南方医科大学学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (1): 166-174.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2026.01.18
王喆1,2( ), 孔柯瑜3, 金明昊3, 伍信儒3, 范文轩3, 翟赞京3, 胡子豪1,2, 牛琳2, 齐岩松2(
), 孔柯瑜3, 金明昊3, 伍信儒3, 范文轩3, 翟赞京3, 胡子豪1,2, 牛琳2, 齐岩松2( ), 徐永胜1,2(
), 徐永胜1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2025-06-27
出版日期:2026-01-20
发布日期:2026-01-16
通讯作者:
齐岩松,徐永胜
E-mail:jonna170308@163.com;malaqinfu@126.com;xys_sportsmedicine@126.com
作者简介:王 喆,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: jonna170308@163.com
基金资助:
Zhe WANG1,2( ), Keyu KONG3, Minghao JIN3, Sonu NG3, Wenxuan FAN3, Zanjing ZHAI3, Zihao HU1,2, Lin NIU2, Yansong QI2(
), Keyu KONG3, Minghao JIN3, Sonu NG3, Wenxuan FAN3, Zanjing ZHAI3, Zihao HU1,2, Lin NIU2, Yansong QI2( ), Yongsheng XU1,2(
), Yongsheng XU1,2( )
)
Received:2025-06-27
Online:2026-01-20
Published:2026-01-16
Contact:
Yansong QI, Yongsheng XU
E-mail:jonna170308@163.com;malaqinfu@126.com;xys_sportsmedicine@126.com
摘要:
目的 探讨叶酸(FA)修饰的髌下脂肪垫间充质干细胞(IPFP-MSCs)来源外泌体(Exos)通过调控巨噬细胞M1/M2极化改善膝骨关节炎(KOA)炎症微环境的作用。 方法 提取培养IPFP-MSCs,加入FA进行处理,利用超速离心法分离Exos。将RAW264.7细胞分为对照组(未处理)、脂多糖(LPS)组(加入LPS)、LPS+Exos组(加入LPS及Exos)和LPS+FA-Exos组(加入LPS及FA修饰的Exos),分别处理12 h。采用透射电镜、纳米颗粒跟踪分析和Western blot鉴定外泌体,使用共聚焦显微镜观察其摄取情况。通过qRT-PCR、ELISA、流式细胞术和免疫荧光检测各组促炎因子(IL-1β、IL-6、TNF-α、iNOS)与抗炎因子(ARG1、MRC1、CD206)表达水平。 结果 透射电镜显示IPFP-Exos呈典型杯状,CD9与CD81蛋白表达阳性;共聚焦结果证实其可被巨噬细胞摄取。qRT-PCR与ELISA结果表明,LPS+FA-Exos组促炎因子IL-1β、IL-6、TNF-α、NOS2表达较LPS组显著下降(P<0.0001),抗炎因子ARG1、MRC1表达升高(P<0.0001)。流式检测显示,FA-Exos组CD86阳性比例下降,CD206及其比值升高(P<0.0001)。免疫荧光显示FA-Exos组iNOS表达减少(P=0.0478),CD206表达增强(P=0.0003)。 结论 FA-Exos可有效调控巨噬细胞由M1型向M2型极化,免疫调节作用优于未修饰Exos,这种双重调控机制可有效缓解关节腔促炎微环境,为KOA的靶向治疗提供了新型外泌体修饰策略。
王喆, 孔柯瑜, 金明昊, 伍信儒, 范文轩, 翟赞京, 胡子豪, 牛琳, 齐岩松, 徐永胜. 叶酸预处理髌下脂肪垫来源间充质干细胞来源的外泌体调控巨噬细胞极化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2026, 46(1): 166-174.
Zhe WANG, Keyu KONG, Minghao JIN, Sonu NG, Wenxuan FAN, Zanjing ZHAI, Zihao HU, Lin NIU, Yansong QI, Yongsheng XU. Exosomes from folic acid-treated subpatellar fat pad-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote M2 polarization of macrophages in vitro[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2026, 46(1): 166-174.
