Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (8): 1581-1588.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.08.02
Zhixin DU1,2( ), Yueyang WANG1, Liping YANG1,2(
), Yueyang WANG1, Liping YANG1,2( ), Junlin HOU1(
), Junlin HOU1( ), Jianhua SUN2, Pengbei FAN3, Yaohui WANG1, Xiaolin LI1
), Jianhua SUN2, Pengbei FAN3, Yaohui WANG1, Xiaolin LI1
Received:2025-02-11
Online:2025-08-20
Published:2025-09-05
Contact:
Liping YANG, Junlin HOU
E-mail:dzx19961212@163.com;bioylp@126.com;houjunlin2005@163.com
Supported by:Zhixin DU, Yueyang WANG, Liping YANG, Junlin HOU, Jianhua SUN, Pengbei FAN, Yaohui WANG, Xiaolin LI. Prenatal fear stress impairs cognitive development in offspring rats by disrupting placental amino acid transport[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(8): 1581-1588.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.08.02
| Name of primers | Primer sequence 5'-3' |
|---|---|
| GAPDH-F | CTGGAGAAACCTGCCAAGTATG |
| GAPDH-R | GGTGGAAGAATGGGAGTTGCT |
| Slc38a2-F | CGTTCACCTCCTCCTCAAGACT |
| Slc38a2-R | TTCAGATACCACAGCCCATTCG |
| Slc38a1-F | CGTTCACCTCCTCCTCAAGACT |
| Slc38a1-R | TTCAGATACCACAGCCCATTCG |
| Slc38a4-F | ATGAAGATGCCGAAAGTCAGAAG |
| Slc38a4-R | GGTGAACCGAGTAGAGCGATAGA |
| Slc43a1-F | TTCTATTCCAGTCTATGCCCAGC |
| Slc43a1-R | CAAGGCCATAAGAGTGCAGGAT |
| Slc43a2-F | TGGGCATCATCATGGACAAGTAT |
| Slc43a2-R | AAGGTAACTGCTGAGGAAGCGTAG |
| Slc6a6-F | GAAGGGTTATCGTCGGGAAAT |
| Slc6a6-R | ATACATGCCACCCTCCGTCA |
| Slc1a1-F | ATCGTGGTAGGAGTCTTGGTTCG |
| Slc1a1-R | AGGATTACAGCAATGACGGTGGT |
| Slc6a9-F | ACTACGCAGCCAGCTTCTCCTT |
| Slc6a9-R | TGGTAGTGGTTGTAAGTGATTGGC |
Tab.1 Sequences of primers for RT-qPCR
| Name of primers | Primer sequence 5'-3' |
|---|---|
| GAPDH-F | CTGGAGAAACCTGCCAAGTATG |
| GAPDH-R | GGTGGAAGAATGGGAGTTGCT |
| Slc38a2-F | CGTTCACCTCCTCCTCAAGACT |
| Slc38a2-R | TTCAGATACCACAGCCCATTCG |
| Slc38a1-F | CGTTCACCTCCTCCTCAAGACT |
| Slc38a1-R | TTCAGATACCACAGCCCATTCG |
| Slc38a4-F | ATGAAGATGCCGAAAGTCAGAAG |
| Slc38a4-R | GGTGAACCGAGTAGAGCGATAGA |
| Slc43a1-F | TTCTATTCCAGTCTATGCCCAGC |
| Slc43a1-R | CAAGGCCATAAGAGTGCAGGAT |
| Slc43a2-F | TGGGCATCATCATGGACAAGTAT |
| Slc43a2-R | AAGGTAACTGCTGAGGAAGCGTAG |
| Slc6a6-F | GAAGGGTTATCGTCGGGAAAT |
| Slc6a6-R | ATACATGCCACCCTCCGTCA |
| Slc1a1-F | ATCGTGGTAGGAGTCTTGGTTCG |
| Slc1a1-R | AGGATTACAGCAATGACGGTGGT |
| Slc6a9-F | ACTACGCAGCCAGCTTCTCCTT |
| Slc6a9-R | TGGTAGTGGTTGTAAGTGATTGGC |
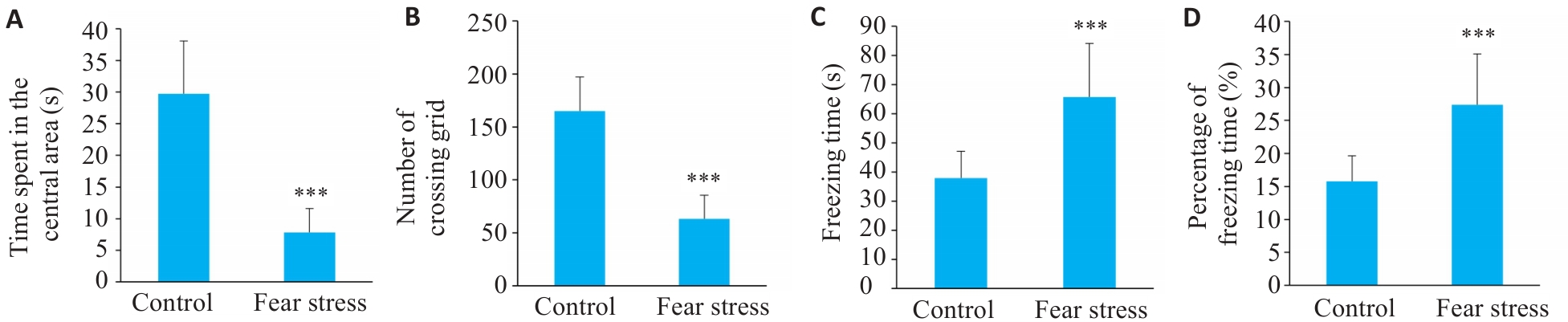
Fig.1 Impact of prenatal fear stress on behaviors of pregnant rats. A: Time spent in the central area in open field test; B: Number of grid crossings in open field test; C: Freezing time in contextual Fear Paradigm; D: Percentage of freezing time in contextual Fear Paradigm. ***P<0.001 vs Control group.
