南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (10): 2082-2091.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.10.04
• • 上一篇
邱晓慧1( ), 王檬2, 唐江解3, 周建大4, 金晨5(
), 王檬2, 唐江解3, 周建大4, 金晨5( )
)
收稿日期:2024-12-05
出版日期:2025-10-20
发布日期:2025-10-24
通讯作者:
金晨
E-mail:keyi0540658@163.com;oyqn845ifgi265@163.com
作者简介:邱晓慧,博士,副研究员,E-mail: keyi0540658@163.com
基金资助:
Xiaohui QIU1( ), Meng WANG2, Jiangjie TANG3, Jianda ZHOU4, Chen JIN5(
), Meng WANG2, Jiangjie TANG3, Jianda ZHOU4, Chen JIN5( )
)
Received:2024-12-05
Online:2025-10-20
Published:2025-10-24
Contact:
Chen JIN
E-mail:keyi0540658@163.com;oyqn845ifgi265@163.com
摘要:
目的 探讨负载人脐带间充质干细胞(hUCMSC)外泌体(hUCMSC-exos)的壳聚糖(CS)水凝胶(Exos@CS-Gel)改善糖尿病伤口愈合的机制。 方法 提取hUCMSC外泌体并制备Exos@CS-Gel,通过细胞划痕和CCK-8实验评估其对人脐静脉内皮细胞(HUVEC)增殖与迁移的影响。采用链脲佐菌素诱导建立糖尿病大鼠全层皮肤伤口模型,将24只大鼠随机分为4组:Exos@CS-Gel组(100 µg hUCMSC-exos溶于100 µL 24% CS水凝胶)、hUCMSC-exos组(100 µg hUCMSC-exos溶于100 µL PBS)、CS水凝胶组(100 µL 24% CS水凝胶)和对照组(100 µL PBS),局部注射覆盖伤口后,通过免疫组化、HE染色、免疫荧光及 qRT-PCR 评估伤口愈合效果及机制。 结果 成功提取 hUCMSC-exos 并制备 Exos@CS-Gel。体外实验显示,Exos@CS-Gel促进HUVEC增殖与迁移(P<0.05)。体内实验结果显示,术后14 d Exos@CS-Gel 组伤口愈合率达92.7%,高于hUCMSC-exos组(9.12%)、CS水凝胶组(16.28%)和对照组(25.98%)(P<0.05),微血管密度、血管内皮生长因子和转化生长因子β-1表达水平均升高。 结论 Exos@CS-Gel 可提高外泌体体外生存能力,通过促进血管生成与细胞增殖等机制加速糖尿病伤口愈合。
邱晓慧, 王檬, 唐江解, 周建大, 金晨. 负载人脐带间充质干细胞外泌体的壳聚糖水凝胶促进慢性糖尿病大鼠的伤口愈合[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(10): 2082-2091.
Xiaohui QIU, Meng WANG, Jiangjie TANG, Jianda ZHOU, Chen JIN. Chitosan hydrogel loaded with human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promotes healing of chronic diabetic wounds in rats[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(10): 2082-2091.
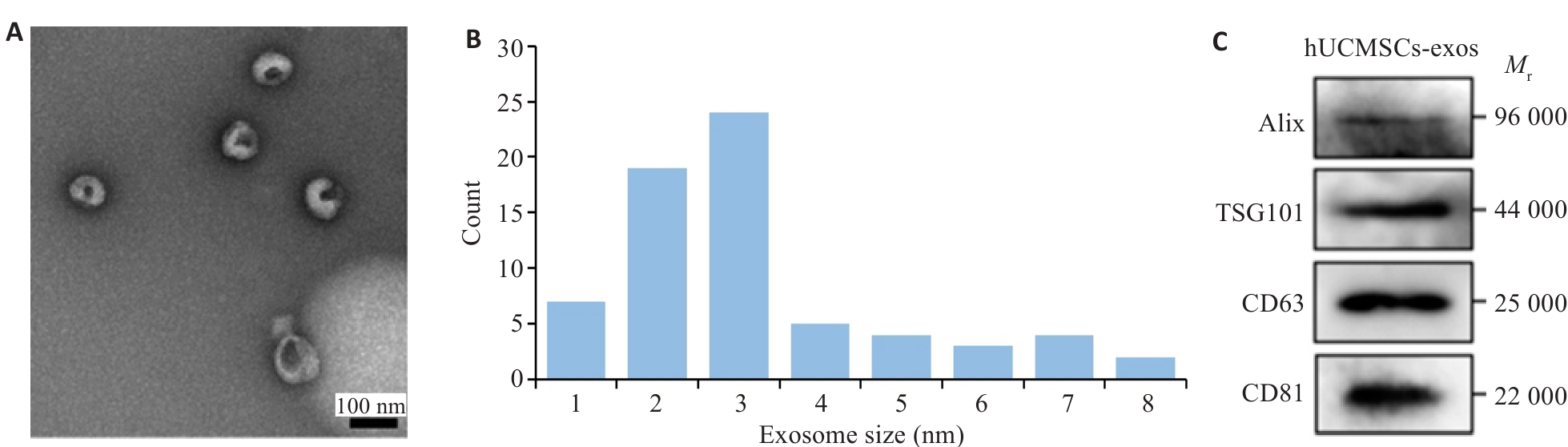
图1 外泌体提取及特征
Fig.1 Isolation and characterization of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (HUVECs)-derived exosomes (hUCMSC-exos). A: Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) of hUCMSC-exos. B: Histogram showing the diameter and concentration distribution of hUCMSC-exos. C: Western blotting of exosomal markers (Alix, TSG101, CD63, and CD81) in hUCMSC-exos.
