Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (7): 1397-1408.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.07.06
Previous Articles Next Articles
Ying YU1( ), Li TU1, Yang LIU1, Xueyi SONG1, Qianqian SHAO1, Xiaolong TANG1,2(
), Li TU1, Yang LIU1, Xueyi SONG1, Qianqian SHAO1, Xiaolong TANG1,2( )
)
Received:2024-11-20
Online:2025-07-20
Published:2025-07-17
Contact:
Xiaolong TANG
E-mail:18697540284@163.com;txljd2006@126.com
Supported by:Ying YU, Li TU, Yang LIU, Xueyi SONG, Qianqian SHAO, Xiaolong TANG. The TGF‑β/miR-23a-3p/IRF1 axis mediates immune escape of hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting major histocompatibility complex class I[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1397-1408.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.07.06
| Genes | Primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| HLA-A | F:ACCCTCGTCCTGCTACTCTC |
| R:CTGTCTCCTCGTCCCAATACT | |
| U6 | F:AGAGAAGATTAGCATGGCCCCTG |
| R:ATCCAGTGCAGGGTC CGAGG | |
| GAPDH | F:CAGGAGGCATTGCTGATGAT |
| R:GAAGGCTGGGGCTCATTT | |
| miR-23a-3p | F:AGCGCCTATCACATTGCCAGG |
| R:ATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGG | |
| miR-106b-5p | F: TGCGGCAACACCAGTCGATGG |
| R: CCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGT | |
| miR-17-5p | F: GCGCAAAGTGCTTACAGTGC |
| R:AGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATT | |
| miR-24-2-5p | F: GCGGTGCCTACTGAGCTGA |
| R:AGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATT |
Tab.1 Sequences of primers for RT-qPCR
| Genes | Primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| HLA-A | F:ACCCTCGTCCTGCTACTCTC |
| R:CTGTCTCCTCGTCCCAATACT | |