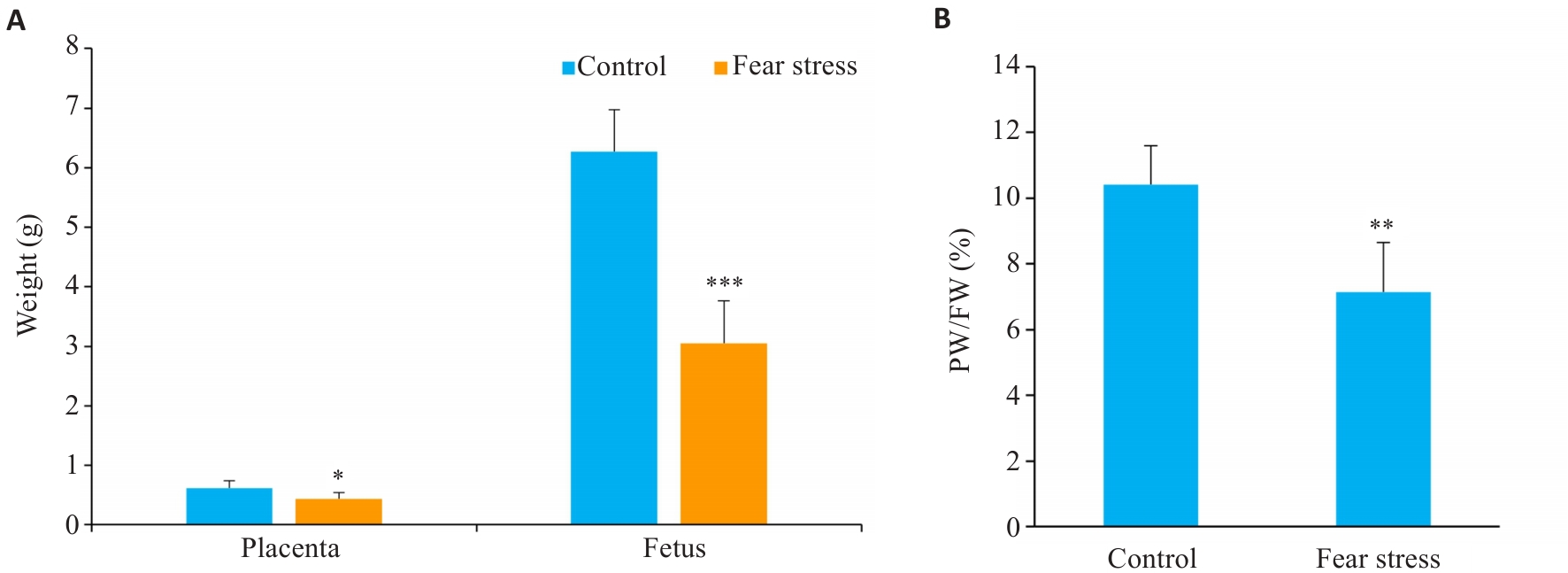
Fig.2 Impact of prenatal fear stress on placental weight (PW) and fetal weight (FW). A: Placental and fetal weight; B: Placental-Fetal ratio. *P<0.05,**P<0.01,***P<0.001 vs Control group.
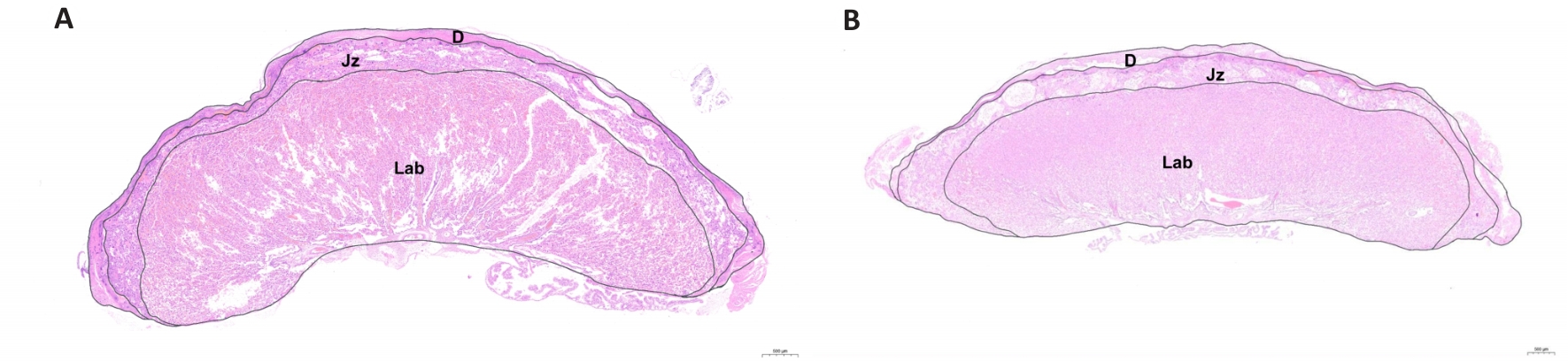
Fig.3 Effect of prenatal fear stress on placental structure (HE staining, Scale bar=500 μm). A: Control group. B: Fear stress group. D: Decidua zone; Jz: Junctional zone; Lab: Labyrinth zone.
