南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (4): 880-892.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.04.24
• • 上一篇
李煜桐1,2( ), 宋杏钰1,2, 孙蕊旭1,2, 董璇1,2, 刘宏伟1,2(
), 宋杏钰1,2, 孙蕊旭1,2, 董璇1,2, 刘宏伟1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2025-02-17
出版日期:2025-04-20
发布日期:2025-04-28
通讯作者:
刘宏伟
E-mail:liyutong@gdmu.edu.cn;lhwhongwei@gdmu.edu.cn
作者简介:李煜桐,在读本科生,E-mail: liyutong@gdmu.edu.cn
基金资助:
Yutong LI1,2( ), Xingyu SONG1,2, Ruixu SUN1,2, Xuan DONG1,2, Hongwei LIU1,2(
), Xingyu SONG1,2, Ruixu SUN1,2, Xuan DONG1,2, Hongwei LIU1,2( )
)
Received:2025-02-17
Online:2025-04-20
Published:2025-04-28
Contact:
Hongwei LIU
E-mail:liyutong@gdmu.edu.cn;lhwhongwei@gdmu.edu.cn
摘要:
目的 基于生物信息学分析探究吡咯啉-5-羧酸还原酶-1(PYCR1)作为泛癌生物标志物的潜力,并探究其在膀胱癌(BLCA)中的表达、功能及临床意义。 方法 通过生物信息学分析PYCR1与泛癌患者预后、免疫微环境重塑、肿瘤突变负荷及微卫星不稳定性的关联。在TCGA-BLCA数据集中通过单因素和多因素回归分析PYCR1作为BLCA患者独立预后风险因素的潜力,并构建临床决策模型。利用IMvigor210中的BLCA队列鉴定PYCR1作为免疫治疗效果评估独立因子的潜力。基于pRRophetic药物库筛选PYCR1高表达时BLCA治疗耐受的潜在化疗药物。CMap-XSum算法和分子对接技术用于筛选并验证小分子PYCR1抑制剂。 结果 PYCR1高表达与多种肿瘤不良预后、免疫细胞浸润、肿瘤突变负荷及微卫星不稳定性显著相关(r>0.3)。PYCR1在BLCA中过表达,PYCR1高表达与BLCA预后差密切相关(HR:1.14,95% CI: 1.02-1.68,P=0.006)。PYCR1高表达时西妥昔单抗、5-氟尿嘧啶、多柔比星等抗肿瘤药物IC50提高(P<0.0001)。 结论 PYCR1是癌症潜在的预后生物标志物和治疗靶点,PYCR1高表达是BLCA患者不良预后的独立危险因素,其具有良好的临床决策能力,是预测化疗药物敏感性和免疫治疗效果的指标。
李煜桐, 宋杏钰, 孙蕊旭, 董璇, 刘宏伟. PYCR1的泛癌分析及其对膀胱癌化疗和免疫治疗应答的潜在预测价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 880-892.
Yutong LI, Xingyu SONG, Ruixu SUN, Xuan DONG, Hongwei LIU. A pan-cancer analysis of PYCR1 and its predictive value for chemotherapy and immunotherapy responses in bladder cancer[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 880-892.
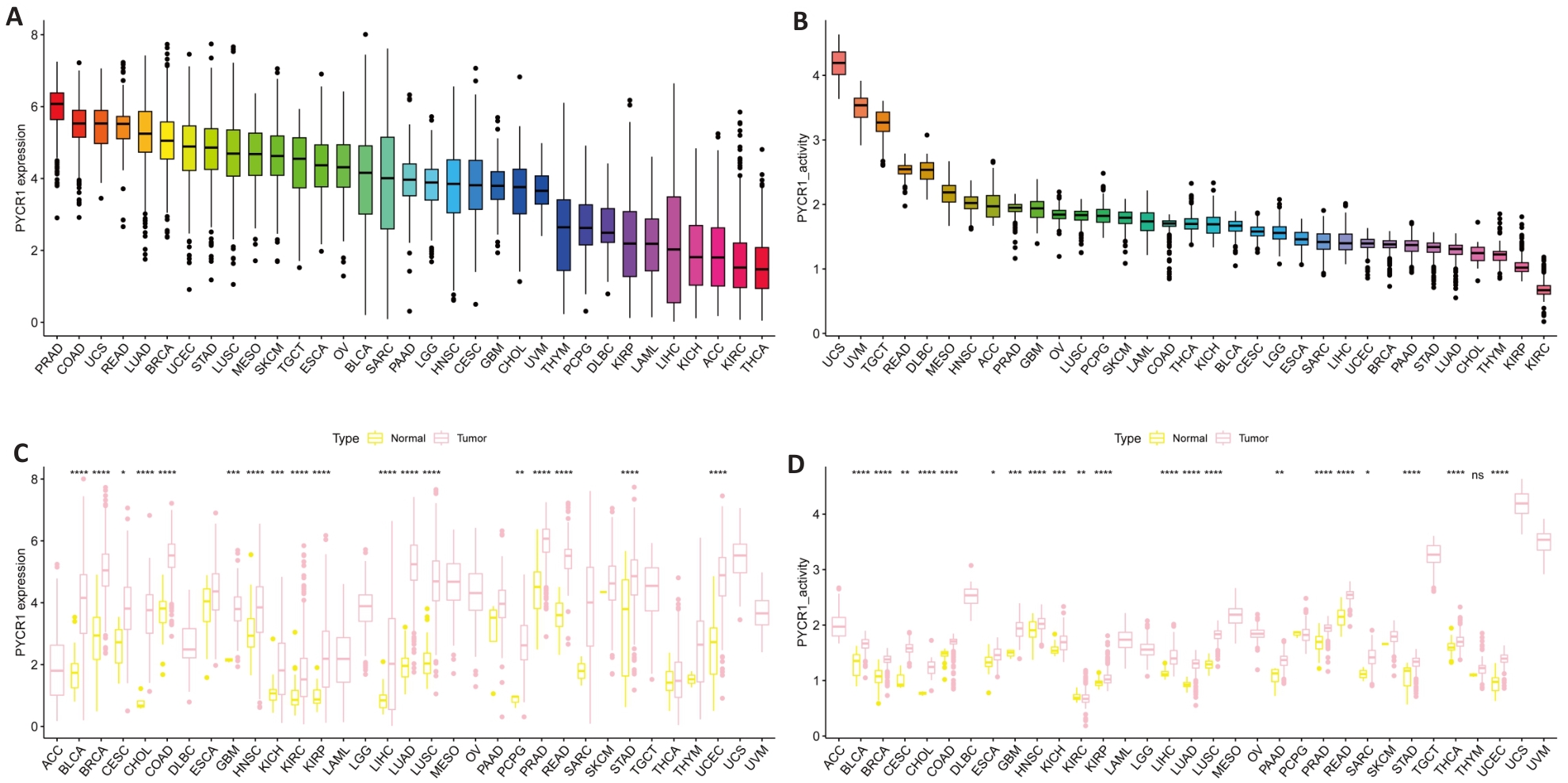
图1 泛癌中PYCR1的表达
Fig.1 Expression of PYCR1 in pan-cancer. A, B: mRNA and protein expression levels of PYCR1 in UCSC Xena and GTEx pan-cancer data. C, D: Differences in mRNA and protein expression levels of PYCR1 between cancer and adjacent tissues in 33 cancers. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001 vs control group.
