南方医科大学学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (1): 23-33.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2026.01.03
赵贝1( ), 吕政仪2(
), 吕政仪2( ), 季丁汝1, 田书心1, 吴雨欣1, 李星震1, 周杰1, 方剑乔1, 梁宜1(
), 季丁汝1, 田书心1, 吴雨欣1, 李星震1, 周杰1, 方剑乔1, 梁宜1( )
)
收稿日期:2025-05-26
出版日期:2026-01-20
发布日期:2026-01-16
通讯作者:
梁宜
E-mail:984722585@qq.com;aprilv_kuco@icloud.com;liangyiwww@126.com
作者简介:赵 贝,硕士,中医师,E-mail: 984722585@qq.com基金资助:
Bei ZHAO1( ), Zhengyi LÜ2(
), Zhengyi LÜ2( ), Dingru JI1, Shuxin TIAN1, Yuxin WU1, Xingzhen LI1, Jie ZHOU1, Jianqiao FANG1, Yi LIANG1(
), Dingru JI1, Shuxin TIAN1, Yuxin WU1, Xingzhen LI1, Jie ZHOU1, Jianqiao FANG1, Yi LIANG1( )
)
Received:2025-05-26
Online:2026-01-20
Published:2026-01-16
Contact:
Yi LIANG
E-mail:984722585@qq.com;aprilv_kuco@icloud.com;liangyiwww@126.com
Supported by:摘要:
目的 观察慢性术后疼痛(CPSP)小鼠疼痛行为学指标的时间动态特征,并从背根神经节(DRG)层面初步筛选介导CPSP的关键物质。 方法 采用足底切口术(INC)联合足背注射前列腺素E2(PGE2)建立慢性术后疼痛小鼠(I/P)模型。根据手术方式与给药不同,将小鼠随机分为假手术+生理盐水组(SI/NS)、假手术+PGE2组(SI/PGE2)和手术+PGE2组(I/P),观察实验小鼠造模后不同时间点机械缩足阈(PWTs)、热缩足潜伏期(PWLs)和冷缩足反应时间(WDs)变化。根据给药和取材时间不同,将小鼠分为SI/NS组、模型第1天组、模型第8天组,利用RNA-Seq技术建立CPSP早期(PGE2诱导后第1天)和维持期(PGE2诱导后第8天)小鼠背根神经节基因表达谱,通过样本相关性分析、差异表达基因分析、富集分析筛选重要介导物质,采用RT-qPCR和ELISA检测目标物质基因及蛋白表达情况。根据手术方式与给药不同,将小鼠随机分为SI/P+Veh组、I/P+Veh组、I/P+药物组,通过鞘内注射CX3CL1中和抗体(Ab)或CX3CR1选择性拮抗剂(JMS-17-2)等药理学实验,探索下游相关受体的作用。 结果 I/P小鼠足底切口疼痛在术后14 d内恢复,经PGE2二次诱发后PWTs持续降低至PGE2注射后第10天WDs持续延长至第12天;PWLs未发生持续性变化。生信分析显示,CPSP早期和维持期实验小鼠DRG差异表达基因为975、895个,共同参与介导的交集差异基因524个。富集分析表明“细胞膜”富集基因数目最多,涉102个基因;“质膜”富集显著性最大(P<0.001);“CX3C 趋化因子受体结合”等条目富集因子最大(Rich Factor=1)。与SI/NS组相比,CPSP早期趋化因子相关差异基因中表达差异最大为Cx3cl1(FC Cx3cl1 =2.08),其次为Cxcl14(FC Cxcl14 =1.99)。RT-qPCR和ELISA结果显示CPSP早期I/P小鼠患侧DRG中Cx3cl1、Cxcl14基因和相关蛋白表达较SI/NS组增加(P<0.05),维持期小鼠则较早期组降低(P<0.05)。PGE2诱导前鞘内注射CX3CL1中和抗体可阻止CPSP发生。单次鞘内注射CX3CR1拮抗剂可一定程度翻转CPSP维持期疼痛。 结论 CPSP小鼠机械痛觉异常、冷痛觉异常持续至PGE2注射后第10天,热痛觉敏化不显著。背根神经节趋化因子尤其是CX3CL1可能介导慢性术后疼痛发生。
赵贝, 吕政仪, 季丁汝, 田书心, 吴雨欣, 李星震, 周杰, 方剑乔, 梁宜. 慢性术后痛小鼠痛行为时间动态特征及背根神经节关键物质筛选[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2026, 46(1): 23-33.
Bei ZHAO, Zhengyi LÜ, Dingru JI, Shuxin TIAN, Yuxin WU, Xingzhen LI, Jie ZHOU, Jianqiao FANG, Yi LIANG. Temporal changes of chronic postsurgical pain in mice: the regulatory role of CX3CL1 in the dorsal root ganglion[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2026, 46(1): 23-33.