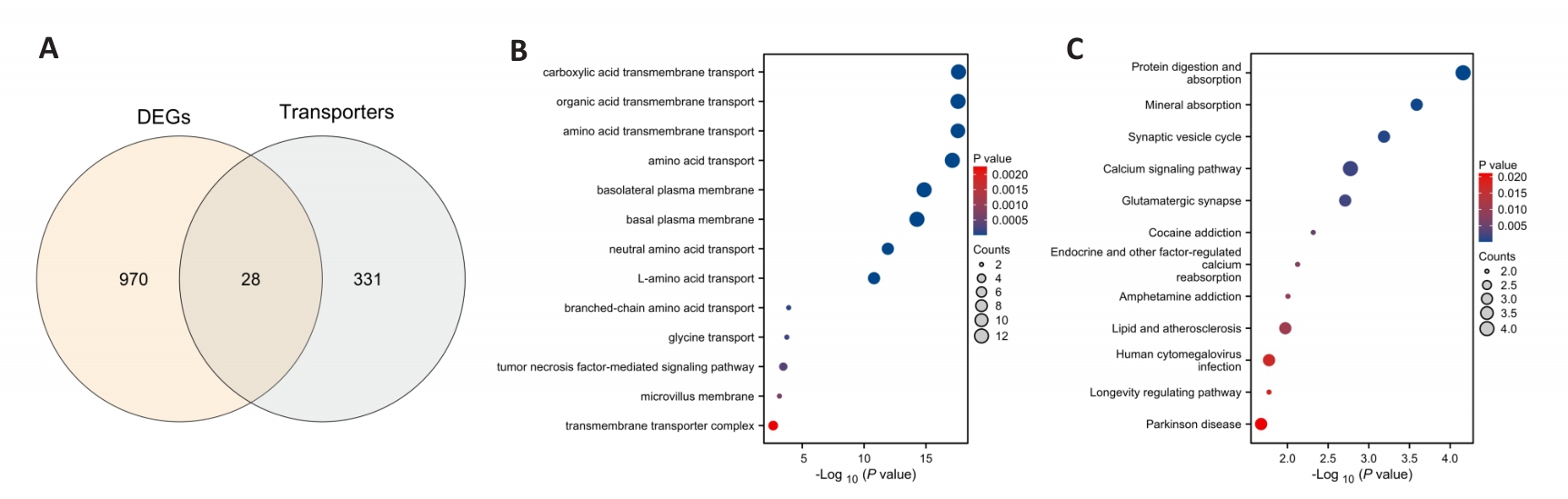
Fig.4 Bioinformatics analysis of the placenta under prenatal fear stress. A: Venn diagram. B: Gene ontology analysis. C: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes pathway analysis. DEGs: Differentially expressed genes.
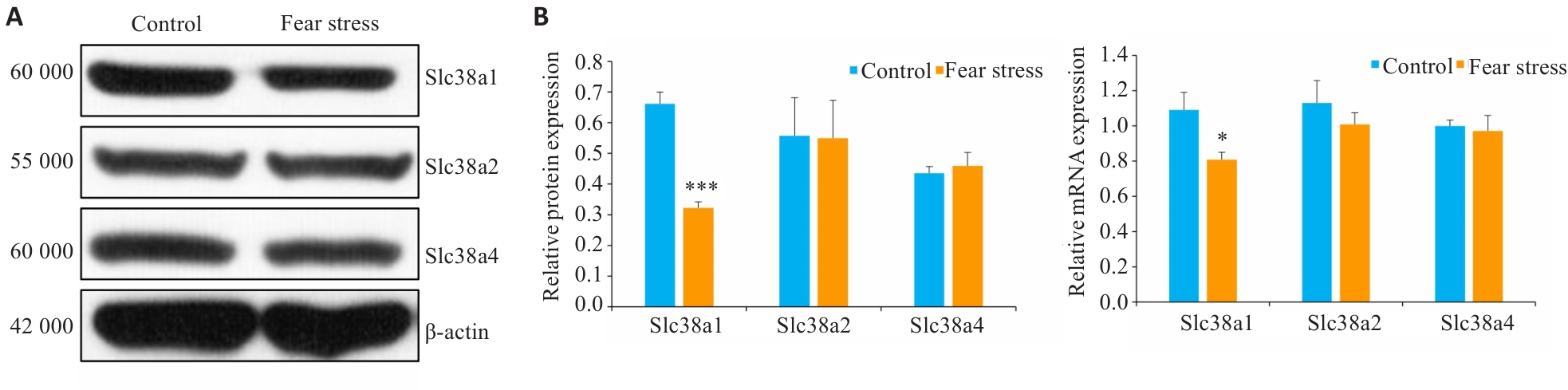
Fig.5 Effect of prenatal fear stress on protein (A) and mRNA (B) expressions of system A amino acid transporters in the placenta. *P<0.05, ***P<0.001 vs Control group.