| Gene | Forward (5′-3′) | Reverse (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| ARG1 | CCACAGTCTGGCAGTTGGAAG | GGTTGTCAGGGGAGTGTTGATG |
| MRC1 | GGCTGATTACGAGCAGTGGA | CATCACTCCAGGTGAACCCC |
| TNF-α | GCCTCTTCTCATTCCTGCTTGTGG | GTGGTTTGTGAGTGTGAGGGTCT |
| IL-1β | TCGCAGCAGCACATCAACAAGAG | AGGTCCACGGGAAAGACACAGG |
| NOS2 | ACTCAGCCAAGCCCTCACCTAC | TCCAATCTCTGCCTATCCGTCTCG |
| IL-6 | CTTCTTGGGACTGATGCTGGTGAC | AGGTCTGTTGGGAGTGGTATCCTC |
| GADPH | GGCAAGTTCAACGGCACAG | CGCCAGTAGACTCCACGACAT |
表1 qRT- PCR对差异表达miRNA的引物序列
Tab.1 Primer sequence for qRT-PCR
| Gene | Forward (5′-3′) | Reverse (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| ARG1 | CCACAGTCTGGCAGTTGGAAG | GGTTGTCAGGGGAGTGTTGATG |
| MRC1 | GGCTGATTACGAGCAGTGGA | CATCACTCCAGGTGAACCCC |
| TNF-α | GCCTCTTCTCATTCCTGCTTGTGG | GTGGTTTGTGAGTGTGAGGGTCT |
| IL-1β | TCGCAGCAGCACATCAACAAGAG | AGGTCCACGGGAAAGACACAGG |
| NOS2 | ACTCAGCCAAGCCCTCACCTAC | TCCAATCTCTGCCTATCCGTCTCG |
| IL-6 | CTTCTTGGGACTGATGCTGGTGAC | AGGTCTGTTGGGAGTGGTATCCTC |
| GADPH | GGCAAGTTCAACGGCACAG | CGCCAGTAGACTCCACGACAT |
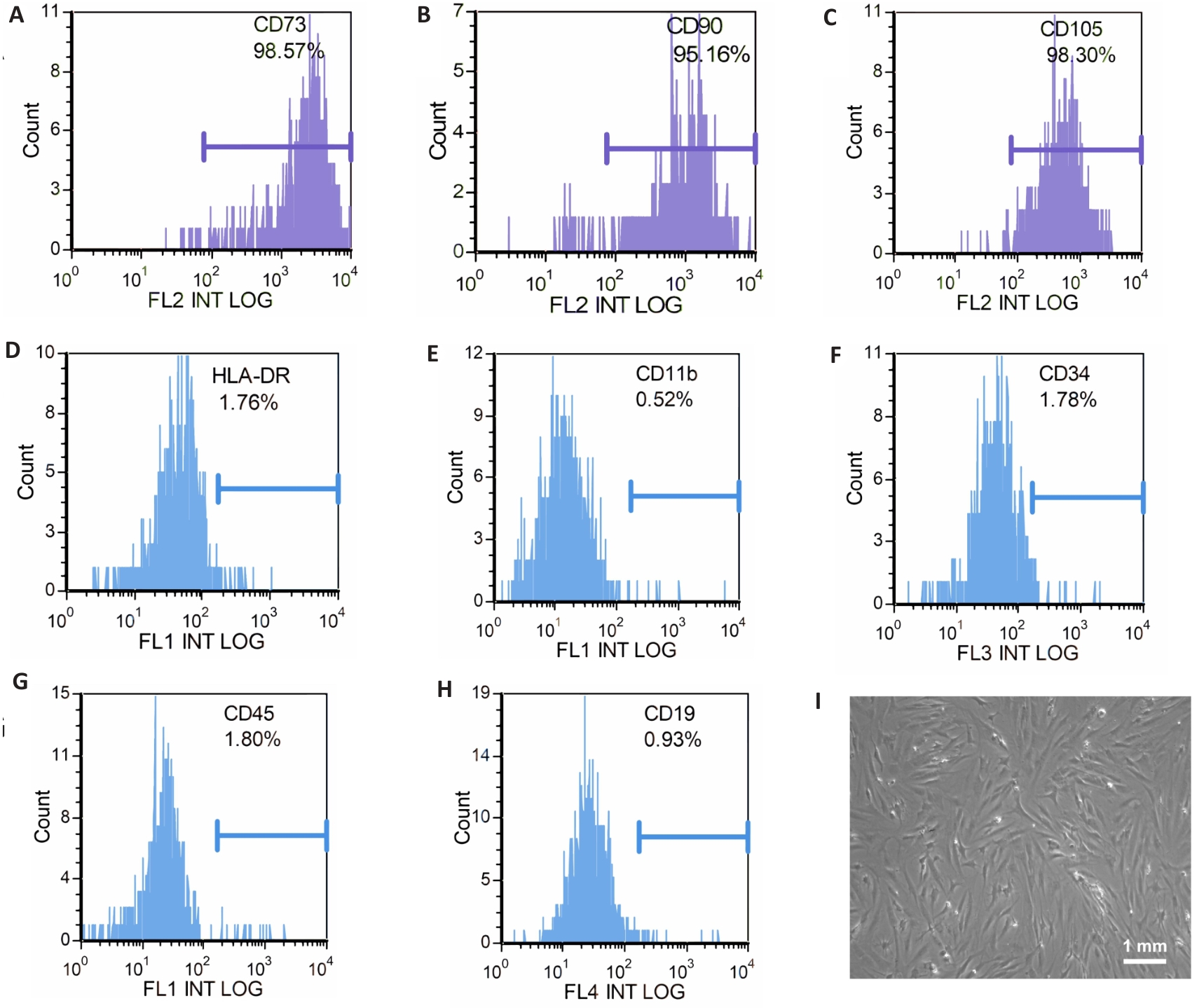
图1 IPFP-MSCs流式细胞术鉴定(A-H)及光学显微镜镜下图像(I)
Fig.1 Identification of infrapatellar fat pad mesenchymal stem cells (IPFP-MSCs) by flow cytometry (A-H) and under optical microscope (I).
