南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (3): 494-505.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.03.07
收稿日期:2024-11-20
出版日期:2025-03-20
发布日期:2025-03-28
通讯作者:
高磊
E-mail:1197448288@qq.com;raygaolei@smu.edu.cn
作者简介:黄 妍,在读本科生,E-mail: 1197448288@qq.com
基金资助:
Yan HUANG1( ), Xi CHEN1, Mengchen QIN1, Lei GAO1,2,3(
), Xi CHEN1, Mengchen QIN1, Lei GAO1,2,3( )
)
Received:2024-11-20
Online:2025-03-20
Published:2025-03-28
Contact:
Lei GAO
E-mail:1197448288@qq.com;raygaolei@smu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
目的 基于网络药理学和体内实验验证分析活络效灵丹促进组织修复的潜在核心靶点与免疫调控机制。 方法 基于网络药理学筛选活络效灵丹的活性成分以及疾病作用靶点,利用STRING数据库构建PPI筛选核心蛋白,并进行GO、KEGG富集分析以及分子对接预测活络效灵丹的药理机制。体内实验:通过斑马鱼药毒实验评估活络效灵丹的毒性作用,并将3 dpf幼鱼尾鳍切除95%建立斑马鱼尾鳍截断模型,设置模型组(胚胎水)、活络效灵丹低、中、高浓度干预组(10、20、40 μg/mL),通过再生面积观察和qPCR检测评估活络效灵丹促进组织再生的药效及核心靶点。利用巨噬细胞和中性粒细胞双荧光标记的转基因斑马鱼,观察免疫细胞在不同修复阶段的迁移情况,qPCR检测组织再生不同时间段巨噬细胞的分型。 结果 筛选出活络效灵丹中活性成分与组织修复共有149个交集靶点,其中核心靶点有AKT1、IL-6、TNF-α、EGFR、STAT3,结合GO和KEGG富集分析提示活络效灵丹主要通过JAK-STAT信号通路、黏附连接、对细胞迁移的正向调控等发挥作用。药毒实验显示,药物安全浓度为40 μg/mL,致死浓度为320 μg/mL,超过80 μg/mL活络效灵丹可导致斑马鱼幼鱼出现肾脏、心包水肿及血管发育不良。体内实验中,与模型组相比,活络效灵丹药物干预组斑马鱼尾鳍修复面积增高(P<0.05),同时显著抑制IL-6、TNF-α,激活AKT1、EGFR、STAT3基因的表达(P<0.05)。活络效灵丹可以调节再生部位中性粒细胞和巨噬细胞的聚集,并在组织再生不同时间段调节M1和M2型巨噬细胞的极化(P<0.05)。 结论 在斑马鱼尾鳍再生过程中,活络效灵丹通过多成分、多靶点和多通路机制显著促进组织修复。其功能可能涉及调节伤口局部的免疫细胞迁移及巨噬细胞极化,从而有效减轻炎症反应,促进愈合进程。
黄妍, 陈曦, 秦梦晨, 高磊. 活络效灵丹促进斑马鱼尾鳍再生的核心靶点与免疫调控机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 494-505.
Yan HUANG, Xi CHEN, Mengchen QIN, Lei GAO. Core targets and immune regulatory mechanisms of Huoluo Xiaoling Pellet for promoting zebrafish fin regeneration[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 494-505.
| Gene | Sequence of FP (5'-3') | Sequence of RP (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| Zf β-actin | ATGGATGAGGAAATCGCTGCC | CTCCTGATGTCTGGGTCGTC |
| Zf PCNA | TATGGACTCCTCTCATGTGTCTCTG | GTGATGATGTCTTCATTTCCAGCAC |
| Zf AKT1 | GATTACGGTCGTGCGGTGGA | TCCACCTAACCGCTGCATGG |
| Zf EGFR | GTGACCCGTCCCGCTATCTG | GTGGGGTCTGGGATGTAGCG |
| Zf STAT3 | AACGTGCAGCCCATTTTCGC | CCACGGAAACAAGCGCAGTC |
