Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (9): 1712-1719.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.09.11
Previous Articles Next Articles
Hanjun ZUO( ), Zhaoda DUAN, Zhao WANG, Tao GUO, Jinsha SHI, Haolong SHI, Juanjuan LI(
), Zhaoda DUAN, Zhao WANG, Tao GUO, Jinsha SHI, Haolong SHI, Juanjuan LI( )
)
Received:2024-01-23
Online:2024-09-20
Published:2024-09-30
Contact:
Juanjuan LI
E-mail:zhj2020320@163.com;lijuanjuan@kmmu.edu.cn
Supported by:Hanjun ZUO, Zhaoda DUAN, Zhao WANG, Tao GUO, Jinsha SHI, Haolong SHI, Juanjuan LI. Gastrodin improves microglia-mediated inflammatory response after hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in neonatal rats via PI3K/AKT pathway[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1712-1719.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.09.11
| Primer | Sequence (5'-3') |
|---|---|
| TGF-β1 F | GCTGAACCAAGGAGACGGAA |
| TGF-β1 R | TCTTCTCTGTGGAGCGTTGAT |
| TNF-α F | ACCCTCACACTCACAAACCA |
| TNF-α R | GGCAGAGAGGAGGTTGACTTT |
| β-actin F | GTGGGAATGGGTCAGAAGGA |