| Concentration | IGT (℃) | Gelation time at 37 ℃ (s) |
|---|---|---|
| 20% | 17.2±1.4 | 92.7±6.3 |
| 22% | 16.3±1.2 | 78.5±5.2 |
| 24% | 14.2±1.5 | 66.3±3.4 |
| 26% | 12.9±1.1 | 51.2±2.7 |
| 28% | 11.8±0.9 | 46.9±2.9 |
表1 不同浓度Exos@CS-Gel IGT和 37 ℃时凝胶化时间
Tab.1 Initial gelation temperature (IGT) of different concentrations of Exos@CS-Gel and their gelation time at 37 ℃ (Mean±SD)
| Concentration | IGT (℃) | Gelation time at 37 ℃ (s) |
|---|---|---|
| 20% | 17.2±1.4 | 92.7±6.3 |
| 22% | 16.3±1.2 | 78.5±5.2 |
| 24% | 14.2±1.5 | 66.3±3.4 |
| 26% | 12.9±1.1 | 51.2±2.7 |
| 28% | 11.8±0.9 | 46.9±2.9 |
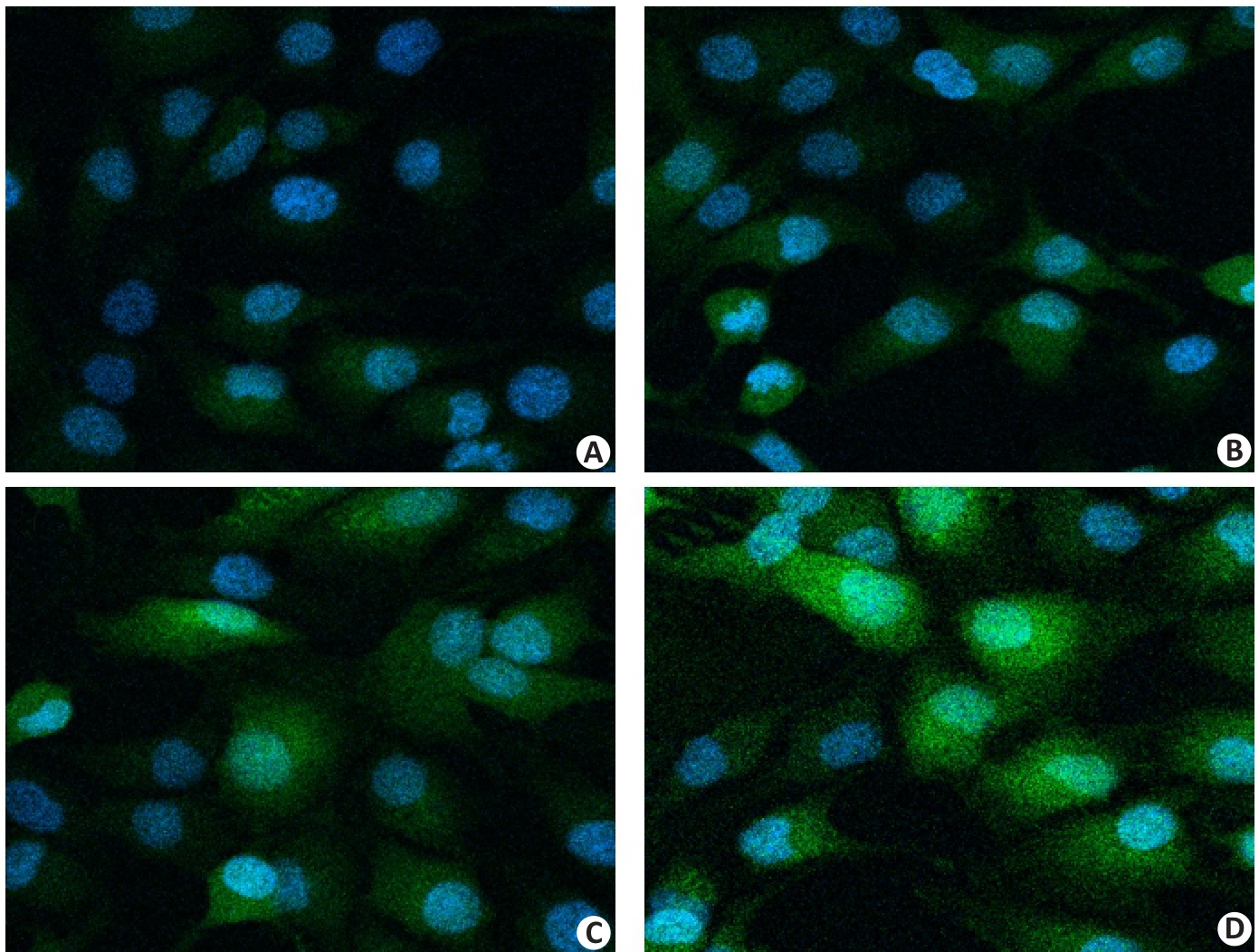
图2 PKH67染色追踪外泌体的细胞定位情况
Fig.2 Cellular localization of exosomes tracked by PKH67 staining (Original magnification: ×400). A: PBS group. B: CS group. C: hUCMSCs-exos group. D: Exos@CS-Gel group. Green indicates PKH67 (exosome staining dye), and blue indicates DAPI (nuclear staining dye).