| U6 | F:AGAGAAGATTAGCATGGCCCCTG |
| R:ATCCAGTGCAGGGTC CGAGG | |
| GAPDH | F:CAGGAGGCATTGCTGATGAT |
| R:GAAGGCTGGGGCTCATTT | |
| miR-23a-3p | F:AGCGCCTATCACATTGCCAGG |
| R:ATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGG | |
| miR-106b-5p | F: TGCGGCAACACCAGTCGATGG |
| R: CCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGT | |
| miR-17-5p | F: GCGCAAAGTGCTTACAGTGC |
| R:AGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATT | |
| miR-24-2-5p | F: GCGGTGCCTACTGAGCTGA |
| R:AGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATT |
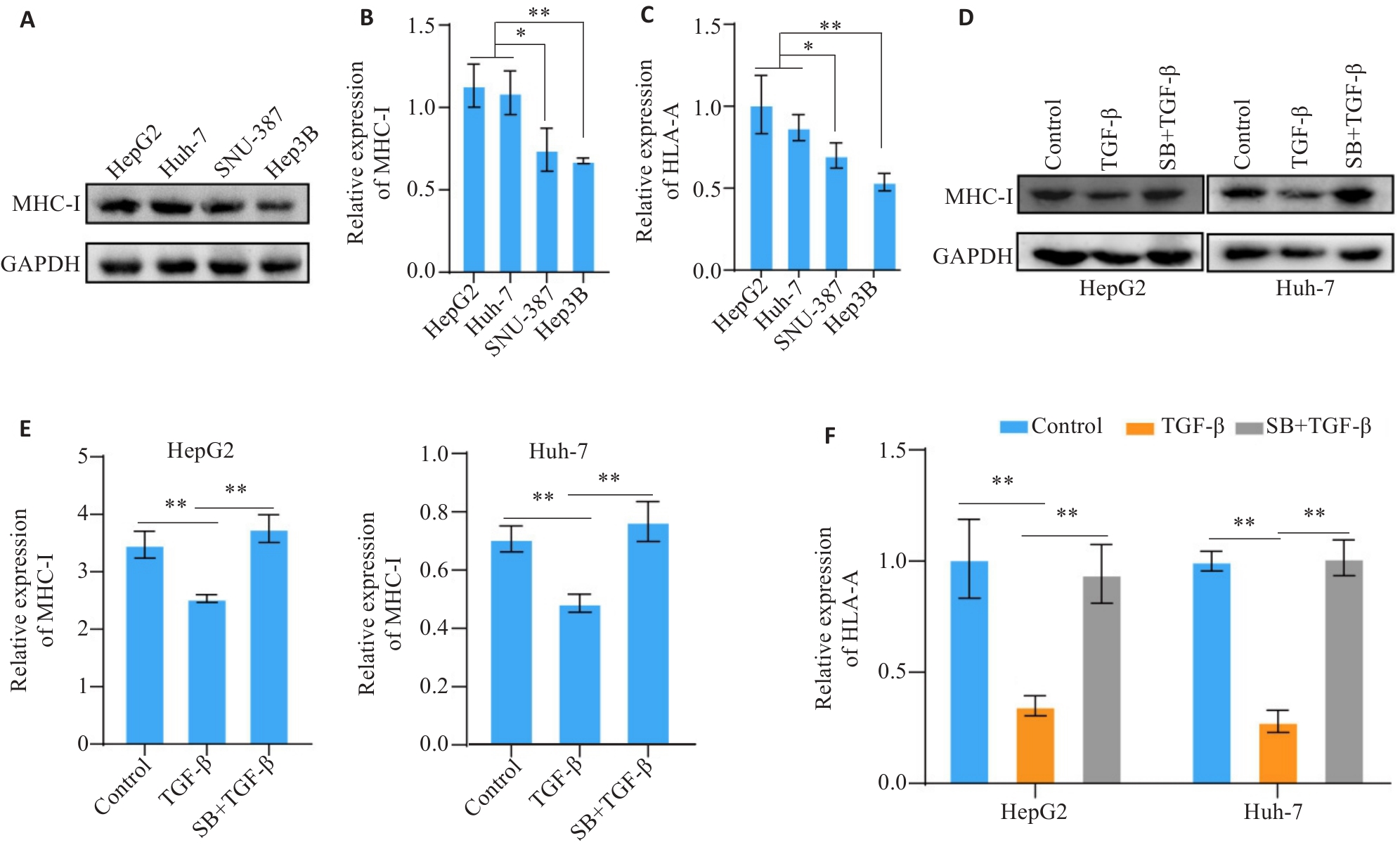
Fig.1 TGF-β down-regulates the expression of MHC-I molecules in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell lines. A, B: Western blotting of MHC-I protein expression in 4 human HCC cell lines. C: RT-PCR analysis of HLA-A mRNA expression in 4 human HCC cell lines. D, E: Western blotting of MHC-I protein expression in TGF-β-treated HCC cells. F: RT-PCR analysis of HLA-A mRNA expression in TGF-β-treated HCC cells. SB: SB-431542. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.

Fig.2 TGF-β affects PBMC activation and reduces its toxicity and killing effect against HCC cells. A: CCK-8 assay for assessing HCC cell viability in the co-culture models with different treatments. B, C: Clonogenic assay for quantifying colony formation capacity of HCC cells in the co-culture models in different treatment groups. D: LDH release assay for evaluating cytotoxicity in the co-culture models with different treatments. E, F: JC-1 staining for assessing mitochondrial membrane potential of HCC cells in the co-culture models. G: ELISA for detecting TNF-α secretion by activated T cells in the co-culture systems in different groups. H: Flow cytometry for analyzing CD8+ T cell percentage with high expression of CD69 in the co-culture models in different groups. