Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (5): 1047-1055.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.05.18
Previous Articles Next Articles
Jun ZHENG( ), Zhihua WANG(
), Zhihua WANG( ), Xiaojun HU, Xiang HE, Yingfang FAN(
), Xiaojun HU, Xiang HE, Yingfang FAN( )
)
Received:2024-10-25
Online:2025-05-20
Published:2025-05-23
Contact:
Yingfang FAN
E-mail:zs2022088@smu.edu.cn;3070013808@qq.com;fanxifan@smu.edu.cn
Jun ZHENG, Zhihua WANG, Xiaojun HU, Xiang HE, Yingfang FAN. 3D visualization-based classification of left intrahepatic vessels and its application in precision hepatectomy[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 1047-1055.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.05.18
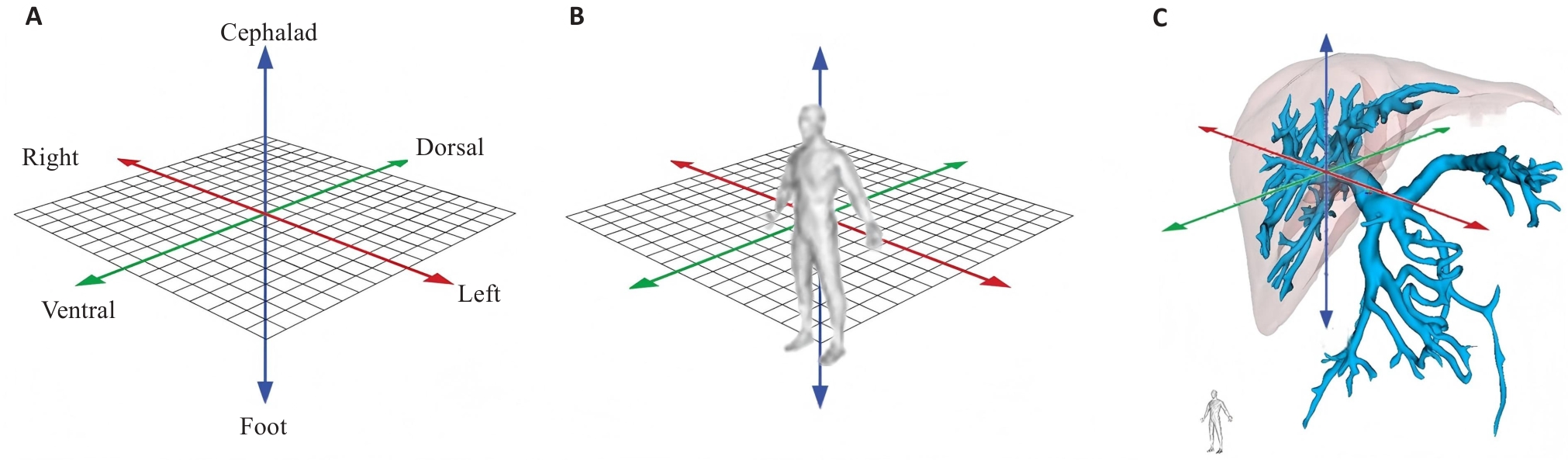
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of 3D directions of blood vessels. A: Schematic diagram of 3D space. B: Schematic diagram of the anatomical position. C: Schematic diagram of the vascular spatial orientation in the anatomical position.