| Index | Cancers | HR | 95% CI | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OS | SARC KIRP KIRC ESCA ACC LGG | 1.29 2.01 1.59 1.22 1.68 0.78 | 1.13-1.47 1.58-2.54 1.40-1.80 0.94-1.59 1.28-2.21 0.60-1.00 0.96-3.35 0.67-1.01 1.37-2.09 1.44-1.87 1.18-4.23 1.25-1.92 1.12-2.47 0.74-4.82 1.27-2.24 1.59-2.15 0.90-1.65 1.09-1.45 2.92-1003.87 2.27-4.20 | <0.001 <0.01 <0.01 0.022 0.022 0.017 |
| PFS | UVM LGG KIRP KIRC KICH ACC | 1.79 0.82 1.69 1.64 2.24 1.54 | 0.032 0.013 <0.01 <0.01 0.020 <0.01 | |
| DFS | ACC | 1.66 | 0.024 | |
| DSS | PCPG ACC KIRC ESCA SARC PRAD KIRP | 1.88 1.69 1.85 1.22 1.26 54.17 3.09 | 0.022 0.028 <0.01 0.043 0.047 0.030 <0.01 |
表1 泛癌中PYCR1的预后意义
Tab.1 Prognostic significance of PYCR1 in pan-cancer
| Index | Cancers | HR | 95% CI | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OS | SARC KIRP KIRC ESCA ACC LGG | 1.29 2.01 1.59 1.22 1.68 0.78 | 1.13-1.47 1.58-2.54 1.40-1.80 0.94-1.59 1.28-2.21 0.60-1.00 0.96-3.35 0.67-1.01 1.37-2.09 1.44-1.87 1.18-4.23 1.25-1.92 1.12-2.47 0.74-4.82 1.27-2.24 1.59-2.15 0.90-1.65 1.09-1.45 2.92-1003.87 2.27-4.20 | <0.001 <0.01 <0.01 0.022 0.022 0.017 |
| PFS | UVM LGG KIRP KIRC KICH ACC | 1.79 0.82 1.69 1.64 2.24 1.54 | 0.032 0.013 <0.01 <0.01 0.020 <0.01 | |
| DFS | ACC | 1.66 | 0.024 | |
| DSS | PCPG ACC KIRC ESCA SARC PRAD KIRP | 1.88 1.69 1.85 1.22 1.26 54.17 3.09 | 0.022 0.028 <0.01 0.043 0.047 0.030 <0.01 |
| Cancers | Description |
|---|---|
| CESC | Maturity-onset diabetes of the young, Glutathione metabolism, Melanoma Olfactory Transduction, Maturity-onset diabetes of the young, Ascorbic Acid Metabolism Taurine and Hypotaurine Metabolism, Taste transduction, Hedgehog signaling pathway Ascorbic Acid Metabolism, Autophagy, Pentose and Glucuronate Interconversions Lysine Degradation, Arginine and Proline Metabolism, Basal Cell Carcinoma Folate biosynthesis, Autophagy, Cytosolic DNA sensing by cGAS Other glycan degradation, Autophagy, Butanoate Metabolism Primary immunodeficiency, Viral myocarditis, Graft-Versus-Host Disease Viral myocarditis, Maturity-onset diabetes of the young, Glutathione metabolism |
| LUSC | |
| LIHC | |
| THYM | |
| LAML | |
| CHOL | |
| UCS | |
| THCA | |
| KICH | |
| HNSC | Ascorbic Acid Metabolism, Porphyrin and Chlorophyll Metabolism, Metabolism of xenobiotics by cytochrome P450 |
| UCEC | Olfactory Transduction, Autophagy, Autoimmune thyroid disorders |
| STAD | Dilated cardiomyopathy, Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy, Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy |
