Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (11): 2055-2062.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.11.01
Yuanyuan WANG1,2( ), Tianjiao LAI2, Danxia CHU2, Jing BAI2, Shuping YAN2, Haixia QIN1, Ruixia GUO2(
), Tianjiao LAI2, Danxia CHU2, Jing BAI2, Shuping YAN2, Haixia QIN1, Ruixia GUO2( )
)
Received:2024-05-09
Accepted:2024-10-29
Online:2024-11-20
Published:2024-11-29
Contact:
Ruixia GUO
E-mail:wyy15973143013@163.com;grxcdxzzu@163.com
Supported by:Yuanyuan WANG, Tianjiao LAI, Danxia CHU, Jing BAI, Shuping YAN, Haixia QIN, Ruixia GUO. Megestrol acetate plus metformin for fertility-sparing treatment of atypical endometrial hyperplasia and early-stage endometrial adenocarcinoma: a prospective study[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(11): 2055-2062.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.11.01
| Group | n | CR | PR | SD | PD | Response rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Met+MA | 30 | 21 (70.0%) | 4 (13.3%) | 4 (13.3%) | 1 (3.3%) | 83.3% |
| MA | 28 | 17 (60.7%) | 6 (21.4%) | 4 (14.3%) | 1 (3.6%) | 82.1% |
| χ2 | 1.070* | |||||
| P | 0.889 | |||||
Tab.1 Response distribution in the control and combined treatment groups after 6 months of treatment [n (%)]
| Group | n | CR | PR | SD | PD | Response rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Met+MA | 30 | 21 (70.0%) | 4 (13.3%) | 4 (13.3%) | 1 (3.3%) | 83.3% |
| MA | 28 | 17 (60.7%) | 6 (21.4%) | 4 (14.3%) | 1 (3.6%) | 82.1% |
| χ2 | 1.070* | |||||
| P | 0.889 | |||||
| Group | n | CR | PR | SD | PD | Response rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Met+MA | 32* | 26 (81.3%) | 3 (9.4%) | 2 (3.1%) | 1 (3.1%) | 90.7% |
| MA | 26 | 20 (76.9%) | 3 (11.5%) | 1 (3.8%) | 2 (7.7%) | 88.4% |
| χ2 | 0.163 | |||||
| P | 0.983 | |||||
Tab.2 Response distribution in the two groups after 9 months of treatment [n (%)]
| Group | n | CR | PR | SD | PD | Response rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Met+MA | 32* | 26 (81.3%) | 3 (9.4%) | 2 (3.1%) | 1 (3.1%) | 90.7% |
| MA | 26 | 20 (76.9%) | 3 (11.5%) | 1 (3.8%) | 2 (7.7%) | 88.4% |
