南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (3): 595-602.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.03.17
殷丽霞1,3( ), 牛民主2, 张可妮1,3, 耿志军2, 胡建国1,2, 李江艳1,2, 李静1,2(
), 牛民主2, 张可妮1,3, 耿志军2, 胡建国1,2, 李江艳1,2, 李静1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2024-12-03
出版日期:2025-03-20
发布日期:2025-03-28
通讯作者:
李静
E-mail:lixiayin311@163.com;sdlj13409@163.com
作者简介:殷丽霞,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: lixiayin311@163.com
基金资助:
Lixia YIN1,3( ), Minzhu NIU2, Keni ZHANG1,3, Zhijun GENG2, Jianguo HU1,2, Jiangyan LI1,2, Jing LI1,2(
), Minzhu NIU2, Keni ZHANG1,3, Zhijun GENG2, Jianguo HU1,2, Jiangyan LI1,2, Jing LI1,2( )
)
Received:2024-12-03
Online:2025-03-20
Published:2025-03-28
Contact:
Jing LI
E-mail:lixiayin311@163.com;sdlj13409@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
目的 探索升麻素(CIM)对小鼠克罗恩病(CD)样结肠炎的作用以及可能的机制。 方法 30只体质量20~23 g(6~8周龄)的C57BL/6雄性小鼠随机分为空白对照组、2,4,6-三硝基苯磺酸(TNBS)组和CIM组,10只/组。TNBS组使用TNBS灌肠建立CD样结肠炎模型,CIM组经TNBS灌肠后每日灌胃CIM(12.5 mg/kg)。通过记录小鼠体质量变化和疾病活动指数(DAI)评分,测量结肠长度,进行HE染色炎症评分以及检测肠黏膜中炎症因子水平评估CIM对小鼠结肠炎的作用;采用免疫荧光及免疫印记检测小鼠肠屏障损伤;流式细胞术检测各组小鼠肠系膜淋巴结中辅助性T细胞亚群的比例;通过网络药理学预测CIM潜在作用靶点,KEGG富集分析筛选关键通路,分子对接验证CIM与MAPK通路核心蛋白的结合能力;Western blotting验证MAPK信号通路的改变。 结果 CIM干预改善了TNBS诱导的小鼠体质量降低和结肠缩短,同时DAI评分和结肠组织炎症评分低于TNBS组(P<0.05)。ELISA和PCR检测结果显示,同TNBS组相比,CIM降低小鼠肠黏膜组织中促炎因子(IFN-γ和IL-17)的水平并促进抗炎因子(IL-4和IL-10)表达(P<0.05)。免疫荧光结果显示,CIM可改善TNBS诱导的小鼠上皮细胞Claudin-1的缺失和移位,以及杯状细胞的减少(P<0.05);免疫印记数据提示CIM组小鼠结肠黏膜中Claudin-1和ZO-1表达高于TNBS组(P<0.05)。流式细胞术检测结果表明CIM干预后肠系膜淋巴结中Th1和Th17细胞比例下降,而Th2及Treg细胞比例升高(P<0.05)。KEGG富集分析发现CIM对肠炎的作用可能与MAPK信号通路相关,分子对接显示,CIM与MAPK通路核心靶点之间有很好的结合,免疫印记结果显示p-JNK、p-ERK和p-p38在CIM组的小鼠肠黏膜中表达低于TNBS组(P<0.05)。 结论 CIM可改善肠屏障损伤从而缓解TNBS诱导的小鼠克罗恩病样结肠炎,这与其抑制MAPK信号通路的激活调节小鼠肠道Th1/Th2和Th17/Treg平衡有关。
殷丽霞, 牛民主, 张可妮, 耿志军, 胡建国, 李江艳, 李静. 升麻素抑制MAPK通路调节辅助性T细胞免疫平衡改善小鼠克罗恩病样结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 595-602.
Lixia YIN, Minzhu NIU, Keni ZHANG, Zhijun GENG, Jianguo HU, Jiangyan LI, Jing LI. Cimifugin ameliorates Crohn's disease-like colitis in mice by modulating Th-cell immune balance via inhibiting the MAPK pathway[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 595-602.
