Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (11): 2220-2226.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.11.19
Jiaxin LI1( ), Yi LIU2, Xiangjie LIU3, Longhe XU2(
), Yi LIU2, Xiangjie LIU3, Longhe XU2( ), Yongzhe LIU1,2(
), Yongzhe LIU1,2( )
)
Received:2024-05-25
Online:2024-11-20
Published:2024-11-29
Contact:
Longhe XU, Yongzhe LIU
E-mail:546087930@qq.com;longhexu@hotmail.com;lyzgao@163.com
Jiaxin LI, Yi LIU, Xiangjie LIU, Longhe XU, Yongzhe LIU. Acute kidney injury after laparoscopic radical nephrectomy: role of the renin-angiotensin system and the predictive value of its activation status[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(11): 2220-2226.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.11.19
| Characteristics | AKI group (n=57) | Non-AKI group (n=25) | t /χ2/Z | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | 59.65±9.71 | 58.32±8.59 | 0.58 | 0.56 |
| Gender (male/female) | 41/16 | 11/14 | 5.84 | 0.02 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.58±3.29 | 25.04±2.60 | -0.72 | 0.48 |
| Smoking [n (%)] | 16 (28.1%) | 6 (4%) | 0.15 | 0.70 |
| Alcohol consumption[n (%)] | 12 (21.1%) | 8 (32%) | 1.13 | 0.29 |
| Combined disease [n (%)] | ||||
| Diabetes | 6 (10.5%) | 2 (8%) | 0.13 | 0.72 |
| Cardiovascular disease | 3 (5.3%) | 1 (4%) | 0.06 | 0.81 |
| blood volume | 100 (50, 200) | 100 (50, 250) | -0.67 | 0.50 |
| urine output | 100 (50, 175) | 100 (50, 100) | -0.85 | 0.40 |
| Crystalloid solution (mL) | 1000 (1000, 1500) | 1500 (1000, 1500) | -1.57 | 0.12 |
| Surgery time (min) | 160 (111.5, 222) | 170 (111.5, 195) | -0.08 | 0.94 |
| sCr (mmol/L) | 70.29±11.67 | 65.48±12.59 | -1.68 | 0.09 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2 ) | 94.42±12.97 | 97.68±15.89 | 0.54 | 0.60 |
Tab. 1 Comparison of baseline data between the two groups
| Characteristics | AKI group (n=57) | Non-AKI group (n=25) | t /χ2/Z | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | 59.65±9.71 | 58.32±8.59 | 0.58 | 0.56 |
| Gender (male/female) | 41/16 | 11/14 | 5.84 | 0.02 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.58±3.29 | 25.04±2.60 | -0.72 | 0.48 |
| Smoking [n (%)] | 16 (28.1%) | 6 (4%) | 0.15 | 0.70 |
| Alcohol consumption[n (%)] | 12 (21.1%) | 8 (32%) | 1.13 | 0.29 |
| Combined disease [n (%)] | ||||
| Diabetes | 6 (10.5%) | 2 (8%) | 0.13 | 0.72 |
| Cardiovascular disease | 3 (5.3%) | 1 (4%) | 0.06 | 0.81 |
| blood volume | 100 (50, 200) | 100 (50, 250) | -0.67 | 0.50 |
| urine output | 100 (50, 175) | 100 (50, 100) | -0.85 | 0.40 |
| Crystalloid solution (mL) | 1000 (1000, 1500) | 1500 (1000, 1500) | -1.57 | 0.12 |