| Gene | Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| Cx3cl1 forward | CAGAGGAGCAGGCAGGACAG |
| Cx3cl1 reverse | CTTCAGAGCAGGAGAGACCCATC |
| Cxcl14 forward | TCCGGTCAGCATGAGGCTCC |
| Cxcl14 reverse | CACCCTATTCTTCGTAGACC |
| Ccr5 forward | GTTGTTTTGGAGAACGCCCC |
| Ccr5 reverse | CAACACTGCTCCGAAACTGC |
| Il7 forward | CTAGCAACTGGCAAGGAGGAC |
| Il7 reverse | CCTGTAAGTGGAAGCATGGC |
| β-actin forward | ACTGGAACGGTGAAGGTGAC |
| β-actin reverse | AGAGAAGTGGGGTGGCTTTT |
表1 RT-qPCR引物序列
Tab.1 Primer sequences for RT-qPCR
| Gene | Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| Cx3cl1 forward | CAGAGGAGCAGGCAGGACAG |
| Cx3cl1 reverse | CTTCAGAGCAGGAGAGACCCATC |
| Cxcl14 forward | TCCGGTCAGCATGAGGCTCC |
| Cxcl14 reverse | CACCCTATTCTTCGTAGACC |
| Ccr5 forward | GTTGTTTTGGAGAACGCCCC |
| Ccr5 reverse | CAACACTGCTCCGAAACTGC |
| Il7 forward | CTAGCAACTGGCAAGGAGGAC |
| Il7 reverse | CCTGTAAGTGGAAGCATGGC |
| β-actin forward | ACTGGAACGGTGAAGGTGAC |
| β-actin reverse | AGAGAAGTGGGGTGGCTTTT |
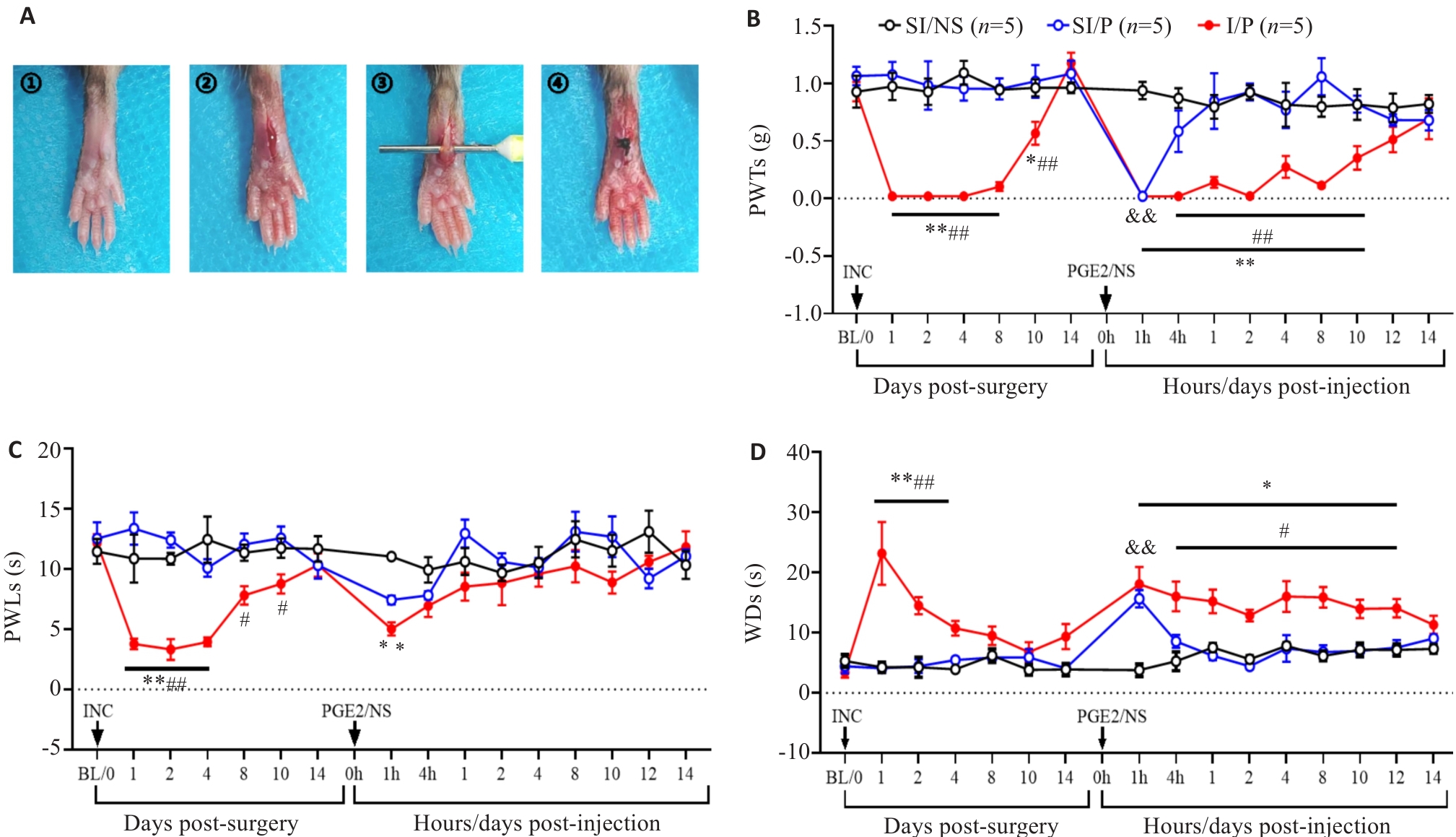
图1 CPSP模型的建立和小鼠疼痛行为学指标的变化
Fig.1 Temporal changes of pain-related behaviors in the mouse models of chronic postsurgical pain (CPSP). A: Schematic diagram of plantar incision for inducing CPSP in mice. B: Changes in mechanical paw withdrawal thresholds (PWTs) after plantar incision and after PGE2 injection in each group. C: Changes in thermal paw withdrawal latencies (PWLs) after plantar incision and after PGE2 injection in each group. D: Changes in cold withdrawal durations (WDs) of the mice after plantar incision and after PGE2 injection. INC: Incision. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 I/P vs SI/NS; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 I/P vs SI/P; &&P<0.01 SI/P vs SI/NS.