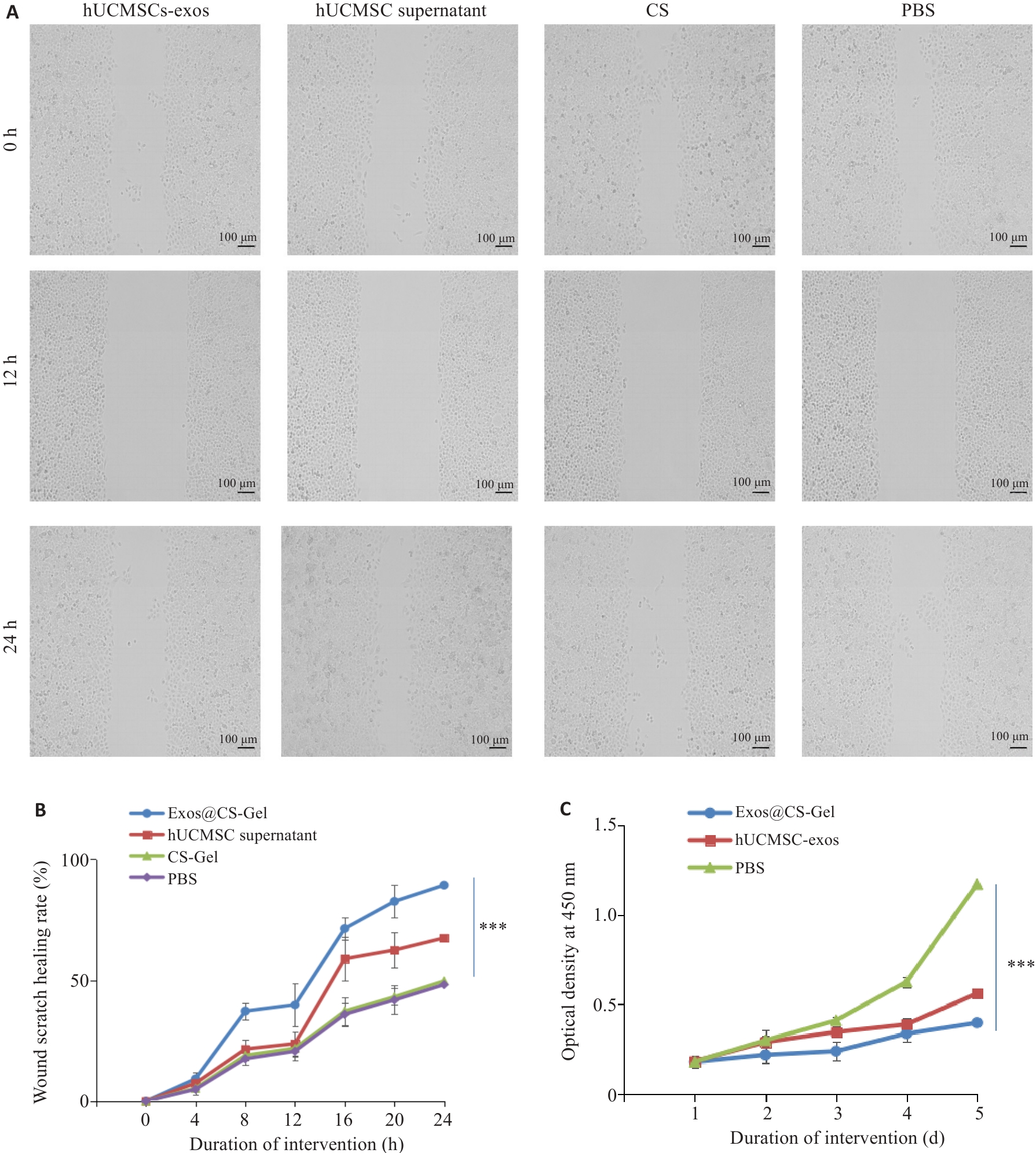
图3 Exos@CS-Gel对HUVEC迁移和增殖的影响
Fig.3 Effect of Exos@CS-Gel on HUVEC migration and proliferation. A: Wound healing assay showing the effect of Exos@CS-Gel on HUVEC cell migration ability. B: Comparison of wound healing rates among different groups. C: CCK-8 assay evaluating the effect of Exos@CS-Gel on HUVEC proliferation ability. ***P<0.001.
