南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (4): 844-852.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.04.20
收稿日期:2024-11-14
出版日期:2025-04-20
发布日期:2025-04-28
通讯作者:
边兆英
E-mail:zxy4118050022@smu.edu.cn;zybian@smu.edu.cn
作者简介:张晓瑜,硕士,E-mail: zxy4118050022@smu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Xiaoyu ZHANG( ), Hao WANG, Dong ZENG, Zhaoying BIAN(
), Hao WANG, Dong ZENG, Zhaoying BIAN( )
)
Received:2024-11-14
Online:2025-04-20
Published:2025-04-28
Contact:
Zhaoying BIAN
E-mail:zxy4118050022@smu.edu.cn;zybian@smu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
目的 提出一种基于中心指导与交替优化的低剂量CT图像恢复方法(FedGP)。 方法 FedGP框架革新了传统的联邦学习模式,采用无固定中央服务器的结构,每个机构交替担任中心服务器。该方法采用机构调制的CT图像恢复网络作为客户端局部训练的核心,通过中心指导和交替优化的联邦学习方法,中央服务器利用本地标记数据指导客户端局部网络训练,从而显著提升多机构低剂量CT图像恢复模型的泛化能力。 结果 在低管电流和稀疏角度CT图像恢复任务中,与其他对比的联邦学习方法相比,FedGP方法的CT图像结果在视觉和定量评估上均有明显优势,FedGP获得了最高的PSNR指标(40.25和38.84)、最高的SSIM指标(0.95和0.92)以及最低的RMSE指标(2.39和2.56)。此外,FedGP的消融实验结果表明基于中心指导与交替优化的联邦学习框架能更好适应各机构之间的数据异构性,确保模型在各类成像条件下的稳健性和泛化能力。 结论 本文提出的FedGP为解决CT成像异质性问题提供了一个更灵活的FL框架,可以更好地适应不同参与方的数据特征,提高模型在多样化成像几何的泛化能力。
张晓瑜, 王昊, 曾栋, 边兆英. 基于中心指导与交替优化的低剂量CT图像恢复方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 844-852.
Xiaoyu ZHANG, Hao WANG, Dong ZENG, Zhaoying BIAN. A low-dose CT image restoration method based on central guidance and alternating optimization[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 844-852.
