Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (7): 1554-1562.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.07.23
Previous Articles Next Articles
Yitong LIU1( ), Ke ZHAO2,3(
), Ke ZHAO2,3( ), Xiaodong WANG2,3(
), Xiaodong WANG2,3( )
)
Received:2025-04-03
Online:2025-07-20
Published:2025-07-17
Contact:
Ke ZHAO, Xiaodong WANG
E-mail:liuyitong@stu2021.jnu.edu.cn;zhaoke@mail.sysu.edu.cn;wangxd33@mail.sysu.edu.cn
Yitong LIU, Ke ZHAO, Xiaodong WANG. Lip and oral cancers in East Asia from 1990 to 2035: trends of disease burden and future projections[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1554-1562.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.07.23
| Region | China (excluding Taiwan Province of China) | Taiwan Province of China | Japan | Mongolia | Republic of Korea | Democratic People's Republic of Korea |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Incidence (per 100 000) (95%UI) | ||||||
| 1990 | 1.25 (1.05, 1.44) | 5.07 (4.65, 5.46) | 4.15 (3.93, 4.32) | 3.85 (2.74, 5.30) | 4.08 (3.50, 4.80) | 1.45 (1.05, 2.01) |
| 2021 | 3.96 (3.18, 4.91) | 27.50 (24.57, 30.71) | 11.92 (10.34, 13.14) | 5.44 (3.89, 7.20) | 19.94 (15.59, 24.44) | 2.48 (1.73, 3.36) |
| TRC | 2.17 (1.35, 3.18) | 4.42 (3.76, 5.20) | 1.87 (1.57, 2.10) | 0.41 (-0.08, 1.16) | 3.89 (2.64, 5.23) | 0.71 (0.12, 1.54) |
Prevalence (per 100 000) (95%UI) | ||||||
| 1990 | 3.40 (2.86, 3.94) | 23.18 (21.19, 25.08) | 15.05 (14.38, 15.67) | 1.71 (1.21, 2.35) | 1.40 (1.21, 1.63) | 4.78 (3.40, 6.64) |
| 2021 | 15.12 (12.1, 18.57) | 137.92 (123.15, 154.58) | 38.2 (34.07, 41.39) | 1.82 (1.29, 2.42) | 5.21 (4.07, 6.35) | 8.71 (6.09, 12.05) |
| TRC | 3.45 (2.32, 4.80) | 4.95 (4.22, 5.85) | 1.54 (1.31, 1.73) | 0.06 (-0.30, 0.63) | 2.72 (1.80, 3.64) | 0.82 (0.15, 1.77) |