| Gene | Primer sequences (5'-3') |
|---|---|
| IL-17A | F:GGCCCTCAGACTACCTCAAC |
| R:TCTCGACCCTGAAAGTGAAGG | |
| IL-4 | F:CCCCAGCTAGTTGTCATCCTG |
| R:CAAGTGATTTTTGTCGCATCCG | |
| IL-10 | F:GCTGGACAACATACTGCTAACC |
| R:ATTTCCGATAAGGCTTGGCAA | |
| IFN-γ | F:ACAGCAAGGCGAAAAAGGATG |
| R:TGGTGGACCACTCGGATGA | |
| GAPDH | F:TGACCTCAACTACATGGTCTACA |
| R:CTTCCCATTCTCGGCCTTG |
表1 RT-qPCR的引物序列
Tab.1 Primer sequences for RT-qPCR
| Gene | Primer sequences (5'-3') |
|---|---|
| IL-17A | F:GGCCCTCAGACTACCTCAAC |
| R:TCTCGACCCTGAAAGTGAAGG | |
| IL-4 | F:CCCCAGCTAGTTGTCATCCTG |
| R:CAAGTGATTTTTGTCGCATCCG | |
| IL-10 | F:GCTGGACAACATACTGCTAACC |
| R:ATTTCCGATAAGGCTTGGCAA | |
| IFN-γ | F:ACAGCAAGGCGAAAAAGGATG |
| R:TGGTGGACCACTCGGATGA | |
| GAPDH | F:TGACCTCAACTACATGGTCTACA |
| R:CTTCCCATTCTCGGCCTTG |
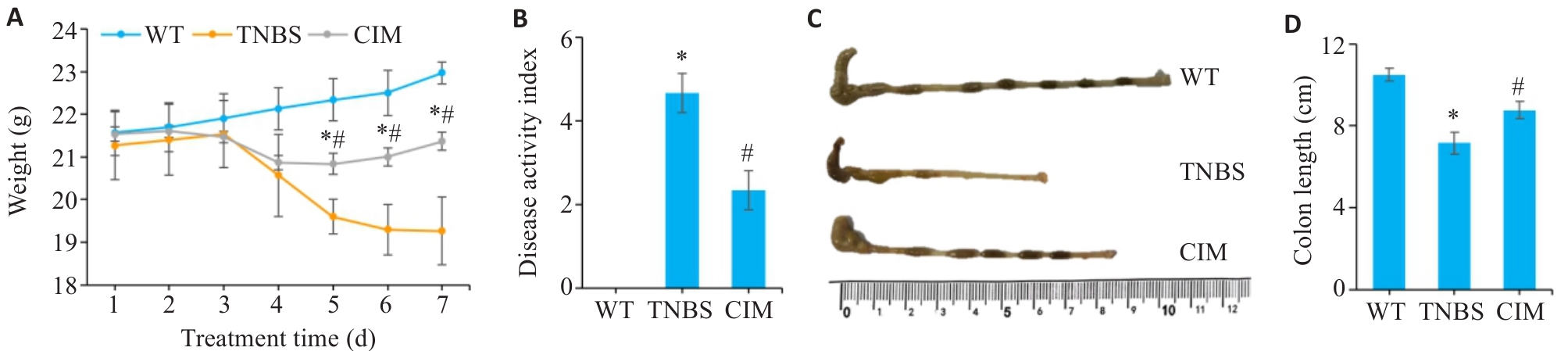
图1 CIM对小鼠实验性结肠炎症状的影响
Fig.1 Effect of cimifugin (CIM) on symptoms of TNBS-induced colitis in mice. A: Daily body weight changes of the mice in each group. B: Changes in DAI scores of the mice in each group. C: Gross observation of the mouse colon in each group. D: Comparison of colonic lengths of the mice among the 3 groups. *P<0.05 vs WT; #P<0.05 vs TNBS. WT: Type; TNBS: 2,4,6-trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid.
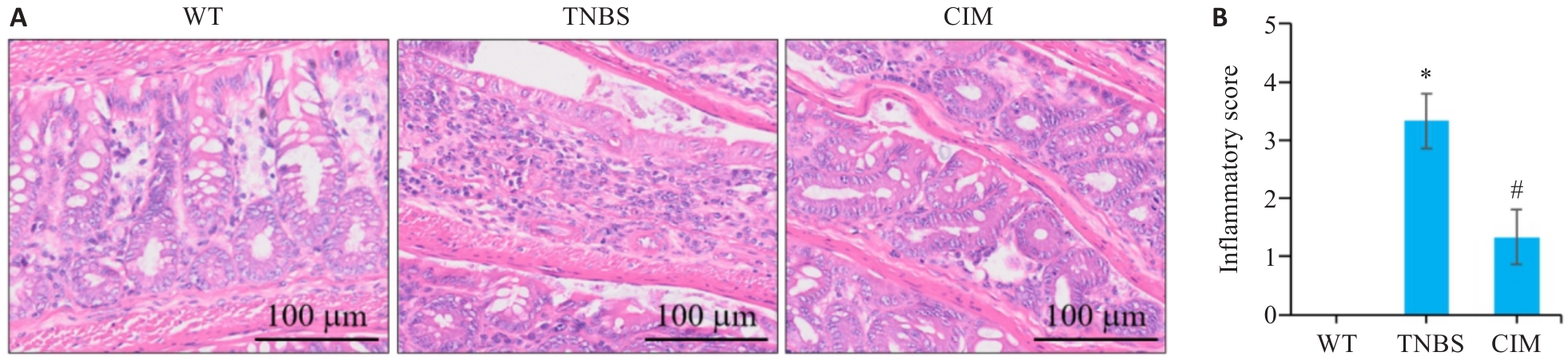
图2 CIM对小鼠实验性结肠炎肠组织损伤的影响
Fig.2 Effect of CIM on intestinal tissue damage in mice with TNBS-induced colitis. A: HE staining of mouse colon tissues. B: Inflammation scores of mouse colon tissue in each group. *P<0.05 vs WT; #P<0.05 vs TNBS.
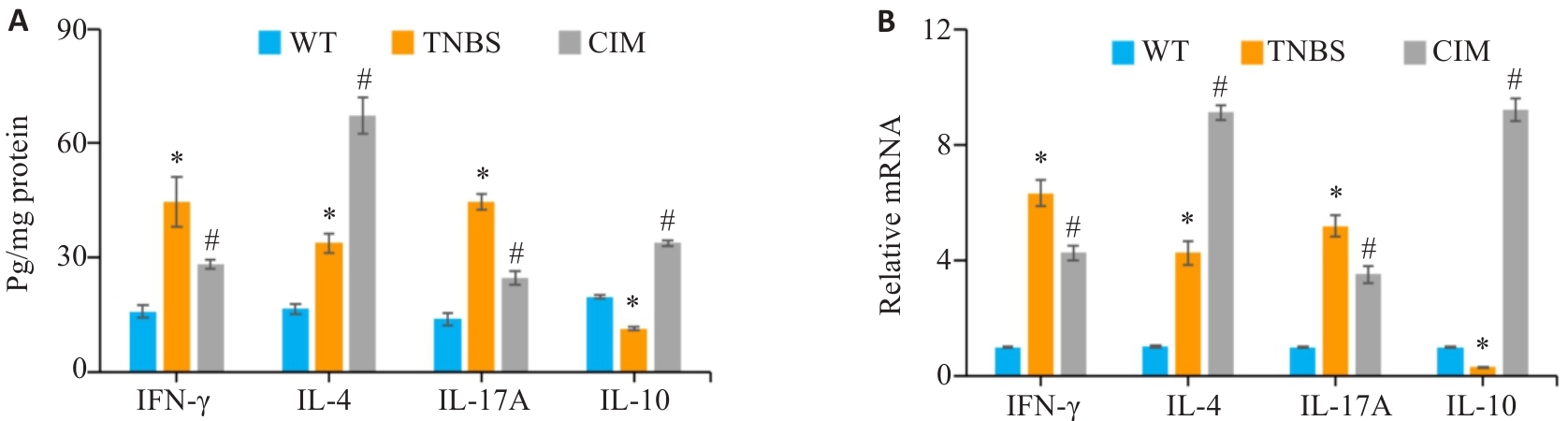
图3 CIM对小鼠实验性结肠炎肠黏膜炎症状况的影响
Fig.3 Effect of CIM on intestinal mucosa inflammation of the mice in each group. A: Levels of inflammatory factors in the colonic mucosa detected by ELISA. B: mRNA expressions of inflammatory factors in the colonic mucosa detected by PCR. *P<0.05 vs WT; #P<0.05 vs TNBS.