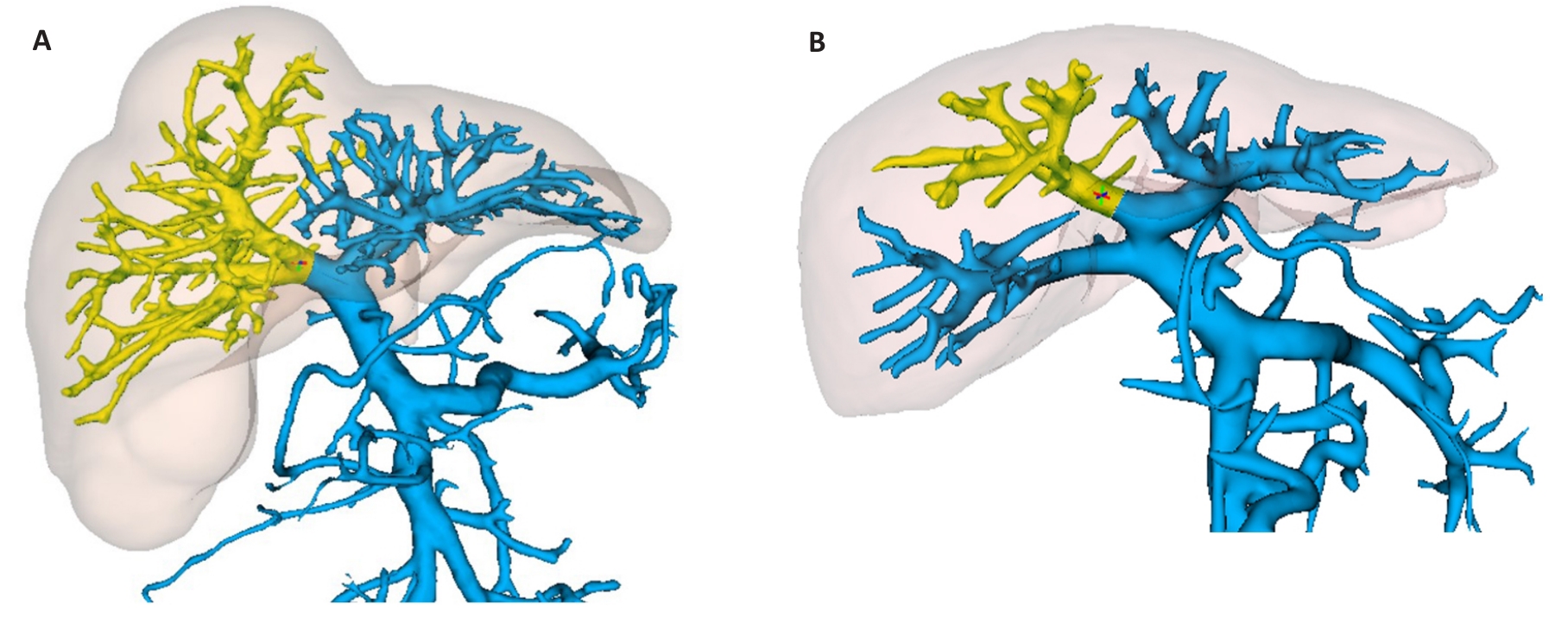
Fig.2 3D classification of the main portal vein. A: The left hepatic portal vein has independent origin, and the yellow vessel is the right branch of the portal vein. B: The right anterior branch of the portal vein and the left branch of the portal vein have a common trunk, and the yellow vessel is the right anterior branch of the portal vein.
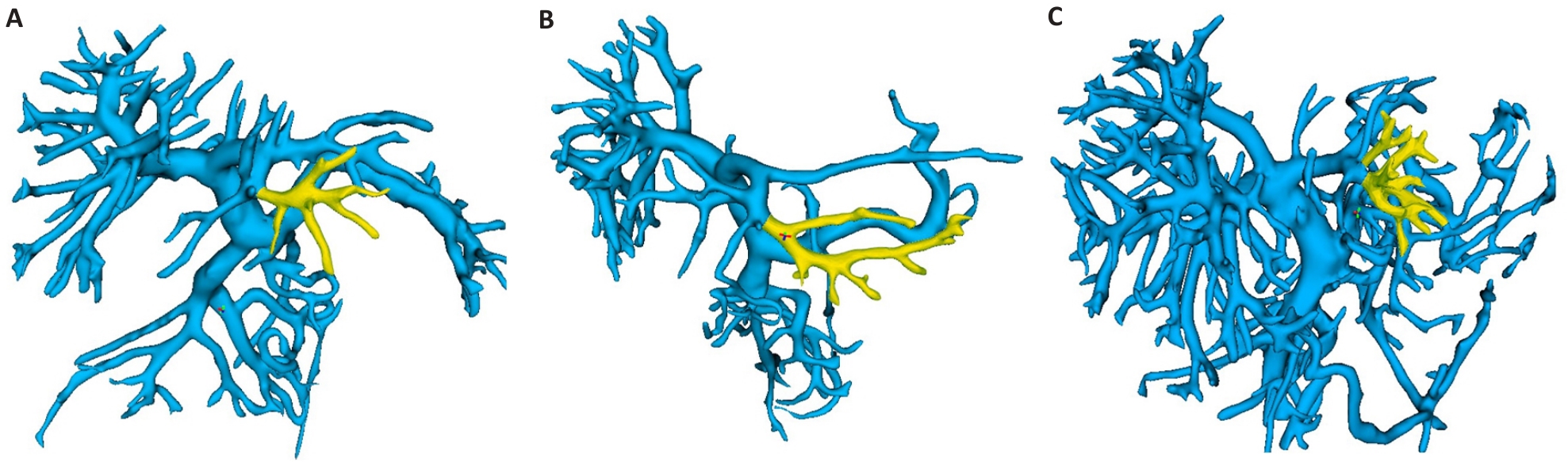
Fig.4 3D classification of segment III of the portal vein. The yellow vessel is the branch of the segment III of the portal vein. A: Branched are distributed in the cephalad and ventral left quadrant. B: Branches are distributed in the foot and ventral left quadrant. C: Branches in both quadrants at the same time.