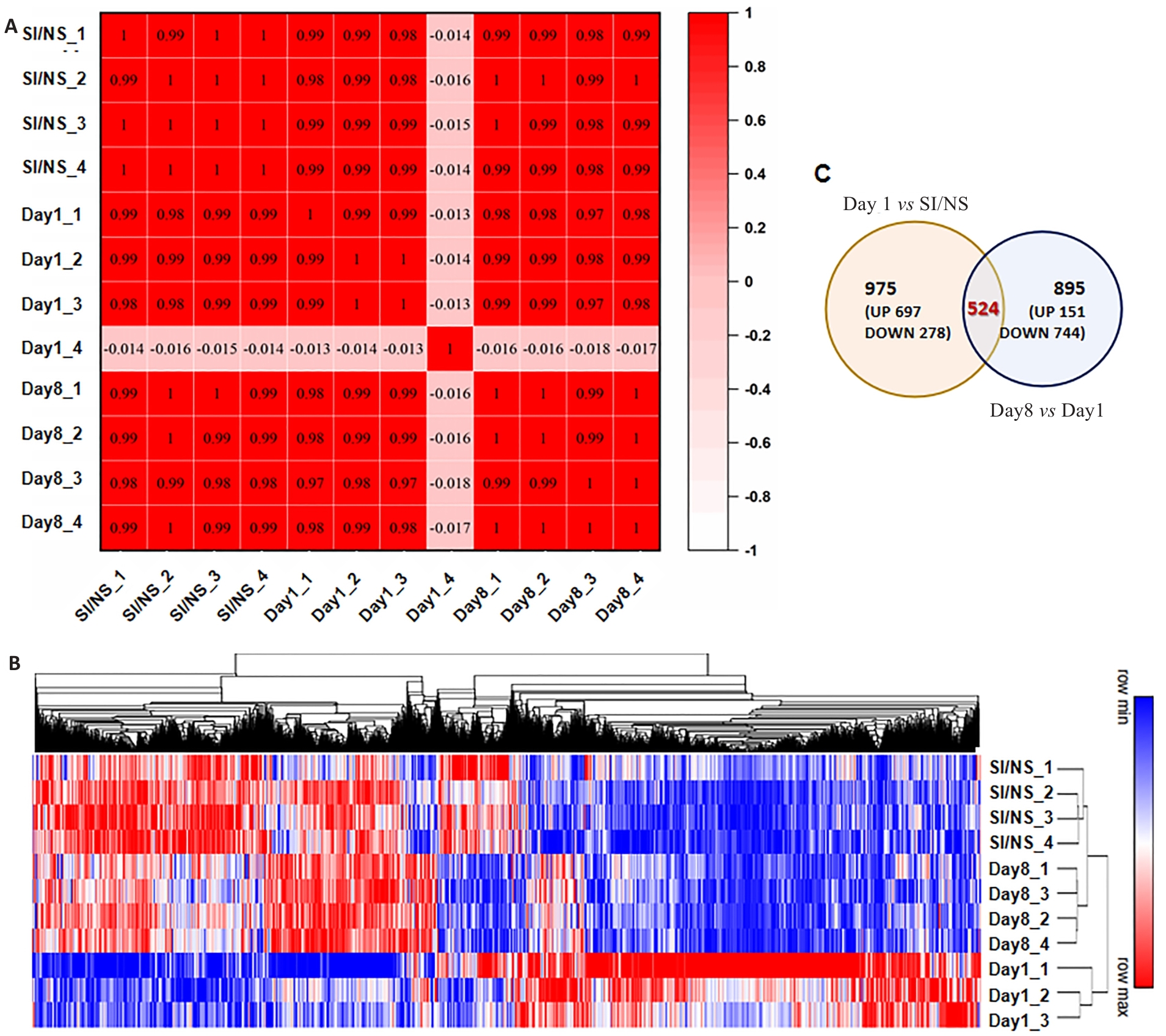
图2 不同时间点I/P小鼠DRGs基因表达情况
Fig.2 Gene expression profile in dorsal root ganglion (DRGs) of the mice with CPSP at different time points. A: Heat map of correlation coefficient of each sample (Numbers in the box are Pearson correlation coefficients between the corresponding two samples). B: Heat map and hierarchical clustering of differential gene expression in each sample (P<0.05 and |log2FC|>0.3 were the threshold criteria for differentially expressed genes). C: Venn diagram of DEGs between groups.
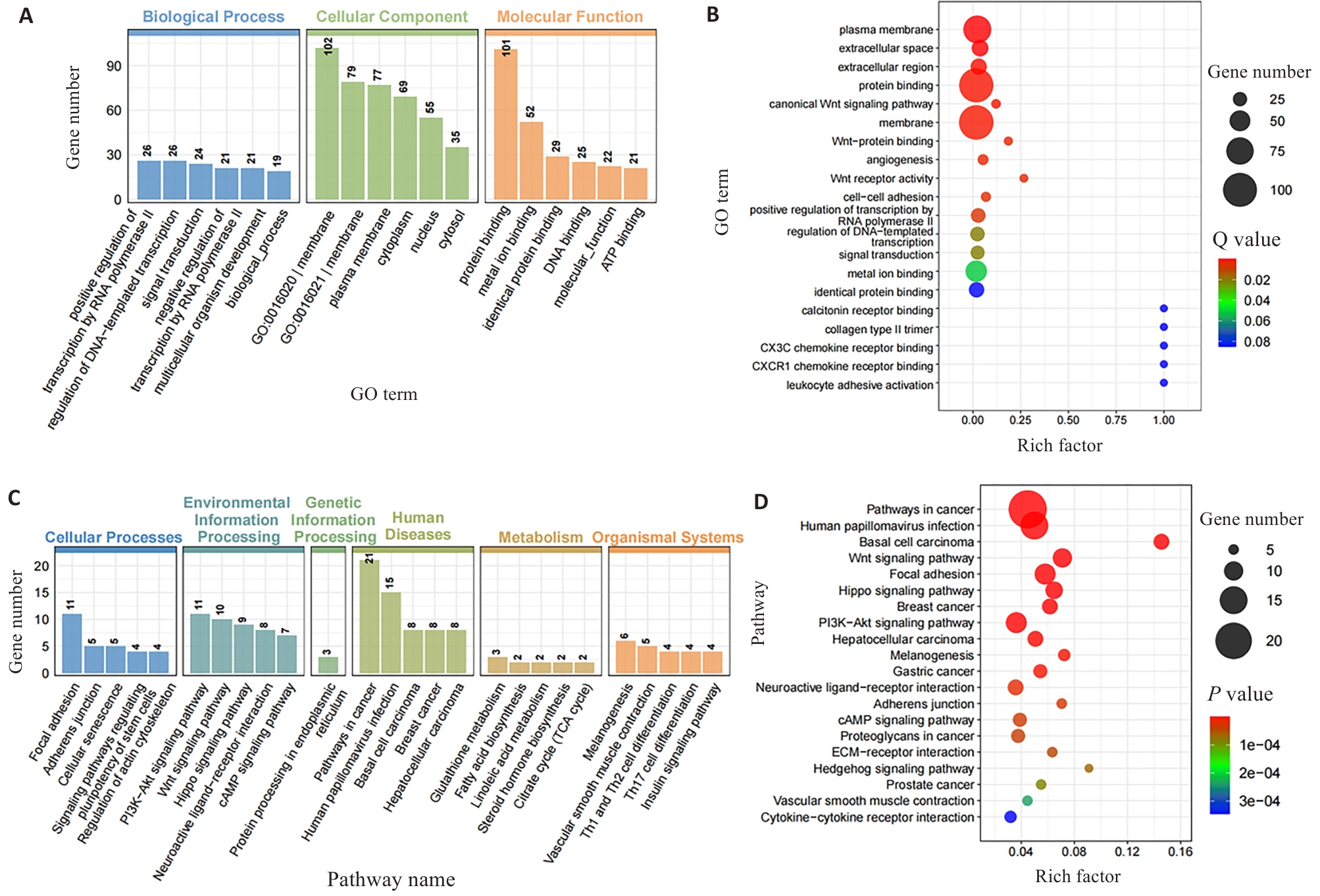
图3 I/P小鼠DRGs交集差异基因GO和KEGG富集分析
Fig.3 GO and KEGG enrichment analysis of differentially expressed genes at the intersection DEGs in CPSP mice. A: GO enrichment bar chart of the intersection DEGs between Day1vs. SI/NS and Day8 vs. Day1 (Ranked by the number of significantly enriched genes). B: GO enrichment scatter plot of intersection DEGs. C: KEGG enrichment bar chart of intersection DEGs. D: KEGG enrichment scatter plot of intersection DEGs.
