Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (6): 1260-1269.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.06.15
Qiongqiong HU1( ), Wenpei LI1,2, Lixia XU1, Ruilei GUAN1, Dongya ZHANG1, Jiaojiao JIANG1, Ning WANG1, Gaiqing YANG1,2(
), Wenpei LI1,2, Lixia XU1, Ruilei GUAN1, Dongya ZHANG1, Jiaojiao JIANG1, Ning WANG1, Gaiqing YANG1,2( )
)
Received:2024-12-05
Online:2025-06-20
Published:2025-06-27
Contact:
Gaiqing YANG
E-mail:zxyyhqq0915@163.com;zxyyygq@163.com
Qiongqiong HU, Wenpei LI, Lixia XU, Ruilei GUAN, Dongya ZHANG, Jiaojiao JIANG, Ning WANG, Gaiqing YANG. Neurospecific transmembrane protein 240 colocalizes with peroxisomes and activates Rho GDP dissociation inhibitor β[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1260-1269.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.06.15
| Gene | Sequences (5'-3') |
|---|---|
18S-F 18S-R | AGTCCCTGCCCTTTGTACACA CGATCCGAGGGCCTCACTA |
| Tmem240-F | TGCTTGATGGACATGAACGC |
| Tmem240-R | TAGTTCTCGGAGGCGTCCAC |
| Bex4_F | GGGGGAAATGTCCGAAGGAAA |
| Bex4_R | CCTGCACTACAAATCTCCCAAC |
| Fdft1_F | AGAGTGGCGGTTCACTGAGA |
| Fdft1_R | GAGAAAGGCCAATTCCCACCA |
| Slc2a3-F | TCATCAATGCACCTGAGACAATC |
| Slc2a3-R | GTCCCTCACTTGGTAGGTCTT |
| Arhgdib_F | CAACACACATACCGGACTGG |
| Arhgdib_R | TGTTTGTCGTCATCCGTGAAG |
| Insig1_F | CTAGTGCTCTTCTCATTTGGCG |
| Insig1_R | AGGGATACAGTAAACCGACAACA |
| Hmgcr_F | AGAGCGAGTGCATTAGCAAAG |
| Hmgcr_R | GATTGCCATTCCACGAGCTAT |
| Hmgcs1_F | AACTGGTGCAGAAATCTCTAGC |
| Hmgcs1_R | GGTTGAATAGCTCAGAACTAGCC |
| SPP1_F | AGCAAGAAACTCTTCCAAGCAA |
| SPP1_R | GTGAGATTCGTCAGATTCATCCG |
| Fam78b_F | TGCGCTACAAGACCCCTTACT |
| Fam78b_R | CTGATGGCTTTTACTCTCCCTTC |
| Arhgdia-F | AAGGACGATGAAAGCCTCCG |