Mortality (per 100 000) (95%UI) | ||||||
| 1990 | 0.84 (0.71, 0.96) | 2.11 (1.95, 2.28) | 1.31 (1.24, 1.35) | 1.39 (0.98, 1.92) | 0.67 (0.59, 0.77) | 0.88 (0.64, 1.19) |
| 2021 | 1.68 (1.33, 2.09) | 9.59 (8.63, 10.61) | 3.98 (3.3, 4.36) | 1.22 (0.85, 1.62) | 1.46 (1.15, 1.75) | 1.39 (0.97, 1.87) |
| TRC | 1.00 (0.50, 1.64) | 3.54 (3.00, 4.18) | 2.04 (1.67, 2.26) | -0.12 (-0.42, 0.36) | 1.18 (0.65, 1.67) | 0.57 (0.04, 1.38) |
DALYs (per 100 000) (95%UI) | ||||||
| 1990 | 25.11 (21.05, 29.10) | 71.85 (65.87, 77.38) | 34.35 (33.07, 35.28) | 41.48 (29.49, 57.14) | 20.92 (18.40, 24.24) | 27.84 (19.96, 38.5) |
| 2021 | 43.44 (34.27, 54.63) | 292.07 (262.97, 324.45) | 69.09 (60.94, 73.92) | 38.41 (27.28, 51.27) | 34.45 (26.63, 41.54) | 40.29 (27.55, 55.84) |
| TRC | 0.73 (0.28, 1.30) | 3.07 (2.58, 3.65) | 1.01 (0.84, 1.12) | -0.07 (-0.38, 0.44) | 0.65 (0.23, 1.03) | 0.45 (-0.07, 1.20) |
Tab.1 The incidence, prevalence, mortality and disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) of lip and oral cancer in East Asia
| Region | China (excluding Taiwan Province of China) | Taiwan Province of China | Japan | Mongolia | Republic of Korea | Democratic People's Republic of Korea |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Incidence (per 100 000) (95%UI) | ||||||
| 1990 | 1.25 (1.05, 1.44) | 5.07 (4.65, 5.46) | 4.15 (3.93, 4.32) | 3.85 (2.74, 5.30) | 4.08 (3.50, 4.80) | 1.45 (1.05, 2.01) |
| 2021 | 3.96 (3.18, 4.91) | 27.50 (24.57, 30.71) | 11.92 (10.34, 13.14) | 5.44 (3.89, 7.20) | 19.94 (15.59, 24.44) | 2.48 (1.73, 3.36) |
| TRC | 2.17 (1.35, 3.18) | 4.42 (3.76, 5.20) | 1.87 (1.57, 2.10) | 0.41 (-0.08, 1.16) | 3.89 (2.64, 5.23) | 0.71 (0.12, 1.54) |
Prevalence (per 100 000) (95%UI) | ||||||
