南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (12): 2573-2584.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.12.05
• • 上一篇
李晓丰1( ), 叶桃春1,2,5, 席露1,3,5, 李春桥1,4,5, 刘慧慧1,3,5(
), 叶桃春1,2,5, 席露1,3,5, 李春桥1,4,5, 刘慧慧1,3,5( )
)
收稿日期:2025-06-20
出版日期:2025-12-20
发布日期:2025-12-22
通讯作者:
刘慧慧
E-mail:bitou780@163.com;gzylhh@163.com
作者简介:李晓丰,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: bitou780@163.com
基金资助:
Xiaofeng LI1( ), Taochun YE1,2,5, Lu XI1,3,5, Chunqiao LI1,4,5, Huihui LIU1,3,5(
), Taochun YE1,2,5, Lu XI1,3,5, Chunqiao LI1,4,5, Huihui LIU1,3,5( )
)
Received:2025-06-20
Online:2025-12-20
Published:2025-12-22
Contact:
Huihui LIU
E-mail:bitou780@163.com;gzylhh@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
目的 探讨肥胖哮喘与单纯哮喘差异表达基因并进行验证并观察针刺作用对哮喘小鼠气道慢性炎症的影响。 方法 从GEO数据库下载GSE110551的数据文件,进一步构建WGCNA网络,找出影响肥胖哮喘的关键基因,选取WGCNA中与T cells相关性最高的green模块,联合使用lasso回归和SVM特征选择算法筛选出在肥胖哮喘中的特征基因。选取5~6周龄C57BL/6J小鼠50只分为对照组(CON,普通饲料喂养)、肥胖组(FA,高脂饲料喂养)、肥胖哮喘组(FAA,高脂饲料喂养+OVA致敏)、地塞米松肥胖哮喘组(DEX,高脂饲料喂养+OVA致敏+地塞米松2 mg/kg灌胃)和针刺肥胖哮喘组(ACU,高脂饲料喂养+OVA致敏+针刺治疗)动物模型,10只/组。使用Western blotting、qPCR、流式细胞术等技术分析各组小鼠关键基因表达及针刺治疗对肥胖哮喘气道炎症的影响。 结果 筛选出FAM126B和VNN1作为后续研究的关键基因。通过动物实验发现Vnn1和FAM126B在肥胖哮喘组较其他各组表达明显增加,Treg细胞比例减少,肺部炎症浸润明显(P<0.05)。给予针刺及地塞米松干预后炎性细胞明显减少,且针刺肥胖哮喘组Treg细胞比例较肥胖哮喘组增加(P<0.001)。HIF-1α是哮喘炎症的关键调节因子,肥胖哮喘组表达明显增加,针刺及地塞米松治疗皆降低其表达(P<0.001)。 结论 筛选出的Vnn1和FAM126B可能作为肥胖哮喘患者治疗的关键基因,针刺治疗可能通过降低其表达而下调HIF-1α,提高Treg细胞数量。
李晓丰, 叶桃春, 席露, 李春桥, 刘慧慧. 针刺降低Vnn1/FAM126B基因表达进而减轻肥胖哮喘小鼠的气道慢性炎症[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(12): 2573-2584.