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
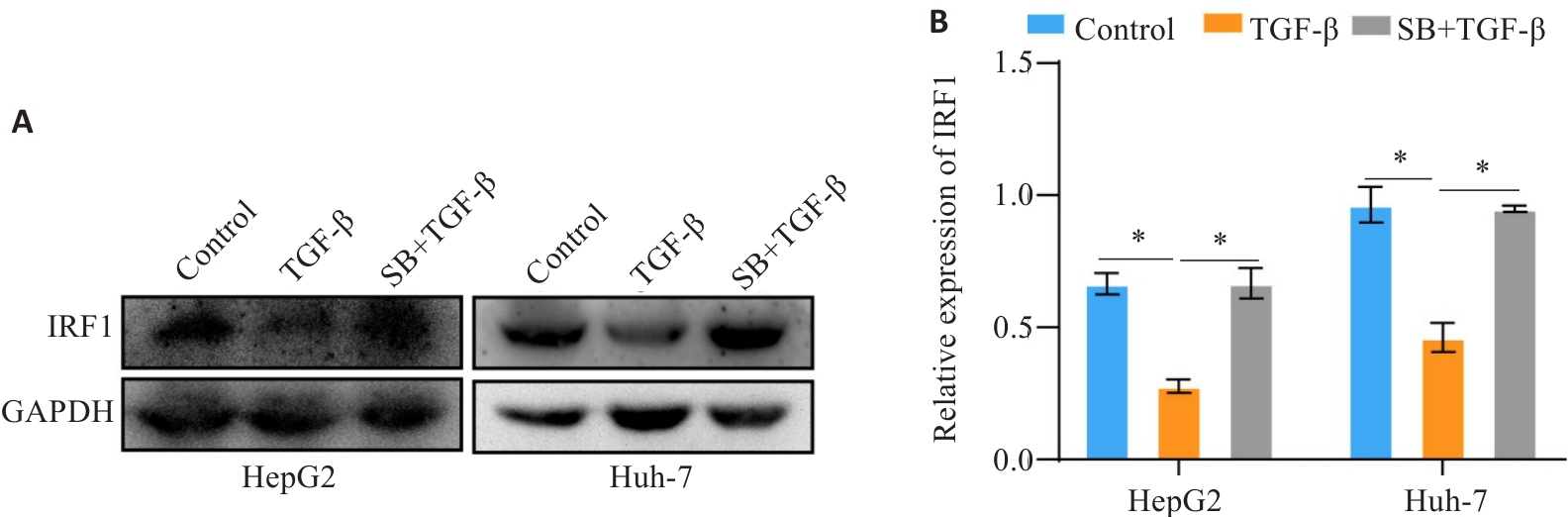
Fig.3 TGF‑β decreases the expression level of IRF1. A, B: Western blotting for detecting the expression level of IRF1 in TGF-β treated cells. *P<0.05.
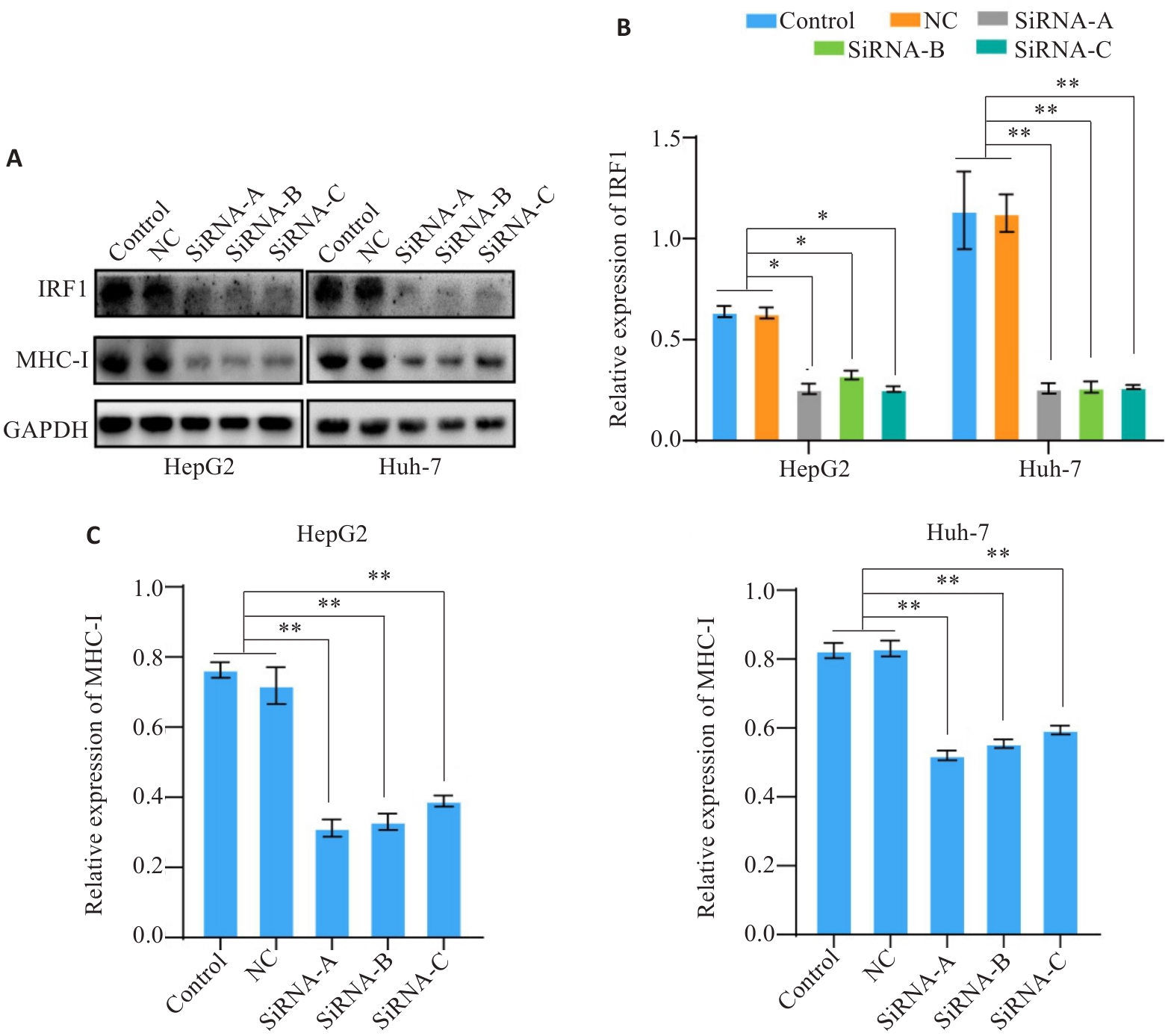
Fig.4 Expression level of IRF1 affects the expression of MHC-I. A-C: Western blotting for detecting expression levels of IRF1 and MHC-I in HCC cells after IRF1 knockdown. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
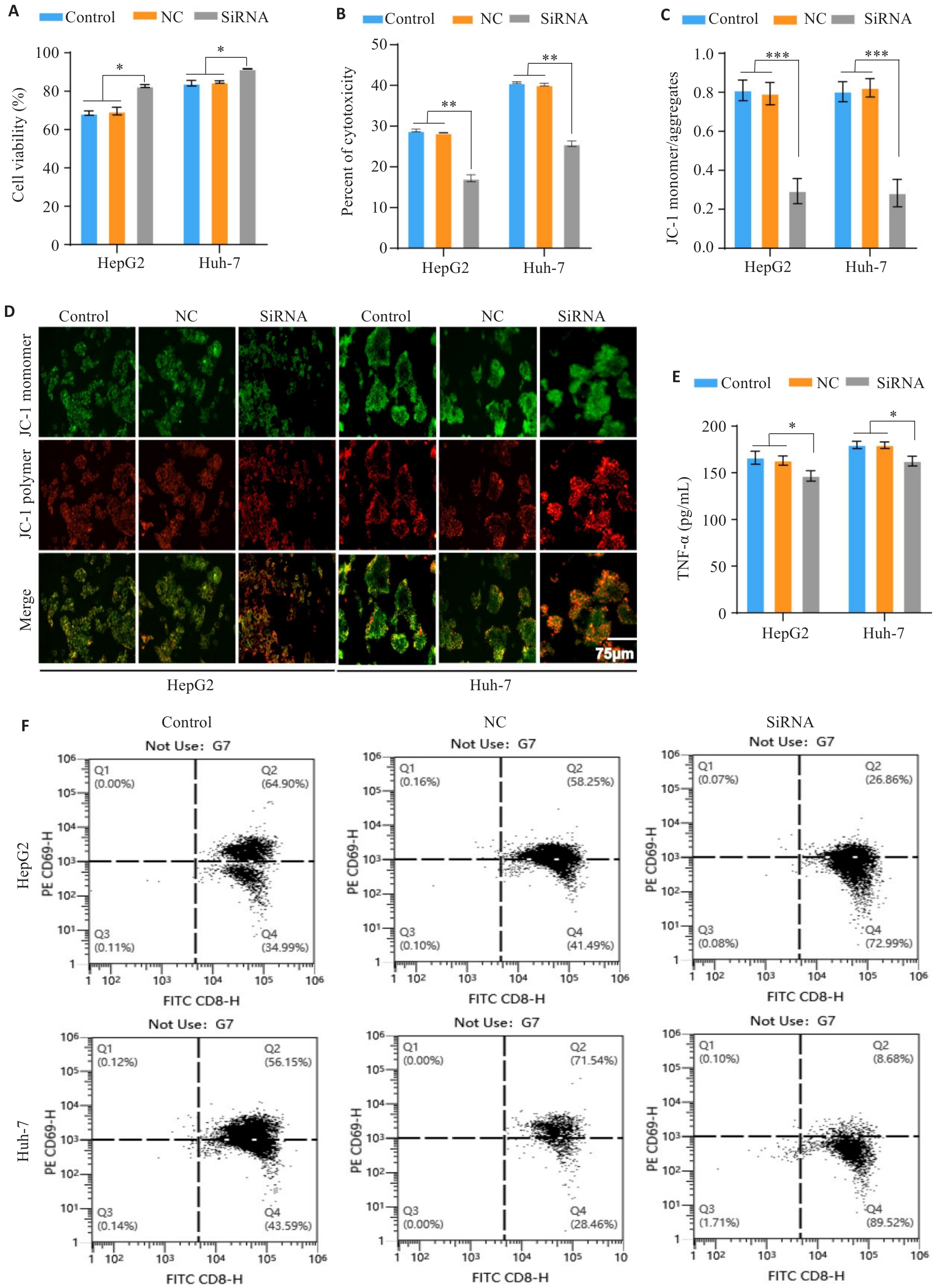
Fig.5 Expression of IRF1 affects PBMC activation and reduces its toxicity and killing effect on HCC cells. A: CCK-8 assay for assessing viability of HCC cells with different treatments in the co-culture models. B: LDH release assay for evaluating tumor cell cytotoxicity in the co-culture systems. C,D: JC-1 staining assessing mitochondrial membrane potential of HCC cells in the co-culture models with different treatments. E: ELISA of TNF-α secretion by activated T cells in the co-culture systems. F: Flow cytometric analysis of percentage of CD8+ T cells with high CD69 expression in the co-culture models. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
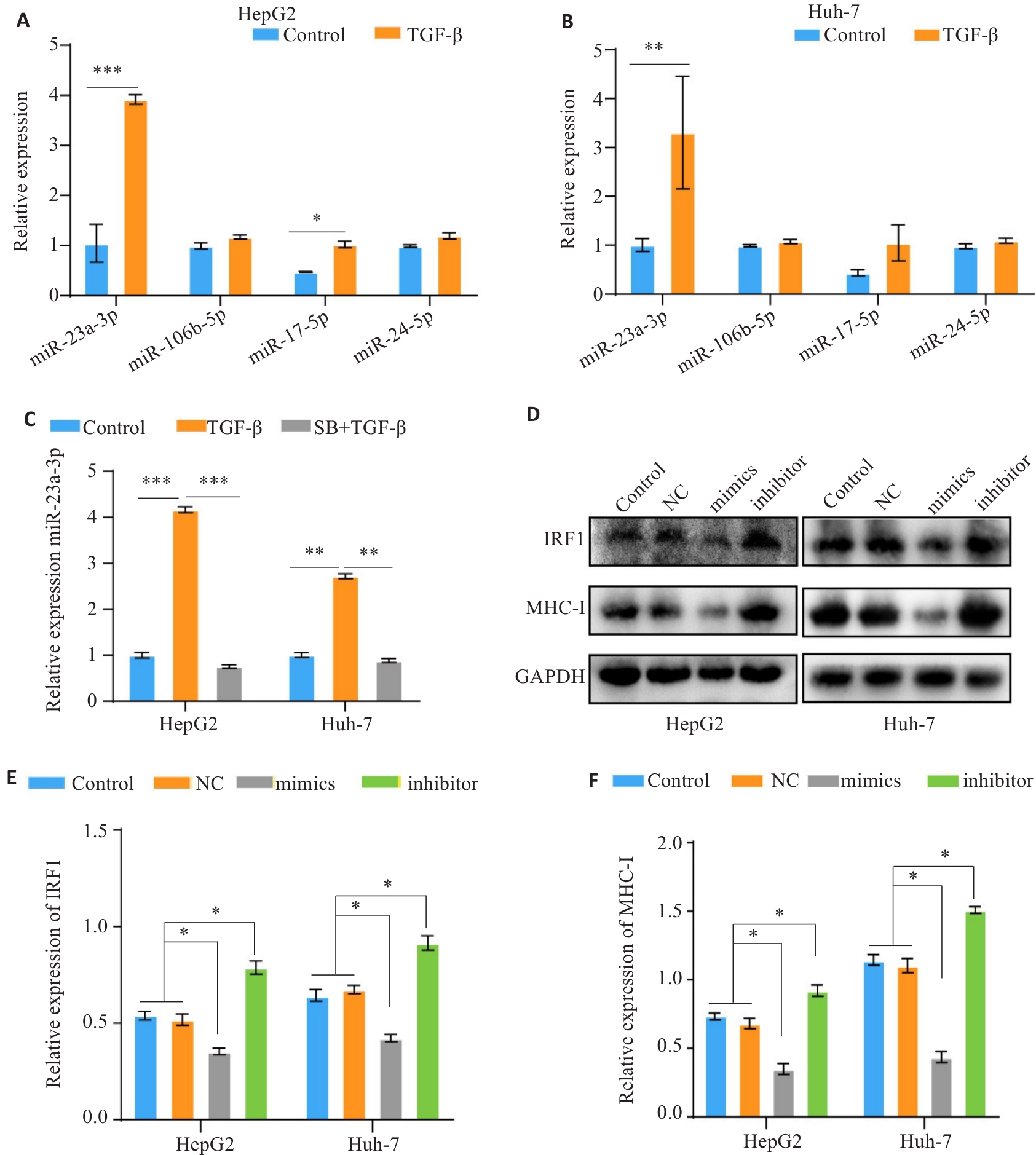