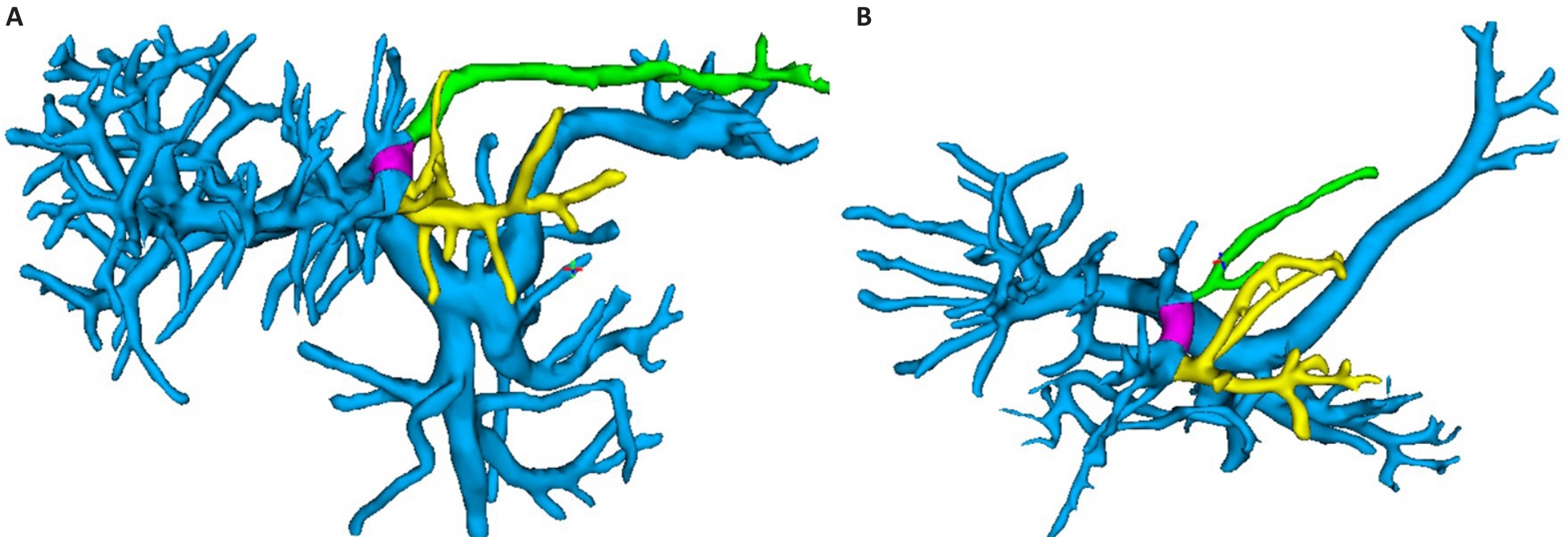
Fig.5 3D classification of the left lateral lobe of the portal vein. The yellow vessel is the branch of portal vein segment III, the green vessel is the branch of portal vein segment II, and the purple vessel has the shortest distance between them. A: The distance between the origins of the portal vein branch in segments II and III is less than 2 cm. B: The distance is more than 2 cm.