| 1990 | 3.40 (2.86, 3.94) | 23.18 (21.19, 25.08) | 15.05 (14.38, 15.67) | 1.71 (1.21, 2.35) | 1.40 (1.21, 1.63) | 4.78 (3.40, 6.64) |
| 2021 | 15.12 (12.1, 18.57) | 137.92 (123.15, 154.58) | 38.2 (34.07, 41.39) | 1.82 (1.29, 2.42) | 5.21 (4.07, 6.35) | 8.71 (6.09, 12.05) |
| TRC | 3.45 (2.32, 4.80) | 4.95 (4.22, 5.85) | 1.54 (1.31, 1.73) | 0.06 (-0.30, 0.63) | 2.72 (1.80, 3.64) | 0.82 (0.15, 1.77) |
Mortality (per 100 000) (95%UI) | ||||||
| 1990 | 0.84 (0.71, 0.96) | 2.11 (1.95, 2.28) | 1.31 (1.24, 1.35) | 1.39 (0.98, 1.92) | 0.67 (0.59, 0.77) | 0.88 (0.64, 1.19) |
| 2021 | 1.68 (1.33, 2.09) | 9.59 (8.63, 10.61) | 3.98 (3.3, 4.36) | 1.22 (0.85, 1.62) | 1.46 (1.15, 1.75) | 1.39 (0.97, 1.87) |
| TRC | 1.00 (0.50, 1.64) | 3.54 (3.00, 4.18) | 2.04 (1.67, 2.26) | -0.12 (-0.42, 0.36) | 1.18 (0.65, 1.67) | 0.57 (0.04, 1.38) |
DALYs (per 100 000) (95%UI) | ||||||
| 1990 | 25.11 (21.05, 29.10) | 71.85 (65.87, 77.38) | 34.35 (33.07, 35.28) | 41.48 (29.49, 57.14) | 20.92 (18.40, 24.24) | 27.84 (19.96, 38.5) |
| 2021 | 43.44 (34.27, 54.63) | 292.07 (262.97, 324.45) | 69.09 (60.94, 73.92) | 38.41 (27.28, 51.27) | 34.45 (26.63, 41.54) | 40.29 (27.55, 55.84) |
| TRC | 0.73 (0.28, 1.30) | 3.07 (2.58, 3.65) | 1.01 (0.84, 1.12) | -0.07 (-0.38, 0.44) | 0.65 (0.23, 1.03) | 0.45 (-0.07, 1.20) |
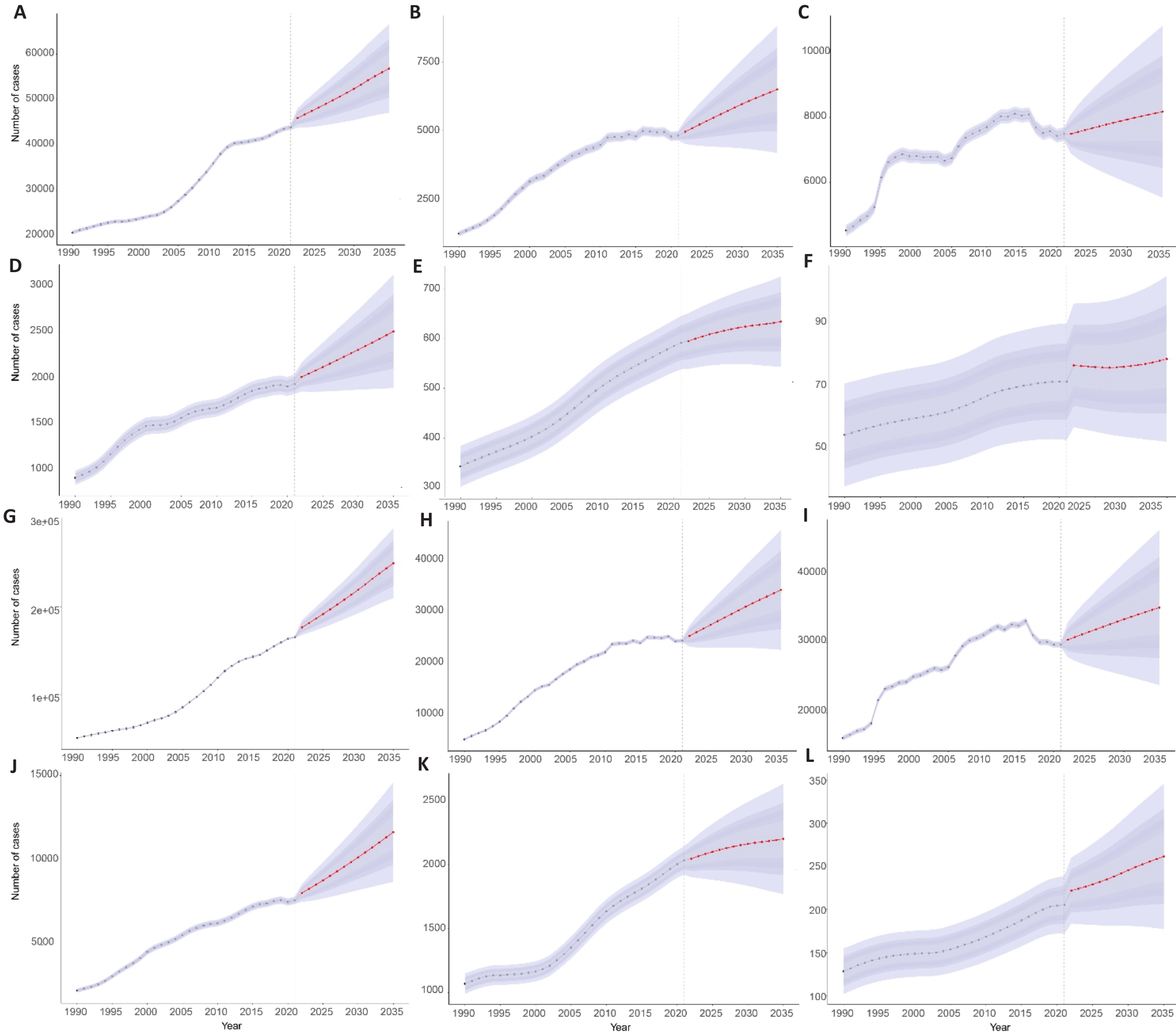
Fig.5 Prevalence trends of lip and oral cancer in East Asia from 1990 to 2021 and projections from 2021 to 2035. A-F: Incidences in China (excluding Taiwan Province of China), Taiwan Province of China, Japan, Republic of Korea, Democratic People's Republic of Korea, and Mongolia, respectively; G-L: Prevalence in China (excluding Taiwan Province of China), Taiwan Province of China, Japan, Republic of Korea, Democratic People's Republic of Korea, and Mongolia, respectively.