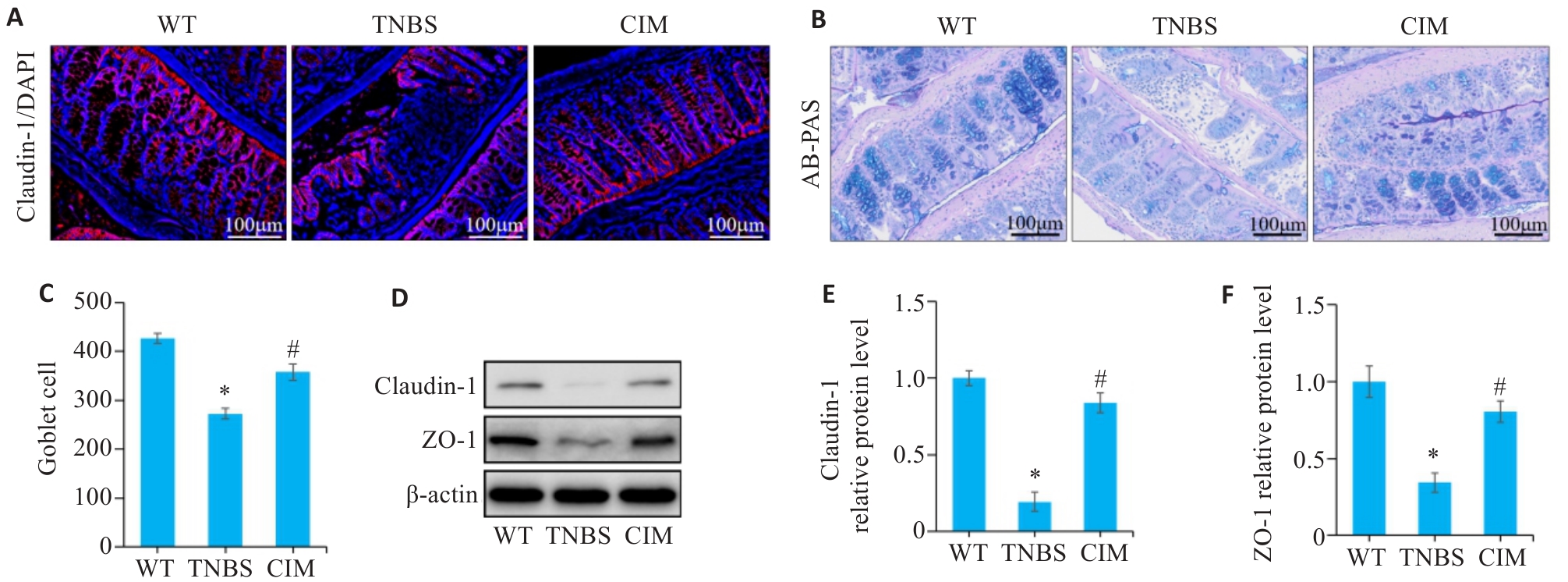
图4 CIM对小鼠实验性结肠炎肠屏障损伤的影响
Fig.4 Effect of CIM on intestinal barrier damage in mice with TNBS-induced colitis. A: Immunofluorescence staining of claudin-1 in the colon of the mice in each group. B: AB-PAS staining of mouse colon. C: Numbers of goblet cells based on AB-PAS staining. D-F: Western blotting for detecting expression levels of ZO-1 and claudin-1 in colonic mucosal tissue. *P<0.05 vs WT; #P<0.05 vs TNBS.