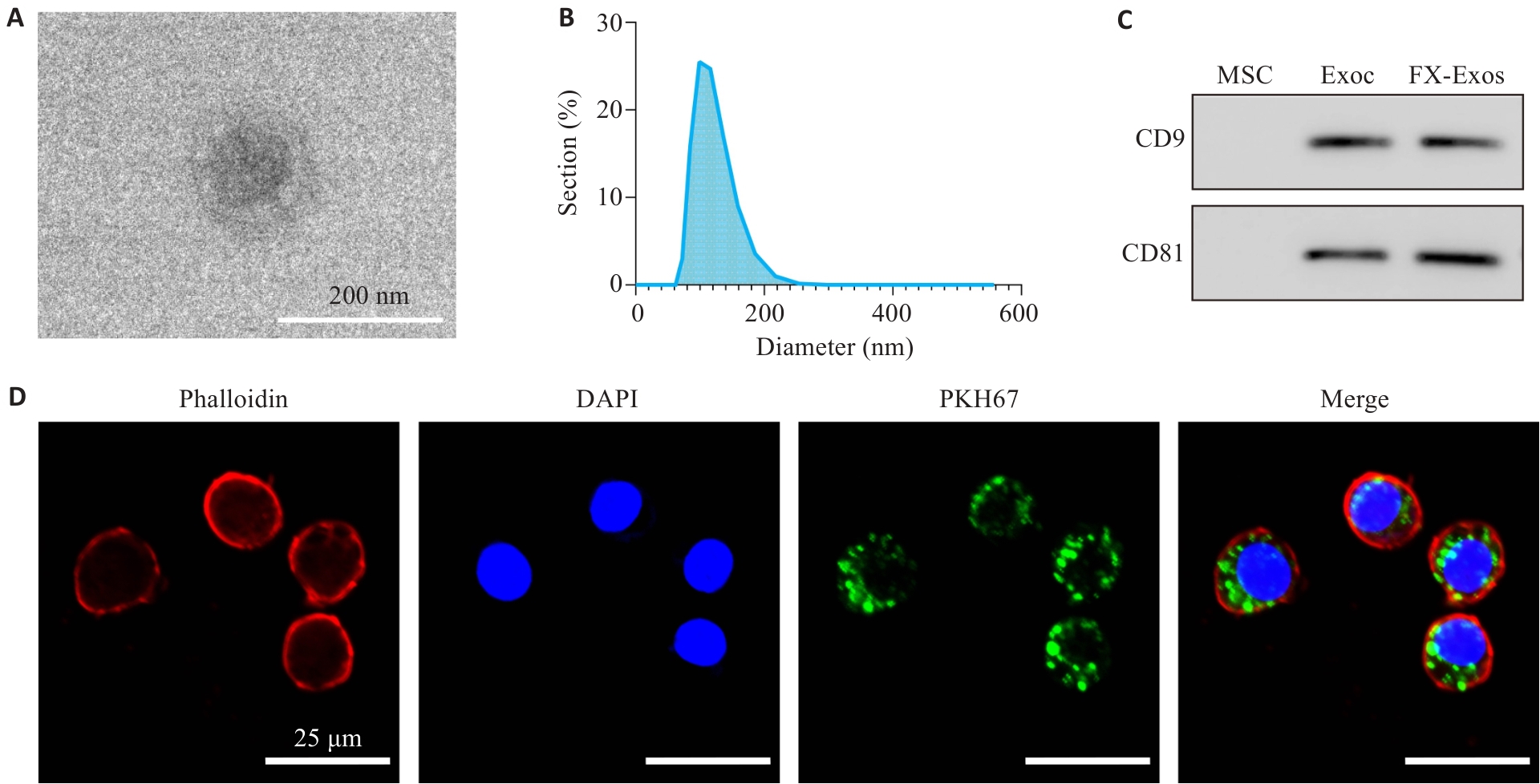
图2 IPFP-Exos的鉴定及其在RAW264.7巨噬细胞中的分布
Fig.2 Identification of exosomes from IPFP-MSCs (IPFP-Exos) and its distribution in RAW264.7 macrophages. A: TEM observation showing cup-shaped IPFP-Exos. B: NTA showing homogenous diameter of the vesicles. C: Positive expression of surface markers CD9 and CD81 on IPFP-Exos; D: Confocal microscopy for observing distribution of IPFP-Exos in RAW264.7 macrophages.