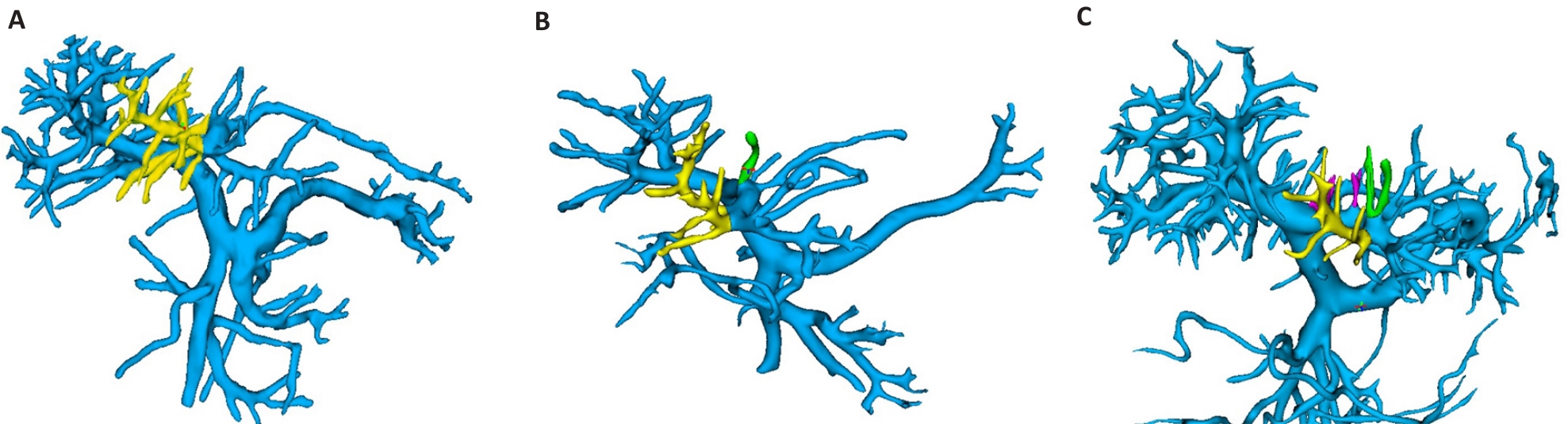
Fig.6 3D classification of portal vein of segment IV. The yellow vessel is from the capsular part of the branch of segment IV, the green vessels is from the sagittal part of the branch of segment IV, and the purple vessel is from the transverse part of the branch of segment IV. A: The branch of the capsular part is clustered and there is no branch in the sagittal part. B: Capsular partial branch + sagittal partial branch. C: Capsular partial branch + sagittal partial branch + transverse partial branch.
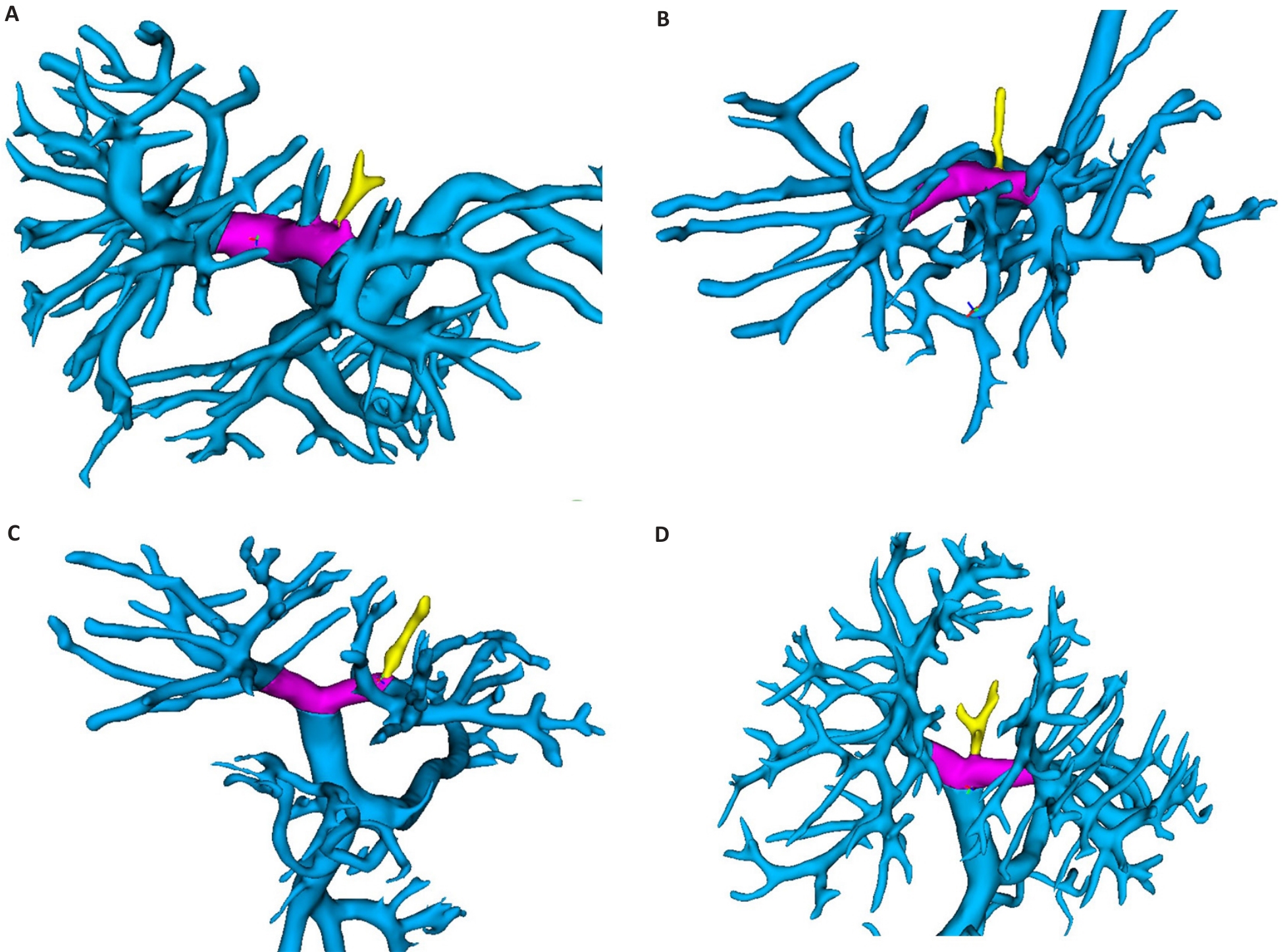