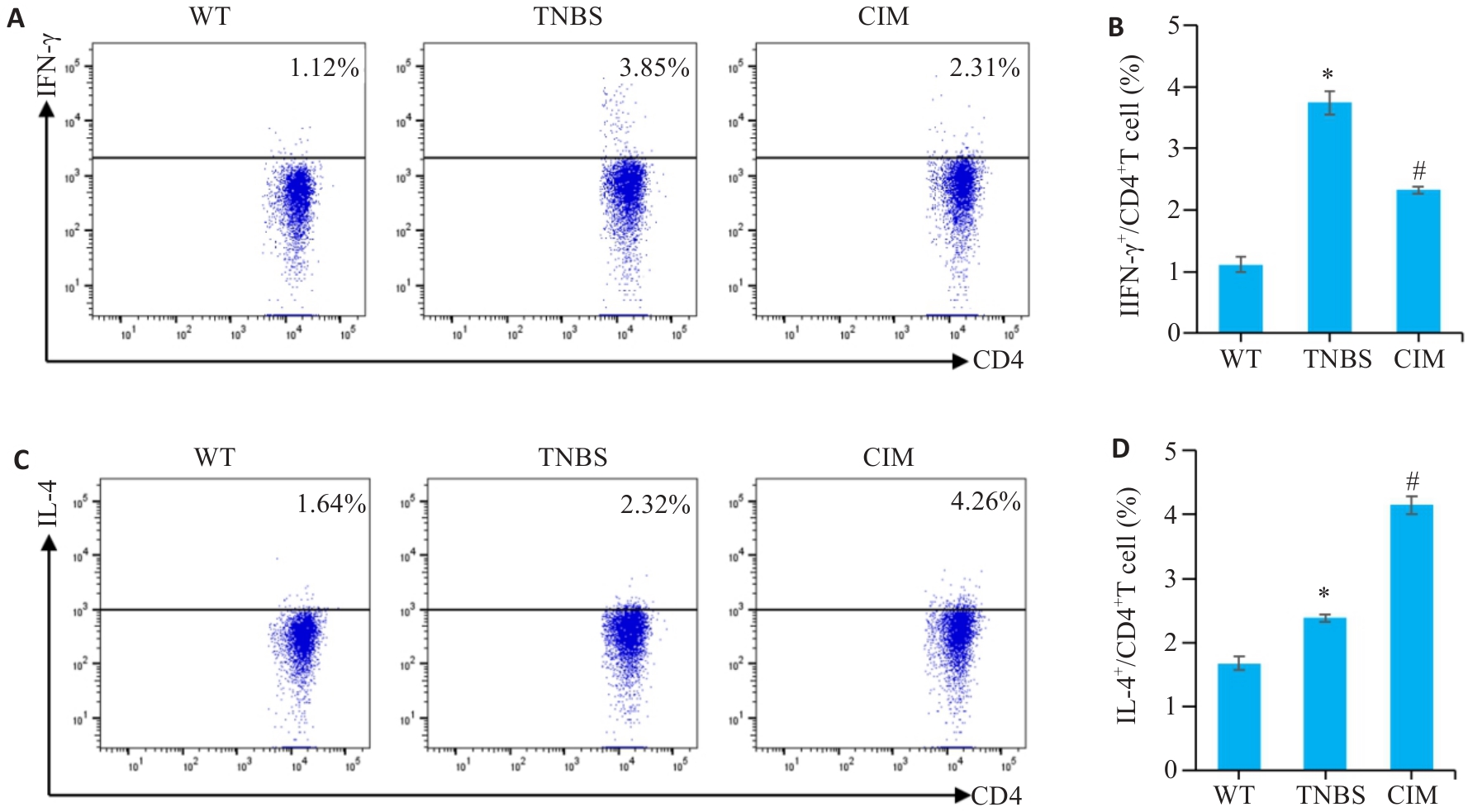
图5 CIM对实验性结肠炎小鼠Th1/Th2细胞应答平衡的影响
Fig.5 Effect of CIM on balance of Th1/Th2 cell response in mice with TNBS-induced colitis. A, B: Assessment of Th1 cell percentage in mouse mesenteric lymph nodes by flow cytometry. C, D: Assessment of Th2 cell percentage in mouse mesenteric lymph nodes by flow cytometry. *P<0.05 vs WT; #P<0.05 vs TNBS.
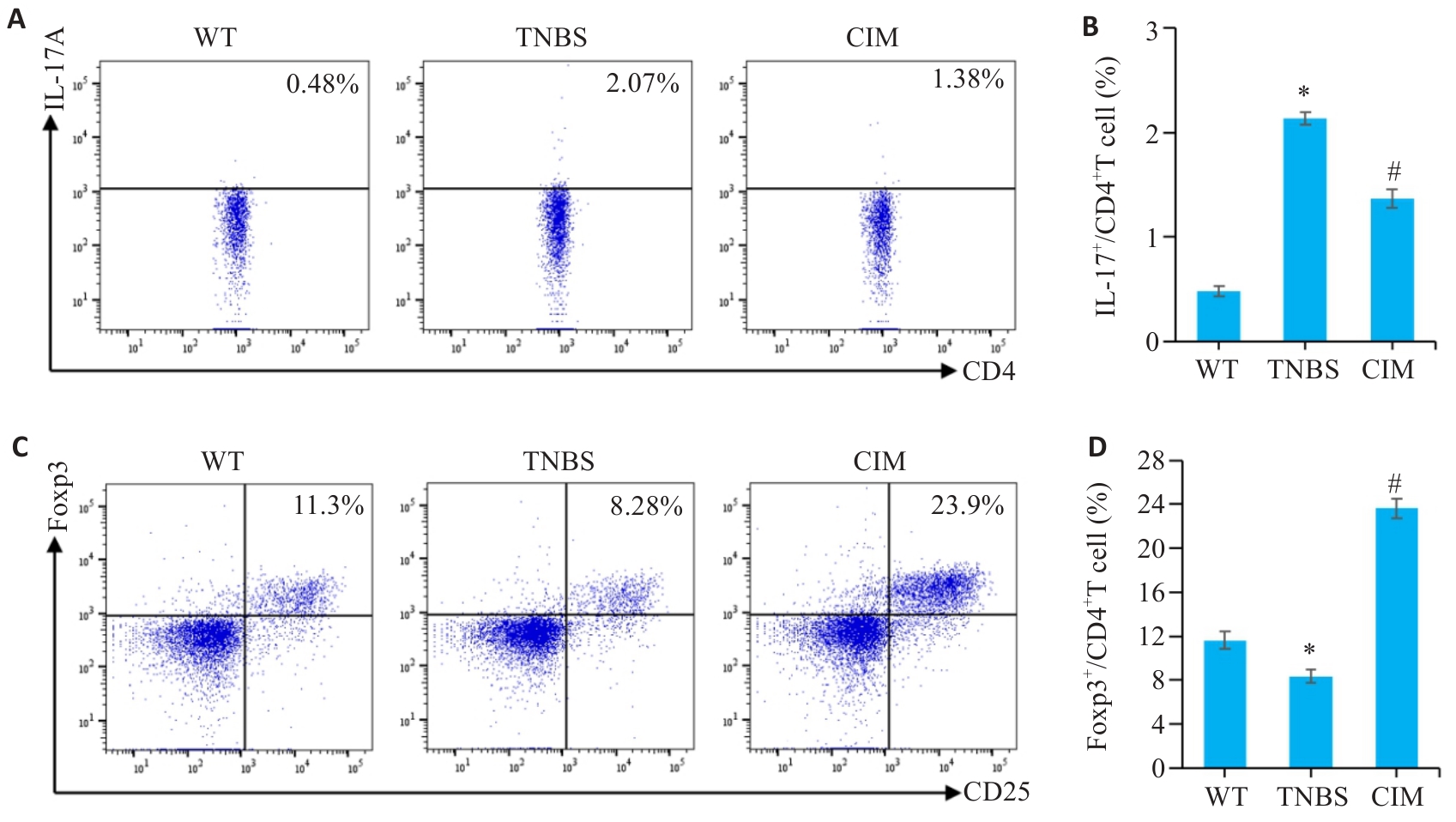
图6 CIM对实验性结肠炎小鼠Th17/Treg细胞应答平衡的影响
Fig.6 Effect of CIM on balance of Th17/Treg cell response in mice with TNBS-induced colitis. A, B: Assessment of Th17 cell percentage in mouse mesenteric lymph nodes by flow cytometry. C, D: Assessment of Treg cell percentage in mouse mesenteric lymph nodes by flow cytometry. *P<0.05 vs WT; #P<0.05 vs TNBS.