| Simulation parameter | Site #1 | Site #2 | Site #3 | Site #4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of projection views | 896 | 512 | 768 | 896 |
| Number of detector bins | 1008 | 1024 | 904 | 1008 |
| Length of a detector bin (mm) | 0.5480 | 0.6500 | 0.6000 | 0.5480 |
| Length of a voxel (mm) | 0.7421 | 0.7500 | 0.7000 | 0.7421 |
| DSD (mm) | 800.0 | 750.1 | 946.7 | 800.0 |
| DSO (mm) | 550.0 | 476.8 | 538.5 | 550.0 |
| Condition 1:Dose level (X-ray intensities) | 1×105 | 3×105 | 1×105 | 3×105 |
| Condition 2:Sampling scale | 8 | 6 | 6 | 8 |
表1 各机构数据集的实验仿真参数
Tab.1 Experimental simulation parameters for each site dataset
| Simulation parameter | Site #1 | Site #2 | Site #3 | Site #4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of projection views | 896 | 512 | 768 | 896 |
| Number of detector bins | 1008 | 1024 | 904 | 1008 |
| Length of a detector bin (mm) | 0.5480 | 0.6500 | 0.6000 | 0.5480 |
| Length of a voxel (mm) | 0.7421 | 0.7500 | 0.7000 | 0.7421 |
| DSD (mm) | 800.0 | 750.1 | 946.7 | 800.0 |
| DSO (mm) | 550.0 | 476.8 | 538.5 | 550.0 |
| Condition 1:Dose level (X-ray intensities) | 1×105 | 3×105 | 1×105 | 3×105 |
| Condition 2:Sampling scale | 8 | 6 | 6 | 8 |
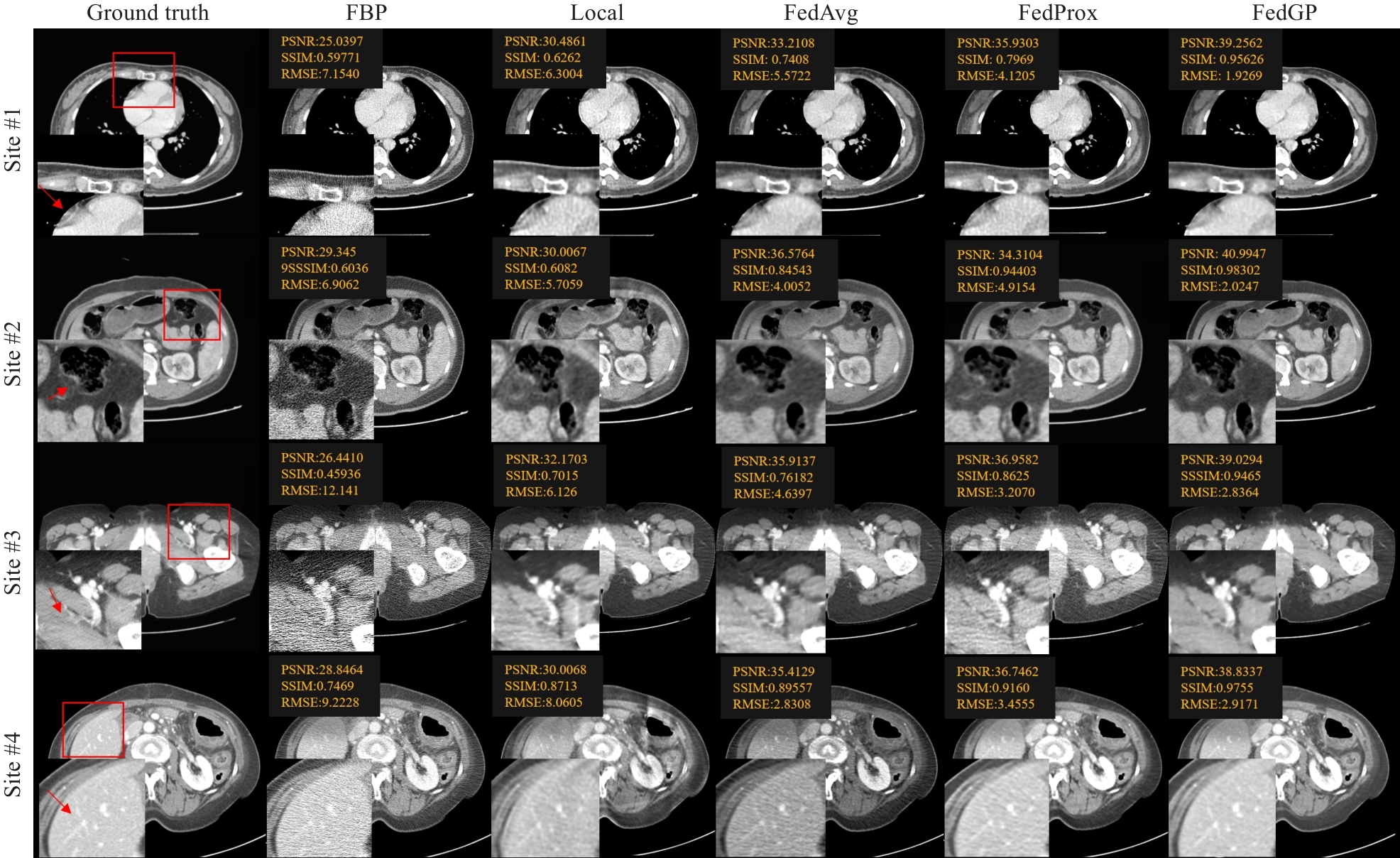
图2 FedGP及对比方法在低管电流实验中机构1-4数据集的代表性图像结果和ROI
Fig.2 Representative images and ROIs for site 1-4 in the low-dose CT experiment generated by FedGP and other methods (results of site 1-4 shows window [-200, 200]).