| β-actin R | TACATGGCTGGGGTGTTGAA |
Tab.1 Primer sequence for RT-qPCR
| Primer | Sequence (5'-3') |
|---|---|
| TGF-β1 F | GCTGAACCAAGGAGACGGAA |
| TGF-β1 R | TCTTCTCTGTGGAGCGTTGAT |
| TNF-α F | ACCCTCACACTCACAAACCA |
| TNF-α R | GGCAGAGAGGAGGTTGACTTT |
| β-actin F | GTGGGAATGGGTCAGAAGGA |
| β-actin R | TACATGGCTGGGGTGTTGAA |
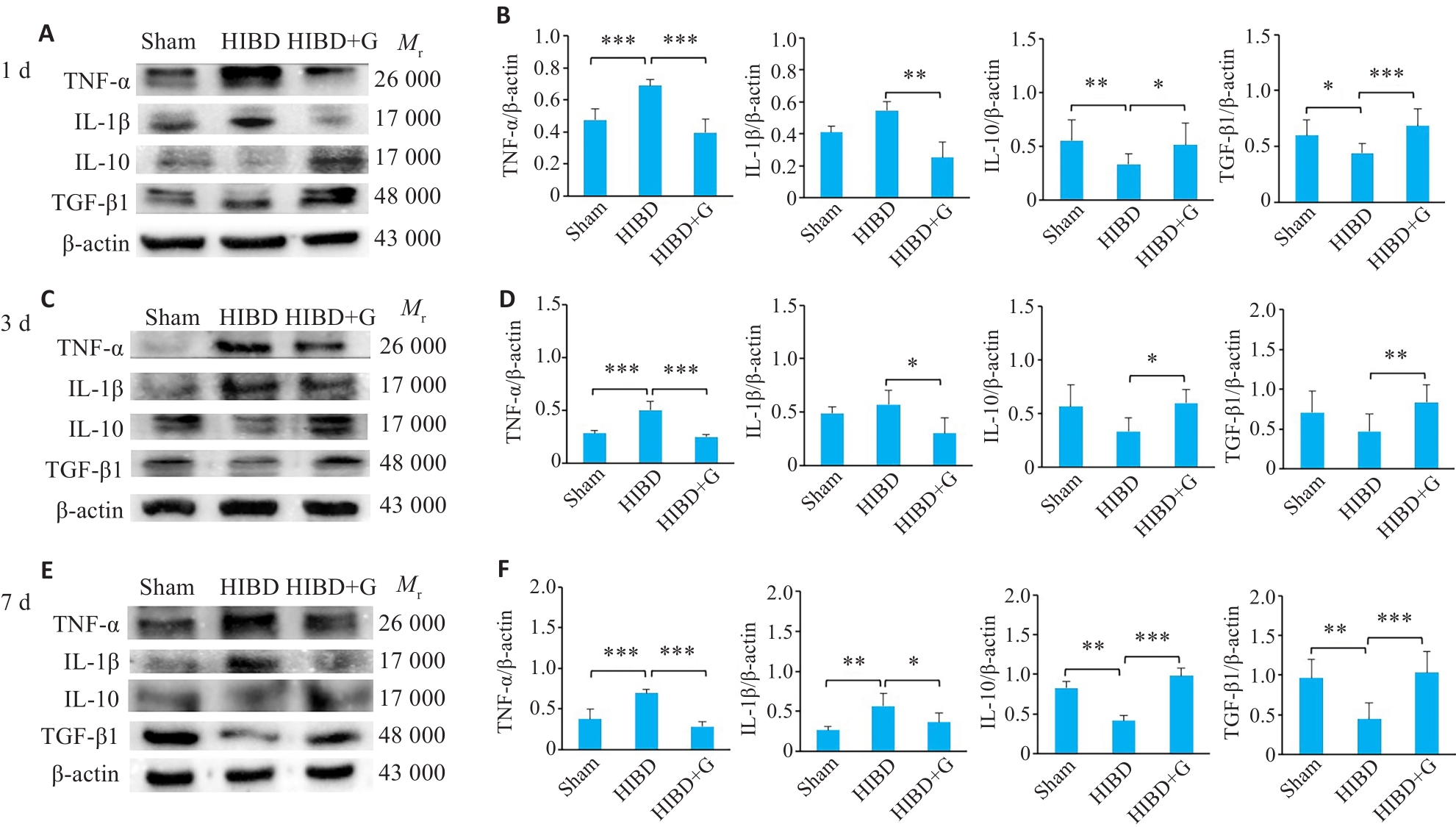
Fig.1 Effect of gastrodin on expressions of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-10 and TGF-β1 proteins in the in brain tissue of neonatal rats at 1 day, 3 days, and 7 days after HIBD detected by Western blotting. A, C, E: Protein blots of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-10, and TGF-β1. B, D, F: Quantification of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-10, and TGF-β1 expression levels. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 (n=3).
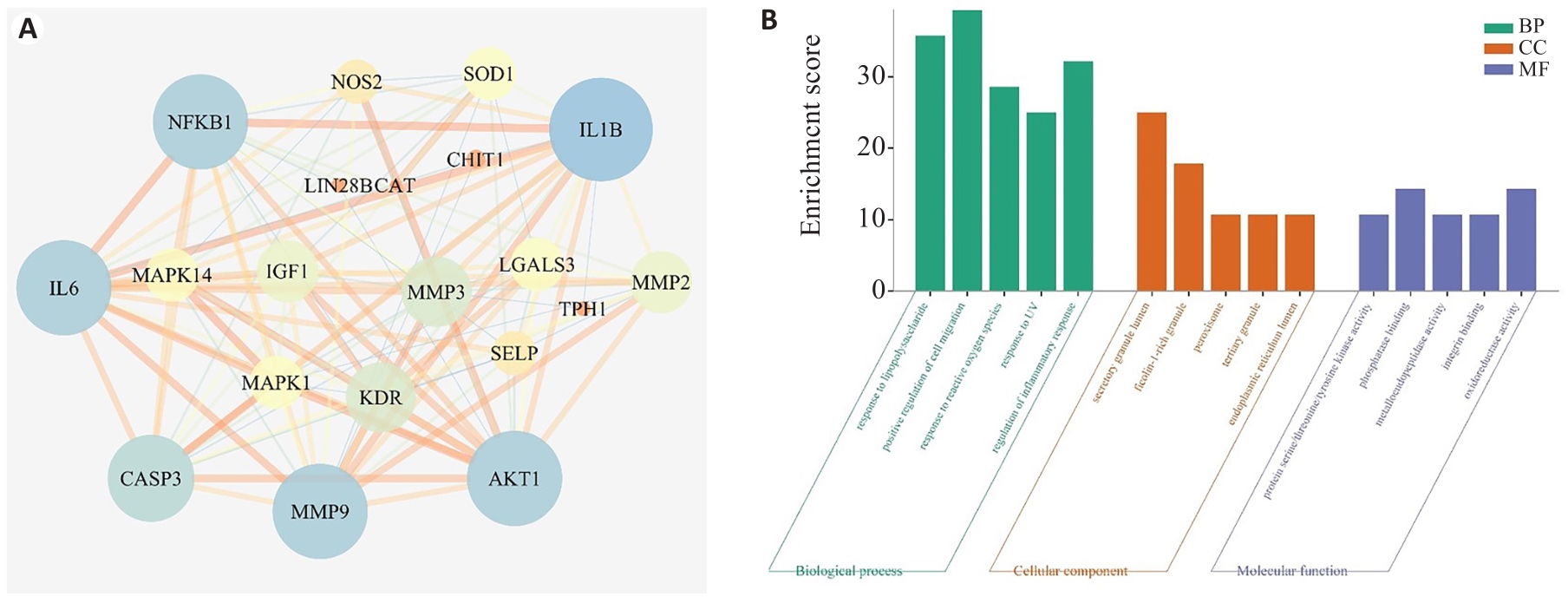
Fig.2 PPI network diagram and GO enrichment analysis of potential core target of gastrodin treatment of HIBD. A: PPI network diagram. B: GO enrichment analysis.