Xiaofeng LI, Taochun YE, Lu XI, Chunqiao LI, Huihui LIU. Acupuncture alleviates chronic airway inflammation in obese asthmatic mice by downregulating Vnn1 and FAM126B[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(12): 2573-2584.
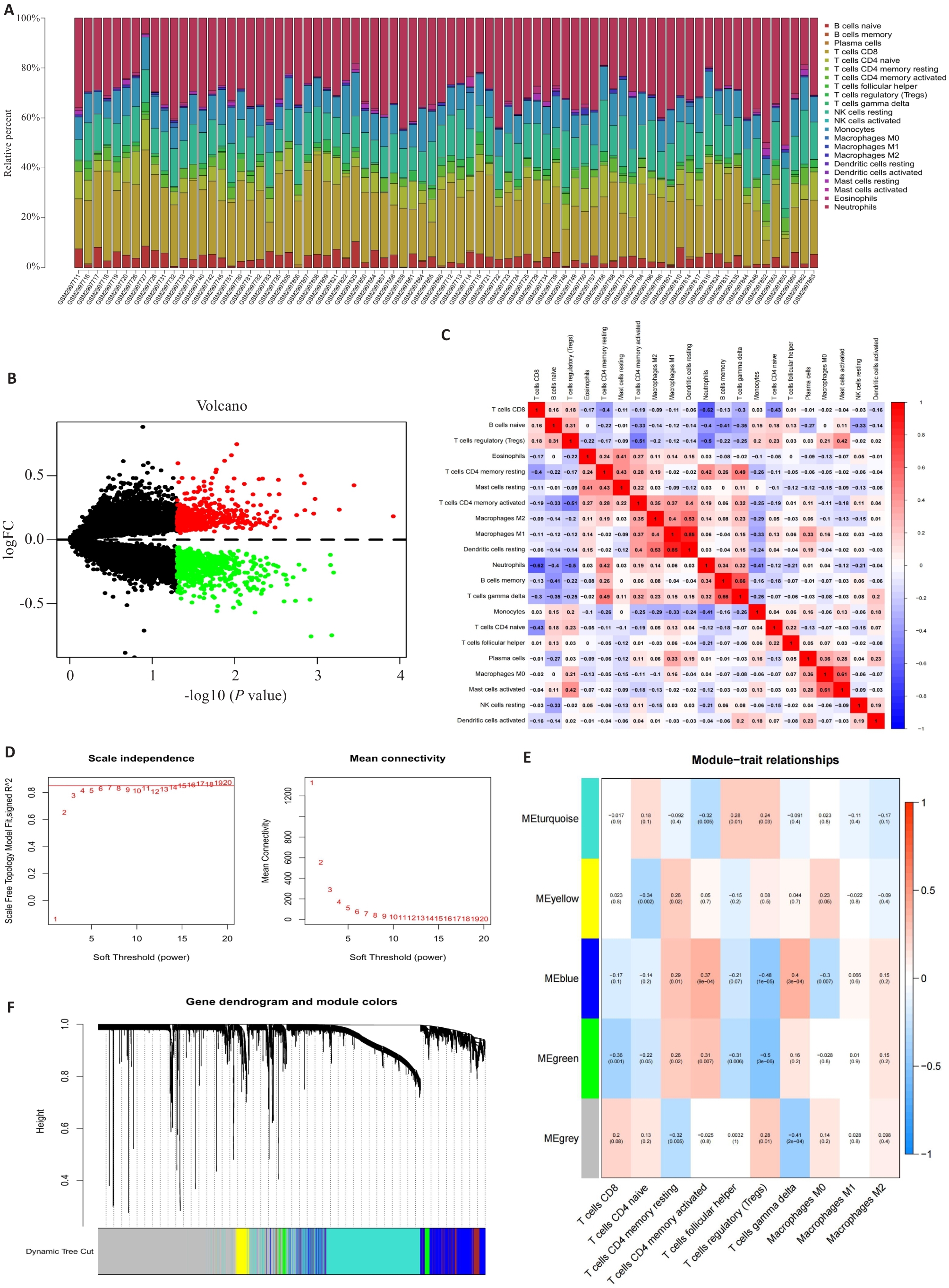
图1 差异表达基因(DEGs)的筛选:免疫浸润和WGCNA
Fig.1 Analysis of the differentially expressed genes (DEGs): Immune Infiltration and WGCNA. A: Stacked bar graph showing immune infiltration of multiple samples from GSE110551. B: Volcano plots showing the differences in gene expressions. C: Heat map showing the connections among different immune cell types. D: Selection of a soft threshold in a weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA). E: Results of hierarchical clustering based on gene expression data. F: Heat map showing connections of different modules and the specific features of each cell.
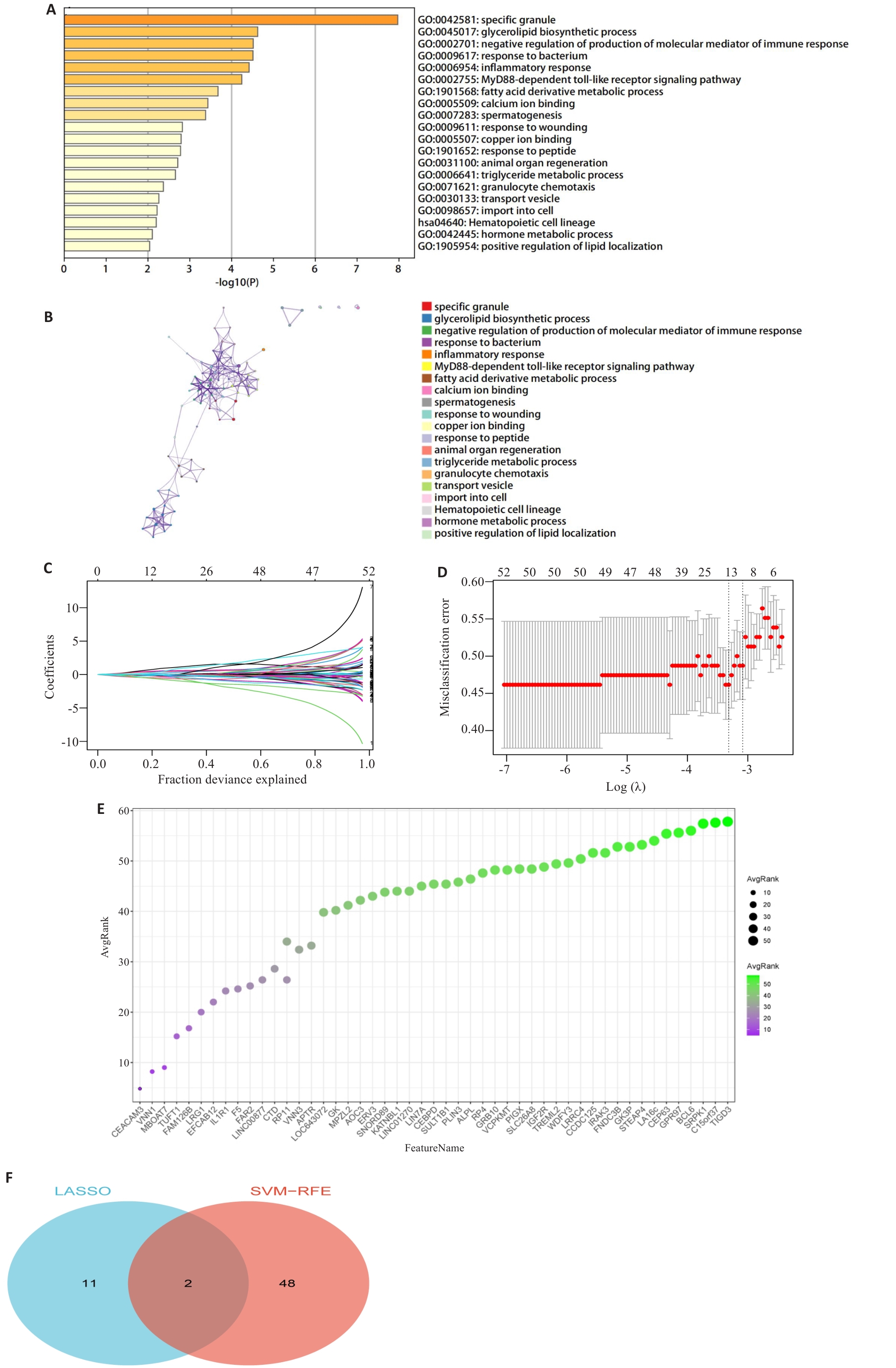
图2 差异表达基因(DEGs)的筛选:GO/KEGG富集分析和机器学习
Fig.2 Screening of the DEGs using GO/KEGG enrichment analysis and machine learning. A,B: Results of pathway analysis of genes in the green module using the Metascape website. C: Lasso regression curve diagram. D: Selection of the optimal λ value to balance model complexity and predictive performance. E: Evaluation of feature genes in obesity-asthma using the Support Vector Machine Recursive Feature Elimination (SVM-RFE) algorithm. F: Venn diagram of LASSO and SVM-RFE: two intersecting genes, FAM126B and VNN1, were obtained.