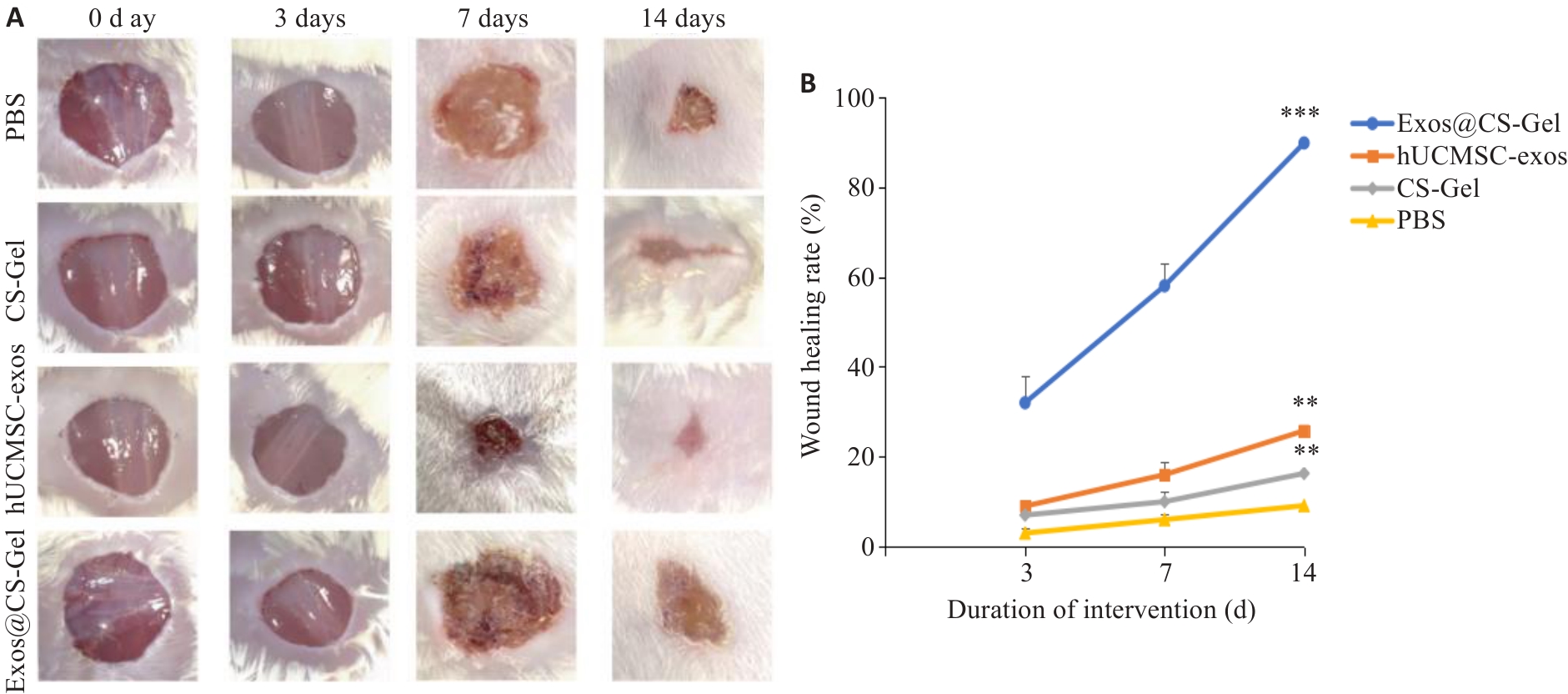
图4 各组大鼠伤口愈合情况
Fig.4 Wound healing c in each group of rats. A: Representative wound images of each group on days 0, 3, 7, 14. B: Comparison of wound area changes over time among the groups. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs PBS group.
