南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (4): 736-743.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.04.08
• • 上一篇
吕雪彩1,2,3( ), 刘艳红1,2,3, 韩诗怡1,2, 张浩赟1, 侯爱生1,2, 周志康1, 史立凯1, 高洁1, 曹江北1, 张宏1,2, 米卫东1,2,3(
), 刘艳红1,2,3, 韩诗怡1,2, 张浩赟1, 侯爱生1,2, 周志康1, 史立凯1, 高洁1, 曹江北1, 张宏1,2, 米卫东1,2,3( )
)
收稿日期:2024-11-22
出版日期:2025-04-20
发布日期:2025-04-28
通讯作者:
米卫东
E-mail:524339563@qq.com;wwdd1962@163.com
作者简介:吕雪彩,在读博士研究生,主治医师,E-mail: 524339563@qq.com
基金资助:
Xuecai LÜ1,2,3( ), Yanhong LIU1,2,3, Shiyi HAN1,2, Haoyun ZHANG1, Aisheng HOU1,2, Zhikang ZHOU1, Likai SHI1, Jie GAO1, Jiangbei CAO1, Hong ZHANG1,2, Weidong MI1,2,3(
), Yanhong LIU1,2,3, Shiyi HAN1,2, Haoyun ZHANG1, Aisheng HOU1,2, Zhikang ZHOU1, Likai SHI1, Jie GAO1, Jiangbei CAO1, Hong ZHANG1,2, Weidong MI1,2,3( )
)
Received:2024-11-22
Online:2025-04-20
Published:2025-04-28
Contact:
Weidong MI
E-mail:524339563@qq.com;wwdd1962@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
目的 探讨老年患者胃肠道手术后综合并发症的危险因素。 方法 纳入2020年4月~2022年4月全国17个中心1388例行择期胃肠道手术的老年患者。主要结局指标是术后30 d内综合并发症发生率,包括手术相关并发症、中枢神经精神系统、呼吸系统、心血管系统、消化系统并发症以及急性肾损伤。根据是否发生至少1种并发症将患者分为并发症组和无并发症组。比较两组患者基线资料,术前功能状态,术中麻醉和手术因素,用药情况、是否使用神经阻滞及术后镇痛等参数,采用单因素和多因素Logistic回归分析术后并发症的独立危险因素,并探讨术后急性疼痛与各系统并发症的相关性。 结果 老年患者胃肠手术后综合并发症发生率为50.8%(705/1388)。多因素分析显示,年龄[OR(95% CI):1.026(1.006~1.046)]、预后营养指数[OR(95% CI):0.998(0.997~1.000)]、术前生活质量评分[OR(95% CI): 0.094(0.018~0.500)]、失血量 [OR(95% CI):1.002(1.001~1.003)]以及术后急性疼痛[OR(95% CI): 1.308(1.033~1.657)]与术后并发症的发生率相关。术后重度疼痛患者神经精神系统并发症(27.2% vs 19.8%)、手术相关并发症(17.3% vs 10.2%)以及心血管系统并发症(3.6% vs 1.7%)的发生率显著升高。 结论 高龄、术前营养状态差、生活质量评分低、术中失血多以及术后急性疼痛控制不佳是老年患者胃肠道手术后并发症的独立危险因素。术后急性疼痛与多系统并发症存在显著相关性。
吕雪彩, 刘艳红, 韩诗怡, 张浩赟, 侯爱生, 周志康, 史立凯, 高洁, 曹江北, 张宏, 米卫东. 老年患者胃肠道手术后综合并发症的危险因素——一项多中心观察性研究[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 736-743.
Xuecai LÜ, Yanhong LIU, Shiyi HAN, Haoyun ZHANG, Aisheng HOU, Zhikang ZHOU, Likai SHI, Jie GAO, Jiangbei CAO, Hong ZHANG, Weidong MI. Risk factors for overall postoperative complications in elderly patients undergoing gastrointestinal surgeries: a multicenter observational study[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(4): 736-743.