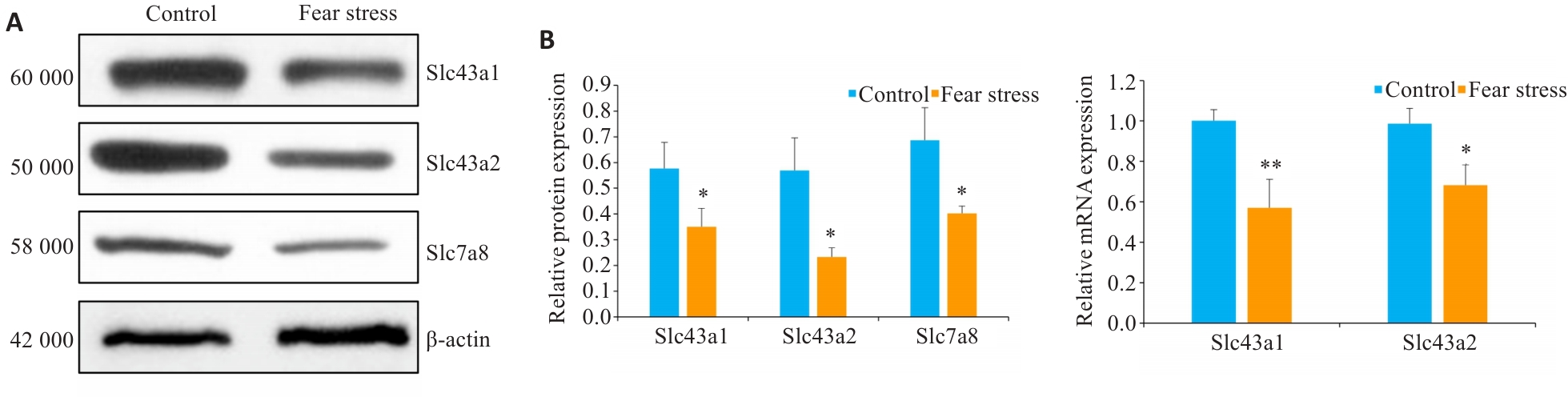
Fig.6 Effect of prenatal fear stress on protein (A) and mRNA (B) expressions of system L amino acid transporters in the placenta. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs Control group.
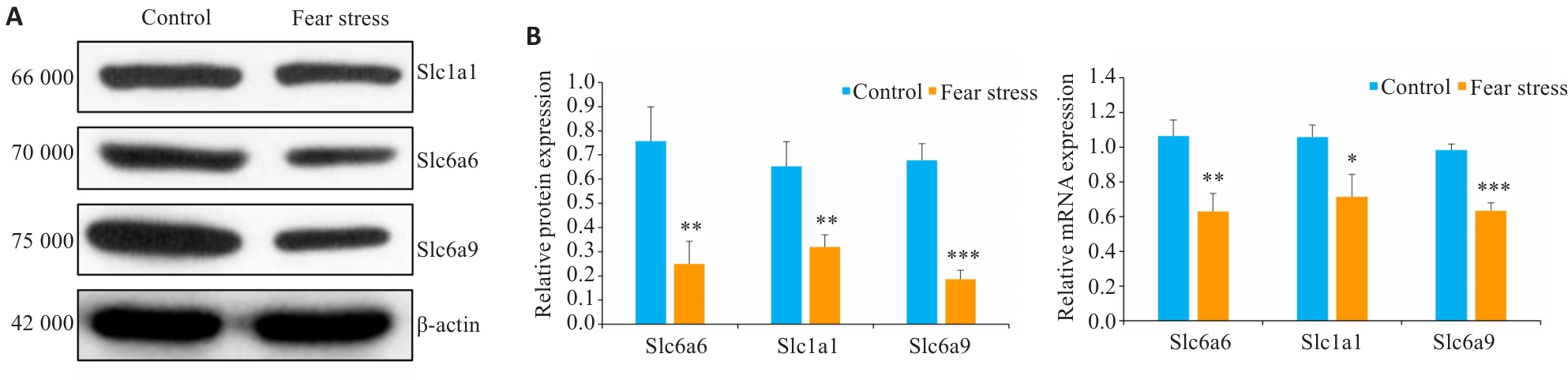
Fig.7 Effect of prenatal fear stress on protein (A) and mRNA (B) expressions of Slc6a6, Slc1a1 and Slc6a9. *P<0.05, **P<0.01,***P<0.001 vs Control group.