Fig.7 3D classification of the fourth hilar vessel. The yellow vessel is the short portal vessel, and the purple vessel is the transverse portal vein. A: The branches supplying the Spiegel lobes. B: The branches supplying caudate lobulocaval part. C: The branch supplying segment II. D: The branches supplying segment IVa.
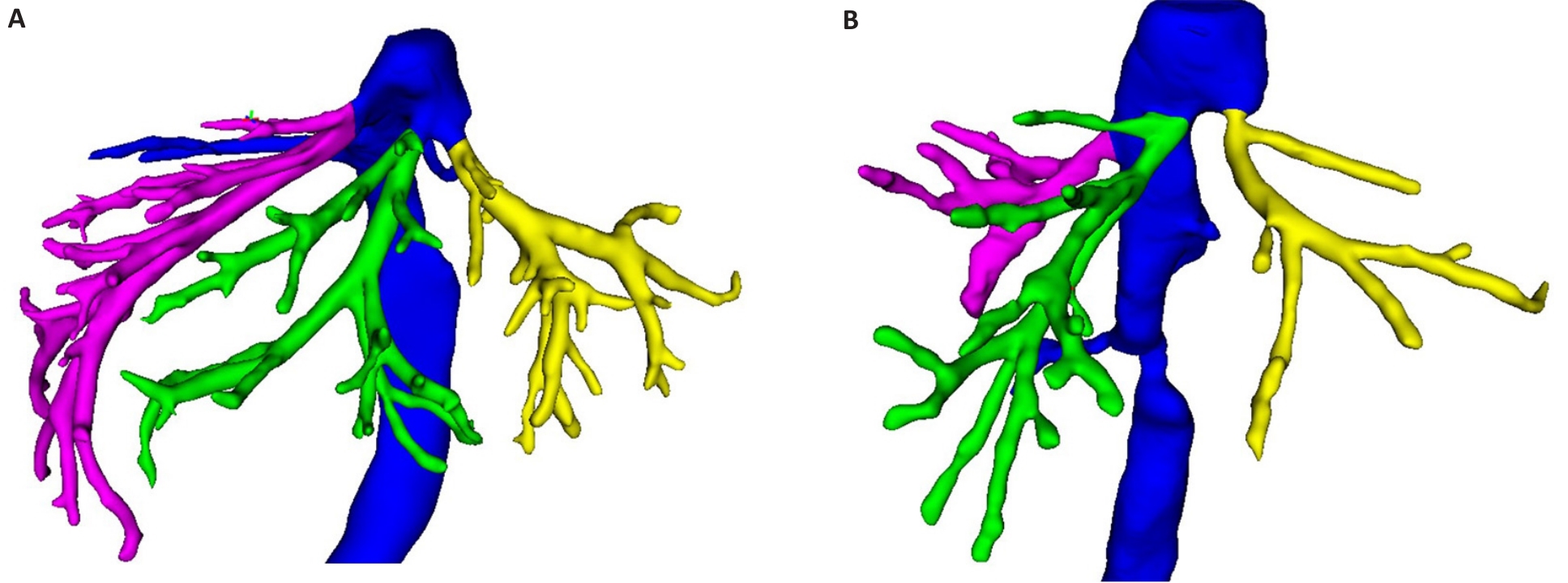
Fig.8 3D classification of the liver vein. The yellow vessel is the left liver vein, the green vessel is the middle liver vein, and the purple vessel is the right liver vein. A: The left liver vein and the middle liver vein drained into the inferior vena cava. B: The left, middle, and right hepatic veins join the inferior vena cava alone.