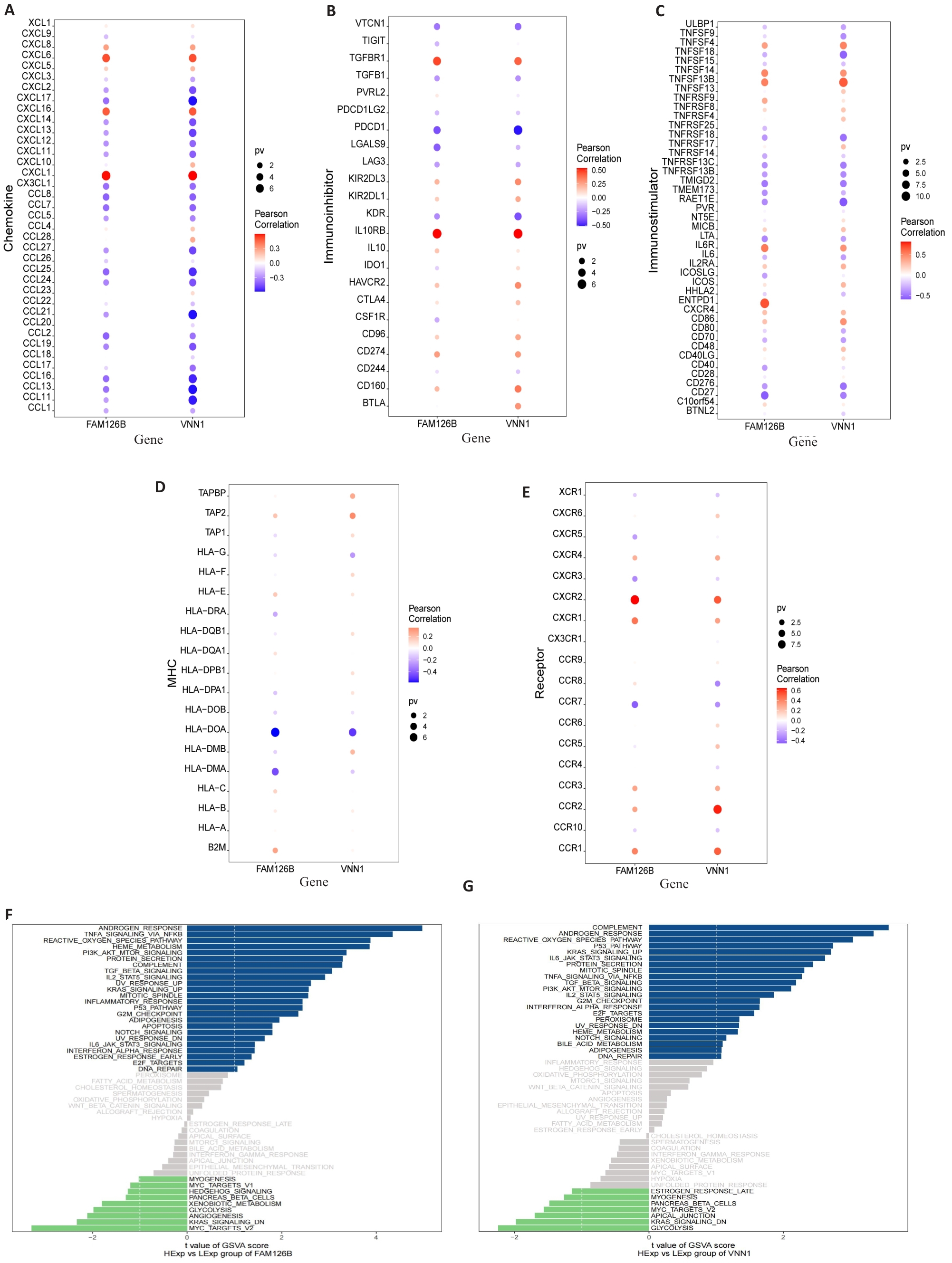
图3 FAM126B和VNN1涉及的免疫因子、GSVA分析
Fig.3 Immunological factors associated with FAM126B and VNN1 and GSVA analysis. A-E: Bubble plots showing the correlation between different chemokines, immunosuppressive factors, immunostimulatory factors, MHC, chemokine receptors, and the two specific genes (FAM126B and VNN1). F-G: GSVA bar charts for FAM126B and VNN1. Patients with high FAM126B and VNN1 expressions exhibit enrichment in different signaling pathways.