| [1] | G B D 2019 Lip O, da Cunha AR, Compton K,et al. The global, regional, and national burden of adult lip, oral, and pharyngeal cancer in 204 countries and territories: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2019[J]. JAMA Oncol, 2023, 9(10): 1401-16. |
| [2] | Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(3): 209-49. doi:10.3322/caac.21660 |
| [3] | Su SY, Chen WT, Chiang CJ, et al. Oral cancer incidence rates from 1997 to 2016 among men in Taiwan: Association between birth cohort trends and betel nut consumption[J]. Oral Oncol, 2020, 107: 104798. doi:10.1016/j.oraloncology.2020.104798 |
| [4] | Su MJ, Ho CH, Yeh CC. Association of alcohol consumption, betel nut chewing, and cigarette smoking with mortality in patients with head and neck cancer among the Taiwanese population: a nationwide population-based cohort study[J]. Cancer Epidemiol, 2024, 89: 102526. doi:10.1016/j.canep.2024.102526 |
| [5] | Jian XC, Jian Y, Wu XS, et al. Oral submucous fibrosis transforming into squamous cell carcinoma: a prospective study over 31 years in mainland China[J]. Clin Oral Investig, 2021, 25(4): 2249-56. doi:10.1007/s00784-020-03541-9 |
| [6] | Sunguc C, Hawkins MM, Winter DL, et al. Risk of subsequent primary oral cancer in a cohort of 69, 460 5-year survivors of childhood and adolescent cancer in Europe: the PanCareSurFup study[J]. Br J Cancer, 2023, 128(1): 80-90. doi:10.1038/s41416-022-02016-w |
| [7] | Yang YY, Ning H, Liang BH, et al. Exploring factors influencing patient delay behavior in oral cancer: the development of a risk prediction model in western China[J]. Healthcare (Basel), 2024, 12(22): 2252. doi:10.3390/healthcare12222252 |
| [8] | Ng SW, Syamim Syed Mohd Sobri SN, Zain RB, et al. Barriers to early detection and management of oral cancer in the Asia Pacific region[J]. J Health Serv Res Policy, 2022, 27(2): 133-40. doi:10.1177/13558196211053110 |
| [9] | Tatokoro M, Matsuo N. The impact of aging on symptom prevalence and management in terminally ill patients with cancer[J]. J Pain Symptom Manage, 2022, 63(2): 251-9. doi:10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2021.09.001 |
| [10] | Hu YN, Zhong R, Li HY, et al. Effects of betel quid, smoking and alcohol on oral cancer risk: a case-control study in Hunan Province, China[J]. Subst Use Misuse, 2020, 55(9): 1501-8. doi:10.1080/10826084.2020.1750031 |
| [11] | Yang YH, Warnakulasuriya S, Yang HF, et al. Public health measures to reduce Areca nut and betel quid use for control of oral cancer in Taiwan[J]. Oral Oncol, 2020, 108: 104915. doi:10.1016/j.oraloncology.2020.104915 |
| [12] | Kim YT, Kang MJ, Lee BA, et al. Risk factors and incidence of oral tumors: Findings from a longitudinal population-based study[J]. Oral Dis, 2025, 31(3): 846-56. doi:10.1111/odi.15125 |
| [13] | Liu BW, Shen MX, Xiong JM, et al. Synergistic effects of betel quid chewing, tobacco use (in the form of cigarette smoking), and alcohol consumption on the risk of malignant transformation of oral submucous fibrosis (OSF): a case-control study in Hunan Province, China[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol, 2015, 120(3): 337-45. doi:10.1016/j.oooo.2015.04.013 |
| [14] | Hu YJ, Chen J, Zhong WS, et al. Trend analysis of betel nut-associated oral cancer and health burden in China[J]. Chin J Dent Res, 2017, 20(2): 69-78. |
| [15] | Pinheiro LC, Reshetnyak E, Akinyemiju T, et al. Social determinants of health and cancer mortality in the Reasons for Geographic and Racial Differences in Stroke (REGARDS) cohort study[J]. Cancer, 2022, 128(1): 122-30. doi:10.1002/cncr.33894 |
| [16] | Zaitsu T, Saito T, Kawaguchi Y. The oral healthcare system in Japan[J]. Healthcare (Basel), 2018, 6(3): 79. doi:10.3390/healthcare6030079 |
| [17] | Rai P, Ng A, Intekhab I, et al. Oral cancer in Asia - a systematic review[J]. Adv Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2022, 8: 100366. doi:10.1016/j.adoms.2022.100366 |
| [18] | Nagao T, Warnakulasuriya S. Screening for oral cancer: Future prospects, research and policy development for Asia[J]. Oral Oncol, 2020, 105: 104632. doi:10.1016/j.oraloncology.2020.104632 |
| [19] | GBD 2021 Diseases and Injuries Collaborators. Global incidence, prevalence, years lived with disability (YLDs), disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs), and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 371 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990-2021: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021[J]. Lancet, 2024, 403(10440): 2133-61. |