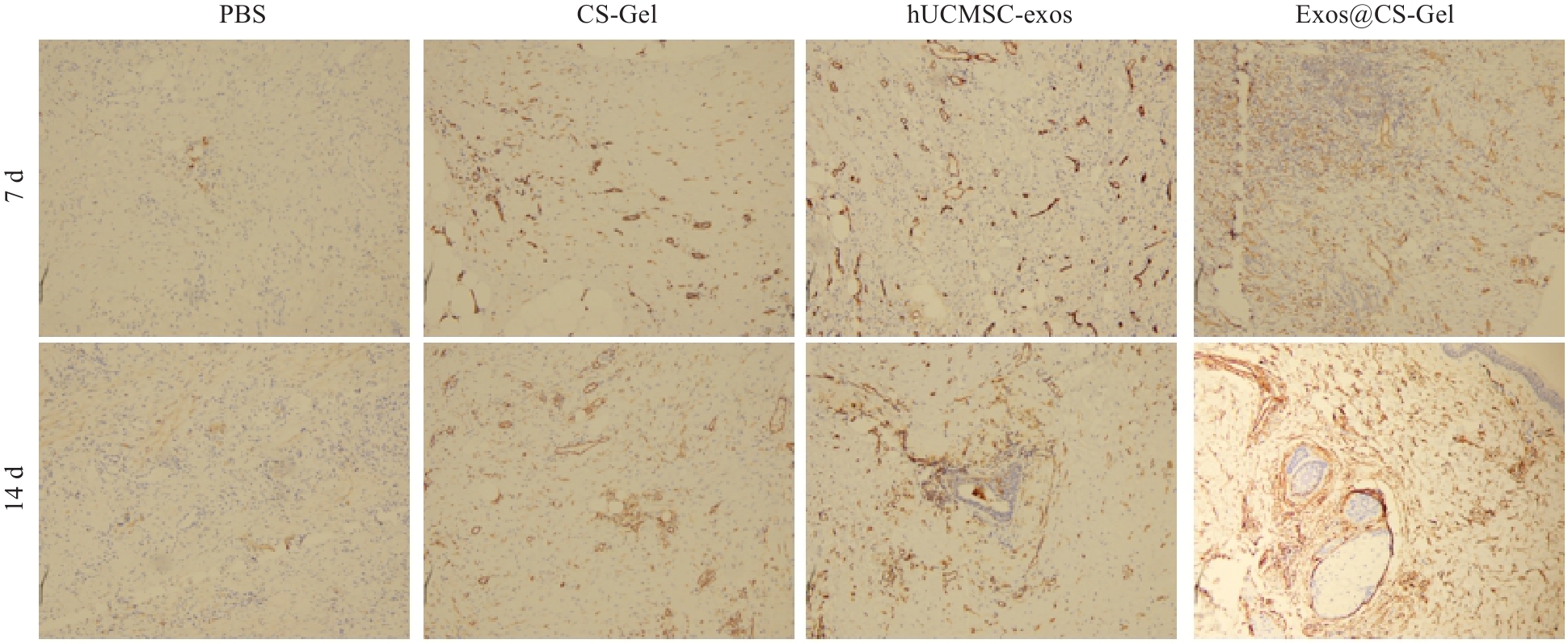
图6 Exos@CS-Gel对大鼠伤口组织血管生成的影响
Fig.6 Effect of Exos@CS-Gel on angiogenesis in rat wound tissues assess by immunohistochemical detection of CD31 expression (vascular endothelial cell marker) in the wound tissues from each group on day 7 and 14 after the treatments (immunohistochemical staining, ×100).
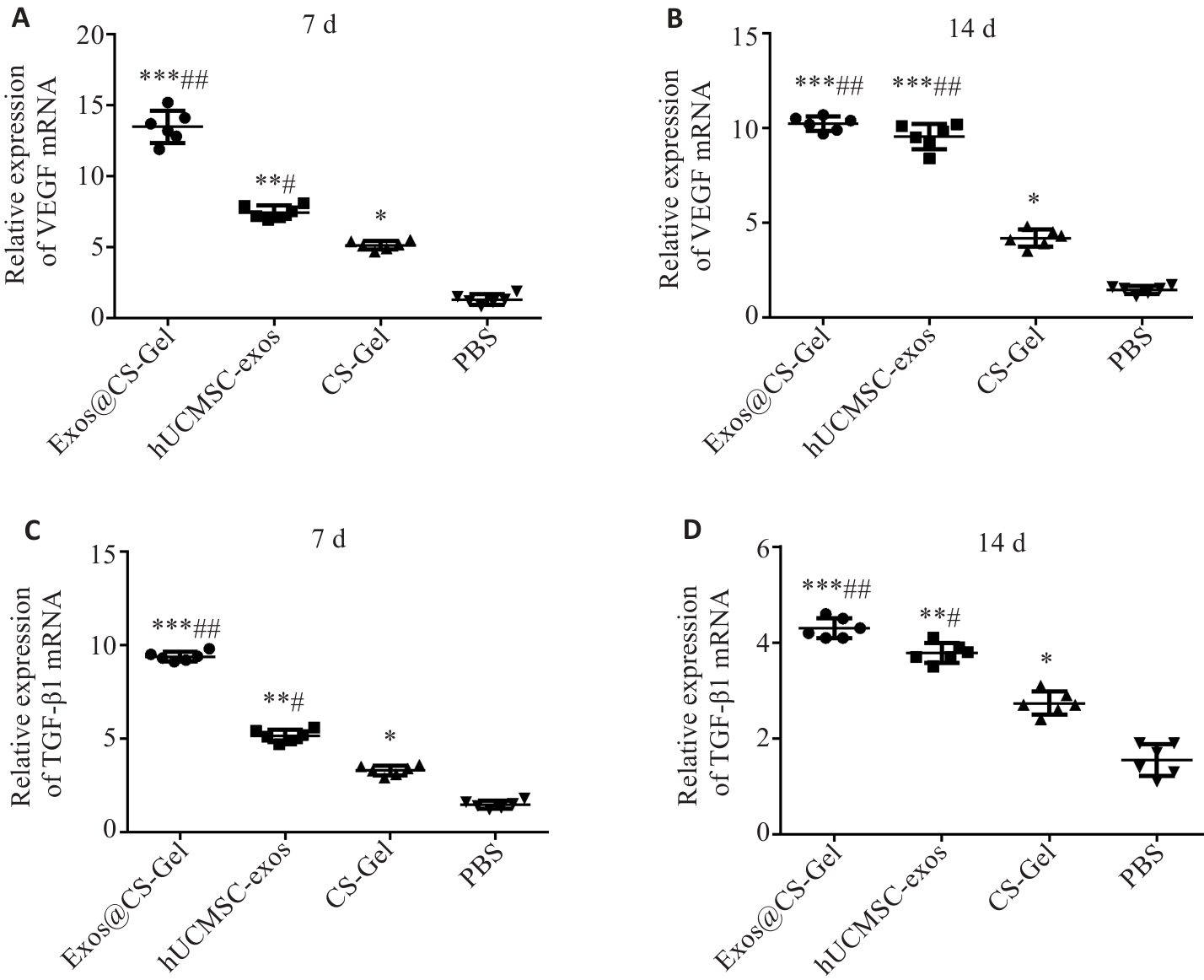
图8 Exos@CS-Gel对大鼠伤口组织对VEGF和 TGFβ-1表达水平的影响
Fig.8 Effect of Exos@CS-Gel on VEGF and TGF-β1 expression levels in rat wound tissues, assessed by qRT-PCR of mRNA expression levels of VEGF (A, B) and TGF-β1 (C, D) in the wound granulation tissues on day 7 and day 14 after treatments. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs PBS group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 vs CS-Gel group.
| [1] | McGuire J, Thomson A, Kennedy PG. The biomechanics of diabetic foot amputation[J]. Wounds, 2021: WNDS20210414-2. doi:10.25270/wnds/041421.01 |
| [2] | Jiang PN, Li QH, Luo YH, et al. Current status and progress in research on dressing management for diabetic foot ulcer[J]. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2023, 14: 1221705. doi:10.3389/fendo.2023.1221705 |
| [3] | Ferreira G, Faria S, Carvalho A, et al. Relaxation intervention to improve diabetic foot ulcer healing: Results from a pilot randomized controlled study[J]. Wound Repair Regen, 2023, 31(4): 528-41. doi:10.1111/wrr.13085 |
| [4] | Pereira MG, Vilaça M, Pedras S, et al. Wound healing and healing process in patients with diabetic foot ulcers: a survival analysis study[J]. Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 2023, 198: 110623. doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2023.110623 |
| [5] | Rehman ZU, Khan J, Noordin S. Diabetic foot ulcers: contemporary assessment and management[J]. J Pak Med Assoc, 2023, 73(7): 1480-7. doi:10.47391/jpma.6634 |
| [6] | Deng HB, Li BH, Shen Q, et al. Mechanisms of diabetic foot ulceration: a review[J]. J Diabetes, 2023, 15(4): 299-312. doi:10.1111/1753-0407.13372 |
| [7] | Ju YK, Hu Y, Yang P, et al. Extracellular vesicle-loaded hydrogels for tissue repair and regeneration[J]. Mater Today Bio, 2022, 18: 100522. doi:10.1016/j.mtbio.2022.100522 |
| [8] | Zou JX, Yang WN, Cui WS, et al. Therapeutic potential and mechanisms of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes as bioactive materials in tendon-bone healing[J]. J Nanobio-technology, 2023, 21(1): 14. doi:10.1186/s12951-023-01778-6 |
| [9] | Wang T, Gao HQ, Wang DZ, et al. Stem cell-derived exosomes in the treatment of Melasma and its percutaneous penetration[J]. Lasers Surg Med, 2023, 55(2): 178-89. doi:10.1002/lsm.23628 |
