenjie XU, Xue CHEN, Diandian WEI, Yun WANG. Luteolin inhibits proliferation of lung cancer A549 cells by increasing ROS production and inhibiting the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway and HO-1 expression[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(12): 2367-2374.
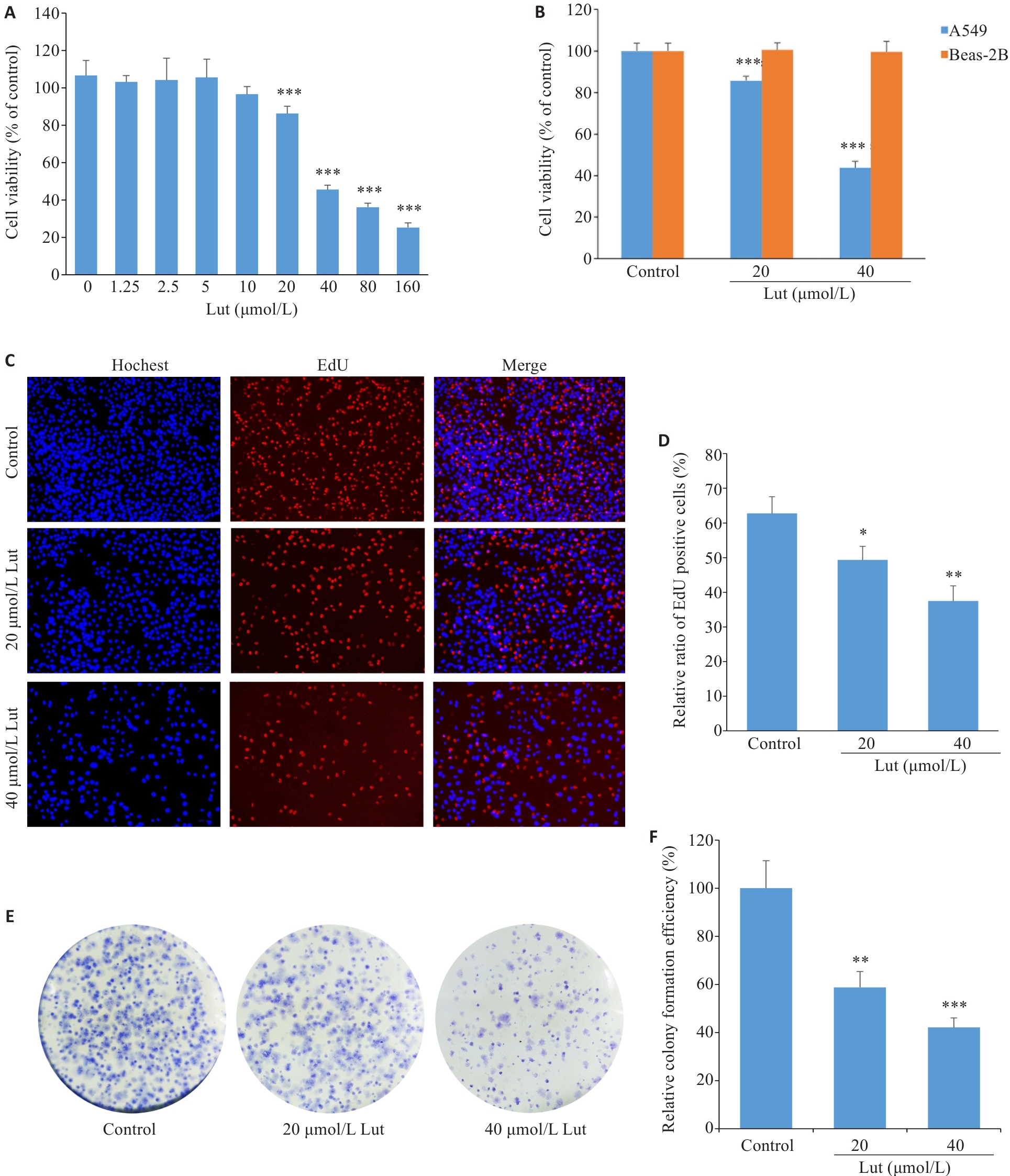
图1 Lut抑制A549细胞的活力、增殖和克隆形成能力
Fig.1 Luteolin (Lut) inhibits viability, proliferation, and clone-forming ability of A549 cells. A: MTT assay of A549 cells treated with different concentrations of luteolin for 48 h. B: MTT assay of A549 and Beas-2B cells treated with 20 and 40 μmol/L luteolin for 48 h. C, D: EdU assay of A549 cells treated with 20 and 40 μmol/L luteolin for 48 h (Original magnification: ×100). E, F: Clone formation assay of A549 cells treated with 20 and 40 μmol/L luteolin for 48 h. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs control.