| Surgery time (min) | 160 (111.5, 222) | 170 (111.5, 195) | -0.08 | 0.94 |
| sCr (mmol/L) | 70.29±11.67 | 65.48±12.59 | -1.68 | 0.09 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2 ) | 94.42±12.97 | 97.68±15.89 | 0.54 | 0.60 |
| Variable | Time | AKI group (n=57) | Non-AKI group (n=25) | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urinary aldosterone (pg/mL) | T1 | 362.63±53.87 | 381.27±38.26 | 0.122 |
| T2 | 433.65±44.95 | 407.34±51.29 | 0.022 | |
| Plasma ACE 2 (pg/mL) | T1 | 219.74±29.84 | 210.82±33.05 | 0.233 |
| T2 | 210.88±36.68 | 230.60±35.13 | 0.026 | |
| Plasma Ang 1-7 (pg/mL) | T1 | 176.15±24.46 | 172.63±24.71 | 0.551 |
| T2 | 191.71±31.22 | 206.82±25.45 | 0.036 | |
| Plasma Nrf-2 (ng/mL) | T1 | 1024.12±245.77 | 978.27±204.63 | 0.417 |
| T2 | 1213.26±177.50 | 1314.99±172.10 | 0.018 | |
| Plasma IL-10 (pg/mL) | T1 | 361.55±41.98 | 360.01±42.52 | 0.879 |
| T2 | 331.06±40.14 | 351.49±40.67 | 0.038 |
Tab. 2 Comparison of aldosterone and unconventional pathway indices before (T1) and at 24 after the operation (T2) between the two groups (Mean±SD)
| Variable | Time | AKI group (n=57) | Non-AKI group (n=25) | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urinary aldosterone (pg/mL) | T1 | 362.63±53.87 | 381.27±38.26 | 0.122 |
| T2 | 433.65±44.95 | 407.34±51.29 | 0.022 | |
| Plasma ACE 2 (pg/mL) | T1 | 219.74±29.84 | 210.82±33.05 | 0.233 |
| T2 | 210.88±36.68 | 230.60±35.13 | 0.026 | |
| Plasma Ang 1-7 (pg/mL) | T1 | 176.15±24.46 | 172.63±24.71 | 0.551 |
| T2 | 191.71±31.22 | 206.82±25.45 | 0.036 | |
| Plasma Nrf-2 (ng/mL) | T1 | 1024.12±245.77 | 978.27±204.63 | 0.417 |
| T2 | 1213.26±177.50 | 1314.99±172.10 | 0.018 | |
| Plasma IL-10 (pg/mL) | T1 | 361.55±41.98 | 360.01±42.52 | 0.879 |
| T2 | 331.06±40.14 | 351.49±40.67 | 0.038 |
| Characteristics | r | P |
|---|---|---|
| Urinary aldosterone (pg/mL) | -0.294 | 0.007 |
| Plasma ACE 2 (pg/mL) | 0.241 | 0.029 |
| Plasma Ang 1-7 (pg/mL) | 0.179 | 0.108 |
| Plasma Nrf-2 (ng/mL) | 0.274 | 0.013 |
| Plasma IL-10 (pg/mL) | 0.293 | 0.008 |
Tab.3 Correlation analysis for evaluating the association of aldosterone and unconventional RAS pathway indices with eGRF 24 h post-surgery
| Characteristics | r | P |
|---|---|---|
| Urinary aldosterone (pg/mL) | -0.294 | 0.007 |
| Plasma ACE 2 (pg/mL) | 0.241 | 0.029 |
| Plasma Ang 1-7 (pg/mL) | 0.179 | 0.108 |
| Plasma Nrf-2 (ng/mL) | 0.274 | 0.013 |
| Plasma IL-10 (pg/mL) | 0.293 | 0.008 |
| Characteristics | Time | r | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urinary aldosterone (pg/mL) | T1 | -0.172 | 0.123 |
| T2 | 0.241 | 0.029 | |
| Plasma ACE 2 (pg/mL) | T1 | 0.97 | 0.387 |