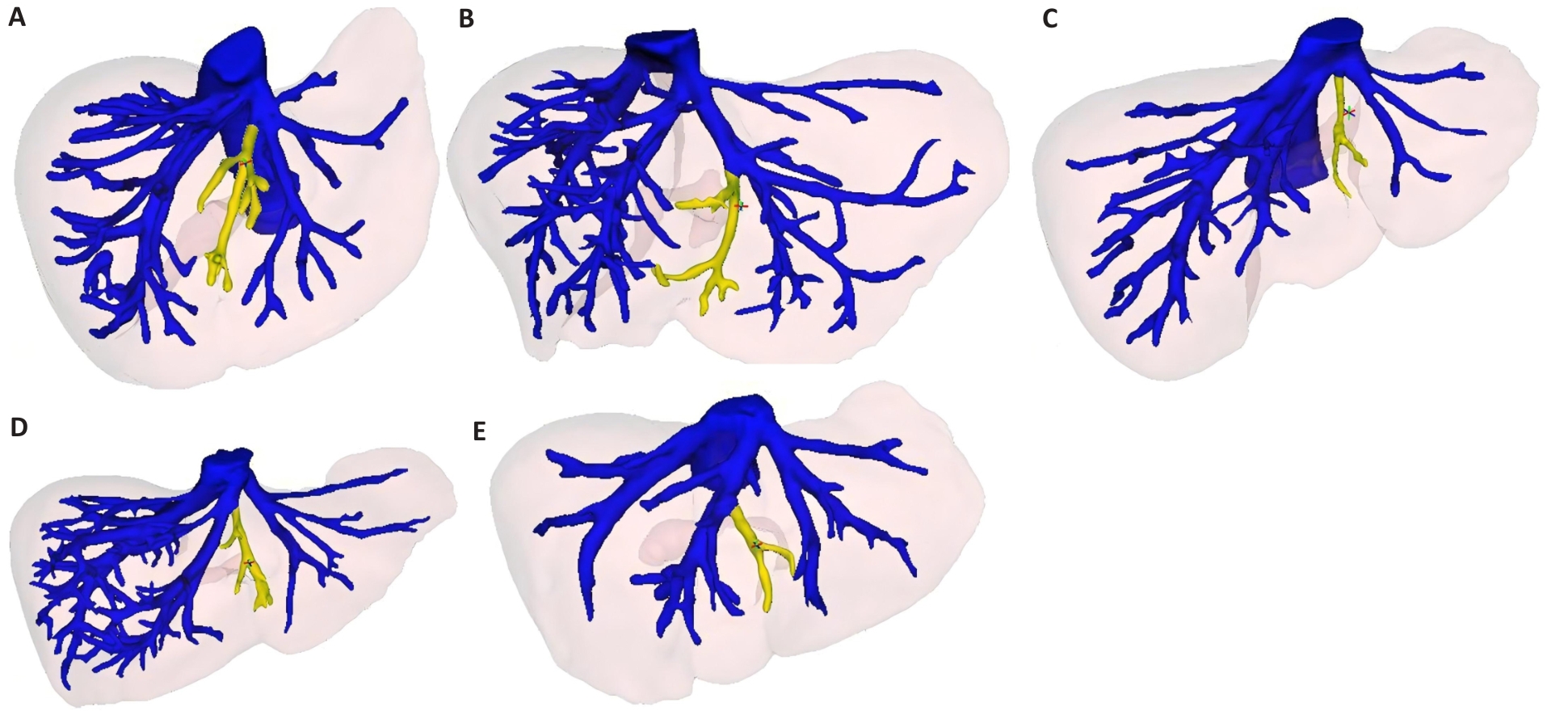
Fig.9 3D classification of the umbilical fissure vein. The yellow vessel is the umbilical fissure vein. A: The umbilical fissure vein merges into the root of the left liver vein within 2 cm. B: The umbilical fissure vein merges 2 cm outside the root of the left hepatic vein. C: Umbilical fissure vein merges into the inferior vena cava. D: The umbilical fissure vein merges into the root of the middle liver vein within 2 cm. E: The umbilical fissure vein merges 2 cm from the root of the middle hepatic vein.