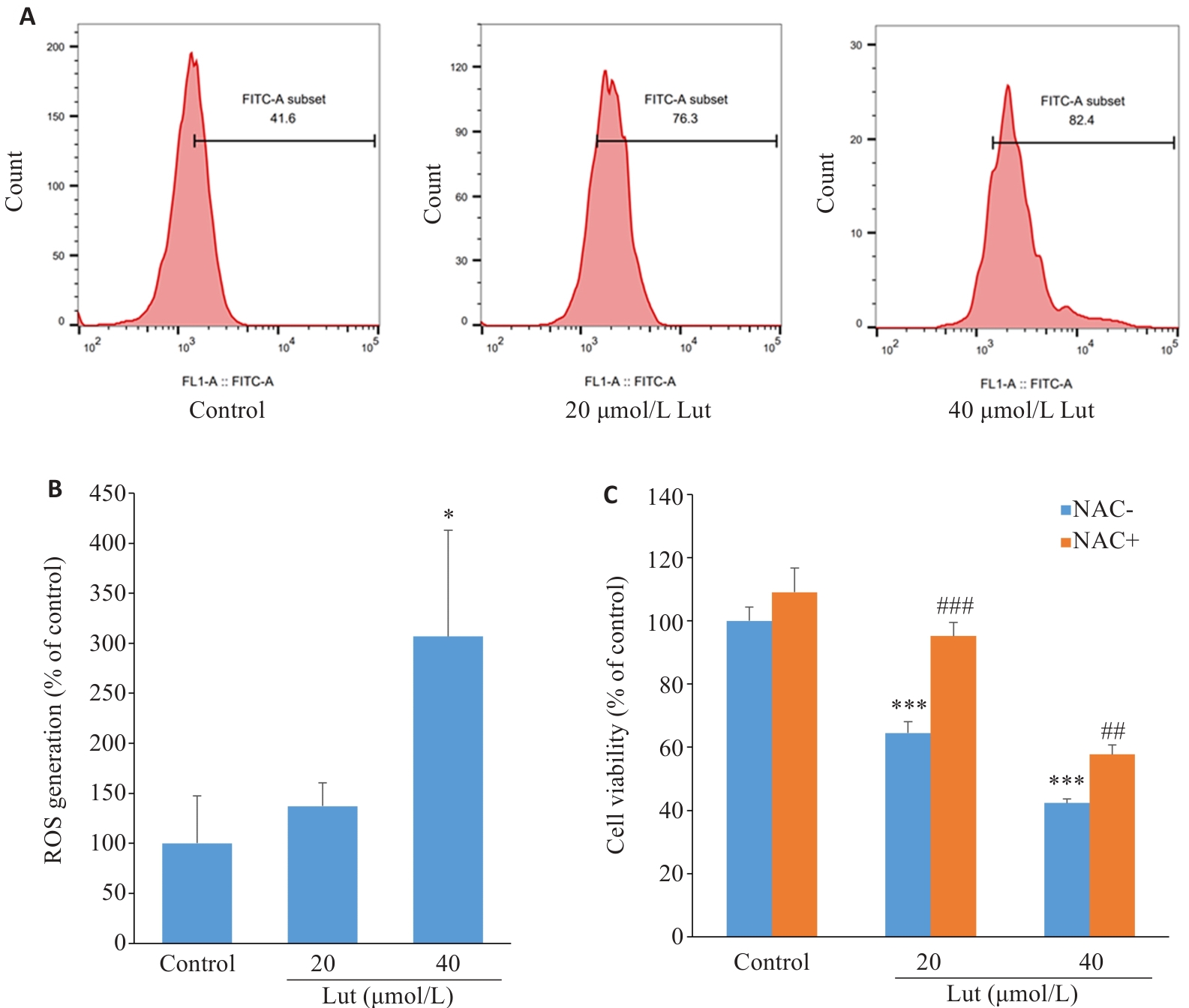
图2 Lut诱导A549细胞氧化应激
Fig.2 Luteolin induces oxidative stress in A549 cells. A, B: Detection of intracellular ROS levels in luteolin-treated A549 cells by flow cytometry. C: MTT assay of A549 cells treated with luteolin in the presence or absence of NAC for 48 h. *P<0.05, ***P<0.001vs control; ##P<0.01,###P<0.001 vs NAC- group.