| Site | Method | PSNR | SSIM | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Site #1 | FBP | 26.203±1.134 | 0.532±0.092 | 8.372±1.496 |
| Local | 30.812±2.512 | 0.702±0.123 | 6.712±1.824 | |
| FedAvg | 33.024±3.114 | 0.785±0.095 | 6.348±1.251 | |
| FedProx | 34.553±2.127 | 0.822±0.071 | 5.945±1.915 | |
| FedGP | 39.870±2.206 | 0.957±0.022 | 2.815±0.731 | |
Site #2 | FBP | 29.305±1.452 | 0.612±0.079 | 6.215±1.372 |
| Local | 32.100±3.421 | 0.715±0.125 | 5.214±2.067 | |
| FedAvg | 36.420±3.985 | 0.891±0.042 | 5.118±1.718 | |
| FedProx | 35.100±3.530 | 0.854±0.136 | 4.571±2.120 | |
| FedGP | 41.450±1.893 | 0.946±0.029 | 2.425±0.581 | |
Site #3 | FBP | 26.912±0.852 | 0.482±0.134 | 12.791±1.936 |
| Local | 31.702±2.634 | 0.659±0.112 | 7.142±2.025 | |
| FedAvg | 35.510±3.178 | 0.703±0.109 | 4.512±1.614 | |
| FedProx | 34.510±3.170 | 0.799±0.105 | 4.194±1.850 | |
| FedGP | 39.925±1.951 | 0.923±0.046 | 2.105±0.842 | |
Site #4 | FBP | 28.510±1.528 | 0.732±0.118 | 10.051±1.925 |
| Local | 30.582±3.282 | 0.775±0.097 | 8.832±1.153 | |
| FedAvg | 36.112±3.024 | 0.815±0.093 | 3.785±1.831 | |
| FedProx | 35.821±3.965 | 0.902±0.052 | 3.275±2.162 | |
| FedGP | 39.752±2.742 | 0.960±0.029 | 2.217±1.358 |
表2 机构1-4在跨机型低管电流CT实验测试集的定量评估结果
Tab.2 Quantitative metrics of site 1-4 on the multi-institutional low-mAs CT experimental test set (Mean±SD)