| χ2 | 0.163 | |||||
| P | 0.983 | |||||
| Group | CR patients (n) | PR time | CR time | Total time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Met+MA | 26 | 3.59±1.26 | 4.78±2.26 | 7.83±2.03 |
| MA | 20 | 3.98±1.36 | 5.49±2.08 | 8.49±2.11 |
| t | 1.049 | 1.419 | 1.384 | |
| P | 0.288 | 0.163 | 0.172 |
Tab.3 Mean PR and CR time of the patients in the two groups (month)
| Group | CR patients (n) | PR time | CR time | Total time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Met+MA | 26 | 3.59±1.26 | 4.78±2.26 | 7.83±2.03 |
| MA | 20 | 3.98±1.36 | 5.49±2.08 | 8.49±2.11 |
| t | 1.049 | 1.419 | 1.384 | |
| P | 0.288 | 0.163 | 0.172 |
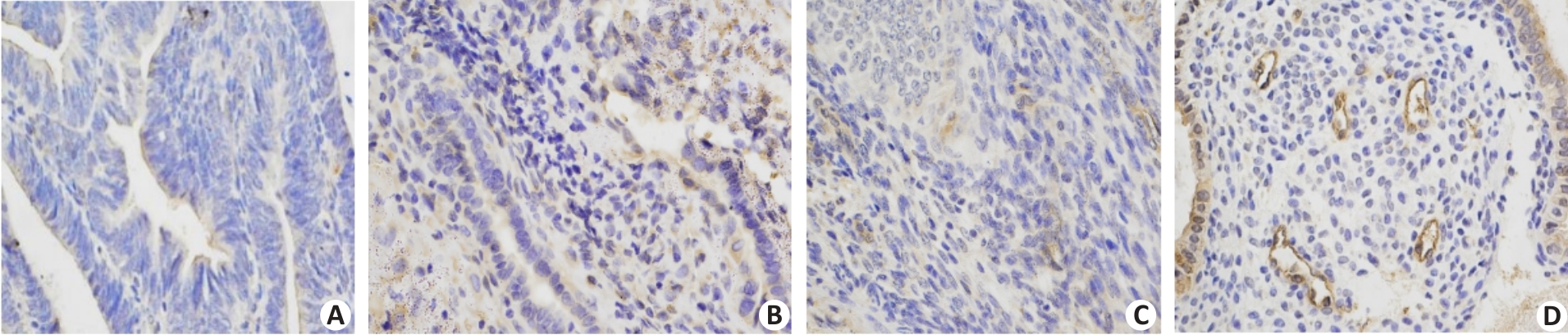
Fig.1 Immunohistochemical staining for IGFBP-rP1 in endometrial tissues of the patients in MA and combined treatment groups. A, B: Negative IGFBP-rP1 expression in MA group both before treatment (A) and after CR (B). C, D: In the combined treatment group, IGFBP-rP1 was negative before treatment (C) but positive after CR (D).
| Group | n | IGFBP-rP1 | p-Akt | p-AMPK | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Negative | Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | Positive | ||
| MA | 20 | 0 (0 | 4 ( | 16 (80%) | 4 (20%) | ||
| Met+MA | 26 | 3 ( | |||||
| χ2 | 9.385 | 3.409 | |||||
| P | 0.002 | 0.065 | |||||
Tab.4 Endometrial IGFBP-rP1, p-Akt and p-AMPK positivity in the two groups after treatment [n (%)]
| Group | n | IGFBP-rP1 | p-Akt | p-AMPK | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Negative | Positive | Negative | Positive | Negative | Positive | ||
| MA | 20 | 0 (0 | 4 ( | 16 (80%) | 4 (20%) | ||
| Met+MA | 26 | 3 ( | |||||
| χ2 | 9.385 | 3.409 | |||||
| P | 0.002 | 0.065 | |||||
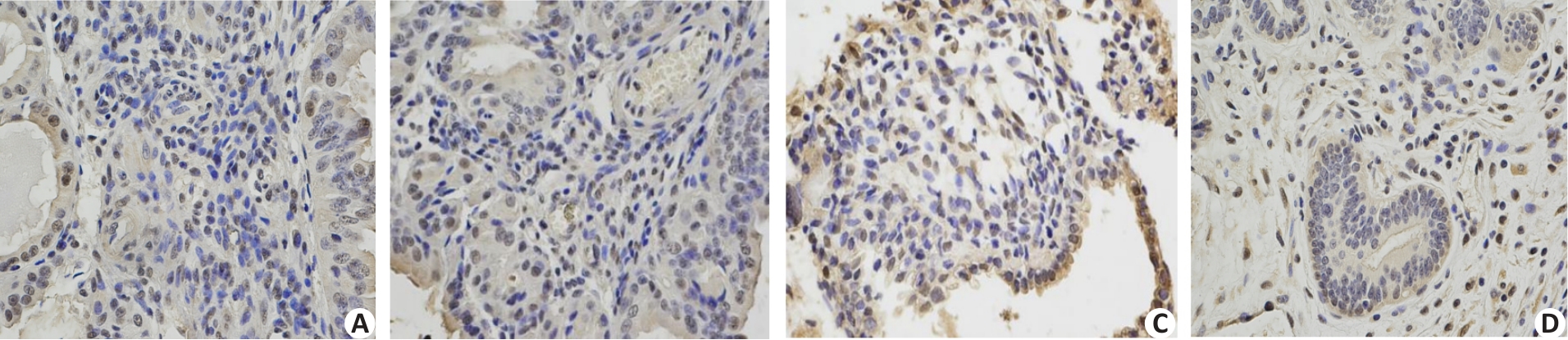
Fig.2 Immunohistochemical staining for p-Akt in endometrial tissues of the patients in MA and combined treatment groups. The endometrial tissue was positive for p-Akt in MA group before treatment (A) and remained positive after treatment (B); in the combined treatment group, p-Akt was positive before treatment (C) but became negative after treatment (D).