| Arhgdia-R | GGTCAGTCGAGTCACAATGACA |
| Arhgdig-F | GTCAACTCCATCAGATGAGGTG |
| Arhgdig-R | GGGGTCCATAATGGGTGGC |
Tab.1 Primer sequences for qPCR
| Gene | Sequences (5'-3') |
|---|---|
18S-F 18S-R | AGTCCCTGCCCTTTGTACACA CGATCCGAGGGCCTCACTA |
| Tmem240-F | TGCTTGATGGACATGAACGC |
| Tmem240-R | TAGTTCTCGGAGGCGTCCAC |
| Bex4_F | GGGGGAAATGTCCGAAGGAAA |
| Bex4_R | CCTGCACTACAAATCTCCCAAC |
| Fdft1_F | AGAGTGGCGGTTCACTGAGA |
| Fdft1_R | GAGAAAGGCCAATTCCCACCA |
| Slc2a3-F | TCATCAATGCACCTGAGACAATC |
| Slc2a3-R | GTCCCTCACTTGGTAGGTCTT |
| Arhgdib_F | CAACACACATACCGGACTGG |
| Arhgdib_R | TGTTTGTCGTCATCCGTGAAG |
| Insig1_F | CTAGTGCTCTTCTCATTTGGCG |
| Insig1_R | AGGGATACAGTAAACCGACAACA |
| Hmgcr_F | AGAGCGAGTGCATTAGCAAAG |
| Hmgcr_R | GATTGCCATTCCACGAGCTAT |
| Hmgcs1_F | AACTGGTGCAGAAATCTCTAGC |
| Hmgcs1_R | GGTTGAATAGCTCAGAACTAGCC |
| SPP1_F | AGCAAGAAACTCTTCCAAGCAA |
| SPP1_R | GTGAGATTCGTCAGATTCATCCG |
| Fam78b_F | TGCGCTACAAGACCCCTTACT |
| Fam78b_R | CTGATGGCTTTTACTCTCCCTTC |
| Arhgdia-F | AAGGACGATGAAAGCCTCCG |
| Arhgdia-R | GGTCAGTCGAGTCACAATGACA |
| Arhgdig-F | GTCAACTCCATCAGATGAGGTG |
| Arhgdig-R | GGGGTCCATAATGGGTGGC |
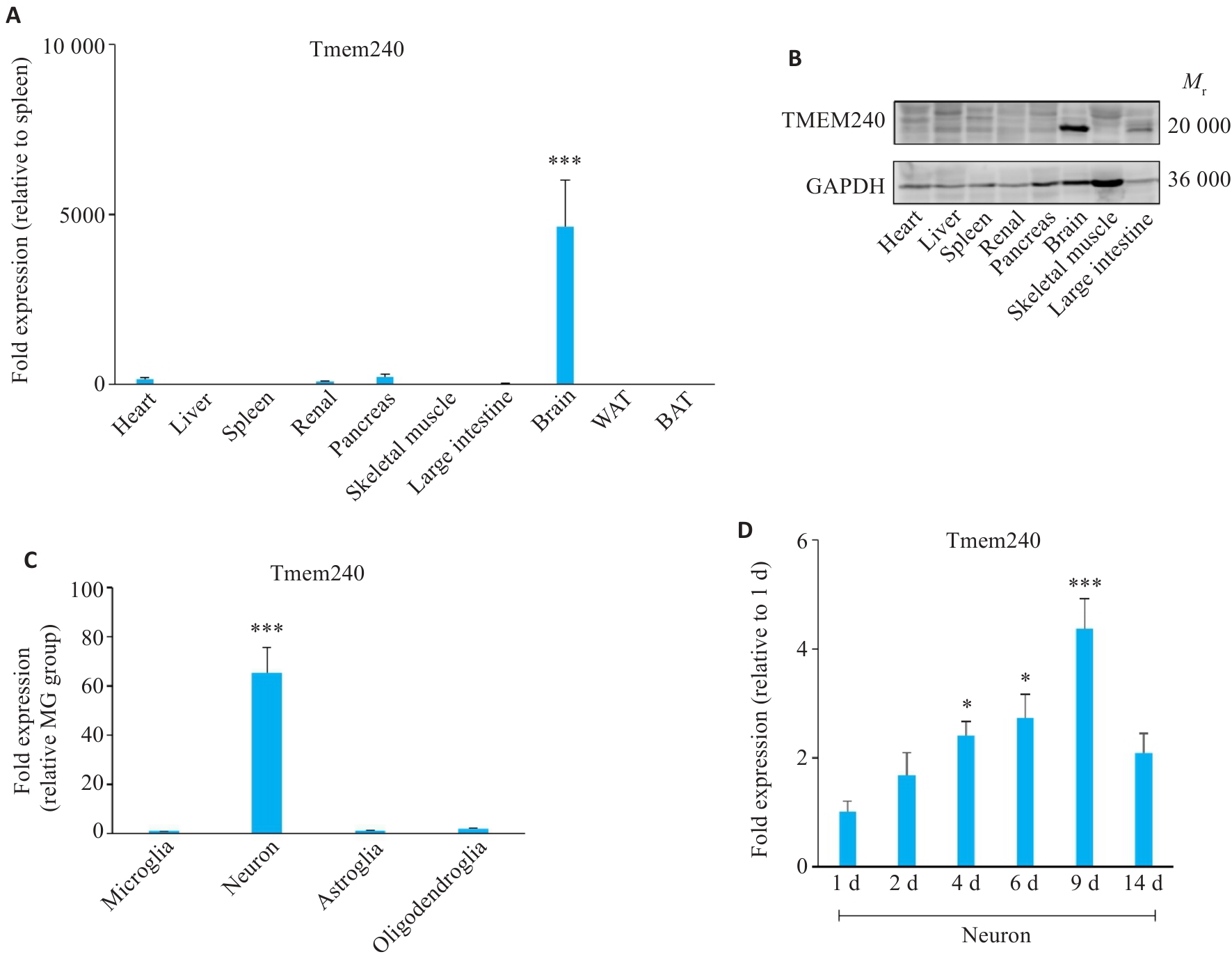
Fig.1 TMEM240 shows neuron-specific expression. A: qPCR detection of Tmem240 mRNA levels in various tissues of C57BL/6 mice (n=3; ***P<0.001 vs spleen). B: Western blotting for analyzing TMEM240 protein levels in different tissues of C57BL/6 mice (n=3). C: qPCR profiling of Tmem240 mRNA in neurons, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and microglia of C57BL/6 mice (n=3; ***P<0.001 vs microglia group). D: qPCR quantification of Tmem240 mRNA in cultured neurons at different time points (n=3; *P<0.05, ***P<0.001 vs 1 day group).