| Zf TLR4 | GACCGTGTTTGTTCGCTGCC | TTCAACTACAGCCCCACGGC |
| Zf NOS2 | CGGATCAGGAGGAGGATCGC | CGTGCTGCAAGTGCCGAAAT |
| Zf IL10 | CGCTTCTTCTTTGCGACTGTGCT | TCACCATATCCCGCTTGAGTTCC |
| Zf TNF-α | GCTGGATCTTCAAAGTCGGGTGTA | TGTGAGTCTCAGCACACTTCCATC |
| Zf TGF-β | GAACTCGCTTTGTCTCCA | TACAGTCGCAGTATAACCTCA |
| Zf IL-6 | CGGCATTTGAAGGGGTCAGGA | TGGCCTCCAGCAGTCGTTTG |
| Zf IL-1β | TGGACTTCGCAGCACAAAATG | CACTTCACGCTCTTGGATGA |
| Zf fgf20a | AAAAGCTGTCAGCCGAGTGT | TGGACGTCCCATCTTTGTTG |
| Zf msxb | ACACTTTGTCGAGCGTTTCGG | TCTTGTGCTTGCGTAAGGTGC |
| Zf IL4 | GGGATCCTGAATGGGAAAGGGG | AAGCCATTCCTGCTTGGCAGA |
| Zf IL13 | CTGGCCTGTCCGGTGTCAAAT | CTTCATCAGCAGCGTGACTCCT |
| Zf ARG1 | GGCCAGCCGATGTCTTACCT | GGGTCCAGCGCATCAATGTC |
| Zf ifng1 | GATGGGCTTTGCCTGGGGAG | TGCCAGCCTCTCCTTTGTAGC |
表1 用于定量mRNA表达的引物
Tab.1 Primers used to quantify mRNA expression
| Gene | Sequence of FP (5'-3') | Sequence of RP (5'-3') |
|---|---|---|
| Zf β-actin | ATGGATGAGGAAATCGCTGCC | CTCCTGATGTCTGGGTCGTC |
| Zf PCNA | TATGGACTCCTCTCATGTGTCTCTG | GTGATGATGTCTTCATTTCCAGCAC |
| Zf AKT1 | GATTACGGTCGTGCGGTGGA | TCCACCTAACCGCTGCATGG |
| Zf EGFR | GTGACCCGTCCCGCTATCTG | GTGGGGTCTGGGATGTAGCG |
| Zf STAT3 | AACGTGCAGCCCATTTTCGC | CCACGGAAACAAGCGCAGTC |
| Zf TLR4 | GACCGTGTTTGTTCGCTGCC | TTCAACTACAGCCCCACGGC |
| Zf NOS2 | CGGATCAGGAGGAGGATCGC | CGTGCTGCAAGTGCCGAAAT |
| Zf IL10 | CGCTTCTTCTTTGCGACTGTGCT | TCACCATATCCCGCTTGAGTTCC |
| Zf TNF-α | GCTGGATCTTCAAAGTCGGGTGTA | TGTGAGTCTCAGCACACTTCCATC |
| Zf TGF-β | GAACTCGCTTTGTCTCCA | TACAGTCGCAGTATAACCTCA |
| Zf IL-6 | CGGCATTTGAAGGGGTCAGGA | TGGCCTCCAGCAGTCGTTTG |
| Zf IL-1β | TGGACTTCGCAGCACAAAATG | CACTTCACGCTCTTGGATGA |
| Zf fgf20a | AAAAGCTGTCAGCCGAGTGT | TGGACGTCCCATCTTTGTTG |
| Zf msxb | ACACTTTGTCGAGCGTTTCGG | TCTTGTGCTTGCGTAAGGTGC |
| Zf IL4 | GGGATCCTGAATGGGAAAGGGG | AAGCCATTCCTGCTTGGCAGA |
| Zf IL13 | CTGGCCTGTCCGGTGTCAAAT | CTTCATCAGCAGCGTGACTCCT |
| Zf ARG1 | GGCCAGCCGATGTCTTACCT | GGGTCCAGCGCATCAATGTC |
| Zf ifng1 | GATGGGCTTTGCCTGGGGAG | TGCCAGCCTCTCCTTTGTAGC |