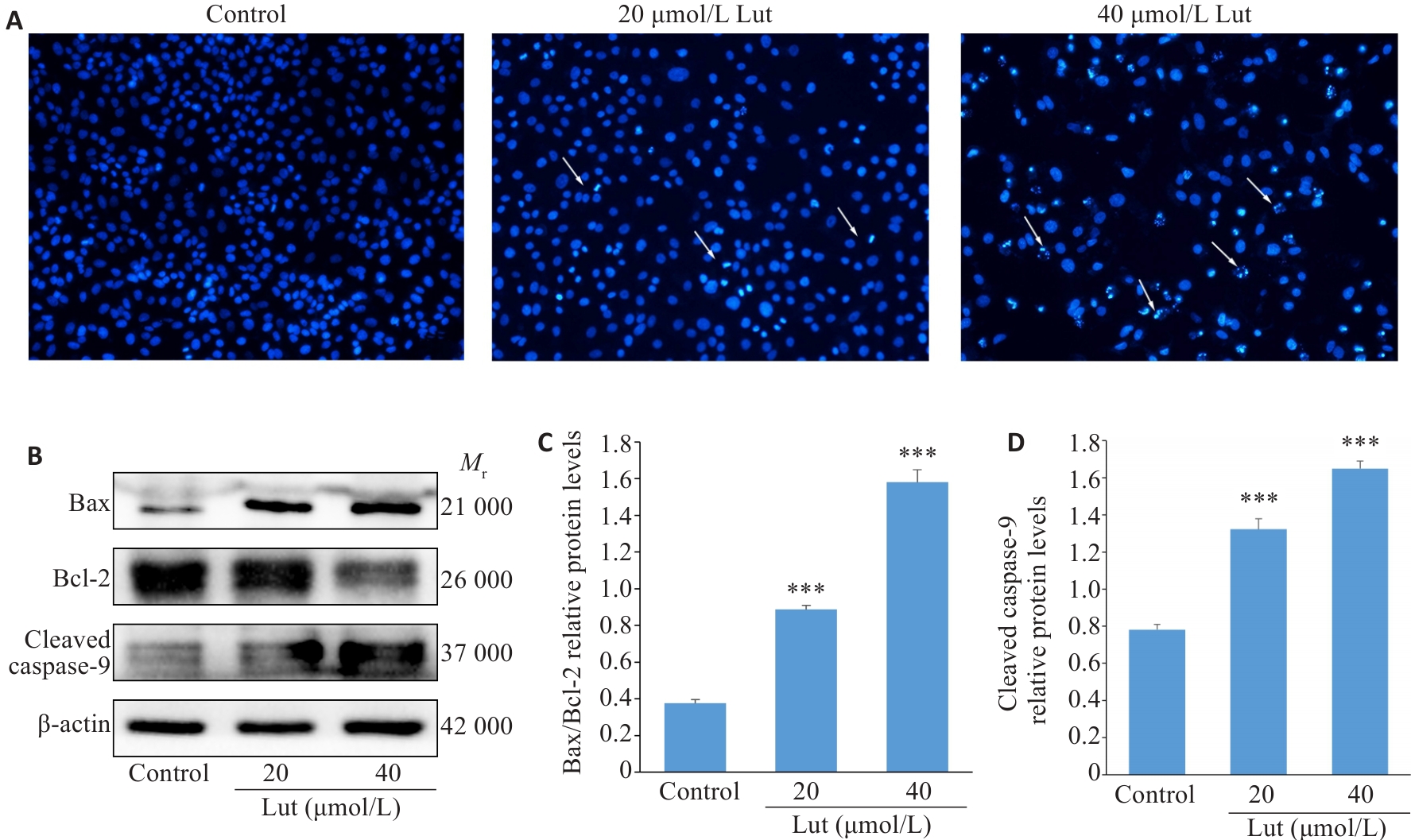
图3 Lut诱导A549细胞凋亡
Fig.3 Luteolin induces apoptosis of A549 cells. A: Hoechst 33258 staining of luteolin-treated A549 cells (×100). B-D: Western blotting for detecting expression levels of Bax, Bcl-2, cleaved-caspase-9 in luteolin-treated A549 cells. ***P<0.001 vs control.