| 1 | Takamoto T, Makuuchi M. Precision surgery for primary liver cancer[J]. Cancer Biol Med, 2019, 16(3): 475-85. |
| 2 | Liao KX, Yang KJ, Cao L, et al. Laparoscopic anatomical versus non-anatomical hepatectomy in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomised controlled trial[J]. Int J Surg, 2022, 102: 106652. |
| 3 | Sugioka A, Kato Y, Tanahashi Y. Systematic extrahepatic Glissonean pedicle isolation for anatomical liver resection based on Laennec's capsule: proposal of a novel comprehensive surgical anatomy of the liver[J]. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci, 2017, 24(1): 17-23. |
| 4 | Zeng N, Tao HS, Fang CH, et al. Individualized preoperative planning using three-dimensional modeling for Bismuth and Corlette type III hilar cholangiocarcinoma[J]. World J Surg Oncol, 2016, 14(1): 44. |
| 5 | Jian Y, Haisu T, Chihua F, et al. Clinical applications of three-dimensional visualization model of arteries supplying the extrahepatic bile duct for patients with biliary obstruction[J]. Am Surg, 2017, 83(1): 8-15. |
| 6 | Cai W, Fan YF, Hu HY, et al. Postoperative liver volume was accurately predicted by a medical image three dimensional visualization system in hepatectomy for liver cancer[J]. Surg Oncol, 2017, 26(2): 188-94. |
| 7 | Lim JSH, Shelat VG. 3D laparoscopy and fluorescence imaging can improve surgical precision for hepatectomy[J]. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr, 2024, 13(3): 544-7. |
| 8 | Chen H, Wang Y, Xie Z, et al. Application effect of ICG fluorescence real-time imaging technology in laparoscopic hepatectomy[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12: 819960. |
| 9 | Zhang P, Luo HL, Zhu W, et al. Real-time navigation for laparoscopic hepatectomy using image fusion of preoperative 3D surgical plan and intraoperative indocyanine green fluorescence imaging[J]. Surg Endosc, 2020, 34(8): 3449-59. |
| 10 | Fujiyama Y, Wakabayashi T, Mishima K, et al. Latest findings on minimally invasive anatomical liver resection[J]. Cancers: Basel, 2023, 15(8): 2218. |
| 11 | 夏穗生, 曾祥熙, 屠頤珠, 等. 肝门外科解剖[J]. 骨科, 1964(2): 81-7. |
| 12 | Yan PN, Tan WF, Yang XW, et al. Applied anatomy of small branches of the portal vein in transverse groove of hepatic hilum[J]. Surg Radiol Anat, 2014, 36(10): 1071-7. |
| 13 | 范应方, 向 飞, 蔡 伟, 等. 基于三维可视化技术的右半肝门静脉3D分型及分段[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2016, 36(1): 26-31. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4254.2016.01.05 |
| 14 | Zhang J, Guo X, Qiao Q, et al. Anatomical study of the hepatic veins in segment 4 of the liver using three-dimensional visualization[J]. Front Surg, 2021, 8: 702280. |
| 15 | Liu ZY, Shen TN, Xia KX, et al. Classification of variant portal vein anatomy based on three-dimensional CT: surgical implications[J]. Surg Radiol Anat, 2024, 46(8): 1177-84. |
| 16 | 禚孝颖, 董 蒨, 吴琳琳, 等. 基于Hisense计算机辅助手术系统的门静脉主干分型的研究[J]. 精准医学杂志, 2019, 34(5): 416-20. DOI: 10.13362/j.jpmed.201905010 |
| 17 | Wang BY, Ou CF, Yu JG, et al. Three-dimensional visual technique based on CT lymphography data combined with methylene blue in endoscopic sentinel lymph node biopsy for breast cancer[J]. Eur J Med Res, 2022, 27(1): 274. |