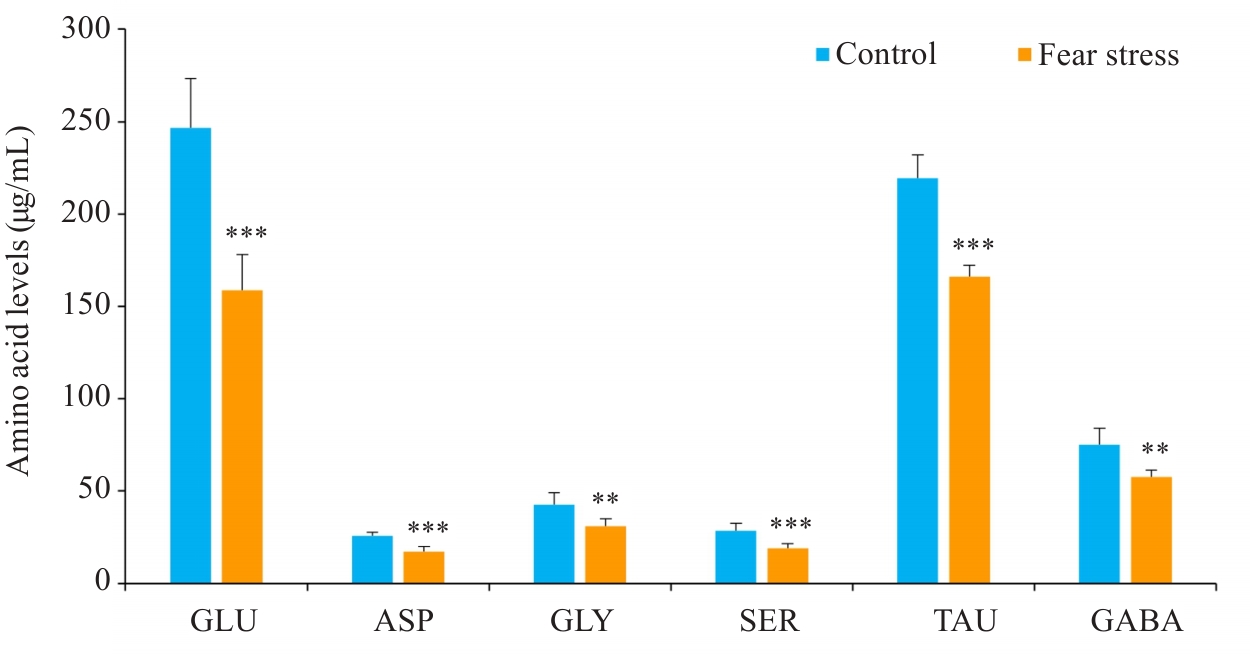
Fig.8 Effect of prenatal fear stress on serum amino acid levels in fetal mice.GLU: Glutamate; ASP: Aspartate; GLY: Glycine; SER: Serine; TAU: Taurine; GABA: Gamma-aminobutyric acid. **P<0.01,***P<0.001 vs Control group.
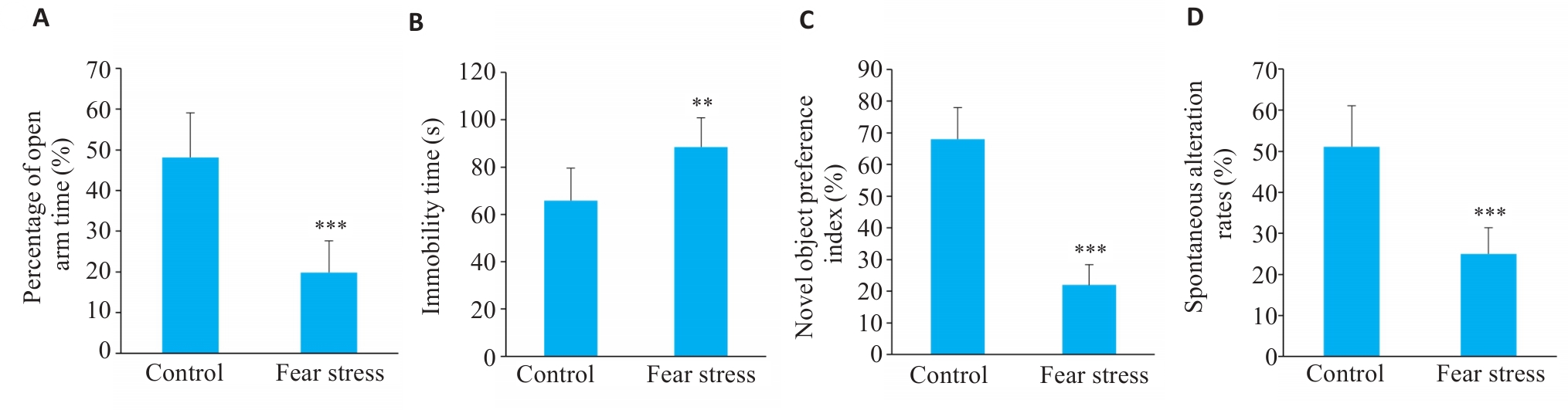
Fig.9 Effect of prenatal fear stress on behaviors of adult offspring rats. A: Percentage of open arm time in elevated plus maze test. B: Immobility time in tail suspension test. C: Novel object preference index in novel object recognition test. D: Spontaneous alternation rate in Y-maze test (n=10). **P<0.01,***P<0.001 vs Control group.