图3 活络效灵丹治疗组织修复交集靶点GO功能(A)和KEGG通路富集分析图(B)
Fig.3 GO function (A) and KEGG pathway (B) enrichment analysis diagram of Huoluo Xiaoling Pellet-tissue repair intersection targets.
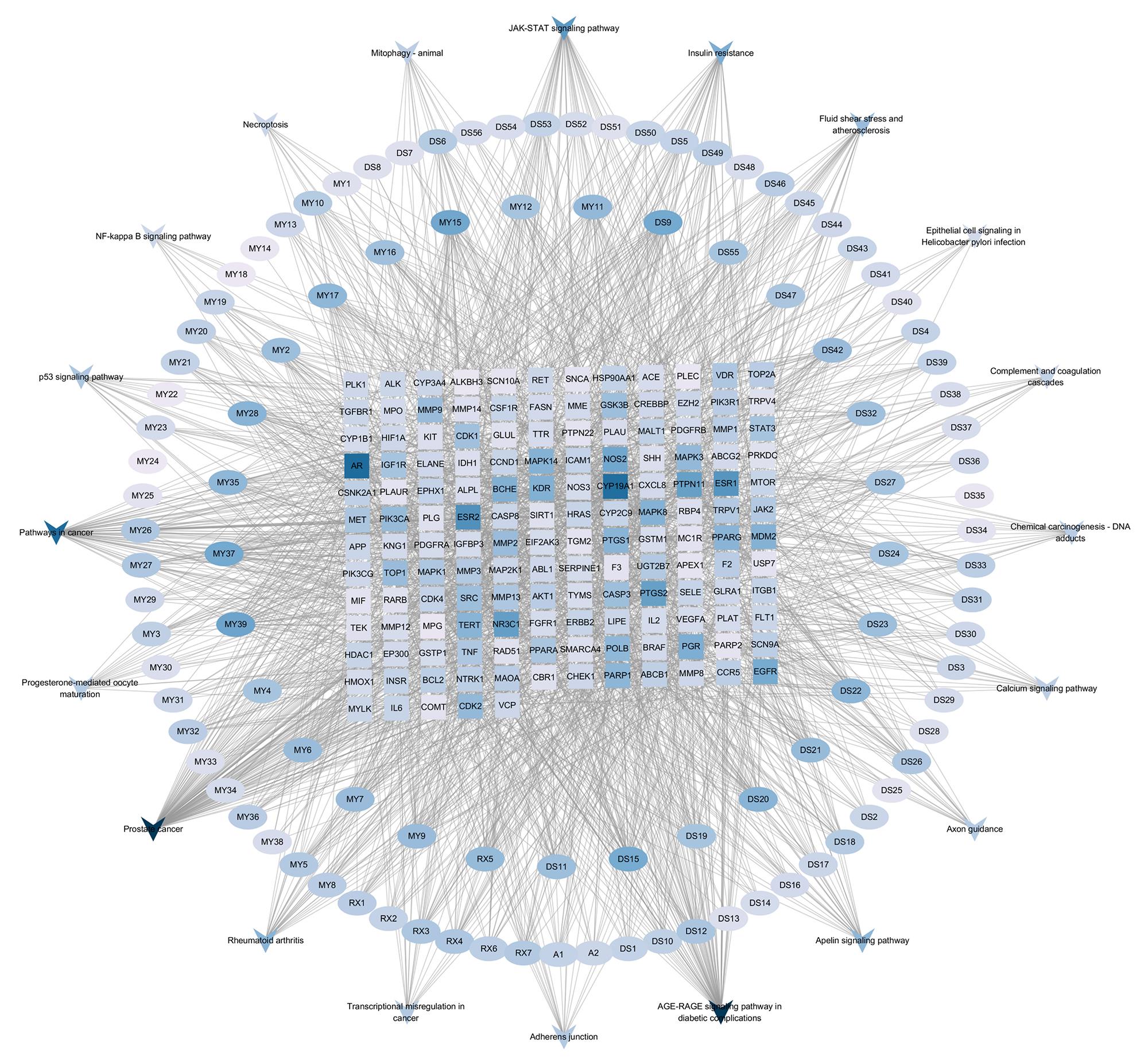
图4 活络效灵丹治疗组织修复"活性成分-靶点-信号通路"网络
Fig.4 "Active ingredient-target-signaling pathway" network of Huoluo Xiaoling Pellet for promoting tissue repair. Elliptical markers represent active ingredients, rectangular markers represent the targets, and inverted triangle markers represent the signaling pathways. DG, DS, RX, and MY denote Danggui, Danshen, Ruxiang, and Moyao, respectively.
| Number | Mol ID | Active ingredient | Degree | Betweenness centrality | Closeness centrality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MY39 | MOL000490 | petunidin | 37 | 0.02587001 | 0.4317817 |
| MY15 | MOL001033 | diayangambin | 36 | 0.02263804 | 0.42630745 |
| DS9 | MOL000006 | luteolin | 35 | 0.01654172 | 0.42902711 |
| MY37 | MOL001164 | [(5S, 6R, 8R, 9Z)-8-methoxy-3, 6, 10-trimethyl-4-oxo-6, 7, 8, 11-tetrahydro-5H-cyclodeca[b]furan-5-yl] acetate | 35 | 0.01612 | 0.42630745 |
| DS15 | MOL007049 | 4-methylenemiltirone | 34 | 0.01770958 | 0.42362205 |
| DS20 | MOL007061 | methylenetanshinquinone | 29 | 0.01130007 | 0.41965679 |
| MY28 | MOL001095 | isofouquierone | 29 | 0.0106332 | 0.40573152 |
| DS22 | MOL007064 | przewalskin b | 28 | 0.00999823 | 0.41194487 |
| MY17 | MOL001045 | (13E, 17E, 21E)-8-hydroxypolypodo-13, 17, 21-trien-3-one | 27 | 0.01052943 | 0.40943683 |
| MY35 | MOL001148 | 3β-hydroxydammar-24-ene | 27 | 0.00947679 | 0.41194487 |
表2 活络效灵丹度值排名前10的活性成分
Tab.2 Top 10 active ingredients in Huoluo Xiaoling Pellet
| Number | Mol ID | Active ingredient | Degree | Betweenness centrality | Closeness centrality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MY39 | MOL000490 | petunidin | 37 | 0.02587001 | 0.4317817 |
| MY15 | MOL001033 | diayangambin | 36 | 0.02263804 | 0.42630745 |
| DS9 | MOL000006 | luteolin | 35 | 0.01654172 | 0.42902711 |