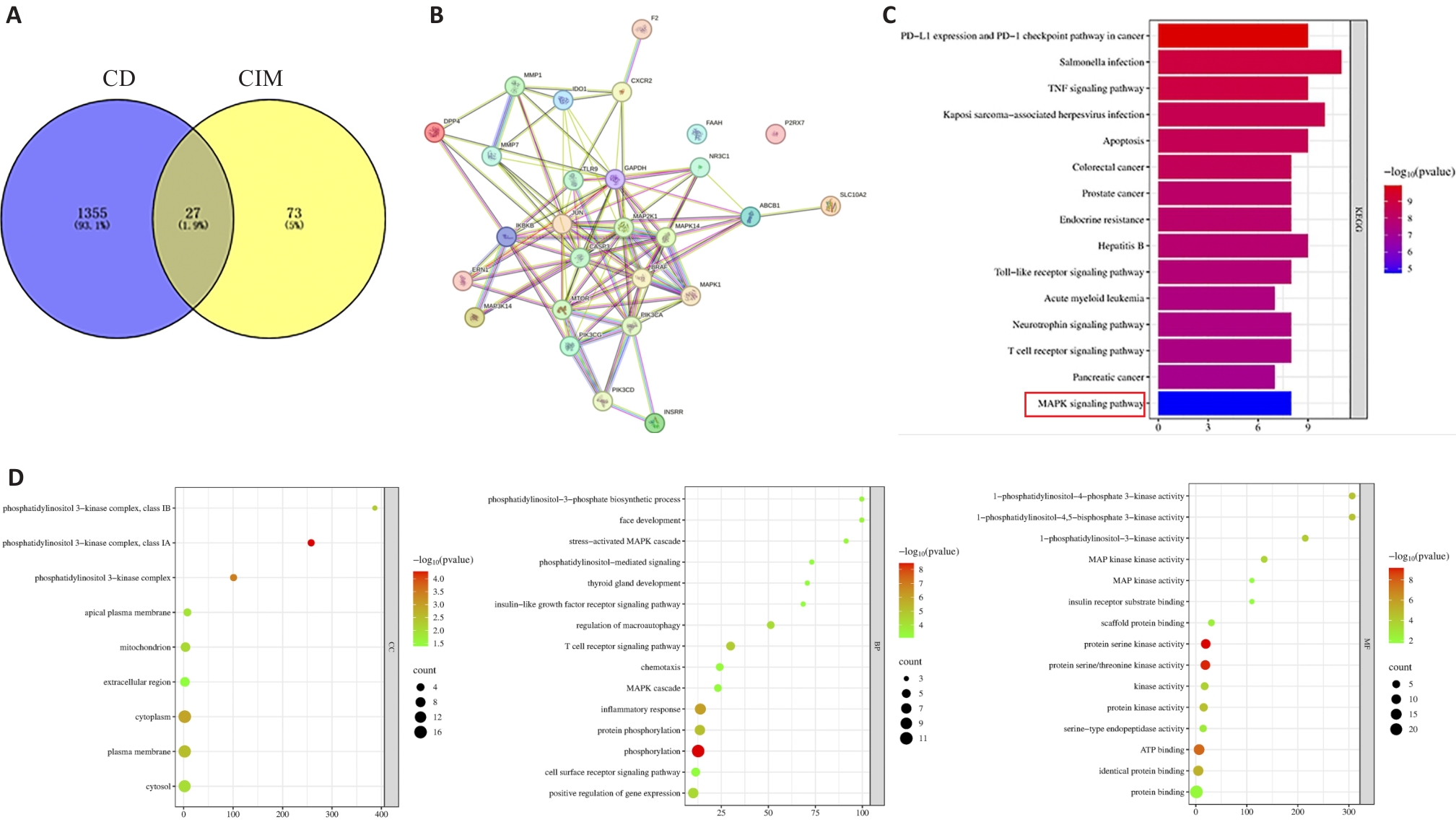
图7 CIM网络药理学及分子对接
Fig.7 CIM network pharmacology and molecular docking. A:Venn diagram. B:PPI network diagram. C:KEGG analysis. D:GO analysis(CC, BP, MF).