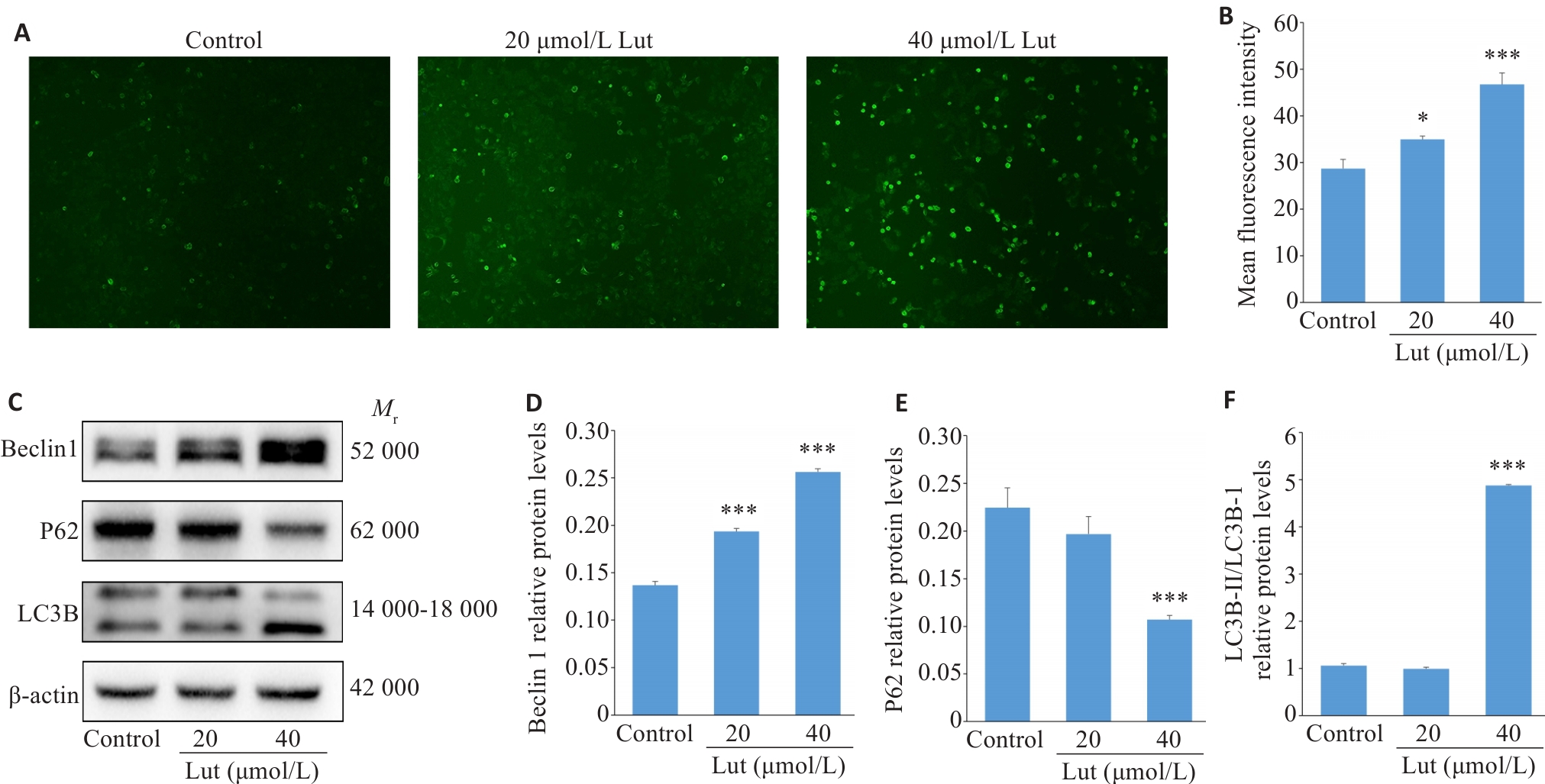
图4 Lut诱导A549细胞自噬
Fig.4 Luteolin induces autophagy in A549 cells. A, B: MDC staining for detecting autophagy in luteolin-treated A549 cells (×100). C-F: Western blotting for detecting expression levels of autophagy-related proteins Beclin 1, P62, and LC3B in luteolin-treated A549 cells. *P<0.05, ***P<0.001 vs control.