| MY37 | MOL001164 | [(5S, 6R, 8R, 9Z)-8-methoxy-3, 6, 10-trimethyl-4-oxo-6, 7, 8, 11-tetrahydro-5H-cyclodeca[b]furan-5-yl] acetate | 35 | 0.01612 | 0.42630745 |
| DS15 | MOL007049 | 4-methylenemiltirone | 34 | 0.01770958 | 0.42362205 |
| DS20 | MOL007061 | methylenetanshinquinone | 29 | 0.01130007 | 0.41965679 |
| MY28 | MOL001095 | isofouquierone | 29 | 0.0106332 | 0.40573152 |
| DS22 | MOL007064 | przewalskin b | 28 | 0.00999823 | 0.41194487 |
| MY17 | MOL001045 | (13E, 17E, 21E)-8-hydroxypolypodo-13, 17, 21-trien-3-one | 27 | 0.01052943 | 0.40943683 |
| MY35 | MOL001148 | 3β-hydroxydammar-24-ene | 27 | 0.00947679 | 0.41194487 |
| Active ingredient | AKT1 | IL6 | TNF | EGFR | STAT3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Petunidin | -8.945 | -5.695 | -8.657 | -6.666 | -5.256 |
| Diayangambin | -9.256 | -4.711 | -6.801 | -6.224 | -4.331 |
| Luteolin | -9.539 | -6.244 | -8.509 | -7.556 | -5.601 |
[(5S, 6R, 8R, 9Z)-8-methoxy-3, 6, 10-trimethyl-4-oxo-6, 7, 8, 11- tetrahydro-5H-cyclodeca[b]furan-5-yl] acetate | -8.202 | -5.165 | -7.881 | -6.628 | -4.732 |
| 4-methylenemiltirone | -10.652 | -6.558 | -8.393 | -8.194 | -5.372 |
表3 分子对接结合能预测
Tab.3 Molecular docking binding energy prediction
| Active ingredient | AKT1 | IL6 | TNF | EGFR | STAT3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Petunidin | -8.945 | -5.695 | -8.657 | -6.666 | -5.256 |
| Diayangambin | -9.256 | -4.711 | -6.801 | -6.224 | -4.331 |
| Luteolin | -9.539 | -6.244 | -8.509 | -7.556 | -5.601 |
[(5S, 6R, 8R, 9Z)-8-methoxy-3, 6, 10-trimethyl-4-oxo-6, 7, 8, 11- tetrahydro-5H-cyclodeca[b]furan-5-yl] acetate | -8.202 | -5.165 | -7.881 | -6.628 | -4.732 |
| 4-methylenemiltirone | -10.652 | -6.558 | -8.393 | -8.194 | -5.372 |
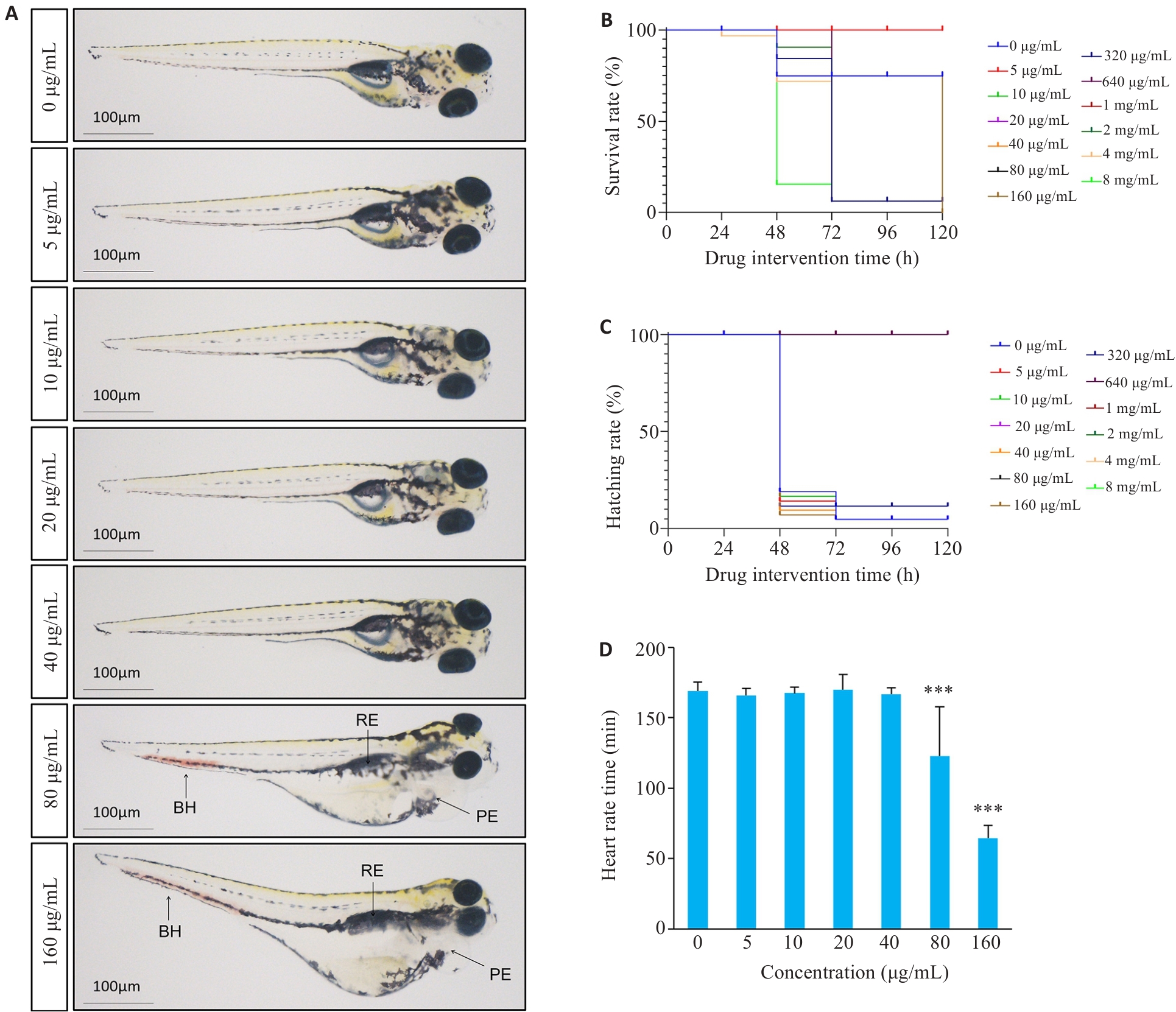
图5 活络效灵丹对斑马鱼幼鱼的毒性作用
Fig.5 Toxic effects of Huoluo Xiaoling Pellet extract on zebrafish larvae (Mean±SD, n=30). A: Effect of Huoluo Xiaoling Pellet extract on zebrafish larvae growth and development (VD: Vasodilation; RE: Renal edema; PE: Pericardial edema). B: Survival rate. C: Hatching rate. D: Heart rate. ***P<0.001 vs 0 μg/mL group.