| Parameter | Total (n=1388) | No postoperative complications (n=683) | Have postoperative complications (n=705) | OR (95% CI) | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | 71.0 (68.0, 76.0) | 71.0 (68.0, 75.0) | 72.0 (68.0, 76.0) | 1.028 (1.008-1.048) | 0.005 |
| Gender [n (%)] | 1.002 (0.804-1.250) | 0.984 | |||
| Female | 906 (65.3%) | 446 (65.3%) | 460 (65.2%) | ||
| Male | 482 (34.7%) | 237 (34.7%) | 245 (34.8%) | ||
| Height (cm) | 164.6 (160.0, 170.0) | 165.0 (160.0, 170.0) | 164.6 (160.0, 170.0) | 1.001 (0.998-1.014) | 0.884 |
| Weight (kg) | 63.7 (57.0, 70.0) | 63.7 (57.0, 70.0) | 63.7 (57.0, 70.0) | 0.997 (0.987-1.007) | 0.541 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.5 (21.3, 25.4) | 23.5 (21.3, 25.6) | 23.5 (21.4, 25.1) | 0.985 (0.953-1.018) | 0.374 |
| ASA | 1.262 (1.001-1.590) | 0.049 | |||
| Ⅰ-Ⅱ | 978 (70.5%) | 498 (72.9%) | 480 (68.1%) | ||
| Ⅲ-Ⅴ | 410 (29.5%) | 185 (27.1%) | 225 (31.9%) | ||
| Medical History [n (%)] | |||||
| Hypertension | 605 (43.6%) | 289 (42.3%) | 316 (44.8%) | 1.107 (0.896-1.369) | 0.346 |
| Diabetes | 290 (20.9%) | 131 (19.2%) | 159 (22.6%) | 1.227 (0.946-1.591) | 0.123 |
| Coronary heart disease | 188 (13.5%) | 88 (12.9%) | 100 (14.2%) | 1.118 (0.821-1.521) | 0.479 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 79 (5.7%) | 31 (4.5%) | 48 (6.8%) | 1.537 (0.966-2.445) | 0.070 |
| Respiratory disease | 55 (4.0%) | 21 (3.1%) | 34 (4.8%) | 1.597 (0.917-2.781) | 0.098 |
| Kidney disease | 66 (4.8%) | 29 (4.2%) | 37 (5.2%) | 1.249 (0.759-2.055) | 0.381 |
| Smoking | 432 (31.1%) | 218 (31.9%) | 214 (30.4%) | 0.930 (0.741-1.167) | 0.529 |
| Alcohol consumption | 410 (29.5%) | 207 (30.3%) | 203 (28.8%) | 0.930 (0.738-1.171) | 0.537 |
| Preoperative chronic pain | 255 (18.4%) | 106 (15.5%) | 149 (21.1%) | 1.459 (1.108-1.920) | 0.007 |
| Preoperative nutritional support | 163 (11.7%) | 71 (10.4%) | 92 (13.0%) | 1.294 (0.931-1.798) | 0.125 |
| Preoperative psychological and functional status | |||||
| Frailty [n (%)] | 35 (2.5%) | 14 (2.0%) | 21 (3.0%) | 1.467 (0.740-2.909) | 0.272 |
| EQ-5D | 1.0 (0.9, 1.0) | 1.0 (0.9, 1.0) | 0.9 (0.9, 1.0) | 0.073 (0.014-0.380) | 0.002 |
| EQ-VAS | 76.0 (70.0, 80.0) | 76.0 (75.0, 80.0) | 76.0 (70.0, 80.0) | 0.992 (0.984-1.000) | 0.060 |
| MET | 0.719 (0.483-1.070) | 0.104 | |||
| <4 | 108 (7.8%) | 45 (6.6%) | 63 (8.9%) | ||
| ≥4 | 1280 (92.2%) | 638 (93.4%) | 642 (91.1%) | ||
| Preoperative laboratory test | |||||
| PNI | 42.3 (37.4, 126.3) | 42.9 (38.1, 139.0) | 41.7 (36.8, 89.5) | 0.998 (0.997-1.000) | 0.043 |
| Albumin (g/L) | 39.0 (36.2, 41.2) | 39.0 (36.5, 41.0) | 39.0 (36.0, 41.3) | 0.995 (0.984-1.006) | 0.401 |
| Hemoglobin (g/L) | 120.6 (108.0, 134.0) | 122.0 (109.0, 135.0) | 120.3 (106.0, 134.0) | 0.996 (0.991-1.001) | 0.120 |
| Glucose (µmol/L) | 5.5 (4.8, 5.8) | 5.5 (4.8, 5.8) | 5.5 (4.8, 5.8) | 1.021 (0.956-1.091) | 0.531 |
| Intraoperative medication | |||||
| Consumption of opioids (mg) | 143.5 (50.0, 232.9) | 140.0 (50.0, 230.0) | 148.0 (45.0, 240.0) | 1.000 (0.999-1.001) | 0.796 |
| NSAIDs [n (%)] | 529 (38.1%) | 264 (38.7%) | 265 (37.6%) | 0.956 (0.770-1.187) | 0.683 |
| Dexmedetomidine [n (%)] | 333 (24.0%) | 174 (25.5%) | 159 (22.6%) | 0.852 (0.666-1.090) | 0.203 |
| Surgical/Anesthetic parameters | |||||