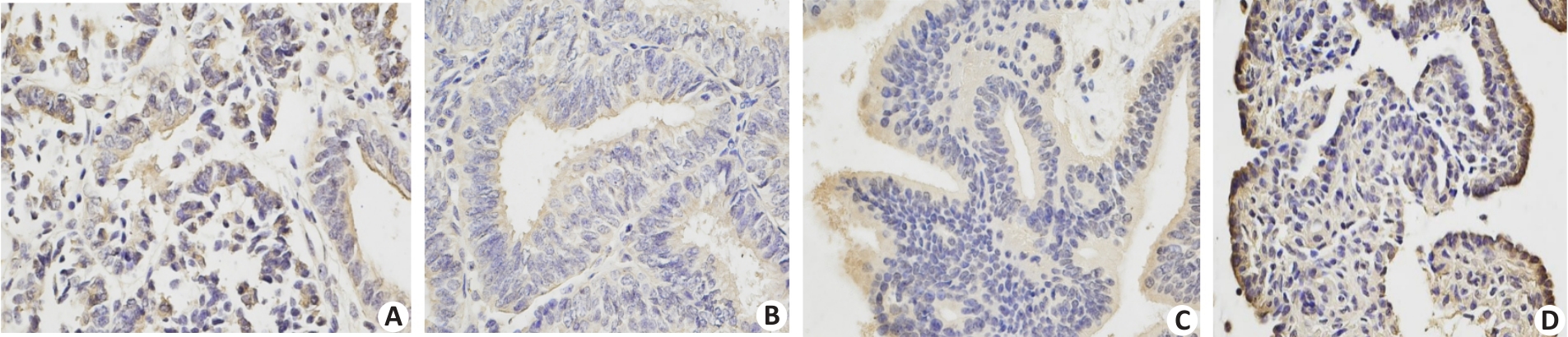
Fig.3 Immunohistochemical staining for endometrial p-AMPK expressions in MA and combined treatment groups. The expression of p-Akt was negative in MA group before treatment (A) and remained so after treatment (B); in the combined treatment group, p-Akt was negative before treatment (C) but became positive after treatment (D).