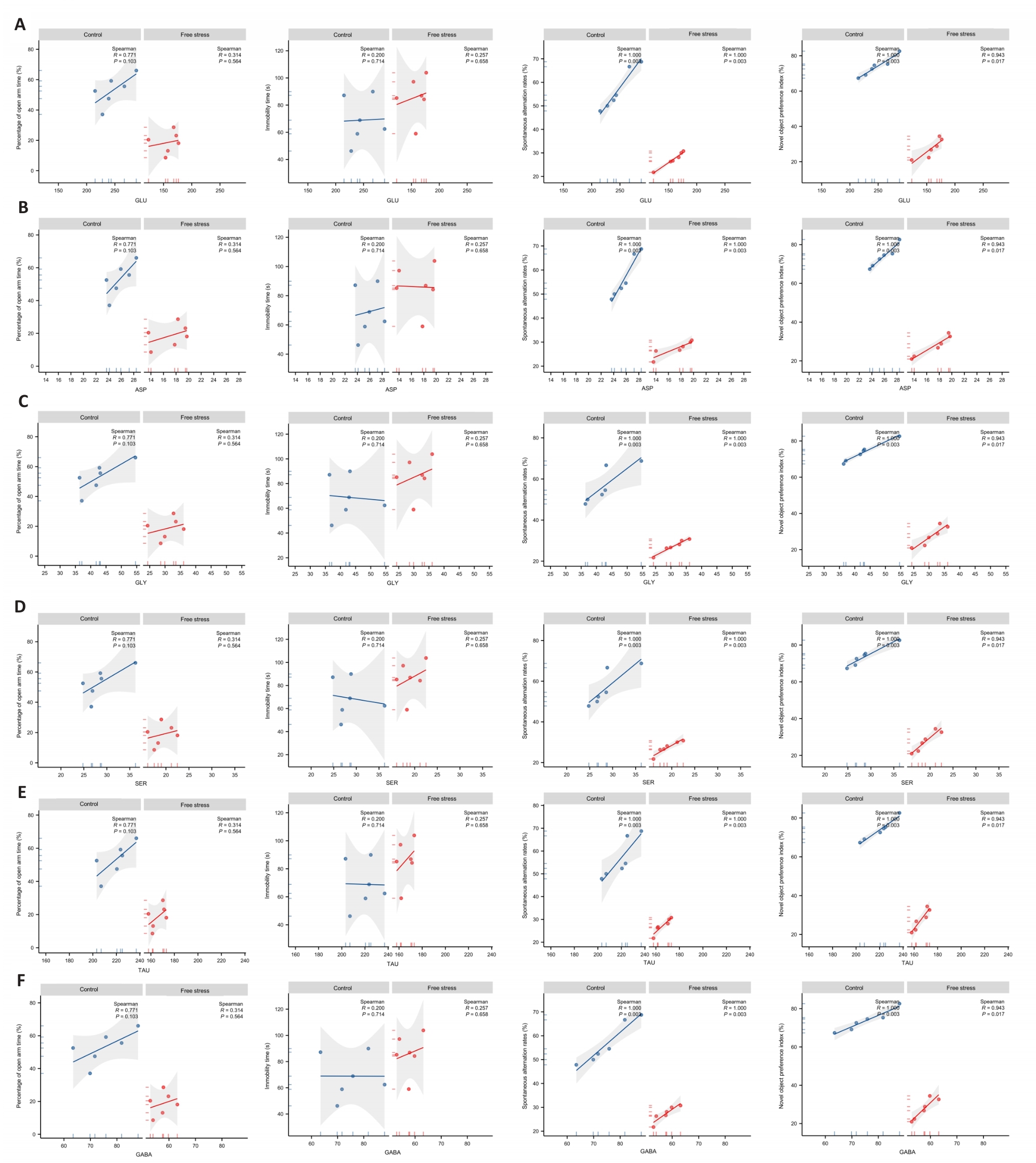
Fig.10 Correlation analysis of serum glutamate (A), aspartate (B), glycine (C), serine (D), taurine (E) and gamma-aminobutyric acid (F) levels with behavioral performance in fetal rats.
| [1] | Li B, Liu T, Ma D, et al. Association of fear of childbirth and postpartum depression with perceived partner response during pregnancy[J]. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth, 2025, 25(1): 211. doi:10.1186/s12884-025-07332-6 |
| [2] | Jing Q, Jie J, Ke X, et al. The relationship between fear of childbirth and prenatal depression in pregnant women during pregnancy: a cross-lagged analysis[J]. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth, 2025, 25(1): 192. doi:10.1186/s12884-025-07321-9 |
| [3] | Levendosky AA, Grimm KJ, Lonstein JS, et al. Pinpointing the timing of prenatal stress associated with infant biobehavioral reactivity[J]. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 2025, 173: 107368. doi:10.1016/j.psyneuen.2025.107368 |
| [4] | Li L, Zhang W, Sun C, et al. Scutellariae Radix ameliorates prenatal stress-induced anxiety-like and depression-like behavior in the offspring via reversing HPA axis hyperfunction and ameliorating neurodevelopmental dysfunction[J]. Dev Neurosci, 2024: 1-19. doi:10.1159/000543152 |
| [5] | Cheng J, Jin H, Zhang Y, et al. Small for gestational age children at risk: Identifying placenta-brain axis genes as biomarkers for early prediction of neurodevelopmental delay[J]. Life Sci, 2025, 365: 123450. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2025.123450 |
| [6] | Castro-Quintas A, Palma-Gudiel H, Eixarch E, et al. Placental epigenetic signatures of maternal distress in glucocorticoid-related genes and newborn outcomes: a study of Spanish primiparous women[J]. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol, 2025, 90: 36-47. doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2024.10.001 |
| [7] | Botía M, Escribano D, Tecles F, et al. Changes in Cortisol, cortisone and 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type II activity in saliva during pregnancy and lactation in sows[J]. Domest Anim Endocrinol, 2024, 89: 106875. doi:10.1016/j.domaniend.2024.106875 |
| [8] | Heynen JP, McHugh RR, Boora NS, et al. Urinary 1H NMR metabolomic analysis of prenatal maternal stress due to a natural disaster reveals metabolic risk factors for non-communicable diseases: the QF2011 Queensland flood study[J]. Metabolites, 2023, 13(4): 579. doi:10.3390/metabo13040579 |
| [9] | Cho SKS, Darby JRT, Saini BS, et al. Late-gestation maternal undernutrition induces circulatory redistribution while preserving uteroplacental function independent of fetal glycaemic state[J]. J Physiol, 2024, 602(24): 7065-83. doi:10.1113/jp287171 |
| [10] | Liu S, Hua L, Mo X, et al. Comparative impact of alternate-day fasting and time-restricted feeding on placental function and fetal development in maternal obesity[J]. Nutrients, 2024, 17(1): 25. doi:10.3390/nu17010025 |
| [11] | Oliveira TRDP, Lima-Oliveira DP, de Paula MBM, et al. Consequences of the modulation of gestational resistance training intensity for placental cell composition and nutrient transporter expression[J]. Placenta, 2025, 161: 55-64. doi:10.1016/j.placenta.2025.01.012 |
| [12] | Pereira-Carvalho D, Chagas Valim AC, Borba Vieira Andrade C, et al. Sex-specific effect of antenatal Zika virus infection on murine fetal growth, placental nutrient transporters, and nutrient sensor signaling pathways[J]. FASEB J, 2024, 38(13): e23799. doi:10.1096/fj.202301951rr |
| [13] | Schroeder M, Fuenzalida B, Yi N, et al. LAT1-dependent placental methionine uptake is a key player in fetal programming of metabolic disease[J]. Metabolism, 2024, 153: 155793. doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2024.155793 |
| [14] | Jia Q, Guo X, Cao Q, et al. Assisted reproductive technology causes reduced expression of amino acid transporters in human full-term placentas[J]. Pathol Res Pract, 2022, 239: 154169. doi:10.1016/j.prp.2022.154169 |