Fig.7 TGF-β down-regulates MHC-I expression via miR-23a-3p/IRF1. A, B: RT-PCR for analyzing expression levels of miR-23a-3p, miR-106b-5p, miR-17-5p, and miR-24-2-5p in HCC cells after TGF-β treatment. C: RT-qPCR analysis of miR-23a-3p expression in TGF-β-treated cells. D-F: Western blotting of IRF1 and MHC-I protein expressions in HCC cells following modulation of miR-23a-3p expression level. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
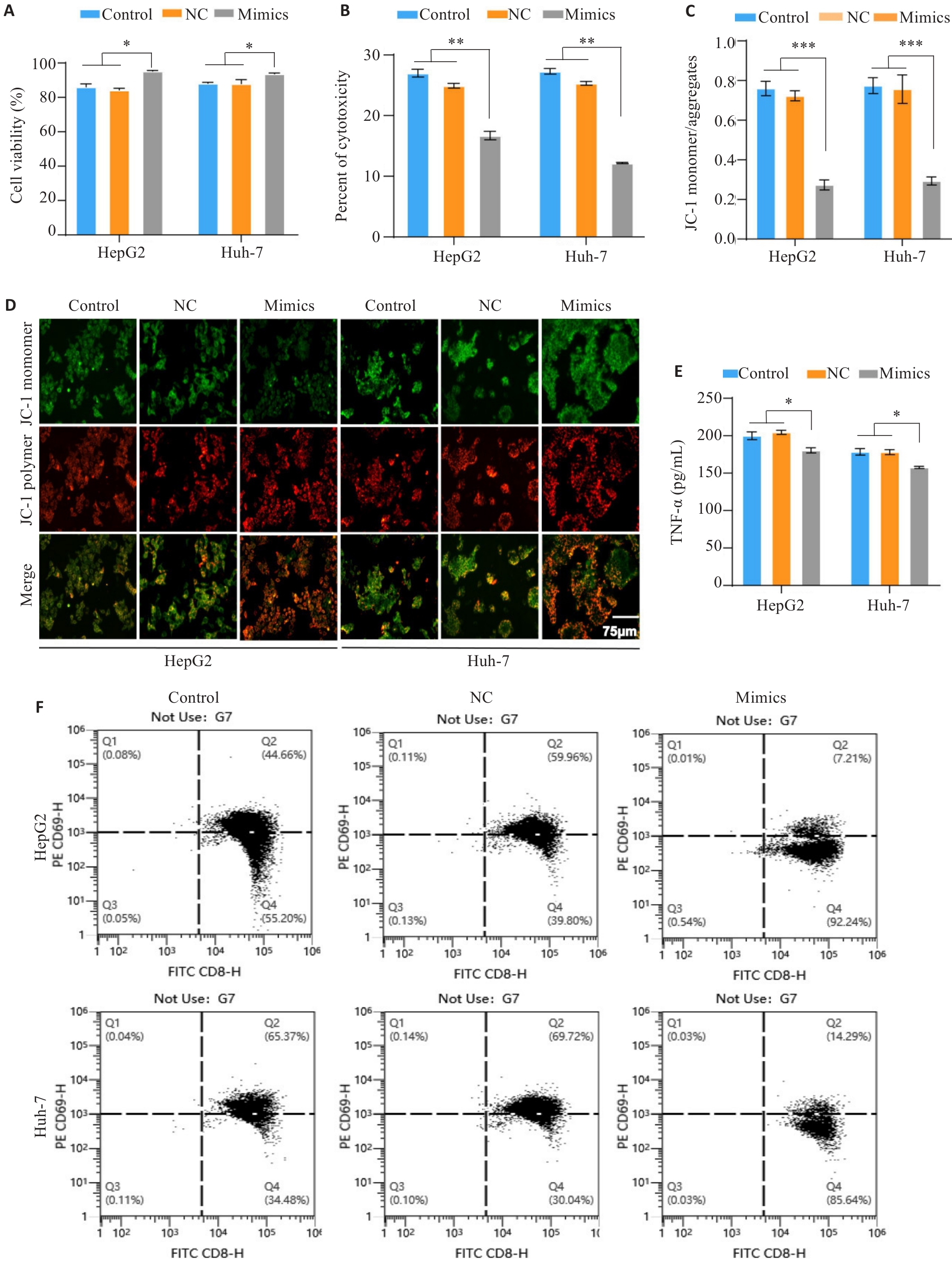
Fig.8 MiR-23a-3p affects PBMC activation and reduces its cytotoxicity and killing effect on HCC cells. A: CCK-8 assay of viability of HCC cells with different treatments in the co-culture models. B: LDH release assay for evaluating tumor cell cytotoxicity in the co-culture systems with different treatments. C, D: JC-1 staining for assessing mitochondrial membrane potential of the tumor cells in the co-culture models. E: ELISA quantification of TNF-α secretion by activated T cells in the co-culture systems. F: Flow cytometric analysis of the proportion of CD8+ T cells with high CD69 expression in the co-culture models. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
| [1] | Chakraborty E, Sarkar D. Emerging therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)[J]. Cancers: Basel, 2022, 14(11): 2798. doi:10.3390/cancers14030504 |
| [2] | Tümen D, Heumann P, Gülow K, et al. Pathogenesis and current treatment strategies of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Biomedicines, 2022, 10(12): 3202. doi:10.3390/biomedicines10123202 |
| [3] | Huang J, Tsang WY, Fang XN, et al. FASN inhibition decreases MHC-I degradation and synergizes with PD-L1 checkpoint blockade in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cancer Res, 2024, 84(6): 855-71. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-23-0966 |
