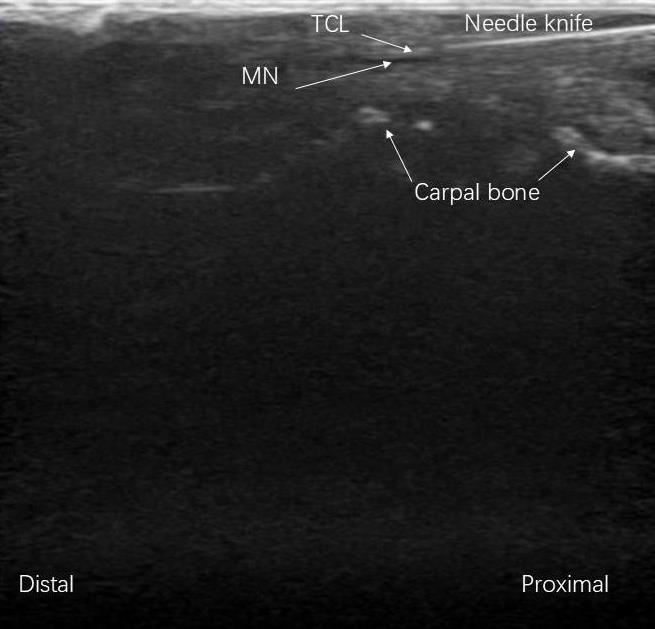
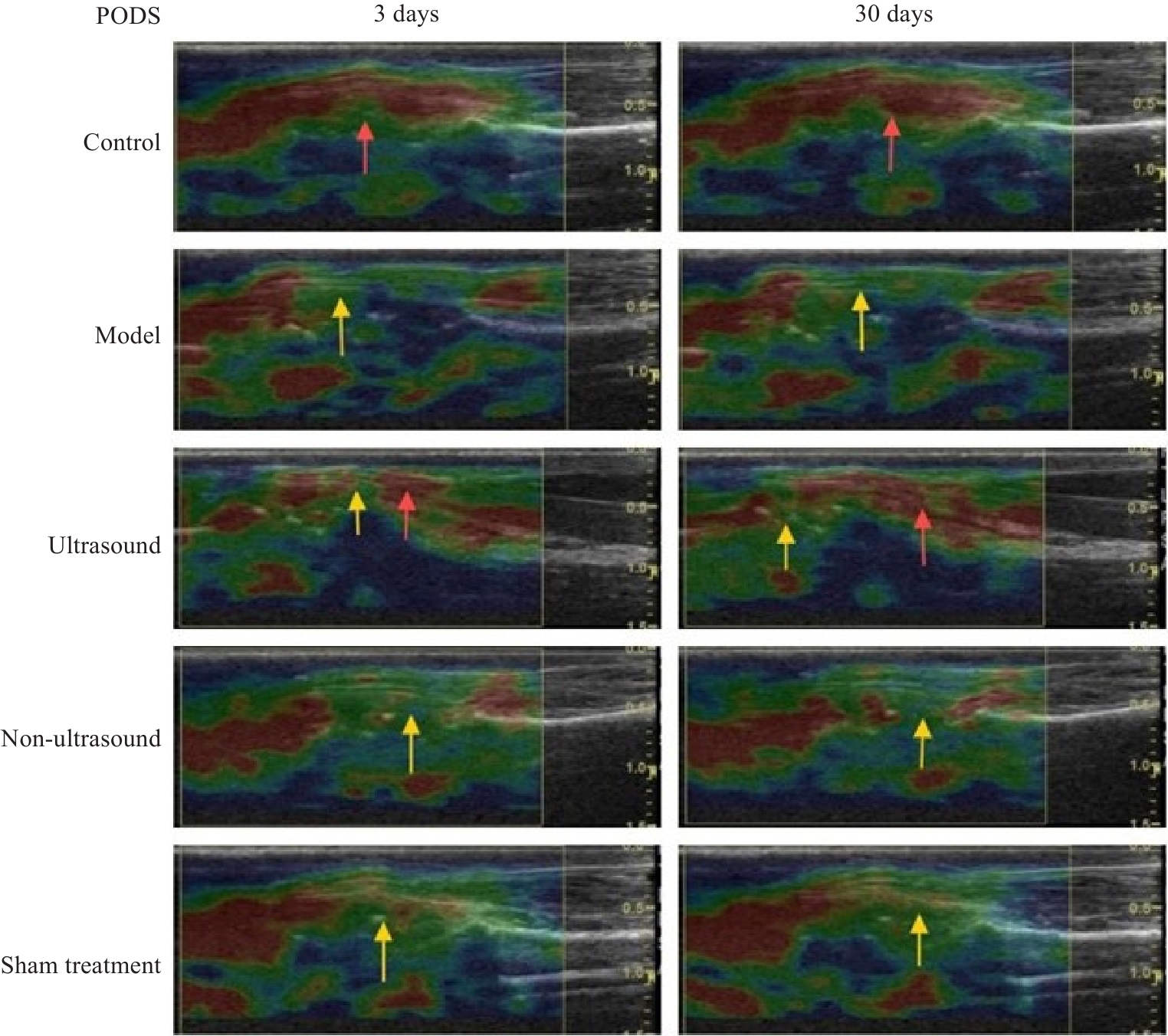
| [1] |
Osiak K, Elnazir P, Walocha JA, et al. Carpal tunnel syndrome: state-of-the-art review[J]. Folia Morphol (Warsz), 2022, 81(4): 851-62. doi:10.5603/fm.a2021.0121
|
| [2] |
Ari B, Akcicek M, Tasci I.et al. Correlations between transverse carpal ligament thickness measured on ultrasound and severity of carpal tunnel syndrome on electromyography and disease duration.[J]. Hand Surg Rehabil, 2022, 41(3): 377-83. doi:10.1016/j.hansur.2022.02.006
|
| [3] |
Wallace JL. Prostaglandin biology in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Gastroenterol Clin North Am, 2001, 30(4): 971-80. doi:10.1016/s0889-8553(05)70223-5
|
| [4] |
McLoughlin RM, Hurst SM, Nowell MA.et al. Differential regulation of neutrophil-activating chemokines by IL-6 and its soluble receptor isoforms[J]. J Immunol, 2004, 172(9): 5676-83. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.172.9.5676
|
| [5] |
Raucci F, Saviano A, Casillo GM, et al. IL-17-induced inflammation modulates the mPGES-1/PPAR‑γ pathway in monocytes/macro-phages[J]. Br J Pharmacol, 2022, 179(9): 1857-73. doi:10.1111/bph.15413
|
| [6] |
周俏吟, 申毅锋, 邱祖云, 等.超声引导针刀松解术在四肢末端病的临床解剖学中的应用研究[J].中国医药导报, 2023, 20(18): 20-4.
|
| [7] |
周俏吟.超声引导下针刀松解腕横韧带治疗腕管综合征的作用机制研究[D].福建中医药大学, 2023.
|
| [8] |
陈国良, 江大平, 许晓文. 分析腕管综合征患者接受高频超声与肌电图诊断的效果[J].中国医疗器械信息, 2024, 30(16): 129-31.
|
| [9] |