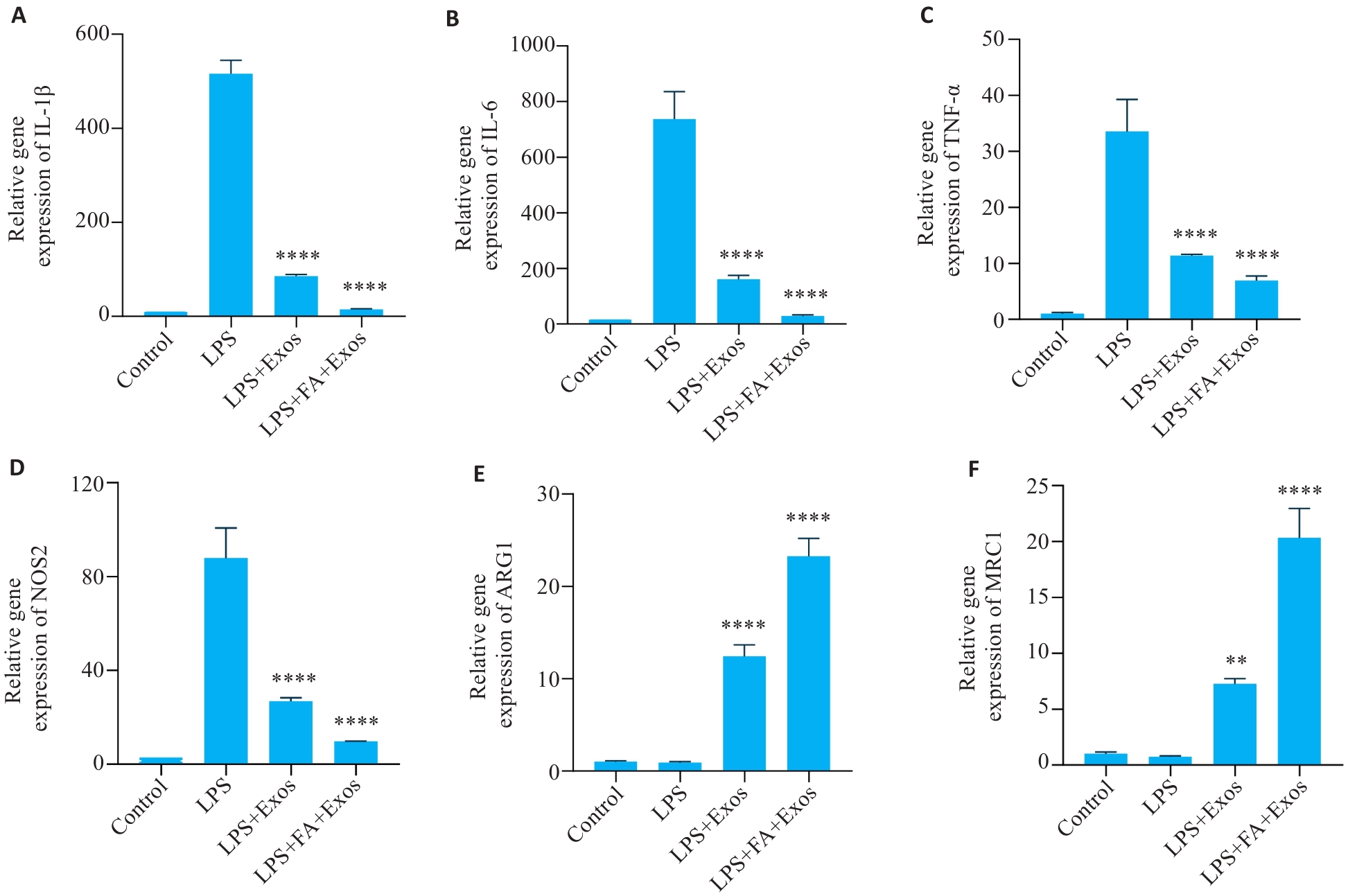
图3 IL-1β、IL-6、TNF-α、NOS2、ARG1和MRC1的mRNA表达水平
Fig.3 Changes in the mRNA expression levels of IL-1β (A), IL-6 (B), TNF-α (C), NOS2(D), ARG1 (E) and MRC1 (F) (n=3). **P<0.01, ****P<0.0001 vs LPS group.
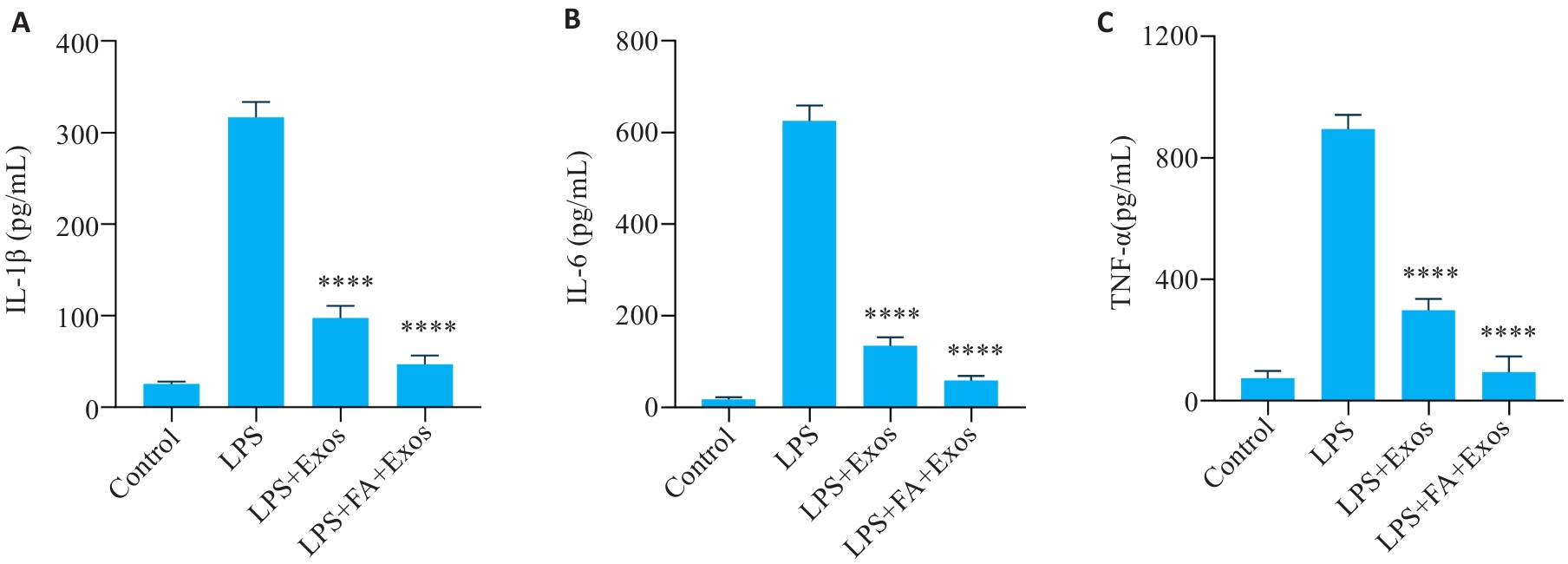
图4 ELISA检测细胞上清IL-1β、IL-6和TNF-α的表达
Fig.4 Results of ELISA for detecting expression levels of IL-1β (A), IL-6 (B) and TNF-α (C) in the cell supernatant (n=5). ****P<0.0001 vs LPS group.