| Site | Method | PSNR | SSIM | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Site #1 | FBP | 26.203±1.134 | 0.532±0.092 | 8.372±1.496 |
| Local | 30.812±2.512 | 0.702±0.123 | 6.712±1.824 | |
| FedAvg | 33.024±3.114 | 0.785±0.095 | 6.348±1.251 | |
| FedProx | 34.553±2.127 | 0.822±0.071 | 5.945±1.915 | |
| FedGP | 39.870±2.206 | 0.957±0.022 | 2.815±0.731 | |
Site #2 | FBP | 29.305±1.452 | 0.612±0.079 | 6.215±1.372 |
| Local | 32.100±3.421 | 0.715±0.125 | 5.214±2.067 | |
| FedAvg | 36.420±3.985 | 0.891±0.042 | 5.118±1.718 | |
| FedProx | 35.100±3.530 | 0.854±0.136 | 4.571±2.120 | |
| FedGP | 41.450±1.893 | 0.946±0.029 | 2.425±0.581 | |
Site #3 | FBP | 26.912±0.852 | 0.482±0.134 | 12.791±1.936 |
| Local | 31.702±2.634 | 0.659±0.112 | 7.142±2.025 | |
| FedAvg | 35.510±3.178 | 0.703±0.109 | 4.512±1.614 | |
| FedProx | 34.510±3.170 | 0.799±0.105 | 4.194±1.850 | |
| FedGP | 39.925±1.951 | 0.923±0.046 | 2.105±0.842 | |
Site #4 | FBP | 28.510±1.528 | 0.732±0.118 | 10.051±1.925 |
| Local | 30.582±3.282 | 0.775±0.097 | 8.832±1.153 | |
| FedAvg | 36.112±3.024 | 0.815±0.093 | 3.785±1.831 | |
| FedProx | 35.821±3.965 | 0.902±0.052 | 3.275±2.162 | |
| FedGP | 39.752±2.742 | 0.960±0.029 | 2.217±1.358 |
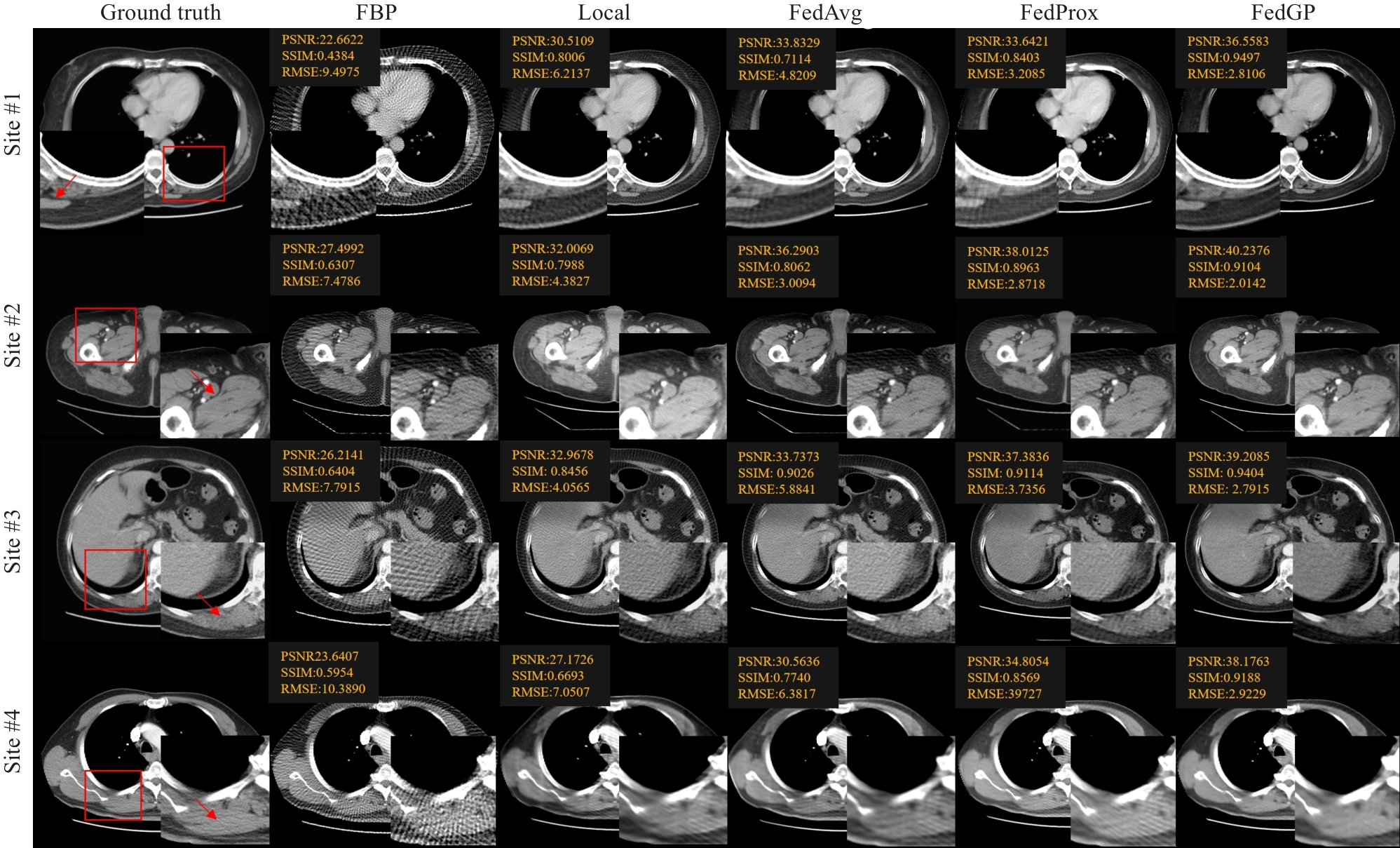
图3 FedGP及对比方法在稀疏角度CT实验中机构1-4数据集的代表性图像结果和ROI
Fig.3 Representative images and ROIs for site 1-4 in the sparse-view CT experiment generated by FedGP and other methods (results of site 1-4 shows window [-200, 200]).