| [4] | Chen Y, Qian Y, Huang W, et al. Chronic stress promotes tumor immune evasion via the suppression of MHC-I expression and the upregulation of PD-L1[J]. Am J Cancer Res, 2022, 12(11): 5286-99. |
| [5] | Cruz FM, Chan A, Rock KL. Pathways of MHC I cross-presentation of exogenous antigens[J]. Semin Immunol, 2023, 66: 101729. doi:10.1016/j.smim.2023.101729 |
| [6] | Dhatchinamoorthy K, Colbert JD, Rock KL. Cancer immune evasion through loss of MHC class I antigen presentation[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 636568. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.636568 |
| [7] | Yamamoto K, Venida A, Yano J, et al. Autophagy promotes immune evasion of pancreatic cancer by degrading MHC-I[J]. Nature, 2020, 581(7806): 100-5. doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2229-5 |
| [8] | Wu X, Li T, Jiang R, et al. Targeting MHC-I molecules for cancer: function, mechanism, and therapeutic prospects[J]. Mol Cancer, 2023, 22(1): 194. doi:10.1186/s12943-023-01899-4 |
| [9] | Xin X, Cheng X, Zeng F, et al. The role of TGF-β/SMAD signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma: from mechanism to therapy and prognosis[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2024, 20(4): 1436-51. doi:10.7150/ijbs.89568 |
| [10] | Gough NR, Xiang XY, Mishra L. TGF-β signaling in liver, pancreas, and gastrointestinal diseases and cancer[J]. Gastroenterology, 2021, 161(2): 434-52.e15. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2021.04.064 |
| [11] | Derynck R, Jarrett JA, Chen EY, et al. Human transforming growth factor-beta complementary DNA sequence and expression in normal and transformed cells[J]. Nature, 1985, 316(6030): 701-5. doi:10.1038/316701a0 |