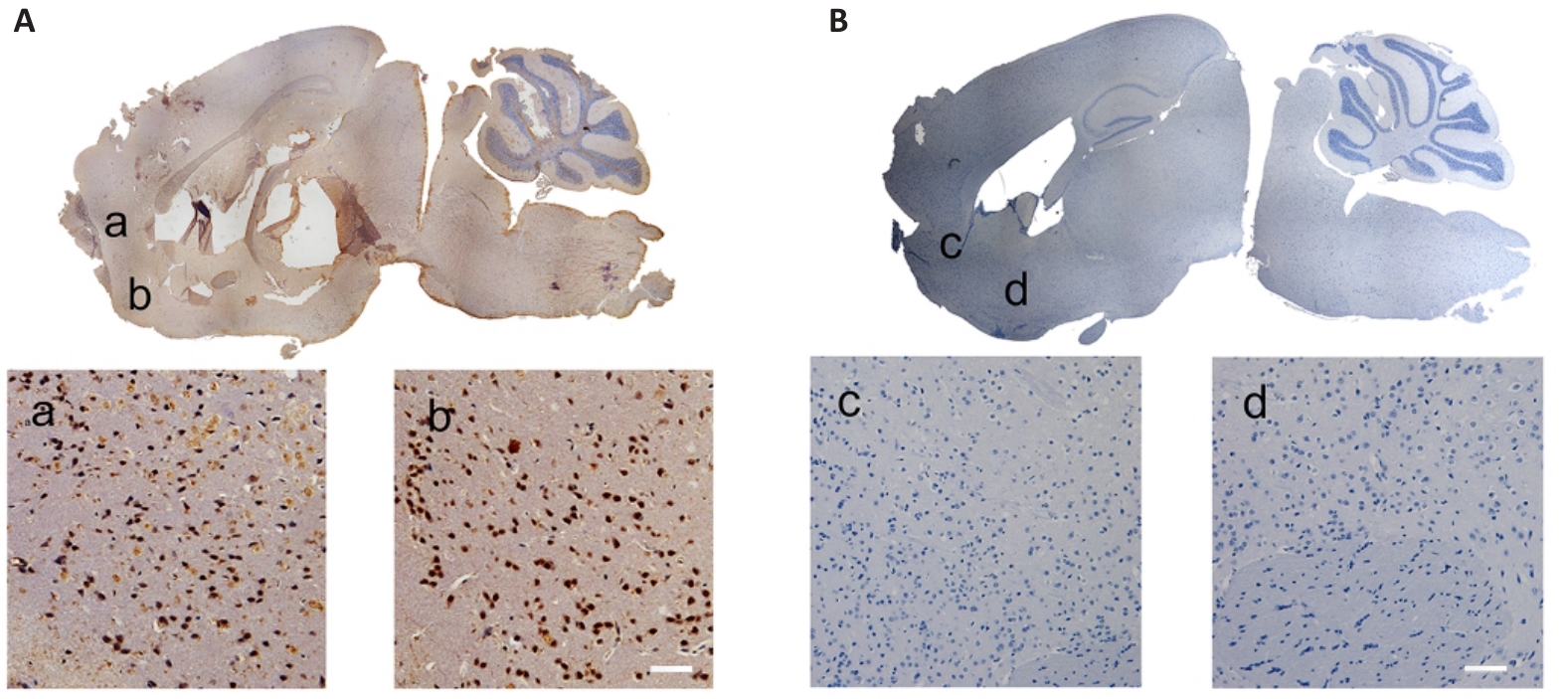
Fig.2 Distribution of TMEM240 expression in mouse brain tissues (Scale bar=40 μm). A: In situ hybridization of C57BL/6 mouse brain tissue reveals abundant TMEM240 expression. B: No probe control group. a-d shows magnified views of the corresponding selected areas.
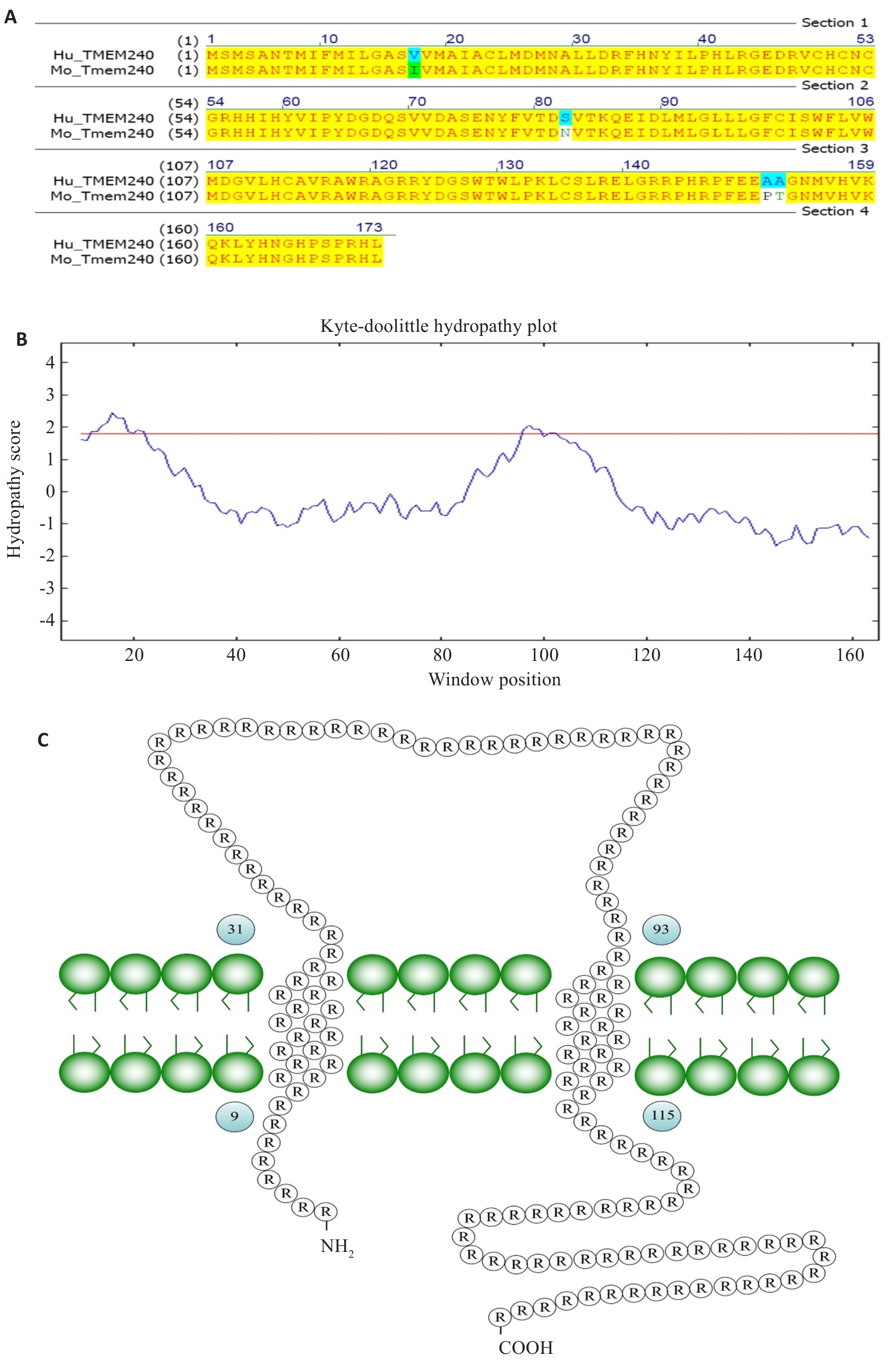
Fig.3 Analysis of transmembrane structure of TMEM240. A: The sequence homology between human and murine TMEM240 proteins is 97.69%. B: Hydrophobicity plot of TMEM240. C: Schematic representation of transmembrane topology of TMEM240.