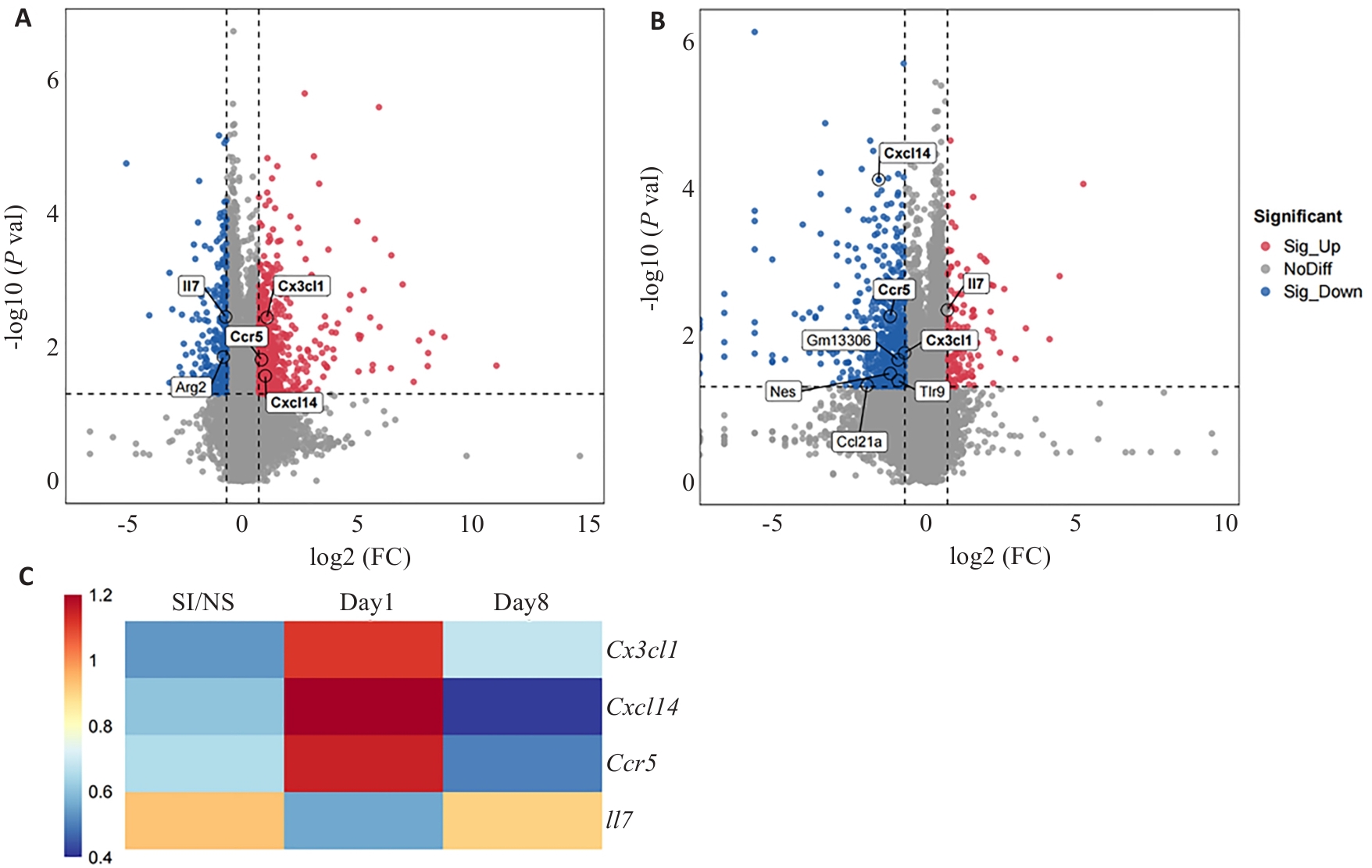
图4 不同时间点CPSP小鼠DRGs趋化因子相关基因表达情况
Fig.4 Expression of chemokine-related genes in DRGs of mice with CPSP at different time points. A: Volcano plot of differentially expressed genes in day 1 and SI/NS groups (Chemokine-related genes are marked). B: Volcano plot of differentially expressed genes in day 8 and day 1 groups. C: Table of differential genes associated with chemokines between the groups. All chemokine-related genes are extracted using GO terms.