| Blood loss (mL) | 100.0 (50.0, 128.7) | 60.0 (50.0, 128.7) | 100.0 (50.0, 128.7) | 1.002 (1.001-1.003) | <0.001 |
| Duration of surgery (min) | 191.5 (143.3, 240.0) | 185.0 (136.0, 230.0) | 198.4 (150.0, 250.0) | 1.002 (1.001-1.003) | 0.002 |
| Location of surgery [n (%)] | 0.930 (0.746-1.160) | 0.521 | |||
| Gastrectomy | 481 (34.7%) | 231 (33.8%) | 250 (35.5%) | ||
| Enterectomy | 907 (65.3%) | 452 (66.2%) | 455 (64.5%) | ||
| Type of surgery [n (%)] | 1.194 (0.934-1.527) | 0.157 | |||
| Open | 1050 (75.6%) | 528 (77.3%) | 522 (74.0%) | ||
| Minimally invasive | 338 (24.4%) | 155 (22.7%) | 183 (26.0%) | ||
| Anesthesia methods [n (%)] | 0.843 (0.621-1.145) | 0.275 | |||
| GA | 1197 (86.2%) | 582 (85.2%) | 615 (87.2%) | ||
| GA+RA | 191 (13.8%) | 101 (14.8%) | 90 (12.8%) | ||
| Postoperative analgesia methods [n (%)] | 0.191 | ||||
| No | 480 (34.6%) | 286 (36.5%) | 194 (34.6%) | ||
| Intravenous analgesia | 784 (56.5%) | 432 (55.2%) | 352 (56.5%) | 1.201 (0.954, 1.512) | |
| Others | 124 (8.9%) | 65 (8.3%) | 59 (9.8%) | 1.338 (0.900, 1.990) | |
| Postoperative acute pain | 1.359 (1.079-1.712) | 0.009 | |||
| Mild to moderate pain | 973 (70.1%) | 501 (73.4%) | 472 (67.0%) | ||
| Severe pain | 415 (29.9%) | 182 (26.6%) | 233 (33.0%) |
表1 患者的一般资料及单因素分析
Tab.1 Demographic characteristics and univariate analysis of the patients
| Parameter | Total (n=1388) | No postoperative complications (n=683) | Have postoperative complications (n=705) | OR (95% CI) | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | 71.0 (68.0, 76.0) | 71.0 (68.0, 75.0) | 72.0 (68.0, 76.0) | 1.028 (1.008-1.048) | 0.005 |
| Gender [n (%)] | 1.002 (0.804-1.250) | 0.984 | |||
| Female | 906 (65.3%) | 446 (65.3%) | 460 (65.2%) | ||
| Male | 482 (34.7%) | 237 (34.7%) | 245 (34.8%) | ||
| Height (cm) | 164.6 (160.0, 170.0) | 165.0 (160.0, 170.0) | 164.6 (160.0, 170.0) | 1.001 (0.998-1.014) | 0.884 |
| Weight (kg) | 63.7 (57.0, 70.0) | 63.7 (57.0, 70.0) | 63.7 (57.0, 70.0) | 0.997 (0.987-1.007) | 0.541 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.5 (21.3, 25.4) | 23.5 (21.3, 25.6) | 23.5 (21.4, 25.1) | 0.985 (0.953-1.018) | 0.374 |
| ASA | 1.262 (1.001-1.590) | 0.049 | |||
| Ⅰ-Ⅱ | 978 (70.5%) | 498 (72.9%) | 480 (68.1%) | ||
| Ⅲ-Ⅴ | 410 (29.5%) | 185 (27.1%) | 225 (31.9%) | ||
| Medical History [n (%)] | |||||
| Hypertension | 605 (43.6%) | 289 (42.3%) | 316 (44.8%) | 1.107 (0.896-1.369) | 0.346 |
| Diabetes | 290 (20.9%) | 131 (19.2%) | 159 (22.6%) | 1.227 (0.946-1.591) | 0.123 |
| Coronary heart disease | 188 (13.5%) | 88 (12.9%) | 100 (14.2%) | 1.118 (0.821-1.521) | 0.479 |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 79 (5.7%) | 31 (4.5%) | 48 (6.8%) | 1.537 (0.966-2.445) | 0.070 |
| Respiratory disease | 55 (4.0%) | 21 (3.1%) | 34 (4.8%) | 1.597 (0.917-2.781) | 0.098 |
| Kidney disease | 66 (4.8%) | 29 (4.2%) | 37 (5.2%) | 1.249 (0.759-2.055) | 0.381 |
| Smoking | 432 (31.1%) | 218 (31.9%) | 214 (30.4%) | 0.930 (0.741-1.167) | 0.529 |
| Alcohol consumption | 410 (29.5%) | 207 (30.3%) | 203 (28.8%) | 0.930 (0.738-1.171) | 0.537 |
| Preoperative chronic pain | 255 (18.4%) | 106 (15.5%) | 149 (21.1%) | 1.459 (1.108-1.920) | 0.007 |
| Preoperative nutritional support | 163 (11.7%) | 71 (10.4%) | 92 (13.0%) | 1.294 (0.931-1.798) | 0.125 |
| Preoperative psychological and functional status | |||||