| ACC | Glycosaminoglycan degradation, Hedgehog signaling pathway, Olfactory Transduction |
| SKCM | Primary immunodeficiency, Linoleic acid metabolism, Graft-Versus-Host Disease |
| LUAD | Olfactory Transduction, Autophagy, RIG-I-like Receptor signaling pathway |
| TGCT | Allograft rejection, Graft-Versus-Host Disease, Primary immunodeficiency |
| READ | Cytosolic DNA sensing by cGAS, Autoimmune thyroid disorders, Autophagy |
| LGG | Pentose and Glucuronate Interconversions, Ascorbic Acid Metabolism, Porphyrin and Chlorophyll Metabolism |
| BRCA | Olfactory Transduction, Cytosolic DNA sensing by cGAS, Autoimmune thyroid disorders |
| COAD | Taste transduction, Olfactory Transduction, Cytosolic DNA sensing by cGAS |
| BLCA | Maturity-onset diabetes of the young, Valine, Leucine, and Isoleucine Degradation, Graft-Versus-Host Disease |
表2 泛癌中PYCR1调控的分子功能(前3)
Tab.2 Top 3 molecular functions regulated by PYCR1 in pan-cancer
| Cancers | Description |
|---|---|
| CESC | Maturity-onset diabetes of the young, Glutathione metabolism, Melanoma Olfactory Transduction, Maturity-onset diabetes of the young, Ascorbic Acid Metabolism Taurine and Hypotaurine Metabolism, Taste transduction, Hedgehog signaling pathway Ascorbic Acid Metabolism, Autophagy, Pentose and Glucuronate Interconversions Lysine Degradation, Arginine and Proline Metabolism, Basal Cell Carcinoma Folate biosynthesis, Autophagy, Cytosolic DNA sensing by cGAS Other glycan degradation, Autophagy, Butanoate Metabolism Primary immunodeficiency, Viral myocarditis, Graft-Versus-Host Disease Viral myocarditis, Maturity-onset diabetes of the young, Glutathione metabolism |
| LUSC | |
| LIHC | |
| THYM | |
| LAML | |
| CHOL | |
| UCS | |
| THCA | |
| KICH | |
| HNSC | Ascorbic Acid Metabolism, Porphyrin and Chlorophyll Metabolism, Metabolism of xenobiotics by cytochrome P450 |
| UCEC | Olfactory Transduction, Autophagy, Autoimmune thyroid disorders |
| STAD | Dilated cardiomyopathy, Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy, Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy |
| ACC | Glycosaminoglycan degradation, Hedgehog signaling pathway, Olfactory Transduction |
| SKCM | Primary immunodeficiency, Linoleic acid metabolism, Graft-Versus-Host Disease |
| LUAD | Olfactory Transduction, Autophagy, RIG-I-like Receptor signaling pathway |
| TGCT | Allograft rejection, Graft-Versus-Host Disease, Primary immunodeficiency |
| READ | Cytosolic DNA sensing by cGAS, Autoimmune thyroid disorders, Autophagy |