| T2 | -0.26 | 0.018 | |
| Plasma Ang 1-7 (pg/mL) | T1 | 0.09 | 0.424 |
| T2 | -0.212 | 0.056 | |
| Plasma Nrf-2 (ng/mL) | T1 | 0.126 | 0.258 |
| T2 | -0.285 | 0.009 | |
| Plasma IL-10 (pg/mL) | T1 | 0.053 | 0.635 |
| T2 | -0.237 | 0.032 |
Tab. 4 Correlation analysis of aldosterone and unconventional pathway indices with AKI before (T1) and at 24 after the operation (T2) in the two groups
| Characteristics | Time | r | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urinary aldosterone (pg/mL) | T1 | -0.172 | 0.123 |
| T2 | 0.241 | 0.029 | |
| Plasma ACE 2 (pg/mL) | T1 | 0.97 | 0.387 |
| T2 | -0.26 | 0.018 | |
| Plasma Ang 1-7 (pg/mL) | T1 | 0.09 | 0.424 |
| T2 | -0.212 | 0.056 | |
| Plasma Nrf-2 (ng/mL) | T1 | 0.126 | 0.258 |
| T2 | -0.285 | 0.009 | |
| Plasma IL-10 (pg/mL) | T1 | 0.053 | 0.635 |
| T2 | -0.237 | 0.032 |
| Characteristics | Univariate analysis | Multivariate analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | P | OR | 95% CI | P | |
| Urinary aldosterone (pg/mL) | 1.01 | 1.00-1.001 | 0.026 | 1.002 | 1.000~1.004 | 0.030 |
| Plasma ACE 2 (pg/mL) | 0.98 | 0.97-0.998 | 0.030 | 0.997 | 0.994~1.000 | 0.073 |
| Plasma Ang 1-7 (pg/mL) | 0.98 | 0.96-0.998 | 0.041 | 0.998 | 0.994~1.001 | 0.143 |
| Plasma Nrf-2 (ng/mL) | 0.99 | 0.99-0.999 | 0.023 | 0.999 | 0.999~1.000 | 0.042 |
| Plasma IL-10 (pg/mL) | 0.99 | 0.97-0.999 | 0.044 | 1.001 | 0.998~1.004 | 0.516 |
Tab.5 Univariate and multivariate logistic regression analysis to identify the factors influencing AKI after LRN
| Characteristics | Univariate analysis | Multivariate analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | P | OR | 95% CI | P | |
| Urinary aldosterone (pg/mL) | 1.01 | 1.00-1.001 | 0.026 | 1.002 | 1.000~1.004 | 0.030 |
| Plasma ACE 2 (pg/mL) | 0.98 | 0.97-0.998 | 0.030 | 0.997 | 0.994~1.000 | 0.073 |
| Plasma Ang 1-7 (pg/mL) | 0.98 | 0.96-0.998 | 0.041 | 0.998 | 0.994~1.001 | 0.143 |
| Plasma Nrf-2 (ng/mL) | 0.99 | 0.99-0.999 | 0.023 | 0.999 | 0.999~1.000 | 0.042 |
| Plasma IL-10 (pg/mL) | 0.99 | 0.97-0.999 | 0.044 | 1.001 | 0.998~1.004 | 0.516 |
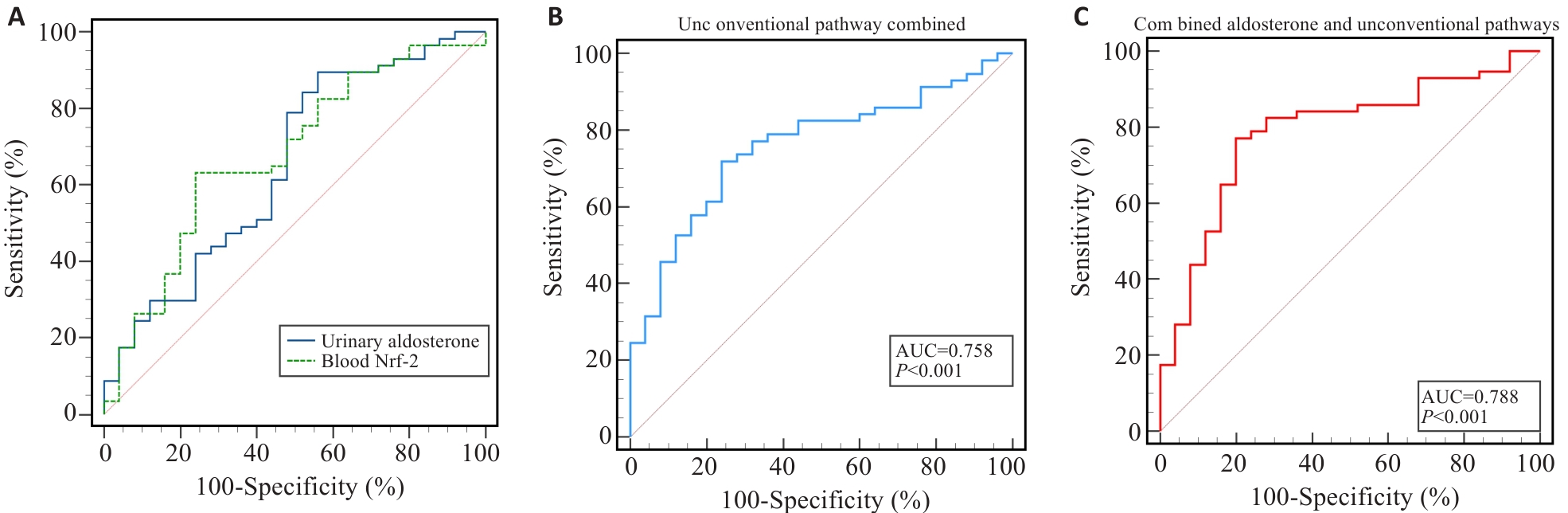
Fig.1 ROC analysis for evaluating the predictive efficacy of aldosterone and unconventional pathway indicators for AKI. A: ROC analysis of the predictive value of urinary aldosterone and plasma Nrf-2 for predicting postoperative AKI. B: ROC analysis of the predictive value of the indicators combined of the unconventional RAS pathway for AKI at 24 h postoperatively. C: ROC analysis of the predictive value of urinary aldosterone combined with the indicators of unconventional RAS pathway for AKI at 24 h postoperatively.