| Frailty [n (%)] | 35 (2.5%) | 14 (2.0%) | 21 (3.0%) | 1.467 (0.740-2.909) | 0.272 |
| EQ-5D | 1.0 (0.9, 1.0) | 1.0 (0.9, 1.0) | 0.9 (0.9, 1.0) | 0.073 (0.014-0.380) | 0.002 |
| EQ-VAS | 76.0 (70.0, 80.0) | 76.0 (75.0, 80.0) | 76.0 (70.0, 80.0) | 0.992 (0.984-1.000) | 0.060 |
| MET | 0.719 (0.483-1.070) | 0.104 | |||
| <4 | 108 (7.8%) | 45 (6.6%) | 63 (8.9%) | ||
| ≥4 | 1280 (92.2%) | 638 (93.4%) | 642 (91.1%) | ||
| Preoperative laboratory test | |||||
| PNI | 42.3 (37.4, 126.3) | 42.9 (38.1, 139.0) | 41.7 (36.8, 89.5) | 0.998 (0.997-1.000) | 0.043 |
| Albumin (g/L) | 39.0 (36.2, 41.2) | 39.0 (36.5, 41.0) | 39.0 (36.0, 41.3) | 0.995 (0.984-1.006) | 0.401 |
| Hemoglobin (g/L) | 120.6 (108.0, 134.0) | 122.0 (109.0, 135.0) | 120.3 (106.0, 134.0) | 0.996 (0.991-1.001) | 0.120 |
| Glucose (µmol/L) | 5.5 (4.8, 5.8) | 5.5 (4.8, 5.8) | 5.5 (4.8, 5.8) | 1.021 (0.956-1.091) | 0.531 |
| Intraoperative medication | |||||
| Consumption of opioids (mg) | 143.5 (50.0, 232.9) | 140.0 (50.0, 230.0) | 148.0 (45.0, 240.0) | 1.000 (0.999-1.001) | 0.796 |
| NSAIDs [n (%)] | 529 (38.1%) | 264 (38.7%) | 265 (37.6%) | 0.956 (0.770-1.187) | 0.683 |
| Dexmedetomidine [n (%)] | 333 (24.0%) | 174 (25.5%) | 159 (22.6%) | 0.852 (0.666-1.090) | 0.203 |
| Surgical/Anesthetic parameters | |||||
| Blood loss (mL) | 100.0 (50.0, 128.7) | 60.0 (50.0, 128.7) | 100.0 (50.0, 128.7) | 1.002 (1.001-1.003) | <0.001 |
| Duration of surgery (min) | 191.5 (143.3, 240.0) | 185.0 (136.0, 230.0) | 198.4 (150.0, 250.0) | 1.002 (1.001-1.003) | 0.002 |
| Location of surgery [n (%)] | 0.930 (0.746-1.160) | 0.521 | |||
| Gastrectomy | 481 (34.7%) | 231 (33.8%) | 250 (35.5%) | ||
| Enterectomy | 907 (65.3%) | 452 (66.2%) | 455 (64.5%) | ||
| Type of surgery [n (%)] | 1.194 (0.934-1.527) | 0.157 | |||
| Open | 1050 (75.6%) | 528 (77.3%) | 522 (74.0%) | ||
| Minimally invasive | 338 (24.4%) | 155 (22.7%) | 183 (26.0%) | ||
| Anesthesia methods [n (%)] | 0.843 (0.621-1.145) | 0.275 | |||
| GA | 1197 (86.2%) | 582 (85.2%) | 615 (87.2%) | ||
| GA+RA | 191 (13.8%) | 101 (14.8%) | 90 (12.8%) | ||
| Postoperative analgesia methods [n (%)] | 0.191 | ||||
| No | 480 (34.6%) | 286 (36.5%) | 194 (34.6%) | ||
| Intravenous analgesia | 784 (56.5%) | 432 (55.2%) | 352 (56.5%) | 1.201 (0.954, 1.512) | |
| Others | 124 (8.9%) | 65 (8.3%) | 59 (9.8%) | 1.338 (0.900, 1.990) | |
| Postoperative acute pain | 1.359 (1.079-1.712) | 0.009 | |||
| Mild to moderate pain | 973 (70.1%) | 501 (73.4%) | 472 (67.0%) | ||
| Severe pain | 415 (29.9%) | 182 (26.6%) | 233 (33.0%) |
| Postoperative complications | n (%) |
|---|---|
| Overall complications | 705 (50.8%) |
| Respiratory complications | 451 (32.5%) |
| Pulmonary infection | 341 (24.6%) |
| Respiratory failure | 7 (0.5%) |
| Pleural effusion | 60 (4.3%) |
| Atelectasis | 19 (1.4%) |
| Pneumothorax | 20 (1.4%) |
| Bronchiostenosis | 3 (0.2%) |
| Aspiration pneumonia | 2 (0.1%) |
| Pulmonary embolism | 3 (0.2%) |
| Pulmonary edema | 2 (0.1%) |
| Neuropsychiatric complications | 306 (22.0%) |
| Stroke | 12 (0.9%) |
| Delirium | 231 (16.6%) |
| Depression | 91 (6.6%) |
| Procedure-related complications | 171 (12.3%) |
| Surgical site infection | 143 (10.3%) |
| Anastomotic leakage | 47 (3.4%) |
| Ileus | 21 (1.5%) |
| Chylous fistula | 2 (0.1%) |
| Acute Kidney Injury | 53 (3.8%) |