| LGG | Pentose and Glucuronate Interconversions, Ascorbic Acid Metabolism, Porphyrin and Chlorophyll Metabolism |
| BRCA | Olfactory Transduction, Cytosolic DNA sensing by cGAS, Autoimmune thyroid disorders |
| COAD | Taste transduction, Olfactory Transduction, Cytosolic DNA sensing by cGAS |
| BLCA | Maturity-onset diabetes of the young, Valine, Leucine, and Isoleucine Degradation, Graft-Versus-Host Disease |
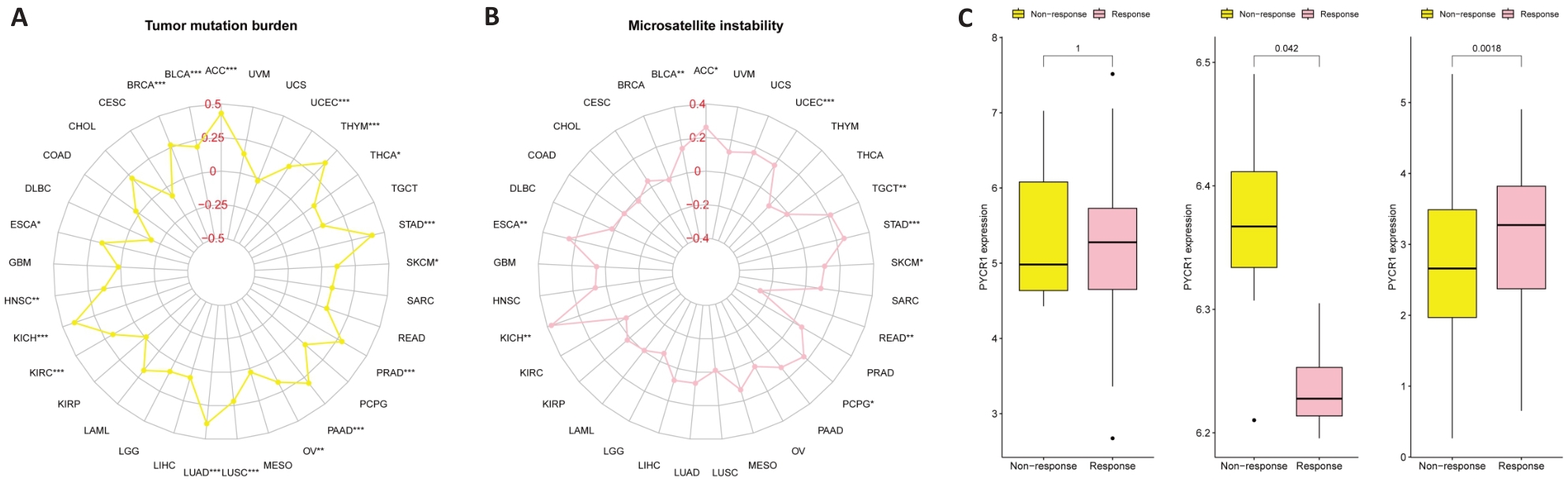
图4 泛癌中PYCR1评估TMB、MSI以及免疫治疗获益的潜力
Fig.4 Potential of PYCR1 for assessing tumor mutation burden (TMB), microsatellite instability (MSI) and immune therapy benefits in pan-cancer. A: Correlation of PYCR1 with TMB and MSI. B: Correlation of PYCR1 with benefits of anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in SKCM patients in the SKCM immunotherapy cohort. C: Correlation of PYCR1 with benefits of anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy in RCC patients in the metastatic RCC immunotherapy cohort. D: Correlation of PYCR1 with immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy benefit in patients with BLCA in the IMvigor210 cohort.
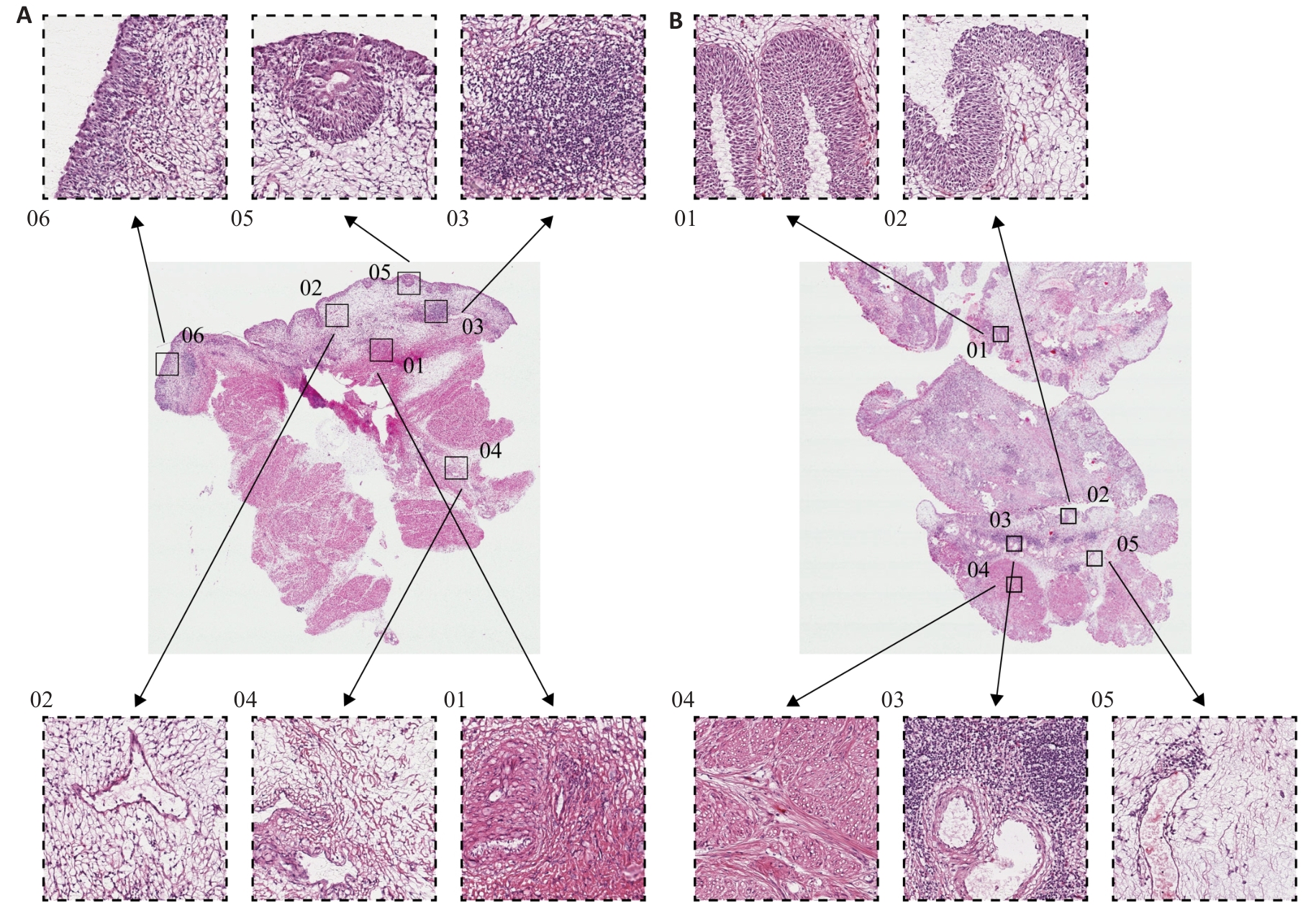
图6 PYCR1高表达和低表达的BLCA组织学特征
Fig.6 Histological features of BLCA with high and low PYCR1 expressions. A: HE staining profile of BLCA tissue with high PYCR1 expression level (Original magnification: ×1000). B: HE staining profile of BLCA tissue with low PYCR1 expression level (×1000).

图7 沉默PYCR1对BLCA细胞系增殖能力的影响
Fig.7 Effect of PYCR1 silencing on proliferative capacity of BLCA cell lines. A: mRNA expression levels of PYCR1 in BLCA cell lines and SV-HUC-1. **P<0.01 vs SV-HUC-1. B: Verification of PYCR1 silencing efficiency. C: Effect of PYCR1 silencing on proliferation of T24 and UM-UC-3 cells. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs si-NC.
| Characteristics | HR | 95% CI | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | 1.05 | 1.02-1.07 | <0.001 |
| Tumor classification | 1.25 | 1.04-1.49 | 0.016 |
| Copy number variation | 0.97 | 0.79-1.19 | 0.764 |
| Gender | 0.95 | 0.55-1.65 | 0.858 |
| Grade | 2.02 | 0.49-8.29 | 0.327 |
| Hypermethylation | 0.93 | 0.79-1.09 | 0.377 |
| Hypomethylation | 0.92 | 0.78-1.08 | 0.044 |
| Tumor mutation burden | 1.10 | 0.85-1.44 | 0.457 |
| PYCR1 | 1.23 | 0.99-1.87 | 0.032 |
| Race | 0.91 | 0.67-1.24 | 0.544 |
| Single nucleotide variation | 1.00 | 0.99-1.01 | 0.027 |
| Stage | 1.60 | 1.19-2.15 | 0.002 |
表3 单因素回归分析识别BLCA危险因素