| [12] | Derynck R, Turley SJ, Akhurst RJ. TGFβ biology in cancer progression and immunotherapy[J]. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 2021, 18(1): 9-34. doi:10.1038/s41571-020-0403-1 |
| [13] | Desbois M, Udyavar AR, Ryner L, et al. Integrated digital pathology and transcriptome analysis identifies molecular mediators of T-cell exclusion in ovarian cancer[J]. Nat Commun, 2020, 11(1): 5583. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-19408-2 |
| [14] | Martini M, Testi MG, Pasetto M, et al. IFN-gamma-mediated upmodulation of MHC class I expression activates tumor-specific immune response in a mouse model of prostate cancer[J]. Vaccine, 2010, 28(20): 3548-57. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2010.03.007 |
| [15] | Pan M, Luo M, Liu L, et al. EGR1 suppresses HCC growth and aerobic glycolysis by transcriptionally downregulating PFKL[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2024, 43(1): 35. doi:10.1186/s13046-024-02957-5 |
| [16] | Wang Y, Deng B. Hepatocellular carcinoma: molecular mechanism, targeted therapy, and biomarkers[J]. Cancer Metastasis Rev, 2023, 42(3): 629-52. doi:10.1007/s10555-023-10084-4 |
| [17] | Du G, Dou C, Sun P, et al. Regulatory T cells and immune escape in HCC: understanding the tumor microenvironment and advancing CAR-T cell therapy[J]. Front Immunol, 2024, 15: 1431211. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2024.1431211 |
| [18] | Bates JP, Derakhshandeh R, Jones L, et al. Mechanisms of immune evasion in breast cancer[J]. BMC Cancer, 2018, 18(1): 556. doi:10.1186/s12885-018-4441-3 |