| Site | Method | PSNR | SSIM | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Site #1 | FBP | 24.500±4.462 | 0.586±0.073 | 9.542±3.983 |
| Local | 30.655±2.582 | 0.713±0.119 | 6.823±1.479 | |
| FedAvg | 32.812±3.014 | 0.820±0.156 | 5.017±1.633 | |
| FedProx | 33.875±3.227 | 0.818±0.115 | 4.194±1.850 | |
| FedGP | 37.990±1.788 | 0.918±0.041 | 2.682±0.732 | |
Site #2 | FBP | 27.765±1.295 | 0.705±0.109 | 8.985±2.267 |
| Local | 31.980±2.756 | 0.728±0.084 | 5.372±1.846 | |
| FedAvg | 35.230±2.252 | 0.834±0.128 | 4.282±1.552 | |
| FedProx | 37.645±2.918 | 0.869±0.051 | 3.026±0.742 | |
| FedGP | 40.320±1.625 | 0.930±0.038 | 2.315±0.625 | |
Site #3 | FBP | 28.674±3.741 | 0.658±0.105 | 7.459±2.330 |
| Local | 31.185±2.790 | 0.769±0.094 | 5.372±1.905 | |
| FedAvg | 33.295±2.180 | 0.845±0.042 | 4.573±1.637 | |
| FedProx | 36.380±2.093 | 0.870±0.055 | 3.960±1.553 | |
| FedGP | 39.186±1.587 | 0.928±0.042 | 2.778±0.751 | |
Site #4 | FBP | 22.984±4.181 | 0.572±0.136 | 11.195±3.780 |
| Local | 27.290±3.475 | 0.688±0.120 | 7.291±1.955 | |
| FedAvg | 32.547±2.226 | 0.752±0.096 | 6.062±1.434 | |
| FedProx | 33.785±1.589 | 0.820±0.075 | 3.493±1.092 | |
| FedGP | 37.868±1.077 | 0.915±0.040 | 2.477±0.311 |
表3 机构1-4在跨机型稀疏角度CT实验测试集的定量评估结果
Tab.3 Quantitative metrics results of Site 1-4 on the multi-institutional sparse-view CT experimental test set (Mean±SD)