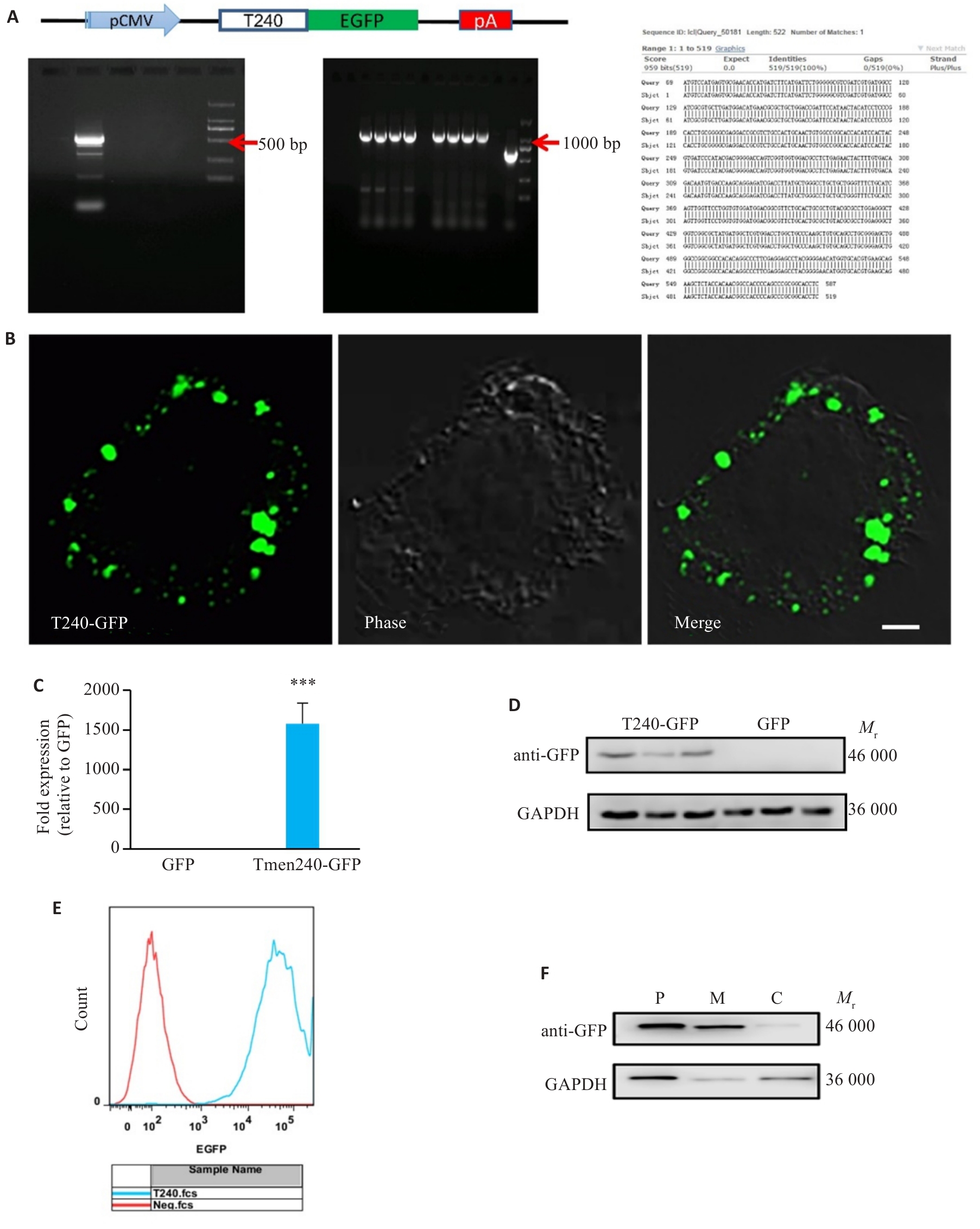
Fig.4 Construction of Tmem240-overexpressing Neuro-2a cells. A: Schematic diagram of the Tmem240-pEGFP-N1 plasmid construct. B: Confocal microscopy observation of Neuro 2a cells transfected with pEGFP-Tmem240 eukaryotic expression plasmid showing distribution intracellular Tmem240 expression (Scale bar=2 μm). C: qPCR validation of Tmem240 overexpression in Neuro 2a cells at the mRNA level (n=3). D: Western blotting confirming TMEM240 overexpression in Neuro 2a cells (n=3). E: Flow cytometry detection of Tmem240-pEGFP-N1 positive rate. F: Western blotting of TMEM240 expression in membrane (M), cytoplasmic (C), and total proteins (P) of Neuro 2a cells overexpressing Tmem240. ***P<0.001 vs GFP control.