| [10] | Liu YY, Zhang MW, Liao Y, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote murine skin wound healing by neutrophil and macrophage modulations revealed by single-cell RNA sequencing[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14: 1142088. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1142088 |
| [11] | Zhang KY, Zhao XN, Chen XN, et al. Enhanced therapeutic effects of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes with an injectable hydrogel for hindlimb ischemia treatment[J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2018, 10(36): 30081-91. doi:10.1021/acsami.8b08449 |
| [12] | Li ZT, Xing XL, Zhao CR, et al. A rapid interactive chitosan-based medium with antioxidant and pro-vascularization properties for infected burn wound healing[J]. Carbohydr Polym, 2024, 333: 121991. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2024.121991 |
| [13] | 陈金妙, 朱灵颖, 廖米荣, 等. 糖尿病慢性伤口感染患者的临床特点及伤口愈合的危险因素分析[J]. 中国现代医生, 2022, 60(27): 50-4. |
| [14] | Bi HS, Li H, Zhang C, et al. Stromal vascular fraction promotes migration of fibroblasts and angiogenesis through regulation of extracellular matrix in the skin wound healing process[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2019, 10(1): 302. doi:10.1186/s13287-019-1415-6 |
| [15] | Kim J, Lee CB, Shin Y, et al. sEVs from tonsil-derived mesenchymal stromal cells alleviate activation of hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrosis through miR-486-5p[J]. Mol Ther, 2021, 29(4): 1471-86. doi:10.1016/j.ymthe.2020.12.025 |
| [16] | Keramaris NC, Kaptanis S, Moss HL, et al. Endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) and mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) in bone healing[J]. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther, 2012, 7(4): 293-301. doi:10.2174/157488812800793081 |
| [17] | Wang LM, Chen J, Song J, et al. Activation of the Wnt/β‑catenin signalling pathway enhances exosome production by hucMSCs and improves their capability to promote diabetic wound healing[J]. J Nanobiotechnology, 2024, 22(1): 373. doi:10.1186/s12951-024-02650-x |
| [18] | Teng LP, Maqsood M, Zhu M, et al. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells accelerate diabetic wound healing via promoting M2 macrophage polarization, angiogenesis, and collagen deposition[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(18): 10421. doi:10.3390/ijms231810421 |