| [20] | GBD 2021 Risk Factors Collaborators. Global burden and strength of evidence for 88 risk factors in 204 countries and 811 subnational locations, 1990-2021: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021[J]. Lancet, 2024, 403(10440): 2162-203. |
| [21] | Warnakulasuriya S, Chen TH. Areca nut and oral cancer: evidence from studies conducted in humans[J]. J Dent Res, 2022, 101(10): 1139-46. doi:10.1177/00220345221092751 |
| [22] | Yang YH. Oral cancer in Taiwan[J]. Oral Dis, 2025, 31(5): 1455-66. doi:10.1111/odi.15076 |
| [23] | Chuang SL, Su WW, Chen SL, et al. Population-based screening program for reducing oral cancer mortality in 2, 334, 299 Taiwanese cigarette smokers and/or betel quid chewers[J]. Cancer, 2017, 123(9): 1597-609. doi:10.1002/cncr.30517 |
| [24] | Zhang XY, Xie WH, Ye H, et al. Mortality and disease burden of oral cancer in China: a time-trend analysis on the China Death Surveillance Database from 2006 to 2021[J]. BMC Oral Health, 2024, 24(1): 938. doi:10.1186/s12903-024-04717-5 |
| [25] | Badarch J, Batbaatar S, Paulik E. Prevalence and correlates of poor oral hygiene among school-going students in Mongolia[J]. Dent J (Basel), 2021, 9(2): 12. doi:10.3390/dj9020012 |
| [26] | Webster J, Santos JA, Hogendorf M, et al. Implementing effective salt reduction programs and policies in low- and middle-income countries: learning from retrospective policy analysis in Argentina, Mongolia, South Africa and Vietnam[J]. Public Health Nutr, 2022, 25(3): 805-16. doi:10.1017/s136898002100344x |
| [27] | Chimed-Ochir O, Delgermaa V, Takahashi K, et al. Mongolia health situation: based on the global burden of disease study 2019[J]. BMC Public Health, 2022, 22(1): 5. doi:10.1186/s12889-021-12070-3 |
| [28] | Zhang JY, Lu YB, Li HR, et al. Lip and oral cavity cancer burden and related risk factors in China: estimates and forecasts from 1990 to 2049[J]. Healthcare (Basel), 2022, 10(9): 1611. doi:10.3390/healthcare10091611 |
| [29] | Saraswat N, Pillay R, Everett B, et al. Knowledge, attitudes and practices of South Asian immigrants in developed countries regarding oral cancer: an integrative review[J]. BMC Cancer, 2020, 20(1): 477. doi:10.1186/s12885-020-06944-9 |
| [30] | Yu ZR, Ma XM, Xiao HY, et al. Disease burden and attributable risk factors of lip and oral cavity cancer in China from 1990 to 2021 and its prediction to 2031[J]. Front Public Health, 2024, 12: 1419428. doi:10.3389/fpubh.2024.1419428 |
| [31] | Ghanem AS, Memon HA, Nagy AC. Evolving trends in oral cancer burden in Europe: a systematic review[J]. Front Oncol, 2024, 14: 1444326. doi:10.3389/fonc.2024.1444326 |
| [32] | Lenoci D, Moresco E, Cavalieri S, et al. Oral cancer in young adults: incidence, risk factors, prognosis, and molecular biomarkers[J]. Front Oncol, 2024, 14: 1452909. doi:10.3389/fonc.2024.1452909 |
| [33] | Montégut L, López-Otín C, Kroemer G. Aging and cancer[J]. Mol Cancer, 2024, 23(1): 106. doi:10.1186/s12943-024-02020-z |
| [34] | Fane M, Weeraratna AT. How the ageing microenvironment influences tumour progression[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2020, 20(2): 89-106. doi:10.1038/s41568-019-0222-9 |
| [35] | Matsuda Y, Jayasinghe RD, Zhong H, et al. Oral health management and rehabilitation for patients with oral cancer: a narrative review[J]. Healthcare (Basel), 2022, 10(5): 960. doi:10.3390/healthcare10050960 |
| [36] | Sanna M, Gao W, Chiu YW, et al. Tobacco control within and beyond WHO MPOWER: outcomes from Taiwan SimSmoke[J]. Tob Control, 2020, 29(1): 36-42. doi:10.1136/tobaccocontrol-2018-054544 |
| [37] | Chen RH, Chang HY, Hsu YT, et al. Harm from others' drinking among young adults in Taiwan: Predictors and deteriorating quality of life[J]. Drug Alcohol Rev, 2024, 43(6): 1483-92. doi:10.1111/dar.13903 |
| [38] | Flor LS, Reitsma MB, Gupta V, et al. The effects of tobacco control policies on global smoking prevalence[J]. Nat Med, 2021, 27(2): 239-43. doi:10.1038/s41591-020-01210-8 |
| [39] | Tamil Selvan S, Yeo XX, van der Eijk Y. Which countries are ready for a tobacco endgame A scoping review and cluster analysis[J]. Lancet Glob Health, 2024, 12(6): e1049-58. doi:10.1016/s2214-109x(24)00085-8 |