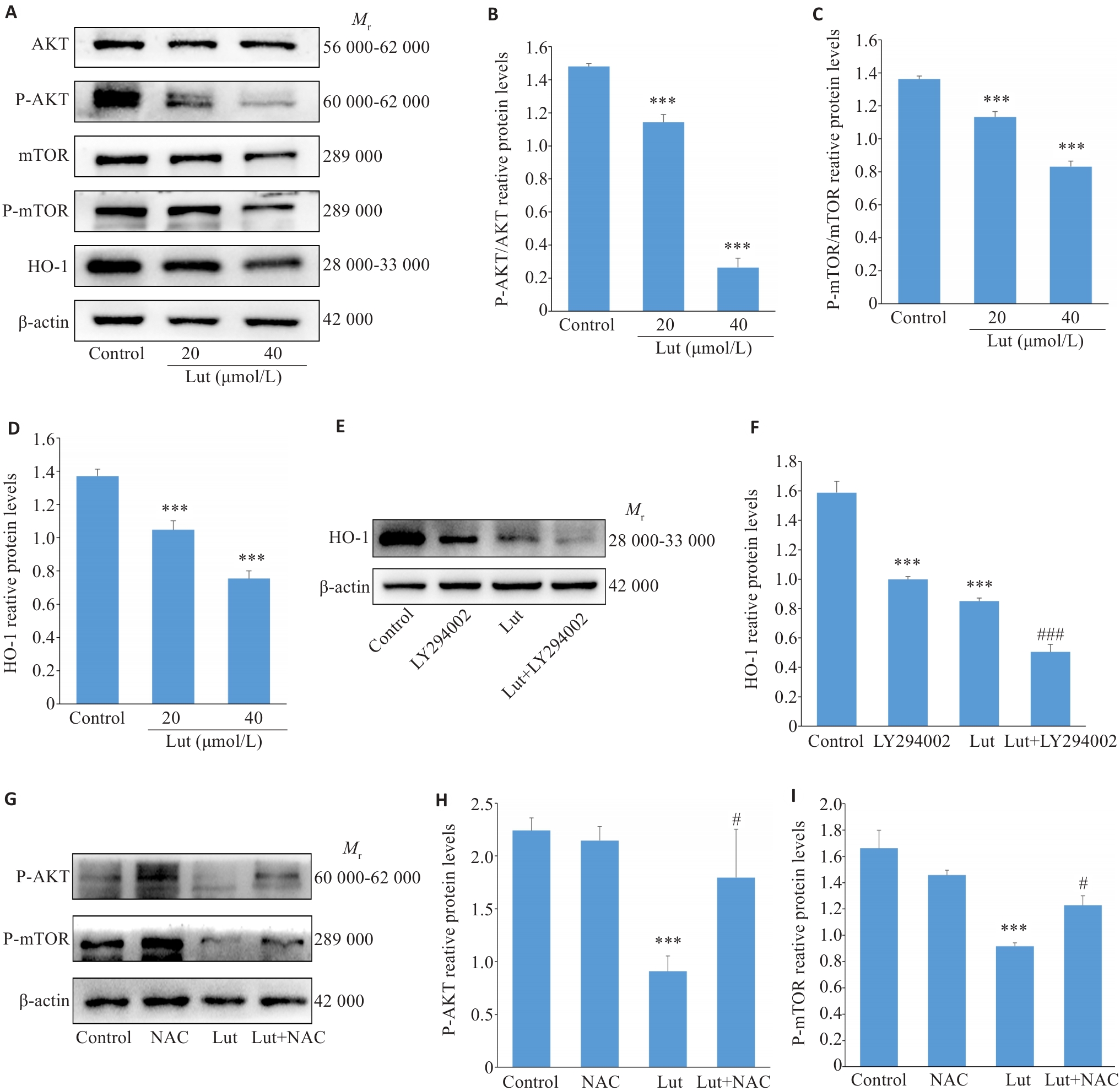
图5 Lut对A549细胞AKT/mTOR通路、HO-1蛋白水平的改变
Fig.5 Luteolin-induced changes in AKT/mTOR signaling and HO-1 protein levels in A549 cells. A-D: Western blotting for detecting expression levels of AKT, P-AKT, mTOR, P-mTOR, and HO-1 proteins in luteolin-treated A549 cells. E, F: Western blotting for detecting HO-1 protein expression levels in A549 cells treated with luteolin in the presence or absence of LY294002 for 48 h. G-I: Western blotting of P-AKT and P-mTOR protein expression levels in A549 cells treated with luteolin in the presence or absence of NAC for 48 h. ***P<0.001 vs control; #P<0.05, ###P<0.001 vs Lut group.