| [15] | Duan BB, Ran SJ, Wu L, et al. Maternal supplementation spermidine during gestation improves placental angiogenesis and reproductive performance of high prolific sows[J]. J Nutr Biochem, 2025, 136: 109792. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2024.109792 |
| [16] | 张玉荣, 王瑞忠, 陈 蕊, 等. 产前应激子代大鼠海马Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的改变诱导抑郁和焦虑样行为[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2019, 39(2): 222-6. doi:10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2019.09.15 |
| [17] | Aldinger JK, Abele H, Kranz A. Prenatal maternal psychological stress (PMPS) and its effect on the maternal and neonatal outcome: a retrospective cohort study[J]. Healthcare: Basel, 2024, 12(23): 2431. doi:10.3390/healthcare12232431 |
| [18] | Ren FY, Zhu XW, Liu JN, et al. Associations of multiple risk factors with prenatal depression and anxiety: Evidence from the Tianjin Birth Cohort (TJBC) study[J]. J Affect Disord, 2024, 366: 411-22. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2024.08.122 |
| [19] | Wu Y, De Asis-Cruz J, Limperopoulos C. Brain structural and functional outcomes in the offspring of women experiencing psychological distress during pregnancy[J]. Mol Psychiatry, 2024, 29(7): 2223-40. doi:10.1038/s41380-024-02449-0 |
| [20] | 宋 琦, 杜志欣, 杨丽萍, 等. 恐惧应激对妊娠期大鼠胎盘葡萄糖转运体表达水平的影响[J]. 中国实验动物学报, 2024, 32(7): 828-35. |
| [21] | Jiang Y, Zhang T, Yang LP, et al. Downregulation of FTO in the hippocampus is associated with mental disorders induced by fear stress during pregnancy[J]. Behav Brain Res, 2023, 453: 114598. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2023.114598 |
| [22] | 吴永叶, 杨丽萍, 张振强, 等. 五行音乐对孕期恐应激子代社交行为的影响及机制研究[J]. 中国比较医学杂志, 2024, 34(4): 28-34. |
| [23] | Li QH, Zhang QZ, Su SL, et al. Maternal fish oil supplementation enhances nutrient transport in the placenta and milk biosynthesis in the mammary gland via the GPR120 signaling pathway[J]. J Adv Res, 2024, 1232(24): 607-16. |
| [24] | Vrooman LA, Rhon-Calderon EA, Suri KV, et al. Placental abnormalities are associated with specific windows of embryo culture in a mouse model[J]. Front Cell Dev Biol, 2022, 10: 884088. doi:10.3389/fcell.2022.884088 |
| [25] | Wang L, Wang H, Luo J, et al. Decorin promotes decidual M1-like macrophage polarization via mitochondrial dysfunction resulting in recurrent pregnancy loss[J]. Theranostics, 2022, 12(17): 7216-36. doi:10.7150/thno.78467 |
| [26] | Kadife E, Harper A, De Alwis N, et al. SLC38A4 amino acid transporter expression is significantly lower in early preterm intrauterine growth restriction complicated placentas[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 24(1): 403. doi:10.3390/ijms24010403 |
| [27] | Bourdon A, Hannigsberg J, Misbert E, et al. Maternal supplementation with citrulline or arginine during gestation impacts fetal amino acid availability in a model of intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR)[J]. Clin Nutr, 2020, 39(12): 3736-43. doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2020.03.036 |
| [28] | Rosario FJ, Barentsen K, Powell TL, et al. Trophoblast-specific overexpression of the LAT1 increases transplacental transport of essential amino acids and fetal growth in mice[J]. PNAS Nexus, 2024, 3(6): pgae207. doi:10.1093/pnasnexus/pgae207 |
| [29] | Furukawa T, Fukuda A. Maternal taurine as a modulator of Cl- homeostasis as well as of Glycine/GABAA receptors for neocortical development[J]. Front Cell Neurosci, 2023, 17: 1221441. doi:10.3389/fncel.2023.1221441 |
| [30] | Noorlander CW, de Graan PNE, Nikkels PGJ, et al. Distribution of glutamate transporters in the human placenta[J]. Placenta, 2004, 25(6): 489-95. doi:10.1016/j.placenta.2003.10.018 |
| [31] | Crouse MS, McLean KJ, Greseth NP, et al. The effects of maternal nutrient restriction and day of early pregnancy on the location and abundance of neutral amino acid transporters in beef heifer utero-placental tissues[J]. J Anim Sci, 2020, 98(7): skaa197. doi:10.1093/jas/skaa197 |
| [32] | McColl ER, Piquette-Miller M. Poly(I: C) alters placental and fetal brain amino acid transport in a rat model of maternal immune activation[J]. Am J Reprod Immunol, 2019, 81(6): e13115. doi:10.1111/aji.13115 |