| Compound | Target | PDB | Energy (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CIM | MAP3K14 | 8YHW | -8.4 |
| CIM | MAP2K1 | 3EQI | -8.3 |
| CIM | MAPK14 | 6SFO | -8.2 |
| CIM | MAPK1 | 6SLG | -7.6 |
| CIM | IKBKB | 4KIK | -7.5 |
| CIM | BRAF | 5VYK | -6.7 |
| CIM | CASP3 | 1RE1 | -6.5 |
| CIM | JUN | 6Y3V | -5.7 |
表2 分子对接结果
Tab.2 Molecular docking results
| Compound | Target | PDB | Energy (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CIM | MAP3K14 | 8YHW | -8.4 |
| CIM | MAP2K1 | 3EQI | -8.3 |
| CIM | MAPK14 | 6SFO | -8.2 |
| CIM | MAPK1 | 6SLG | -7.6 |
| CIM | IKBKB | 4KIK | -7.5 |
| CIM | BRAF | 5VYK | -6.7 |
| CIM | CASP3 | 1RE1 | -6.5 |
| CIM | JUN | 6Y3V | -5.7 |
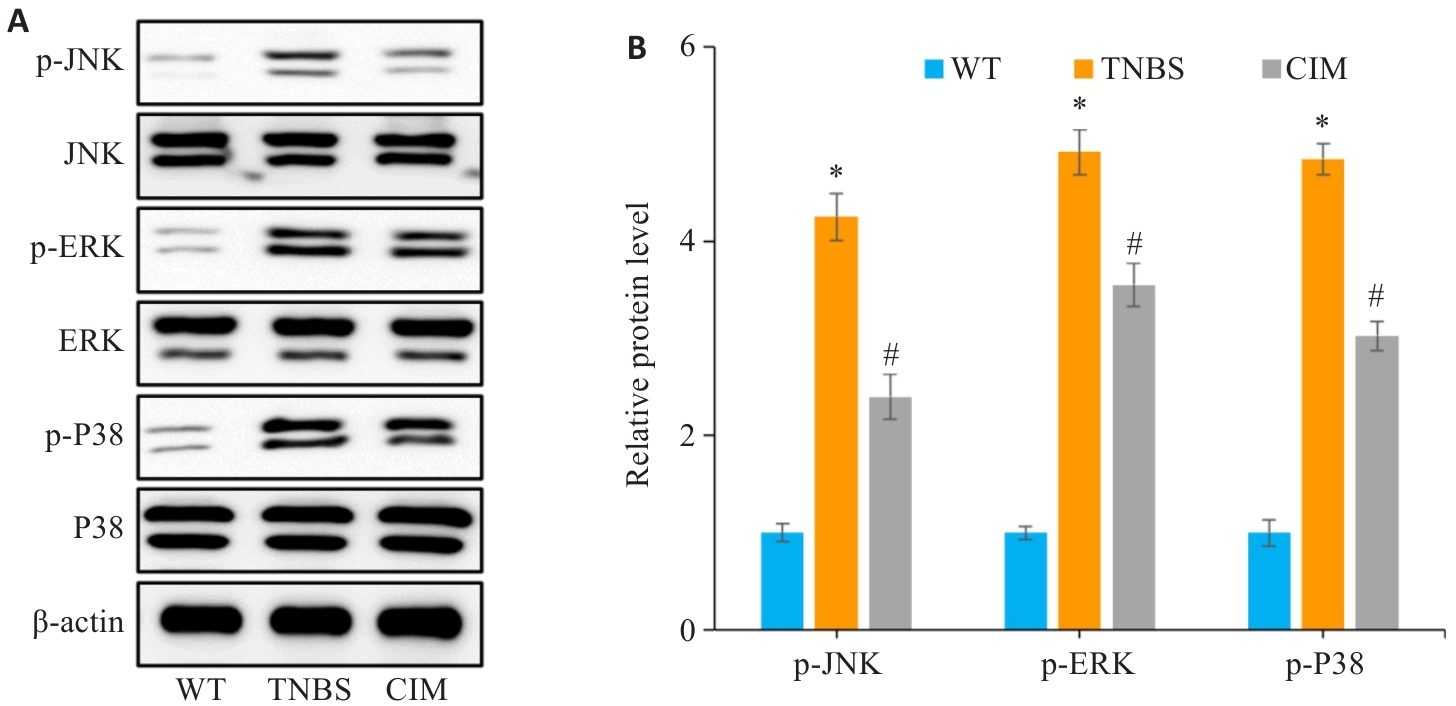
图8 验证MAPK信号通路是否参与CIM改善小鼠实验性结肠炎
Fig.8 Verification of the role of the MAPK signaling pathway in mediating the therapeutic effect of CIM on TNBS-induced colitis in mice. A, B: Expressions of key proteins of the MAPK pathway (p-p38, p-ERK and p-JNK) detected in the intestinal mucosal tissues of the mice by Western blotting. *P<0.05 vs WT; #P<0.05 vs TNBS.