| Gastrointestinal complications | 32 (2.3%) |
| Gastroparesis | 9 (0.6%) |
| Diarrhea | 16 (1.2%) |
| Gastrointestinal bleeding | 10 (0.7%) |
| Cardiovascular complications | 32 (2.3%) |
| Myocardial infarction | 4 (0.3%) |
| Heart failure | 3 (0.2%) |
| Angina | 1 (0.1%) |
| Arrhythmia | 25 (1.8%) |
| Cardiac arrest or death | 2 (0.1%) |
表2 术后并发症发生情况
Tab.2 Statistics of the occurrence of postoperative complications in these patients
| Postoperative complications | n (%) |
|---|---|
| Overall complications | 705 (50.8%) |
| Respiratory complications | 451 (32.5%) |
| Pulmonary infection | 341 (24.6%) |
| Respiratory failure | 7 (0.5%) |
| Pleural effusion | 60 (4.3%) |
| Atelectasis | 19 (1.4%) |
| Pneumothorax | 20 (1.4%) |
| Bronchiostenosis | 3 (0.2%) |
| Aspiration pneumonia | 2 (0.1%) |
| Pulmonary embolism | 3 (0.2%) |
| Pulmonary edema | 2 (0.1%) |
| Neuropsychiatric complications | 306 (22.0%) |
| Stroke | 12 (0.9%) |
| Delirium | 231 (16.6%) |
| Depression | 91 (6.6%) |
| Procedure-related complications | 171 (12.3%) |
| Surgical site infection | 143 (10.3%) |
| Anastomotic leakage | 47 (3.4%) |
| Ileus | 21 (1.5%) |
| Chylous fistula | 2 (0.1%) |
| Acute Kidney Injury | 53 (3.8%) |
| Gastrointestinal complications | 32 (2.3%) |
| Gastroparesis | 9 (0.6%) |
| Diarrhea | 16 (1.2%) |
| Gastrointestinal bleeding | 10 (0.7%) |
| Cardiovascular complications | 32 (2.3%) |
| Myocardial infarction | 4 (0.3%) |
| Heart failure | 3 (0.2%) |
| Angina | 1 (0.1%) |
| Arrhythmia | 25 (1.8%) |
| Cardiac arrest or death | 2 (0.1%) |
| Factor | b | SE | Wald | OR (95% CI) | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | 0.026 | 0.010 | 6.710 | 1.026(1.006-1.046) | 0.010 |
| Preoperative PNI | -0.002 | 0.001 | 4.352 | 0.998(0.997-1.000) | 0.037 |
| Preoperative EQ-5D | -2.369 | 0.855 | 7.681 | 0.094(0.018-0.500) | 0.006 |
| Blood loss (mL) | 0.002 | 0.000 | 21.013 | 1.002(1.001-1.003) | <0.001 |
| Postoperative acute pain (Mild to moderate pain/severe pain) | 0.269 | 0.121 | 4.959 | 1.308(1.033-1.657) | 0.026 |
表3 术后综合并发症的多因素分析
Tab.3 Multivariate analysis of postoperative complications in these patients
| Factor | b | SE | Wald | OR (95% CI) | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | 0.026 | 0.010 | 6.710 | 1.026(1.006-1.046) | 0.010 |
| Preoperative PNI | -0.002 | 0.001 | 4.352 | 0.998(0.997-1.000) | 0.037 |
| Preoperative EQ-5D | -2.369 | 0.855 | 7.681 | 0.094(0.018-0.500) | 0.006 |
| Blood loss (mL) | 0.002 | 0.000 | 21.013 | 1.002(1.001-1.003) | <0.001 |
| Postoperative acute pain (Mild to moderate pain/severe pain) | 0.269 | 0.121 | 4.959 | 1.308(1.033-1.657) | 0.026 |
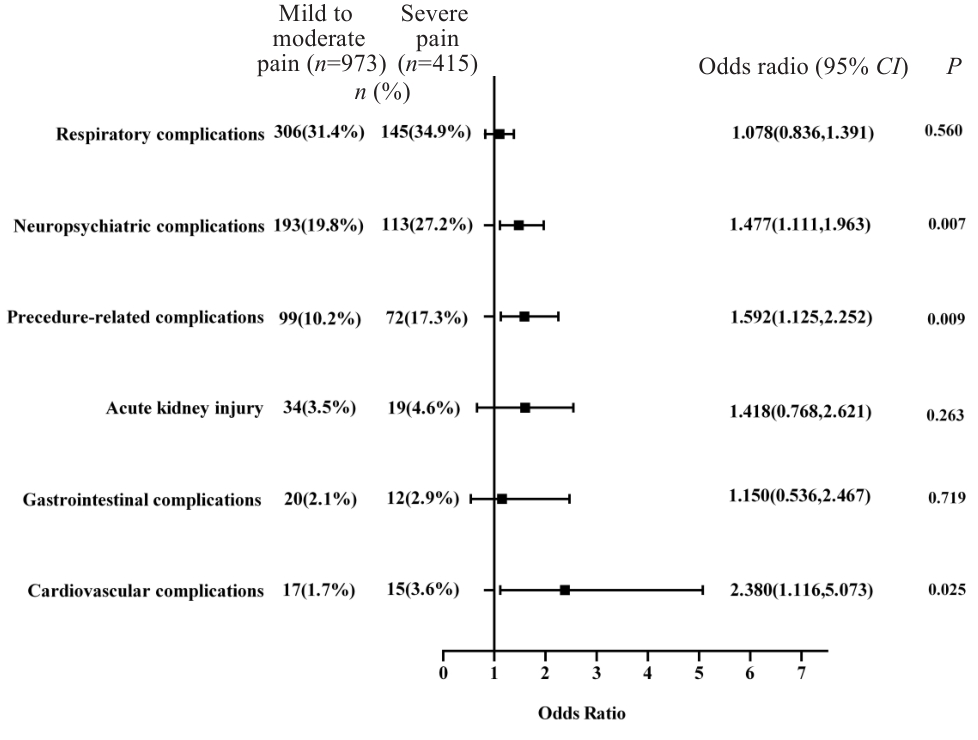
图2 术后急性疼痛对各系统并发症影响的森林图
Fig.2 Forest plot of the effect of acute postoperative pain on postoperative complications in elderly patients undergoing gastrointestinal surgeries.
| 1 | Jakobson T, Karjagin J, Vipp L, et al. Postoperative complications and mortality after major gastrointestinal surgery[J]. Medicina, 2014, 50(2): 111-7. |
| 2 | Calderón-Larrañaga A, Vetrano DL, Ferrucci L, et al. Multimorbidity and functional impairment-bidirectional interplay, synergistic effects and common pathways[J]. J Intern Med, 2019, 285(3): 255-71. |