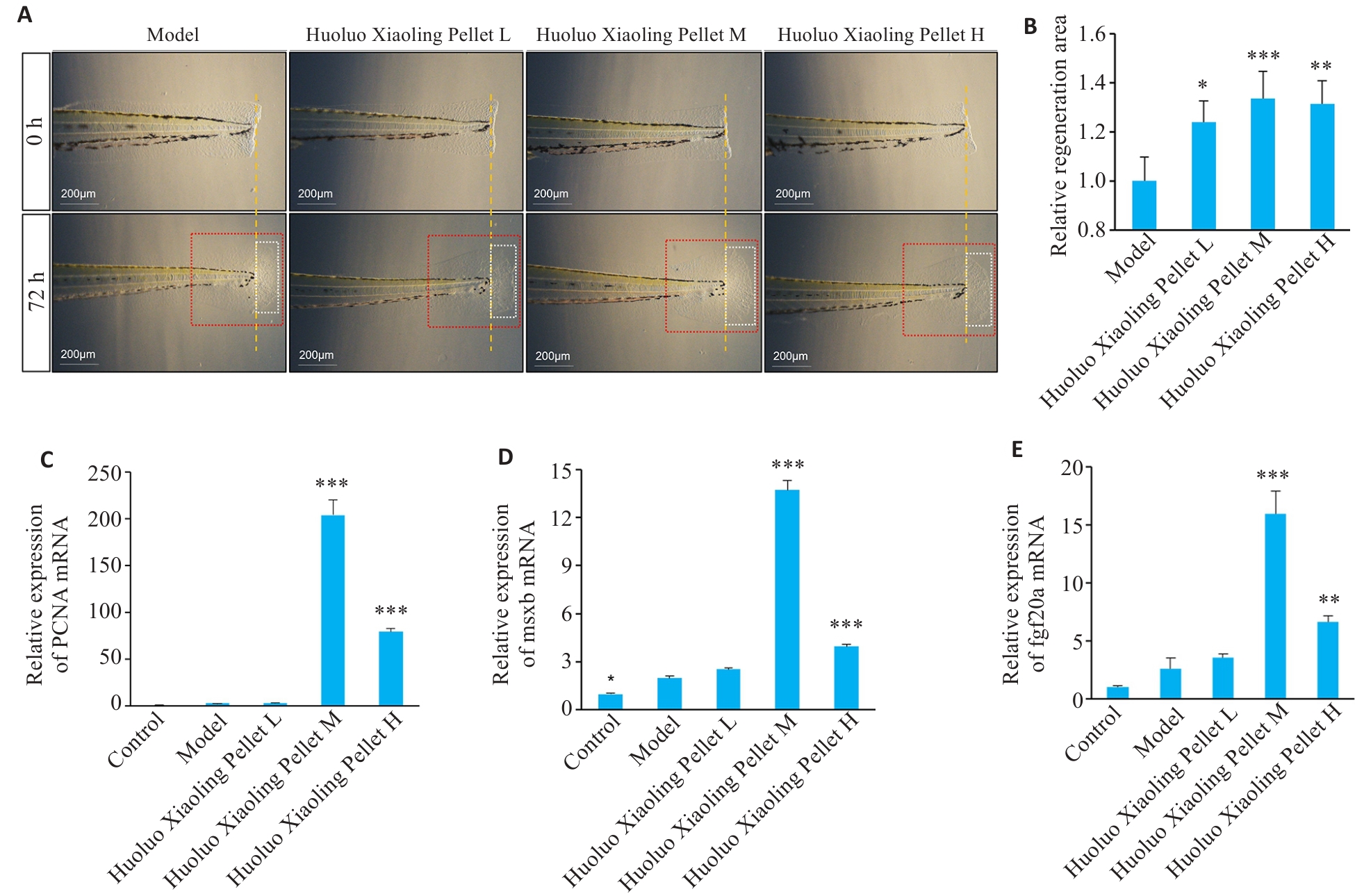
图6 不同浓度活络效灵丹干预斑马鱼尾鳍组织修复
Fig.6 Effect of different concentrations of Huoluo Xiaoling Pellet extract on tail fin tissue defect repair in the zebrafish. A: Changes in tail fin defect of the zebrafish after treatment with formulated medium (model group) and low-, medium-, and high-dose Huoluo Xiaoling Pellet extract. B: Relative area of tail fin tissue repair measured 72 h post-surgery in different groups (Mean±SD, n=4). C-E: Expression levels of PCNA, msxb and fgf20a mRNA in zebrafish 72 h after tail fin amputation (Mean±SD, n=3). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs Model group.