| [19] | Yan CC, Xv Y, Lin Z, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes accelerate diabetic wound healing via ameliorating oxidative stress and promoting angiogenesis[J]. Front Bioeng Biotechnol, 2022, 10: 829868. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2022.829868 |
| [20] | 蒋 杨, 陈 博, 王贤君, 等. 人脐带间充质干细胞治疗肺部疾病的研究与应用进展[J]. 临床肺科杂志, 2022, 27(1): 124-9. |
| [21] | He SH, Hou TY, Zhou JL, et al. Endothelial cells promote migration of mesenchymal stem cells via PDGF-BB/PDGFR β-src-Akt in the context of inflammatory microenvironment upon bone defect[J]. Stem Cells Int, 2022, 2022: 2401693. doi:10.1155/2022/2401693 |
| [22] | Song YL, You YC, Xu XY, et al. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes biopotentiated extracellular matrix hydrogels accelerate diabetic wound healing and skin regeneration[J]. Adv Sci (Weinh), 2023, 10(30): e2304023. doi:10.1002/advs.202304023 |
| [23] | 张丁丁, 郭 荣, 赵松峰, 等. 载锰单原子纳米酶和驱蛔素的壳聚糖水凝胶制备及其抗幽门螺杆菌活性[J]. 中草药, 2024, 55(6): 1925-34. |
| [24] | 由子樱, 伍彦霖, 孙一民, 等. 搭载米诺环素-壳聚糖纳米粒复合水凝胶用于牙周炎治疗的初步研究[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2023, 41(1): 11-20. |
| [25] | Kwon SK, Song JJ, Cho CG, et al. Polycaprolactone spheres and theromosensitive Pluronic F127 hydrogel for vocal fold augmen-tation: in vivo animal study for the treatment of unilateral vocal fold palsy[J]. Laryngoscope, 2013, 123(7): 1694-703. doi:10.1002/lary.23879 |
| [26] | Wang CG, Wang M, Xu TZ, et al. Engineering bioactive self-healing antibacterial exosomes hydrogel for promoting chronic diabetic wound healing and complete skin regeneration[J]. Theranostics, 2019, 9(1): 65-76. doi:10.7150/thno.29766 |
| [27] | Yang MY, Li JP, Gu P, et al. The application of nanoparticles in cancer immunotherapy: Targeting tumor microenvironment[J]. Bioact Mater, 2021, 6(7): 1973-87. doi:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2020.12.010 |
| [28] | Amiri Z, Molavi AM, Amani A, et al. Fabrication, characterization and wound-healing properties of core-shell SF@chitosan/ZnO/Astragalus arbusculinus gum nanofibers[J]. Nanomedicine (Lond), 2024, 19(6): 499-518. doi:10.2217/nnm-2023-0311 |
| [29] | le Noble F, Kupatt C. Interdependence of angiogenesis and arteriogenesis in development and disease[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(7): 3879. doi:10.3390/ijms23073879 |
| [30] | Idrovo JP, Yang WL, Jacob A, et al. Combination of adrenomedullin with its binding protein accelerates cutaneous wound healing[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(3): e0120225. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0120225 |
| [31] | Oviedo-Socarrás T, Vasconcelos AC, Barbosa IX, et al. Diabetes alters inflammation, angiogenesis, and fibrogenesis in intra-peritoneal implants in rats[J]. Microvasc Res, 2014, 93: 23-9. doi:10.1016/j.mvr.2014.02.011 |