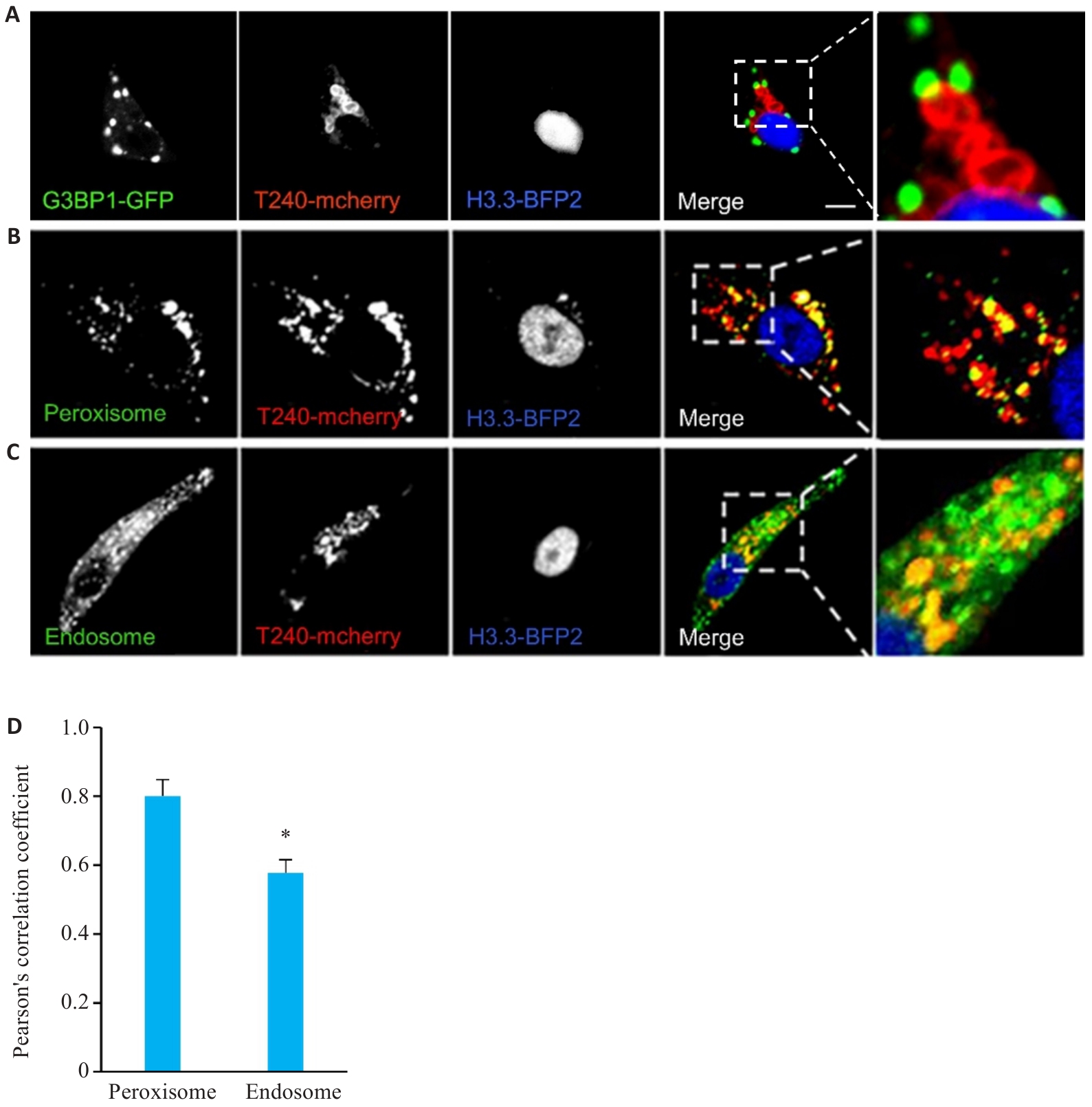
Fig.5 Intracellular distribution of TMEM240. A: Confocal microscopy analysis of colocalization between pLVX-mcherry-TMEM240 (T240-mCherry, red) and G3BP1 (green) in HepG2 cells. B, C: Confocal microscopy observation of colocalization of pLVX-mcherry-TMEM240 (red) with peroxisome (PXMP2) and endosome (RAb5b) in HepG2 cells, with the nuclei stained blue by H3.3-BFP2 (Scale bar=10 μm). D: Pearson's correlation coefficient assessment of fluorescence overlap between pLVX-mcherry-TMEM240, peroxisome (PXMP2), and endosome (RAb5b) using Image-Pro software. Data represents mean scores (Mean±SD) from 3 independent experiments comprising a total of 60 cells for each condition. *P<0.05 vs PXMP2 group.