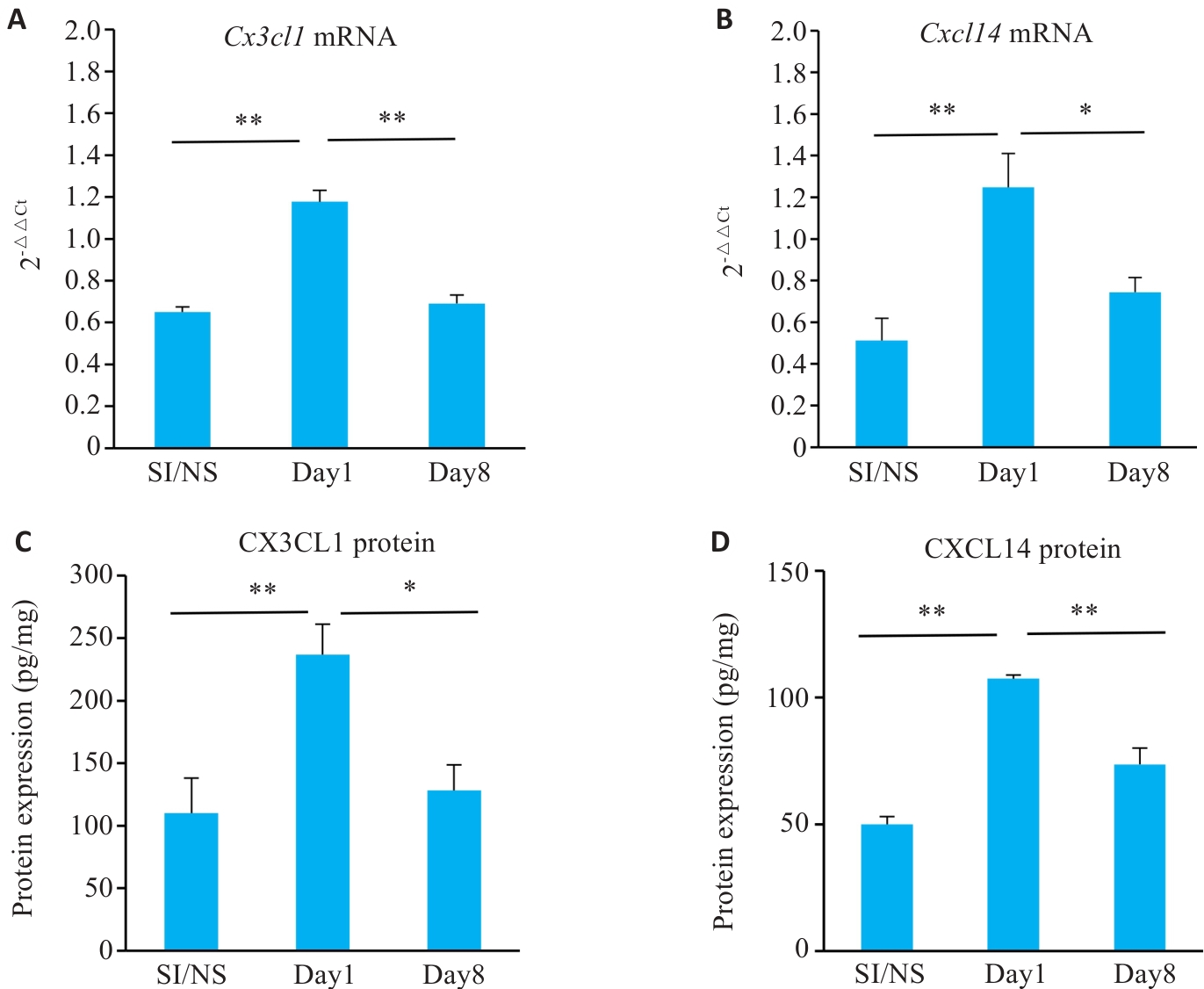
图5 各组小鼠CPSP不同时期靶物质基因表达情况
Fig.5 Gene and protein expression of Cx3c11 and Cxc114 in different stages of CPSP. A: Cx3cl1 mRNA expression levels in ipsilateral DRGs of the mice at each time point. B: Cxcl14 mRNA expression levels in ipsilateral DRGs of the mice at each time point. C: CX3CL1 protein expression in ipsilateral DRGs of the mice at each time point. D: CXCL14 protein expression in ipsilateral DRGs of the mice at each time point. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
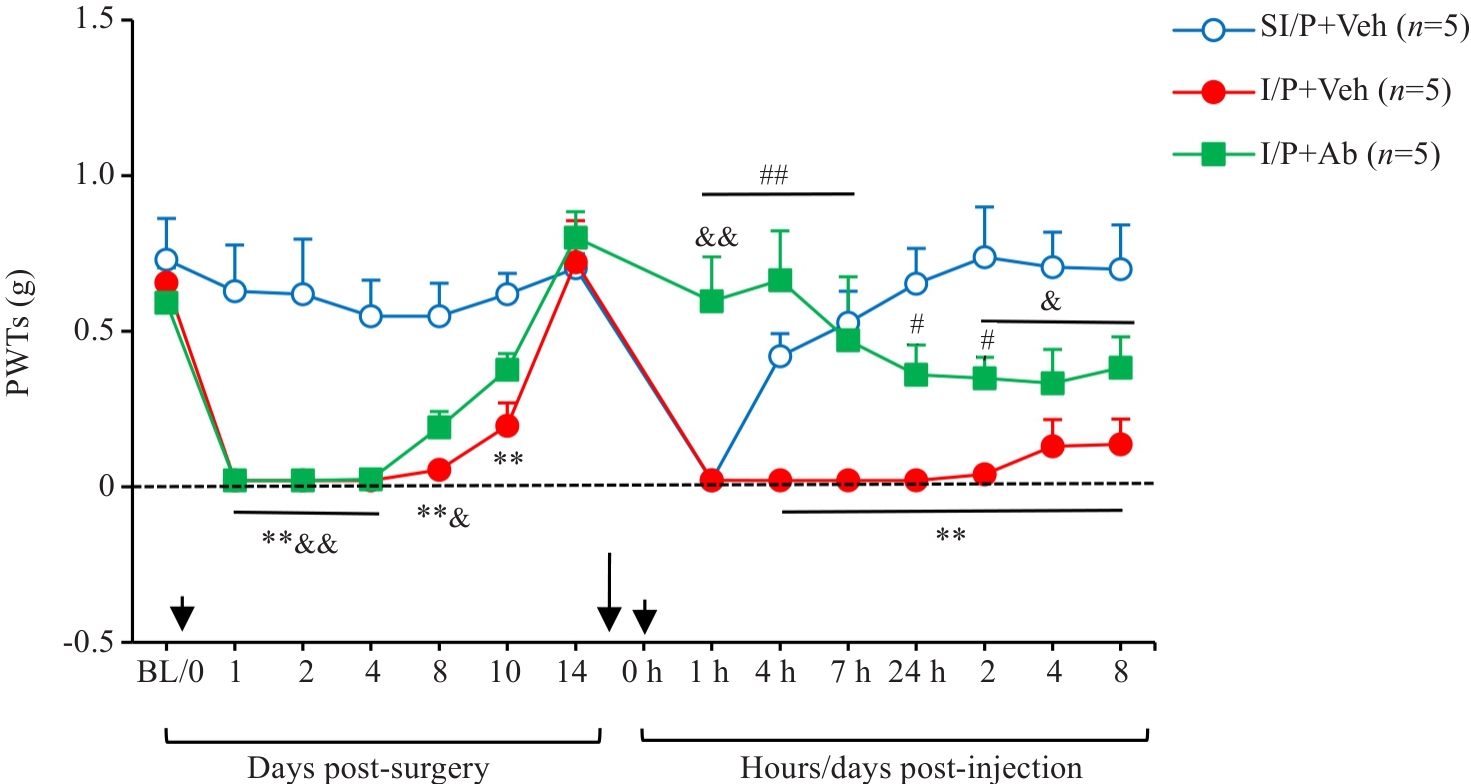
图6 各组实验小鼠鞘内注射CX3CL1中和抗体的镇痛效应
Fig.6 Intrathecal injection of CX3CL1 neutralizing antibody (5 µg/10 µL) 10 min prior to PGE2 injection significantly modulates mechanical PWTs in INC/PGE2 mice. **P<0.01 I/P+Veh vs SI/P+Veh group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 I/P+Ab vs I/P+Veh group; &P<0.05, &&P<0.01 I/P+Ab vs SI/P+Veh group. Ab: CX3CL1-neutralizing antibody; Veh: Vehicle, goat IgG control (1 µL/10 µL).