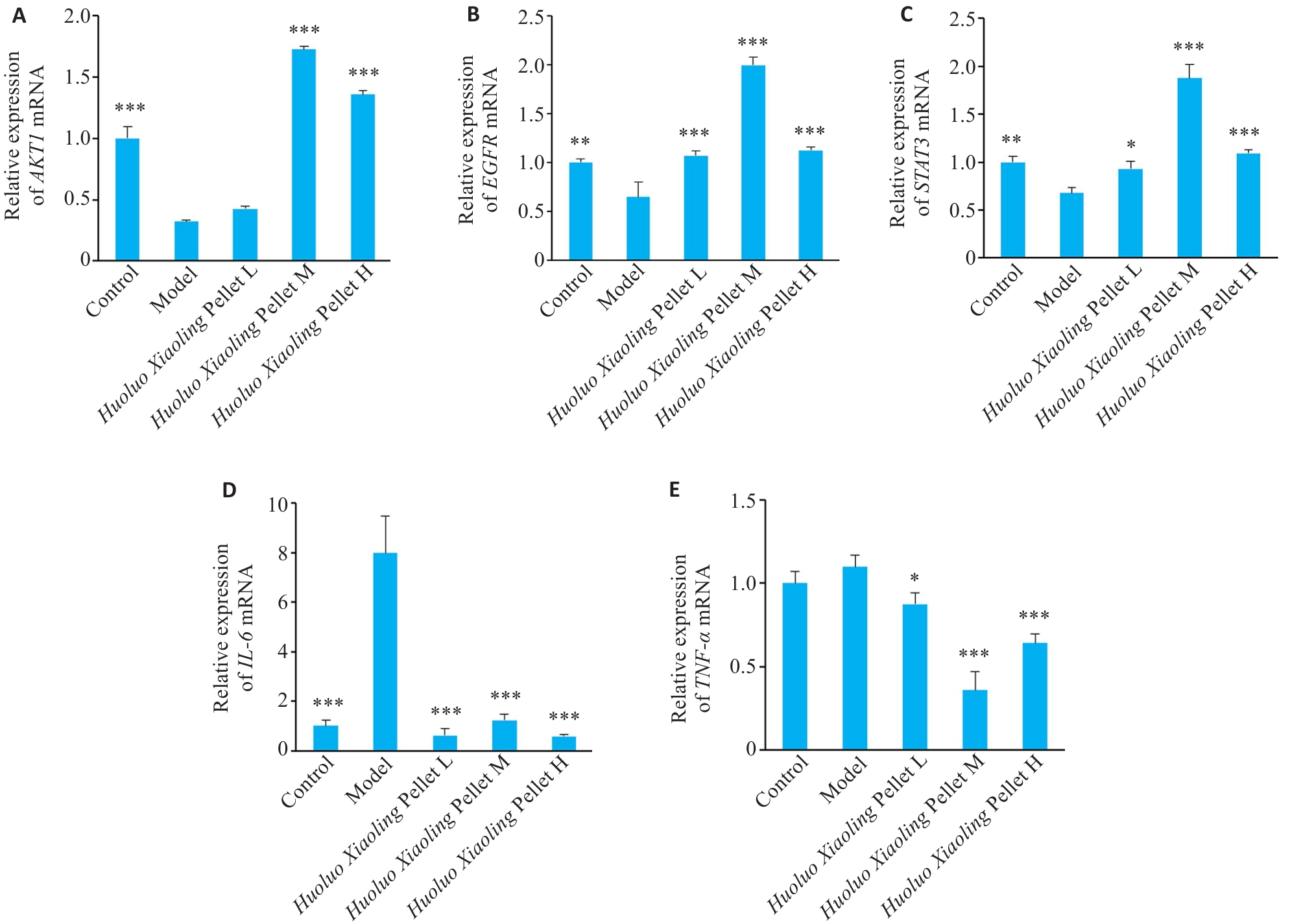
图7 不同浓度活络效灵丹干预斑马鱼尾鳍修复相关核心靶点表达
Fig.7 Effect of different concentrations of Huoluo Xiaoling Pellet extract on expressions of the core targets related to tail fin repair in zebrafish (Mean±SD, n=3). A-E: The mRNA expression levels of AKT1, EGFR, STAT3, IL-6, and TNF-α in zebrafish 72 h after tail fin amputation. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs Model group.

图8 活络效灵丹调节斑马鱼尾鳍伤口处不同时期巨噬细胞和中性粒细胞的迁移
Fig.8 Huoluo Xiaoling Pellet regulates migration of macrophages and neutrophils in the wound of zebrafish tail fin (Mean±SD, n=3). A, B: Distribution of macrophages and neutrophils at the injury site of the tail fin of zebrafish at 24 h and 48 h. C, D: Statistical analysis of macrophage and neutrophil migration to the tissue repair site at 24 h and 48 h. E: The mRNA expression levels of ifng1 in zebrafish detected by qPCR. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs Model group; #P<0.05 vs 48 h Model group.
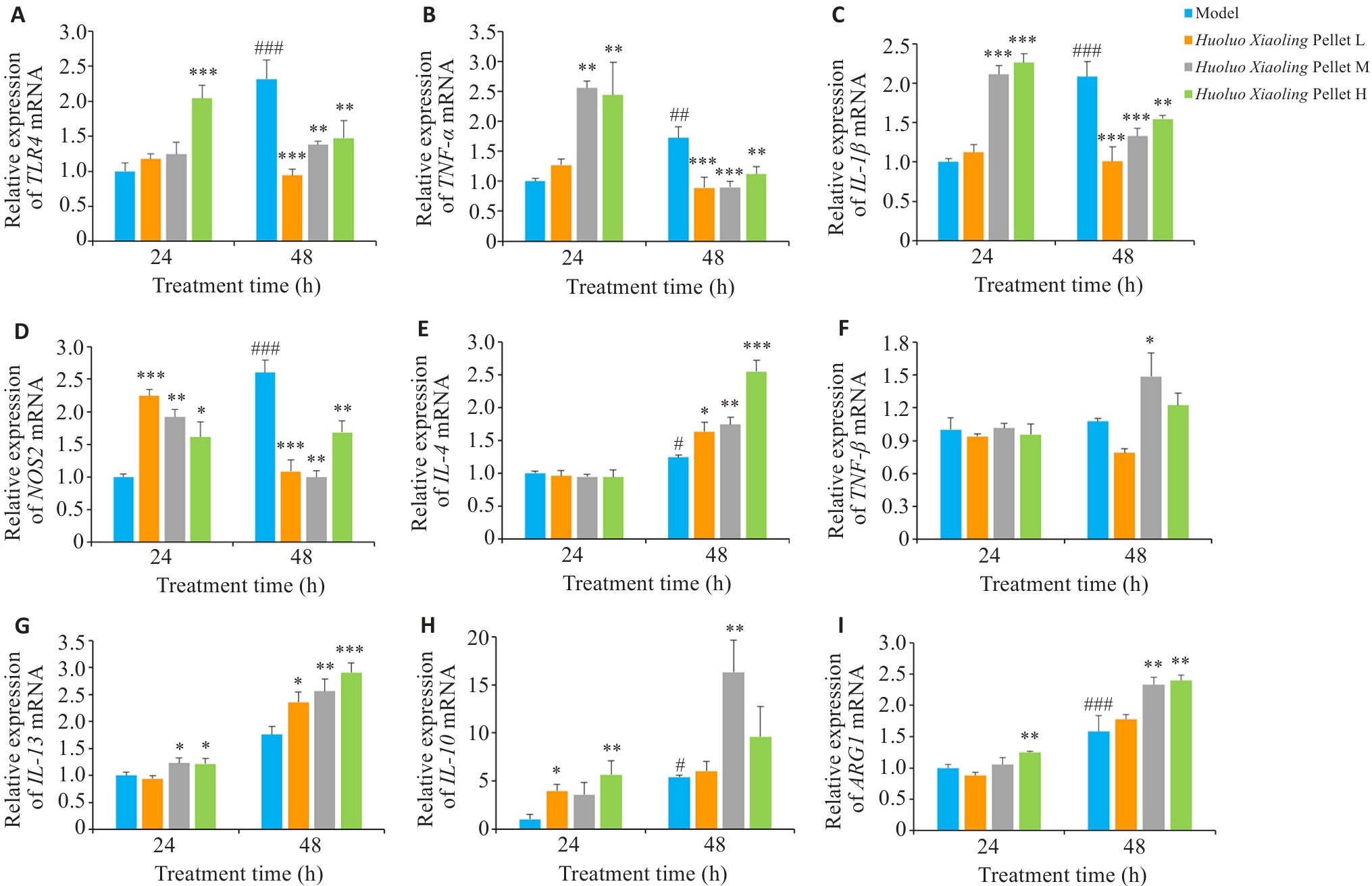
图9 活络效灵丹调节再生不同阶段巨噬细胞分型标记物的表达
Fig.9 Huoluo Xiaoling Pellet regulates expressions of macrophage subset markers at different stages of tissue regeneration (Mean±SD, n=3). A-I: The mRNA expression levels of TLR4, TNF-α, IL-1β, NOS2, IL-4, TGF-β, IL-13, IL-10 and ARG1 in zebrafish detected by qPCR. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs Model group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01, ###P<0.001 vs 48 h Model group.
| 1 | Xiong Y, Mi BB, Lin Z, et al. The role of the immune microenvironment in bone, cartilage, and soft tissue regeneration: from mechanism to therapeutic opportunity[J]. Mil Med Res, 2022, 9(1): 65. |
| 2 | Eming SA, Martin P, Tomic-Canic M. Wound repair and regeneration: mechanisms, signaling, and translation[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2014, 6(265): 265sr6. |
| 3 | Gurtner GC, Werner S, Barrandon Y, et al. Wound repair and regeneration[J]. Nature, 2008, 453(7193): 314-21. |
| 4 | Mosser DM, Edwards JP. Exploring the full spectrum of macrophage activation[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2008, 8(12): 958-69. |
| 5 | (明)王肯堂. 证治准绳-四-疡医: 六卷[M]. 上海卫生出版社, 1958. |
| 6 | 鄢红玉, 万 飞, 郭剑华, 等. 活络效灵丹加减方对大鼠急性软组织损伤的保护作用及机制初探[J]. 重庆医学, 2019, 48(16): 2737-42. |
| 7 | 徐英姿, 韩向东. 关于活络效灵丹的浅析[J]. 四川中医, 2014, 32(9): 28-30. |
| 8 | 孔令钧. 血瘀证患者与细胞粘附分子表达的关系[J]. 山东大学学报: 医学版, 2004, 42(3): 346-8. |