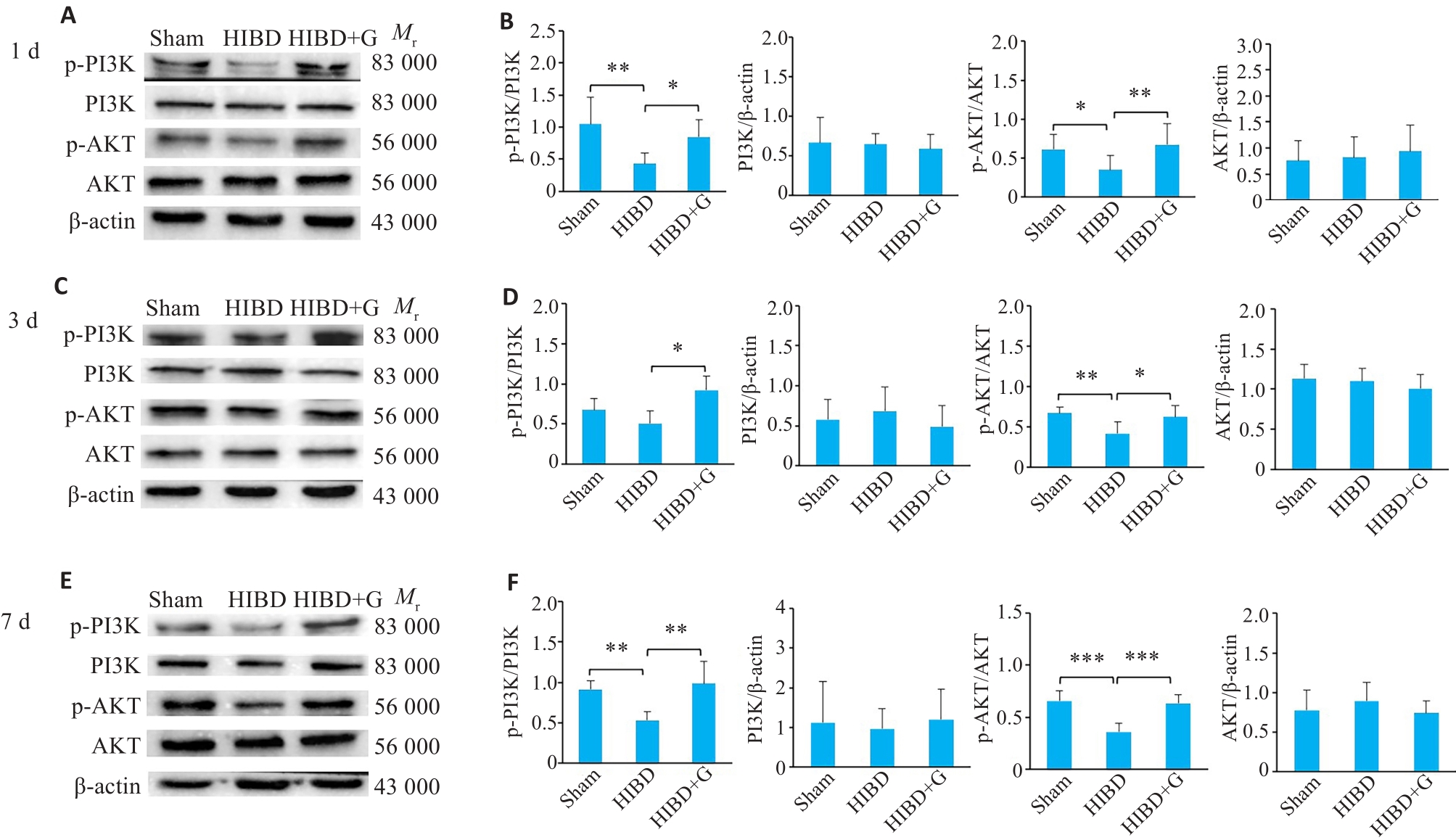
Fig.5 Effect of gastrodin on expressions of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in activated microglia of neonatal rats at 1 day, 3 days, and 7 days after HIBD detected by Western blotting. A, C, E: Western blots of the related proteins in PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. B, D, F: Quantification of P-PI3K, PI3K, P-AKT, and AKT protein levels. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 (n=3).