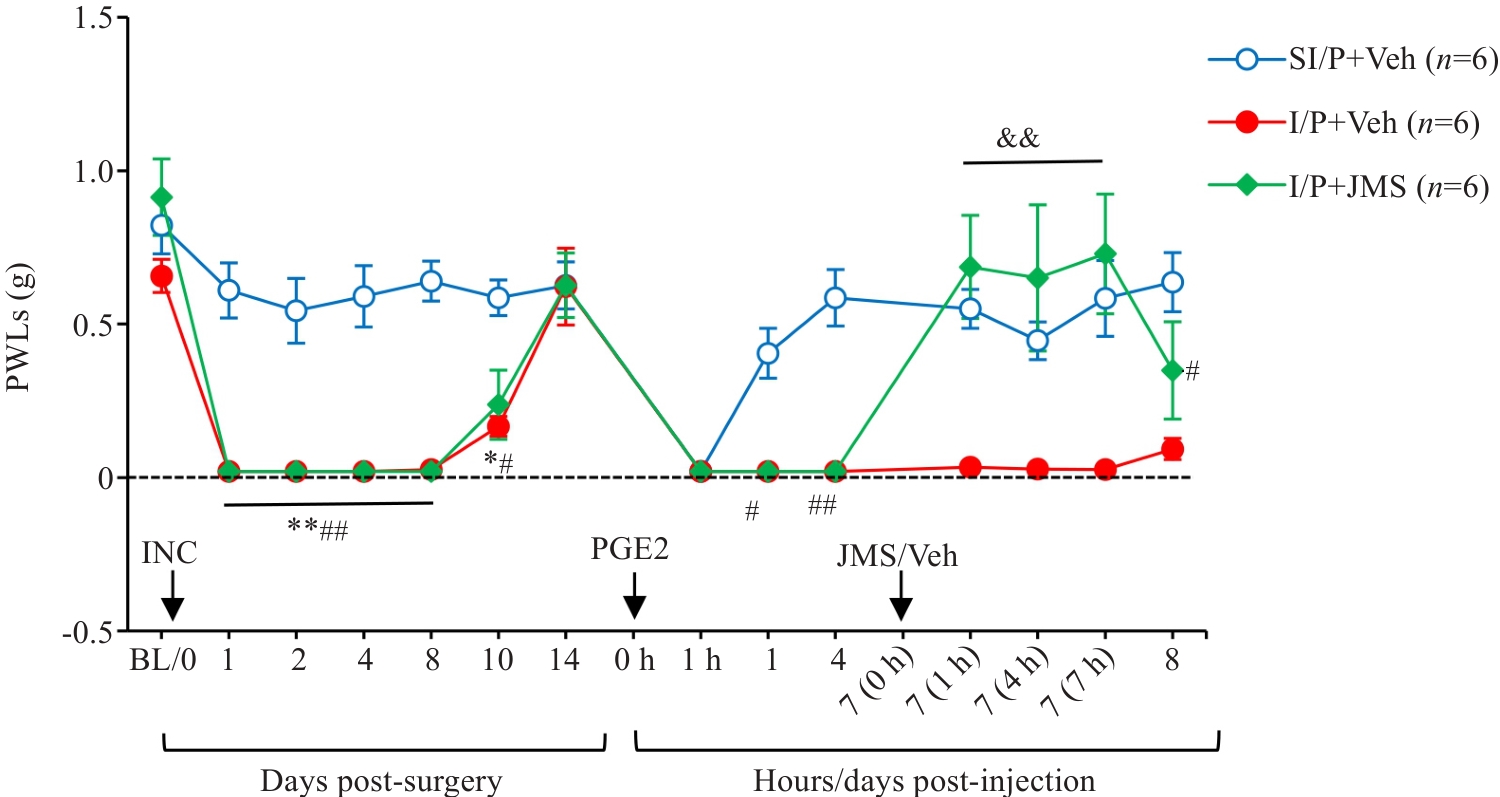
图7 选择性拮抗CX3CR1对实验小鼠痛行为的影响
Fig.7 Effects of intrathecal injection of JMS17-2 (75 µg/10 µL), a selective CX3CR1 antagonist, on Day 7 post-PGE2 injection, on PWTs in CPSP mice. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 I/P+Veh vs SI/P+Veh; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 I/P+JMS vs SI/P+Veh; &&P<0.01 I/P+JMS vs I/P+Veh. I/P: INC/PGE2; SI/P: Sham INC/PGE2; JMS: CX3CR1-selective antagonist JMS17-2; Veh: Corn oil vehicle.