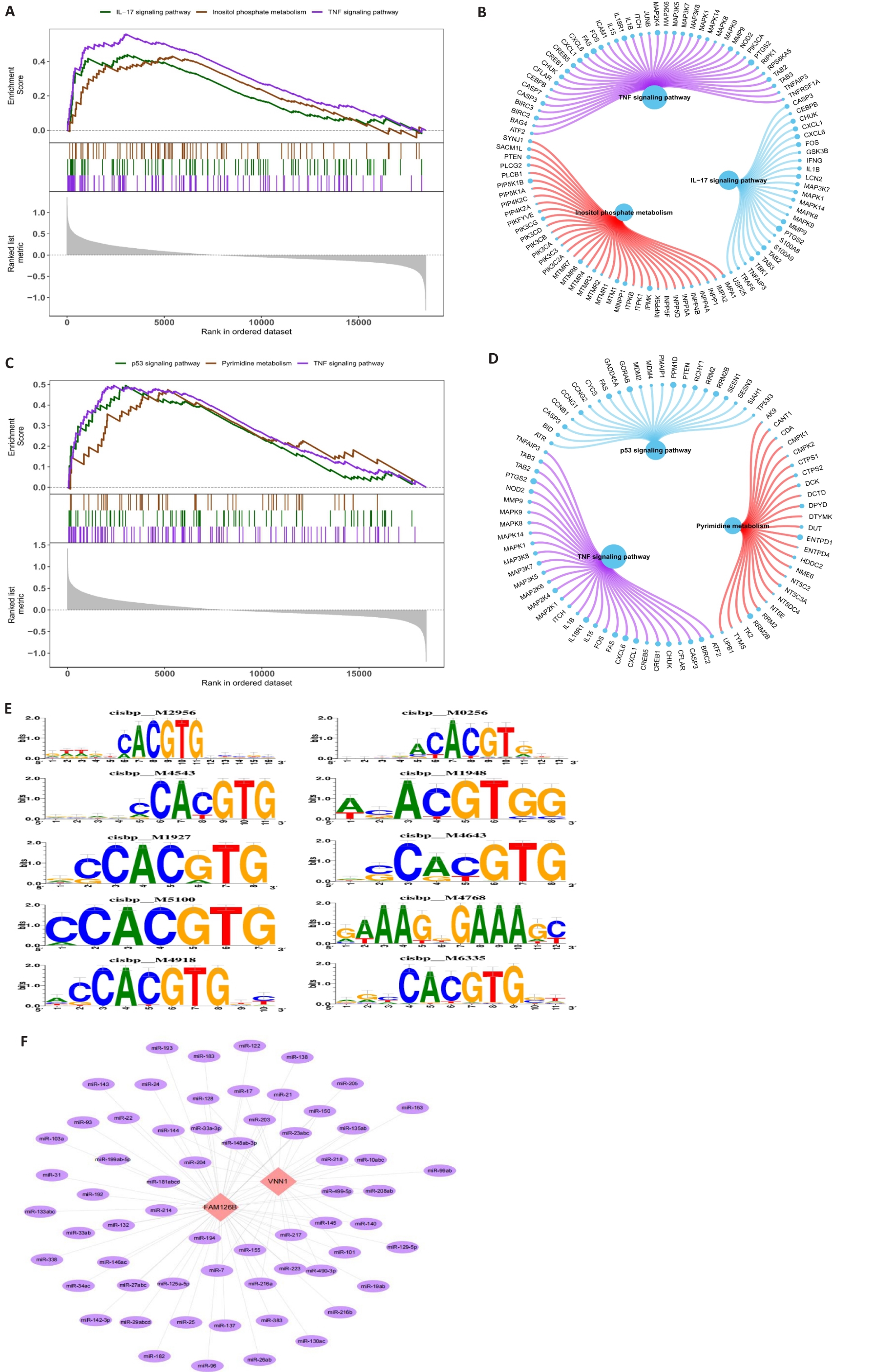
图4 FAM126B和VNN1的GSEA分析、多个转录因子共同调控富集分析以及mRNA-miRNA关系
Fig.4 GSEA analysis of FAM126B and VNN1, co-regulation enrichment analysis of multiple transcription factors, and mRNA-miRNA relationships. A,B: GSEA results and network diagram of FAM126B, enriched in the IL-17 signaling pathway, inositol phosphate metabolism, and TNF signaling pathway. C, D: GSEA results and network diagram for VNN1, enriched in the p53 signaling pathway, pyrimidine metabolism, and TNF signaling pathway. E: Enrichment analysis and motif-TF annotation of transcription factors. F: miRNA network diagram for FAM1268 and VNN1 using Cytoscape.
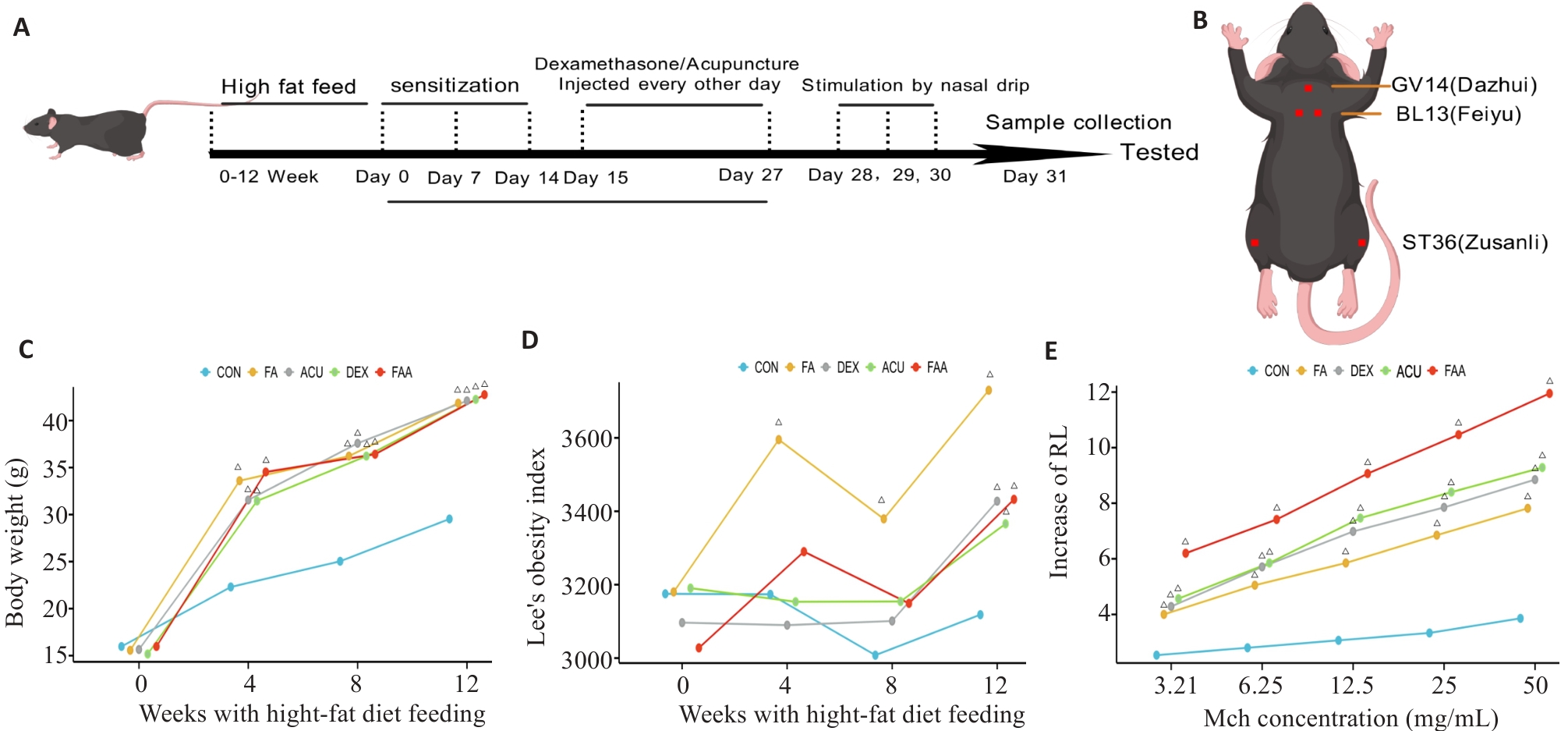
图5 肥胖哮喘小鼠模型及小鼠体质量随时间的变化
Fig.5 Obese asthma modeling in mice and weekly changes of the related parameters of the mice. A: Flow chart of animal experiment. B: Location of mice acupoints. C: Line chart of body