| [32] | Chuar PF, Ng YT, Phang SCW, et al. Tocotrienol-rich vitamin E (tocovid) improved nerve conduction velocity in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in a phase II double-blind, randomized controlled clinical trial[J]. Nutrients, 2021, 13(11): 3770. doi:10.3390/nu13113770 |
| [1] | 马倩倩, 牛钰琪, 左铭钰, 李鑫, 符竣轲, 王瑾瑾. 鬼箭羽通过抑制AGEs-RAGE信号转导通路改善晚期糖基化终末产物诱导的小鼠肾足细胞损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(9): 1938-1945. |
| [2] | 薄海美, 曹新营, 邢平川, 王志军. 外泌体来源的miR-1275通过上调淋巴细胞中IL-38的表达抑制脓毒症心肌细胞凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(8): 1608-1615. |
| [3] | 韩瑞敏, 赵曼可, 袁俊芳, 史振红, 王珍, 王德峰. 枯草杆菌二联活菌肠溶胶囊调节2型糖尿病合并昼夜节律紊乱小鼠糖脂代谢的作用机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(7): 1490-1497. |
| [4] | 涂舒谕, 陈祥宇, 李程辉, 黄丹萍, 张莉. 补阳还五汤通过调控外泌体miR-590-5p介导的巨噬细胞极化延缓大鼠血管衰老[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1251-1259. |
| [5] | 苏维, 赖厚桦, 唐昕, 周群, 唐亚纯, 符浩, 陈选才. Apelin通过激活 FGF2/FGFR1通路促进膀胱癌增殖、迁移及血管生成[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1289-1296. |
| [6] | 董妍妍, 张可敬, 储俊, 储全根. 抵当汤含药血清通过PI3K/Akt/mTOR信号通路增强高糖诱导的大鼠肾小球内皮细胞自噬[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 461-469. |
| [7] | 孙红燕, 卢国庆, 付程文, 徐梦文, 朱小翌, 邢国权, 刘乐强, 柯雨菲, 崔乐妹, 陈睿旸, 王磊, 康品方, 唐碧. 槲皮素通过调控L型钙通道改善糖尿病大鼠心肌损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 531-541. |
| [8] | 许怀文, 翁丽, 薛鸿. CXCL12可作为2型糖尿病合并慢性阻塞性肺疾病的潜在治疗靶点[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 100-109. |
| [9] | 郭克磊, 李颖利, 宣晨光, 侯紫君, 叶松山, 李林运, 陈丽平, 韩立, 卞华. 益气养阴化浊通络方通过调控miR-21a-5p/FoxO1/PINK1介导的线粒体自噬减轻糖尿病肾病小鼠的足细胞损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 27-34. |
| [10] | 陈志亮, 杨永刚, 黄霞, 成彦, 瞿媛, 衡琪琪, 符羽佳, 李可薇, 顾宁. 外泌体miRNA差异表达可作为诊断慢性心力衰竭合并高尿酸血症患者新型分子标志物及靶基因功能分析[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 43-51. |
| [11] | 何思齐, 文楠, 陈勋, 王跃, 张艇, 牟雁东. 枸杞糖肽可减轻放射治疗后人牙龈成纤维细胞来源的外泌体导致的成骨抑制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1752-1759. |
| [12] | 姜一凡, 李小荣, 耿嘉逸, 陈永锋, 唐碧, 康品方. 槲皮素通过抑制HMGB1/RAGE/NF-κB信号通路减轻糖尿病引起的大鼠肾脏损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1769-1775. |
| [13] | 戴荣, 曹泽平, 刘传娇, 葛永, 程梦, 王伟丽, 陈义珍, 张磊, 王亿平. 清肾颗粒通过调控外泌体、miR-330-3p以及CREBBP表达抑制小鼠肾纤维化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1431-1440. |
| [14] | 刘本菊, 王业磊, 任海文, 欧丽雯, 邓轩, 黄梦欣, 吴鑫, 龚权. 3-甲基腺嘌呤通过抑制AKT信号减轻糖尿病小鼠的早期肾损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1236-1242. |
| [15] | 王瑾瑾, 崔文飞, 窦雪伟, 尹冰磊, 牛钰琪, 牛羚, 闫国立. 鬼箭羽通过调节EGFR酪氨酸激酶抑制剂耐药信号通路延缓糖尿病肾病的进展[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1243-1255. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||