| Site | Method | PSNR | SSIM | RMSE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Site #1 | FBP | 24.500±4.462 | 0.586±0.073 | 9.542±3.983 |
| Local | 30.655±2.582 | 0.713±0.119 | 6.823±1.479 | |
| FedAvg | 32.812±3.014 | 0.820±0.156 | 5.017±1.633 | |
| FedProx | 33.875±3.227 | 0.818±0.115 | 4.194±1.850 | |
| FedGP | 37.990±1.788 | 0.918±0.041 | 2.682±0.732 | |
Site #2 | FBP | 27.765±1.295 | 0.705±0.109 | 8.985±2.267 |
| Local | 31.980±2.756 | 0.728±0.084 | 5.372±1.846 | |
| FedAvg | 35.230±2.252 | 0.834±0.128 | 4.282±1.552 | |
| FedProx | 37.645±2.918 | 0.869±0.051 | 3.026±0.742 | |
| FedGP | 40.320±1.625 | 0.930±0.038 | 2.315±0.625 | |
Site #3 | FBP | 28.674±3.741 | 0.658±0.105 | 7.459±2.330 |
| Local | 31.185±2.790 | 0.769±0.094 | 5.372±1.905 | |
| FedAvg | 33.295±2.180 | 0.845±0.042 | 4.573±1.637 | |
| FedProx | 36.380±2.093 | 0.870±0.055 | 3.960±1.553 | |
| FedGP | 39.186±1.587 | 0.928±0.042 | 2.778±0.751 | |
Site #4 | FBP | 22.984±4.181 | 0.572±0.136 | 11.195±3.780 |
| Local | 27.290±3.475 | 0.688±0.120 | 7.291±1.955 | |
| FedAvg | 32.547±2.226 | 0.752±0.096 | 6.062±1.434 | |
| FedProx | 33.785±1.589 | 0.820±0.075 | 3.493±1.092 | |
| FedGP | 37.868±1.077 | 0.915±0.040 | 2.477±0.311 |
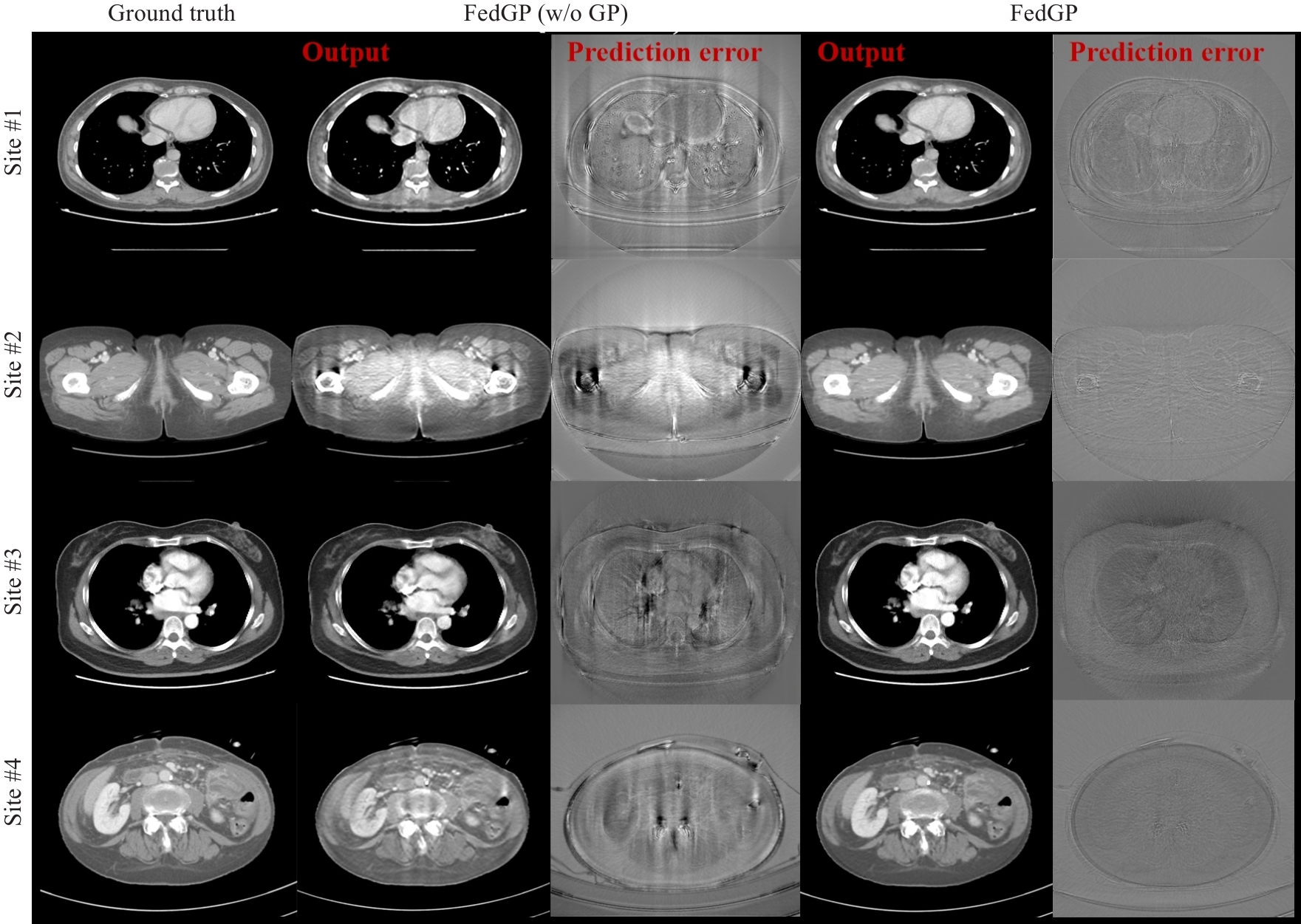
图4 FedGP及FedGP(w/o GP)在低管电流CT实验的代表性图像结果和预测误差
Fig.4 Representative reconstruction results and prediction errors of FedGP and FedGP (w/o GP) in the low-mAs CT reconstruction experiment (results of Site 1-4 shows window [-160, 240]).