weight changes of the mice. D: Line chart of lee's index in mice. E: Line chart of RF test of the mice. △P<0.05 vs COH. CON: Normal feeding group; FA: High-fat diet feeding group; ACU: High-fat feeding group with OVA sensitization and treatment with acupuncture; DEX: High-fat feeding group with OVA sensitization and 2 mg/kg dexamethasone gavage; FAA: High-fat feeding and OVA sensitization group.

图6 动物实验HE染色和血常规结果
Fig.6 HE staining of the lung tissues and blood routine results in each group. A-F: Pathological inflammatory cell infiltration in mice, including lymphocytes, eosinophils, and neutrophils (×100). The inflammation score was 0 in CON group, 1 in FA group, 3 in ACU group, 4 in DEX group, and 5 in FAA group. G: Mouse blood routine test results for neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocyte and eosinophils. △P<0.05 vs CON group; ○P<0.05 vs FA group; &P<0.05 vs ACU group; *P<0.05 vs DXE group.
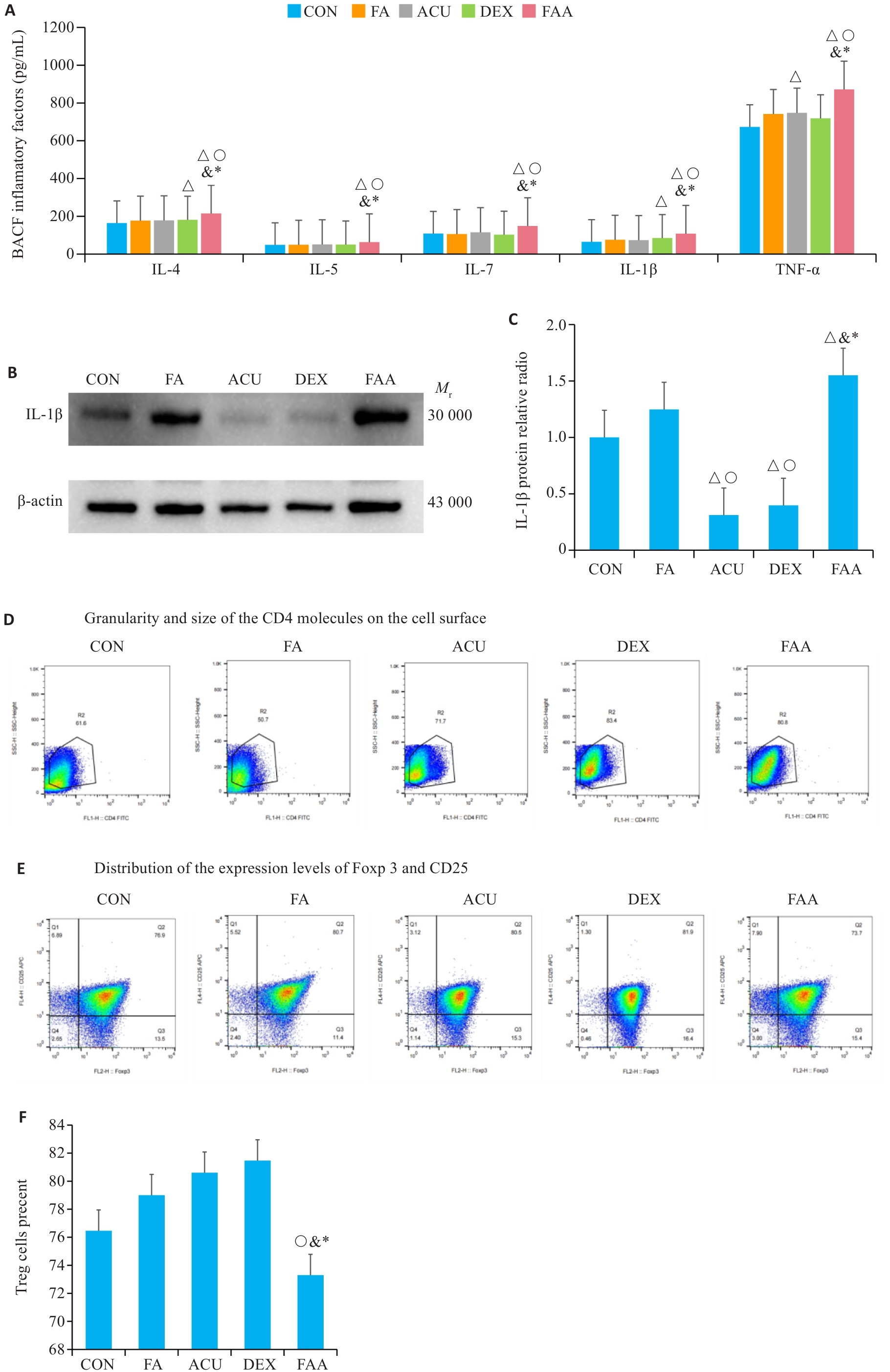
图7 针刺与地塞米松治疗效果
Fig.7 Therapeutic effects of acupuncture and dexamethasone in the mouse models. A: ELISA detection results of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid for IL-4, IL-5, IL-17, IL-1β, and TNF-α. B, C: Western blotting for detecting IL-1β expressions in each group. D-F: Flow cytometry for analysis of Treg cells. △P<0.05 vs CON group; ○P<0.05 vs FA group; &P<0.05 vs ACU group; *P<0.05 vs DXE group.
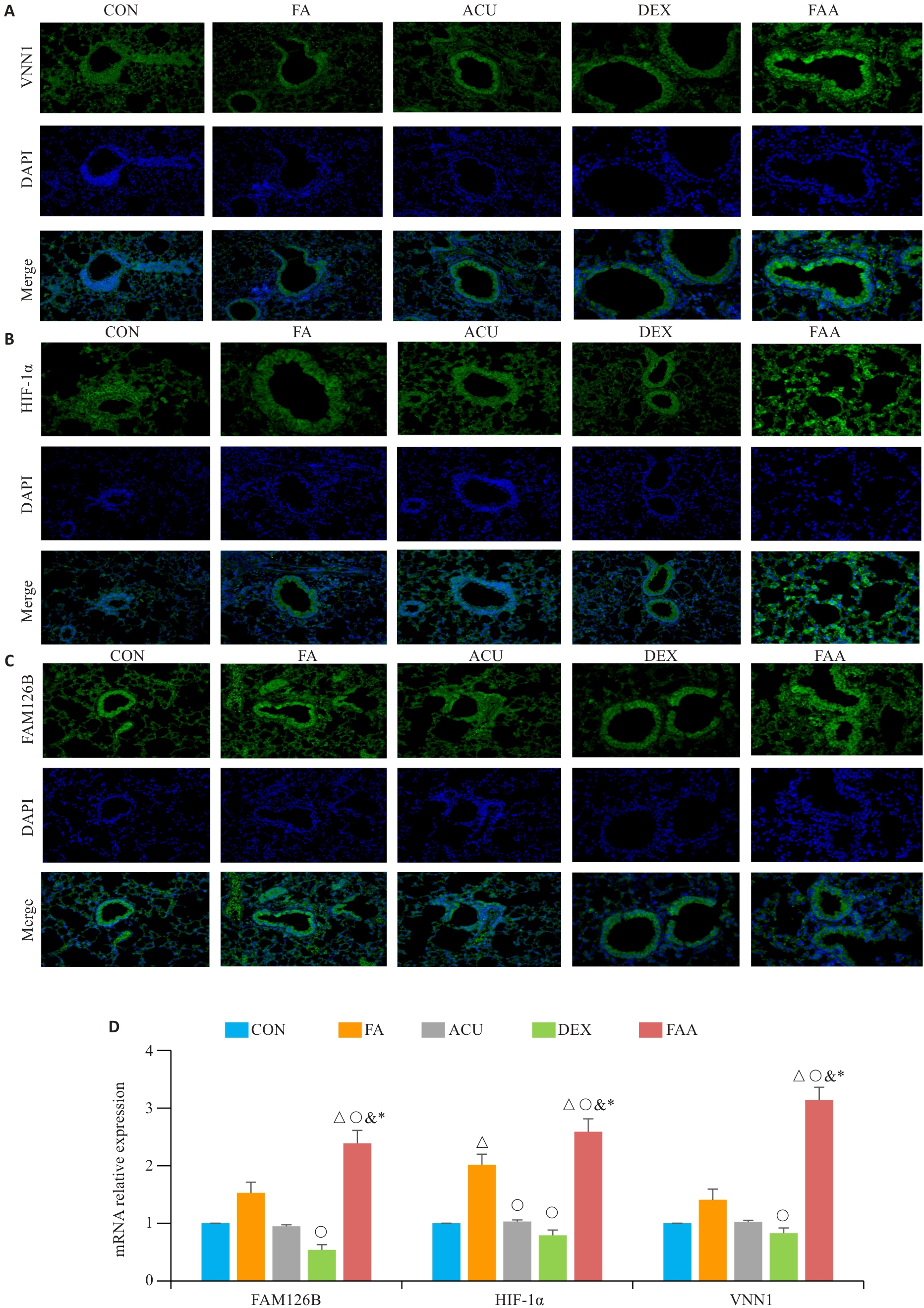
图8 HIF-1α、FAM126B和Vnn1在肥胖哮喘中的表达情况
Fig.8 Expression of HIF-1α, FAM126B and Vnn1 in mice with obese asthma. A-C: Immunofluorescence staining of Vnn1, FAM126B, and HIF-1α in the lung tissues (×100). D: Bar charts showing mRNA expression levels of HIF-1α, Vnn-1 and FAM126B in the lung tissues. △P<0.05 vs CON group; ○P<0.05 vs FA group; &P<0.05 vs ACU group; *P<0.05 vs DXE group.