| 1 | Liang WJ, Zhang W, Tian JY, et al. Advances in carbohydrate-based nanoparticles for targeted therapy of inflammatory bowel diseases: a review[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2024, 281: 136392. |
| 2 | Peyrin-Biroulet L, Ghosh S, Lee SD, et al. Effect of risankizumab on health-related quality of life in patients with Crohn's disease: results from phase 3 MOTIVATE, ADVANCE and FORTIFY clinical trials[J]. Aliment Pharmacol Ther, 2023, 57(5): 496-508. |
| 3 | Chen RR, Li C, Zheng JQ, et al. Lymphocyte subsets for predicting inflammatory bowel disease progression and treatment response: a systematic review[J]. Front Immunol, 2024, 15: 1403420. |
| 4 | Leibovitzh H, Lee SH, Garay JAR, et al. Immune response and barrier dysfunction-related proteomic signatures in preclinical phase of Crohn's disease highlight earliest events of pathogenesis[J]. Gut, 2023, 72(8): 1462-71. |
| 5 | Chang JT. Pathophysiology of inflammatory bowel diseases[J]. N Engl J Med, 2020, 383(27): 2652-64. |
| 6 | Duan SH, Cao YB, Chen PR, et al. Circulating and intestinal regulatory T cells in inflammatory bowel disease: a systemic review and meta-analysis[J]. Int Rev Immunol, 2024, 43(2): 83-94. |
| 7 | Rivera Rodríguez R, Johnson JJ. Terpenes: Modulating anti-inflammatory signaling in inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2023, 248: 108456. |
| 8 | Wei XN, Leng XH, Liang JW, et al. Pharmacological potential of natural medicine Astragali Radix in treating intestinal diseases[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2024, 180: 117580. |
| 9 | Zhu N, Zhu LY, Zhang XL, et al. Triptolide attenuates irritable bowel syndrome via inhibiting ODC1[J]. BMC Gastroenterol, 2023, 23(1): 202. |
| 10 | 李晴晴, 黄 菊, 孙 洋, 等. 乙酰紫堇灵通过抑制肠上皮细胞凋亡改善三硝基苯磺酸诱导的小鼠克罗恩病样结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(8): 1306-14. |
| 11 | 杨 子, 赵天豪, 程 阳, 等. 香叶木素通过调节小鼠的肠道免疫平衡减轻克罗恩病样结肠炎: 基于抑制PI3K/AKT通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(3): 474-82. |
| 12 | Duan J, Hu XT, Li T, et al. Cimifugin suppresses NF-κB signaling to prevent osteoclastogenesis and periprosthetic osteolysis[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2021, 12: 724256. |
| 13 | Zhang H, Xiong ZK, He YS, et al. Cimifugin improves intestinal barrier dysfunction by upregulating SIRT1 to regulate the NRF2/HO-1 signaling pathway[J]. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol, 2024. |
| 14 | Huang CY, Tan HS, Song MY, et al. Maternal Western diet mediates susceptibility of offspring to Crohn's-like colitis by deoxycholate generation[J]. Microbiome, 2023, 11(1): 96. |
| 15 | Li CL, Liu MG, Deng L, et al. Oxyberberine ameliorates TNBS-induced colitis in rats through suppressing inflammation and oxidative stress via Keap1/Nrf2/NF‑κB signaling pathways[J]. Phytomedicine, 2023, 116: 154899. |
| 16 | Gu XQ, Chen YY, Qian PY, et al. Cimifugin suppresses type 2 airway inflammation by binding to SPR and regulating its protein expression in a non-enzymatic manner[J]. Phytomedicine, 2023, 111: 154657. |
| 17 | Huang LY, Qian WW, Xu YH, et al. Mesenteric adipose tissue contributes to intestinal fibrosis in Crohn's disease through the ATX-LPA axis[J]. J Crohns Colitis, 2022, 16(7): 1124-39. |
| 18 | 韩康宁, 胡俊杰, 李 娟, 等. 二妙四土汤调控JAK/STAT通路治疗湿热型湿疹大鼠的药效与作用机制探讨[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2024,[Epub ahead of print]. |
| 19 | Li XW, Di QQ, Li XL, et al. Kumujan B suppresses TNF-α-induced inflammatory response and alleviates experimental colitis in mice[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2024, 15: 1427340. |
| 20 | Liu AM, Zhao W, Zhang BX, et al. Cimifugin ameliorates imiquimod-induced psoriasis by inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammation via NF-κB/MAPK pathway[J]. Biosci Rep, 2020, 40(6): BSR20200471. |
| 21 | Han B, Dai Y, Wu HY, et al. Cimifugin inhibits inflammatory responses of RAW264.7 cells induced by lipopolysaccharide[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2019, 25: 409-17. |
| 22 | Xiang ZJ, Zhang BB, Cao SY, et al. SPH7854, a gut-limited RORγt antagonist, ameliorates TNBS-induced experimental colitis in rat[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2024, 140: 112884. |
| 23 | Chen GX, Ran X, Li B, et al. Sodium butyrate inhibits inflammation and maintains epithelium barrier integrity in a TNBS-induced inflammatory bowel disease mice model[J]. EBioMedicine, 2018, 30: 317-25. |
| 24 | 李前昆, 宾东华, 尹园缘, 等. 参苓白术散对克罗恩病大鼠炎症因子IL-1β、IL-1、IL-17C、IL-10及IL-4的影响[J]. 湖南中医药大学学报, 2023, 43(8): 1361-7. |