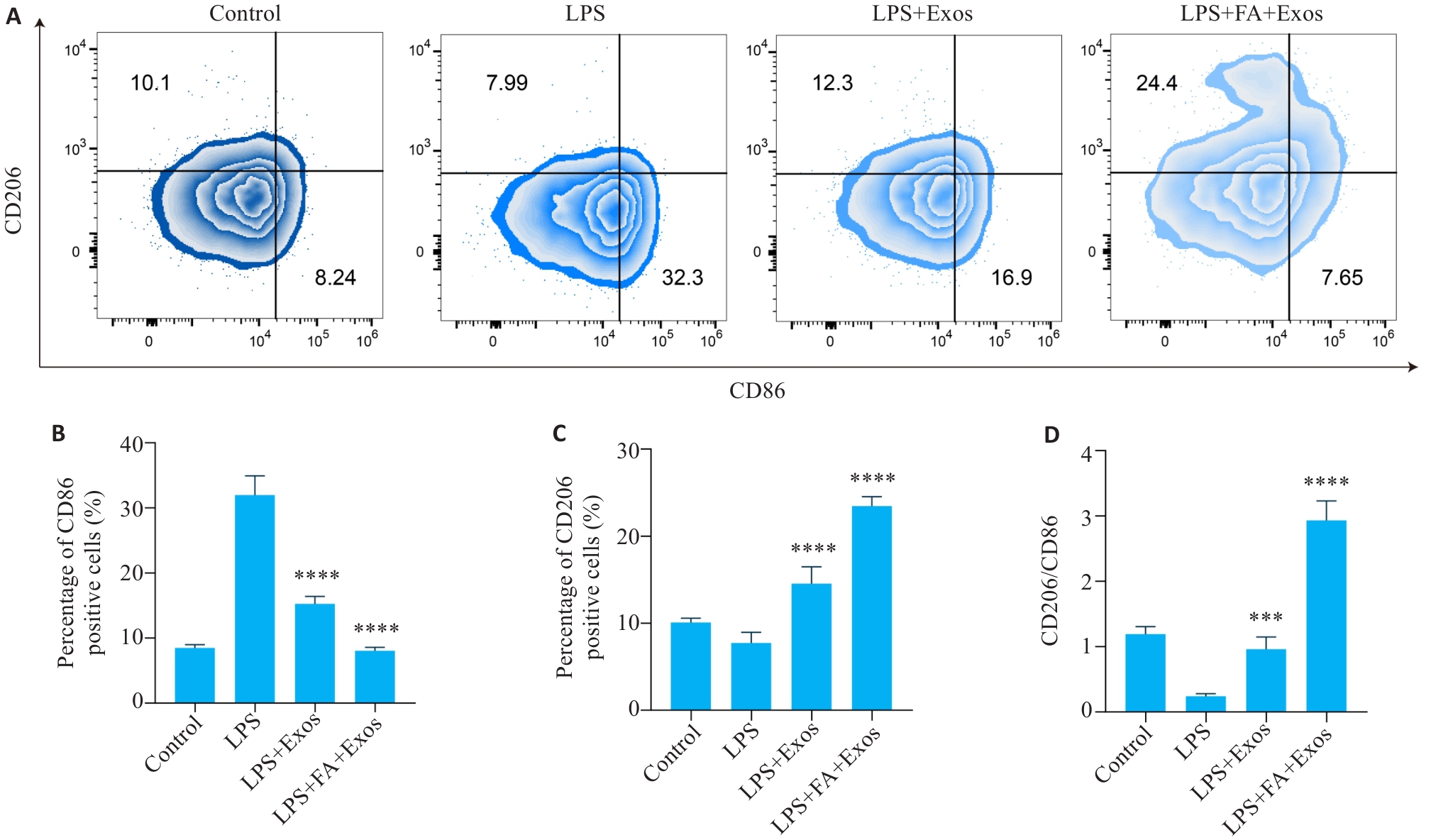
图5 流式细胞术检测RAW264.7巨噬细胞CD86和CD206的表达
Fig.5 Expressions of CD86 and CD206 in RAW264.7 macrophages incubated with the exosomes detected by flow cytometry. A: Two-dimensional density maps of flow cytometry showing the expression of M1-type marker CD86 and M2-type marker CD206 in different groups. B: Bar chart of the percentage of CD86-positive cells in different groups. C: Bar chart of the percentage of CD206-positive cells in different groups. D: The ratio of CD206/CD86 in different groups. (n=4/5). ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001 vs LPS group.
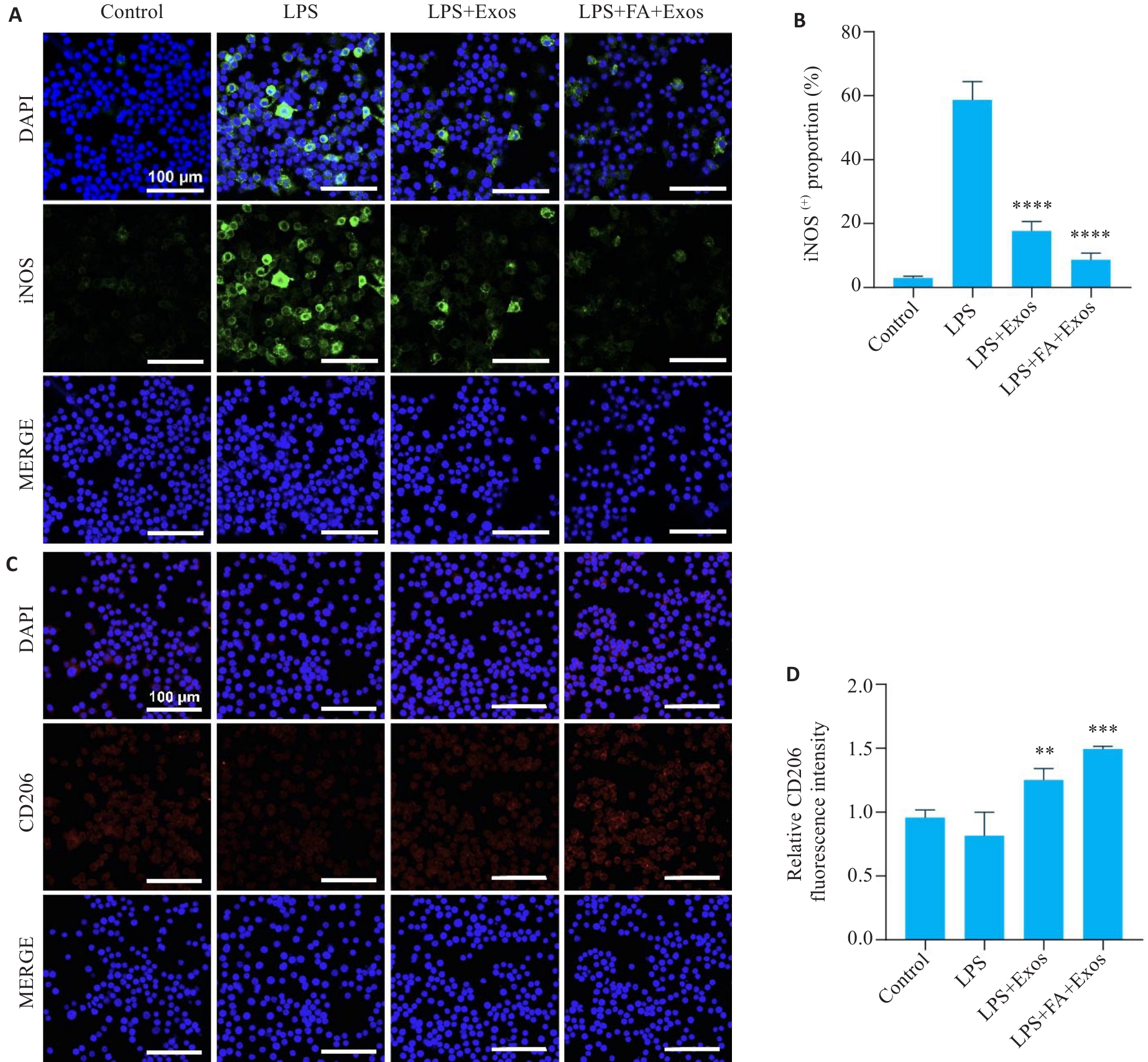
图6 RAW264.7巨噬细胞iNOS与CD206免疫荧光染色
Fig.6 Immunofluorescence staining of iNOS and CD206 in RAW264.7 macrophages incubated with the exosomes. A: Expression of iNOS in RAW264.7 cells in different treatment groups. B: Statistical analysis of the proportion of iNOS-positive cells in each group. C: Expression of CD206 in RAW264.7 cells in different groups. D: Statistical analysis of the fluorescence intensity of CD206 in each group (n=3). **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001 vs LPS group.
| [1] | Yue LD, Berman J. What is osteoarthritis?[J]. Jama, 2022, 327(13): 1300. doi:10.1001/jama.2022.1980 |
| [2] | GBD 2021 Osteoarthritis Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of osteoarthritis, 1990-2020 and projections to 2050: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021[J]. Lancet Rheumatol, 2023, 5(9): e508-22. |
| [3] | Cui A, Li H, Wang D, et al. Global, regional prevalence, incidence and risk factors of knee osteoarthritis in population-based studies[J]. EClinicalMedicine, 2020, 29/30: 100587. |
| [4] | Xie JW, Huang ZY, Yu XJ, et al. Clinical implications of macrophage dysfunction in the development of osteoarthritis of the knee[J]. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev, 2019, 46: 36-44. doi:10.1016/j.cytogfr.2019.03.004 |
| [5] | Coryell PR, Diekman BO, Loeser RF. Mechanisms and therapeutic implications of cellular senescence in osteoarthritis[J]. Nat Rev Rheumatol, 2021, 17(1): 47-57. doi:10.1038/s41584-020-00533-7 |
| [6] | Moulin D, Sellam J, Berenbaum F, et al. The role of the immune system in osteoarthritis: mechanisms, challenges and future directions[J]. Nat Rev Rheumatol, 2025, 21(4): 221-36. doi:10.1038/s41584-025-01223-y |
| [7] | De Roover A, Escribano-Núñez A, Monteagudo S, et al. Fundam-entals of osteoarthritis: inflammatory mediators in osteoarthritis[J]. Osteoarthr Cartil, 2023, 31(10): 1303-11. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2023.06.005 |
| [8] | Mathieu M, Martin-Jaular L, Lavieu G, et al. Specificities of secretion and uptake of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles for cell-to-cell communication[J]. Nat Cell Biol, 2019, 21(1): 9-17. doi:10.1038/s41556-018-0250-9 |
| [9] | Che Z, Yan W, Zhao Q. Extracellular vesicles in the mesenchymal stem cell/macrophage axis: potential targets for inflammatory treatment[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2025, 26(6): 2827. doi:10.3390/ijms26062827 |