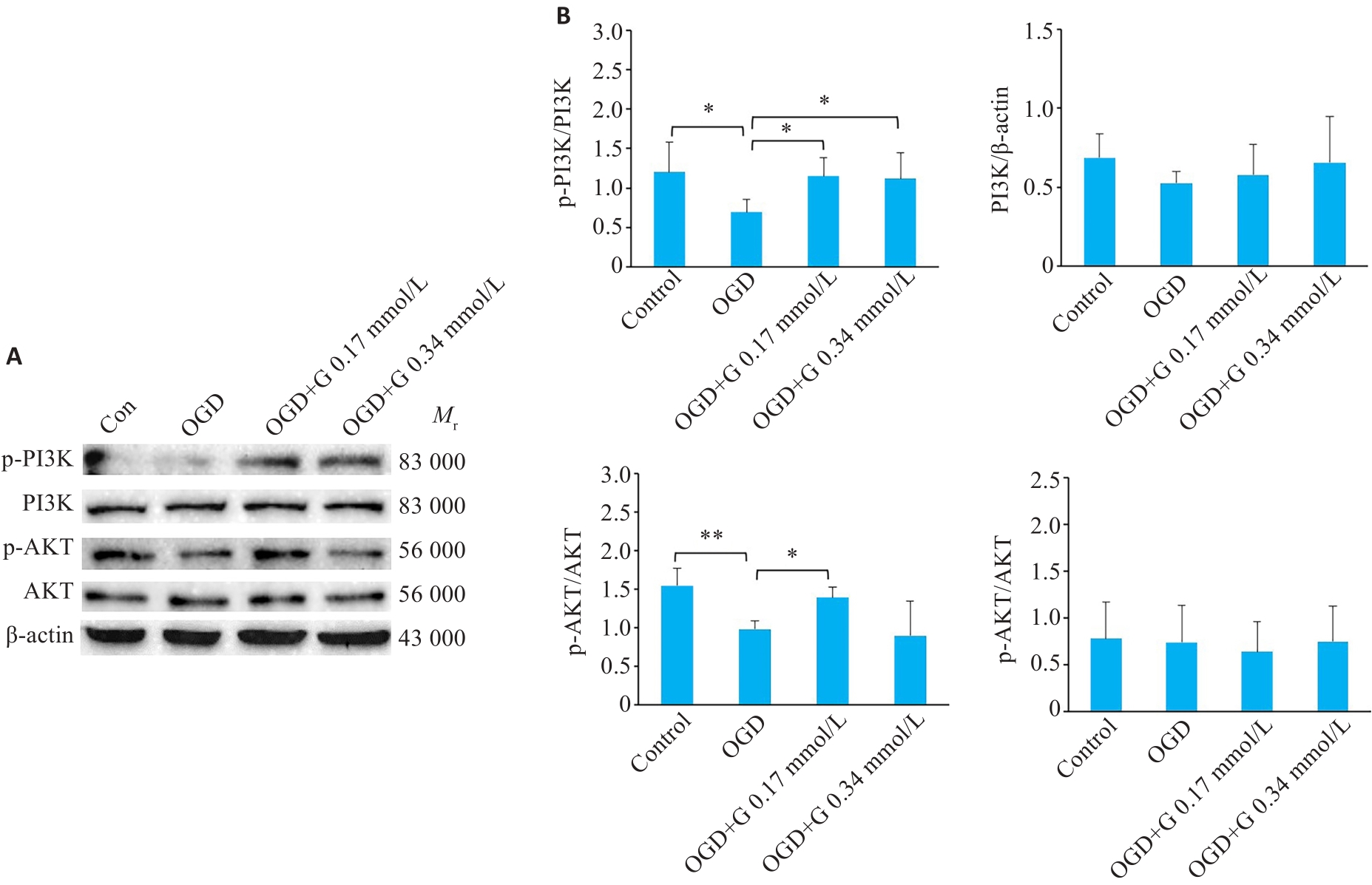
Fig.6 Effect of gastrodin on expression of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in activated microglia BV-2 cells after OGD detected by western blotting. A: Western blots of the related proteins in PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in BV-2 cells. B: Quantification of P-PI3K, PI3K, P-AKT, and AKT protein levels. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 (n=3).