| 1 | Trojano G, Olivieri C, Tinelli R, et al. Conservative treatment in early stage endometrial cancer: a review [J]. Acta Biomed, 2019, 90(4): 405-10. |
| 2 | Gallos ID, Yap J, Rajkhowa M, et al. Regression, relapse, and live birth rates with fertility-sparing therapy for endometrial cancer and atypical complex endometrial hyperplasia: a systematic review and metaanalysis [J]. Am J Obstet Gynecol, 2012, 207(4): 266. e1-12. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajog.2012.08.011 |
| 3 | Mekuria AN, Ayele Y, Tola A, et al. Monotherapy with metformin versus sulfonylureas and risk of cancer in type 2 diabetic patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. J Diabetes Res, 2019, 2019: 7676909. DOI: 10.1155/2019/7676909 |
| 4 | Mitsuhashi A, Shozu M. New therapeutic approaches for the fertility-sparing treatment of endometrial cancer [J]. J Obstet Gynaecol Res, 2020, 46(2): 215-22. DOI: 10.1111/jog.14155 |
| 5 | Foretz M, Hébrard S, Leclerc J, et al. Metformin inhibits hepatic gluconeogenesis in mice independently of the LKB1/AMPK pathway via a decrease in hepatic energy state [J]. J Clin Invest, 2010, 120(7): 2355-69. DOI: 10.1172/jci40671 |
| 6 | Zimmermann M, Arachchige-Don AP, Donaldson MS, et al. Cyclin G2 promotes cell cycle arrest in breast cancer cells responding to fulvestrant and metformin and correlates with patient survival [J]. Cell Cycle, 2016, 15(23): 3278-95. DOI: 10.1080/15384101.2016.1243189 |
| 7 | Tay KC, Tan LT, Chan CK, et al. Formononetin: a review of its anticancer potentials and mechanisms [J]. Front Pharmacol, 2019, 10: 820. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00820 |
| 8 | Heckman-Stoddard BM, DeCensi A, Sahasrabuddhe VV, et al. Repurposing metformin for the prevention of cancer and cancer recurrence [J]. Diabetologia, 2017, 60(9): 1639-47. DOI: 10.1007/s00125-017-4372-6 |
| 9 | Practice Committee of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine. Electronic address: ASRM@asrm.org; Practice Committee of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine. Role of metformin for ovulation induction in infertile patients with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): a guideline [J]. Fertil Steril, 2017, 108(3): 426-1. |
| 10 | Mitsuhashi A, Kiyokawa T, Sato Y, et al. Effects of metformin on endometrial cancer cell growth in vivo: a preoperative prospective trial [J]. Cancer, 2014, 120(19): 2986-95. DOI: 10.1002/cncr.28853 |
| 11 | Mitsuhashi A, Sato Y, Kiyokawa T, et al. Phase II study of medroxyprogesterone acetate plus metformin as a fertility-sparing treatment for atypical endometrial hyperplasia and endometrial cancer [J]. Ann Oncol, 2016, 27(2): 262-6. DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdv539 |
| 12 | Baxter RC. Signaling pathways of the insulin-like growth factor binding proteins [J]. Endocr Rev, 2023, 44(5): 753-78. DOI: 10.1210/endrev/bnad008 |
| 13 | Oh Y, Nagalla SR, Yamanaka Y, et al. Synthesis and characterization of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein (IGFBP)-7. Recombinant human mac25 protein specifically binds IGF-I and -II [J]. J Biol Chem, 1996, 271(48): 30322-5. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.271.48.30322 |
| 14 | Mohd Nafi SN, Siti Azrin AH, Mat Zin AA, et al. Expression of IGFBP-rP1 in ovarian and breast cancers in association with diabetes mellitus status. Malays J Pathol, 2019, 41(1): 33-9. |
| 15 | Baker J, Obermair A, Gebski V, et al. Efficacy of oral or intrauterine device-delivered progestin in patients with complex endometrial hyperplasia with atypia or early endometrial adenocarcinoma: a meta-analysis and systematic review of the literature [J]. Gynecol Oncol, 2012, 125(1): 263-70. DOI: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2011.11.043 |
| 16 | Gadducci A, Spirito N, Baroni E, et al. The fertility-sparing treatment in patients with endometrial atypical hyperplasia and early endometrial cancer: a debated therapeutic option [J]. Gynecol Endocrinol, 2009, 25(10): 683-91. DOI: 10.1080/09513590902733733 |