| 18 | 关明山, 周 波, 韩 娜, 等. 空间封闭点云的八象限三角剖分算法[J]. 哈尔滨理工大学学报, 2009, 14(3): 20-4. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2683.2009.03.006 |
| 19 | Cheng YF, Huang TL, Lee TY, et al. Variation of the intrahepatic portal vein; angiographic demonstration and application in living-related hepatic transplantation[J]. Transplant Proc, 1996, 28(3): 1667-8. |
| 20 | Atri M, Bret PM, Fraser-Hill MA. Intrahepatic portal venous variations: prevalence with US[J]. Radiology, 1992, 184(1): 157-8. |
| 21 | 杨陈凤麟, 李 尧, 王 鑫, 等.“门理论”在微创解剖性肝切除术中的应用与展望 [J].中国实用外科杂志, 2024, 44(3): 341-5. |
| 22 | Cazauran JB, Pâris L, Rousset P, et al. Anatomy of the right anterior sector of the liver and its clinical implications in surgery[J]. J Gastrointest Surg, 2018, 22(10): 1819-31. |
| 23 | Zhang K, Zhang SG, Jiang Y, et al. Laparoscopic hepatic left lateral lobectomy combined with fiber choledochoscopic exploration of the common bile duct and traditional open operation[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2008, 14(7): 1133-6. |
| 24 | 李 斌, 姜小清. 重视“门短静脉” 解剖在围肝门手术中的意义[J]. 中国实用外科杂志, 2019, 39(2): 145-8. |
| 25 | 李 斌, 邱智泉, 闫培宁, 等. “第四肝门” 在围肝门外科的临床意义[J]. 中国普外基础与临床杂志, 2016, 23(11): 1308-10. |
| 26 | Goldsmith NA, Woodburne RT. The surgical anatomy pertaining to liver resection[J]. Surg Gynecol Obstet, 1957, 105(3): 310-8. |
| 27 | Nakamura S, Tsuzuki T. Surgical anatomy of the hepatic veins and the inferior vena Cava [J]. Surg Gynecol Obstet, 1981, 152(1): 43-50. |
| 28 | Tani K, Shindoh J, Akamatsu N, et al. Venous drainage map of the liver for complex hepatobiliary surgery and liver transplantation[J]. HPB, 2016, 18(12): 1031-8. |
| 29 | Kawasaki S, Makuuchi M, Miyagawa S, et al. Extended lateral segmentectomy using intraoperative ultrasound to obtain a partial liver graft[J]. Am J Surg, 1996, 171(2): 286-8. |
| 30 | 董家鸿, 叶 晟. 开启精准肝胆外科的新时代[J]. 中华普外科手术学杂志: 电子版, 2016, 10(3): 181-4. DOI: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.1674-3946.2016.03.001 |
| 31 | Kobayashi K, Hasegawa K, Kokudo T, et al. Extended segmentectomy II to left hepatic vein: importance of preserving umbilical fissure vein to avoid congestion of segment III[J]. J Am Coll Surg, 2017, 225(3): e5-11. |
| [1] | . Application of 3D visualization and 3D printing in individualized precision surgery for Bismuth-Corlette type III and IV hilar cholangiocarcinoma [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2020, 40(08): 1172-1177. |
| [2] | . Clinical practice guidelines for precision diagnosis and treatment of complex liver tumor guided by three-dimensional visualization technology (version 2019) [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2020, 40(03): 297-307. |
| [3] | Guidelines for application of computer-assisted indocyanine green molecular fluorescence imaging in diagnosis and surgical navigation of liver tumors (2019). [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2019, 39(10): 1127-. |
| [4] |
.
Application of 3D visualization, 3D printing and 3D laparoscopy in the diagnosis and surgical treatment of hepatic tumors [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2015, 35(05): 639-. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||