| 9 | 廖奕华, 艾 陵, 张道亮, 等. 冠心病血瘀证患者免疫功能的初步研究[J]. 辽宁中医杂志, 1998, 25(2): 58-9. |
| 10 | Zhang P, Zhang DF, Zhou WA, et al. Network pharmacology: towards the artificial intelligence-based precision traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Brief Bioinform, 2023, 25(1): bbad518. |
| 11 | Marques IJ, Lupi E, Mercader N. Model systems for regeneration: zebrafish[J]. Development, 2019, 146(18): dev167692. |
| 12 | Howe K, Clark MD, Torroja CF, et al. The zebrafish reference genome sequence and its relationship to the human genome[J]. Nature, 2013, 496(7446): 498-503. |
| 13 | 陈家奎. slc20a1b调控斑马鱼造血干祖细胞的功能研究及机制初探[D]. 广州: 南方医科大学, 2021. |
| 14 | 王和鸣. 中医伤科学[M]. 北京: 中国中医药出版社, 2002. |
| 15 | 清)吴 谦. 医宗金鉴: 九十卷[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 1963. |
| 16 | 吴虓飞, 高晓新, 高 阳, 等. 活络效灵丹颗粒对大鼠的长期毒性试验研究[J]. 药物评价研究, 2016, 39(6): 973-82. |
| 17 | Whitehead GG, Makino S, Lien CL, et al. fgf20 is essential for initiating zebrafish fin regeneration[J]. Science, 2005, 310(5756): 1957-60. |
| 18 | Thummel R, Enright JM, Kassen SC, et al. Pax6a and Pax6b are required at different points in neuronal progenitor cell proliferation during zebrafish photoreceptor regeneration[J]. Exp Eye Res, 2010, 90(5): 572-82. |
| 19 | Sigismund S, Avanzato D, Lanzetti L. Emerging functions of the EGFR in cancer[J]. Mol Oncol, 2018, 12(1): 3-20. |
| 20 | 曾鸿孟. MEBT/MEBO对大鼠难愈合创面中PTEN/AKT/VEGF信号系统表达的影响[D]. 南宁: 广西中医药大学, 2017. |
| 21 | Sun JC, Zhao HQ, Shen CA, et al. Tideglusib promotes wound healing in aged skin by activating PI3K/Akt pathway[J]. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2022, 13(1): 269. |
| 22 | Liu JF, Guo S, Jiang KF, et al. miR-488 mediates negative regulation of the AKT/NF‑κB pathway by targeting Rac1 in LPS-induced inflammation[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2020, 235(5): 4766-77. |
| 23 | Sano S, Itami S, Takeda K, et al. Keratinocyte-specific ablation of Stat3 exhibits impaired skin remodeling, but does not affect skin morphogenesis[J]. EMBO J, 1999, 18(17): 4657-68. |
| 24 | Bouchery T, Harris N. Neutrophil-macrophage cooperation and its impact on tissue repair[J]. Immunol Cell Biol, 2019, 97(3): 289-98. |
| 25 | Qin MC, Ou RX, He WY, et al. Salvianolic acid B enhances tissue repair and regeneration by regulating immune cell migration and Caveolin-1-mediated blastema formation in zebrafish[J]. Phytomedicine, 2024, 130: 155553. |