| 3 | Scholz AM, Oldroyd C, McCarthy K, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of risk factors for postoperative delirium among older patients undergoing gastrointestinal surgery[J]. Br J Surg, 2016, 103(2): e21-8. |
| 4 | Wang XY, Yu DD, Du YR, et al. Risk factors of delirium after gastrointestinal surgery: a meta-analysis[J]. J Clin Nurs, 2023, 32(13/14): 3266-76. |
| 5 | Li YL, Huang HF, Le Y. Risk factors and predictive value of perioperative neurocognitive disorders in elderly patients with gastrointestinal tumors[J]. BMC Anesthesiol, 2021, 21(1): 193. |
| 6 | Zhong Y, Cao Z, Baumer D, et al. Incidence and risk factors for postoperative gastrointestinal dysfunction occurrence after gastrointestinal procedures in US patients[J]. Am J Surg, 2023, 226(5): 675-81. |
| 7 | Kawashima J, Sahara K, Yamagishi S. Prophylactic negative pressure wound therapy following colorectal perforation: defining the risk factors for delayed wound healing[J]. Surg Today, 2023, 53(6): 728-35. |
| 8 | Yokozuka K, Tomita K, Nakagawa M, et al. New risk factors of postoperative complications in elective gastrointestinal surgery of elderly patients: a prospective cohort study[J]. BMC Surg, 2021, 21(1): 173. |
| 9 | 曹 庆, 章文毅, 马 彭. 胃肠恶性肿瘤术后第2天NLR/ALB预测术后总并发症价值[J]. 交通医学, 2022(5): 479-82. |
| 10 | Hirahara N, Tajima Y, Fujii Y, et al. Prediction of postoperative complications and survival after laparoscopic gastrectomy using preoperative Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index in elderly gastric cancer patients[J]. Surg Endosc, 2021, 35(3): 1202-9. |
| 11 | Sasahara M, Kanda M, Ito S, et al. The preoperative prognostic nutritional index predicts short-term and long-term outcomes of patients with stage II/III gastric cancer: analysis of a multi-institution dataset[J]. Dig Surg, 2020, 37(2): 135-44. |
| 12 | Ripollés-Melchor J, Ramírez-Rodríguez JM, Casans-Francés R, et al. Association between use of enhanced recovery after surgery protocol and postoperative complications in colorectal surgery: the postoperative outcomes within enhanced recovery after surgery protocol (POWER) study[J]. JAMA Surg, 2019, 154(8): 725-36. |
| 13 | López-Otín C, Blasco MA, Partridge L, et al. The hallmarks of aging[J]. Cell, 2013, 153(6): 1194-217. |
| 14 | Clegg A, Young J, Iliffe S, et al. Frailty in elderly people[J]. Lancet, 2013, 381(9868): 752-62. |
| 15 | 陆文良, DewanSheileshKumar, 郑松柏. 住院老年手术患者围术期并发症与死亡情况分析[J]. 中华老年医学杂志, 2013, 32(12): 1319-21. |
| 16 | Sun Y, Ji Y, Wu K, et al. Association of nutritional status with clinical outcomes of stroke patients with acute anterior circulation large vessel occlusion after emergency endovascular treatment[J]. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao, 2022, 42(9): 1397-402. |
| 17 | Yang Y, Gao P, Song Y, et al. The prognostic nutritional index is a predictive indicator of prognosis and postoperative complications in gastric cancer: a meta-analysis[J]. Eur J Surg Oncol, 2016, 42(8): 1176-82. |
| 18 | Hirahara N, Tajima Y, Fujii Y, et al. High preoperative prognostic nutritional index is associated with less postoperative complication-related impairment of long-term survival after laparoscopic gastrectomy for gastric cancer[J]. J Gastrointest Surg, 2020, 24(12): 2852-5. |
| 19 | Tanaka S, Ando K, Kobayashi K, et al. The dual presence of frailty and locomotive syndrome is associated with a greater decrease in the EQ-5D-5L index[J]. Nagoya J Med Sci, 2021, 83(1): 159-67. |