| [10] | Otahal A, Kramer K, Neubauer M, et al. Culture of Hoffa fat pad mesenchymal stem/stromal cells on microcarrier suspension in vertical wheel bioreactor for extracellular vesicle production[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2024, 15(1): 61. doi:10.1186/s13287-024-03681-9 |
| [11] | Shen D, He Z. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes regulate the polarization and inflammatory response of macrophages via miR-21-5p to promote repair after myocardial reperfusion injury[J]. Ann Transl Med, 2021, 9(16): 1323. doi:10.21037/atm-21-3557 |
| [12] | Kou M, Huang L, Yang J, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles for immunomodulation and regeneration: a next generation therapeutic tool[J]?. Cell Death Dis, 2022, 13(7): 580. doi:10.1038/s41419-022-05034-x |
| [13] | 张梦莹, 李 志, 裴纬亚, 等. M2型巨噬细胞来源的外泌体lncRNA NR_028113.1通过激活JAK2/STAT3通路促进巨噬细胞的极化 [J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(3): 393-9. |
| [14] | 涂舒谕, 陈祥宇, 李程辉, 等. 补阳还五汤通过调控外泌体miR-590-5p介导的巨噬细胞极化延缓大鼠血管衰老 [J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1251-9. |
| [15] | Kouroupis D, Kaplan LD, Best TM. Human infrapatellar fat pad mesenchymal stem cells show immunomodulatory exosomal signatures[J]. Sci Rep, 2022, 12: 3609. doi:10.1038/s41598-022-07569-7 |
| [16] | Wang Z, Hu Z, Niu L, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis based on rat model[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2025, 16: 1588841. doi:10.3389/fphar.2025.1588841 |
| [17] | Kostyusheva A, Romano E, Yan N, et al. Breaking barriers in targeted therapy: advancing exosome isolation, engineering, and imaging[J]. Adv Drug Deliv Rev, 2025, 218: 115522. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2025.115522 |
| [18] | Fan JH, Xu HX, Qin ZZ, et al. Folic acid protects against kidney damage in mice with diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting M1 macrophage polarization via nuclear factor-k-gene binding pathway[J]. Altern Ther Health Med, 2023, 29(6): 418-20. |
| [19] | Feng D, Zhou Y, Xia M, et al. Folic acid inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in RAW264.7 macrophages by suppressing MAPKs and NF-κB activation[J]. Inflamm Res, 2011, 60(9): 817-22. doi:10.1007/s00011-011-0337-2 |
| [20] | Kolb AF, Petrie L. Folate deficiency enhances the inflammatory response of macrophages[J]. Mol Immunol, 2013, 54(2): 164-72. doi:10.1016/j.molimm.2012.11.012 |
| [21] | Puig-Kröger A, Sierra-Filardi E, Domínguez-Soto A, et al. Folate receptor beta is expressed by tumor-associated macrophages and constitutes a marker for M2 anti-inflammatory/regulatory macro-phages[J]. Cancer Res, 2009, 69(24): 9395-403. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-09-2050 |
| [22] | Jin Y, Zhang Q, Qin X, et al. Carbon dots derived from folic acid attenuates osteoarthritis by protecting chondrocytes through NF-κB/MAPK pathway and reprogramming macrophages[J]. J Nanobiotechnology, 2022, 20(1): 469. doi:10.1186/s12951-022-01681-6 |
| [23] | Kim HI, Park J, Zhu Y, et al. Recent advances in extracellular vesicles for therapeutic cargo delivery[J]. Exp Mol Med, 2024, 56(4): 836-49. doi:10.1038/s12276-024-01201-6 |
| [24] | Zeng H, Guo S, Ren X, et al. Current strategies for exosome cargo loading and targeting delivery[J]. Cells, 2023, 12(10): 1416. doi:10.3390/cells12101416 |