| 1 | Susantitaphong P, Cruz DN, Cerda J, et al. World incidence of AKI: a meta-analysis[J]. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol, 2013, 8(9): 1482-93. |
| 2 | Hur M, Park SK, Yoo S, et al. The association between intraoperative urine output and postoperative acute kidney injury differs between partial and radical nephrectomy[J]. Sci Rep, 2019, 9(1): 760. |
| 3 | Iwai M, Horiuchi M. Devil and angel in the renin-angiotensin system: ace-angiotensin II-AT1 receptor axis vs. ACE2-angiotensin-(1-7)-Mas receptor axis[J]. Hypertens Res, 2009, 32(7): 533-6. |
| 4 | Sharma N, Anders HJ, Gaikwad AB. Fiend and friend in the renin angiotensin system: an insight on acute kidney injury[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2019, 110: 764-74. |
| 5 | Martín-Fernández B, Rubio-Navarro A, Cortegano I, et al. Aldosterone induces renal fibrosis and inflammatory M1-macrophage subtype via mineralocorticoid receptor in rats[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(1): e0145946. |
| 6 | Fang F, Liu GC, Zhou XH, et al. Loss of ACE2 exacerbates murine renal ischemia-reperfusion injury[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(8): e71433. |
| 7 | Abdel-Hakeem EA, Abdel Hafez SMN, Kamel BA, et al. Angiotensin 1-7 mitigates rhabdomyolysis induced renal injury in rats via modulation of TLR-4/NF-kB/iNOS and Nrf-2/heme-oxygenase-1 signaling pathways[J]. Life Sci, 2022, 303: 120678. |
| 8 | Cheruku SR, Raphael J, Neyra JA, et al. Acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery: prediction, prevention, and management[J]. Anesthesiology, 2023, 139(6): 880-98. |
| 9 | Franzén S, Semenas E, Taavo M, et al. Renal function during sevoflurane or total intravenous propofol anaesthesia: a single-centre parallel randomised controlled study[J]. Br J Anaesth, 2022, 128(5): 838-48. |
| 10 | Kim NY, Chae D, Lee J, et al. Development of a risk scoring system for predicting acute kidney injury after minimally invasive partial and radical nephrectomy: a retrospective study[J]. Surg Endosc, 2021, 35(4): 1626-35. |
| 11 | Ellis RJ, del Vecchio SJ, Ng KL, et al. Factors associated with acutely elevated serum creatinine following radical tumour nephrectomy: the Correlates of Kidney Dysfunction-Tumour Nephrectomy Database study[J]. Transl Androl Urol, 2017, 6(5): 899-909. |
| 12 | Blasi ER, Rocha R, Rudolph AE, et al. Aldosterone/salt induces renal inflammation and fibrosis in hypertensive rats[J]. Kidney Int, 2003, 63(5): 1791-800. |
| 13 | Rafiq K, Hitomi H, Nakano D, et al. Pathophysiological roles of aldosterone and mineralocorticoid receptor in the kidney[J]. J Pharmacol Sci, 2011, 115(1): 1-7. |
| 14 | Otsuka H, Abe M, Kobayashi H. The effect of aldosterone on cardiorenal and metabolic systems[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(6): 5370. |
| 15 | Dudoignon E, Moreno N, Deniau B, et al. Activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system is associated with Acute Kidney Injury in COVID-19[J]. Anaesth Crit Care Pain Med, 2020, 39(4): 453-5. |
| 16 | Cheungpasitporn W, Thongprayoon C, Srivali N, et al. Preoperative renin-angiotensin system inhibitors use linked to reduced acute kidney injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Nephrol Dial Transplant, 2015, 30(6): 978-88. |