| 20 | VanDenKerkhof EG, Hopman WM, Reitsma ML, et al. Chronic pain, healthcare utilization, and quality of life following gastrointestinal surgery[J]. Can J Anaesth, 2012, 59(7): 670-80. |
| 21 | Strik C, van den Beukel B, van Rijckevorsel D, et al. Risk of pain and gastrointestinal complaints at 6Months after elective abdominal surgery[J]. J Pain, 2019, 20(1): 38-46. |
| 22 | de Boer HD, Detriche O, Forget P. Opioid-related side effects: postoperative ileus, urinary retention, nausea and vomiting, and shivering. A review of the literature[J]. Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol, 2017, 31(4): 499-504. |
| 23 | Rodríguez-Palma EJ, Huerta de la Cruz S, Islas-Espinoza AM, et al. Nociplastic pain mechanisms and toll-like receptors as promising targets for its management[J]. Pain, 2024, 165(10): 2150-64. |
| 24 | Vergne-Salle P, Bertin P. Chronic pain and neuroinflammation[J]. Joint Bone Spine, 2021, 88(6): 105222. |
| 25 | Jin ZS, Hu J, Ma DQ. Postoperative delirium: perioperative assessment, risk reduction, and management[J]. Br J Anaesth, 2020, 125(4): 492-504. |
| 26 | Zywiel MG, Prabhu A, Perruccio AV, et al. The influence of anesthesia and pain management on cognitive dysfunction after joint arthroplasty: a systematic review[J]. Clin Orthop Relat Res, 2014, 472(5): 1453-66. |
| 27 | Hung KC, Weng HL, Chen IW. Association between pre-operative depression and postoperative pain outcomes[J]. Anaesthesia, 2024, 79(6): 663-4. |
| 28 | Gaudillière B, Fragiadakis GK, Bruggner RV, et al. Clinical recovery from surgery correlates with single-cell immune signatures[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2014, 6(255): 255ra131. |
| 29 | Watt DG, McSorley ST, Horgan PG, et al. Enhanced recovery after surgery: which components, if any, impact on the systemic inflammatory response following colorectal surgery? : a systematic review[J]. Medicine, 2015, 94(36): e1286. |
| 30 | de la Motte L, Kehlet H, Vogt K, et al. Preoperative methylprednisolone enhances recovery after endovascular aortic repair: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial[J]. Ann Surg, 2014, 260(3): 540-8;discussion548-9. |
| 31 | Lindberg-Larsen V, Ostrowski SR, Lindberg-Larsen M, et al. The effect of pre-operative methylprednisolone on early endothelial damage after total knee arthroplasty: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial[J]. Anaesthesia, 2017, 72(10): 1217-24. |
| 32 | Lunn TH, Kristensen BB, et al. Effect of high-dose preoperative methylprednisolone on pain and recovery after total knee arthroplasty: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial[J]. Br J Anaesth, 2011, 106(2): 230-8. |
| 33 | Steinthorsdottir KJ, Kehlet H, Aasvang EK. Surgical stress response and the potential role of preoperative glucocorticoids on post-anesthesia care unit recovery[J]. Minerva Anestesiol, 2017, 83(12): 1324-31. |
| 34 | Toner AJ, Ganeshanathan V, Chan MT, et al. Safety of perioperative glucocorticoids in elective noncardiac surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Anesthesiology, 2017, 126(2): 234-48. |
| 35 | Lv XC, Zhang HY, Gao J, et al. Intraoperative dexmedetomidine on postoperative pain in gastrointestinal surgery: an observational study[J]. Int J Surg, 2023, 109(4): 887-95. |