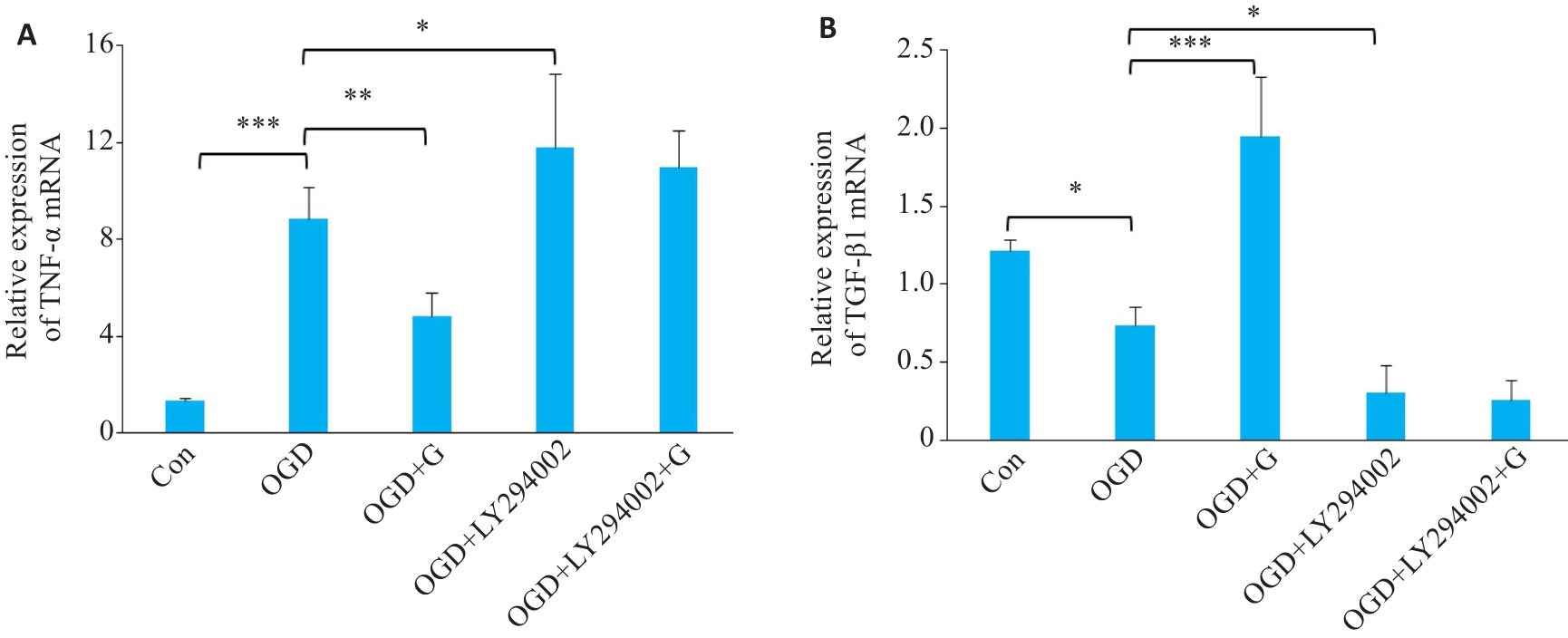
Fig.8 Effect of gastrodin and LY294002 on TNF-α (A) and TGF-β1 mRNA (B) expressions in BV-2 cells with OGD detected by RT-qPCR. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 (n=3).