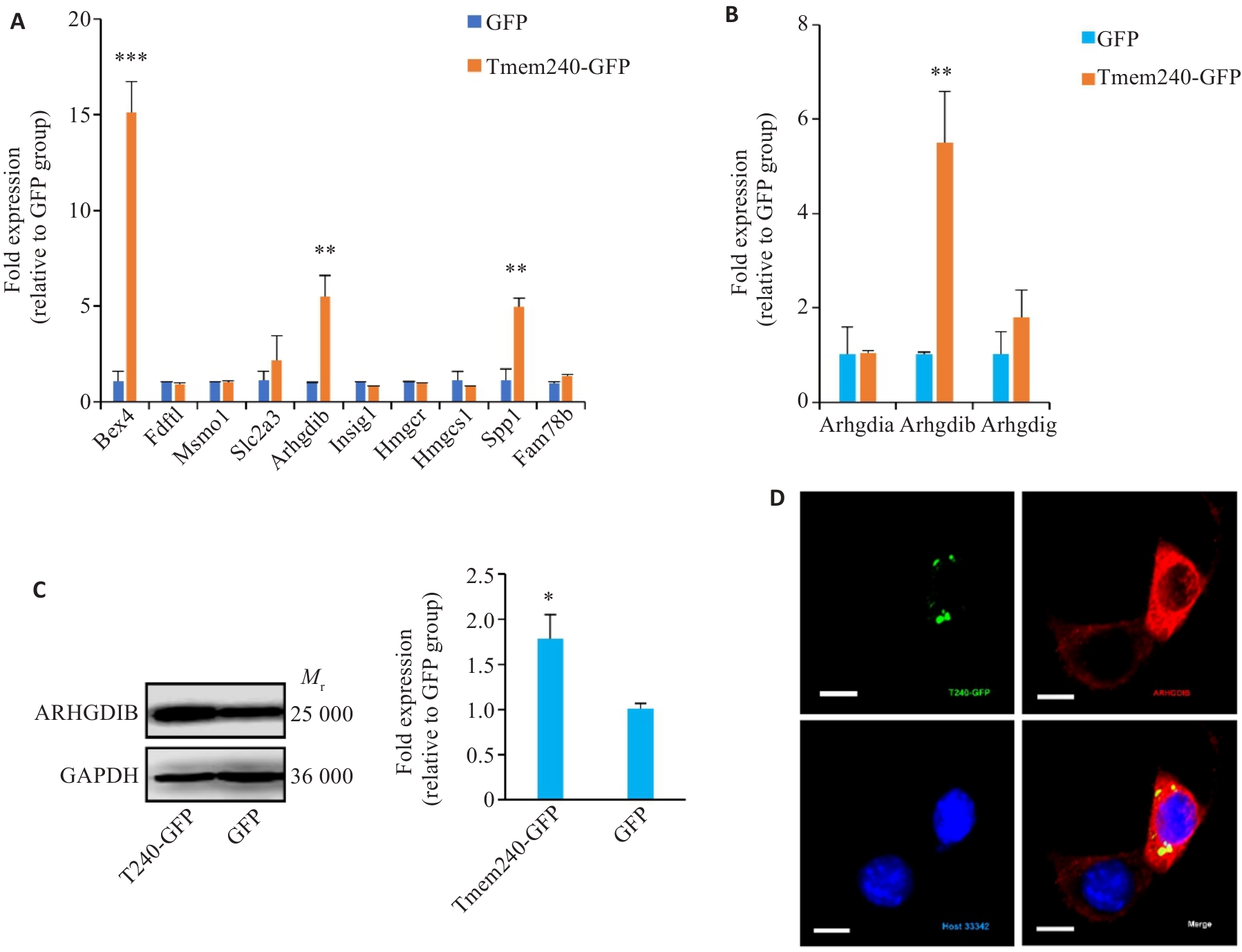
Fig.6 Investigation of biological functions of TMEM240. A: qPCR analysis of gene expression levels in Neuro2A cells overexpressing Tmem240 (n=3). B: qPCR validation of Arhgdia, Arhgdib, and Arhgdig mRNA expression levels in Neuro2a cells overexpressing Tmem240 (n=3). C: Western blotting analysis of the impact of Tmem240 overexpression on ARHGDIB protein levels in Neuro2a cells (n=3). D: Immunofluorescence assessment of the effect of Tmem240 overexpression on ARHGDIB expression levels in Neuro2a cells (×800). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs GFP controll.