| 25 | Zhou Y, Xiong XY, Cheng Z, et al. Ginsenoside Rb1 alleviates DSS-induced ulcerative colitis by protecting the intestinal barrier through the signal network of VDR, PPARγ and NF-κB[J]. Drug Des Devel Ther, 2024, 18: 4825-38. |
| 26 | Zhou LY, Zhu LG, Wu XM, et al. Decreased TMIGD1 aggravates colitis and intestinal barrier dysfunction via the BANF1-NF‑κB pathway in Crohn’s disease[J]. BMC Med, 2023, 21(1): 287. |
| 27 | Hou QH, Huang JX, Ayansola H, et al. Intestinal stem cells and immune cell relationships: potential therapeutic targets for inflammatory bowel diseases[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 11: 623691. |
| 28 | Naama M, Telpaz S, Awad A, et al. Autophagy controls mucus secretion from intestinal goblet cells by alleviating ER stress[J]. Cell Host Microbe, 2023, 31(3): 433-46. e4. |
| 29 | Gustafsson JK, Johansson MEV. The role of goblet cells and mucus in intestinal homeostasis[J]. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 19(12): 785-803. |
| 30 | Clough JN, Omer OS, Tasker S, et al. Regulatory T-cell therapy in Crohn's disease: challenges and advances[J]. Gut, 2020, 69(5): 942-52. |
| 31 | Zeng F, Shi YH, Wu CN, et al. A drug-free nanozyme for mitigating oxidative stress and inflammatory bowel disease[J]. J Nanobio-technology, 2022, 20(1): 107. |
| 32 | Kosinsky RL, Gonzalez MM, Saul D, et al. The FOXP3+ pro-inflammatory T cell: a potential therapeutic target in Crohn's disease[J]. Gastroenterology, 2024, 166(4): 631-44. e17. |
| 33 | Feng YJ, Li YY. The role of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease[J]. J Dig Dis, 2011, 12(5): 327-32. |
| 34 | Li JH, Jia JH, Teng Y, et al. Gastrodin alleviates DSS-induced colitis in mice through strengthening intestinal barrier and modulating gut microbiota[J]. Foods, 2024, 13(15): 2460. |
| 35 | Broom OJ, Widjaya B, Troelsen J, et al. Mitogen activated protein kinases: a role in inflammatory bowel disease[J]? Clin Exp Immunol, 2009, 158(3): 272-80. |
| 36 | Liu ML, Ding JH, Zhang HM, et al. Lactobacillus casei LH23 modulates the immune response and ameliorates DSS-induced colitis via suppressing JNK/p-38 signal pathways and enhancing histone H3K9 acetylation[J]. Food Funct, 2020, 11(6): 5473-85. |
| [1] | 李国永, 黎仁玲, 刘艺婷, 柯宏霞, 李菁, 王新华. 牛蒡子治疗小鼠病毒性肺炎后肺纤维化的机制:基于代谢组学、网络药理学和实验验证方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1185-1199. |
| [2] | 牛民主, 殷丽霞, 乔通, 尹林, 张可妮, 胡建国, 宋传旺, 耿志军, 李静. 旱莲苷A通过调控JAK2/STAT3通路抑制M1型巨噬细胞极化改善葡聚糖硫酸钠诱导的小鼠结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1297-1306. |
| [3] | 黄菊, 殷丽霞, 牛民主, 耿志军, 左芦根, 李静, 胡建国. 紫花前胡苷通过抑制肠上皮细胞焦亡改善2,4,6-三硝基苯磺酸诱导的小鼠实验性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 261-268. |
| [4] | 刘硕, 李静, 吴兴旺. Swertiamarin通过抑制肠上皮细胞细胞凋亡改善TNBS诱导的实验性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1545-1552. |
| [5] | 王南, 石斌, 马小兰, 吴伟超, 曹佳. FMRP通过激活RAS/MAPK信号通路抑制结直肠肿瘤细胞的铁死亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 885-893. |
| [6] | 戎圣炜, 李宏芳, 魏怡然, 冯子航, 甘 露, 邓仲豪, 赵 亮. 锌指蛋白-36缺陷抑制小鼠的成骨细胞分化:基于激活ERK/MAPK通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(4): 697-705. |
| [7] | 席 进, 张 敏, 张永玉, 张 晨, 张雨路, 王 锐, 申 林, 李 静, 宋 雪. 上调KLF11可改善结肠炎模型小鼠的肠道炎症:基于抑制JAK2/STAT3信号通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(4): 765-772. |
| [8] | 牛民主, 殷丽霞, 段婷, 黄菊, 李静, 耿志军, 胡建国, 宋传旺. 川续断皂苷VI通过抑制PI3K/AKT/NF-κB通路拮抗肠上皮细胞凋亡缓解TNBS诱导的小鼠克罗恩病样结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(12): 2335-2346. |
| [9] | 刘桐佳, 王万伦, 张 婷, 刘 爽, 边艳超, 张传领, 肖 瑞. 小鼠初级精母细胞GC-2中TUBB4B的表达及其对NF-κB和MAPK信号通路的调控[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(6): 1002-1009. |
| [10] | 邵荣瑢, 杨 子, 张文静, 张 诺, 赵雅静, 张小凤, 左芦根, 葛思堂. 茯苓酸缓解小鼠克罗恩病:基于抑制PI3K/AKT信号通路拮抗肠上皮细胞凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(6): 935-942. |
| [11] | 杨 子, 赵天豪, 程 阳, 周约青, 李岳彤, 王欣茹, 张小凤, 左芦根, 葛思堂. 香叶木素通过调节小鼠的肠道免疫平衡减轻克罗恩病样结肠炎:基于抑制PI3K/AKT通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(3): 474-482. |
| [12] | 周 慧, 张雨晴, 甘 超, 范喜瑞, 戚之琳, 齐世美. 圣草次苷抑制肝细胞癌SMMC-7721细胞的增殖和迁移:基于激活ROS/MAPKs信号轴[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(3): 412-419. |
| [13] | 曾心靛, 陈 利, 周 鹏, 唐 婷, 陈 曦, 胡 丹, 王 川, 陈丽丽. 鹦鹉热衣原体III型分泌蛋白SINC通过激活MAPK/ERK信号通路促进宿主细胞自噬[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(2): 294-299. |
| [14] | 刘峥璐, 宣成睿, 韩希然, 郑泽泽, 肖 瑞, 宝鲁日, 徐晓艳. LASS2/TMSG1过表达抑制人肺癌A549细胞增殖和促进A549细胞凋亡:基于上调神经酰胺和p38 MAPK进而启动级联信号传导通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(2): 166-174. |
| [15] | 张嘉发, 杨灿洪, 张淑芬, 曹婷婷, 彭 瑞, 郭蔚泓, 严予苹, 谢淑婷, 彭晓佳, 吕田明, 黄添容. 莱菔硫烷通过下调MAPK/NF-κB信号通路逆转Aβ纤维介导的M1型小胶质细胞极化和神经炎症介导的神经干细胞程序性坏死[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(12): 2132-2138. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||