| 1 | He SY, Xia CF, Li H, et al. Cancer profiles in China and comparisons with the USA: a comprehensive analysis in the incidence, mortality, survival, staging, and attribution to risk factors[J]. Sci China Life Sci, 2024, 67(1): 122-31. |
| 2 | Varghese R, Efferth T, Ramamoorthy S. Carotenoids for lung cancer chemoprevention and chemotherapy: promises and controversies[J]. Phytomedicine, 2023, 116: 154850. |
| 3 | Klaunig JE, Kamendulis LM, Hocevar BA. Oxidative stress and oxidative damage in carcinogenesis[J]. Toxicol Pathol, 2010, 38(1): 96-109. |
| 4 | Panieri E, Santoro MM. ROS homeostasis and metabolism: a dangerous liason in cancer cells[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2016, 7(6): e2253. |
| 5 | Huang R, Chen H, Liang JY, et al. Dual role of reactive oxygen species and their application in cancer therapy[J]. J Cancer, 2021, 12(18): 5543-61. |
| 6 | Zhang HB, Ma L, Kim E, et al. Rhein induces oral cancer cell apoptosis and ROS via suppresse AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in vitro and in vivo [J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(10): 8507. |
| 7 | Liou YF, Chen PN, Chu SC, et al. Thymoquinone suppresses the proliferation of renal cell carcinoma cells via reactive oxygen species-induced apoptosis and reduces cell stemness[J]. Environ Toxicol, 2019, 34(11): 1208-20. |
| 8 | Gong XM, Smith JR, Swanson HM, et al. Carotenoid lutein selectively inhibits breast cancer cell growth and potentiates the effect of chemotherapeutic agents through ROS-mediated mechanisms[J]. Molecules, 2018, 23(4): 905. |
| 9 | Fan JJ, Ren DM, Wang JX, et al. Bruceine D induces lung cancer cell apoptosis and autophagy via the ROS/MAPK signaling pathway in vitro and in vivo [J]. Cell Death Dis, 2020, 11(2): 126. |
| 10 | NavaneethaKrishnan S, Rosales JL, Lee KY. ROS-mediated cancer cell killing through dietary phytochemicals[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2019, 2019: 9051542. |
| 11 | Yao WS, Lin Z, Shi PY, et al. Delicaflavone induces ROS-mediated apoptosis and inhibits PI3K/AKT/mTOR and Ras/MEK/Erk signaling pathways in colorectal cancer cells[J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2020, 171: 113680. |
| 12 | Liu YH, Shi CJ, He Z, et al. Inhibition of PI3K/AKT signaling via ROS regulation is involved in Rhein-induced apoptosis and enhancement of oxaliplatin sensitivity in pancreatic cancer cells[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2021, 17(2): 589-602. |
| 13 | Imran M, Rauf A, Abu-Izneid T, et al. Luteolin, a flavonoid, as an anticancer agent: a review[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2019, 112: 108612. |
| 14 | You YJ, Wang R, Shao NY, et al. Luteolin suppresses tumor proliferation through inducing apoptosis and autophagy via MAPK activation in glioma[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2019, 12: 2383-96. |
| 15 | Wu L, Lin YD, Gao SY, et al. Luteolin inhibits triple-negative breast cancer by inducing apoptosis and autophagy through SGK1-FOXO3a-BNIP3 signaling[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2023, 14: 1200843. |
| 16 | Yang HB, Zhao YY, Song W, et al. The inhibition of β‑catenin activity by luteolin isolated from Paulownia flowers leads to growth arrest and apoptosis in cholangiocarcinoma[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2024, 254(Pt 1): 127627. |
| 17 | Geng AZ, Luo L, Ren FY, et al. MiR-29a-3p inhibits endometrial cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting VEGFA/CD C42/PAK1[J]. BMC Cancer, 2021, 21(1): 843. |