| [1] | 冯 艺, 许军军, 林夏清, 等. 慢性术后或创伤后疼痛[J]. 中国疼痛医学杂志, 2021, 27(4): 241-5. |
| [2] | Fletcher D, Stamer UM, Pogatzki-Zahn E, et al. Chronic postsurgical pain in Europe: an observational study[J]. Eur J Anaesthesiol, 2015, 32(10): 725-34. doi:10.1097/eja.0000000000000319 |
| [3] | 金菊英, 彭丽桦, 杜洵松, 等. 手术后慢性疼痛的流行病学调查和危险因素分析[J]. 中国疼痛医学杂志, 2015, 21(7): 505-12. |
| [4] | 韩 琦, 冯 艺. 术后急、慢性疼痛危险因素研究进展[J]. 中国疼痛医学杂志, 2020, 26(11): 849-53. |
| [5] | Richebé P, Capdevila X, Rivat C. Persistent postsurgical pain: pathophysiology and preventative pharmacologic considerations[J]. Anesthesiology, 2018, 129(3): 590-607. doi:10.1097/aln.0000000000002238 |
| [6] | Inyang KE, Burton MD, Szabo-Pardi T, et al. Indirect AMP-activated protein kinase activators prevent incision-induced hyperalgesia and block hyperalgesic priming, whereas positive allosteric modulators block only priming in mice[J]. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 2019, 371(1): 138-50. doi:10.1124/jpet.119.258400 |
| [7] | Pogatzki EM, Raja SN. A mouse model of incisional pain[J]. Anesthesiology, 2003, 99(4): 1023-7. doi:10.1097/00000542-200310000-00041 |
| [8] | Xu JJ, Gao P, Wu Y, et al. G protein-coupled estrogen receptor in the rostral ventromedial medulla contributes to the chronification of postoperative pain[J]. CNS Neurosci Ther, 2021, 27(11): 1313-26. doi:10.1111/cns.13704 |
| [9] | Kehlet H, Jensen TS, Woolf CJ. Persistent postsurgical pain: risk factors and prevention[J]. Lancet, 2006, 367(9522): 1618-25. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(06)68700-x |
| [10] | Tillu DV, Melemedjian OK, Asiedu MN, et al. Resveratrol engages AMPK to attenuate ERK and mTOR signaling in sensory neurons and inhibits incision-induced acute and chronic pain[J]. Mol Pain, 2012, 8: 5. doi:10.1186/1744-8069-8-5 |
| [11] | 甄思佳, 赵 贝, 郑博习, 等. 背根神经节嘌呤受体亚型P2X3R介导小鼠术后急—慢痛转化[J]. 中国药理学通报, 2023, 39(7): 1282-8. |
| [12] | Baptista-de-Souza D, Tavares-Ferreira D, Megat S, et al. Sex differences in the role of atypical PKC within the basolateral nucleus of the amygdala in a mouse hyperalgesic priming model[J]. Neurobiol Pain, 2020, 8: 100049. doi:10.1016/j.ynpai.2020.100049 |
| [13] | Guo ZB, Tang L, Wang LP, et al. The analgesic effects of ulinastatin either as a single agent or in combination with sufentanil: a novel therapeutic potential for postoperative pain[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2021, 907: 174267. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174267 |
| [14] | Pak DJ, Yong RJ, Kaye AD, et al. Chronification of pain: mechanisms, current understanding, and clinical implications[J]. Curr Pain Headache Rep, 2018, 22(2): 9. doi:10.1007/s11916-018-0666-8 |
| [15] | Li CS, Yang Y, Liu SF, et al. Stress induces pain transition by potentiation of AMPA receptor phosphorylation[J]. J Neurosci, 2014, 34(41): 13737-46. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.2130-14.2014 |
| [16] | Banik RK, Woo YC, Park SS, et al. Strain and sex influence on pain sensitivity after plantar incision in the mouse[J]. Anesthesiology, 2006, 105(6): 1246-53. doi:10.1097/00000542-200612000-00025 |
| [17] | Chaplan SR, Bach FW, Pogrel JW, et al. Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw[J]. J Neurosci Methods, 1994, 53(1): 55-63. doi:10.1016/0165-0270(94)90144-9 |
| [18] | Hargreaves K, Dubner R, Brown F, et al. A new and sensitive method for measuring thermal nociception in cutaneous hyperalgesia[J]. Pain, 1988, 32(1): 77-88. doi:10.1016/0304-3959(88)90026-7 |
| [19] | Yoon C, Wook YY, Sik NH, et al. Behavioral signs of ongoing pain and cold allodynia in a rat model of neuropathic pain[J]. Pain, 1994, 59(3): 369-76. doi:10.1016/0304-3959(94)90023-x |
| [20] | 张晓光, 郄文斌, 屠伟峰, 等. 围术期目标导向全程镇痛管理中国专家共识(2021版)[J]. 中华疼痛学杂志, 2021, 17(2): 119-25. |
| [21] | Brennan TJ, Vandermeulen EP, Gebhart GF. Characterization of a rat model of incisional pain[J]. Pain, 1996, 64(3): 493-502. doi:10.1016/0304-3959(95)01441-1 |
| [22] | Reichling DB, Levine JD. Critical role of nociceptor plasticity in chronic pain[J]. Trends Neurosci, 2009, 32(12): 611-8. doi:10.1016/j.tins.2009.07.007 |
| [23] | Sun Y, Sahbaie P, Liang DY, et al. Epigenetic regulation of spinal CXCR2 signaling in incisional hypersensitivity in mice[J]. Anesthesiology, 2013, 119(5): 1198-208. doi:10.1097/aln.0b013e31829ce340 |
| [24] | Sahbaie P, Sun Y, Liang DY, et al. Curcumin treatment attenuates pain and enhances functional recovery after incision[J]. Anesth Analg, 2014, 118(6): 1336-44. doi:10.1213/ane.0000000000000189 |
| [25] | Matsuda M, Oh-Hashi K, Yokota I, et al. Acquired exchange protein directly activated by cyclic adenosine monophosphate activity induced by p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in primary afferent neurons contributes to sustaining postincisional nociception[J]. Anesthesiology, 2017, 126(1): 150-62. doi:10.1097/aln.0000000000001401 |
| [26] | 胡海宇, 丁家威, 吴叶琪, 等. 电针对痛觉敏化大鼠背根神经节蛋白酶激活受体2的影响[J]. 针刺研究, 2018, 43(1): 14-9. |
| [27] | Jiang BC, Liu T, Gao YJ. Chemokines in chronic pain: cellular and molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential[J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2020, 212: 107581. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107581 |