Tab.3 Univariate analysis for identifying prognostic risk factors for BLCA
| Characteristics | HR | 95% CI | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | 1.05 | 1.02-1.07 | <0.001 |
| Tumor classification | 1.25 | 1.04-1.49 | 0.016 |
| Copy number variation | 0.97 | 0.79-1.19 | 0.764 |
| Gender | 0.95 | 0.55-1.65 | 0.858 |
| Grade | 2.02 | 0.49-8.29 | 0.327 |
| Hypermethylation | 0.93 | 0.79-1.09 | 0.377 |
| Hypomethylation | 0.92 | 0.78-1.08 | 0.044 |
| Tumor mutation burden | 1.10 | 0.85-1.44 | 0.457 |
| PYCR1 | 1.23 | 0.99-1.87 | 0.032 |
| Race | 0.91 | 0.67-1.24 | 0.544 |
| Single nucleotide variation | 1.00 | 0.99-1.01 | 0.027 |
| Stage | 1.60 | 1.19-2.15 | 0.002 |
| Characteristics | HR | 95% CI | Assignment and Attributes | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | 1.04 | 1.02-1.07 | Continuous variable | 0.001 |
| Tumor classification | 1.16 | 0.95-1.41 | 0= LumP,1= LumNS,2= LumU,3= Stroma-rich,4= Ba/Sq,5= NE-like | 0.135 |
| Hypomethylation | 0.89 | 0.75-1.05 | Continuous variable | 0.162 |
| PYCR1 | 1.14 | 1.02-1.68 | Continuous variable | 0.006 |
| Single nucleotide variation | 1.00 | 0.99-1.01 | Continuous variable | 0.019 |
| Stage | 1.49 | 1.10-2.04 | 0= I-II,1= III-IV | 0.011 |
表4 多因素回归分析识别BLCA独立预后风险因素
Tab.4 Multivariate analysis for identifying independent prognostic risk factors for BLCA
| Characteristics | HR | 95% CI | Assignment and Attributes | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | 1.04 | 1.02-1.07 | Continuous variable | 0.001 |
| Tumor classification | 1.16 | 0.95-1.41 | 0= LumP,1= LumNS,2= LumU,3= Stroma-rich,4= Ba/Sq,5= NE-like | 0.135 |
| Hypomethylation | 0.89 | 0.75-1.05 | Continuous variable | 0.162 |
| PYCR1 | 1.14 | 1.02-1.68 | Continuous variable | 0.006 |
| Single nucleotide variation | 1.00 | 0.99-1.01 | Continuous variable | 0.019 |
| Stage | 1.49 | 1.10-2.04 | 0= I-II,1= III-IV | 0.011 |
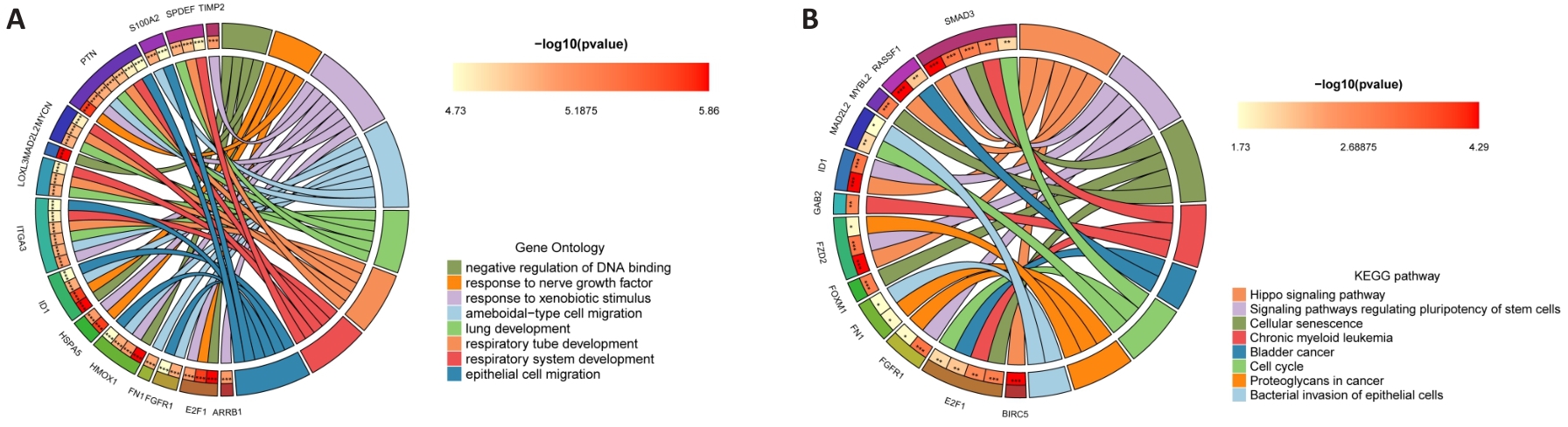
图10 PYCR1促进BLCA进展调控的分子机制
Fig.10 Molecular mechanism of PYCR1 for promoting BLCA progression. A, B: GO and KEGG signaling pathway enrichment analysis circle diagram of PYCR1 co-expressed genes.
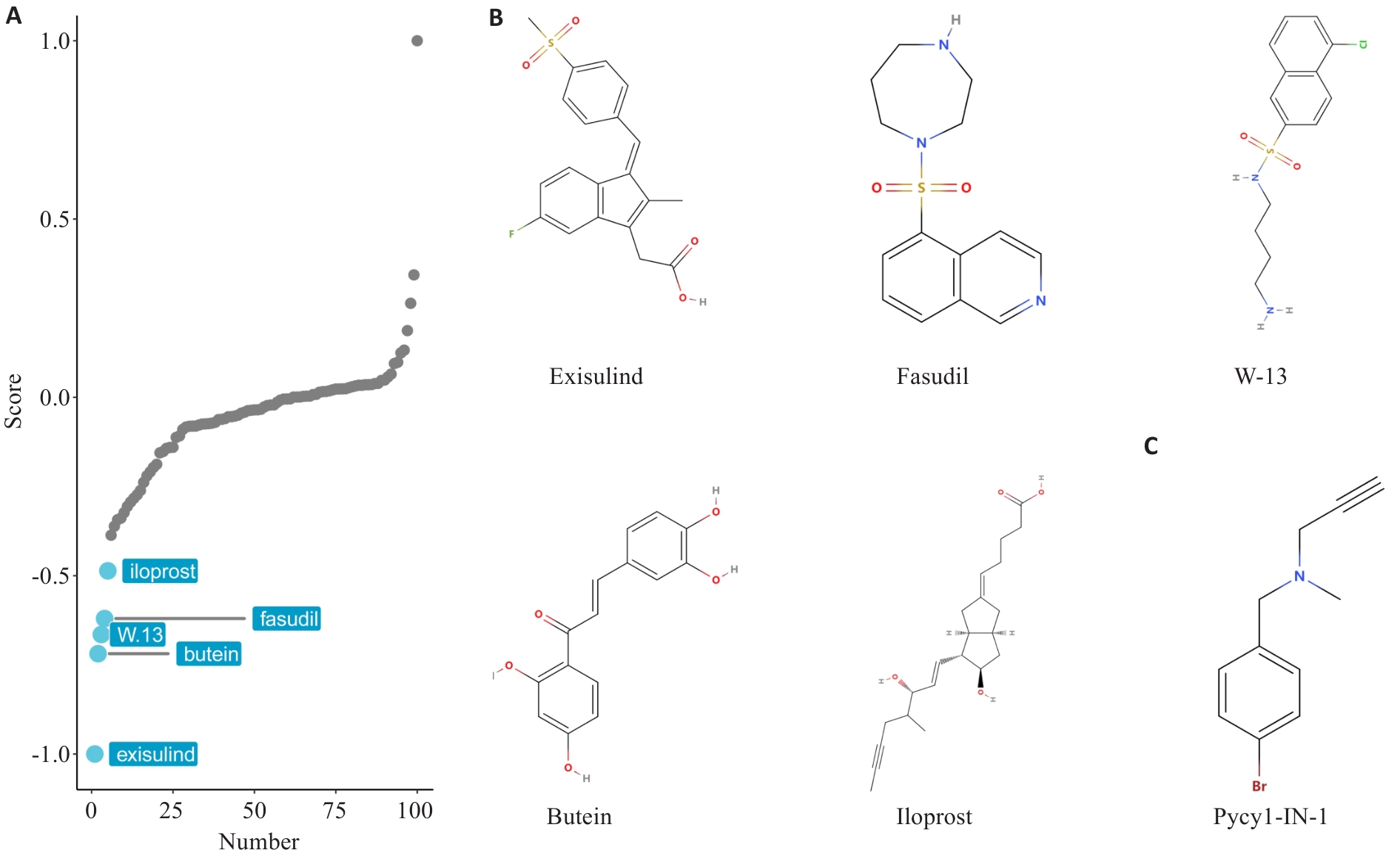
图12 基于PYCR1表达谱的小分子药物虚拟筛选
Fig.12 Virtual screening of small molecule drugs based on PYCR1 expression profiling. A: Screening for small molecule drugs in BLCA patients based on PYCR1 expression profile using XSum algorithm. B: Likely compound structures of candidate small molecule inhibitors of PYCR1. C: Known PYCR1 inhibitor Pycr1-IN-1 is used as the positive control.