| 1 | Berrington de González A, Darby S. Risk of cancer from diagnostic X-rays: estimates for the UK and 14 other countries[J]. Lancet, 2004, 363(9406): 345-51. |
| 2 | Brenner DJ, Hall EJ. Computed tomography: an increasing source of radiation exposure[J]. N Engl J Med, 2007, 357(22): 2277-84. |
| 3 | Murase K, Nanjo T, Ii S, et al. Effect of X-ray tube current on the accuracy of cerebral perfusion parameters obtained by CT perfusion studies[J]. Phys Med Biol, 2005, 50(21): 5019-29. |
| 4 | Meng MQ, Wang YB, Zhu MM, et al. Dual-task learning for low-dose CT simulation and denoising[C]//7th International Conference on Image Formation in X-Ray Computed Tomography. June 12-16, 2022. Baltimore, USA. SPIE, 2022: 602-607. |
| 5 | Li DY, Bian ZY, Li S, et al. Noise characteristics modeled unsupervised network for robust CT image reconstruction[J]. IEEE Trans Med Imaging, 2022, 41(12): 3849-61. |
| 6 | You CY, Li G, Zhang Y, et al. CT super-resolution GAN constrained by the identical, residual, and cycle learning ensemble (GAN-CIRCLE)[J]. IEEE Trans Med Imaging, 2020, 39(1): 188-203. |
| 7 | He J, Wang YB, Ma JH. Radon inversion via deep learning[J]. IEEE Trans Med Imaging, 2020, 39(6): 2076-87. |
| 8 | Xia WJ, Lu ZX, Huang YQ, et al. MAGIC: manifold and graph integrative convolutional network for low-dose CT reconstruction[J]. IEEE Trans Med Imag, 2021, 40(12): 3459-72. |
| 9 | Han Y, Ye JC. Framing U-Net via deep convolutional framelets: application to sparse-view CT[J]. IEEE Trans Med Imaging, 2018, 37(6): 1418-29. |
| 10 | Kim B, Shim H, Baek J. A streak artifact reduction algorithm in sparse-view CT using a self-supervised neural representation[J]. Med Phys, 2022, 49(12): 7497-515. |
| 11 | Lee M, Kim H, Kim HJ. Sparse-view CT reconstruction based on multi-level wavelet convolution neural network[J]. Phys Med, 2020, 80: 352-62. |
| 12 | Voigt P, von dem Bussche A. The EU general data protection regulation (GDPR): a practical guide[M]. Cham, Switzerland: Springer International Publishing, 2017. |
| 13 | Sheller MJ, Edwards B, Anthony Reina G, et al. Federated learning in medicine: facilitating multi-institutional collaborations without sharing patient data[J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1): 12598. |
| 14 | Fallah A, Mokhtari A, Ozdaglar A. Personalized federated learning: a meta-learning approach[EB/OL]. 2020: 2002.07948. . |
| 15 | Li T, Sahu AK, Talwalkar A, et al. Federated learning: challenges, methods, and future directions[J]. IEEE Signal Process Mag, 2020, 37(3): 50-60. |
| 16 | McMahan HB, Moore E, Ramage D, et al. Communication-efficient learning of deep networks from decentralized data[EB/OL]. 2016: 1602.05629. . |
| 17 | Yang ZY, Xia WJ, Lu ZX, et al. Hypernetwork-based personalized federated learning for multi-institutional CT imaging[EB/OL]. 2022: 2206.03709. . |
| 18 | 陈世宣, 曾 栋, 边兆英, 等. 基于联邦特征学习的多机型低剂量CT重建算法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 333-43. |