| 18 | Zhou XJ, Chen Y, Wang FF, et al. Artesunate induces autophagy dependent apoptosis through upregulating ROS and activating AMPK-mTOR-ULK1 axis in human bladder cancer cells[J]. Chem Biol Interact, 2020, 331: 109273. |
| 19 | Liu SJ, Bu QQ, Tong JS, et al. MiR-486 responds to apoptosis and autophagy by repressing SRSF3 expression in ovarian granulosa cells of dairy goats[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(10): 8751. |
| 20 | Zhao YJ, Guo WY, Gu XL, et al. Repression of deoxynivalenol-triggered cytotoxicity and apoptosis by mannan/β‑glucans from yeast cell wall: involvement of autophagy and PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling pathway[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2020, 164: 1413-21. |
| 21 | Chu N, Zhang X, Chen S, et al. Luteolin has a significant protective effect against cadmium-induced injury in lung epithelial Beas-2B cells[J]. J South Med Univ, 2021, 41(5): 729-35. |
| 22 | Hseu YC, Lee MS, Wu CR, et al. The chalcone flavokawain B induces G2/M cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in human oral carcinoma HSC-3 cells through the intracellular ROS generation and downregulation of the Akt/p38 MAPK signaling pathway[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2012, 60(9): 2385-97. |
| 23 | Amawi H, Ashby CR Jr, Tiwari AK. Cancer chemoprevention through dietary flavonoids: what's limiting[J]? Chin J Cancer, 2017, 36(1): 50. |
| 24 | Holmström KM, Finkel T. Cellular mechanisms and physiological consequences of redox-dependent signalling[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2014, 15(6): 411-21. |
| 25 | Li XM, Hou YN, Zhao JT, et al. Combination of chemotherapy and oxidative stress to enhance cancer cell apoptosis[J]. Chem Sci, 2020, 11(12): 3215-22. |
| 26 | Ullah A, Razzaq A, Alfaifi MY, et al. Sanguinarine attenuates lung cancer progression via oxidative stress-induced cell apoptosis[J]. Curr Mol Pharmacol, 2024, 17: e18761429269383. |
| 27 | Wang T, Wu X, Al Rudaisat M, et al. Curcumin induces G2/M arrest and triggers autophagy, ROS generation and cell senescence in cervical cancer cells[J]. J Cancer, 2020, 11(22): 6704-15. |
| 28 | Wang Q, Wang HD, Jia Y, et al. Luteolin induces apoptosis by ROS/ER stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in gliomablastoma[J]. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol, 2017, 79(5): 1031-41. |
| 29 | Zhou CC, Qian WK, Li J, et al. High glucose microenvironment accelerates tumor growth via SREBP1-autophagy axis in pancreatic cancer[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2019, 38(1): 302. |
| 30 | Zhang N, Xue ML, Wang Q, et al. Inhibition of fucoidan on breast cancer cells and potential enhancement of their sensitivity to chemotherapy by regulating autophagy[J]. Phytother Res, 2021, 35(12): 6904-17. |
| 31 | Sun Y, Qiao YN, Liu Y, et al. Ent-Kaurane diterpenoids induce apoptosis and ferroptosis through targeting redox resetting to overcome cisplatin resistance[J]. Redox Biol, 2021, 43: 101977. |
| 32 | Pistritto G, Trisciuoglio D, Ceci C, et al. Apoptosis as anticancer mechanism: function and dysfunction of its modulators and targeted therapeutic strategies[J]. Aging, 2016, 8(4): 603-19. |
| 33 | Sahoo G, Samal D, Khandayataray P, et al. A review on caspases: key regulators of biological activities and apoptosis[J]. Mol Neurobiol, 2023, 60(10): 5805-37. |
| 34 | Bortnik S, Gorski SM. Clinical applications of autophagy proteins in cancer: from potential targets to biomarkers[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2017, 18(7): 1496. |