| [25] | Abbasi R, Alamdari-Mahd G, Maleki-Kakelar H, et al. Recent advances in the application of engineered exosomes from mesenchymal stem cells for regenerative medicine[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2025, 989: 177236. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2024.177236 |
| [26] | Kalluri R, LeBleu VS. The biology,function, and biomedical applications of exosomes[J]. Science, 2020, 367(6478): eaau6977. doi:10.1126/science.aau6977 |
| [27] | Hu X, Ni S, Zhao K, et al. Bioinformatics-led discovery of osteoarthritis biomarkers and inflammatory infiltrates[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 871008. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.871008 |
| [28] | Knights AJ, Redding SJ, Maerz T. Inflammation in osteoarthritis: the latest progress and ongoing challenges[J]. Curr Opin Rheumatol, 2023, 35(2): 128-34. doi:10.1097/bor.0000000000000923 |
| [29] | Yuan Z, Jiang D, Yang M, et al. Emerging roles of macrophage polarization in osteoarthritis: mechanisms and therapeutic strategies[J]. Orthop Surg, 2024, 16(3): 532-50. doi:10.1111/os.13993 |
| [30] | Ma YD, Yang HY, Zong XQ, et al. Artificial M2 macrophages for disease-modifying osteoarthritis therapeutics[J]. Biomaterials, 2021, 274: 120865. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2021.120865 |
| [31] | Liao S, Yang M, Li D, et al. Comprehensive bulk and single-cell transcriptome profiling give useful insights into the characteristics of osteoarthritis associated synovial macrophages[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 1078414. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.1078414 |
| [32] | Lin C, Wan Y, Xu Y, et al. Molecular features and diagnostic modeling of synovium- and IPFP-derived OA macrophages in the inflammatory microenvironment via scRNA-seq and machine learning[J]. J Orthop Surg Res, 2025, 20(1): 382. doi:10.1186/s13018-025-05793-1 |
| [33] | Liao HJ, Chang CH, Huang CF, et al. Potential of using infrapatellar-fat-pad-derived mesenchymal stem cells for therapy in degenerative arthritis: chondrogenesis, exosomes, and transcription regulation[J]. Biomolecules, 2022, 12(3): 386. doi:10.3390/biom12030386 |
| [34] | Zhong YC, Wang SC, Han YH, et al. Recent advance in source, property, differentiation, and applications of infrapatellar fat pad adipose-derived stem cells[J]. Stem Cells Int, 2020, 2020: 2560174. doi:10.1155/2020/2560174 |
| [35] | Wu JY, Kuang L, Chen C, et al. miR-100-5p-abundant exosomes derived from infrapatellar fat pad MSCs protect articular cartilage and ameliorate gait abnormalities via inhibition of mTOR in osteoarthritis[J]. Biomaterials, 2019, 206: 87-100. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.03.022 |
| [36] | Wu JY, Wu JH, Xiang W, et al. Engineering exosomes derived from TNF‑α preconditioned IPFP-MSCs enhance both yield and therapeutic efficacy for osteoarthritis[J]. J Nanobiotechnol, 2024, 22(1): 555. doi:10.1186/s12951-024-02795-9 |
| [37] | Rai A, Claridge B, Lozano J, et al. The discovery of extracellular vesicles and their emergence as a next-generation therapy[J]. Circ Res, 2024, 135(1): 198-221. doi:10.1161/circresaha.123.323054 |