| Ligands | ID | Cavity volume (Å3) | Vina score (kcal/mol) | Center (x, y, z) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pycr1-IN-1 | C1 | 436 | -5.2 | 34, 58, 14 |
| C2 | 377 | -4.5 | 31, 63, 1 | |
| C3 | 316 | -4.7 | 9, 60, -6 | |
| Exisulind | C2 | 377 | -7.1 | 31, 63, 1 |
| C4 | 232 | -7.1 | 1, 66, -5 | |
| C3 | 316 | -6.8 | 9, 60, -6 | |
| Fasudil | C1 | 436 | -7 | 34, 58, 14 |
| C4 | 232 | -6.5 | 1, 66, -5 | |
| C5 | 142 | -6.4 | 40, 83, -2 | |
| Butein | C4 | 232 | -6.6 | 1, 66, -5 |
| C2 | 377 | -6.5 | 31, 63, 1 | |
| C1 | 436 | -6.3 | 34, 58, 14 | |
| Iloprost | C1 | 436 | -6.3 | 34, 58, 14 |
| C2 | 377 | -6.2 | 31, 63, 1 | |
| C4 | 232 | -6.1 | 1, 66, -5 | |
| W-13 | C1 | 436 | -6.2 | 34, 58, 14 |
| C2 | 377 | -6 | 31, 63, 1 | |
| C4 | 232 | -5.9 | 1, 66, -5 |
表5 小分子抑制剂-PYCR1蛋白复合物构象结合能(前3)
Tab.5 Conformational binding energies of small molecule inhibitor-PYCR1 protein complexes (Top 3)
| Ligands | ID | Cavity volume (Å3) | Vina score (kcal/mol) | Center (x, y, z) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pycr1-IN-1 | C1 | 436 | -5.2 | 34, 58, 14 |
| C2 | 377 | -4.5 | 31, 63, 1 | |
| C3 | 316 | -4.7 | 9, 60, -6 | |
| Exisulind | C2 | 377 | -7.1 | 31, 63, 1 |
| C4 | 232 | -7.1 | 1, 66, -5 | |
| C3 | 316 | -6.8 | 9, 60, -6 | |
| Fasudil | C1 | 436 | -7 | 34, 58, 14 |
| C4 | 232 | -6.5 | 1, 66, -5 | |
| C5 | 142 | -6.4 | 40, 83, -2 | |
| Butein | C4 | 232 | -6.6 | 1, 66, -5 |
| C2 | 377 | -6.5 | 31, 63, 1 | |
| C1 | 436 | -6.3 | 34, 58, 14 | |
| Iloprost | C1 | 436 | -6.3 | 34, 58, 14 |
| C2 | 377 | -6.2 | 31, 63, 1 | |
| C4 | 232 | -6.1 | 1, 66, -5 | |
| W-13 | C1 | 436 | -6.2 | 34, 58, 14 |
| C2 | 377 | -6 | 31, 63, 1 | |
| C4 | 232 | -5.9 | 1, 66, -5 |
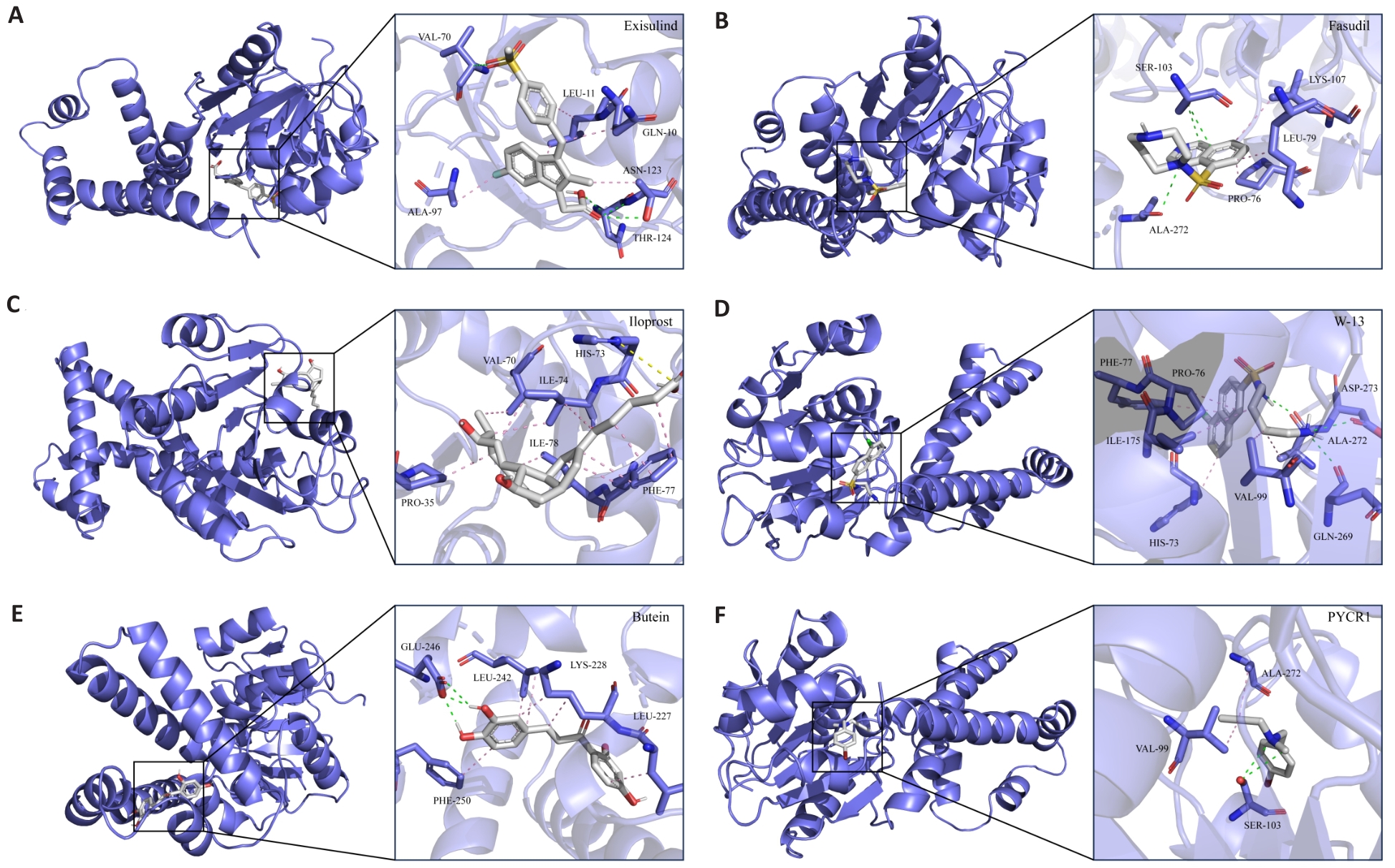
图13 候选化合物与蛋白受体互作模式图
Fig.13 Interaction pattern of candidate compounds with protein receptors. A-F: 3D interaction pattern diagram between candidate small molecule inhibitors and receptor protein PYCR1. Gray stick model represents subsequent small molecule inhibitors, the blue stick model represents PYCR1 side chain amino acid residues, the pink dashed line represents hydrophobic interactions, the green dashed line represents hydrogen bonding interactions, and the yellow dashed line represents alkyl interactions.