| [19] | Ye D, Zhou S, Dai XY, et al. Targeting the MHC-I endosomal-lysosomal trafficking pathway in cancer: From mechanism to immunotherapy[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta BBA Rev Cancer, 2024, 1879(5): 189161. doi:10.1016/j.bbcan.2024.189161 |
| [20] | Dersh D, Hollý J, Yewdell JW. A few good peptides: MHC class I-based cancer immunosurveillance and immunoevasion[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2021, 21(2): 116-28. doi:10.1038/s41577-020-0390-6 |
| [21] | Qiao X, Cheng Z, Xue K, et al. Tumor-associated macrophage-derived exosomes LINC01592 induce the immune escape of esophageal cancer by decreasing MHC-I surface expression[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2023, 42(1): 289. doi:10.1186/s13046-023-02871-2 |
| [22] | Kong J, Xu S, Zhang P, et al. CXCL1 promotes immune escape in colorectal cancer by autophagy-mediated MHC-I degradation[J]. Hum Immunol, 2023, 84(12): 110716. doi:10.1016/j.humimm.2023.09.002 |
| [23] | Wang XC, Eichhorn PJA, Thiery JP. TGF-β, EMT, and resistance to anti-cancer treatment[J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 2023, 97: 1-11. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2023.10.004 |
| [24] | Aashaq S, Batool A, Mir SA, et al. TGF-β signaling: a recap of SMAD-independent and SMAD-dependent pathways[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2022, 237(1): 59-85. doi:10.1002/jcp.30529 |
| [25] | Lee JH, Massagué J. TGF-β in developmental and fibrogenic EMTs[J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 2022, 86: 136-45. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2022.09.004 |