| 1 | Le K, Song ZP, Deng J, et al. Quercetin alleviates neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury by inhibiting microglia-derived oxidative stress and TLR4-mediated inflammation[J]. Inflamm Res, 2020, 69(12): 1201-13. |
| 2 | Lawn JE, Blencowe H, Oza S, et al. Every Newborn: progress, priorities, and potential beyond survival[J]. Lancet, 2014, 384(9938): 189-205. |
| 3 | Douglas-Escobar M, Weiss MD. Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: a review for the clinician[J]. JAMA Pediatr, 2015, 169(4): 397-403. |
| 4 | Zalewska T, Jaworska J, Ziemka-Nalecz M. Current and experimental pharmacological approaches in neonatal hypoxic- ischemic encephalopathy[J]. Curr Pharm Des, 2015, 21(11): 1433-9. |
| 5 | Gunn AJ, Thoresen M. Neonatal encephalopathy and hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy[J]. Handb Clin Neurol, 2019, 162: 217-37. |
| 6 | Wassink G, Davidson JO, Dhillon SK, et al. Therapeutic hypothermia in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy[J]. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep, 2019, 19(2): 2. |
| 7 | Wood T, Osredkar D, Puchades M, et al. Treatment temperature and insult severity influence the neuroprotective effects of therapeutic hypothermia[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 23430. |
| 8 | Wu YW, Mathur AM, Chang T, et al. High-dose erythropoietin and hypothermia for hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: a phase II trial[J]. Pediatrics, 2016, 137(6): e20160191. |
| 9 | Hagberg H, Mallard C, Ferriero DM, et al. The role of inflammation in perinatal brain injury[J]. Nat Rev Neurol, 2015, 11(4): 192-208. |
| 10 | Deng WB. Neurobiology of injury to the developing brain[J]. Nat Rev Neurol, 2010, 6(6): 328-36. |
| 11 | Zhou DD, Ji L, Chen YG. TSPO modulates IL-4-induced microglia/macrophage M2 polarization via PPAR‑γ pathway[J]. J Mol Neurosci, 2020, 70(4): 542-9. |
| 12 | Kim HJ, Moon KD, Lee DS, et al. Ethyl ether fraction of Gastrodia elata Blume protects amyloid beta peptide-induced cell death[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2003, 84(1): 95-8. |
| 13 | Kim HJ, Moon KD, Oh SY, et al. Ether fraction of methanol extracts of Gastrodia elata, a traditional medicinal herb, protects against kainic acid-induced neuronal damage in the mouse hippocampus[J]. Neurosci Lett, 2001, 314(1/2): 65-8. |
| 14 | Zeng XH, Zhang SM, Zhang L, et al. A study of the neuroprotective effect of the phenolic glucoside gastrodin during cerebral ischemia in vivo and in vitro [J]. Planta Med, 2006, 72(15): 1359-65. |
| 15 | Deng CJ, Chen HZ, Meng ZY, et al. Gastrodin and vascular dementia: advances and current perspectives[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2022: 2563934. |
| 16 | Liu Y, Gao JL, Peng M, et al. A review on central nervous system effects of gastrodin[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2018, 9: 24. |
| 17 | Zhang JQ, Li LY, Liu Q, et al. Gastrodin programs an Arg-1+ microglial phenotype in hippocampus to ameliorate depression- and anxiety-like behaviors via the Nrf2 pathway in mice[J]. Phytomedicine, 2023, 113: 154725. |
| 18 | Guo J, Zhang XL, Bao ZR, et al. Gastrodin regulates the Notch signaling pathway and Sirt3 in activated microglia in cerebral hypoxic-ischemia neonatal rats and in activated BV-2 microglia[J]. Neuromolecular Med, 2021, 23(3): 348-62. |
| 19 | Zhu M, Li D, Wu Y, et al. TREM-2 promotes macrophage-mediated eradication of Pseudomonas aeruginosa via a PI3K/Akt pathway[J]. Scand J Immunol, 2014, 79(3): 187-96. |
| 20 | Lv MR, Li B, Wang MG, et al. RETRACTED: activation of the PI3K-Akt pathway promotes neuroprotection of the δ‑opioid receptor agonist against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat models[J]. Biomedecine Pharmacother, 2017, 93: 230-7. |