| [1] | Grasemann H, Holguin F. Oxidative stress and obesity-related asthma[J]. Paediatr Respir Rev, 2021, 37: 18-21. doi:10.1016/j.prrv.2020.05.004 |
| [2] | Bhatraju NK, Agrawal A. Mitochondrial dysfunction linking obesity and asthma[J]. Ann Am Thorac Soc, 2017, 14(): S368-73. doi:10.1513/annalsats.201701-042aw |
| [3] | van der Wiel E, Ten Hacken NHT, van den Berge M, et al. Eosinophilic inflammation in subjects with mild-to-moderate asthma with and without obesity: disparity between sputum and biopsies[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2014, 189(10): 1281-4. doi:10.1164/rccm.201310-1841le |
| [4] | Wang YF, Zhao L, Gao LW, et al. Health policy and public health implications of obesity in China[J]. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, 2021, 9(7): 446-61. doi:10.1016/s2213-8587(21)00118-2 |
| [5] | Rabadán-Chávez G, Díaz de la Garza RI, Jacobo-Velázquez DA. White adipose tissue: Distribution, molecular insights of impaired expandability, and its implication in fatty liver disease[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta BBA Mol Basis Dis, 2023, 1869(8): 166853. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2023.166853 |
| [6] | Kim HY, Lee HJ, Chang YJ, et al. Interleukin-17-producing innate lymphoid cells and the NLRP3 inflammasome facilitate obesity-associated airway hyperreactivity[J]. Nat Med, 2014, 20(1): 54-61. doi:10.1038/nm.3423 |
| [7] | Silverpil E, Lindén A. IL-17 in human asthma[J]. Expert Rev Respir Med, 2012, 6(2): 173-86. doi:10.1586/ers.12.12 |
| [8] | Burbank AJ, Schworer SA, Sood A, et al. Airway IL-1β associates with IL-5 production following dust mite allergen inhalation in humans[J]. Respir Res, 2021, 22(1): 309. doi:10.1186/s12931-021-01903-9 |
| [9] | Kudo M, Melton AC, Chen C, et al. IL-17A produced by αβ T cells drives airway hyper-responsiveness in mice and enhances mouse and human airway smooth muscle contraction[J]. Nat Med, 2012, 18(4): 547-54. doi:10.1038/nm.2684 |
| [10] | Crotty Alexander LE, Akong-Moore K, Feldstein S, et al. Myeloid cell HIF-1α regulates asthma airway resistance and eosinophil function[J]. J Mol Med (Berl), 2013, 91(5): 637-44. doi:10.1007/s00109-012-0986-9 |
| [11] | Byun Y, Choi YC, Jeong Y, et al. miR-200c downregulates HIF-1α and inhibits migration of lung cancer cells[J]. Cell Mol Biol Lett, 2019, 24: 28. doi:10.1186/s11658-019-0152-2 |
| [12] | 刘慧慧, 刘嘉羿, 彭美玉, 等. 针刺对气道重塑小鼠TGF-β1/Smads通路的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2018, 38(11): 1372-7. |
| [13] | Athar M, Manhas A, Rana N, et al. Computational and bioinformatics tools for understanding disease mechanisms[J]. Biocell, 2024, 48(6): 935-44. doi:10.32604/biocell.2024.049891 |
| [14] | China Association of Acupuncture and Moxibustion. 实验动物常用穴位名称与定位 第3部分: 小鼠[J]. 世界针灸杂志: 英文版, 2025, 35(2): 160-6. |
| [15] | Gomez-Llorente MA, Romero R, Chueca N, et al. Obesity and asthma: a missing link[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2017, 18(7): 1490. doi:10.3390/ijms18071490 |
| [16] | Frohnert BI, Bernlohr DA. Glutathionylated products of lipid peroxidation: a novel mechanism of adipocyte to macrophage signaling[J]. Adipocyte, 2014, 3(3): 224-9. doi:10.4161/adip.28851 |
| [17] | Li RJ, Wen YX. Association of body mass index with asthma occurrence and persistence in adolescents: a retrospective study of NHANES (2011–2018)[J]. Heliyon, 2023, 9(9): e20092. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20092 |
| [18] | Uribe-Querol E, Rosales C. Neutrophils actively contribute to obesity-associated inflammation and pathological complications[J]. Cells, 2022, 11(12): 1883. doi:10.3390/cells11121883 |
| [19] | Bartucci R, Salvati A, Olinga P, et al. Vanin 1: its physiological function and role in diseases[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(16): 3891. doi:10.3390/ijms20163891 |
| [20] | Chen SY, Zhang WX, Tang CQ, et al. Vanin-1 is a key activator for hepatic gluconeogenesis[J]. Diabetes, 2014, 63(6): 2073-85. doi:10.2337/db13-0788 |
| [21] | Berruyer C, Martin FM, Castellano R, et al. Vanin-1-/ - mice exhibit a glutathione-mediated tissue resistance to oxidative stress[J]. Mol Cell Biol, 2004, 24(16): 7214-24. doi:10.1128/mcb.24.16.7214-7224.2004 |