| 26 | Wynn TA, Vannella KM. Macrophages in tissue repair, regeneration, and fibrosis[J]. Immunity, 2016, 44(3): 450-62. |
| 27 | Yaghi OK, Hanna BS, Kent Langston P, et al. A discrete 'early-responder' stromal-cell subtype orchestrates immunocyte recruitment to injured tissue[J]. Nat Immunol, 2023, 24(12): 2053-67. |
| 28 | Lohmann N, Schirmer L, Atallah P, et al. Glycosaminoglycan-based hydrogels capture inflammatory chemokines and rescue defective wound healing in mice[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2017, 9(386): eaai9044. |
| 29 | Gocher AM, Workman CJ, Vignali DAA. Interferon-γ: teammate or opponent in the tumour microenvironment[J]? Nat Rev Immunol, 2022, 22(3): 158-72. |
| 30 | Mantovani A, Sica A, Locati M. Macrophage polarization comes of age[J]. Immunity, 2005, 23(4): 344-6. |
| 31 | Mantovani A, Biswas SK, Galdiero MR, et al. Macrophage plasticity and polarization in tissue repair and remodelling[J]. J Pathol, 2013, 229(2): 176-85. |
| [1] | 郭新邓, 郭卓琳, 孙冬梅, 邹丽芳, 区锦莹, 余林中, 卢子滨, 曹惠慧, 刘俊珊. 连翘配方颗粒与饮片的抗炎、抗肿瘤和抑菌效果的比较研究[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 594-604. |
| [2] | 张榆雪, 蓝洁莹, 马昕怡, 周琼, 秦梦晨, 高磊. 化橘红配方颗粒通过维持铁稳态并抑制脂质过氧化和铁死亡缓解斑马鱼脂肪性肝病[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(12): 2265-2275. |
| [3] | 郭志华, 王志鹏, 曾琳玲, 纪雪霞. 丙泊酚对不同发育时期斑马鱼鞘磷脂蛋白表达的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(10): 1810-1814. |
| [4] | 周丹,戴丽霞,刘小莲,阙富昌,许玉燕,罗昕,祝瑶露,刘叔文,李亦蕾,余乐. 硼替佐米与obatoclax双重阻断蛋白质降解途径对人急性T淋巴白血病细胞具有协同抗肿瘤作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2019, 39(04): 401-. |
| [5] | 刘川,林春水,郭培培,张昕,朱晓勤. 胚胎期斑马鱼丙泊酚暴露可下调髓鞘碱性蛋白的表达[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2018, 38(09): 1115-. |
| [6] | 陈毅飞,彭菊,房淼,刘怡,聂玲辉,莫志贤,朱玲玲. 钩藤碱对甲基苯丙胺依赖斑马鱼行为学的影响及机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2016, 36(11): 1541-. |
| [7] | 郑新春,刘莉,戴文聪,王坤元,陈小辉,赵灵凤,黄志斌,侯金林. 过度喂养建立斑马鱼幼鱼肥胖模型[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2016, 36(01): 20-. |
| [8] | 殷果,姚芳,陈小辉,王楠,王惠丽,常红恩,苑召虎,吴炳义. 酒精能够减少斑马鱼胚胎的神经前体细胞并抑制其神经元和神经胶质细胞的分化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2014, 34(11): 1555-. |
| [9] | 王坤元,刘莉,戴文聪,陈小辉,郑新春,侯金林. 二乙基亚硝胺诱导建立斑马鱼肝纤维化模型[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2014, 34(06): 777-. |
| [10] | 颜广 ,刘伟 ,戴朝霞 ,王鹍 ,刘靖 ,赵灵凤 ,黄志斌 ,陈小辉 ,马宁 ,孟萍 ,许孟畅 ,温子龙 ,张文清. 一种斑马鱼原始造血髓系细胞突变体的研究[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2011, 31(05): 755-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||