| 21 | Tu XK, Zhang HB, Shi SS, et al. 5-LOX inhibitor zileuton reduces inflammatory reaction and ischemic brain damage through the activation of PI3K/akt signaling pathway[J]. Neurochem Res, 2016, 41(10): 2779-87. |
| 22 | Liu SJ, Liu XY, Li JH, et al. Gastrodin attenuates microglia activation through renin-angiotensin system and Sirtuin3 pathway[J]. Neurochem Int, 2018, 120: 49-63. |
| 23 | Chen Z, Hu Y, Lu RF, et al. MicroRNA-374a-5p inhibits neuroinflammation in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy via regulating NLRP3 inflammasome targeted Smad6[J]. Life Sci, 2020, 252: 117664. |
| 24 | Karve IP, Taylor JM, Crack PJ. The contribution of astrocytes and microglia to traumatic brain injury[J]. Br J Pharmacol, 2016, 173(4): 692-702. |
| 25 | Shrivastava SK, Dalko E, Delcroix-Genete D, et al. Uptake of parasite-derived vesicles by astrocytes and microglial phagocytosis of infected erythrocytes may drive neuroinflammation in cerebral malaria[J]. Glia, 2017, 65(1): 75-92. |
| 26 | Nayak D, Roth TL, McGavern DB. Microglia development and function[J]. Annu Rev Immunol, 2014, 32: 367-402. |
| 27 | Lalancette-Hébert M, Gowing G, Simard A, et al. Selective ablation of proliferating microglial cells exacerbates ischemic injury in the brain[J]. J Neurosci, 2007, 27(10): 2596-605. |
| 28 | Tsuji S, di Martino E, Mukai T, et al. Aggravated brain injury after neonatal hypoxic ischemia in microglia-depleted mice[J]. J Neuroinflammation, 2020, 17(1): 111. |
| 29 | Serdar M, Kempe K, Rizazad M, et al. Early pro-inflammatory microglia activation after inflammation-sensitized hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in neonatal rats[J]. Front Cell Neurosci, 2019, 13: 237. |
| 30 | Dai JN, Zong Y, Zhong LM, et al. Gastrodin inhibits expression of inducible NO synthase, cyclooxygenase-2 and proinflammatory cytokines in cultured LPS-stimulated microglia via MAPK pathways[J]. PLoS One, 2011, 6(7): e21891. |
| 31 | Peng Z, Wang H, Zhang R, et al. Gastrodin ameliorates anxiety-like behaviors and inhibits IL-1beta level and p38 MAPK phosphorylation of hippocampus in the rat model of posttraumatic stress disorder[J]. Physiol Res, 2013, 62(5): 537-45. |
| 32 | Jafari M, Ghadami E, Dadkhah T, et al. PI3k/AKT signaling pathway: erythropoiesis and beyond[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2019, 234(3): 2373-85. |
| 33 | Wang JT, Ma WM, Liu YD. Long non-coding RNA HULC promotes bladder cancer cells proliferation but inhibits apoptosis via regulation of ZIC2 and PI3K/AKT signaling pathway[J]. Cancer Biomark, 2017, 20(4): 425-34. |
| 34 | Choudhury R, Bonacci T, Wang XX, et al. The E3 ubiquitin ligase SCF(cyclin F) transmits AKT signaling to the cell-cycle machinery[J]. Cell Rep, 2017, 20(13): 3212-22. |
| 35 | Xian MH, Cai JL, Zheng KN, et al. Aloe-emodin prevents nerve injury and neuroinflammation caused by ischemic stroke via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR and NF-κB pathway[J]. Food Funct, 2021, 12(17): 8056-67. |
| 36 | Wang XS, Tian Z, Zhang N, et al. Protective effects of gastrodin against autophagy-mediated astrocyte death[J]. Phytother Res, 2016, 30(3): 386-96. |
| [1] | Xuan WU, Jiamin FANG, Weiwei HAN, Lin CHEN, Jing SUN, Qili JIN. High PRELID1 expression promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer cells and is associated with poor prognosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1535-1542. |
| [2] | Bing XIA, Jin PENG, Jiuyang DING, Jie WANG, Guowei TANG, Guojie LIU, Yun WANG, Changwu WAN, Cuiyun LE. ATF3 regulates inflammatory response in atherosclerotic plaques in mice through the NF-κB signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1131-1142. |