| [28] | Subbarayan MS, Joly-Amado A, Bickford PC, et al. CX3CL1/CX3CR1 signaling targets for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases[J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2022, 231: 107989. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2021.107989 |
| [29] | Holmes FE, Arnott N, Vanderplank P, et al. Intra-neural administration of fractalkine attenuates neuropathic pain-related behaviour[J]. J Neurochem, 2008, 106(2): 640-9. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05419.x |
| [30] | Bian C, Wang ZC, Yang JL, et al. Up-regulation of interleukin-23 induces persistent allodynia via CX3CL1 and interleukin-18 signaling in the rat spinal cord after tetanic sciatic stimulation[J]. Brain Behav Immun, 2014, 37: 220-30. doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2013.12.011 |
| [31] | Souza GR, Talbot J, Lotufo CM, et al. Fractalkine mediates inflammatory pain through activation of satellite glial cells[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2013, 110(27): 11193-8. doi:10.1073/pnas.1307445110 |
| [32] | Gowhari Shabgah A, Haleem Al-Qaim Z, Markov A, et al. Chemokine CXCL14; a double-edged sword in cancer development[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2021, 97: 107681. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107681 |
| [33] | Westrich JA, Vermeer DW, Colbert PL, et al. The multifarious roles of the chemokine CXCL14 in cancer progression and immune responses[J]. Mol Carcinog, 2020, 59(7): 794-806. doi:10.1002/mc.23188 |
| [34] | Liu M, Zhang SB, Luo YX, et al. NFATc2-dependent epigenetic upregulation of CXCL14 is involved in the development of neuropathic pain induced by paclitaxel[J]. J Neuroinflammation, 2020, 17(1): 310. doi:10.1186/s12974-020-01992-1 |
| [35] | Wang YY, Weng XL, Wang LY, et al. HIC1 deletion promotes breast cancer progression by activating tumor cell/fibroblast crosstalk[J]. J Clin Invest, 2018, 128(12): 5235-50. doi:10.1172/jci99974 |
| [36] | Witte A, Rohlfing AK, Dannenmann B, et al. The chemokine CXCL14 mediates platelet function and migration via direct interaction with CXCR4[J]. Cardiovasc Res, 2021, 117(3): 903-17. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvaa080 |
| [37] | Chang TM, Chiang YC, Lee CW, et al. CXCL14 promotes metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer through ACKR2-depended signaling pathway[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2023, 19(5): 1455-70. doi:10.7150/ijbs.79438 |
| [38] | Xu YY, Deng CZ, Chen HM, et al. Osteosarcoma cells secrete CXCL14 that activates integrin α11β1 on fibroblasts to form a lung metastatic niche[J]. Cancer Res, 2024, 84(7): 994-1012. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-23-1307 |
| [39] | Lu Y, Jiang BC, Cao DL, et al. Chemokine CCL8 and its receptor CCR5 in the spinal cord are involved in visceral pain induced by experimental colitis in mice[J]. Brain Res Bull, 2017, 135: 170-8. doi:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2017.10.009 |
| [40] | Zhong SS, Liu FX, Giniatullin R, et al. Blockade of CCR5 suppresses paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathic pain caused by increased deoxycholic acid[J]. Cell Rep, 2023, 42(11): 113386. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113386 |
| [41] | Jonsjö MA, Olsson GL, Wicksell RK, et al. The role of low-grade inflammation in ME/CFS (Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome)-associations with symptoms[J]. Psychoneuro-endocrinology, 2020, 113: 104578. doi:10.1016/j.psyneuen.2019.104578 |
| [1] | 许怀文, 翁丽, 薛鸿. CXCL12可作为2型糖尿病合并慢性阻塞性肺疾病的潜在治疗靶点[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(1): 100-109. |
| [2] | 武若杰, 刘 睿, 张一粟, 李晓红. 帕瑞昔布钠改善腹腔镜下直肠癌根治术患者的炎症微环境并促进患者恢复:基于下调CXCL8-CXCR1/2表达[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 363-369. |
| [3] | 兰 玉, 王凯风, 蓝智贤, 周何琪, 孙 剑. 脱醇红酒抑制肝细胞癌的发生和发展:基于诱导细胞周期的阻滞和凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(8): 1297-1305. |
| [4] | 余嘉珍, 莫 亚. 近视小鼠巩膜成纤维细胞的基因表达谱:基于单细胞RNA测序的生物信息学分析[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(7): 1087-1092. |
| [5] | 张津玮,张小宝,钱海涛,崔吉正,顾小萍. 右美托咪定可减轻大鼠胫骨骨折手术所致的术后认知功能障碍[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2019, 39(03): 292-. |
| [6] | 许晓玲,柳英,陈青阁,黄通亮,高基民. SA/hI-TAC双功能融合蛋白的制备及其生物学功能鉴定[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2015, 35(12): 1715-. |
| [7] | 师阿盟,董蕾,史海涛,贾淼,郭晓燕,姜炅,秦斌. 趋化因子受体7在胃癌组织及细胞中的表达及意义[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2014, 34(12): 1780-. |
| [8] | 钱坤,廖雯婷,李建军,蒋鸿涛,周浩,龙建华,秦国庆,王毅. 齐墩果酸协同环孢素A延长大鼠移植肾的存活时间[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2014, 34(06): 843-. |
| [9] | 卢金昌,王晋,雍碧城,宋国徽,赵志强,唐清连,邹昌业,尹军强,谢显彪,沈靖南. 趋化因子CXCL14在骨肉瘤中的表达及其与预后的关系[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2013, 33(06): 798-. |
| [10] | 陈劲松,张波,潘从泽,任磊,陈韵岱. MCP-3对人脐静脉内皮细胞表达ICAM-1、VCAM-1、TF/TFPI及其凋亡的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2013, 33(01): 86-. |
| [11] | 焦赫娜,任飞,蔡宏伟. 不同剂量氯诺昔康对子宫切除术患者免疫功能的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2010, 30(08): 1844-1846. |
| [12] | 赵金红; 王健; 江水清; 项桂菊;. 慢性乙型肝炎患者CXC趋化因子Mig的表达[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2006, 26(11): 1589-1592. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||