| [38] | Chen M, Lu Y, Liu Y, et al. Injectable microgels with hybrid exosomes of chondrocyte-targeted FGF18 gene-editing and self-renewable lubrication for osteoarthritis therapy[J]. Adv Mater, 2024, 36(16): e2312559. doi:10.1002/adma.202312559 |
| [39] | Chen M, Liu Y, Cao Y, et al. Remodeling the proinflammatory microenvironment in osteoarthritis through interleukin-1 beta tailored exosome cargo for inflammatory regulation and cartilage regeneration[J]. ACS Nano, 2025, 19(4): 4924-41. doi:10.1021/acsnano.4c16785 |
| [40] | Pathrikar TV, Baby HM, Hakim B, et al. Cartilage-targeting exosomes for delivery of receptor antagonist of interleukin-1 in osteoarthritis treatment[J]. Osteoarthritis Cartilage, 2025, 33(7): 835-47. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2025.02.785 |
| [41] | Feng CX, Xiong ZY, Wang C, et al. Folic acid-modified Exosome-PH20 enhances the efficiency of therapy via modulation of the tumor microenvironment and directly inhibits tumor cell metastasis[J]. Bioact Mater, 2021, 6(4): 963-74. doi:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2020.09.014 |
| [1] | 李楠, 张亮, 郭俏凤, 周越, 刘长江. 有氧运动通过调控miR-221-3p介导的脂肪组织巨噬细胞极化改善小鼠胰岛素抵抗[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2026, 46(1): 74-82. |
| [2] | 薄海美, 曹新营, 邢平川, 王志军. 外泌体来源的miR-1275通过上调淋巴细胞中IL-38的表达抑制脓毒症心肌细胞凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(8): 1608-1615. |
| [3] | 张兆君, 吴琼, 谢苗苗, 叶洳吟, 耿晨晨, 石纪雯, 杨清玲, 王文锐, 石玉荣. 层状双氢氧化物负载si-NEAT1通过miR-133b/PD-L1轴调控乳腺癌紫杉醇耐药及巨噬细胞极化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(8): 1718-1731. |
| [4] | 付长龙, 徐鹭, 陈若岚, 杨竟航, 罗雁, 黄艳峰. 透骨消痛胶囊通过激活CXCL12/GDF5通路修复骨关节炎小鼠的软骨损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1122-1130. |
| [5] | 涂舒谕, 陈祥宇, 李程辉, 黄丹萍, 张莉. 补阳还五汤通过调控外泌体miR-590-5p介导的巨噬细胞极化延缓大鼠血管衰老[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1251-1259. |
| [6] | 牛民主, 殷丽霞, 乔通, 尹林, 张可妮, 胡建国, 宋传旺, 耿志军, 李静. 旱莲苷A通过调控JAK2/STAT3通路抑制M1型巨噬细胞极化改善葡聚糖硫酸钠诱导的小鼠结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1297-1306. |
| [7] | 田芷华, 杨青青, 陈欣, 张方方, 钟柏茂, 曹虹. 精胺抑制巨噬细胞中GBP5介导的NLRP3炎性小体活化减轻感染肠道病毒71型的新生小鼠脏器损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(5): 901-910. |
| [8] | 俞佳雯, 周薏, 钱春美, 穆蓝, 阙任烨. 铁过载诱导的小鼠肝纤维化过程影响巨噬细胞M2极化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 684-691. |
| [9] | 富丽萍, 袁立霞, 王杰, 陈学蓝, 柯桂芝, 黄煜, 杨心仪, 刘刚. 近十年低强度脉冲超声在肌骨疾病治疗中的应用进展[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 661-668. |
| [10] | 邹金华, 王惠, 张冬艳. SLC1A5通过促进M2型巨噬细胞极化促进肝癌进展[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 269-284. |
| [11] | 付长龙, 陈若岚, 徐诗淇, 游锦欣, 林晴, 黄艳峰. 巴戟天多糖通过靶向lncRNA XIST调控糖酵解-焦亡延缓小鼠骨关节炎软骨细胞退变[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(12): 2541-2550. |
| [12] | 张芡, 刘博文, 雷丽, 王晔, 张馨月, 毛樟坤, 唐鹏, 张金梅, 杨佳宜, 彭彦茜, 刘泽. 丝氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂E1过表达通过诱导M2型巨噬细胞极化促进三阴性乳腺癌细胞增殖与紫杉醇耐药[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(12): 2551-2560. |
| [13] | 刘新新, 徐迎芮, 盛红娜, 刘昊. 人源脐带间充质干细胞移植通过Chi3l1抑制M1型巨噬细胞极化减轻1型糖尿病小鼠的炎症反应[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(12): 2738-2746. |
| [14] | 邱晓慧, 王檬, 唐江解, 周建大, 金晨. 负载人脐带间充质干细胞外泌体的壳聚糖水凝胶促进慢性糖尿病大鼠的伤口愈合[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(10): 2082-2091. |
| [15] | 麦泳欣, 周舒婷, 温蕊嘉, 张锦芳, 詹冬香. 桃叶珊瑚苷通过抑制NF-κb信号通路减轻小鼠的膝骨关节炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(10): 2104-2110. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||