| [22] | Wei Y, Dong M, Zhong L, et al. Regulation of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis activity and immunologic function contributed to the anti-inflammatory effect of acupuncture in the OVA-induced murine asthma model[J]. Neurosci Lett, 2017, 636: 177-83. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2016.11.001 |
| [23] | Shi LZ, Wang RN, Huang GH, et al. HIF1alpha-dependent glycolytic pathway orchestrates a metabolic checkpoint for the differentiation of TH17 and Treg cells[J]. J Exp Med, 2011, 208(7): 1367-76. doi:10.1084/jem.20110278 |
| [24] | Huerta-Yepez S, Baay-Guzman GJ, Bebenek IG, et al. Hypoxia inducible factor promotes murine allergic airway inflammation and is increased in asthma and rhinitis[J]. Allergy, 2011, 66(7): 909-18. doi:10.1111/j.1398-9995.2011.02594.x |
| [25] | Zhu YP, Wu F, Gui WW, et al. A positive feedback regulatory loop involving the lncRNA PVT1 and HIF-1α in pancreatic cancer[J]. J Mol Cell Biol, 2021, 13(9): 676-89. doi:10.1093/jmcb/mjab042 |
| [26] | Guo JL, Wang GQ, Liu T, et al. Acupuncture improves chronic cerebral ischemia by inhibiting the CKLF1/HIF-1α/VEGF/Notch1 signaling pathway[J]. CNS Neurosci Ther, 2025, 31(3): e70246. doi:10.1111/cns.70246 |
| [27] | Liu HH, Liu JY, Peng MY, et al. Effect of acupuncture on TGF-β1/Smads pathway in mice with airway remodeling mic[J]. J South Med Univ, 2018, 38(11): 1372-7. |
| [28] | Xiao C, Biagini Myers JM, Ji H, et al. Vanin-1 expression and methylation discriminate pediatric asthma corticosteroid treatment response[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2015, 136(4): 923-31.e3. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2015.01.045 |
| [29] | Zhang ZZ, He YW, Liu H, et al. NLRP3 regulates ferroptosis via the JAK2/STAT3 pathway in asthma inflammation: Insights from in vivo and in vitro studies[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2024, 143(Pt 2): 113416. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113416 |
| [1] | 王心恒, 邵小涵, 李童童, 张璐, 杨勤军, 叶卫东, 童佳兵, 李泽庚, 方向明. 平喘宁方通过调控HMGB1/Beclin-1轴介导的自噬改善患寒哮证大鼠的气道炎症[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1153-1162. |
| [2] | 董梦璐, 朱恬, 马俊文, 杜晓红, 冯媛. 复氧改善间歇性缺氧所致的肥胖大鼠下丘脑瘦素反应性降低[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1696-1703. |
| [3] | 肖静, 李盈, 方敏, 巩红, 李文, 张春艳, 陈方尧, 张岩, 韩拓. 甘油三酯-葡萄糖指数与非肥胖型非酒精性脂肪性肝病的相关性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(7): 1266-1271. |
| [4] | 包汉生, 王苏童, 吕穆杰, 王永成, 姜 萍, 李 晓. 激活α7nAchR促进肥胖小鼠的脂肪稳态和米色脂肪生成及产热作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 499-506. |
| [5] | 王坤, 方昊翔, 曹晓梅, 朱子衡. miR-139-5p调控Notch/RBP-J/Hes1轴促进支气管哮喘骨髓间充质干细胞“归巢”[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(12): 2283-2290. |
| [6] | 黄 奕, 林丽珊, 黄浩华, 董航明. VDAC1通过诱导气道上皮细胞铁死亡参与屋尘螨诱导的哮喘小鼠气道炎症[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(8): 1333-1338. |
| [7] | 周 蓓, 李 静, 方晨圆, 黄亚楠, 桑贵蕊, 陶少平, 何春玲. 二甲双胍/维格列汀和利拉鲁肽对肥胖合并2型糖尿病患者的临床疗效比较[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(3): 436-442. |
| [8] | 叶 潇, 宋迎香, 赵 瑜, 朱大龙. 脂肪组织黏膜相关恒定T细胞通过分泌白介素4调节小鼠脂肪棕色化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(11): 1881-1885. |
| [9] | 吴江豪, 吴永鑫, 杨韵菲, 余 靖, 傅 饶, 孙 悦, 肖 谦. Mibefradil可改善肥胖小鼠骨骼肌的质量、功能和结构[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(7): 1032-1037. |
| [10] | 黄浩华, 乔妤婕, 黄 奕, 董航明. HSP90α通过调控气道上皮细胞内质网应激加重屋尘螨诱导的哮喘气道炎症[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(3): 347-353. |
| [11] | 杨淑銮, 赵文驱, 彭显如, 蓝紫涵, 黄俊文, 韩慧珊, 陈 颖, 蔡绍曦, 赵海金. 抑制TAK1可加重甲苯二异氰酸酯诱导的哮喘小鼠气道炎症[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(2): 181-189. |
| [12] | 许 婷, 崔 壮, 王俊洁, 冯 媛, 谢 仁, 李丹青, 彭 婧, 黄 蓉, 李涛平. 芳香烃受体通过介导Th17/Treg分化调控蟑螂过敏原诱导的哮喘[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(5): 716-721. |
| [13] | 丁孟汝, 王国栋, 袁平川, 何曙光, 邵太丽, 柳春燕, 孔 祥. 多糖调控糖脂代谢的作用及其机制研究进展[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(3): 471-474. |
| [14] | 张 玲, 李贵芳, 苏莉莉, 杜 磊, 周东雷, 程晓芸, 林紫薇, 曲 伸. 黑棘皮病和非黑棘皮病患者的总睾酮水平与胰岛素抵抗的相关性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(12): 1780-1786. |
| [15] | 王 坤, 朱慧志, 杨 磊, 徐晴雯, 任冯春, 刘向国. 抑制Notch1/Jagged1通路可促进大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞“归巢”并改善哮喘[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(10): 1464-1472. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||