| 17 | Kalogiannidis I, Agorastos T. Conservative management of young patients with endometrial highly-differentiated adenocarcinoma [J]. J Obstet Gynaecol, 2011, 31(1): 13-17. DOI: 10.3109/01443615.2010.532249 |
| 18 | Luque-Ramírez M, Nattero-Chávez L, Ortiz Flores AE, et al. Combined oral contraceptives and/or antiandrogens versus insulin sensitizers for polycystic ovary syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Hum Reprod Update, 2018, 24(2): 225-41. DOI: 10.1093/humupd/dmx039 |
| 19 | Lv Z, Guo Y. Metformin and its benefits for various diseases [J]. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2020, 11: 191. DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00191 |
| 20 | Ushijima K, Yahata H, Yoshikawa H, et al. Multicenter phase II study of fertility-sparing treatment with medroxyprogesterone acetate for endometrial carcinoma and atypical hyperplasia in young women [J]. J Clin Oncol, 2007, 25(19): 2798-803. DOI: 10.1200/jco.2006.08.8344 |
| 21 | Yamazawa K, Hirai M, Fujito A, et al. Fertility-preserving treatment with progestin, and pathological criteria to predict responses, in young women with endometrial cancer [J]. Hum Reprod, 2007, 22(7): 1953-8. DOI: 10.1093/humrep/dem088 |
| 22 | Wang CJ, Chao A, Yang LY, et al. Fertility-preserving treatment in young women with endometrial adenocarcinoma: a long-term cohort study [J]. Int J Gynecol Cancer, 2014, 24(4): 718-28. DOI: 10.1097/igc.0000000000000098 |
| 23 | Yahata T, Fujita K, Aoki Y, et al. Long-term conservative therapy for endometrial adenocarcinoma in young women [J]. Hum Reprod, 2006, 21(4): 1070-1075. DOI: 10.1093/humrep/dei434 |
| 24 | Park JY, Lee SH, Seong SJ, et al. Progestin re-treatment in patients with recurrent endometrial adenocarcinoma after successful fertility-sparing management using progestin [J]. Gynecol Oncol, 2013, 129(1): 7-11. DOI: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2012.12.037 |
| 25 | Mitsuhashi A, Habu Y, Kobayashi T, et al. Long-term outcomes of progestin plus metformin as a fertility-sparing treatment for atypical endometrial hyperplasia and endometrial cancer patients [J]. J Gynecol Oncol, 2019, 30(6): e90. DOI: 10.3802/jgo.2019.30.e90 |
| 26 | Guo L, Ma J, Tang J, et al. Comparative efficacy and safety of metformin, glyburide, and insulin in treating gestational diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis [J]. J Diabetes Res, 2019, 2019: 9804708. DOI: 10.1155/2019/9804708 |
| 27 | Kim SR, van der Zanden C, Ikiz H, et al. Fertility-sparing management using progestin for young women with endometrial cancer from a population-based study [J]. J Obstet Gynaecol Can, 2018, 40(3): 328-33. DOI: 10.1016/j.jogc.2017.06.037 |
| 28 | Hanawa S, Mitsuhashi A, Shozu M. Antitumor effects of metformin via indirect inhibition of protein phosphatase 2A in patients with endometrial cancer [J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13(2): e0192759. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0192759 |
| 29 | Heidari B, Lerman A, Lalia AZ, et al. Effect of metformin on microvascular endothelial function in polycystic ovary syndrome [J]. Mayo Clin Proc, 2019, 94(12): 2455-66. DOI: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2019.06.015 |
| 30 | Yates MS, Coletta AM, Zhang Q, et al. Prospective randomized biomarker study of metformin and lifestyle intervention for prevention in obese women at increased risk for endometrial cancer [J]. Cancer Prev Res (Phila), 2018, 11(8): 477-90. DOI: 10.1158/1940-6207.capr-17-0398 |
| 31 | Zhang P, Li H, Tan X, et al. Association of metformin use with cancer incidence and mortality: a meta-analysis [J]. Cancer Epidemiol, 2013, 37(3): 207-18. DOI: 10.1016/j.canep.2012.12.009 |
| 32 | Ganie MA, Khurana ML, Nisar S, et al. Improved efficacy of low-dose spironolactone and metformin combination than either drug alone in the management of women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): a six-month, open-label randomized study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2013, 98(9): 3599-607 [J]. DOI: 10.1210/jc.2013-1040 |
| 33 | Zhan Y, Wang J, Ma Y, et al. Serum insulin-like, growth factor binding protein-related protein 1 (IGFBP-rP1) and endometrial cancer risk in Chinese women [J]. Int J Cancer, 2013, 132(2): 411-6. DOI: 10.1002/ijc.27622 |