| 36 | Lu Y, Fang PP, Yu YQ, et al. Effect of intraoperative dexmedetomidine on recovery of gastrointestinal function after abdominal surgery in older adults: a randomized clinical trial[J]. JAMA Netw Open, 2021, 4(10): e2128886. |
| 37 | Liu J, Wang TT, Song J, et al. Effect of esketamine on postoperative analgesia and postoperative delirium in elderly patients undergoing gastrointestinal surgery[J]. BMC Anesthesiol, 2024, 24(1): 46. |
| 38 | Liu Q, Li LH, Wei JW, et al. Correlation and influencing factors of preoperative anxiety, postoperative pain, and delirium in elderly patients undergoing gastrointestinal cancer surgery[J]. BMC Anesthesiol, 2023, 23(1): 78. |
| 39 | Benedetti F, Bernasconi A, Pontiggia A. Depression and neurological disorders[J]. Curr Opin Psychiatry, 2006, 19(1): 14-8. |
| 40 | Levin OS, Vasenina EE. Depression and cognitive decline in elderly: causes and consequences[J]. Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova, 2019, 119(7): 87-94. |
| [1] | 周勇, 吴媛, 曾汇文, 陈翠梅, 谢群, 贺莉萍. 艰难梭菌的感染特征及其危险因素:基于中南地区某市住院腹泻患者的标本[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 998-1003. |
| [2] | 戈 悦, 李建伟, 梁宏开, 侯六生, 左六二, 陈 珍, 卢剑海, 赵 新, 梁静漪, 彭 岚, 包静娜, 段佳欣, 刘 俐, 毛可晴, 曾振华, 胡鸿彬, 陈仲清. VA-ECMO患者院内死亡风险预测模型的构建及验证:一项多中心、回顾性、病例对照研究[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 491-498. |
| [3] | 胡嘉伟, 杜芳, 丁璐, 王路翔, 赵巍峰. 合并高血压病的乙型肝炎肝硬化患者发生肝细胞癌的风险评估:一项基于倾向性匹配评分的回顾性队列研究[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(11): 2243-2249. |
| [4] | 蔡涛浓, 卢江丽, 林志君, 罗明睿, 梁海滔, 秦自科, 叶云林. 单中心非肌层浸润性膀胱癌患者行卡介苗灌注治疗的疗效分析[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(3): 488-494. |
| [5] | 张浩轩, 陆 进, 蒋成义, 方美芳. 基于人工智能技术的鼻咽癌风险预测模型的构建与评价[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(2): 271-279. |
| [6] | 唐 巧, 周 超, 张 宁, 何召云, 张晶晶, 付双楠, 李 昕, 刘鹏程, 张田义, 张 瑾, 宫 嫚. 肝硬化可疑自发性细菌性腹膜炎患者的预后及发生死亡的危险因素[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(12): 2043-2052. |
| [7] | 曹 静, 刘海波, 安 琪, 韩 枫. 二甲双胍缓解小鼠放射性皮炎引起的病理性疼痛:基于抑制p38 MAPK/NF-κB信号通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(10): 1815-1820. |
| [8] | 张小凤, 杨 子, 胡秋子, 左芦根, 宋 雪, 耿志军, 李 静, 王月月, 葛思堂, 胡建国. CENPU在结直肠癌组织中高表达并对患者的远期预后有评估价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(8): 1198-1204. |
| [9] | 李晴晴, 邱权威, 张乐乐, 张小凤, 王月月, 耿志军, 葛思堂, 左芦根, 宋 雪, 李 静, 胡建国. ALDH3B1的表达与肿瘤组织病理学和远期预后相关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(5): 633-640. |
| [10] | 何爱萍, 丁心怡, 黄佳利, 罗祥蓉, 孟健夫, 曹 瑛, 高 方, 邹梦晨. 糖尿病足溃疡合并下肢动脉病变的临床特点及相关危险因素[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(4): 604-609. |
| [11] | 赵佳佳, 杨荷雨, 王招娣, 朱海丽, 谢 敏. ANA-12通过靶向阻断BDNF/TrkB信号通路降低大鼠的脊髓炎症和缓解病理性疼痛[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(2): 232-237. |
| [12] | 邓 亚, 王春艳, 付懿铭, 李忠斌, 纪 冬. 慢性药物性肝损伤的复发风险与肝纤维化程度高度相关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(11): 1655-1661. |
| [13] | 翟跃芬, 王虎清, 展淑琴, 吴海琴. 静脉溶栓治疗急性重度脑梗死的疗效及预后的不良相关危险因素:152例随机对照临床试验[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(9): 1426-1430. |
| [14] | 许立倩, 魏 宁, 单美娟, 汪子怡, 叶天成, 梁赛珍, 李 乐, 朱 强, 何路遥, 白建杰, 陈碧霞, 徐金东. 加温湿化高流量鼻导管吸氧可减少老年患者麻醉复苏期缺氧事件发生[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(8): 1265-1269. |
| [15] | 周萌萌, 陈金东, 王 昊, 席斯祺, 甘 田, 赵 亮. 低CHA2DS2-VASc评分的非瓣膜性心房颤动患者的心房血栓形成的独立危险因素[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(8): 1243-1249. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||