| 19 | Solanes A, Palau P, Fortea L, et al. Biased accuracy in multisite machine-learning studies due to incomplete removal of the effects of the site[J]. Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging, 2021, 314: 111313. |
| 20 | Perez E, Strub F, De Vries H, et al. FiLM: visual reasoning with a general conditioning layer[J]. Proc AAAI Conf Artif Intell, 2018, 32(1): 3942-51. |
| 21 | Albarqouni S, Bakas S, Kamnitsas K, et al. Domain adaptation and representation transfer, and distributed and collaborative learning: second MICCAI Workshop, DART 2020, and first MICCAI Workshop, DCL 2020, held in conjunction with MICCAI 2020, Lima, Peru, October 4-8, 2020 , Proceedings[M]. Cham, Switzerland: Springer, 2020. |
| 22 | Zhu HY, Xu JJ, Liu SQ, et al. Federated learning on non-IID data: a survey[J]. Neurocomputing, 2021, 465: 371-90. |
| 23 | Li XX, Jiang MR, Zhang XF, et al. FedBN: federated learning on non-IID features via local batch normalization[EB/OL]. 2021: 2102.07623. . |
| 24 | McCollough C. TU-FG-207A-04: overview of the low dose CT grand challenge[J]. Med Phys, 2016, 43(6Part35): 3759-60. |
| 25 | Moen TR, Chen BY, et al. Low-dose CT image and projection dataset[J]. Med Phys, 2021, 48(2): 902-11. |
| 26 | Ma J, Zhang Y, Gu S, et al. AbdomenCT-1K: is abdominal organ segmentation a solved problem[J]? IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 2022, 44(10): 6695-714. |
| 27 | Deng Y, Wang C, Hui Y, et al. CTSpine 1K: a large-scale dataset for spinal vertebrae segmentation in computed tomography[EB/OL]. 2021: 2105.14711. . |
| 28 | van Aarle W, Palenstijn WJ, Cant J, et al. Fast and flexible X-ray tomography using the ASTRA toolbox[J]. Opt Express, 2016, 24(22): 25129-47. |
| 29 | Zeng D, Huang J, Bian ZY, et al. A simple low-dose X-ray CT simulation from high-dose scan[J]. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci, 2015, 62(5): 2226-33. |
| 30 | Hinton G, Van Der Maaten L. Visualizing data using t-sne journal of machine learning research[J]. Jf Mach Learn Res, 2008, 9: 2579-605. |
| 31 | Li T, Sahu AK, Zaheer M, et al. Federated optimization in heterogeneous networks[J]. Proceed Mach Learn Sys, 2020, 2: 429-50. |
| [1] | 陈世宣, 曾 栋, 边兆英, 马建华. 基于联邦特征学习的多机型低剂量CT重建算法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 333-343. |
| [2] | 周 昊, 曾 栋, 边兆英, 马建华. 基于半监督网络的组织感知CT图像对比度的增强方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(6): 985-993. |
| [3] | 牛善洲, 刘 宏, 刘沛沄, 张梦真, 李 硕, 梁礼境, 李 楠, 刘国良. 基于非局部低秩稀疏矩阵分解的低剂量脑灌注CT图像恢复方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(9): 1309-1316. |
| [4] | 高 琦, 朱曼曼, 李丹阳, 边兆英, 马建华. CT图像的质量评估策略:基于预恢复图像先验信息[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(2): 230-237. |
| [5] | 梁保辉,付亚军,曹明娜. 基于CT检查的正位定位像计算等效水直径[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2020, 40(06): 799-805. |
| [6] | 张蕴婉,刘洋,黄静,曾栋,边兆英,张华,马建华. 正常剂量扫描导引的低剂量心血管CT造影图像恢复[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2013, 33(09): 1299-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||