| [33] | Feng C, Wu Y, Zhang X, et al. Maternal milk fat globule membrane enriched gut L. murinus and circulating SCFAs to improve placental efficiency and fetal development in intrauterine growth restricted mice model[J]. Gut Microbes, 2025, 17(1): 2449095. doi:10.1080/19490976.2024.2449095 |
| [34] | Ferreira-Rodrigues M, Sousa IS, Baptista FI, et al. Stress in utero: prenatal dexamethasone exposure causes greater structural gliovascular alterations in female offspring than in males[J]. Front Neurosci, 2025, 19: 1539867. doi:10.3389/fnins.2025.1539867 |
| [1] | XIE Xiaoxiao, ZHAO Qingdong, HU Lingyun, JIANG Shufang, WANG Xiaoping, ZHANG Wenling, LI Zhen, YOU Yanqin, LU Yanping. Value of non-invasive prenatal testing for rare autosomal trisomies in fetuses [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(12): 2071-2077. |
| [2] | XIE Xiaoxiao, ZHAO Qingdong, FU Yurong, ZHANG Wenling, MENG Yuanguang, LU Yanping. Genetic testing and analysis of 2 cases of trisomy 11 mosaicism [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42(7): 1057-1061. |
| [3] | HE Jianping, TANG Jian, SU Hong, SHEN Cuihua, LUO Shengjun, WANG Haitao, QIAN Yuan, LÜ Mengxin. Whole-transcriptome sequencing analysis of placental differential miRNA expression profile in Down syndrome [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42(3): 418-424. |
| [4] | GAO Junjie, YANG Dandan, CAO Ruoxue, PAN Xueshan, XIA Jun. Therapeutic mechanism of natural astaxanthin against renal clear cell carcinoma based on network pharmacology and bioinformatics [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2021, 41(12): 1763-1772. |
| [5] | . miR-34a-5p regulates viability, invasion and apoptosis of placental trophoblastic cells via modulating CDK6 and PI3K/AKT pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2020, 40(01): 79-86. |
| [6] | . Long non-coding RNAs show different expression profiles and display competing endogenous RNA potential in placenta accreta spectrum disorders [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2019, 39(10): 1253-. |
| [7] | . Vitamin D down-regulates microRNA-21 expression to promote human placental trophoblast cell migration and invasion in vitro [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2019, 39(04): 437-. |
| [8] | . Maternal neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic biomarker for placental inflammatory response in late pregnancy [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2018, 38(09): 1131-. |
| [9] | . Expression of FABP7 in mouse placenta tissue and human trophoblast HTR-8/Svneo cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2017, 37(05): 594-. |
| [10] | . Effect of heat exposure in the second trimester of pregnancy on intrauterine growth of fatal rat and the expression of HSP70, Bax and Bcl-2 of placenta [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2017, 37(01): 89-. |
| [11] | . Effect of di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate exposure on placental development in pregnant mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2016, 36(04): 467-. |
| [12] |
.
Expression of progesterone-induced blocking factor in severe preeclampsia and its association with immune tolerance imbalance [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2015, 35(06): 848-. |
| [13] | . Relationship between fetal growth restriction and angiogenesis factors [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2014, 34(07): 1068-. |
| [14] | GAO Yun-fei1,YU Yan-hong1,LI Zhi-qin2 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,Nanfang Hospital1,Department of Cellular Biology2,Southern Medical University,Guangzhou 510515,China. Differential expression of adrenomedullin in the placentas of women with normal and preeclamptic pregnancies in late term [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2006, 26(12): 1828-1830. |
| [15] | ZHANG Li-ying, YU Yan-hong, HU Mao-lan. Association between ultrasonographic signs of placental premature aging and pregnancy outcome [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2005, 25(03): 318-320. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||