| 1 | Kang H, Lee CJ. Transmembrane proteins with unknown function (TMEMs) as ion channels: electrophysiological properties, structure, and pathophysiological roles[J]. Exp Mol Med, 2024, 56(4): 850-60. doi:10.1038/s12276-024-01206-1 |
| 2 | Herrera-Quiterio GA, Encarnación-Guevara S. The transmembrane proteins (TMEM) and their role in cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer[J]. Front Oncol, 2023, 13: 1244740. doi:10.3389/fonc.2023.1244740 |
| 3 | Forrest AS, Joyce TC, Huebner ML, et al. Increased TMEM16A-encoded calcium-activated chloride channel activity is associated with pulmonary hypertension[J]. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol, 2012, 303(12): C1229-43. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00044.2012 |
| 4 | Christopher KJ, Wang BL, Kong Y, et al. Forward genetics uncovers Transmembrane protein 107 as a novel factor required for ciliogenesis and Sonic hedgehog signaling[J]. Dev Biol, 2012, 368(2): 382-92. doi:10.1016/j.ydbio.2012.06.008 |
| 5 | Zhao Y, Hu J, Miao G, et al. Transmembrane protein 208: a novel ER-localized protein that regulates autophagy and ER stress[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(5): e64228. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0064228 |
| 6 | Millay DP, O’Rourke JR, Sutherland LB, et al. Myomaker is a membrane activator of myoblast fusion and muscle formation[J]. Nature, 2013, 499(7458): 301-5. doi:10.1038/nature12343 |
| 7 | Medina MW, Bauzon F, Naidoo D, et al. Transmembrane protein 55B is a novel regulator of cellular cholesterol metabolism[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2014, 34(9): 1917-23. doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.302806 |
| 8 | Zhang Z, Bai M, Barbosa GO, et al. Broadly conserved roles of TMEM131 family proteins in intracellular collagen assembly and secretory cargo trafficking[J]. Sci Adv, 2020, 6(7): eaay7667. doi:10.1126/sciadv.aay7667 |
| 9 | Marx S, Dal Maso T, Chen JW, et al. Transmembrane (TMEM) protein family members: Poorly characterized even if essential for the metastatic process[J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 2020, 60: 96-106. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.08.018 |
| 10 | Li CY, Ou RW, Chen YP, et al. Mutation analysis of TMEM family members for early-onset Parkinson's disease in Chinese population[J]. Neurobiol Aging, 2021, 101: 299.e1-299.e6. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2020.11.005 |
| 11 | Jiao HS, Yuan P, Yu JT. TMEM106B aggregation in neuro-degenerative diseases: linking genetics to function[J]. Mol Neurodegener, 2023, 18(1): 54. doi:10.1186/s13024-023-00644-1 |
| 12 | Li L, Khatibi NH, Hu Q, et al. Transmembrane protein 166 regulates autophagic and apoptotic activities following focal cerebral ischemic injury in rats[J]. Exp Neurol, 2012, 234(1): 181-90. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2011.12.038 |
| 13 | Seki T, Sato M, Kibe Y, et al. Lysosomal dysfunction and early glial activation are involved in the pathogenesis of spinocerebellar Ataxia type 21 caused by mutant transmembrane protein 240[J]. Neurobiol Dis, 2018, 120: 34-50. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2018.08.022 |
| 14 | Delplanque J, Devos D, Huin V, et al. TMEM240 mutations cause spinocerebellar Ataxia 21 with mental retardation and severe cognitive impairment[J]. Brain, 2014, 137(10): 2657-63. doi:10.1093/brain/awu202 |
| 15 | Chang SC, Liew PL, Ansar M, et al. Hypermethylation and decreased expression of TMEM240 are potential early-onset biomarkers for colorectal cancer detection, poor prognosis, and early recurrence prediction[J]. Clin Epigenetics, 2020, 12(1): 67. doi:10.1186/s13148-020-00855-z |
| 16 | Lin RK, Su CM, Lin SY, et al. Hypermethylation of TMEM240 predicts poor hormone therapy response and disease progression in breast cancer[J]. Mol Med, 2022, 28(1): 67. doi:10.1186/s10020-022-00474-9 |
| 17 | Bian S, Wang Y, Zhou Y, et al. Integrative single-cell multiomics analyses dissect molecular signatures of intratumoral hetero-geneities and differentiation states of human gastric cancer[J]. Natl Sci Rev, 2023, 10(6): nwad094. doi:10.1093/nsr/nwad094 |
| 18 | Ward JM, La Spada AR. Identification of the SCA21 disease gene: remaining challenges and promising opportunities[J]. Brain, 2014, 137(10): 2626-8. doi:10.1093/brain/awu217 |
| 19 | Yahikozawa H, Miyatake S, Sakai T, et al. A Japanese family of spinocerebellar Ataxia type 21: clinical and neuropathological studies[J]. Cerebellum, 2018, 17(5): 525-30. doi:10.1007/s12311-018-0941-6 |
| 20 | Zeng S, Zeng J, He M, et al. Spinocerebellar Ataxia type 21 exists in the Chinese Han population[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 19897. doi:10.1038/srep19897 |
| 21 | D’Ambrosi N, Milani M, Apolloni S. S100A4 in the physiology and pathology of the central and peripheral nervous system[J]. Cells, 2021, 10(4): 798. doi:10.3390/cells10040798 |
| 22 | Brennan FH, Coulthard LG, Alawieh AM, et al. Editorial: complement in the development and regeneration of the nervous system[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 694810. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.694810 |
| 23 | Tikhonova MA, Shvaikovskaya AA, Zhanaeva SY, et al. Concordance between the in vivo content of neurospecific proteins (BDNF, NSE, VILIP-1, S100B) in the hippocampus and blood in patients with epilepsy[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 25(1): 502. doi:10.3390/ijms25010502 |
| 24 | Tikhonova MA, Zhanaeva SY, Shvaikovskaya AA, et al. Neurospecific molecules measured in periphery in humans: how do they correlate with the brain levels? A systematic review[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(16): 9193. doi:10.3390/ijms23169193 |