Chen YT, Miller Olson EK, Lee SH, et al. Assessing Diagnostic and Severity Grading Accuracy of Ultrasound Measurements for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Compared to Electrodiagnostics[J]. PMR, 2021,13(8): 852-61. doi:10.1002/pmrj.12533
|
| [10] |
Chen J, Fowler JR. Comparison of diagnostic accuracy of electrodiagnostic testing and ultrasonography for carpal tunnel syndrome[J]. Hand (N Y), 2023, 18(3): 407-12. doi:10.1177/15589447211038701
|
| [11] |
Lee SK, Hwang SY, An YS, et al. The influence of transverse carpal ligament thickness on treatment decisions for idiopathic mild to moderate carpal tunnel syndrome[J]. Ann Plast Surg, 2020, 85(2): 127-34. doi:10.1097/sap.0000000000002386
|
| [12] |
Wu H, Yang K, Chang X, et al. Evaluation of the transverse carpal ligament in carpal tunnel syndrome by shear wave elastography: a non-invasive approach of diagnosis and management[J]. Front Neurol, 2022, 13: 901104. doi:10.3389/fneur.2022.901104
|
| [13] |
Ahmed A, Malik G, Imtiaz H, et al. Assessment of carpal tunnel syndrome with ultrasonography[J]. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad, 2022, 34(2): 295-9. doi:10.55519/jamc-02-9892
|
| [14] |
Freeland AE, Tucci MA, Barbieri RA, et al. Biochemical evaluation of serum and flexor tenosynovium in carpal tunnel syndrome[J]. Microsurgery, 2002, 22(8): 378-85. doi:10.1002/micr.10065
|
| [15] |
Tucci MA, Barbieri RA, Freeland AE. Biochemical and histological analysis of the flexor tenosynovium in patients with carpal tunnel syndrome[J]. Biomed Sci Instrum, 1997, 33: 246-51.