| [1] | Xuecai LÜ, Yanhong LIU, Shiyi HAN, Haoyun ZHANG, Aisheng HOU, Zhikang ZHOU, Likai SHI, Jie GAO, Jiangbei CAO, Hong ZHANG, Weidong MI. Risk factors for overall postoperative complications in elderly patients undergoing gastrointestinal surgeries: a multicenter observational study [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 736-743. |
| [2] | Ping YUAN, Xiuli HU, Guojia QI, Xiu DAI, Xiangyuan CHU, Weihang CHEN, Xiuquan SHI. Poor sleep quality contributes to occurrence of posttraumatic stress disorder in trauma patients [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(6): 1166-1172. |
| [3] | Yong ZHOU, Yuan WU, huiwen ZENG, Cuimei CHEN, Qun XIE, Liping HE. Analysis of Clostridioides difficile infection characteristics and risk factors in patients hospitalized for diarrhea in 3 university hospitals in a mid-south city of China [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(5): 998-1003. |
| [4] | GE Yue, LI Jianwei, LIANG Hongkai, HOU Liusheng, ZUO Liuer, CHEN Zhen, LU Jianhai, ZHAO Xin, LIANG Jingyi, PENG Lan, BAO Jingna, DUAN Jiaxin, LIU Li, MAO Keqing, ZENG Zhenhua, HU Hongbin, CHEN Zhongqing. Construction and validation of an in-hospital mortality risk prediction model for patients receiving VA-ECMO: a retrospective multi-center case-control study [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(3): 491-498. |
| [5] | Jiawei HU, Fang DU, Lu DING, Luxiang WANG, Weifeng ZHAO. Risk assessment of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with hepatitis B-related cirrhosis and hypertension: a propensity score matching-based retrospective cohort study [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(11): 2243-2249. |
| [6] | ZHANG Haoxuan, LU Jin, JIANG Chengyi, FANG Meifang. Construction and evaluation of an artificial intelligence-based risk prediction model for death in patients with nasopharyngeal cancer [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(2): 271-279. |
| [7] | TANG Qiao, ZHOU Chao, ZHANG Ning, HE Zhaoyun, ZHANG Jingjing, FU Shuangnan, LI Xin, LIU Pengcheng, ZHANG Tianyi, ZHANG Jin, GONG Man. Prognosis and risk factors for mortality in cirrhotic patients with probable spontaneous bacterial peritonitis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(12): 2043-2052. |
| [8] | LI Jiaxin, XIAO Yan, LIAO Juan, YANG Chunxia. Temporal trend and contributing factors of depressive symptoms in Chinese menopausal women: analysis based on CHARLS panel data [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42(7): 1038-1043. |
| [9] | HE Aiping, DING Xinyi, HUANG Jiali, LUO Xiangrong, MENG Jianfu, CAO Ying, GAO Fang, ZOU Mengchen. Clinical characteristics and risk factors of lower extremity arterial disease in patients with diabetic foot ulcer [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42(4): 604-609. |
| [10] | DENG Ya, WANG Chunyan, FU Yiming, LI Zhongbin, JI Dong. A high relapse risk of chronic drug-induced liver injury is correlated with a greater severity of liver fibrosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42(11): 1655-1661. |
| [11] | ZHAI Yuefen, WANG Huqing, ZHAN Shuqin, WU Haiqin. Efficacy of intravenous thrombolysis for acute severe cerebral infarction and risk factors of poor prognosis: a randomized controlled trial in 152 cases [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2021, 41(9): 1426-1430. |
| [12] | ZHOU Mengmeng, CHEN Jindong, WANG Hao, XI Siqi, GAN Tian, ZHAO Liang. Independent risk factors of atrial thrombosis in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation and low CHA2DS2-VASc scores [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2021, 41(8): 1243-1249. |
| [13] | . Incidence of enteral feeding intolerance and its risk factors in patients with oral and maxillofacial malignancies [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2021, 41(7): 1114-1118. |
| [14] | . Relapse of ankylosing spondylitis and its predictors after withdrawal of tumor necrosis factor-α inhibitors: a 52-week follow-up study [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2021, 41(5): 633-639. |
| [15] | . Clinicopathological characteristics and risk factors of station 4L lymph node metastasis of left non-small cell lung cancer [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2020, 40(12): 1793-1798. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||