| 35 | Jovanović L, Nikolić A, Dragičević S, et al. Prognostic relevance of autophagy-related markers p62, LC3, and Beclin1 in ovarian cancer[J]. Croat Med J, 2022, 63(5): 453-60. |
| 36 | Li W, Cai ZN, Mehmood S, et al. Polysaccharide FMP-1 from Morchella esculenta attenuates cellular oxidative damage in human alveolar epithelial A549 cells through PI3K/AKT/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2018, 120(Pt A): 865-75. |
| 37 | Li H, Song F, Duan LR, et al. Paeonol and danshensu combination attenuates apoptosis in myocardial infarcted rats by inhibiting oxidative stress: roles of Nrf2/HO-1 and PI3K/Akt pathway[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 23693. |
| 38 | Hu YW, Liu Y, Guo EY, et al. Naphtho-γ-pyrone dimers from an endozoic Aspergillus niger and the effects of coisolated monomers in combination with cisplatin on a cisplatin-resistant A549 cell line[J]. J Nat Prod, 2021, 84(7): 1889-97. |
| 39 | Kim YC, Guan KL. mTOR: a pharmacologic target for autophagy regulation[J]. J Clin Invest, 2015, 125(1): 25-32. |
| 40 | Yang JL, Pi CC, Wang GH. Inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway by apigenin induces apoptosis and autophagy in hepatocellular carcinoma cells[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2018, 103: 699-707. |
| [1] | 常笑语, 张瀚文, 曹红亭, 侯玲, 孟鑫, 陶虹, 罗彦, 李光华. 热应激对大鼠胸主动脉内皮细胞生物钟基因 Bmal1和细胞周期蛋白表达水平的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1353-1362. |
| [2] | 李玮怡, 江露, 张宗星, 陈丹, 包卓玛, 黄丽, 袁林. 强骨康疏方通过抑制HIF-1α/BNIP3自噬信号通路减少类风湿性关节炎大鼠的破骨细胞分化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1389-1396. |
| [3] | 王心恒, 邵小涵, 李童童, 张璐, 杨勤军, 叶卫东, 童佳兵, 李泽庚, 方向明. 平喘宁方通过调控HMGB1/Beclin-1轴介导的自噬改善患寒哮证大鼠的气道炎症[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1153-1162. |
| [4] | 杨毓甲, 杨丽芳, 吴雅玲, 段兆达, 于春泽, 吴春云, 于建云, 杨力. 大麻二酚经PERK-eIF2α-ATF4-CHOP通路减轻多重脑震荡大鼠的神经元内质网应激和凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1240-1250. |
| [5] | 周礼华, 张汛, 郁瑛瑛, 张畔畔. Nrf2/HO-1抗氧化通路调控氯氰菊酯诱导的小鼠海马氧化损伤的机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(5): 893-900. |
| [6] | 陈悦, 肖林雨, 任侣, 宋雪, 李静, 胡建国. 水晶兰苷通过抑制PI3K/AKT信号通路减少神经元凋亡改善脊髓损伤后小鼠的运动功能[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 774-784. |
| [7] | 储菲, 陈孝华, 宋博文, 杨晶晶, 左芦根. 苏荠宁黄酮通过抑制PI3K/AKT信号通路拮抗肠上皮细胞凋亡改善小鼠实验性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 819-828. |
| [8] | 张毅, 沈昱, 万志强, 陶嵩, 柳亚魁, 王栓虎. CDKN3高表达促进胃癌细胞的迁移和侵袭:基于调控p53/NF-κB信号通路和抑制胃癌细胞凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 853-861. |
| [9] | 董妍妍, 张可敬, 储俊, 储全根. 抵当汤含药血清通过PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号通路增强高糖诱导的大鼠肾小球内皮细胞自噬[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 461-469. |
| [10] | 刘洋, 贾亿卿, 李程程, 毛汉丁, 刘树元, 单毅. 右美托咪定通过激活Nrf2/HO-1通路减轻热应激诱导的人骨骼肌细胞胀亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 603-613. |
| [11] | 廖茗, 钟文华, 张冉, 梁娟, 徐文陶睿, 万文珺, 吴超, 李曙. 源自蛇毒的蛋白C激活剂通过调控HIF-1α抑制BNIP3活性氧生成保护人脐静脉内皮细胞免受缺氧-复氧损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 614-621. |
| [12] | 陈镝, 吕莹, 郭怡欣, 张怡荣, 王蕊璇, 周小若, 陈雨欣, 武晓慧. 双氢青蒿素可显著增强阿霉素诱导的三阴性乳腺癌细胞凋亡:基于负向调控STAT3/HIF-1α通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 254-260. |
| [13] | 宾禹, 李子雯, 左素微, 孙思诺, 李敏, 宋佳茵, 林旭, 薛刚, 吴靖芳. 载脂蛋白C1高表达通过激活JAK2/STAT3信号通路促进甲状腺乳头状癌细胞的增殖并抑制凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 359-370. |
| [14] | 郭克磊, 李颖利, 宣晨光, 侯紫君, 叶松山, 李林运, 陈丽平, 韩立, 卞华. 益气养阴化浊通络方通过调控miR-21a-5p/FoxO1/PINK1介导的线粒体自噬减轻糖尿病肾病小鼠的足细胞损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 27-34. |
| [15] | 展俊平, 黄硕, 孟庆良, 范围, 谷慧敏, 崔家康, 王慧莲. 缺氧微环境下补阳还五汤通过抑制BNIP3-PI3K/Akt通路抑制类风湿关节炎滑膜成纤维细胞的线粒体自噬[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 35-42. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||