|
| [16] |
Rempel D, Dahlin L, Lundborg G. Pathophysiology of nerve compression syndromes: Response of peripheral nerves to loading[J]. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 1999, 81(11): 1600-10. doi:10.2106/00004623-199911000-00013
|
| [17] |
Robben E, Dusar FR, Weyns V, et al. Ultrasound measurement of subsynovial connective tissue thickness in the carpal tunnel: An intrarater/interrater reliability and agreement study[J]. Hand Surg Rehabil, 2023, 42(6): 505-11. doi:10.1016/j.hansur.2023.08.006
|
| [18] |
Nishida K, Yamasaki S, Ito Y, et al.FcεRI-mediated mast cell degranulation requires calcium-independent microtubule-dependent translocation of granules to the plasma membrane[J]. J Cell Biol, 2005, 170(1): 115-26. doi:10.1083/jcb.200501111
|
| [19] |
Tsuge K, Inazumi T, Shimamoto A, , et al.Molecular mechanisms underlying prostaglandin E2-exacerbated inflammation and immune diseases[J]. Int Immunol, 2019, 31(9): 597-606. doi:10.1093/intimm/dxz021
|
| [20] |
Onishi RM, Gaffen SL. Interleukin-17 and its target genes: mechanisms of interleukin-17 function in disease[J]. Immunology, 2010, 129(3): 311-21. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2567.2009.03240.x
|
| [21] |
Fossiez F, Banchereau J, Murray R, et al. Interleukin-17[J]. Int Rev Immunol, 1998, 16(5/6): 541-51. doi:10.3109/08830189809043008
|
| [22] |
Murakami M, Naraba H, Tanioka T, et al. Regulation of prostaglandin E2 biosynthesis by inducible membrane-associated prostaglandin E2 synthase that acts in concert with cyclooxygenase-2[J]. J Biol Chem, 2000, 275(42): 32783-92. doi:10.1074/jbc.m003505200
|
| [23] |
Akaogi J, Nozaki T, Satoh M, et al. Role of PGE2 and EP receptors in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis and as a novel therapeutic strategy[J]. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets, 2006, 6(4): 383-94. doi:10.2174/187153006779025711
|
| [24] |
Genova A, Dix O, Saefan A, et al. Carpal tunnel syndrome: a review of literature[J]. Cureus, 2020, 12(3): e7333.
|
| [25] |
段承琪, 郭建明, 陈小波. 轻中度腕管综合征物理治疗的研究进展[J]. 实用手外科杂志, 2025, 39(1): 82-4.
|
| [26] |
Malakootian M, Soveizi M, Gholipour A, et al. Pathophysiology, diagnosis, treatment, and genetics of carpal tunnel syndrome: a review[J]. Cell Mol Neurobiol, 2023, 43(5): 1817-31. doi:10.1007/s10571-022-01297-2
|
| [27] |
刘子文, 刘文辉, 韩 海, 等. 正中神经主干联合返支松解治疗中重度腕管综合征的临床效果[J]. 中国卫生标准管理, 2024, 15(16): 80-4.
|
| [28] |
Castro-Menéndez M, Balvís-Balvís P, Oiartzabal-Alberdi I,et al.Percutaneous ultrasound-guided section of the transverse carpal ligament vs open surgery for the surgical treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS)[J]. Rev Esp Cir Ortop Traumatol, 2023, 67(4): T297-308. doi:10.1016/j.recot.2023.02.023
|
| [29] |
Saaiq M. Presentation and outcome of carpal tunnel syndrome with mini incision open carpal tunnel release[J]. Med J Islam Repub Iran, 2021, 35: 67. doi:10.47176/mjiri.35.67
|
| [30] |
Jin G Q, Yang J, Li C Y, et al. Treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome with mini-incision decompression[J]. China J Orthop Traumatol, 2012, 25(1): 58-61.
|
| [31] |
David I. Sonography-guided carpal tunnel release[J]. Hand Clin, 2022, 38(1): 75-82. doi:10.1016/j.hcl.2021.08.007
|
| [32] |
Zhou Q, Shen Y, Zhu X, et al. Ultrasound-guided percutaneous release procedures in the transverse carpal ligament by acupotomy: A cadaveric study[J]. Front Surg, 2023, 9: 906109. doi:10.3389/fsurg.2022.906109
|
 ), Qiaoyin ZHOU(
), Qiaoyin ZHOU( ), Shen LUO, Weilin LIN, Xinyao HUANG, Ying CAO
), Shen LUO, Weilin LIN, Xinyao HUANG, Ying CAO