| 17 | Nakamura Y, Kobayashi H, Tanaka S, et al. Association between plasma aldosterone and markers of tubular and glomerular damage in primary aldosteronism[J]. Clin Endocrinol, 2021, 94(6): 920-6. |
| 18 | Donoghue M, Hsieh F, Baronas E, et al. A novel angiotensin-converting enzyme-related carboxypeptidase (ACE2) converts angiotensin I to angiotensin 1-9[J]. Circ Res, 2000, 87(5): E1-9. |
| 19 | Simões E Silva AC, Teixeira MM. ACE inhibition, ACE2 and angiotensin‑(1-7) axis in kidney and cardiac inflammation and fibrosis[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2016, 107: 154-62. |
| 20 | Wong DW, Oudit GY, Reich H, et al. Loss of angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (Ace2) accelerates diabetic kidney injury[J]. Am J Pathol, 2007, 171(2): 438-51. |
| 21 | Bae EH, Konvalinka A, Fang F, et al. Characterization of the intrarenal renin-angiotensin system in experimental alport syndrome[J]. Am J Pathol, 2015, 185(5): 1423-35. |
| 22 | Bae EH, Fang F, Williams VR, et al. Murine recombinant angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 attenuates kidney injury in experimentalAlport syndrome[J]. Kidney Int, 2017, 91(6): 1347-61. |
| 23 | Lu W, Kang J, Hu K, et al. Angiotensin-(1-7) relieved renal injury induced by chronic intermittent hypoxia in rats by reducing inflammation, oxidative stress and fibrosis[J]. Braz J Med Biol Res, 2017, 50(1): e5594. |
| 24 | Zhu Y, Xu DL, Deng F, et al. Angiotensin (1-7) attenuates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury by regulating the NF‑κB pathway[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2021, 12: 601909. |
| 25 | Wei W, Ma N, Fan XY, et al. The role of Nrf2 in acute kidney injury: novel molecular mechanisms and therapeutic approaches[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2020, 158: 1-12. |
| 26 | Guerrero-Hue M, Rayego-Mateos S, Vázquez-Carballo C, et al. Protective role of Nrf2 in renal disease[J]. Antioxidants, 2020, 10(1): 39. |
| 27 | Liu MC, Grigoryev DN, Crow MT, et al. Transcription factor Nrf2 is protective during ischemic and nephrotoxic acute kidney injury in mice[J]. Kidney Int, 2009, 76(3): 277-85. |
| 28 | Nezu M, Souma T, Yu L, et al. Transcription factor Nrf2 hyperactivation in early-phase renal ischemia-reperfusion injury prevents tubular damage progression[J]. Kidney Int, 2017, 91(2): 387-401. |
| 29 | Li JW, Li L, Wang S, et al. Resveratrol alleviates inflammatory responses and oxidative stress in rat kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury and H2O2-induced NRK-52E cells via the Nrf2/TLR4/NF-κB pathway[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2018, 45(4): 1677-89. |
| 30 | Sakai KJ, Nozaki Y, Murao Y, et al. Protective effect and mechanism of IL-10 on renal ischemia-reperfusion injury[J]. Lab Invest, 2019, 99(5): 671-83. |
| 31 | Wei W, Zhao YB, Zhang Y, et al. The role of IL-10 in kidney disease[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2022, 108: 108917. |
| 32 | Verma SK, Garikipati VNS, Krishnamurthy P, et al. Interleukin-10 inhibits bone marrow fibroblast progenitor cell-mediated cardiac fibrosis in pressure-overloaded myocardium[J]. Circulation, 2017, 136(10): 940-53. |
| 33 | Tibi S, Zeynalvand G, Mohsin H. Role of the renin angiotensin aldosterone system in the pathogenesis of sepsis-induced acute kidney injury: a systematic review[J]. J Clin Med, 2023, 12(14): 4566. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||