| 25 | Schröder B, Wrocklage C, Hasilik A, et al. Molecular charac-terisation of 'transmembrane protein 192' (TMEM192), a novel protein of the lysosomal membrane[J]. Biol Chem, 2010, 391(6): 695-704. doi:10.1515/bc.2010.062 |
| 26 | Hanein S, Perrault I, Roche O, et al. TMEM126A, encoding a mitochondrial protein, is mutated in autosomal-recessive nonsyn-dromic optic atrophy[J]. Am J Hum Genet, 2009, 84(4): 493-8. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2009.03.003 |
| 27 | Wesoly J, Pstrąg N, Derylo K, et al. Structural, topological, and functional characterization of transmembrane proteins TMEM213, 207, 116, 72 and 30B provides a potential link to ccRCC etiology[J]. Am J Cancer Res, 2023, 13(5): 1863-83. doi:10.62347/cred7532 |
| 28 | Homa M, Loyens A, Eddarkaoui S, et al. The TMEM240 protein, mutated in SCA21, is expressed in Purkinje cells and synaptic terminals[J]. Cerebellum, 2020, 19(3): 358-69. doi:10.1007/s12311-020-01112-y |
| 29 | Parker DM, Tauber D, Parker R. G3BP1 promotes intermolecular RNA-RNA interactions during RNA condensation[J]. Mol Cell, 2025, 85(3): 571-84. e7. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2024.11.012 |
| 30 | Protter DSW, Parker R. Principles and properties of stress granules[J]. Trends Cell Biol, 2016, 26(9): 668-79. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2016.05.004 |
| 31 | Schmit K, Michiels C. TMEM proteins in cancer: a review[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2018, 9: 1345. doi:10.3389/fphar.2018.01345 |
| 32 | 宋 玲, 张 洪, 范月莹, 等. 跨膜蛋白家族与癌症的发生发展[J]. 生命的化学, 2021, 41(10): 2168-76. |
| 33 | Liu L, Cui J, Zhao Y, et al. KDM6A-ARHGDIB axis blocks metastasis of bladder cancer by inhibiting Rac1[J]. Mol Cancer, 2021, 20(1): 77. doi:10.1186/s12943-021-01369-9 |
| [1] | Guanglü HE, Wanyu CHU, Yan LI, Xin SHENG, Hao LUO, Aiping XU, Mingjie BIAN, Huanhuan ZHANG, Mengya WANG, Chao ZHENG. Orexin-A promotes motor function recovery of rats with spinal cord injury by regulating ionotropic glutamate receptors [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 1023-1030. |
| [2] | Yue CHEN, Linyu XIAO, Lü REN, Xue SONG, Jing LI, Jianguo HU. Monotropein improves motor function of mice with spinal cord injury by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway to suppress neuronal apoptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 774-784. |
| [3] | Qiaoyan CAI, Yaoyao XU, Yuxing LIN, Haowei LIN, Junpeng ZHENG, Weixiang ZHANG, Chunyu ZHAO, Yupeng LIN, Ling ZHANG. Qingda Granules alleviate brain damage in spontaneously hypertensive rats by modulating the miR-124/STAT3 signaling axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(1): 18-26. |
| [4] | LI Yanxiang, GUO Yongxin, CAO Fuyang, GUO Shuting, XUE Dinghao, ZHOU Zhikang, HAO Xinyu, TONG Li, FU Qiang. Inhibition of glutamatergic neurons in the dorsomedial periaqueductal gray alleviates excessive defensive behaviors of mice with post-traumatic stress disorder [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(3): 420-427. |
| [5] | GUI Jianjun, SUN Xiaodong, WEN Shu, LIU Xin, QIN Bingqing, SANG Ming. Resveratrol protects dopaminergic neurons in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease by regulating the gut-brain axis via inhibiting the TLR4 signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(2): 270-279. |
| [6] | CAO Fuyang, GUO Yongxin, GUO Shuting, ZHOU Zhikang, CAO Jiangbei, TONG Li, MI Weidong. Activation of GABAergic neurons in the zona incerta accelerates anesthesia induction with sevoflurane and propofol without affecting anesthesia maintenance or awakening in mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(5): 718-726. |
| [7] | ZHANG Jingwen, HE Jing, MI Xiaojuan, XU Xianrui, TIAN Ying, YAN Ru. High homocysteine level promotes autophagy and apoptosis of mouse hippocampal HT22 cells through the Notch1/Hes1 signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(10): 1796-1803. |
| [8] | HUANG Weilong, LIANG Feixue. Neural mechanism for modulation of auditory response of the striatum by locomotion [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42(5): 766-771. |
| [9] | SUN Tingting, WANG Yuanyuan, FANG Zhuling, XU Jiajia, MA Shiwen, CHANG Jiuxiang, LIU Gaofeng, GUO Yu, LIU Changqing. Effects of ring finger and tryptophan-aspartic acid 2 on dendritic spines and synapse formation in cerebral cortex neurons of mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42(1): 78-85. |
| [10] | ZHOU Lihua, CHANG Jianrong, GAO Yangli, WANG Chaokai. Procyanidin B2 protects neurons from cypermethrin-induced oxidative stress through the P13K/Akt/Nrf2 signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2021, 41(8): 1158-1164. |
| [11] | . Communication sound recognition and response modification in the secondary auditory cortex of female mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2021, 41(7): 1079-1086. |
| [12] | . Orexin-A inhibits γ-aminobutyric acid current of neonatal rat spinal cord ventral horn neurons by activating OX1R, OX2R and Ca2+-independent PKC [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2021, 41(5): 694-701. |
| [13] | . Vitamin E reduces radiation injury of hippocampal neurons in mice by inhibiting ferroptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2020, 40(08): 1097-1102. |
| [14] | . Etomidate reduces excitability of the neurons and suppresses the function of nAChR ventral horn in the spinal cord of neonatal rats [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2020, 40(05): 676-682. |
| [15] | . Toxicity of dibutyl phthalate in primary cultured rat hippocampal neurons and the toxicological mechanism [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2020, 40(02): 225-232. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||