| [26] | Shi X, Yang J, Deng S, et al. TGF-β signaling in the tumor metabolic microenvironment and targeted therapies[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2022, 15(1): 135. doi:10.1186/s13045-022-01349-6 |
| [27] | Zhou F. Molecular mechanisms of IFN-gamma to up-regulate MHC class I antigen processing and presentation[J]. Int Rev Immunol, 2009, 28(3/4): 239-60. doi:10.1080/08830180902978120 |
| [28] | Zhang J, Guo HJ, Wang LS, et al. Cediranib enhances the transcription of MHC-I by upregulating IRF-1[J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2024, 221: 116036. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2024.116036 |
| [29] | Tan L, Yin T, Xiang H, et al. Aberrant cytoplasmic expression of UHRF1 restrains the MHC-I-mediated anti-tumor immune response[J]. Nat Commun, 2024, 15(1): 8569. doi:10.1038/s41467-024-52902-5 |
| [30] | Cardenas H, Vieth E, Lee J, et al. TGF-β induces global changes in DNA methylation during the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in ovarian cancer cells[J]. Epigenetics, 2014, 9(11): 1461-72. doi:10.4161/15592294.2014.971608 |
| [31] | Guan Z, Song B, Liu F, et al. TGF‑β induces HLA-G expression through inhibiting miR-152 in gastric cancer cells[J]. J Biomed Sci, 2015, 22: 107. doi:10.1186/s12929-015-0177-4 |
| [32] | Zeng XC, Zhang T, Huang DH, et al. RNA interfering targeting human leukocyte antigen-G enhanced immune surveillance mediated by the natural killer cells on hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Ann Clin Lab Sci, 2013, 43(2): 135-44. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||