| 1 | Li Y, Xu J, Bao P, et al. Survival and clinicopathological significance of PYCR1 expression in cancer: A meta-analysis[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12: 985613. |
| 2 | Luo Y, Yu J, Lin Z, et al. Metabolic characterization of sphere-derived prostate cancer stem cells reveals aberrant urea cycle in stemness maintenance[J]. Int J Cancer, 2024, 155(4): 742-55. |
| 3 | Kay EJ, Paterson K, Riera-Domingo C, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts require proline synthesis by PYCR1 for the deposition of pro-tumorigenic extracellular matrix[J]. Nat Metab, 2022, 4(6): 693-710. |
| 4 | Zhou P, Du X, Jia W, et al. Engineered extracellular vesicles for targeted reprogramming of cancer-associated fibroblasts to potentiate therapy of pancreatic cancer[J]. Signal Transduct Target Ther, 2024, 9(1): 151. |
| 5 | Fang K, Sun M, Leng Z, et al. Targeting IGF1R signaling enhances the sensitivity of cisplatin by inhibiting proline and arginine metabolism in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma under hypoxia [J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2023, 42(1): 73. |
| 6 | Li F, Zheng Z, Chen W, et al. Regulation of cisplatin resistance in bladder cancer by epigenetic mechanisms[J]. Drug Resist Updat, 2023, 68: 100938. |
| 7 | Lopez-Beltran A, Cookson M S, Guercio B J, et al. Advances in dia-gnosis and treatment of bladder cancer[J]. Bmj, 2024, 384: e076743. |
| 8 | Rouanne M, Adam J, Radulescu C, et al. BCG therapy down-regulates HLA-I on malignant cells to subvert antitumor immune responses in bladder cancer[J]. J Clin Invest, 2022, 132(12). |
| 9 | Al Hussein Al Awamlh B, Chang SS. Novel Therapies for High-Risk Non-Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer[J]. Curr Oncol Rep, 2023, 25(2): 83-91. |
| 10 | Xu X, Wang Y, Hu X, et al. Effects of PYCR1 on prognosis and immunotherapy plus tyrosine kinase inhibition responsiveness in metastatic renal cell carcinoma patients[J]. Neoplasia, 2023, 43: 100919. |
| 11 | Fan G, Yu B, Tang L, et al. TSPAN8(+) myofibroblastic cancer-associated fibroblasts promote chemoresistance in patients with breast cancer[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2024, 16(741): eadj5705. |
| 12 | Li Z, Jiang Y, Liu J, et al. Exosomes from PYCR1 knockdown bone marrow mesenchymal stem inhibits aerobic glycolysis and the growth of bladder cancer cells via regulation of the EGFR/PI3K/AKT pathway[J]. Int J Oncol, 2023, 63(1). |
| 13 | Zhang J, Yuan S, Cao W, et al. Signature Search Polestar: a comprehensive drug repurposing method evaluation assistant for customized oncogenic signature[J]. Bioinformatics, 2024, 40(9). |
| 14 | Huang X, Tan J, Chen M, et al. Prognostic, Immunological, and Mutational Analysis of MTA2 in Pan-Cancer and Drug Screening for Hepatocellular Carcinoma[J]. Biomolecules, 2023, 13(6). |
| 15 | Huang J, Zhang J L, Ang L, et al. Proposing a novel molecular subtyping scheme for predicting distant recurrence-free survival in breast cancer post-neoadjuvant chemotherapy with close correlation to metabolism and senescence[J]. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2023, 14: 1265520. |
| 16 | Geeleher P, Cox NJ, Huang RS. Clinical drug response can be predicted using baseline gene expression levels and in vitro drug sensitivity in cell lines[J]. Genome Biol, 2014, 15(3): R47. |
| 17 | Yoshihara K, Shahmoradgoli M, Martínez E, et al. Inferring tumour purity and stromal and immune cell admixture from expression data [J]. Nat Commun, 2013, 4: 2612. |
| 18 | Van Calster B, Wynants L, Verbeek JFM, et al. Reporting and Interpreting Decision Curve Analysis: A Guide for Investigators[J]. Eur Urol, 2018, 74(6): 796-804. |
| 19 | Yang C, Zhang H, Chen M, et al. A survey of optimal strategy for signature-based drug repositioning and an application to liver cancer [J]. Elife, 2022, 11. |
| 20 | Subramanian A, Narayan R, Corsello SM, et al. A Next Generation Connectivity Map: L1000 Platform and the First 1,000,000 Profiles [J]. Cell, 2017, 171(6): 1437-52.e17. |
| 21 | Christensen EM, Bogner AN, Vandekeere A, et al. In crystallo screening for proline analog inhibitors of the proline cycle enzyme PYCR1[J]. J Biol Chem, 2020, 295(52): 18316-27. |
| 22 | Liu Z, Sun T, Zhang Z, et al. An 18-gene signature based on glucose metabolism and DNA methylation improves prognostic prediction for urinary bladder cancer[J]. Genomics, 2021, 113(1 Pt 2): 896-907. |
| 23 | Xiao S, Chen J, Wei Y, et al. BHLHE41 inhibits bladder cancer progression via regulation of PYCR1 stability and thus inactivating PI3K/AKT signaling pathway[J]. Eur J Med Res, 2024, 29(1): 302. |
| 24 | Du S, Sui Y, Ren W, et al. PYCR1 promotes bladder cancer by affecting the Akt/Wnt/β‑catenin signaling[J]. J Bioenerg Biomembr, 2021, 53(2): 247-58. |
| 25 | Deng D, Liu F, Liu Z, et al. Robust pyroptosis risk score guides the treatment options and predicts the prognosis of bladder carcinoma [J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 965469. |