| [3] | Yue CHEN, Linyu XIAO, Lü REN, Xue SONG, Jing LI, Jianguo HU. Monotropein improves motor function of mice with spinal cord injury by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway to suppress neuronal apoptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 774-784. |
| [4] | Fei CHU, Xiaohua CHEN, Bowen SONG, Jingjing YANG, Lugen ZUO. Moslosooflavone ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice by suppressing intestinal epithelium apoptosis via inhibiting the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 819-828. |
| [5] | Yanyan DONG, Kejing ZHANG, Jun CHU, Quangen CHU. Didang Decoction-medicated serum enhances autophagy in high glucose-induced rat glomerular endothelial cells via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 461-469. |
| [6] | Ju HUANG, Lixia YIN, Minzhu NIU, Zhijun GENG, Lugen ZUO, Jing LI, Jianguo HU. Nodakenin ameliorates TNBS-induced experimental colitis in mice by inhibiting pyroptosis of intestinal epithelial cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 261-268. |
| [7] | Haonan¹ XU, Fang³ ZHANG, Yuying² HUANG, Qisheng⁴ YAO, Yueqin⁴ GUAN, Hao CHEN. Thesium chinense Turcz. alleviates antibiotic-associated diarrhea in mice by modulating gut microbiota structure and regulating the EGFR/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 285-295. |
| [8] | Yuejiao PEI, Huimin LIU, Yu XIN, Bo LIU. High expression of miR-124 improves cognitive function of sleep-deprived rats by modulating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 340-346. |
| [9] | Junping ZHAN, Shuo HUANG, Qingliang MENG, Wei FAN, Huimin GU, Jiakang CUI, Huilian WANG. Buyang Huanwu Decoction reduces mitochondrial autophagy in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts in hypoxic culture by inhibiting the BNIP3-PI3K/Akt pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 35-42. |
| [10] | Yuru ZHANG, Lei WAN, Haoxiang FANG, Fangze LI, Liwen WANG, Kefei LI, Peiwen YAN, Hui JIANG. Inhibiting miR-155-5p promotes proliferation of human submandibular gland epithelial cells in primary Sjogren's syndrome by negatively regulating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway via PIK3R1 [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 65-71. |
| [11] | Xueli ZHOU, Hua LI, Qingyu CHEN, Meina JIN, Haibo LI, Wei BAI, Chuxuan JIA, Cuiying WEI. Effects of chronic intermittent hypoxia and reoxygenation on insulin resistance and skeletal muscle miR-27a-3p/PPARγ/IRS1/PI3K/AKT expressions in rats [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1729-1737. |
| [12] | Xianheng ZHANG, Jian LIU, Qi HAN, Yiming CHEN, Xiang DING, Xiaolu CHEN. Huangqin Qingrechubi Capsule alleviates inflammation and uric acid and lipid metabolism imbalance in rats with gouty arthritis by inhibiting the PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1450-1458. |
| [13] | Zhijun GENG, Jingjing YANG, Minzhu NIU, Xinyue LIU, Jinran SHI, Yike LIU, Xinyu YAO, Yulu ZHANG, Xiaofeng ZHANG, Jianguo HU. Kuwanon G inhibits growth, migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells by regulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1476-1484. |
| [14] | Shuo LIU, Jing LI, Xingwang WU. Swertiamarin ameliorates 2,4,6-trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid-induced colitis in mice by inhibiting intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1545-1552. |
| [15] | Shan XIANG, Zongxing ZHANG, Lu JIANG, Daozhong LIU, Weiyi LI, Zhuoma BAO, Rui TIAN, Dan CHENG, Lin YUAN. Tujia medicine Toddalia asiatica improves synovial pannus in rats with collagen-induced arthritis through the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(8): 1582-1588. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||