| 34 | Gao J, Suo S, Li J, et al. IGFBP-rP1 affects the proliferation, apoptosis and macrophage polarization of endometrial cancer cells by regulating the PI3K/AKT pathway [J]. Exp Ther Med, 2023, 25(4): 169. DOI: 10.3892/etm.2023.11868 |
| 35 | Alzahrani AS. PI3K/Akt/mTOR inhibitors in cancer: at the bench and bedside [J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 2019, 59: 125-32. DOI: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.07.009 |
| [1] | SHAO Shan, BAI Weichao, ZHOU Pengcheng, LUO Minna, ZHAO Xinhan, LEI Jianjun. Metformin suppresses hypoxia-inducible factor-1α expression in cancer-associated fibroblasts to block tumor-stromal cross-talk in breast cancer [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(3): 428-436. |
| [2] | LI Shuxian, YU Shuping, MU Yaming, WANG Kai, LIU Yu, ZHANG Meihua. Metformin ameliorates PM2.5- induced functional impairment of placental trophoblasts by inhibiting ferroptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(3): 437-446. |
| [3] | YAN Chang, LIU Shuang, SONG Qingzhi, HU Yibing. Metformin inhibits self-renewal of colorectal cancer stem cells by inhibiting mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(8): 1279-1286. |
| [4] | ZHOU Bei, LI Jing, FANG Chenyuan, HUANG Yanan, SANG Guirui, TAO Shaoping, HE Chunling. Comparison of therapeutic effect of metformin hydrochloride/vildagliptin and liraglutide on type 2 diabetes mellitus in obese patients [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(3): 436-442. |
| [5] | WEI Jia, YANG Qiang, LIN Lin, ZHU Canzhan, WEI Jin. Metformin mitigates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity via the AMPK pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(10): 1682-1688. |
| [6] | CAO Jing, LIU Haibo, AN Qi, HAN Feng. Metformin alleviates pathologic pain in mice with radiation dermatitis by inhibiting p38MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(10): 1815-1820. |
| [7] | XU Yu, XU Ting, XIONG Yuanfeng, HUANG Jiayi. Metformin inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of HER-2 positive breast cancer cells possibly through the Hippo-YAP pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42(5): 740-746. |
| [8] | . Metformin inhibits proliferation and functions of regulatory T cells in acidic environment [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2019, 39(12): 1427-1435. |
| [9] | . Metformin inhibits aortic atherosclerosis in mice by regulating actin skeleton in vascular smooth muscle cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2019, 39(11): 1357-1363. |
| [10] | . Efficacy and safety of metformin for Behcet’s disease and its effect on Treg/Th17 balance: a single-blinded, before-after study [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2019, 39(02): 127-. |
| [11] |
.
Effects of metformin on apoptosis induced by advanced glycation end-products and expressions of caspase-3, Bax and Bcl-2 in human dermal fibroblasts in vitro [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2015, 35(06): 898-. |
| [12] |
.
Meilian Xiaoke capsule combined with metformin for protecting islet cells and lowering blood glucose in diabetic rats [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2014, 34(09): 1365-. |
| [13] |
.
Effects of visfatin and metformin on insulin resistance and reproductive endocrine in rats with polycystic ovary syndrome [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2014, 34(09): 1314-. |
| [14] | . Effects of metformin on human oral cancer KB cell proliferation and apoptosis in vitro [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2014, 34(02): 159-. |
| [15] | ZHANG Yu1, ZHANG Yi1, LIN Qiu-hua2 1Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Xiangya Hospital, 2Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Second Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha 410078, China. Progesterone-modulated proteins in human endometrial cancer cell line Ishikawa [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2006, 26(08): 1110-1113. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||