| 26 | Xiong S, Li S, Zeng J, et al. Deciphering the immunological and prognostic features of bladder cancer through platinum-resistance-related genes analysis and identifying potential therapeutic target P4HB[J]. Front Immunol, 2023, 14: 1253586. |
| 27 | Shenoy A, Belugali Nataraj N, Perry G, et al. Proteomic patterns associated with response to breast cancer neoadjuvant treatment[J]. Mol Syst Biol, 2020, 16(9): e9443. |
| 28 | Loriot Y, Petrylak DP, Rezazadeh Kalebasty A, et al. TROPHY-U-01, a phase II open-label study of sacituzumab govitecan in patients with metastatic urothelial carcinoma progressing after platinum-based chemotherapy and checkpoint inhibitors: updated safety and efficacy outcomes[J]. Ann Oncol, 2024, 35(4): 392-401. |
| 29 | Goldenberg DM, Sharkey RM. Antibody-drug conjugates targeting TROP-2 and incorporating SN-38: A case study of anti-TROP-2 sacituzumab govitecan[J]. MAbs, 2019, 11(6): 987-95. |
| 30 | Elbadawy M, Sato Y, Mori T, et al. Anti-tumor effect of trametinib in bladder cancer organoid and the underlying mechanism[J]. Cancer Biol Ther, 2021, 22(5-6): 357-71. |
| 31 | Plumber SA, Tate T, Al-Ahmadie H, et al. Rosiglitazone and trametinib exhibit potent anti-tumor activity in a mouse model of muscle invasive bladder cancer[J]. Nat Commun, 2024, 15(1): 6538. |
| 32 | Wang Z, Li L, Chu C, et al. CUDC‑101 is a potential target inhibitor for the EGFR‑overexpression bladder cancer cells[J]. Int J Oncol, 2023, 63(6). |
| 33 | Vemula D, Jayasurya P, Sushmitha V, et al. CADD, AI and ML in drug discovery: A comprehensive review[J]. Eur J Pharm Sci, 2023, 181: 106324. |
| 34 | Zhang Y, Luo M, Wu P, et al. Application of Computational Biology and Artificial Intelligence in Drug Design[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(21). |
| 35 | Li Y, Miao J, Liu C, et al. Kushenol O Regulates GALNT7/NF-κB axis-Mediated M2 Macrophage Polarization and Efferocytosis in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma[J]. Phytomedicine, 2025: 156373. |
| 36 | Goluboff E T. Exisulind, a selective apoptotic antineoplastic drug [J]. Expert Opin Investig Drugs, 2001, 10(10): 1875-82. |
| 37 | Geng H, Huang C, Xu L, et al. Targeting cellular senescence as a therapeutic vulnerability in gastric cancer[J]. Life Sci, 2024, 346: 122631. |
| 38 | Huang Y, Wang S, Zhang X, et al. Identification of Fasudil as a collaborator to promote the anti-tumor effect of lenvatinib in hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting GLI2-mediated hedgehog signaling pathway[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2024, 200: 107082. |
| [1] | 朱名扬, 王博康, 张秀森, 周克旭, 苗泽宇, 孙江涛. 基线水平CCL19+树突状细胞可有效预测肺腺癌患者免疫治疗的敏感性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(8): 1529-1536. |
| [2] | 陈守峰, 张舒超, 樊伟林, 孙 巍, 刘贝贝, 刘建民, 郭园园. 吡非尼酮联合PD-L1抑制剂抑制小鼠异位膀胱肿瘤的生长[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(2): 210-216. |
| [3] | 李立强, 郭园园, 王成勇, 常睿, 孙巍, 高五岳, 王超, 刘贝贝. miR-204-5p通过靶向负性调控RAB22A促进膀胱癌细胞的恶性生物学行为[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(11): 2235-2242. |
| [4] | 颜秋霞, 曾 鹏, 黄树强, 谭翠钰, 周秀琴, 乔 静, 赵晓英, 冯 玲, 朱振杰, 张国志, 胡 鸿, 陈彩蓉. RBMX通过下调PKM2抑制膀胱癌细胞的增殖、迁移、侵袭和糖酵解[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(1): 9-16. |
| [5] | 张晓林, 吴浩松, 汪 盛. SLC12A8通过JAK/STAT途径促进膀胱癌细胞的增殖、侵袭与迁移并触发上皮间充质转化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(9): 1613-1621. |
| [6] | 张自然, 谭家乐, 于子航, 刘承栋, 王 剑, 吴德华, 白 雪. FARSB对泛肿瘤的预后和冷肿瘤微环境的分层作用:基于整合单细胞和大块组织的DNA测序[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(5): 667-679. |
| [7] | 蔡涛浓, 卢江丽, 林志君, 罗明睿, 梁海滔, 秦自科, 叶云林. 单中心非肌层浸润性膀胱癌患者行卡介苗灌注治疗的疗效分析[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(3): 488-494. |
| [8] | 龚 英, 艾丽飞热·艾麦提, 何宗忠. CD39小分子抑制剂ARL67156增强NK细胞对胃癌细胞的杀伤作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(12): 2006-2014. |
| [9] | 李芮宁, 黄超艺, 洪 畅, 王家仁, 李绮美, 胡诚毅, 崔 浩, 董忠谊, 朱红波, 刘 莉, 肖芦山. 非甾体抗炎药对原发性肝癌抗PD-1疗效的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(5): 698-704. |
| [10] | 付小聪, 余光创, 郭艳芳. 组蛋白赖氨酸去甲基化酶家族在膀胱癌中的表达模式及其潜在作用:基于多组学分析[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(12): 1822-1831. |
| [11] | 林 萱, 毛 铎, 白瑞霞. 三种商品化光敏剂诱导小鼠免疫原性细胞死亡的效果比较[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(12): 1791-1798. |
| [12] | 姚 越, 张 冲, 熊言骏, 韩 兵, 高幸福, 汪 盛. miR-let-7c-5p通过靶向HMGA2抑制膀胱癌细胞侵袭和迁移[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(7): 1022-1029. |
| [13] | 植 曦, 周俊豪, 田 湖, 周冉冉, 黄振辉, 刘存东. SHOX2体外增强膀胱癌细胞的迁移、侵袭和干细胞特性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(7): 995-1001. |
| [14] | 曹 圆, 许 凯, 陈玢屾, 王奕铭, 李炳坤, 李朝明, 徐 鹏. DNMT3b 基因在人膀胱癌组织中的表达及与临床预后的相关性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2020, 40(09): 1295-1300. |
| [15] | 余 淦, 周 辉, 许 凯, 孟丽荣, 郎 斌. 靶向TUG1的mir-29c-3p通过调节CAPN7的表达影响膀胱癌细 胞的迁移和侵袭[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2020, 40(09): 1325-1331. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||